THE CORRELATION OF STUDENTS’ COLLOCATION
MASTERY ON SPEAKING PERFORMANCE
(A STUDY FOR THE SECOND SEMESTER STUDENTS OF
ENGLISH DEPARMENT OF IAIN SALATIGA
IN THE ACADEMIC YEAR OF 2016/2017)
A GRADUATING PAPER
Submitted to the Board of Examiners as a partial fulfillment of the
requirements for the degree of Sarjana Pendidikan (S.Pd)
in English and Education Department
By
NUR ISNAINI FEBRIANA
113 13 097
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
TEACHER TRAINING AND EDUCATION FACULTY
v MOTTO
“Allah burdens not a person beyond his ability.”
vi
DEDICATION
This graduating paper is whole heartedly dedicated to:
My Lord, Allah SWT… Thanks to Allah for giving me guidance and strength in my life, especially to finish this graduating paper. Alhamdulillahirobbilalamin!
My beloved parents: Buseri and Asih Tafrikhah. Thanks for your love, prayer, motivation, and your sacrifice to me. I cannot compare my love for both of you with anything in this world.
My sister and brother, ( Asri, Fitri and Arbi) and all of my big family, thanks a lot for your continued encouragement, advice, and pray.
Someone who always accompany me and always remind me to finish this graduating paper, thank you for loving me Unconditionally.
ix ABSTRACT
Febriana, Nur Isnaini. 2017. “The Correlation of Students’ Collocation Mastery on Speaking Performance for The Second Semester Students of English Deparment of Iain Salatiga In The Academic Year Of 2016/2017”. A Graduating Paper.Teacher Training and Education Faculty.English Education Department.State Institute of Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga. Counselor: Sari Famularsih, S.PdI M.A.
The objectives of this research were to determine and to investigate the influence of students’ collocation mastery toward students’speaking performance of English deparment of IAIN Salatiga in the academic year of 2016/2017. This research will answer these main questions 1) How is the profile of students' mastery on their collocation for the second semester students of English Department of IAIN Salatiga in the academic year of 2016/2017, 2) How is the profile students’ speaking
performance for the second semester students of English Department of IAIN
Salatiga in the academic year of 2016/2017 and 3) Is there any influence of students’ collocation mastery on speaking performance for the second semester students of English department of IAIN Salatiga in the academic year of 2016/2017. This research was conducted from July 17th until Augustus 4th 2017.The sample of this research was the Second Semester English Student of speaking class of IAIN Salatiga in the academic year of 2016/2017. The methodology in this research was
quantitative statistical research design. The result of this research gained the score of r count was 0.229 from the interpretation of r value 0.229 was existing between 0,200 – 0,400. The rcount which 0.229 was smaller than the rtable 0.444. It means that the result of the study indicates that there was correlation between students’ mastery on collocation and their speaking performance, but the correlations were low.
x
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE ... i
DECLARATION ... ii
ATTENTIVE COUNSELOR NOTES ... iii
PAGE OF CERTIFICATION ... iv
xi
CHAPTER II: THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK ... 14
A. Literature Review ... 15
1. Mastery ... 15
2. Collocation ... 15
a. Collocation Classifications ... 16
b. Types of Collocation ... 18
c. Grammatical and Lexical Collocation ... 20
3. Speaking Performance ... 22
a. Definition of Speaking ... 24
b. Types of Classroom Speaking Performance ... 23
CHAPTER III: RESEARCH METHODOLOGY ... 26
xii
CHAPTER IV: DATA ANALYSIS ... 37
A. Data Analysis ... 37
1. Students’ Collocation Mastery ... 38
2. Students’ Speaking Performance ... 39
3. Finding out the Average of Collocation Mastery Score and speaking performance Score ... 40
4. Finding out the Correlation between students’ collocation mastery of speaking performance. ... 43
B. Discussion ... 47
C. Hypothetical Conclusion ... 48
xiii
LIST OF TABLES
Table 2.1Example of errors combining words ... 15
Table 2.2Type of Grammatical ... 20
Table 2.3 Type of lexical collocation ... 22
Table 3.1 Respondents ... 28
Table 3.2 Coverage of Collocation Test ... 30
Table 3.2 Oral rating sheet... 31
Table 4.1 Score of Students’ Collocation Mastery ... 38
Table 4.2 Score of Students’ Speaking Performance ... 39
Table 4.3 Classifies the Range of Scores... 40
Table 4.4 The Squared and multiple of X and Y ... 43
1 CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A. Background of Study
Language is means of communication, language is a system for the expression of meaning and language is viewed as a vehicle for communicating meaning and message (Richards and Rodgers, 1986). Meanwhile, vehicle means a tool which people can use to communicate with others to deliver certain goals or to express their opinions, intentions, hopes and feelings. Language also can eliminate misunderstanding among people because it can explain more about the purpose. Many languages in this world, such as Germany, Chinese, Thai, Bahasa and English as a tool for communication. English is a language that most used by people around the world as an international language.
2
of components must be learned to make a students like native speaker closer. One of important things is to combine the word into a good sentence therefore it is easy and natural. The study about combining the words (noun, adjective, verb and adverb) in English is called collocation.
A collocation is a combination of two or more words which frequently occur together (McCarthy and O’Dell, 2006). It can be difficult for students of English to know which words collocate, as natural collocations are not always logical or guessable. The students probably understand the utterance “There was very hard rain this morning,”but it sound feels unnatural. Please check in this sentence “There was very heavy rain in this morning.” it very different about “hard rain” and “heavy rain” since “hard” is not collocation by “rain” and “heavy” is collocated by “rain” thus it is natural (McCarthy and O’Dell, 2006). One of the most difficult tasks of second or foreign language students is appropriately combining words. Different with native speakers, they have the knowledge about which words go together and how to use the diverse words. The proper use of collocations is crucial to sound like a native speaker (Ellis, 1996).
3
competence in speaking to deliver the aim or information among speaker. Speaking is means through which a person can communicate with others to achieve certain goals or to express their opinions, intentions, hopes and viewpoints. Furthermore, in almost any setting, speaking is the most frequently used language skill (El Fattah,2006).
In speaking, collocation is regarded as a more complicated topic to be mastered. The students should give more attention to their collocation mastery to help them speaking more fluently and naturally. Mc Cathy and O’dell in the English Collocation in Use say that the types of collocation there are adjective and noun, noun and verb, noun and noun, verb and expression with prepositions, verb and adverb, adverb and adjective. All of them facilitate us to combine the word as a collocation.
4 Statement of the Problem
Regarding to the background of study, the proposed statement of the problem are follows:
1. How is the profile of students' mastery on their collocation for the second semester students of English Department of IAIN Salatiga in the performance for the second semester students of English department of IAIN Salatiga in the academic year of 2016/2017?
B. Purpose of Study
This study has certain goals as follow:
5
2. To know how far the students’ speaking performance for the second semester students of English department of IAIN Salatiga in the academic year of 2016/2017.
3. To examine the correlation of students’ collocation mastery on speaking performance for the second semester students of English department of IAIN Salatiga in the academic year of 2016/2017.
C. Benefit of Study
This study expects that the result of the study gives benefit in case of :
1. Theoretical Benefit
The result of this research is expected to be able to encourage the next researcher to conduct further research.
2. Practical Benefit
a. The English Teacher
6
language teaching especially about collocation in speaking performances.
b. The English Students
This study is hoped to be able to improve the students’ interest on collocation and to get more information about relevant case. The students be able to speak more fluently with collocation correctly.
c. The writer
From this study, the writer gets many experiences being useful in the future as an English teacher. The important point is the writer can apply the collocation in speaking performance.
D. Definition of Key Term
1. Mastery
7
2. Collocation
Taken from Lewis (2000) Collocation is the way in which words co-occur in natural text in statistically significant ways. For instance “Jane’s got the yellow hair”, probably be understood by the listener or the reader but it more naturally with “Jane’s got blond hair”. Moreover “yellow” do not collocate with “hair” because it is collocate with “paint” or “flower”.
3. Speaking
Speaking is means through which a person can communicate with others to achieve certain goals or to express their opinions, intentions, hopes and viewpoints. Furthermore, in almost any setting, speaking is the most frequently used language skill (Fattah,2006).
4. Performance
Performance is something performedand accomplishment. In linguistics,performance is one of actual use of language in actual situations (The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language, 2000). According to Marvin Carlson performance is always performance for someone, some audience that recognizes and validates it as performance (Carlson, 2003).
8
1. Population
The population of this research is speaking class for the second semester students of English Education Department of IAIN Salatiga in the academic year of 2016/2017.
2. Sample
Sample is clearly proper for intended population for generalization. The sample of this research consists of 20 students of speaking class of English Education Department of IAIN Salatiga in the academic year of 2016/2017.
3. Techniques of Collecting Data
The writer uses a test and video as a technique of collecting data. The writer will give the collocation test to identify the students’ mastery on collocation. To get the data or information about their speaking performance, the writer uses analyzingvideos from the speaking class in second semester students of English Education Department of IAIN Salatiga in the academic year of 2016/2017.
9
The writer uses a statistic formula to conduct a good arrangement.
a. Calculating the score of students’ collocation mastery by using the
b. Calculating the score of students’ speaking performance:
=Nx100 × 100%∑
By which
Py = score obtained
Ʃ Y = sum of Y
10
c. Calculating the correlation between students’ mastery on collocation and their speaking performance:
= N∑XY (∑X)(∑ )
√{N∑X (∑X) }{N∑Y (∑Y) }
By which:
Rxy = is product moment correlation score between variable X and Y ( students’ mastery on collocation and their speaking performance)
Ʃ X = is the total score of variable X (students’ mastery on collocation)
Ʃ Y = is the score of variable Y (students’ speaking performance)
Ʃ XY = is the total score of variable X and Y (students’ mastery on collocation and their speaking performance)
N = is the number of students
F. Hypothesis
Hypothesis is the purpose statement in quantitative research, but hypotheses advance a predictionabout what the researcher expects to find
11
to at least one hypothesis that provides a prediction about the outcome of the
research.
Related to the possible result of the research, there are two types of hypotheses, null hypothesis and alternative hypothesis. According to John W. Creswell (2012:126)
Null hypothesis is to test in the general population that there is no change, no relationship, and no difference. Alternative hypothesis is the hypothesis that may be true if the null is rejected, it suggests a change, a relationship, or a difference. The null hypothesis is generally symbolized as H0 and the alternative hypothesis as Ha.
Based on the statement above, the writer can take a provisional answer about the correlation of students’ collocation mastery on speaking performance as:
1. H0: There is no significant correlation between students’ collocation mastery on speaking performance in the second semester students of English department of IAIN Salatiga in the Academic year of 2016/2017.
12 G. Previous Researches
In this part, the writer would reviewsome relating previous studies from two collaborative research papers. The first was arranged by Nur Cahyo year 2015 with their study entitled “A Correlative Study between Students’ Lexical Knowledge of Collocations toward Their Reading Comprehension”. The research was aimed to find out the correlation between students’ lexical knowledge of collocation and their reading comprehension on the sixth semester of English Department Students’ of IAIN Salatiga 2014/2015. The population of the research was the Sixth Semester of English Department Students of IAIN Salatiga in the academic year of 2014/2015. The methodology in this research was mixed forms of research design specifically the exploratory-quantitative-statistical research design. The result of calculating the correlation between students’ mastery on collocation and their reading comprehension is 0.6989. From the interpretation of r value, 0.6989 is between 0,600 - 0,800. It indicates that the correlation between students’ lexical knowledge of collocation and their reading comprehension in Sixth semester of IAIN Salatiga in the academic year of 2014/2015 is high.
13
They identified investigating the influence of students’ mastery on collocation toward their writing achievement. The result of this research showed that the Writing achievement significantly improved. Based on the index of correlation rxy count = 0,280, it means that the result of correlation was positive, therefore, the good mastery on collocation of the students were followed by the good writing achievement. In other word the students’ mastery on collocation could influence their writing achievement.
H. Thesis Organization
The first chapter, introduction, introduces the research by giving a description of background of the research, research problem, purpose of study, benefit of study, definition of key term, research methodology, hypothesis, and the outline of the research. The second chapter is the theoretical framework of students’ mastery on collocation and their speaking performance that are discussed.
The third chapter contains the data presentation which shows the data of respondents, data of students’ mastery on collocation and the data of students’ speaking performance.
14
CHAPTER II
THEORITICAL FRAMEWORK
A. Literature Review
1. Mastery
Based on the American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language (2000:1078) Mastery is possession of consummate skill of a subject of the study. According to Webster (1974: 586) mastery is the state of having control over something, superiority in competition, victory, eminent skill or through knowledge. Based on the definition above, mastery can conclude as someone ability to understand about something or knowledge from their experience to their daily activity.
2. Collocation
15
together, such as which verbs and nouns can be used together, and which prepositions and verbs can be used together.
Choosing the right collocation will make speech and writing sound much natural, more native speaker-like, and will express much more clearly and be able to convey not just a general meaning, but something quite precise.For example: people often say heavy rain, or light rain, instead of
strong rain or mild rain, heavygoes well with rain, whereas strong does not. There are many cases in English when it is difficult to know which words go well with the word want to use, because there are no clear rules. Some words just sound right together, while others do not.
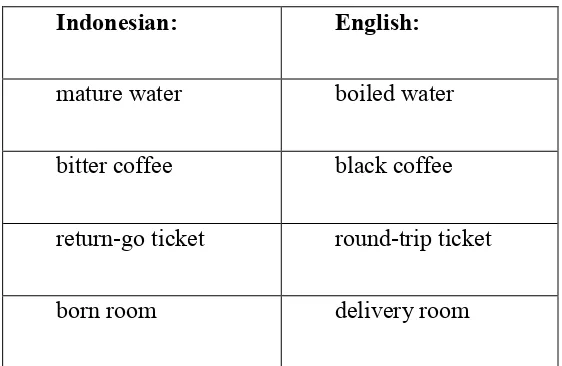
The form is natural to the language in which it occurs but would not sound natural if translated literally into the other language.
Table 2.1 Example of errors combining words
Indonesian: English:
mature water boiled water
bitter coffee black coffee
return-go ticket round-trip ticket
16
These types of errors occur as a result of combining words in the target language inappropriately. It can be difficult for students to know which words collocate, as natural collocations are not always logical or guessable. To make a combination, many words can combine based on the type of the collocation such as verb + noun (e.g. lead a seminar), noun + noun (e.g. word of wisdom), adverb + verb (e.g. flatly contradict). Moreover, these combinations do not make a new meaning because the meaning is from each of word. However, the meaning of some fixed collocations cannot be guessed from the individual word.
a. Collocation Classifications
In the collocation we find the difficulty or facility when make a combination words. Since the words are that collocation are strong, fixed or weak.
1) Strong collocation
17
connected with “hair”. “Inclement weather was expected”, means that “unpleasant weather was expected”. “Inclement” collocates almost exclusively with “weather”. Beside that “I felt deliriously happy”, “deliriously” associated with “happy” not used with “glad” or “sad”. It can be easy us to make a collocation because the one or two words which associated with them.
2) Fixed collocation
Based on McCarthy and O’Dell (2008:8) the fixed collocation is collocation which so strong and cannot be combined in any kind words. The meaning of some fixed collocations cannot be guessed from the individual word. These types are called idioms. For example “I was walking to and fro”. “To” and “fro” cannot be changed by other word because is a completely fixed. “I put up a shelf in the kitchen”, “put up” is a fixed collocation. “She has to cook up an excuse for being late to work”, “cook up” is a fixed. These collocations are called idioms.
3) Weak collocation
18
shoulders, a board accent, and a board hint”. The combination of “board” can be replaced by any word according the type of collocation. “Have a bath, have a drink, have a haircut and hair a rest”. “Do nothing, do the shopping, do your hair and so on”. “Have” and “do” have the other word which combination them.
b. Types of Collocation
In the collocation there are different types, so we can predict the word having collocation or not. According to McCarthy and O’Dell (2005:12) the types consist of:
1) Adjectives and nouns
There are many adjective which can gather with noun, but here will give some adjectives to give obvious example. Here are the examples of collocation adjective + noun.
For example:
19
collocation is “plain truth”. “They have a hard life”. “Hard life” is a collocation of this sentence.
2) Nouns and verbs
Word combinations in these types are nouns and verbs.
For example:
People feel educational standards slipped when the government cut finances
An opportunity arises for her to school in America, so she went and spent a year there.
3) Noun and noun
Nouns and nouns are used in these types. However there is collocation with the pattern a… of… like the sentence “As Sony reads the lies about him, he felt a sugar of anger”. Noun and noun collocations used with uncountable nouns.
For example:
I would like to buy two bars of soaps There is a glass of water on the table.
20
Some verbs collocate with particular preposition expression.
For example:
We had to return home because we had run out of money. When Jean split juice on her new skirt the little girl burst
intotears.
I am going to look up the meaning in the dictionary. 5) Verbs and adverbs
Some verbs have particular adverbs which regularly collocate with them.
For example:
Mary whispered softly in John’s ear.
The accident happened because he was driving dangerously.
After 2 years in London, he speaks English fluently.
6) Adverbs and adjectives
Adverbs oftenhave particular adjectives which regularly collocate with them.
21
They are happily married.
Are you okay? I am deeply concerned about you.\
Rio’s sister was a stunningly attractive woman.
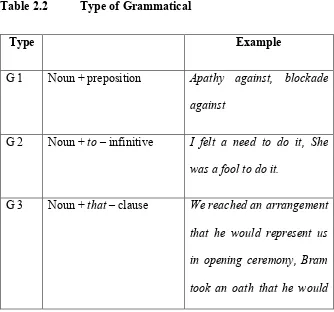
c. Grammatical and Lexical Collocation
By identifying the six groups of types of collocation, collocation was divided into two main collocation groups: lexical and grammatical collocations. Grammatical collocation consists of a noun, an adjective, a verb plus a preposition or grammar structure such as an infinitive and clause. It is characterized by 8 basic types in collocations:
Table 2.2 Type of Grammatical
22
do his duty.
G 4 Preposition + noun by accident, in advance
G 5 Adjective + preposition Afraid of, found of.
G 6 Adjective + to – infinitive The boy is ready to go, it was necessary to work.
G 7 Adjective + that – clause he was afraid that he would fail, it was imperative that I
be here
G 8 Nineteen different verb pattern in English such as verb + to infinitive, verb + bare infinitive, gerund complement patterns
They began to learn, I enjoy
watching television.
The lexical collocation consists of noun, verb, adjective and adverb but it does not contain preposition, infinitive and clause. Here are 7 types of lexical collocation:
23
24
massage to the listeners. In this case, the speaker and listener should be able to understand each other. The speaker can produce the sounds that involved the massages and the listener can receive, process, and response the massages.
Speaking is a part of linguistic performance that takes input from linguistic knowledge. Therefore, linguistic competence refers to the knowledge and ability of individuals for appropriate language use in the communicative. According to Widdowson (1983) cited byDwiWahyuni, the aims of a language teaching course are defined with reference to the four language skills: understanding speech (listening), speaking, reading, and writing. These aims relate to the kind of activity which students are to perform.
b. Types of Classroom Speaking Performance
Brown (2001) identifies six categories apply to the types of classroom speaking performance that students are expected to carry out in classroom. They are:
1) Imitative
25
drilling. Drills in which the students simply repeats a phrase or structure (e.g., “Excuse me.” Or “Can you help me?”) for clarity and accuracy. This, actually, helps a lot in the process of language learning; it gives the students the chance to listen and to repeat orally some language structures that the students may find difficult to construct.
2) Intensive
Intensive speaking goes one step beyond imitative to include anyspeaking performance that is designed for practicing somegrammatical aspect of language. It can be in the form of self-initiated or pair work activity.
3) Responsive However it cannot be extended to dialogue.
26
Transactional language carried out for the purpose of conveying or exchanging specific information is an extended form of responsive language. Dialogues conducted for the purpose of information exchange, such as information gathering- interviews, role plays, or debates. It could be part of pair work as it can be part of group work. Transactional language is often taught more thaninteractional language, as it involves shorter turns, simpler and more predictable language, and can have a measurable result.
5) Interpersonal (dialogue)
Like in the transactional, interpersonal speaking here is also carried out in a dialogue. It is purposed for maintaining social relationships than for the transmission of facts and information. These conversations are little trickier for students because they can involve some factors such as, slang, ellipsis, sarcasm, a casual register, etc. This often makes the students find it difficult to understand the language, or even misunderstood.
6) Extensive (monologue)
27
28 measured. Typically on instruments, so that numbered data can be analyzed using statistical procedures. The final written report has a set structure consisting of introduction literature and theory, methods, results, and discussion (Creswell,2008). Like qualitative researchers, those who engage in this form of inquiry have assumptions about testing theories deductively, building in protections against bias, controlling for alternative explanations and being able to generalize and replicate the findings.
In this research, the writer used correlation research. The correlation research is to test a relationship between or among variables, and to make predictions. Predictions are dependent on the outcome of a strong relationship between or among variables (Alison,2005).
B. Research Settings
29
The writer was conducted in State Institute for Islamic Studies Salatiga (IAIN Salatiga) which located on Jl. Lingkar Selatan Pulutan, Salatiga. There are seven departments in Tarbiyah Faculty and Science Teacher, such as:
a. Education of Religion Teaching b. English Department
c. Arabic of Department
d. Education of Madrasah Ibtidaiyah Teaching e. Education of RaudhatulAtfal Teaching f. Education of Mathematic
g. Education of Science
In addition, in FTIK, there is a department which is suitable for conducting the research, English Department. English Department was chosen because the research is related with speaking performance, which can be conducted in one of the speaking classes.
2. Time of the Research
30 C. Subject of the Study
1. Population
Survey designs are procedures in quantitative research in which administer a survey or questionnaire to identify trends in attitudes, opinions, behaviors, or characteristics of a large group of peopleit’s called the population (Creswell,2012)
In this research, the population is the speaking class students of second semester of English Department of IAIN Salatiga in the academic year of 2016/2017. The total numbers of the students are 78 students.
2. Sample
In another case, sample is the survey designs are procedures in quantitative research in which administer a survey or questionnaire to identify trends in attitudes, opinions, behaviors, or characteristics of a small group of people (Creswell,2012). Accordingly, the subjects taken here are 20 students of Second Semester of English Department Students of IAIN Salatiga in academic year of 2016/2017. From these sample, hopefully, could give some data or information that supports the study.
31
Table 3.1 The Research Respondents
32
18. FHS
19. NJ
20. AM
D. Data Collection
1. Technique of collecting data
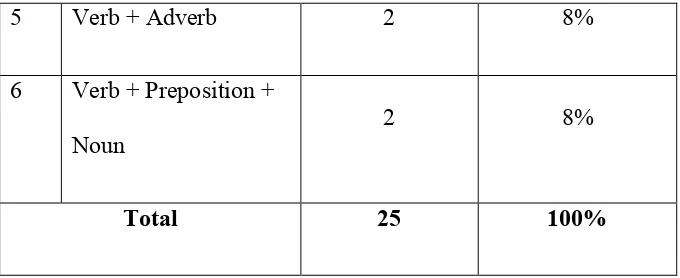
To find the score of collocation mastery of second semester students of English department of IAIN Salatiga in the academic year of 2016/2017, the writer uses a test to collect the data. In the collocation tests the writer gives 25 questions and divided by 2 types. They are 15 questions of multiple-choice and 10 questions of matching type.
33
performance about collocation material with speech in the second semester.
2. Scoring
From the explanation above, the tests are used to knowing the students’ mastery on collocation are multiple choice type and answers-match type, and videos of speaking assessment to know the speaking performance.The test consists of 25 items which are divided into two kinds of test variation. The first test is multiple choices by choosing the correct word to complete the sentence about collocation that consists of 15 items. The second test consists of 10 items of answers-match type questions.
The coverage of the collocation tests will be shown in table:
Table 3.2 Coverage of Collocation Test
No Coverage Frequency Percentage
1 Adjectives + Noun 5 20%
2 Verb + Noun 7 28%
3 Noun + Noun 4 16%
34
5 Verb + Adverb 2 8%
6 Verb + Preposition +
Noun 2 8%
Total 25 100%
According to the table 3.2, there are 25 numbers of questions that have their own frequency by types of collocation. If each number was multiplied by four, so, the highest score would be 100.
To evaluate the speaking performance, there are a large number of measures that indicate speaking performance (Harris,1974). In evaluating the students’ speaking performance, the writer used the Oral English Rating sheet proposed by Harris (1974,84). Based on the Oral English Rating sheet, there are five components that were going to be tested to the students, namely: pronunciation, fluency, grammar, vocabulary and comprehension.
Here is the sample of the Oral rating sheet:
Table 3.2 Oral rating sheet
36
obscure meaning
Makes frequent errors of grammar and word
difficult. Must often rephrase sentences and / or restrict him basic pattern.
2
37 rather strongly affected by language problems.
3
Usually hesitant, often forced into silence by language problems.
2
Speech as so halting
38
make conversation
virtually impossible.
5. Comprehensible
Appears to understand
everything without
difficulty
5
Understands nearly
everything at normal
speed although
Has great difficulty
following what is said. 2
Cannot be said to understand even simple
conversation of
English.
1
In this case, the writer made an equation of making students’
oral tests. The score if each was multiplied by four, so, the highest
39
four. Then multiplies four by four, so, the score of students’ grammar
is 16. Here is the identification of the scores:
fluency, 2 in comprehension and 2 in pronunciation. So, the student’s
total score will be:
The score of speaking based on the five components can be compared
40 were processed in several steps. The first step, the scores and the averages were calculated. In the second step, the process revealed the normality of the distribution of both the data. The last step was finding out the correlation between the two variables, measuring it and then interpreting it as to significant or not. To begin with, the first step was calculating the scores that each student had.
As has been stated, the scoring of the tests was used to find out the average of the tests. The result of the average will then be used to measure the subjects’ mastery of both tests: the mastery of collocation and speaking performance. The average calculated by the formulaas follows:
Calculating the score of students’ mastery on collocation:
41
By which:
Px = score obtained Ʃ X = sum of X
N = number of sample
Calculating the score of students’ speaking performance:
= Nx100 × 100%∑
By which:
Py = score obtained (speaking performance)
Ʃ Y = sum of Y score
N = number of samples
42 CHAPTER IV
DATA ANALYSIS
In this chapter, the writer presents and analyzes the data that have been done by the second semester students of English Department of IAIN Salatiga in the academic year of 2016/2017. The data analyses are about two variables students’ collocation mastery (variable X) and their speaking performance (variable Y). Furthermore, the findings will be used to answer the objectives of the research which is explained in the chapter I. The objectives of the research are:
1. To identify how far the students’ collocation mastery for the second
3. To examine the correlation of students’ collocation mastery on speaking performance for the second semester students of English Department of IAIN Salatiga in the academic year of 2016/2017.
A. Data Analysis
43
The writer used test to obtain the score of students’ collocation mastery (variable x). In composing the test, the writer used both multiple choice tests and matching type tests.
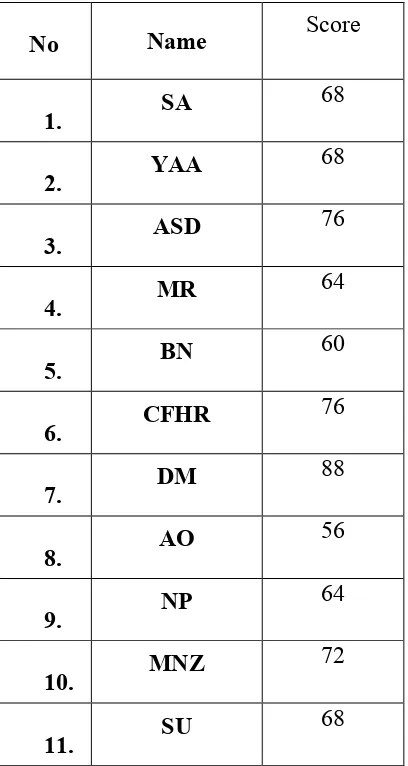
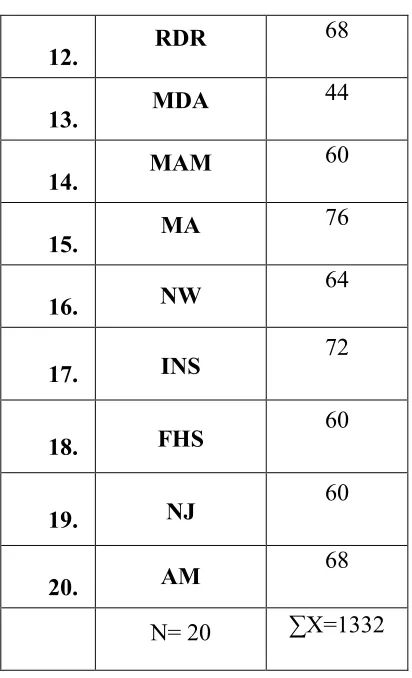
The score of students’ collocation mastery can be seen in the following table:
Table 4.1 Score of Students’ Collocation Mastery
44
Table 4.2 Score of Students’ speaking performance
No Name Score
1. SA 78
2. YAA 78
3. ASD 85
46
Furthermore, the writer will calculate the data to find out the percentage of students’ collocation mastery by using the formula:
Collocation Mastery:
=Nx100 × 100%∑
By which:
Px = score obtained (collocation mastery)
47
=Nx100 × 100%∑
By which
Py = score obtained (speaking performance)
Ʃ Y = sum of Y score
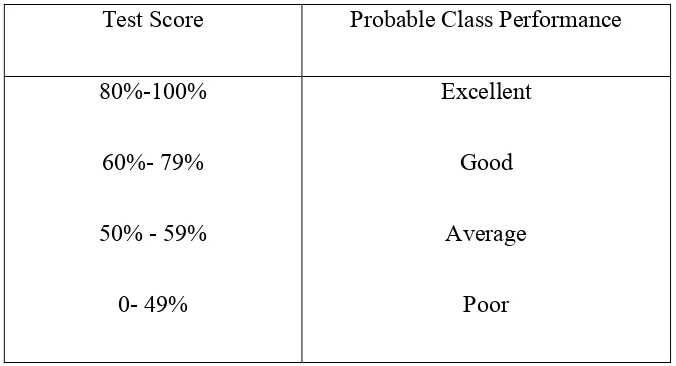
By finding out the average, it is interpreted to what extent is the mastery of collocation mastery and the speaking performance the students have. To determine the mastery and the knowledge level of the students, the result based on the criteria made by Harris (1969,134) who classifies the range of scores with its probable class performance
48
Table 4.3 Classifies the Range of Scores
Test Score Probable Class Performance
80%-100%
This result shows that the students of Second semester of IAIN Salatiga in the academic year of 2016/2017 have a good level in mastering the collocation with grade 6,66and the level of speakingperformance is excellent with grade 81,8.
4. Finding out the Correlation between students’ collocation mastery of
speaking performance.
In this research, the writer uses the correlation product moment to get the correlation between students’ collocation mastery of speaking performance.
50
From table above the writer finds: ƩX = 1332
ƩY = 1637 ƩX² = 90320 ƩY² = 135351 ƩXY = 109364
51
The result of calculating the correlation between students’ collocation mastery and speaking performance is 0,229. From the interpretation of r value, 0,229 is between 0,200 – 0,400. It indicates that there is correlation between students’ collocation mastery and speaking performance in Second semester students of IAIN Salatiga in the academic year of 2016/2017, but the correlation is low.
52
The r value Interpretation
0,800 – 1.00 Very High students’ collocation mastery for the second semester students of English Department of IAIN Salatiga in the academic year of 2016/2017. The data gained by the multiple choices testing and matching type that consist of 25items. The highest score is 88 and the lowest score is 44 of the interval 1-100. The writer concludes that the students of Second semester of IAIN Salatiga in the academic year of 2016/2017 have a good level in collocation mastery with grade 6,66.
53
assessments. The highest score is 95 and the lowest score is 70 of the interval 1-100. Finally the writer concludes that the students’ speaking performance in Second semester students of English Department of IAIN Salatiga in the academic year of 2016/2017 is excellent with grade 81,8.
The last discussion is the correlation of students’ collocation mastery on speaking performance for the second semester students of English Department of IAIN Salatiga in the academic year of 2016/2017. To know the correlation between students’ collocation mastery and speaking performance, the writer uses Pearson product moment formula. The result of calculating is 0,229 and the number of sample is 20. It means that the result of correlation is positive and there are correlation between students’ mastery on collocation and their speakingperformance although the correlation is low, because from the interpretation of r 0,229 exists between 0,200 – 0,400 shows that the correlation is low.
54 C. Hypothetical Conclusion
The calculation of product moment correlation analysis is 0,229 and the score of critical r table is 0.444 in the level of significant of 5% and the number of sample is 20 students. In this way r-calculation ≤ r-table by which 0,229 ≤ 0.444 so Ho is accepted. Ho is “There is no significant correlation between students’ collocation mastery on speaking performance in the second semester students of English department of IAIN Salatiga in the Academic year of 2016/2017”.
55 CHAPTER V
CLOSURE
In this chapter, the writer presents the conclusion that is related with three objectives of the research. The firstly is to know how far is the profile of students' mastery on their collocation. The second is to know how the profile students’ speaking performance. The last is the correlation of students’ collocation mastery on speaking performance for the second semester students of English department of IAIN Salatiga in the academic year of 2016/2017. Moreover, the writer would like to give some suggestion to the teacher, students, or other researcher.
A. Conclusion
Based on the data findings and discussion in the previous chapter, the writer concluded the result of the study as follows:
1. The Profile Students’ Mastery on Collocation of the Second Semester Students
56
2. The Profile Students’ Speaking Performances of the Second Semester Students
According the writer, the profile students’ speaking performance of the Second Semester Students of English Department of IAIN Salatiga in the Academic Year of 2016/2017 is excellent. Proven by the percentage of students’ writing achievement, it is 81,8 %.
3. The Correlation of Students’ Collocation Mastery on Speaking Performance Yes, there is any correlation between the students’ collocation mastery on their speaking performance. Based on the data analysis in the chapter IV, the writer gains the score of r count is 0.229 from the interpretation of r value 0.229 is existing between 0,200 – 0,400. The rcount which is 0.229 is smaller than the rtable which is 0.444. It means that H0 is accepted; while Ha
57 B. Suggestions
Based those conclusions, the writer would like to propose some suggestions for the English teachers, the students, and the other researchers. The writer hopes it will be useful for them.
1. For English Teachers
a. The English teacher should be more introduce the collocation to the students.
b. The teacher can more often use collocation in the class.
c. The teacher can combine the task of speaking performance use collocation.
d. The teacher should be creative in teaching collocation.
2. The Students
The students should improve their collocation mastery as follow: a. Increasing their knowledge related with collocation.
b. Keeping in mind the pair of words which used together. c. Identifying the collocation in a text by underlining it.
d. Practicing the collocation in a sentence or in daily speaking. e. Using the collocation dictionary when you find the difficulty.
58 3. For the Other Researcher
59
REFFERENCES
Abousenna, M. (1994).“Opening Speech. Global Age: Issues in English Language Education”. Proceedings of 13th National Symposium on
English Language Teaching. March 30- April 1 , 1993. CEDELT,Ain Shams University.
American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language, (2000:1078). Arikunto,S.2002.ProsedurPenelitian(5threv.edn).Jakarta:PTRinekaCipta.Ba
chman& Palmer, (1996).Defining Communicative Competence.
Bachman & Palmer.Language Testing in Practice.Oxford University Press.1996
Brown.(2001). Teaching by Principle an Interactive Approach to Language Pedagogy.
Byrne,Donn. Teaching Oral English.n.d. Longman
Cahyo, Nur.(2015). A Correlative Study between Students’ Lexical Knowledge of Collocations toward Their Reading Comprehension.
Carlson, Marvin.(2003). Performance A Critical Introduction.
Creswell, John W. (2012).Educational research.United States of America: Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data.
Creswell, John W.(2009). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approache. United States of America: Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data.
60
Harris, D.P.(1969). Testing English as a Second Language. New York: McGrawHill Book Company.
Henter, Ramona.(2013).Developing Metacognitive Skills As A Foundation Of Learning A Foreign Language.
Huang, Heng-Tsung Danny.(2010). Modeling the relationships among
topical knowledge, anxiety, and integrated speaking test
performance: A structural equation modeling approach.The
University of Texas at Austin, ProQuest Dissertations Publishing.
Lewis, Michael.(2000).Teaching Collocation: Further Development in the Lexical Approach. Boston: Thomson.
Carlson, Marvin. n.d. Performance:A Critical Introduction. New York and London.Routledge.
McCarthy, Michael & Felicity O’Dell.(2005). English Collocation in use. Cambridge: Cambridge Press.
Nation & Newton.(2009).Teaching ESL/EFL Listening and Speaking.NewYork :Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data.
Nuray Bayar Muluk.(2009).Effects of listening ability on speaking, writing and reading skills of children who were suspected of auditory processing
difficulty.Journalhomepage:www.elsevier.com/locate/ijporl. Oxford Learner‘s Pocket Dictionary.(2011).
61
Shiamaabd El Fattah.2006. The Effectiveness of a Task- Based Instruction program in Developing the English Language Speaking Skills of Secondary Stage Student. Ain Shams University Women’s college Curricula and Methods of teaching Department.
The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language.(2000).
Wahyuni, Dwi,.Linguistic Competence and Speaking Performance of English Education Study Program Students of Sriwijaya University.
Webster, A Merriam. (1974). The New Grolier Webster International Dictionary. Grolier
62
63
Address :Tawang Sari Rt.02 / Rw.01, Grogolan, Karanggede, Boyolali
E-mail/Phone Number : [email protected] / +6281319185594 Education : 1. 2000-2005 : SD NegeriGrogolan
2. 2005-2008 :MTs N Karanggede 3. 2008-2011 :SMKPelitaSalatiga 4. 2013-2017 :IAINSalatiga
September, 12th 2017
64 I. Collocation Mastery Test
Name : Nim :
I. Complete each of the following sentences using the correct collocation!
1. My father likes ________ in the morning.
a. strong tea b. Powerful tea c. Hard tea 2. I cannot come to your house because it is ________.
a. Hard rain b. Strong rain c. Heavy rain 3. This snack is ________
a. Rich flavor b. Rich taste c. Rich sensation 4. I can ________ by myself
a. do homework b. Make homework c. Work homework
5. My son's teacher says he doesn't ________ attention in his lessons. a. Give b. Pay c. Do 6. So many ________ in the sky.
a. A cluster of bees b. a swarm of bees c. Lot of bees 7. I would like to buy two ________ of soaps.
a. Bars b. Stick c. Slice 8. We had to return home because we had ________.
a. run out of money b. Spend out of money c. Use out of money
9. Mary ________ in John’s ear.
a. Whispered tenderly b. Whispered weakly c. whispered softly 10.You should ________ regularly .
65
11.I don't think we should________ a decision yet; we should wait. a. Do b. make c.create 12.Only 31% of the students who ________ the final exam passed it.
a. Took b. had c.made 13.To make yourself fit, you just need ________ exercise.
a. repeated b. Continual c.regular 14.I don't like this at all. It's a really ________ affair.
a. Unfair b.blunt c. ugly
15.She was a / an ________ wife who loved her husband more than anything else in the whole universe.
a. Devoted b. sincere c. intelligent
II. Take a look at the following questions and decide which collocation are the best match!
1. Many stories about how the world _______. 2. It’s never easy to _______ a relationship. 3. I _______ a bad dream last night.
4. Many European countries use the euro as their standard unit of _______. 5. You must _______ your application before January.
6. They have a _______ life.
7. Her _______ of flower is the best of all.
8. I am going to _______ up the meaning in the dictionary. 9. The accident happened because he was _______ dangerously. 10.More than 10.000 people _______ in the experiment.
66 II. Speaking performance Task
1. Watch the movie entitle “Homeless to Harvard”. 2. Make some review about the movie.
3. Retell and answer the questions: a. What the gist of the film?
b. What have you learned from the film?
c. What the connection of the film with your own story? 4. Using collocation in your speech.
67
The Answer Key of Collocation Mastery Test I. Multiple Choices Test
4. standard unit of currency 5. send your application 6. hard life