A PRAGMATICS ANALYSIS ON PUBLIC SERVICE ANNOUNCEMENTS
IN TIME, NEWSWEEK, AND READER’S DIGEST MAGAZINES
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Christina Sudyasjayanti
Student Number: 071214088
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
i
A PRAGMATICS ANALYSIS ON PUBLIC SERVICE ANNOUNCEMENTS
IN TIME, NEWSWEEK, AND READER’S DIGEST MAGAZINES
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Christina Sudyasjayanti
Student Number: 071214088
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
iv
He makes all things beautiful, in His time.
“In His Time”
Dedicated to my beloved parents: …. Bapak J. S Adi Sugijanta
vii
ABSTRACT
Sudyasjayanti, Christina. (2012). A Pragmatics Analysis on Public Service Announcements in Time, Newsweek, and Reader’s Digest Magazines. Yogyakarta: English Education Study Program Sanata Dharma University.
Public Service Announcement (PSA) is a kind of non-commercial advertisement which intends to serve public interest by raising awareness of an issue, affecting public attitudes, and potentially stimulating action. The message on PSA usually contains a certain meaning that is difficult to interpret. Further, communication process requires that the message should be understood to make successful persuasion in advertisement. There are two questions would be answered through this research: 1) How does the headline of the PSAs obey Grice’s Cooperative Principle? 2) How do the headline and subhead on PSAs presuppose to express the speaker’s meaning?
Grice’s CP has four guidelines to achieve successful communication process. They were maxim of quality, maxim of quantity, maxim of relevance, and maxim of manner. Besides, advertisements usually express the indirect ideas rather than the direct ideas. Thus, it is important to find out the indirect idea that is expressed on advertisement through finding out the presupposition. This research on presupposition would lead the reader to find the presupposition function in advertisement.
The method used in this qualitative research was document analysis. The researcher took 22 PSAs from Time, Newesweek, and Reader’s Digest published on January 2010 up to March 2011. The advertisements were limited on display advertisements. The researcher was the primary instrument in this research. In order to analyze the data, the researcher has conducted several steps that proposed by Creswell (1998) as cited by Leedy and Ormrod (2005, p.151). They are: 1) organizing the data, 2) perusing the data, 3) identifying the data, and 4) synthesizing. To answer the second question, the researcher has conducted a library study to gain better understanding of the problem to interpret the possible answer.
The headline identification found that 20 headlines are in agreement with maxim of quality, 20 are in agreement with maxim of quantity, 20 are in agreement with maxim of relevance, and 16 in agreement with maxim of manner. On the other hand, two headlines in disagreement with maxim of quality, two in disagreement with maxim of quantity, two headlines in disagreement with maxim of relevance, and six disagree with maxim of manner. Those in disagreement headlines are aimed at making the advertisement interesting. By finding out the presupposition of headline and subhead, the researcher concluded that the speaker’s meaning usually does not express directly. Presupposition was used to express the persuasive meaning to persuade addressees using the product or service, express the interest meaning to attract addressees to join urgent program, and express the memorable advertisement. Additionally, those PSAs were useful for the English teacher to provide the authentic sources for learning process.
viii
ABSTRAK
Sudyasjayanti, Christina. (2012). A Pragmatics Analysiss on Public Service Announcements in Time, Newsweek, and Reader’s Digest Magazines. Yogyakarta: Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Iklan layanan masyarakat digolongkan kedalam iklan non-komersial yang dimaksudkan untuk memberi keuntungan pada masyarakat dengan meningkatkan kesadaran terhadap isu tertentu, mempengaruhi tingkah laku masyarakat, dan berpotensi menstimulasi suatu tindakan. Pesan yang terkandung dalam iklan layanan masyarakat umumnya membawa suatu makna tertentu yang sulit diinterpretasikan. Lebih lanjut, proses komunikasi membutuhkan pesan yang dapat dimengerti dengan baik dengan tujuan untuk membuat bujukan yang sukses dalam iklan. Dua buah pertanyaan yang akan dijawab dalam penelitian ini adalah: 1) Bagaimanakah kesesuaian headline iklan layanan masyarakat terhadap cooperative principle Grice? 2) Bagaimanakah headline dan subhead dari iklan layanan masyarakat diekpresikan guna mengetahui maksud pengiklan?
Cooperative Principle dari Grice mempunyai empat garis besar guna mencapai proses komunikasi yang berhasil. Keempat garis besar itu ialah maxim of quality, maxim of quantity, maxim of relevance, and maxim of manner. Disamping itu, iklan pada umumnya mengekspresikan gagasan secara tidak langsung daripada gagasan secara langsung, sehingga sangat penting untuk menemukan gagasan yang tidak langsung tersebut dengan menemukan presupposition dari iklan. Selain itu, penemuan dari presupposition tersebut akan menuntun pada fungsi presupposition dalam iklan.
Metode yang digunakan pada penelitian kualitatif ini ialah dokumen analisis. Peneliti mengambil 22 iklan layanan masyarakat dari Time, Newesweek, and Reader’s Digest yang terbit pada Januari 2010 sampai Maret 2011. Iklan yang diambil dibatasi pada iklan display. Peneliti adalah instrument utama dalam penelitian ini. Untuk menganalisa data, peneliti telah melakukan beberapa langkah yang diusulkan oleh Creswell (1998) seperti dikutip dalam Leedy dan Ormrod (2005). Langkah-langkah tersebut ialah: 1) mengorganisir data, 2) mengkaji data, 3) mengidentifikasi data, dan 4) mensintesa (p.151). Untuk menjawab pertanyaan kedua, peneliti telah melakukan studi pustaka untuk mendapatkan pemahaman yang mendalam yang akan digunakan untuk mengurai kemungkinan jawaban.
ix
dalam program penting, dan untuk mengekspresikan iklan agar mudah diingat. Sebagai tambahan, iklan layanan masyarakat tersebut berguna bagi guru Bahasa Inggris untuk memberikan sumber yang autentik bagi proses belajar.
x
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Above all, I would like to praise my Lord and my savior, Jesus Christ. He is the one I have put my life on, thank you for giving me so much love and strength that I could finally accomplish this wonderful project. I thank Him for lots of lessons He has given to make me more mature. All I could say is that I am nothing without Him.
I also would like to express my gratitude to those who have supported me. First, I would like to thank Carla Sih Prabandari, S.Pd., M.Hum., my sponsor, for her guidance and advice in the completion of my thesis. I am grateful to her carefulness to give me the meaningful improvements for my thesis.
Second, I also thank all the lecturers and the staff of English Language Education Study Program for their participation in my “journey.” I thank them
for the knowledge and experiences they have shared. I believed that the knowledge and experiences will be so much useful for me in the future.
Third, my deepest gratitude goes to my beloved parents, Bapak J.S. Adi Sugijanta and Ibu Lusiana Sutinem. Their love shines on me like the sun. Their hopes and prayer are my strength to go through and do all I have to do. My sincere thanks also go to my brother, Agung Prasanto Nugroho who always scoffs to motivate me finish this project. Finally we graduate together.
xi
all my friends in Borrowed Beauty. I thank them for their never-ending support that keeps me strong to move on. This friendship will never end and the memories will remain.
xii
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE PAGE……… i
APPROVAL PAGE……….. ii
DEDICATION PAGE………... iv
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY………. v
PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIAH….………….. vi
ABSTRACT……….. vii
CHAPTER II. REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE A. Theoretical Background…………..………. 9
xiii A. The Headlines Agreement on Grice’s CP Maxims………...……... 35
1. The Maxim of Quality……… 37
2. The Maxim of Quantity……….. 40
3. The Maxim of Relevance………... 42
4. The Maxim of Manner………... 45
B. The Speaker’s Meaning on Headlines and Subheads………. 46
1. Advertisement 1 (WWF)……… 47
2. Advertisement 2 (Tetra Pak)……….. 48
3. Advertisement 3 (World Food Programme)………... 49
4. Advertisement 4 (National Geographic Organisation)………... 50
5. Advertisement 5 (World Food Programme)………. 51
6. Advertisement 6 (World Food Programme)………... 52
7. Advertisement 7 (WWF)……… 54
8. Advertisement 8 (Jesuit Refugee Services)……… 55
9. Advertisement 9 (World Food Programme)………... 56
10. Advertisement 10 (Habitat for Humanity)………... 57
11. Advertisement 11 (Shell)……….. 57
12. Advertisement 12 (WWF)……… 58
xiv
14. Advertisement 14 (Jesuit Refugee Services)……… 59
15. Advertisement 15 (Shell)……….. 60
16. Advertisement 16 (Tetra Pak)……….. 61
17. Advertisement 17 (Heifer International)……….. 61
18. Advertisement 18 (WWF)……… 62
19. Advertisement 19 (Shell)……….. 62
20. Advertisement 20 (EDF for Thailand)………. 63
21. Advertisement 21 (Medical Sans Frontiers)………. 63
22. Advertisement 22 (WWF)……… 64
3. English Language Teacher………. 68
REFERENCES……….. 69
APPENDICES Appendix 1: The List of Advertisement Published………. 70
Appendix 2: The List of Headline………... 71
Appendix 3: The List of Subhead……… 72
Appendix 4: The List of Bodycopy………. 74
Appendix 5: Tabel of Headline Obedience to Grice’s CP Maxims…. 77 Appendix 6: The PSA from Time Magazine………... 79
Appendix 7: The PSA from Newsweek Magazine………... 81
xv
LIST OF TABLES
Table Page
4.1 The amount of headlines obedience
xvi
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure Page
2.1 The Advertisement’s Elements ……… 11
2.2 Constitutive Factors of Speech Event ……… 15 2.3 Human Communication Process by
Peter & Olsen (in Arens, 2006, p.9) ……… 16
2.4 Chocolate Advertisenment ……… 18
2.5 The Relationship of Semantic Meaning and Speaker’s Meaning
(in Fasold & Linton: 2006) ……… 24
3.1 Data Analysis Spiral (based on Creswell,
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter contains six sections that describes the nature of the research. It describes the researcher‟s ideas. This chapter consists of the research background, the problem formulation, the problem limitation, the research objectives, the research benefits, and the definition of terms.
A.Research Background
Advertisement is common in our daily life, as in billboard, magazine, newspaper, and television. Advertisement is usually used to advertise a certain product. Each advertisement has their characteristics. In order to attract people advertisements usually use interesting language and contain a certain message on it. According to Goddard (1998) “the terms of „advertisement‟ and „advertising‟ have, at their root, a Latin word, „adverte‟, meaning „turn towards‟ (p. 9).” AMA (American Marketing Association) on Berkman (1980) describes advertising as,
Bovee and Arens (1986) says, “Stimulate inquiries for information, popularize social cause, change activity habits, decrease waste of resources, communicate political viewpoint, improve public attitude, inform public of new cure, and remind people to give again (p. 579).” It is used as the objectives of noncommercial advertisement.
Advertising is categorized a mass communication; it means that people are involved in. The involved people are the consumer or buyer, the copywriter, and the producer or the businessman. Thus, advertisement should inform the complete information for the consumer; it means that the advertisement should contain the product‟s features, the ingredients, the price, and the location where it to sell. Hence, advertisement is functioned as a persuasive tool to persuade the consumer. Through advertisement, hopefully the consumer would buy the product. Bovée and Arens (1986) say, “advertising is salesmanship in print (p. 5).” Advertisement works as well as a salesman to sell the product. The salesmanship of advertisements has proved by its language to persuade people.
According to Arwood (1983), “Communication refers to the conveyance of an intended message so as to act to alter a hearer‟s attitudes, beliefs, or
makes their advertising interesting to addressee. Goddard (2002) explains that the purpose of it is to make the readers respond quickly or to make us being informed about the services or products clearly. Besides, it makes the meaning of advertising life because the readers understand the message clearly. Thus, in the printed advertisement the advertiser makes it speaks through text. Goddard (2002) says, “The word „text‟ here is used in its widest sense, including visual artifacts as well as verbal language (p.6).” There are many ways to make advertisement interesting, the copywriter uses the attractive picture, font, and words to make the hearer or the reader interested.
Boove and Arens (2006) say, sometimes the copywriters use improvisation in language. They make the improvisation of the standard terms in order to make the advertisements interesting for the readers or listeners and to change the communication. Mostly, the language in advertising uses the figurative language. Goddard (2002) says that the other visual features such as layout and images attract the readers and listeners interest.
A successful communication involves both the addresser and the addressees, because they have a certain role in a communication process. The addresser‟s duty is to deliver the message he/she wants to convey. On the other hand, the addressees‟ duty is to interpret the message from the addressees. In order to make the communication exist, both addresser and addressees should have the same perception about the communication topic. It is aimed to avoid the misunderstanding between them. Besides, both addresser and addressees ought to have the background knowledge about what are they talking about. The conveying message from the addressees could be a statement, command, or question.
This research aims to analyze the language use in advertisement as a communication tool. Besides, the researcher aims to analyze the intention of the advertisement, through analyzing the presupposition of the headline and subhead. In order to limit the research, the researcher will analyze twenty-two Public Service Announcements which have been taken from Time, Newsweek, and Reader’s Digest magazines which have been published on January 2010 up to
B. Problem Formulation
There are two problems which will be discussed in this research. The problems are formulating as follows.
1. How does the headline of the PSAs obey Grice‟s Cooperative Principle?
2. What do the headline and subhead on PSAs presuppose to express the speaker‟s meaning?
C.Problem Limitation
In this research, the researcher analyzes the twenty-two Public Service Announcements taken from Time, Newsweek, and Reader’s Digest magazines published on January 2010 up to March 2011. Bovee and Arens (1986) state, “their particular mission in life, be it politics, welfare, religion, conservation, health, happiness, or love (p.578)” those are the aims of PSA. The researcher chooses the display advertisement. According to Bovee and Arens (1986) the qualification of display advertisement has four major elements; headline, body copy or text, picture or image, and typography (para. 404). The researcher focuses to analyze the headline of PSA because headline is the leading position in advertisement. Arens (2010) says that, “The headline contains the words leading position in the advertisement – the words that will be read first and are situated to draw the most attention (p. 417).”
message. On the second part, the researcher is analyzing the headline and subhead presupposition in order to find out what the speaker intention to say.
D.Research Objectives
The objectives of this research are to answer the questions stated in the problem formulation. This research is aimed to:
1. analyze the headline agreement on Grice‟s CP maxims
2. analyze the headline and subhead presupposition to find out what the speaker‟s intention.
E.Research Benefits
The benefits of this research are:
1. The benefits for English Language learners are:
a. The learners will have a wider perspective in the language of advertising. b. The learners will have a broader study about the meaning.
c. The learners will able to use the appropriate terms used in advertising. If they want to persuade somebody they should use the appropriate words. 2. The benefit for the advertiser:
It helps the advertiser to make the comprehensive advertisement for addressees.
3. The benefit for the future advertisement research:
F. Definition of Terms
1. Pragmatics Analysis
In this study, the researcher focusing on analyzing how succeed an advertisement delivers the message to the addressee and how the headline and subhead express the advertiser‟s meaning. In order to achieve the successful communication between addresser to addressees, the addresser should consider the determined rules. Beside, when the speaker utters something, the speaker should consider the language used and the situation when the speaker speaks in order to avoid misunderstanding. Portner says, as cited by Fasold & Linton (2006), “Pragmatics focuses on the use of language in particular situations; it aims to explain how factors outside of language contribute to both literal and nonliteral meaning which speakers communicate using language (p. 137).” It is supported by Widdowson (1996), “This is not the same as what people mean by the language they use, how they actualize its meaning potential as communicative resource. This is the concern of pragmatics (p. 61).” This pragmatics analysis consider what people mean by the use of language both literal and nonliteral in a particular communication process.
2. Public Service Announcement
advertising used to inform something, persuade or educate the society in order to get the social benefit. The social benefit means the growth of knowledge, attitude awareness, the behavior change on society through some problems, and get the good image in society (para. 104). This research discusses PSA that appeared on the printed media.
3. Time, Newsweek, Reader’s Digest Magazines
9
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
This chapter is divided into two main parts namely theoretical background and theoretical framework. Theoretical description presents the theories related to this research. Meanwhile, the theoretical framework explains the organized theory to accomplish this study.
A.Theoretical Background
This theoretical description is presented in order to obtain a good understanding of language in advertising. This section consists of the theory about advertisement, communication, Grice‟s maxims, presupposition, and sentence and speaker‟s meaning.
1. Advertisement
can be concluded that advertising is communication of nonpersonal information that is useful, relevant, and inviting.
Bove and Arens (1986) mention the basic functions of advertising. The first is to make the product different from other. The second is to inform the society about the product. The third is to pursue the consumer to buy the product or service. The fourth is to spur on the product disseminating. The last is to raise the use of the product. On the other side, Goddard (2002) mentions the purpose of making advertisement by the copywriter, “The whole aim of the copywriters is
to get us to register their communication either for purpose of immediate action or to make favorably disposal terms to the advertised product or service (p. 9).” Therefore, the purposes of advertisement are to inform and to persuade the addressee about the product.
The example of noncommercial advertisement is PSA, Public Service Announcement. Federal Communication Commision (The Museum of Broadcast Communication) explains about the principal definition of PSA:
any announcement (including network) for which no charge is made and promotes programs, activities, or services of federal, state or local governments (e.g. recruiting, sale of bonds, etc.) or the programs, activities, or services of nonprofit organizations (e.g. United way, Red Cross blood donations, etc.) and other announcement regarded a serving community interests, excluding time signals, routine weather announcements and promotional announcements.
Advertising Council. Thus, any kind of advertisement that contains the concept of PSA called Public Service Announcement.
a. The Elements of Advertisement
According to Arens (2006, pp. 407-424), the key in printed advertising is made up of some elements.
Figure: 2.1 The Advertisement’s Elements
1) Headline
It contains the words in leading the advertisement; the word functions to draw the most attention to the advertising. The headline usually appears in a larger type than other part of advertisement. An effective headline can attract attention, engage the audience, explain the visual, lead the audience into the body of the ad, and present selling message. The headline divided into five types; benefit
Headline
Subhead
Bodycopy
headlines functions to promise the audience that experiencing the utility of the product or service will be rewarding, news/information headline functions to awake the readers‟ curiosity, question headline functions to attract the reader to search for the answer to the advertising question in the body of ad, and a command headline functions to make the reader do something through the order given.
2) Subheads
It is a smaller headline that appears above the headline, or called kicker (or overline). Subhead generally appears on boldface or italic. It carries less important information than the headline and formed like a sentence and longer than the headline. Subhead appears in order to give a short explanation about the advertisement.
3) Body Copy
Its function is to tell the readers about the complete sales story, it is also called a text. Body copy contains the features, benefit, and the utility of the product and service.
4) Slogans
Slogans also called as taglines or theme line. Slogans have two major purposes: to provide continuity to a series of ads and to make the advertising brief, repeatable, and memorable in positioning statement.
5) Seal, Logotypes, and Signature
value endorsement for the advertiser‟s product. Logotypes (logos) and signature
cuts (sign cuts) are specially designed to the company or product name.
b. The Requirement of a Good Advertising
The message on advertising is determined by what and how the company tries to express through advertising. In order to make the clear communication, copywriter should have a certain conditional for ads. Bovee and Arens (1986) mentioned the majors of a good copy in advertisement are:
1) Attention
The first objective in making an advertisement is to gain the attention from the customers. It is the major job description for a copywriter. The copy writer should determine the size of the ad and also the place where the ad will be published. 2) Interest
After we have got the customers‟ attention, we should keep their interest by
giving some reasons why they have to choose this product. The advertising should convince and persuade the customers. In this term, the copywriter can use cartoon characters, subhead, interior illustration, storyline copy, or charts and table.
3) Credibility
Nowadays, the customers are cleverer. They demand an evidence to convince themselves. The customers want something that is not manipulated. Credibility sometimes added to the ad by using a presenter.
4) Desire
product; a copywriter should know the customers well. The information of the product should increase customer‟s desire.
5) Action
An advertisement contains an action message. The act can be direct or indirect. In this case a copywriter can insert the implicitly message in the advertisement.
2. Communication
Communication is closely related to advertising. The advertising is a communication media of the speaker to the addressee. As defined by Weilbacher (1984), “The purpose of advertising is to communicate information – logical, emotional, or evaluative – to prospective purchasers or to people who will affect the advertiser‟s future goals in one way or another (p. 459).” Advertising is used for two purposes, to obtain the economical benefit and to affect the addressee.
Beside, Arwood (1983) has a notion that “Communication refers to the conveyance of an intended message so as to act to alter a hearer‟s attitudes, belief,
CONTEXT
ADDRESSER MESSAGE ADDRESSEE
CONTACT
CODE
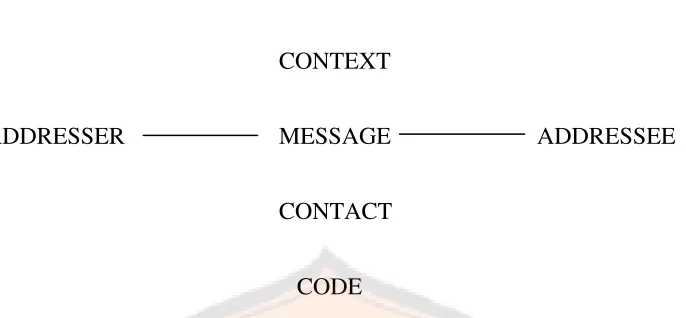
Figure 2.2: Constitutive Factors of Speech Event
There are four variables on his scheme, the first is CONTEXT (the background situation), MESSAGE (the topic), CONTACT (telephone, letter, or face to face), and CODE (spoken or written). The addressee will achieve those variables, which are affected by the addresser, or ran from it. This theory is also related to advertisement as a discourse which communicates the message to the addresser. Therefore, the factors of communicative event also appear on an advertisement in order to deliver the content from the addresser to the addressee.
Another theories that supports Jakobson‟s theory is the Human Communication Process. It shows the plot of communication process up to the process being understood by the addressee. According to Arens (2006a) to create the successful advertisement, the copywriter should understand the substance of communication process which is taken from the core of the role in human communication (para. 8). As cited by Arens (2006b) from Peter and Oslen, he mentions every term appear on the process as the following statement:
The process begins when one party, called the source, formulates an idea,
encoding of a new message. And, of course, all this takes place in an environment characterized by noise – the distracting cacophony of many other messages being sent as the same time by other sources (p. 8).
On figure 2.3 will be referred the human communication process as what has been explained before.
3.
Figure 2.3: Human Communication Process by Peter & Olsen (in Arens, 2006: 9) In a communication, a message which is directed for the addressee should be conveyed. Then, the idea encodes through the addressee‟s background knowledge and it becomes a message. The message contains the addresser‟s concept. After that, the addresser sends the message through a tool. The tool can be a voice, letter, video, text or other devices which are acceptable to the addressee. The addressee receives the message and then turns it to make it understandable. After that, the addressee conveys the feedback to the addresser. This term of communication happen continuously up to the purpose of this communication gained.
have content (p. 203).” An advertisement as a kind of tool should convey a message too.
O‟Grady, Archibald, Avonoff, and Rees-Miller (2010) also says, “A language is often defined as a conventional system for communication (p. 227).” Therefore, there is a close relation between conversation and the language meaning. A conversation consists of words that contain meaning. Advertisement, as the media to communicate the information to the addressee, uses the language to send the message to the addressee.
3. The Grice’s CP Maxims
The Grice‟s maxims discussed about implication that is digging the concepts of how people use language. Grice has four guidelines of the effective and efficient language use on conversation to further co-operative principle. Levinson (1983) cited from H. Paul Grice that, “The co-operative principle make
your contribution such as is required, at the stage at which it occurs, by the accepted purpose or direction of the talk exchange in which you are engaged (p. 101).” According to Grice, the conversation of the addresser and addressee will be achieved if both of them qualify the co-operative principle.
As cited by Fasold & Linton (2006) from Grice there are four maxims of conversation which will conduct the comprehensive communication, they are the maxim of quality, quantity, relevance, and manner (para. 102).
1) The maxim of Quality
(ii)do not say that for which you lack adequate evidence 2) The maxim of Quantity
(i)make your contribution as informative as required for the current purposes of the exchange
(ii)do not make your contribution more informative than is required 3) The maxim of Relevance
make your contributions relevant 4) The maxim of Manner
be perspicuous, and specifically: (i) avoid obscurity
(ii) avoid ambiguity (iii)be brief
(iv) be orderly
The Grice‟s maxims aimed to create a comprehensive conversation. It is important for the advertisement as a term of communication to convey the message from the product to the consumer. In this research, those maxims are used to analyze the advertisement. For example, please look at this following picture.
This advertisement proves headline as the main information and supports by subhead. The headline says, “the FLAVOR of the WEEK! BLACK in WHITE!” Through analyzed the agreement of headline to the Grice‟s maxims found that the headline is in agreement with maxim of quality. It says in agreement with maxim of quality because the headline obeys maxim quality‟s requirement, “do not say what you believe to be false and do not say for that you lack of adequate evidence.” The addresser persuade addressee that this week appears a new flavor that is black in white, it proves by the launching of a new chocolate vanilla taste. Beside, this advertisement agrees with maxim of quantity, relevance, and manner. Thus, according to the requirements of Grice‟s maxims this advertisement‟s headline achieves the cooperative principle because it agrees with all maxims.
not conveying any consequences. That statement took the gentleness of a conversation from the addresser to the addressee, the soft expression. The violation of maxim quantity arises when the addressee give less information, hence, misleading the addresser. On the other hand, maxim relevance shows the addressee the focus of a conversation in order to conclude the purpose of the addressee (O‟Grady et.al, 2010). The headline of an advertisement said, “the Flavor of the Week! Black in White!” This headline obeys the maxim of relevance. Based on the previous explanation that this headline shows the core of conversation that is this week taste, black in white. The violation to maxim relevance happens when the addressee failed to respect it and make a miss communication on a conversation. The feature of maxim manner forces some restrictions: avoid ambiguity, avoid obscurity, be brief, and be orderly. The violation happens when the addressee uses an ambiguous structure. For example, “Proof there really is a God: Chocolate is good for you.” The first phrase, “Proof
there really is a God…” shows the ambiguity both sentence and meaning. It aimed to say “The proof that there is really a God” but the use of the sentence violated the rule of maxim manner. Those are the additional explanation of each of Grice‟s maxims.
appears, in an obvious way, to violate the maxim (p. 161).” Although the comprehensibility of a conversation should qualify those maxims, but violation of those maxims is tolerated.
4. Presupposition
Advertisement as a tool to communicate should have rich style on grasping addressee‟s attention through image and text. In 2002, Goddard says, “it should have become clear that readers do not simply read images in isolation from the verbal text that accompanies them; nor do they read the verbal text without reference to accompanying images(p. 13).” Goddard‟s opinion explains that the visual appearance on advertisement has a great influence to attract the addressees. Moreover, the text in advertisement that helps addressee to get the information about the product and deliver the message. Yule describes that a presupposition is something the speaker assumes to be the case prior to making an utterance (as cited in Yingfang, 2007). Advertisement closely related to presupposition because the advertiser may have the assumption as the main idea in making utterance.
According to Lam (2009), presupposition is often found in advertisements to convey ideas indirectly rather than asserting them directly. The addressee may not be aware of presuppositions in advertisement, but, it is an important component of messages, as meaning only exists within the context of what is in the person‟s mind that provides the meaning. As supported by Goddard (2002), “In area of linguistics which has developed theoretical frameworks for how we
termed presupposition (ideas taken for granted), and it is often suggested that many of our meanings are encoded in this level (p. 38).”
The other expert, Stalnaker, (1974) says that presupposition is closely related to the common ground. The common ground, as cited by Fasold & Linton (2006a), “The common ground is the set of propositions which the participant in a conversation mutually assume(p. 159).” Fasold and Linton (2006b) made the previous statement clearer through the following explanation, “A proposition is a complete thought, a statement which can be true or false (p.142).” When it happens in a normal conversation, where many things are expressed implicitly, both addresser and addressee could have the same assumption that it could be true or false. On the other side, if the statement expresses explicitly the presupposition should come into common ground. Thus, the common share knowledge between the addresser and addressee (common ground) is a part of proposition that become the focus of presupposition. The impression of presupposition based on the common ground of preposition.
5. Sentence Meaning and Speaker’s Meaning
Semantics and Pragmatics are the studies of meaning. As cited in Fasold and Linton (2006) Portner says, “Semantics focuses on the literal meaning of word, phrases, and sentences while Pragmatics focuses on the use of language in particular situations (p. 137).” Semantics concerns on how the grammatical process builds the complex meaning, whether pragmatics aimed to explain the outside factors. It contributes to the speaker‟s speaking (both literal and nonliteral meaning). The research on meaning will always combine both semantics and pragmatics.
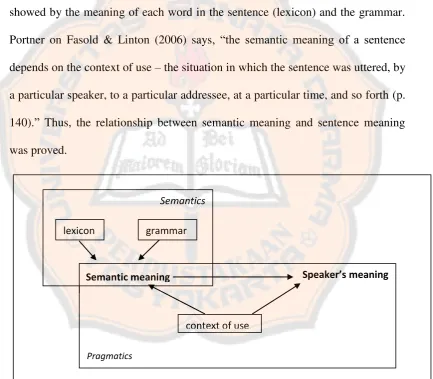
Portner on Fasold and Linton (2006) visualize both semantic and speaker‟s meaning on figure of 2.5. It explains the link between semantic meaning and the speaker‟s meaning. Semantic meaning built from the lexicon and grammar, whether the speaker meaning is as a part of pragmatics. Both semantics meaning and speaker‟s meaning focus on the context of use. Based on the following diagram, the semantics meaning is related to the speaker‟s meaning features. It is showed by the meaning of each word in the sentence (lexicon) and the grammar. Portner on Fasold & Linton (2006) says, “the semantic meaning of a sentence depends on the context of use – the situation in which the sentence was uttered, by a particular speaker, to a particular addressee, at a particular time, and so forth (p. 140).” Thus, the relationship between semantic meaning and sentence meaning was proved.
Figure 2.5: The Relationship of Semantic Meaning and Speaker’s Meaning (in Fasold & Linton: 2006)
Thus, Semantics focuses on the grammar and lexicon for semantic meaning. Pragmatics focuses on the context use between semantic meaning and speaker‟s meaning. Fasold and Linton (2006) say that, “Pragmatics concerns both
Speaker’s meaning
Pragmatics
Semantics
Semantic meaning
lexicon grammar
the relationship between context of use and sentence meaning, and the relationship among sentence meaning, context of use, and speaker‟s meaning (p. 157).” In order to analyze what the speaker‟s intention the researcher use pragmatics.
B.Theoretical Framework
This research considered as the study of meaning in Public Service Announcement. Goddard (2002) says that the purpose of making advertisement is to communicate the information of a product that expected a reason from the addressee. Beside, Peter and Oslen have explained about how the message delivered from the source into the receiver and how the receiver send back the response to the source (Arens, 2006). Regarding to the purpose of advertisement, the explanation says that advertisement is used as a communication tool. Moreover, an advertisement requires a response from the receiver. In order to make a comprehensive communication on advertisement both addresser and addressee should consider the format of advertisement (Arens, 2006). About the requirement of a good advertising is cited from Bovee and Arens (1986).
efficient, and understandable. Those are covers what the speaker meant to say (speaker‟s meaning) and the speaker‟s word meaning (sentence meaning) in the advertisement.
This study focuses the analysis on headline of advertisement because according to Arens (2010a) it attract attention, engage the audience, explain the visual, lead the audience into the body of the ad, and present selling message (para. 417). Arens (2010b) also states:
The headline is the most important thing an adviser says to the prospect. It explains or gives greater meaning to the visual and then immediately dictates the advertiser‟s position in that person‟s mind, whether or not the prospect chooses to read on (p. 417).
27
CHAPTER III
METHODOLOGY
The researcher applied certain methodology to conduct this research. This chapter discusses the systematic process of the methodology that is used in this research. The discussion includes research method, research subject, research instrument, data gathering technique, data analysis technique, and research procedure.
A. Research Method
Qualitative research is the method that is used in this research. Ary, Jacobs, and Razavieh (2002) state, “Qualitative researchers seek to understand a phenomenon by focusing on the total picture rather than breaking it down into variables. The goal is depth understanding rather than a numeric analysis of data (p. 25).” The supported theory from Leedy & Ormrod (2005) states that, “qualitative research focuses on phenomena that occur in natural setting – that is, in the “real world” and involves studying those phenomena in all their complexity (p.133).”
The research is a descriptive research. Bungin (2007) explains that descriptive study involved an in-depth exploration of the object being studied. This research presented the analysis and description of the language meaning as the language phenomenon that exists in the society (para. 68-69). This research is a descriptive research because it is an in-depth study of language advertising in some magazines such as Time, Newsweek, and Reader’s Digest. In conducting the research, the researcher also applied library study. Library study is belongs to the secondary research because it is based on the secondary sources, especially other researchers’ books and articles. The researcher required some theories and references from other researchers and experts to analyze and describe the data.
B. Research Subjects
Time, Newsweek, and Reader’s Digest magazines issued in January 2010 up to March 2011 were the research subjects. The subjects in this research were the display PSA that appears on those magazines. This research focused on the language that is used in the advertisements that gives images and descriptions about them. Advertisement is designed to promote a product, a service or an idea. Bogdan & Biklen (2003) mention that,
C. Research Instruments
The researcher is the primary instrument of this research. Lincoln and Guba (1985) firstly introduced the concept of human as instrument to the scientist, as compiled by Ary et.al (2002) “Because qualitative research studies human experiences and situations, researchers need an instrument flexible enough to capture the complexity of the human experience (p. 424).” It was supported by Merriam (2002) who explains that “a second characteristic of all forms of qualitative research is that the researcher is the primary instrument for the data collection and analysis. (p. 5).” Leedy and Ormrod (2005) also mention about human instrument that, “qualitative researchers believe that the researcher’s ability to interpret and make sense of what he or she sees is critical for understanding any social phenomenon (p. 133).”
D. Data Gathering Technique
The researcher used field notes to gather the data. Field notes used to record the data collection during the observation. Field notes also contained two components the descriptive part and the reflective part. Ary et.al (2002) say that in descriptive part the researcher has to record everything related to the data, it is helped with 5W+1H (para. 426). Instead of the descriptive part it is the reflective part which includes the researcher’s personal feeling. The researcher’s reflection identified as observer comments (OC). When the researcher found the appropriate or inappropriate advertisements, the researcher gave note to that part in order to help the discussion. The researcher also used participant observer method. Bungin (2007) states that this method is a data gathering method which collects the data through observation and sensory perceptions (para. 115). The researcher used the ability to see, watch, feel and touch to obtain the advertisements. In obtaining the advertisements, the researcher employed some steps.
and examined the PSA found. After that, the researcher collected the advertisements by copying them and placing them in a folder.
When collected and grouped, the advertisements were analyzed to answer the two research questions. The researcher would apply library study to analyze the data. The researcher would require some theories and references about language meaning and advertising language. The researcher collected the theories and references from books and journals written by some linguists and other researchers.
E. Data Analysis Techniques
According to Ary et.al (2002) there are three steps to analyze the data, they are organizing, summarizing, then interpreting (para. 89). However, Holliday has a different opinion to analyze the data. Ary et.al (2002) say, “data analysis as the process of making sense, shifting, organizing, cataloguing, selecting, determining themes – processing the data (p. 99).”
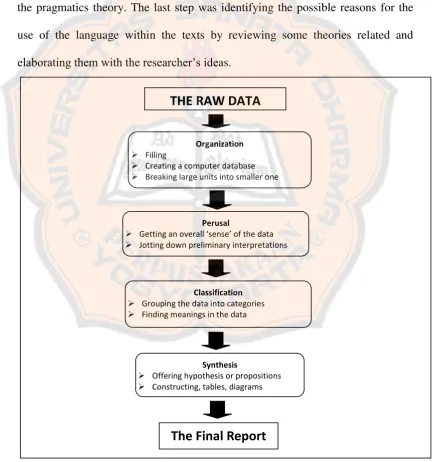
In this analysis, the researcher followed the Creswell’s (1998) steps, called
and paid attention to the details. The third step was identifying the characteristics of the language in the advertisements. The researcher identified how the language was used in the advertisements by paying attention to the comprehensive communication gained. The researcher would also relate the theories and references about the language used in the advertisements and communication with the pragmatics theory. The last step was identifying the possible reasons for the use of the language within the texts by reviewing some theories related and elaborating them with the researcher’s ideas.
Figure 3.1 Data Analyzes Spiral (Leedy and Ormord, 2005)
The Final Report
THE RAW DATA
Synthesis
Offering hypothesis or propositions Constructing, tables, diagrams
Classification Grouping the data into categories Finding meanings in the data
Perusal
Getting an overall ‘sense’ of the data Jotting down preliminary interpretations
Organization Filling
F. Research Procedure
This section summarizes the procedure taken in conducting the research. Merriam (2002) mentions that “there is no standard format for reporting qualitative research (p. 14).” The researcher followed seven steps to conduct the research comprehensively.
1. Selecting the source of data
The first step was selecting the source of data. Time, Newsweek, and Reader’s Digest magazines issued in January 2010 up to March 2011 were the research source.
2. Collecting the data
The second step was collecting the data. The researcher read and examined the PSA found in those magazines. The researcher only selected the display advertisements. The advertisements were photocopied from the magazines and they were folded in a folder to be organized.
3. Organizing the data
4. Analyzing the data
The fourth step was analyzing the data. The advertisements were examined carefully. The researcher then focused on the headline of those advertisements. Then, the language used in headline was analyzed based on the theories and other literature references. Having done the analysis, the researcher described the features and characteristics of the English language that was used in the advertisements.
5. Identifying the possible reasons
The fifth step was identifying the possible reasons of the existing phenomenon. The phenomenon which appears would be criticized by the researcher. The researcher’s interpretations of the phenomenon were also taken into account in this part.
6. Reporting the research
35
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
This chapter presents research results and discussions which have been analyzed. This chapter aims to answer two research questions presented in the previous chapter. They are 1) How does the headline of the PSAs obey Grice‟s CP? 2) What do the headline and subhead of PSA presuppose to express the
speaker‟s meaning?
In the first part, the researcher explains about the Grice‟s maxims is used as the measurement of a successful conversation in PSA. The researcher explains the presupposition finding on the second part. It is divided into two sections, the first section discusses the presupposition on headline and the second section discussed the presupposition on subhead.
A.The PSA Headline Agreement on Grice’s Maxims
maxim of manner. Each maxim is different, but all of them are aimed to obtain a comprehensive communication on advertisements. One headline could in agreement with more than one maxim or in disagreement with more than one maxim. Headline contained the words that function to draw the advertisement‟s attention (Arens, 2006). Headline was the prime indicator of the successful communication. In order to find out whether it was understandable or not, the researcher analyzed the agreement and the disagreement on those maxims.
Based on the data, it is found that fourteen headlines were in agreement with all maxims. On the other hand, there were eight headlines in disagreement with at least one maxim. Those headlines at least obeyed two maxims; there were headline [5], [13], and [22]. Only one headline that in agreement with one maxim, it is headline [16]. Here is the table of headlines agreement to Grice‟s CP, it is showed on the following table.
Tabel 4.1 The Amount of Headlines Agreement on Grice’s Cooperative Principle
GRICE‟S MAXIMS
QUALITY QUANTITY RELEVANCE MANNER
AGREE 20 20 20 16
DISAGREE 2 2 2 6
headline in agreement with maxim of quantity means that the headline lead the addressee into the very subtle guideline conversation. Twenty headlines were in agreement with maxim of relevant which means that the contribution given were relevant. The relevance in a conversation is important because it hopefully give the addressee a nature for summarizing the addresser‟s purpose. Sixteen headlines were in agreement with maxim of manner. It showed that those headlines avoid ambiguity and obscurity. Those headlines were brief, clear, understandable, and arranged orderly.
Through this research, it was found that most headlines obeyed maxim of quality and relevance. On the other hand, most headlines disagree with maxim of manner. The disagreement aims to make the addressee interested to the advertisement. Based on this research, there were many ambiguous and obscure sentences. Those were used to attract the addressee and to make them anxious
about the advertisement‟s purpose.
1. Maxim of Quality
mostly uses convincing statement in order to make the advertisement looks reliable. It is supported by Leetaru (2001), “The Maxim of Quality, however, which enforces veracity of expression, has always been treated as a “grey area” in advertising philosophy, as the purpose of an advertisement is to convince the
reader of the product‟s usefulness to his or her, which occasionally requires
“overselling” it.”
Twenty headlines which obey maxim of quality were, [1], [2], [3], [4], [5], [6], [7], [8], [9], [10], [11], [12], [13], [14], [15], [17], [18], [19], [20], and [21]. Those headlines were said to agree with maxim of quality because they said the true and gave enough evidences to support it. It proved on the following headlines.
[1]
[11]
[18]
According to O‟Grady et.al (2010), “In order to achieve irony or sarcasm, however, it is sometimes possible to abandon The Maxim of Quality and say something that one knows to be false (p. 237).” It supported by Finch (2000), “ So, for example, sarcasm, calling out nice one about something you hate, can be viewed as a form of flout since it only appears to violate the maxim of quality (p. 161).” Through this analysis, the researcher found a headline that abandons the maxim of quality, it was headline [16] and [22].
[16]
[22]
Headline [16] disagreed with maxim of quality because the advertiser expressed the coming up of a dropped thing. A dropped thing usually interpreted as a useless thing, when the addresser said that it should raise, it sounded weird. Nevertheless, the addresser intentionally expressed it on the headline in order to attract the addressees.
Headline [22] is in disagreement with maxim of quality because it was not prove enough evidence to convince addressee. The headline was not representative if it only stated, “It‟s your turn.” it confused addressee‟s interpretation. The addressee will have other interpretation such as; “are you sure?
Is it my turn?” and so on. Those questions made the headline unreliable because
2. Maxim of Quantity
The second requirement for a successful communication between the addresser and the addressee is the agreement to maxim of quantity. Maxim of quantity required the information given from the addressee. The information should informative as it required for the current purpose of exchange and the information should not more informative than it required. Based on analyzes, the researcher found that eighteen headlines were in agreement with maxim of quantity. Besides, there were four headlines disagree with maxim of quantity.
Those headlines were in agreement with the maxim of quantity because they informed the required information for the addressee. They were [1], [2], [3], [4], [6], [7], [8], [9], [10], [11], [12], [13], [14], [15], [17], [18], [19], [20], [21], and [22]. In this section, the researcher provided some headline which in agreement with maxim of quantity.
[4]
The headline is said to agree with maxim of quantity because it informed the required information for addressee. “What does the future hold for us?” appeared as the reflection of people compliment on the way they live and work, it is
[15]
Shell‟s advertisement contained the message to reduce the use of energy, in order to save the energy in the future. This headline was in agreement with maxim of quantity, because it gave the required information. It informed that Feng‟s washing was not clean enough because the residue of fossil fuel burning. In order to make the burning of fossil fuel clean, Shell invited to use natural gas, which is the cleanest burning-fossil fuel.
[17]
Through the sentence on [17] the conversation has been understood because the addressee got the required information. The information about “she” has been answered on headline [17].
Headline [5] and [16] disagree with maxim of quantity. Headline [5] lacked of required information, whereas headline [16] flouted maxim of quantity in order to mislead the addressee.
[5]
information for the addressee. Thus, the information appeared on [5] could not satisfy addressee‟s curiosity.
Headline [16] on, “What comes down must go up,” was a special case on the agreement of maxim quantity. Headline [16] flouted maxim of quantity in order to mislead the addressee. Firstly, the addresser knew that a dropped thing could not rise, but the addresser stated that it “must come up.” The statement aimed to pursue addressee to believe that something dropped could rise. The
information from the addresser made intentionally to mislead addressee‟s
comprehension. Secondly, headline [16] suspended the maxim of quantity by giving less information. The addresser did not explain what is drop and why it comes up. Otherwise, the information on headline [16] appeared in order to make the advertisement interesting.
3. Maxim of Relevance
The other requirement of a comprehensible communication was the relevance of the conversation itself. O‟Grady (2010, p.233) said, “The Maxim of Relevancegives listeners a bottom line for inferring the intent of other speakers.”
These twenty headlines agreed with maxim of relevance. Moreover, the headline expressed the bottom line of the conversation for inferring the other speaker‟s intention.
[2]
Headline [2] agreed to maxim of relevance. In [2], the addresser tried to communicate his purpose. The clarity of the sentence made it understandable that milk, which was served with many additional ingredients, was not good for people
health. Through the relevance of this headline, which is about the speaker‟s
intention, addressee could conclude that milk is best served with fewer ingredients. This relevance created a comprehensive conversation, thus both addresser and addressee understand each other.
[10]
Its bottom line was Habitat for Humanity successes to give them, the homeless people, a new place to live. Through headline [10], the addressee tried to inform that the addressee could join on giving a new house for the less fortunate people. Headline [10] agreed with maxim of relevance because it successfully created the
comprehensive communication by expressing the addresser‟s intent on it.
[8]
The focus of headline [8] was the uniqueness of Cambodian art. The addresser wanted to express the distinctive style of Cambodian. It represented the situation happened there, where there were many land mines in Cambodia. The addressee would find difficulty when the headline appeared because it was not relevant with
what the addresser‟s intention. Thus, headline [8] disagree with maxim of relevance.
14]
The addresser on headline [14] intent to express about Cambodian worried on stepping the landmines. The word “dog poo” represented landmines. The advertisement invited addressee to pay attention on the problem. In this
advertisement what the addresser‟s purpose was difficult to be understood by
addressee because the addresser used symbolism on it. Thus, it could be said that headline [14] disagree with maxim of quantity.
4. Maxim of Manner
Maxim of manner emphasized on the clarity of a statement in a conversation. The clarity of a conversation visible from how it expressed, the statement should brief and orderly. Through the data analysis it was founded that there were sixteen headlines obeyed the maxim of manner and six headlines violated the maxim of manner. The sixteen headlines which obeyed were, [1], [3], [4], [6], [8], [9], [11], [12], [14], [16], [17], [18], [19], [20], [21], and [22]. Those headlines were said to agree with maxim of manner because they were avoid ambiguity and obscurity and provide the brief and orderly headline.
[6]
Headline [6] showed the agreement to maxim of manner because the statement on this headline was brief and arranged in a chronological order.
[9]
The sentence on this headline avoided the ambiguity, there was not double meaning. There was only one meaning, that fighting hunger should be done together. The headline also clear, it did not contained the complicated sentence. It was brief, the addresser directly pointed to the message. The headline was arranged orderly to show the clarity of it.
The headline obeyed maxim of manner because the sentences used were clear. It was avoided the ambiguity and the obscurity. Moreover, the headline briefly explained that the advertisement was aimed to invite people saving the energy for the future.
Beside, headlines [2], [5], [7], [10], [13], and [16] flouted maxim of manner. Those headlines flouted maxim of manner because each headlines
disagree with one or two maxim‟s certainties. Thus, the researcher would explain
some example of the flouting headlines. Headline [2] flouted maxim of manner because the sentence used was not brief. The headline stated “Milk: Best served
with several thousand fewer ingredients.” it made the conveying information unclear for addressee. Headline [5] flouted maxim of manner because the phrase
“HOPE” lead addressee to the obscurity. The addressee could not receive clear information if the phrase was not explained.
Maxim of manner contained four special regulations. There were avoid ambiguity, avoid obscurity, be brief, and be orderly. If the headlines obeyed those regulations, it said obeyed maxim of manner. Sometimes a headline did not obey all of those regulations. Mostly the disobedience caused by the double interpretation of the headline, it called the violation to maxim of manner.
B.The Speaker’s Meaning on Headlines and Subheads
express the speaker‟s intention on the advertisements, thus the analysis focused on the headline and subhead of PSA. Presupposition is related to the advertisement because the advertisement usually conveys ideas indirectly rather than directly. Yule (2007) in Yinfang (2009) says that a presupposition is something the speaker assumes to be the case prior to making an utterance. Thus, presupposition is dealing with something true and already known by both addresser and addressee. Beside, Fasold and Linton (2006) called it as the common ground of a presupposition. It supports by Akmajian (1984) explanation, “and by sharing knowledge of the meaning of an expression E, the hearer can recognize a
speaker‟s message –the speaker‟s communicative intention.” (p.389).
According to Arens (2006), headline is functioned as the leading on advertisement. It contained the words to obtain the addressee‟s attention. Besides, the researcher analyzed the subhead which less informative than headline but it
completed the headline‟s information. Arens (2006) said that subhead appeared in
order to give short explanation about the advertisement. The analysis was aimed to find out the speaker intentions on advertisement. It could lead into the function of presupposition on advertisement.
1. Advertisement 1 (WWF)
This advertisement consisted of headline and subhead. The headline said
the same reason why they have to vote earth, it because the earth was the only one place for living. Besides, the earth damage became the prime notice for human being.
Beside the headline, this advertisement also contained subhead. Subhead is used as the additional information.
Subhead [1]
>>you have been standing somewhere before.
The subhead wanted to convince that what will you choose should express now. Therefore, the subhead aimed to give information about how to declare your choice through visiting the website. Thus, it could conclude that what the speaker intent to say was persuading addressee to choose earth besides your choice before.
2. Advertisement 2 (Tetra Pak)
addresser aimed to persuade addressee to change their habit on serving milk without any ingredients.
3. Advertisement 3 (World Food Programme)
The advertisement from WFP (World Food Programme) was concerned on how to help the starving children around the world. This organization made their action concrete by inviting many people to join their program. It persuaded people to contribute their money for the hungry school children through this organization. The addresser stated the fact that 59 million hungry school children were in less fortunate in this advertisement. The advertisement‟s invitation stated on headline [3], “Let‟s talk about the rescue plan.” The meaning of the headline was the addresser ask addressee to discuss about the rescue plan for those hungry school children, this discussion was crucial for the children. Thus, the addresser provided
some evidence to grasp addressee‟s compassionate. Besides, the presupposition was, >>we will do the rescue. Through the finding of headline‟s presupposition, it was clearly understood that the addresser aimed to do the rescue for the hungry school children. Likewise, through the headline the addressee caught what the addresser intent. Thus, what the addresser intent could be achieved by the addressee. It is meant that the advertisement contained comprehensive communication.
Subhead [3]
>>trillions of financial rescue packages did not help 59 millions hungry school children. This subhead explained that many trillions were spent for financial rescue packages, though, only 1% of those financial rescue packages could make hunger into hope for 59 millions hungry school children. It became the reason why the rescue plan should be discussed. Through find out the presupposition of
subhead [3], it achieved the addresser‟s intent. Thus, why the rescue plan should
be discussed has answered in this subhead. Further, what kind of rescue plan will be discussed based on the finding.
4. Advertisement 4 (National Geographic Organisation)
Beside, the addresser made the promotion interesting through stated
headline [4], “What does the future hold for us?” Headline [4] meant that someone asking about something unpredictable in the future. Moreover, the problem background was the four fundamentals of the way people live. Transportation, urbanisation, communication, technology, and demography were influence the way people live. For example, nowadays people are facilitated to communicate with other through mobile phone; it is a part of technology‟s development. If people did not employ the technology‟s development appropriately, people could not find the newest mobile phone technology. It was only a little example of the technology gave for us. Then, if we did not notice those four fundamentals what will the future hold for us. Based on this analyzes, this headline was representing reflective question.
Through that reflective question, it found the presupposition of headline [4] >>something is inappropriate now, it related to the four fundamentals. Based on this finding, both addresser and addressee are looking at the imprecision on those four fundamentals in the present time. Thus, through headline [4] the addresser aimed to warn people to notice about the future.
5. Advertisement 5 (World Food Programme)