THE EFFECT OF USING QUESTION-ANSWER RELATIONSHIP (QAR)
ON THE
STUDENTS’
ACHIEVEMENT IN READING NARRATIVE TEXT
A THESIS
Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Sarjana Pendidikan
By:
RINDA SARI PUTRI
Registration Number 2103321037
ENGLISH AND LITERATURE DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF LANGUAGES AND ARTS
i
ABSTRACT
Putri, Rinda Sari. 2103321037. The Effect of Using Question-Answer Relationship (QAR) on the Students’ Achievement in Reading Narrative Text. A Thesis. English Department. Faculty of Languages and Arts. States University of Medan. 2015.
This study was aimed at finding out the effect of using Question-Answer Relationship Strategy on the students’ achievement in reading narrative text. This study was an experimental research design. The population of this study was grade X students of SMA Cerdas Murni Tembung with the total number of students was 60 as samples and all of the students was taken by using cluster sampling technique. The students were divided into two groups, namely experimental and control group. The experimental group was taught by using Question-Answer Relationship Strategy, while the control group was taught by using Conventional Strategy. The instrument of collecting data was multiple choice tests administered in pre-test and post-test. To obtain the result of the reliability of the test, Kuder Richardson formula (KR-21) was used. The result of the calculation showed that the reliability of the test was 0.80, which meant that the reliability of the test was high. The data were analyzed by using t-test formula. The result of the analysis showed that tvalue was higher than ttable (3.65 > 2.00) at the level of significance 0.05 with the degree of freedom (df) 58. It means that there is a significant effect of using Question-Answer Relationship Strategy on the students’ achievement in reading narrative text.
ii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Praises and the greatest thanks to Almighty Allah SWT, the most Merciful who has blessed and given time, opportunity, and health to the writer so this thesis
entitled “ The Effect of Using Question-Answer Relationship Strategy on the
Students’ Achievement in Reading Narrative Text” could be completed. This
thesis is aimed to fulfill one of the requirements for the degree of Sarjana Pendidikan at English Department of Language and Arts Faculty, State University of Medan.
During the process of completing this thesis, the writer has worked with a great number of people, through their guidance, suggestions, and comments for which the writer would like to express her sincere gratitude and special thankfulness to :
Prof. Dr. Ibnu Hajar Damanik, M.Si, Rector of State University of
Medan
Dr. Isda Pramuniati, M.Hum, the Dean of Faculty Languages and Arts.
Prof. Dr. Hj. Sumarsih, M.Pd, the Head of English Department.
Dra. Masitowarni Siregar, M.Ed, the Head of English Education Study
Program
Dr. Rahmad Husein, M.Ed., her thesis Consultant.
Prof. Amrin Saragih, M.A., Ph.D, Dr. Anni Holila Pulungan, M.Hum,
iv
E. The Significance of the Study ... 5
CHAPTER II. REVIEW OF LITERATURE ... 6
A. Theoretical Framework ... 6
1. Reading Comprehension ... 6
2. The Nature of Reading Comprehension ... 7
a. Definition of Reading Comprehension ... 7
b. Reading Comprehension as a Process ... 8
c. Factors Affecting Reading Comprehension ... 9
d. Levels of Reading Comprehension ... 10
3. Learning Reading Comprehension ... 12
4. Teaching Reading Comprehension ... 15
5. Genre of the Text ... 17
a. Narrative Text ... 17
6. Question-Answer Relationships Strategy ... 19
a. The Procedure of QAR ... 23
b. The Advantages of Using QAR Strategy ... 25
c. The Steps of QAR Strategy ... 27
B. Relevant Studies ... 28
C. Conceptual Framework ... 29
D. Hypothesis ... 30
CHAPTER III. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY ... 31
A. Research Design ... 31
B. Population and Sample ... 31
C. The Instruments for Collecting Data ... 32
D. Scoring the Test... 33
E. The Research Procedure ... 33
1. Pre Test... 33
2. Treatment ... 34
v
F. The Validity and Reliability of the Test ... 37
1. The Validity of the Test ... 37
2. The Reliability of the Test ... 37
G. The Technique for Analyzing Data ... 38
H. Statistical Hypothesis ... 39
CHAPTER IV. DATA ANALYSIS AND RESEARCH FINDINGS ... 40
A. The Data ... 40
B. Data Analysis ... 43
C. Testing Hypothesis ... 46
D. Research Findings ... 46
CHAPTER V. CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION ... 47
A. Conclusion ... 47
B. Suggestion ... 48
vi
LIST OF TABLE
Pages
Table 1.1 The Score of the Students ... 2
Table 2.1 The Example of Narrative Text ... 18
Table 2.2 The Basic QAR Divisions ... 21
Table 2.3 Model of Question-Answer Relationships ... 24
Table 3.1 Research Design ... 31
Table 3.2 Teaching Procedure in Experimental Group ... 34
Table 3.3 teaching Procedure in Control Group ... 36
Table 4.1 The Score of Pre-Test and Post-Test of Experimental Group ... 41
Table 4.2 The Score of Pre-Test and Post-Test of Control Group ... 42
vii
LIST OF APPENDICES
APPENDICES Page
A. Lesson Plan ... 51
B. Question Sheets ... 95
C. The Scores of Pre Test and Post Test of Experimental Group ... 96
D. The Scores of Pre Test and Post Test of Control Group ... 97
E. The Scores of Reliability of the Test ... 98
F. The Calculation of T-Test for Experimental Group ... 99
G. The Calculation of T-Test for Control Group ... 100
H. The Table of T-Table ... 101
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A. The Background of the Study
From the four language skills, reading is the focus on this thesis. Reading as the one of the language skill that is important should be mastered by the students. Grabe and Stoler (2002:9) state that reading is the ability to draw meaning from the printed page and interpret this information appropriately. It means that without comprehending and interpreting the meaning of the text the reading itself is useless.
The important point to be made about the reading is reading comprehension. To master reading skill, the readers need good comprehension in reading activity. In reading comprehension, reader must be able to get a deeper understanding of information that presented in a text. It means that reading comprehension involves thinking process. According to Westwood (2008:31) reading comprehension is an active thinking process which a reader intentionally constructs meaning to form a deeper understanding of information that presented in a text. An active thinking process involves the activity of linking of new information to the students’ experience or background knowledge.
2
this case, teachers have an important role. The teacher should attempt to activate prior knowledge as much as possible to reading text, allowing students to apply the prior knowledge use while reading.
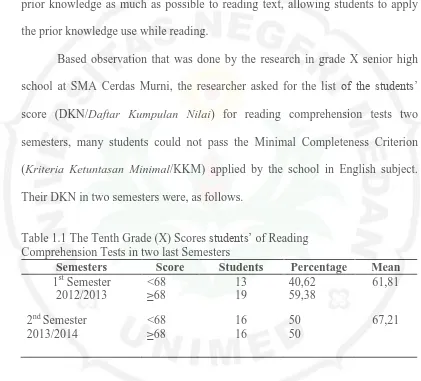
Based observation that was done by the research in grade X senior high school at SMA Cerdas Murni, the researcher asked for the list of the students’ score (DKN/Daftar Kumpulan Nilai) for reading comprehension tests two semesters, many students could not pass the Minimal Completeness Criterion (Kriteria Ketuntasan Minimal/KKM) applied by the school in English subject. Their DKN in two semesters were, as follows.
Table 1.1 The Tenth Grade (X) Scores students’ of Reading Comprehension Tests in two last Semesters
Semesters Score Students Percentage Mean 1st Semester
The Minimal Completeness Criteria ((Kriteria Ketuntasan Minimal/KKM) applied for the tenth grade (X) by school is 68, from the data above, it could be fulfilled that the students’ ability in reading comprehension in that class was still
low. It could be seen from the mean of the students’ score where the mean was
still under the Minimal Completeness Criteria.
3
the questions from the text or the teacher, and then corrected the answers. This situation did not give a good mood in teaching learning activity. The students were bored and the teacher could not give some motivation to the students.
In order to make the teaching process interesting and to reach the purpose of teaching learning process, the teacher needs a special strategy. The purpose of using it is to make the students easy to learn and understand the lesson. In addition to making the student easier to comprehend, using a strategy in comprehending a text can make the teaching learning process more effective and make the students more active. There are many strategies to interact and improve the achievement of
student’s reading comprehension. One of them is Question-Answer Relationships
(QAR) which can be used to frame the questioning activities within the reader cycle guide their modeling of question-asking practice in the before, during and after reading phases (Raphael, Au, 2005). So, The researcher wants to use Question-Answer Relationships (QAR) strategy in teaching reading comprehension so that she knows whether there is a significant effect of using QAR strategy on the students achievement in reading comprehension, especially in reading narrative text.
Raphael (2005) state The Question-Answer Relationship (QAR) strategy helps students understand the different types of questions. It also can improve students’ reading comprehension, it teaches students how to ask question about
4
implementation of QAR strategy will be tested to see if it increases the students’ comprehension. However, in the context of teaching comprehension the effectiveness of the evidence above need to be found. To gain the evidence, the research needs to be conducted.
B. The Problem of Study
Related to the background of the study, the problem of the study is
formulated as the following: “Does apply Question-Answer Relationships (QAR)
strategy significantly affect the students’ comprehension in reading narrative
text?”
C. The Objective of the Study
In relation to the problem, the objective of the study is to find out whether Question-Answer Relationships (QAR) strategy significantly affects the students’ achievement in reading narrative text.
D. The Scope of the Study
5
E. The Significance of the Study
Theoretically, the findings add new horizon to the theories of English learning, particularly on reading comprehension. Practically, the finding will be meaningful for:
1. English teachers. It will be important for the teachers in their attempt to improve their students reading comprehension in narrative through Question-Answer Relationships strategy.
2. Students. It will be also important for the students to overcome their problem in reading especially narrative through Question-Answer Relationships.
47
CHAPTER V
CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTIONS
A. Conclusion
Based on the research finding, it is concluded that there is a significant effect of applying Question-Answer Relationship (QAR) Strategy on students’ reading comprehension. The students taught by applying Question-Answer Relationship (QAR) Strategy (tobserve = 3.65) is higher than without applying Question-Answer Relationship (QAR) Strategy (ttable = 2.00). Therefore, alternative hypothesis (Ha) is accepted and null hypothesis (Ho) is rejected. This is supported by the data analysis results in which the tobserve > ttable (3.65 > 2.00) at the significant level of 0.05.
B. Suggestions
Based on the conclusion above, the researcher suggests that:
1. Teachers apply Question-Answer Relationship (QAR) Strategy in their teaching learning process by focusing on the students so that they get more information from their reading by showing them how to find and use information from a text to answer the questions.
48
49
REFERENCES
Ade. 2013. Improving the Students Reading Comprehension Achievement By Applying the Question-Answer Relationships (QAR) Strategy. Unpublished Thesis. Medan: State University of Medan
Arikunto, S. 2003. Prosedur Penelitian :SuatuPendekatanPraktik: Edisirevisi V. Jakarta: Rineka Cipta.
Best, J.W. 2002. Research in Education. New York: Prentice-hall.
Brown, D.H. 2004. Language Assessment: Principle and Classroom Practices. New York: Pearson Education.
Brown, H. Doughlas. 2001. Teaching by Principles: An Interactive Approach To Language Pedagogy 2nd Ed. New Jersey: Longman.
Cummins, Sean and Mellissa Streiff. 2012. Understanding and Applying the QAR Strategy to Improve Test Scores. Journal of Inquiry & Action in Education, Vol. 4, No.3.
Dorn, Linda. 2006. A Close Look at Meaning in Reading Comprehension: Arkansas Reading Association an Affiliate International Reading Association.
Elfriede. 2012. Improving Students’ Achievement in Reading Comprehension Through Questions-Answer Relationships (QAR) Strategy. Unpublished Thesis. Medan: State University of Medan.
Frank Lyman & Kagan Spencer. 1989. Cooperative Learning Resources for Teacher.
Grabe, William and Stoller, L.Fredericka. 2002. Teaching and Reasearching Reading. England: Pearson Education.
Gerot, l & Wignell, P. 1994. Making Sense of Functional Grammar. Cammeray: Antipodean Educational Enterpries.
Haris, Rapicha. 2014. The Effect of Using Question Answer Relationship (QAR) Strategy on students’ comprehension in Reading Narrative Text. Unpublished Thesis. Medan: State University of Medan.
50
Kinniburgh, Leah H. and Sandra S. Prew. 2010. Question Answer Relationships (QAR) in the Primary Grades: Laying the Foundation for Reading Comprehension. International Journal of Early Childhood Special Education (INT-JECSE), June, Vol. 2, No.1.
Kinniburgh, Lean H. and Abigail Baxter. 2012. Using Question Answer Relationships in Science Instruction to Increase the Reading Achievement of Struggling Readers and Students with Reading Disabilities. Current Issues in Education, August 15, Vol. 15, No. 2. Lado, Robert. 1998. Language Testing. New York: McGraw-Hill Book Company Mikulecky, B.S, and Jeffries, L. 2007. Reading Power. United states of America:
Pearson Education.
Otto, Wayne; Robert Rude and Dixie Lee Spigel. 1979. How to Teach Reading. Madison : The University of Winconsin.
Pearson, P. David & Gallagher, Margaret. C. 1983. The Instruction of Reading Comprehension. Technical Report No. 297. Wasington, Dc: National Ins. Of Education (ED).
Raphael. T.E. & Au, K. H. 2005. QAR : Enhancing Comprehension and Test taking across grades and content areas. The Reading Teaching, 59(3), 206-221.
Raphael, T.E. 1984. Teaching learners about sources of information for answering comprehension questions. Journal of Reading, 27, 303-311.
Raphael, 2006. The Steps of Question-Answer Relationships. Retrieved from http:www.tastasqua.org/superintendet/etqar.html/ accessed on 25 June 2014
Readence, J.E. 2006 Question-Answer Relationship. University of Nevada, Las Vegas.
Snow, Catherine E. 2002. Reading For Understanding: toward a research and development program in reading comprehension. Santa Monica: RAND.
Westwood, Peter. 2008. Reading and Writing Difficulties: what teachers need to know about. Victoria, Australia: ACER Press, pp (32-37)