M odu le 4 – ( L1 2 - L1 8 ) : “
W a t e r sh e d M ode lin g”
St a n da r d m ode lin g a ppr oa ch e s a n d cla ssifica t ion s, syst e m con ce pt St a n da r d m ode lin g a ppr oa ch e s a n d cla ssifica t ion s, syst e m con ce pt for w a t e r sh e d m ode lin g, ove r a ll de scr ipt ion of diffe r e n t h ydr ologic pr oce sse s, m ode lin g of r a in fa ll, r u n off pr oce ss, su bsu r fa ce flow s a n d gr ou n dw a t e r flowg
1 7
N u m e r ica l W a t e r sh e d
1 1 1
L1 7
L1 7 –
N u m e r ica l W a t e r sh e d
M d li
M ode lin g
Topics Cove r e d
Topics Cove r e d
Physically based wat ershed m odeling,
Physically based wat ershed m odeling,
Num erical m odeling, Finit e difference
Num erical m odeling, Finit e difference
m et hod; Finit e elem ent m et hod
m et hod; Finit e elem ent m et hod
m et hod; Finit e elem ent m et hod,
m et hod; Finit e elem ent m et hod,
Com put er m odels
Com put er m odels
W a t e r sh e d M ode lin g
• Transform at ion of rainfall int o runoff over a wat ershed • Generat ion of flow hydrograph for t he out let
• Generat ion of flow hydrograph for t he out let
• Use of t he hydrograph at t he upst ream end t o rout e t o t he downst ream end
H d l i i l t i d l t h t i l t i
• Hydrologic sim ulat ion m odels use m at hem at ical equat ions t o calculat e result s like runoff volum e or peak flow
• Com put er m odels allows param et er variat ion in space and p p p t im e – w it h use of num erical m et hods
• Ease in sim ulat ion of com plex rainfall pat t erns and het erogeneous wat ersheds
12.00
het erogeneous wat ersheds
3 3
H ydr ologic M ode ls
y
g
Model Type
Example of Model
Lumped Parameter
p
Synder Unit Hydrograph
y
y
g
p
Distributed Kinematic
wave
Event
HEC-1, SWMM
Event
HEC 1, SWMM
Continuous
Stanford Watershed Model,
SWMM, HSPF,
,
,
Physically based
HEC-1, SWMM, HSPF
Stochastic
Synthetic stream flows
Stochastic
Synthetic stream flows
Numerical
Explicit kinematic wave
Analytical
Nash IUH
Flow of wat er in a wat ershed is a dist ribut ed process
N e ce ssit y of D ist r ibu t e d m ode ls
Flow of wat er in a wat ershed is a dist ribut ed process Models should be physically based
Governing equat ions – St . Venant equat ions g q q
Com put er m odels- based on t he St . Venant equat ions
Allows com put at ion of flow rat e and wat er level as funct ions
f d t i of space and t im e
Model m ore closely approxim at es t he act ual unst eady
non-uniform nat ure of flow propagat ion in channels p p g
Rainf Rainf all
I filt ti
Channel flow
5 5
Infiltration
H ydr ologic/ H ydr a u lic M ode lin g
Hydrological / Hydraulic m odel- concept ual or
physically based procedure- num erically solving hydrological processes - diagnose or forecast hydrological processes diagnose or forecast processes.
Physical based: descript ion of nat ural syst em using
basic m at hem at ical represent at ion of flows of m ass basic m at hem at ical represent at ion of flows of m ass, m om ent um and various form s of energy.
Dist ribut ed: consider spat ial variat ion of variables &
param et ers.
Applicat ions: Rainfall t o runoff , Surface wat er/
groundwat er assessm ent Flood/ drought predict ions groundwat er assessm ent , Flood/ drought predict ions, Evaluat ion of wat ershed / cat chm ent m anagem ent st rat egies, River basin / Agricult ural wat er
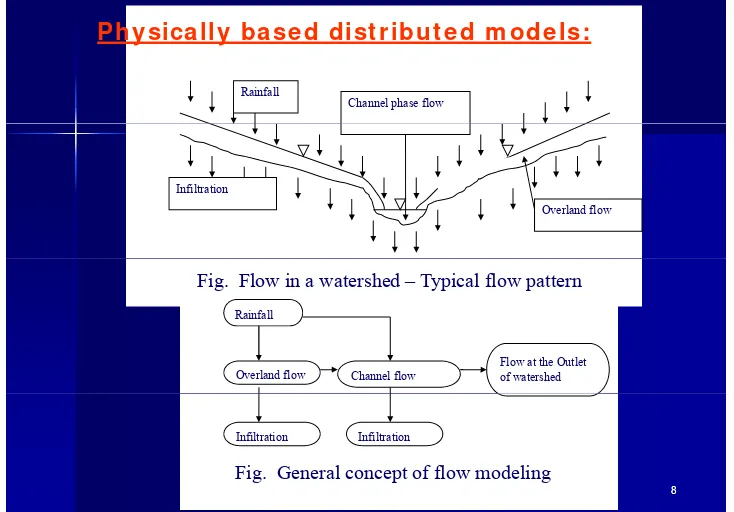
Ph ysica lly ba se d dist r ibu t e d m ode ls:
Rainfall
Channel phase flow
Infiltration Infiltration
Overland flow
Rainfall
Fig. Flow in a watershed – Typical flow pattern
Flow at the Outlet of watershed Channel flow
Overland flow
Infiltration Infiltration
Ph ysica lly
Ph ysica lly Ba se dBa se d M ode lM ode l –– Ove r la n dOve r la n d FlowFlow Equ a t ion s
Equ a t ion s Equ a t ion s Equ a t ion s
Con t in u it y
Con t in u it y e qu a t ione qu a t ion
M om e n t u m
M om e n t u m Equ a t ionEqu a t ion
I n it ia l a n d Bou n da r y con dit ion sy
I C for overland is usually of dry bed condit ion. At t im e t = 0, h = 0 and q = 0 at all nodal point s
Upst ream boundary condit ion is assum ed as zero
9 9
inflow s; h = 0 and q = 0 at all t im es
Gov. Equat ion for Channel Flow
Solut ion Met hodologies
An a lyt ica l m e t h od: For t he given m at hem at ical
form ulat ion, an analyt ical expression involving t he
param et ers and t he independent variables are obt ained using various m at hem at ical procedures.
Main lim it at ion- only for a sm all class of m at hem at ical
form ulat ions w it h sim plified governing equat ions, boundary condit ions & geom et ry, analyt ical solut ions can be obt ained.
Ph ysica l m e t h od: As t he m at hem at ical m odel represent s a
real physical syst em , alt hough on cert ain idealized p y y , g
assum pt ions, variables and param et ers of t he m odel can be considered as having physical dim ensions and can be
analyzed som et im es in t he laborat ory or in t he field it self.
The physical m odels are used less frequent ly since it is
expensive, cum bersom e and difficult in pract ice.
Com pu t a t ion a l m e t h od
11 11
Com put at ional Met hod
I n t he com put at ional m et hod, t he solut ion is
obt ained w it h t he help of som e approxim at e
m et hods using a com put er. Com m only,
num erical m et hods are used t o obt ain solut ion
i t h
t t i
l
t h d
in t he com put at ional m et hod.
Wid
l
f
t h
t i
l f
l t i
&
Wider class of m at hem at ical form ulat ions &
advent of fast com put ers, com put at ional
m odels have becom e t he m ost widely used
m odels have becom e t he m ost widely used
valuable t ool for solving t he engineering
Num erical Modeling
Variet y of num erical m et hods such
as
- M e t h od of ch a r a ct e r ist ics
- Fin it e D iffe r e n ce M e t h od ( FD M )
i i
l
h d (
)
- Fin it e V olu m e M e t h od ( FV M )
- Fin it e Ele m e n t M e t h od ( FEM )
- Fin it e Ele m e n t M e t h od ( FEM )
- Bou n da r y Ele m e n t M e t h od ( BEM )
.
13 13
Finit e Difference Met hod
C i i i f h f i d b
Cont inuous variat ion of t he funct ion concerned by a set
of values at point s on a grid of int ersect ing lines.
The gradient of t he funct ion are t hen represent ed by e g ad e o e u c o a e e ep ese ed by differences in t he values at neighboring point s and a finit e difference version of t he equat ion is form ed.
At point s in t he int erior of t he grid t his equat ion is used At point s in t he int erior of t he grid, t his equat ion is used
t o form a set of sim ult aneous equat ions giving t he value of t he funct ion at a point in t erm s of values at nearby
i t point s.
At t he edges of t he grid, t he value of t he funct ion is
Met hod of charact erist ics ( MOC)
MOC d i l diff i l i f il
MOC - reduce a part ial different ial equat ion t o a fam ily
of ordinary different ial equat ions along which t he
solut ion can be int egrat ed from som e init ial dat a given on a suit able hyper surface
For a first - order PDE, MOC discovers curves ( called
charact erist ic curves or charact erist ics) along which PDE charact erist ic curves or charact erist ics) along which PDE becom es an ODE. I t is solved along t he charact erist ic curves & t ransform ed int o a solut ion for original PDE. V i t f FDM it bl f l i h b li
Variant of FDM – suit able for solving hyperbolic
equat ions
MOC t o sim ulat e advect ion dom inat ed t ransportp Track idealized part icles t hrough flow field
Efficient & m inim ize num erical inst abilit ies
15 15
Finit e Elem ent Met hod
The region of int erest is divided in a m uch m ore
flexible way flexible way
The nodes at which t he value of t he funct ion is found
have t o lie on a grid syst em or on a flexible m esh
h b d d h dl d
The boundary condit ions are handled in a m ore
convenient m anner.
Direct approach, variat ional principle or weight ed Direct approach, variat ional principle or weight ed
Boundary Elem ent Met hod
The part ial different ial equat ions describing t he
dom ain, is t ransform ed in t o an int egral equat ion dom ain, is t ransform ed in t o an int egral equat ion relat ing only t o boundary values.
The m et hod is based on Green’s int egral t heorem .
h b d d d d f h d
The boundary is discret ized inst ead of t he dom ain. A 3- Dim ensional problem reduces t o a
2- Dim ensional problem and 2- Dim ensional problem in 2 Dim ensional problem and 2 Dim ensional problem in t o 1- Dim ensional problem .
BEM is ideally suit ed t o t he solut ion of m any t wo and
h di i l bl i l i i d i l t hree- dim ensional problem s in elast icit y and pot ent ial t heory
Analyt ical Solut ion–Kinem at ic wave
f
Sf
o
S
n
5
• Analyt ical solut ion for one- dim ensional kinem at ic
3
wave equat ions is given by above equat ions ( Jaber and Moht ar, 2003) ; tc is t im e of concent rat ion ( sec) ; tr is
rainfall durat ion ( sec) ; tf is t he sim ulat ion t im e ( sec) ;
Lw is t he lengt h of wat ershed ( m ) in t he direct ion of m ain slope. ( Jaber, F.H., and Moht ar, R.H. ( 2003) . “ St abilit y and accuracy of t wo dim ensional kinem at ic
l d fl d li ” Ad i W t
Fin it e D iffe r e n ce M e t h od ( FD M )
FD M : Calculat ions are perform ed on a grid placed
over t he ( x, t ) plane
Flow and wat er surface elevat ion are obt ained for Flow and wat er surface elevat ion are obt ained for increm ent al t im e and dist ances along t he channel
Ex plicit m e t h ods: calculat es values of velocit y &
d h d b d l k
dept h over a grid syst em based on a previously known dat a for t he river reach
I m plicit m e t h ods:I m plicit m e t h ods: set up a series of sim ult aneousset up a series of sim ult aneous
num erical equat ions over a grid syst em for t he ent ire river & equat ions are solved at each t im e st ep.
Fig: x - t pla n e for fin it e diffe r e n ce sch e m e
19 19
Typical St eps for FDM m odel
– Governing Part ial
Different ial Equat ions wit h Subsidiary condit ions
Subsidiary condit ions
– Divide dom ain int o Grids – Transform at ion by Finit e y
Difference Met hod – Syst em of difference
equat ions equat ions
– Applicat ion of Boundary Condit ions
I,J+1
Δ
y
I-1 J
I J
I+1 J
– Solve by direct or it erat ivem et hod – Solut ion
Δ
y
I 1,J
I,J
I+1,J
Δ
x
I,J-1
Finit e Difference Schem e
There are t hree com m only used finit e difference approxim at ions finit e difference approxim at ions for t he solut ion of PDE
b) Forward difference schem e c) Cent ral difference schem e
1
i-1, j+1 i-1, j+1 i+1, j+1
∆t
i j
i 1 j i+1 j
Finit e Difference
Schem e
∆x ∆x
i, j
i-1, j i+1, j
Cross-sectional view in x-t plane
h0, Q0, t1 h1, Q1, t1 h2, Q2, t2 x-t plane
p
0, 0, 1 1, 1, 1 2, 2, 2
∆t h
0, Q0, t0 h1, Q1, t0 h2, Q2, t0
Fin it e D iffe r e n ce Appr ox im a t ion s
Tem poral derivat ive
t
Spat ial derivat ive
x
Spat ial derivat ive is writ t en using t erm s on know n t im e line
Spat ial and t em poral
derivat ives use unknow n t im e lines for com put at ion
23 23
t erm s on know n t im e line lines for com put at ion
Fin it e Ele m e n t M e t h od
1D- Kinem at ic & Diffusion Wave Models for Overland Flow One- dim ensional m odel wit h linear line elem ent s
One- dim ensional m odel wit h linear line elem ent s Apply Galerkin FEM for 1D cont inuit y equat ion
- - - ( 1)
( 2)
- - - ( 2)
Expansion of Eq considering it for one elem ent is given as Expansion of Eq considering it for one elem ent is given as
Fin it e Ele m e n t M e t h od
Shape funct ion N for a linear elem ent can be expressed as [ N] =
[ N1 N2] Where Ni = 1- ( x/ L) and Nj = x/ L
E t i b it t i t i f f ll
Fin it e Ele m e n t M e t h od
Equat ion can be w rit t en in m at rix form as follows:
( 4) - - - ( 4)
Assem bling t he overland flow line elem ent s and applying im plicit
finit e difference schem e for t im e dom ain
- - - ( 5)
25 25
Fin it e Ele m e n t M e t h od
Aft er rearranging t erm s, t he final form of equat ion as:
Syst em of equat ions will be solved aft er applying t he y q pp y g
boundary condit ions
27 27
Ca se st u dy:
Harsul Wat ershed
( V k R dd 2007) ( Venkat a Reddy, 2007)
Locat ion- Nashik dist rict , Maharasht ra, I ndia Area- 10.929 km2
Area 10.929 km
Maj or Soil class – Gravelly loam
Rem ot ely Sensed Dat a- I RS 1D LI SS I I I im agery of J 1998
January, 1998
Overland flow elem ent s - 144 Overland flow nodes 188 Overland flow nodes - 188
Channel flow elem ent s - 22 Channel flow Elem ent lengt h
- 0.25 km
Average bed widt h - 18 m Slope
Slope
Overland flow Channel flow
M i ’ h
Manning’s roughness Overland flow Channel flow
29 29
Finite element grid map
Ca se st u dy:
Harsul Wat ershed
( Venkat a Reddy 2007) ( Venkat a Reddy, 2007)
Diffusion wave- GAML m odel Calibrat ion - 3 Rainfall event s Calibrat ion - 3 Rainfall event s Validat ion - 2 Rainfall event s
10
0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000
D
August 22, 1997 September 23, 1997 September 26, 1997
2
0 500 1000 1500
D
0 500 1000 1500
D
0 500 1000 1500 Time(min)
0 500 1000 1500 Time(min)
August 21, 1997 August 23, 1997
31 31
Observed & simulated hydrographs of calibration & validation rainfall events
Re fe r e n ce s
Re fe r e n ce s
• Raj Vir Singh ( 2000) , Wat ershed Planning and Managem ent , Yash
Publishing House
• J.V.S Murt hy ( 1991) , Wat ershed Managem ent , New Age int ernat ional
P bli t i
Publicat ions
Venkat a Reddy K., Eldho T. I ., Rao E.P. and Hengade N. ( 2007) “ A
kinem at ic wave based dist ribut ed wat ershed m odel using FEM, GI S and rem ot ely sensed dat a ” Journal of Hydrological Processes 21 2765-rem ot ely sensed dat a. Journal of Hydrological Processes, 21, 2765 2777
Chow , V.T., Maidm ent , D.R., and Mays, L.W. ( 1988) . Applied
Hydrologyy gy, McGraw- Hill, I nc., New York., , ,
Bedient , P.B. and Huber W.C.( 1988) . Hydrology and flood plain
analysis, Addison- Wesley Publishing Com pany., London
Cunderlik, J. M. ( 2003) . “ Hydrologic m odel select ion for t he CFCAS
Tu t or ia ls - Qu e st ion !.?.
I llust rat e t he necessit y of physically based
w at ershed m odeling
w at ershed m odeling.
Develop a concept ual m odel for a t ypical
Develop a concept ual m odel for a t ypical
w at ershed, for physically based m odeling.
w at ershed, for physically based m odeling.
Describe t he m erit s & dem erit s of physical
Describe t he m erit s & dem erit s of physical
m odeling.
m odeling.
33 33
Se lf Eva lu a t ion - Qu e st ion s!.
Q
Why dist ribut ed m odeling required for
w at ershed m odeling?
w at ershed m odeling?.
I llust rat e various solut ion m et hodologies for
problem solut ion
problem solut ion.
Different iat e bet w een explicit & im plicit FDM
schem es.
schem es.
Describe FEM solut ion m et hodology w it h
salient feat ures.
Assign m e n t - Qu e st ion s?.
g
Q
Wit h t he help of a flow chart , illust rat e
hydrologic/ hydraulic m odeling
hydrologic/ hydraulic m odeling.
Describe FDM solut ion m et hodology w it h
salient feat ures
salient feat ures.
Different iat e bet w een FDM & MOC.
Describe BEM solut ion m et hodology w it h
Describe BEM solut ion m et hodology w it h
salient feat ures.
35 35
Un solve d Pr oble m !.
Un solve d Pr oble m !.
St udy t he salient feat ures & problem s of
St udy t he salient feat ures & problem s of
t
h d
I d
t if h
i
t
h d
I d
t if h
i
Dr. T. I. Eldho Dr. T. I. Eldho
Professor, Professor,
Department of Civil Engineering, Department of Civil Engineering, pp gg gg
Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, Mumbai, India, 400 076.
Mumbai, India, 400 076. Email:
Email: [email protected]@iitb.ac.in
37 37
Email:
Email: [email protected]@iitb.ac.in
Phone: (022)
Phone: (022) –– 25767339; Fax: 2576730225767339; Fax: 25767302
http://www.