www.elsevier.com / locate / bres
Interactive report
Changes in estrogen-
a
receptor immunoreactivity during the estrous
1
cycle in lactating dairy cattle
a ,
*
a bFrank J.C.M. van Eerdenburg
, Ineke A.J.J.M. Daemen , Eline M. van der Beek ,
c
Fred W. van Leeuwen
a
Department Farm Animal Health, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Utrecht University, Yalelaan 7, 3584 CL, Utrecht, The Netherlands
b
Human and Animal Physiology Group, Department of Animal Science, Wageningen University, Haarweg 10, 6709 PJ Wageningen, The Netherlands
c
Netherlands Institute for Brain Research, Meibergdreef 33, 1105 AZ Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Accepted 26 August 2000
Abstract
Estradiol is one of the most important hormones in the regulation of estrous behavior, which is at a very low level of expression in the modern dairy cow. In the present study the neuroanatomical distribution of estrogen receptors of thea-subtype (ER-a) in the bovine hypothalamic area is determined with immunocytochemical methods, at various stages of the estrous cycle. During the luteal phase of the cycle, ER-aimmunoreactive cells were found in most of the nuclei that are known to express ER-aimmunoreactivity in other species, like the Bed nucleus of the Stria terminalis, Medial preoptic area, Ventromedial hypothalamus and Arcuate nucleus. During estrus and metestrus, however, no ER-aimmunoreactive cells could be detected in those areas, except for a few in the caudal Arcuate nucleus. The results from the present study indicate that there is a coherent regulation and timing of physiological and behavioral events around ovulation, in which estradiol and its receptor play a key role. 2000 Elsevier Science B.V. All rights reserved.
Theme: Neural basis of behavior
Topic: Hormonal control of reproductive behavior
Keywords: Hypothalamus; Bovine; Sexual behavior; Estradiol; Regulation
To determine the right moment for artificial insemina- tion of potential sites of its action are visualized using tion, a common procedure in dairy farming, a farmer has to immunocytochemistry for ER-a at both follicular and detect his cows in estrus. Recent studies, however, indicate luteal stages of the estrous cycle.
that the intensity of estrus expression by dairy cattle is Brains of adult, non-pregnant cows were obtained at the declining [5,19]. In the regulation of the estrous cycle and abbatoir. The ovaries of the animals were inspected in reproductive behavior, estradiol is one of the most im- order to determine the stage of the estrous cycle. Six portant hormones and estrogen receptor-a the most im- animals were in luteal phase, of which one was at the end portant receptor type [6,8,14,15]. So far, no studies on the of the first follicular growth wave, having one large follicle distribution of ER-a in the bovine brain have been on one of the ovaries. One animal was in proestrus, two reported. Since estradiol could be a factor in the cause of were in estrus, two in the preovulatory phase of metestrus the low estrus expression, in the present study the localiza- and one was just post ovulation. Another was about 1 week post partum, without signs of cyclic activity on the ovaries. Two animals were ovariectomized 13 days prior to perfu-sion.
After killing the cows by rapid decapitation, the heads
1
Published on the World Wide Web on 7 September 2000. were immediately perfused through both carotid arteries *Corresponding author. Tel.: 131-30-253-1248; fax: 1
31-30-252-with 6 l of cold saline containing 25 000 IU heparin. The
1887.
heads were transported to the laboratory and perfused with
E-mail address: [email protected] (F.J.C.M. van
Eer-denburg). phosphate buffered 4% paraformaldehyde containing 0.5%
220 F.J.C.M. van Eerdenburg et al. / Brain Research 880 (2000) 219 –223
glutaraldehyde. The hypothalamus and brainstem were A more detailed description of the specific distribution immersion fixed for 11 h in the same fixative at 48C on a of ER during every phase of the estrous period in the cow, rocking table. however, requires more animals in each stage of the cycle. Serial 80 mm thick sections of the hypothalamus and Also, a more detailed analysis of the up- or down brainstem were cut on a vibratome and immunostained as regulation of ER throughout the estrous period might described previously [18] with H222 [7] as primary reveal indications for the regulatory mechanisms of steroid antibody, biotinylated anti rat-Ig as second antibody receptors. The relatively short duration of estrus and large (Amersham) and the ABC Vectastain Elite procedure. individual variation (4–36 h), combined with a large Sections of animals in different stages of the estrous cycle variation in cycle length (18–24 days) have withheld us so were stained in the same immunocytochemical procedure. far [19].
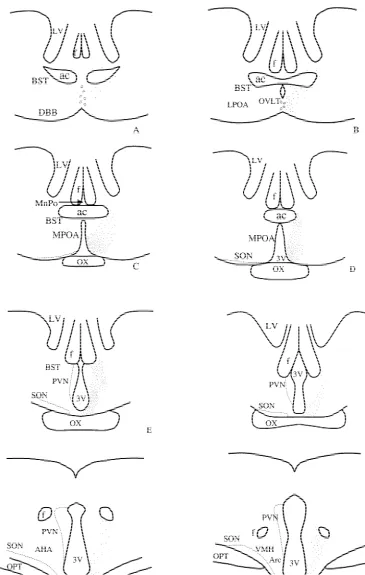
Fig. 1. Schematical drawings of the hypothalamic area of the bovine brain. ER-immunoreactive cells are represented by dots. Each dot represents approximately 10 immuno positive cells. These drawings are obtained from cows in the luteal phase (see text for details). Abbreviations: 3 V5Third ventricle, ac5Anterior commisure, AHA5Anterior hypothalamic area, Arc5Arcuate nucleus, BST5Bed nucleus of Stria terminalis, DBB5Diagonal band of Broca, f5Fornix, LPOA5Lateral preoptic area, ME5Median eminence, MnPo5Median preoptic nucleus, MPOA5Medial preoptic area, mt5
Mammilo-thalamic tract, LV5Lateral ventricle, OPT5Optic tract, OVLT5Organum vasculosum of the Lamina terminalis, OX5Optic chiasm, PVN5
222 F.J.C.M. van Eerdenburg et al. / Brain Research 880 (2000) 219 –223
Fig. 1. (continued )
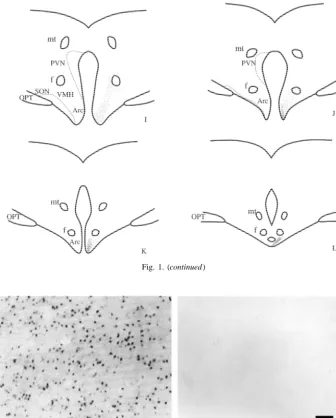
Fig. 2. Photomicrographs of the MPOA of a cow in diestrus (left) and estrus (right) after immunostaining for ER-a. Bar indicates 50mm.
[4] T.J. Dijkhuizen, F.J.C.M. van Eerdenburg, Behavioural signs of
Acknowledgements
oestrus during pregnancy in lactating dairy cows, Vet. Quart. 119 (1997) 194–196.
The authors thank Dr G.L. Greene for his generous [5] R.J. Esslemont, J.H. Balie, M.J. Cooper, Fertility management in supply of H222 antibody. dairy cattle, Collins, London (1985) pp. 70–93.
[6] B. Greco, P. Schwartz, J.D. Blaustein, Estrogen beta colocalizes with other steroid receptors in neurons in the female rat brain. Soc. Neurosci. Abs. 25 (1999) abs 245.12 p. 613.
[7] G.L. Greene, N.B. Sobel, W.J. King, E.V. Jensen, Immunochemical
References
studies of estrogen receptors, J. Steroid. Biochem. 20 (1984) 51–56. [8] M. Kawata, Roles of steroid hormones and their receptors in [1] J.F. Axelson, F.W. van Leeuwen, Differential localization of es- structural organization in the nervous system, Neurosci. Res. 24
trogen receptors in various vasopressin synthesizing nuclei of the rat (1995) 1–46.
brain, J. Neuroendocrinol. 2 (1990) 209–216. [9] Y. Kazunari, M. Kawata, The effect of estrogen on the estrogen [2] J.D. Blaustein, Estrogen receptor-immunoreactivity in rat brain: receptor-immunoreactive cells in the rat medial preoptic nucleus,
rapid effects of estradiol injection, Endocrinology 132 (1993) 1218– Brain Res. 548 (1991) 50–54.
1224. [10] M.N. Lehman, F.J. Ebling, S.M. Moenter, F.J. Karsch, Distribution [3] S.J. Dieleman, M.M. Bevers, H.T.M. Van Tol, A.H. Willemse, of estrogen receptor-immunoreactive cells in the sheep brain,
Peripheral plasma concentrations of oestradiol, progesterone, cor- Endocrinology 133 (1993) 876–886.
tisol, LH and prolactin during the oestrous cycle in the cow, with [11] H.-Y. Li, J.D. Blaustein, G.J. De Vries, G.N. Wade, Estrogen-receptor emphasis on the perioestrous period, Anim. Reprod. Sci. 10 (1986) immunoreactivity in hamster brain: preoptic area, hypothalamus and
[12] C.A. Lisciotto, J.I. Morrell, Circulating gonadal steroid hormones [16] D.W. Pfaff, M. Keiner, Atlas of estradiol-concentrating cells in the regulate estrogen receptor mRNA in the male rat forebrain, Mol. central nervous system of the female rat, J. Comp. Neurol. 151
Brain Res. 20 (1993) 79–90. (1973) 121–158.
[13] Z.C. Lyimo, M. Nielen, W. Ouweltjes, Th.A.M. Kruip, F.J.C.M. Van [17] W.E. Stumpf, M. Sar, D.A. Keefer, Atlas of estrogen target cells in Eerdenburg, Relation between estradiol, cortisol and intensity of rat brain, in: W.E. Stumpf, L.D. Grant (Eds.), Anatomical Neuroen-estrous behavior in dairy cattle, Theriogenology 53 (2000) 1783– docrinology, Karger, Basel, 1975, pp. 104–119.
1795. [18] F.W. Van Leeuwen, S. Chouham, J.F. Axelson, D.F. Swaab, F.J.C.M. [14] K.T. O’Byrne, M.D. Chen, M. Nishimura, C.L. Williams, J.C. Van Eerdenburg, Sex differences in the distribution of estrogen Thalabard, J. Hotchkiss, E. Knobil, Ovarian control of gonadotropin receptors in the septal area and hypothalamus of the domestic pig hormone releasing hormone pulse generator activity in the Rhesus (Sus scrofa), Neuroscience 64 (1995) 261–275.
monkey: duration of the associated hypothalamic signal, Neuroen- [19] J.H. Van Vliet, F.J.C.M. Van Eerdenburg, Sexual activities and docrinology 57 (1993) 588–592. oestrus detection in lactating Holstein cows, Appl. Anim. Behav. [15] S. Ogawa, K.S. Korach, J. Gustafson, D.W. Pfaff, Survival of Sci. 50 (1996) 57–69.