THE USE OF BACKGROUND KNOWLEDGE
STRATEGY TO IMPROVE READING
COMPREHENSION ON THE EIGHTH YEAR
STUDENTS OF SMP MUHAMMADIYAH 2
SAWANGAN MAGELANG IN THE ACADEMIC
YEAR 2015/2016
A GRADUATING PAPER
Submitted to the Board of Examiners as a partial fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Sarjana Pendidikan Islam (S. Pd. I) English
Education Department of Teacher Training and Education Faculty State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga
Directed By:
GUNARTI YULFANI
NIM. 113 11 146
EDUCATION DEPARTMENT OF TEACHER TRAINING AND
EDUCATION FACULTY
STATE INSTITUTE FOR ISLAMIC STUDIES (IAIN)
SALATIGA
5
MOTTOS
“
Surely there is ease after every hardship. Aye, surely there is
ease after every hardship
”
(
QS. Al-Insyirah: 6-7
)
“There is no secret ingredient. It’s just you.”
6
DEDICATION
I truly dedicate this graduating paper to:
1. My beloved parents : Bapak Suroto and Ibu Winarni
2. My beloved grandfather and grandmother : Pak Nani and Yung Nani 3. My husband and daughter : Ahsin Qolbaka and Arsyidaa Mecca Qolbaki 4. My brother : Gunawan Sapodo
5. My big family
6. My beloved teachers from elementary up to university
Thanks for your love, patience, care, support, and prayer in every little step
7
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Alhamdulillahirrobbil’alamin. Praise to Allah SWT, the Most Gracious
and the Most Merciful. Peace be upon the Prophet Muhammad SAW, the last messenger and the best teacher in life.
This graduating paper would not have been completed without the support, advice, help, guidance, and encouragement from institutions and individuals. Therefore, I would like to express special thank you to:
1. Dr. Rahmat Hariyadi, M. Pd., as the Rector of State Institute for Islamic Studies Salatiga.
2. Suwardi, M.Pd. as the Dean of the Teacher Training and Education Faculty
3. Noor Malihah, M.Hum. Ph. D., as the Head of English Education Departement
4. Setia Rini, M. Pd., as consultant of this graduating paper. Thank you for
precious time, advice, guidance, encouragement, and trust given to me during the process of writing this graduating paper from beginning until the end.
5. All lecturers in the English Education Department from whom I have learnt valuable knowledge, lessons and experiences during my study in
IAIN Salatiga. .
6. The principal of SMP Muhammadiyah 2 Sawangan Mr. Arnas Ikhwan Prasetyo, S. Pd., for his motivation and permission so that I conducted my
8
7. I also thank to the students of class VIII A and VIII B for their
participation during the research.
8. My beloved parents, Mr. Suroto and Mrs. Winarni, who always give spirit
to finish my study. Thank you for being patient waiting for me finishing my graduating paper.
9. My husband Ahsin Qolbaka and my beloved daughter Arsyidaa Mecca
Qolbaki, who have joined me in my struggle.
10.My brothers Gunawan Sapodo, thank you for your support.
11.My family Pak Nani, Yung Nani, Lek Narno, Lek Sabar, Mbok Joko, Mbok
Tomo, and all of my big families, who gave me motivation every time.
12.My friends in TBI 2011 Class E, Mbak Sri Suharmi, Mbak Mara, Mbak
Yeni, Mbak Ayu, Mbak Restu, Mbak Indah, Mbak Yeni, Mbak Lailatis, and Mbak Aulia, thanks you for the unforgettable moments and the
togetherness from the first until the last semester. I also would like to say thanks to my entire friends in TBI who can‟t mentioned one by one.
Thanks for your motivation.
13.My friends in Wisma Najma, Wisma Najwa, Wisma Safira, Liqa’ Fatimah,
Liqa’ Aisyah, who have struggled together with me. Besides, I would like
to say thanks to my friends all in KAMMI Komisariat Salatiga and LDK Fathir Ar-Rasyid, who all of my friends there can be close friends and a
family for me.
9
graduating paper is still far from being perfect. Therefore, I always welcome and
appreciate for the criticisms, suggestions, or opinions for the improvement of this graduating paper. I hope this graduating paper can give contribution for the
readers.
10 ABSTRACT
Gunarti Yulfani. 2016. “ The Use of Background Knowledge Strategy to Improve Reading Comprehension on the Eighth Year Students of SMP Muhammadiyah 2 Sawangan Magelang in the Academic Year of
2015/2016”. A Graduating Paper. Educational Faculty English Department State Institute of Islamic Studies (IAIN). Consultant: Setia Rini, M. Pd.
Keywords: background knowledge strategy; reading comprehension
The objective of this research is to improve the teaching and learning process of reading at VIII A and VIII B of SMP Muhammadiyah 2 Sawangan Magelang through background knowledge strategy.
This research is experimental study in which the experimental class and controlled class were conducted by the writer. In this research, the writer taught the students in experimental class by using Background Knowledge Strategy and controlled class by using traditional strategy. The test to both of the class was same in qualities and quantities to keep the reliability of the research. It was given to know how effective of using background knowledge strategy. This research answer these main questions (1) How is the influence of background knowledge strategy implementation on the eighth grade student‟s reading comprehension? (2) How is the significance differences between the students taught with background knowledge strategy and the students taught without background knowledge strategy?
11
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE ... i
DECLARATION ... ii
ATTENTIVE COUNSELOR NOTES ... iii
PAGE OF CERTIFICATION ... iv
MOTTO ... v
DEDICATION ... vi
ACKNOWLEDGMENT ... vii
ABSTRACT ... x
12
1. Principles of Teaching Reading ... 20
2. Creating Condition for Teaching Reading ... 22
3. Teaching Reading for Junior High School Students ... 24
C. Building Background Knowledge Strategy ... 26
1. Definition of Building Background Knowledge Strategy ... 26
2. Making Connection Types in Building Background Knowledge Strategy ... 27
3. Kinds of Background Knowledge Activation Strategies in Reading Comprehension ... 30
D. Reading Comprehension ... 34
1. Definition of Reading Comprehension ... 34
2. Components of Comprehension ... 35
3. Levels of Comprehension ... 36
CHAPTER III: RESEARCH METHODOLOGY A. Time of the Research ... 38
B. Object of the Research ... 39
1. Population ... 39
2. Sample and Sampling Technique ... 39
C. Research Design ... 43
D. Instrument ... 44
E. Research Methodology ... 45
1. Setting of the Research ... 45
2. Subjects of the Study ... 46
3. Data Source ... 46
4. Research Type ... 47
a. Experimental Research ... 47
b. Characteristics of Experimental Research ... 48
c. Procedure of the Research ... 49
d. Data Collection Techniques ... 50
13 CHAPTER IV: Finding and Discussion
A. Finding ... 56
B. Discussion ... 75
CHAPTER V: CLOSURE A. Conclusion ... 89
B. Suggestion ... 92
REFERENCES ... 93
APPENDIXES ... 96
THEACHING LEARNING PROCESS DOCUMENTATIONS ... 97
RPP ... 103
SKK RESULT ... 145
CONCULTATION PAGE ... 151
14
LIST OF TABLES
2.1Standard of Competence and Basic Competencies of Reading... 25
3.1KWL Instructional Scheme ... 32
3.2List of VIII B Class as Experimental Class ... 41
3.3List of VIII A Class as Control Class ... 42
3.4The Differences between Experimental and Control Group ... 43
4.1Reading Comprehension Evaluation Rubric ... 44
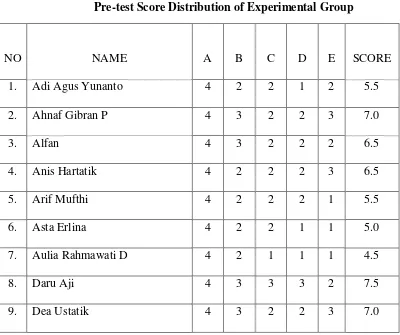
4.2Pre-test Score Distribution of Experimental Group ... 56
4.3Post-test Score Distribution of Experimental Group ... 58
4.4Frequency Distribution and Percentage of the Student‟s Reading Comprehension in Recalling Word Meaning ... 60
4.5Frequency Distribution and Percentage of the Student‟s Reading Comprehension in Drawing Inferences ... 61
4.6Frequency Distribution and Percentage of the Student‟s Reading Comprehension in Finding Answer of Question ... 62
4.7Frequency Distribution and Percentage of the Student‟s Reading Comprehension in Recognizing a Writer Purpose ... 63
4.8Frequency Distribution and Percentage of the Student‟s Reading Comprehension in Following a Structure of a Passage ... 65
4.9Pre-test Score Distribution of Control Group ... 66
4.10 The Post-test Score Distribution of Control Group………….………… 68
4.11 Frequency Distribution and Percentage of the Student‟s Reading Comprehension in Recalling Word Meaning……….……….. 70
4.12 Frequency Distribution and Percentage of the Student‟s Reading Comprehension in Drawing Inferences ……….71
15
4.14 Frequency Distribution and Percentage of the Student‟s Reading Comprehension in Recognizing a Writer Purpose……… 73 4.15 Frequency Distribution and Percentage of the Student‟s Reading
Comprehension in Following a Structure of a Passage ……….…74 4.16 Mean Assessment of Experimental Class and Control Class ………76 4.17 The Score of Student‟s Reading Comprehension in Pre –test
(Experimental Group)……….76
4.18 The Score of Student‟s Reading Comprehension in Pre –test (Control
Group)……….74
78
4.19 The Score of Student‟s Reading Comprehension in Post –test (Experimental Group)……….... 82 4.20 The Score of Student‟s Reading Comprehension in Post –test (Control
16
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A. Backgrounds of the Study
Language is used as a tool for communication among the nations in all
over the world. English is an international language, almost people from other country use English for their communication. English is very important
language.
To study English we need some abilities in writing, speaking, listening, and reading. Reading is one of the most important of the four skills
in learning process, generally English as a foreign language. Being able to read in English is importance, reading becomes essential for everyone in order
to develop their knowledge. Through reading we can get kind of information, enjoyment, knowledge and even problem solution. Being able to read in English is important, because there are many books written in English.
Everyone can learn and understand science, theory, philosophy, news, and many others from other countries.
Reading is a constant process of guessing, and what one brings to the text is often more important than what one finds in it. The students should be taught to use what they know to understand unknown elements, whether these
are ideas or simple word (Grellet, 1981:7). Reading is very necessary for students, because their study understanding depends on their reading
17
from text. The goal, therefore, is to gain an overall understanding of what is
described in the text rather than to obtain meaning from isolated words or sentences (Wolley, 2011:15).
In reading skill, the students must be able to understand, comprehend the text and brings their knowledge well in memory. Because of that, the teacher‟s role is important to design the lesson to make students attack in
reading activities. The common problems concern with the comprehension failure which the students today are increasingly diverse in terms of their
background knowledge and experiences. Their knowledge and experience will influence what the student think. For example, some students have experience
to museum, other students have not experience to museum. Some students have access at home with new media texts or information, while others must depend on schools and libraries to get the internet access. Their knowledge
and experience make each student has different understanding. The writer do interview with English teacher in the school at Monday, 6 July 2015.
From the condition above, the teacher should have match and strategies method that suitable with the condition. It will help each student reach their purpose in processing their understanding. To improve student‟s
reading comprehension, the writer will propose to use building background knowledge strategy to solve the problem in reading comprehension. In
Moreilon (2007: 19), building background knowledge strategy should be applied in teaching reading to connect student‟s new information with prior
18
this strategy will make students ready and feel interesting to the text that given
by the teacher. It is important to increase their motivation especially in reading skill.
One of strategies that researcher uses to meet clear condition of how learners usually do while reading in English learning is using background knowledge strategy. Understanding the importance of background knowledge
is critical because reader have to connect new information with prior knowledge before integrate and organize new information Moreillon
(2007:19). In line with Moreillon, Rosenblatt (1978) in Moreillon (2007:19) developed a theory of reading as a transaction among the reader, the text, and
the intention of the author. She proposed that each reader brings his own feelings, personality, and experiences to the text and that each reader is different each time he revisits a particular text.
The writer emphasizes the research concerns with the building background knowledge by conducting experimental research. It helpful or
necessary for students to understand, comprehend, and learn how to provide them with new background knowledge before they read in reading activities. The research focuses on “The Use of Background Knowledge Strategy to
19 B. Statements of Problem
Based on the background of study above, the problem of the study are as follows:
1. How is the influence of background knowledge strategy implementation on the eighth grade student‟s reading comprehension?
2. How is the significance differences between the students taught with
background knowledge strategy and the students taught without background knowledge strategy?
C. Objectives of the Study
Based on the research statement, this particular study aimed at finding out:
1. To find out the influence of background knowledge strategy implementation on the eighth grade student‟s reading comprehension.
2. To find out the significant differences between the students taught with
background knowledge strategy and taught without background knowledge strategy.
D. Hypothesis of the Study
According to Arikunto (1998:67), a hypothesis could be translated as a
20
This research is to answer the question about whether yes or not the use of building background knowledge is effective to improve student‟s
reading comprehension. To get the answer of the question, the researcher
should propose alternative hypothesis (Ha) and null hypothesis (Ho) as follow: 1. Alternative Hypothesis (Ha)
“Background Knowledge Strategy has effect toward Students Reading
Comprehension” 2. Null Hypothesis (Ho)
“Background Knowledge Strategy has not effect toward Students Reading
Comprehension.”
E. Benefits of the Study
The result of the study is expected to be used theoretically and
practically: 1.Theoretically
a. The result of this study is expected to be able to widen the skill of teachers in using background knowledge strategy in order to improve student‟s reading skill.
21 2.Practically
a. The result of this study is suggested to apply the background knowledge strategy to increase the students‟ competence in English reading skill.
b. The use of background knowledge strategy in reading can help the students more understand, interest to the learning, and enjoyable in doing their tasks associated with the reading materials.
F. Previous Studies
In this study, the research takes three literature reviews from some previous researchers. The first study was conducted by Megasari Nurul
Inayati, graduated from Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University Jakarta (2011). She researched “The Effectiveness of Jigsaw Techniques in Improving
Students’ Reading Comprehension at the Eighth Grade Students of SMP Islam
Parung”. The study focused on using two different classes by employing two
different teaching techniques. She has conclusion that using jigsaw has an
effective influence in teaching English reading comprehension. Using jigsaw can make students have responsibility to teach each other. It means that the students become teachers for their teammates.
The second study was conducted by Dedy Khisbullah entitled
“Improving the Students’ Reading Comprehension Through Retelling
Technique”, the result of this study is there is a significant difference after the
22
comprehend the text and retell it into written form and reveal it in front the
class.
The last study was conducted by Umiyati graduated from Syarif
Hidayatullah State Islamic University Jakarta (2011). She studied “The
Effectiveness of Using Small Group Interaction in Teaching Reading
Comprehension”. She focused on using small group interaction and
whole-class teaching has a significant difference. Her result of this study is there is a significant difference to the students‟ achievement in learning reading
comprehension by using small group interaction than whole-class teaching. In summary, some studies have proven that the use of reading strategy in reading activity can be effective to improve students‟ reading
comprehension. Although the writer has similar topic, „reading‟, but the writer
has different object and strategy of the study. This study concerns to use
building background knowledge strategy to improve students reading comprehension. By doing this research, it is to find out the use of background
knowledge strategy in improving student‟s reading comprehension.
G. Definition of Key Terms
In order to clarify the key terms used in this study, the writer gives limitation of the terms as follows:
1. Background Knowledge
23
author. She posited that each reader brings his own feelings, personality,
and experiences to the text and that each reader is different each time he revisits a particular text.
Background knowledge is what the reader brings to the reading event. Each reader‟s interpretation and each reading of the text are
potentially unique. This theory helps explain our individual responses to
literature, art, and music and can be applied more broadly to our generalized responses in all areas of learning (Moreillon, 2007:19).
2. Strategy
Strategy means a plan intended to achieve particular purpose (Oxford, 2008:439).
3. Reading is a kind of activity in translating written symbols into corresponding sound. Reading skills enable readers to turn writing into
meaning and achieve the goals of independence, comprehension, and fluency.
4. Reading comprehension
According to Woolley (2011:15), reading comprehension is the process of making meaning from text. The goal, therefore, is to gain an
overall understanding of what is described in the text rather than to obtain meaning from isolated words or sentences.
24 H. Place of the Research
This research was conducted in SMP Muhammadiyah 2 Sawangan. This school was selected for the research setting because of the researcher‟s
interest in solving the problems related to the teaching and learning process of reading found in the school. The Further explanation about this school
described as follows:
a. General Information of SMP Muhammadiyah 2 Sawangan Magelang
Junior High School Muhammadiyah 2 Sawangan is one of the islamic junior high school in Sawangan. It is located at Krogowanan,
Sawangan, Magelang. The detail of this school described as follows:
Name of School : SMP Muhammadiyah 2 Sawangan Post Code : 56481
Name of Principal : Arnas Ikhwan Prasetia, S. Pd. Subdistrict : Sawangan
District : Magelang
City : Magelang
Province : Central Java
b. Vision and Mission 1) Vision
The vision of this school is “Excellent on Achievement and
25 2) Mission
a) Implementation of learning and effective guidance and joyful until the students get their best development, appropriate with
their potential.
b) Growing spirit of achievement intensify to all of school members.
c) Encourage and help each student to identify their potential until their potential can be developed optimally.
d) Growing admirable behavior and real practice until the students can be diligent in praying, honest, discipline, sportive,
responsibility, proud, respect to parents and teacher, and love others until the students become good example to their friends and society.
e) Growing full and total comprehension toward Islamic religion and culture of nation and become source of wisdom in action.
c. Situation of SMP Muhammadiyah 2 Sawangan
In this school, the lesson is started at 07.00 a.m., the teacher and the students read the holy Qur‟an together for 10 minutes. The
lesson is finished at 14.00 p.m., except on Friday the lesson ended at
26
a.m. and the second break at 12.00 a.m. to pray Dhuhur together.
English is taught twice a week that is 2 x 40 minutes.
The subjects taught in eighth grade students of SMP
Muhammadiyah 2 Sawangan are Mathematic, TIK, Civic Education, Indonesian Language, English, Javanese, Physic, Penjaskes (sport), Counseling, SBK, Pembiasaan, Aqidah, Akhlak,
Ke-Muhammadiyah-an, Al Qur‟an, Arabic, and Ibadah.
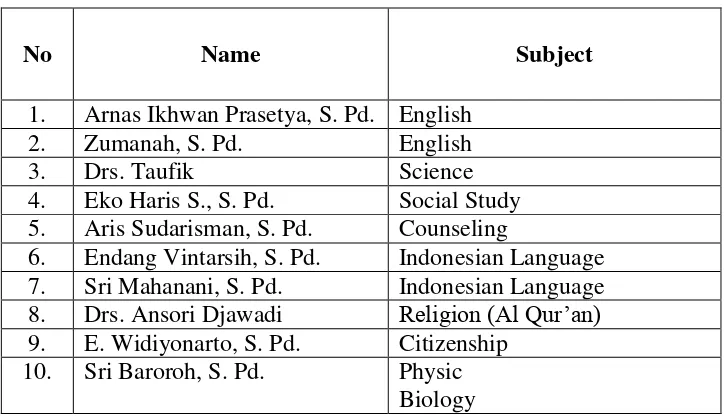
d. Teachers of SMP Muhammadiyah 2 Sawangan
In this school there were 21 teachers in total. Those teachers teach different subject divided into 18 subjects. The lists of the
teachers can be seen on the table below:
Table 3.1
List of Teachers of SMP Muhammadiyah 2 Sawangan in Academic Year of 2015/2016
No Name Subject
1. Arnas Ikhwan Prasetya, S. Pd. English 2. Zumanah, S. Pd. English
3. Drs. Taufik Science
4. Eko Haris S., S. Pd. Social Study 5. Aris Sudarisman, S. Pd. Counseling
6. Endang Vintarsih, S. Pd. Indonesian Language 7. Sri Mahanani, S. Pd. Indonesian Language 8. Drs. Ansori Djawadi Religion (Al Qur‟an) 9. E. Widiyonarto, S. Pd. Citizenship
27
16. Syahrul, S. Pd. I. Religion (PKM, Pembiasaan) 17. Dewi Istikomah, S. Pd. Javanese
Social Study 18. Arif Zuniarti, S. Pd. Biology
Art 19. Syahdani Rochman, S. Pd. Sport
20. Chamid Arifin Aqidah, Akhlaq, Tarikh, Pembiasaan (Dhuha, Sholat Jenazah, Kultum)
21. Atik Mathematic
e. The Subjects of the Research
There were 278 students of SMP Muhammadiyah 2 Sawangan in academic year of 2015/2016. There were 72 students in the first
grade (VII Class) divided into two classes start from VIIA up to VII B. There were 96 students in the second grade classes of VIIIA, VIIIB,
and VIIIC. There were 110 students in the third grade divided into IXA and IXB.
f. Staff Members of SMP Muhammadiyah 2 Sawangan
There are 4 staff members of SMP Muhammadiyah 2 Sawangan consist of 2 staff of administrator employees, 1 staff of
28
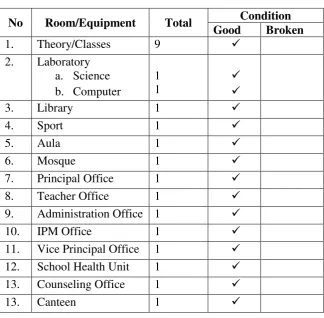
g. Facilities of SMP Muhammadiyah 2 Sawangan
SMP Muhammadiyah 2 Sawangan was built on Institute-Own Area as wide 1760 m² and building area as wide 1260 m². The list of
facilities in SMP Muhammadiyah 2 Sawangan presented on the table below:
Table 3.2
List of Facilities in SMP Muhammadiyah 2 Sawangan No Room/Equipment Total Condition
29 CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
A. Nature of Reading 1. Definition of Reading
There are many definitions of reading. Reading is one of receptive
skills that must be fulfilled in learning a language. There are some definitions about reading proposed by some experts. Johnson (2008: 3) has
some definitions related to reading. He defines reading as:
a. The practice of using a text to create meanings. b. A constantly developing skill.
c. Integrating visual and non-visual information. d. The act of linking one idea to another.
Celce-Murcia (2001: 119) states that reading skill is a process of trying to understand a written text. The reader has to perform a number of simultaneous tasks: decode the message by recognizing the written sign,
interpret the message by assigning meaning to the string of words, and understand what the author‟s intention was. Moreover, Murcia and
Olshtain (2002: 119) states that reading is a process of trying to understand a written text by readers through decoding, interpreting the message and eventually understanding the writer‟s intension. According to Rosenblatt
30
experience is operated on by the text while the text is simultaneously constructed according to the reader‟s understanding and assumptions.
Furthermore, Mikulecky (2008: 1) defines reading as thinking
process which is done consciously or unconsciously. Reading involves the use of strategies to reconstruct the meaning of the reading text in order to achieve the aim. One of the strategies is relating the reading text with the reader‟s background knowledge. In line with Mikulecky, Brown (2004:
189) state that reading is a process of a negotiation of a meaning. It means
that readers combines information from text and their background knowledge to build meaning. Readers have to employ all knowledge in their brain to make sense of text and they pay attention to the text itself for
the words, phrases, clauses, sentences, and the connection between sentences to comprehend the text.
In summary, reading is an activity of receiving information through some stages of thinking process in order to achieve a certain purpose such as decoding, interpreting, reconstruct the meaning, and understanding
written text.
2. Types of Reading
The categorization of reading types purposes for readers or students to know what the purpose of reading. The reading types make it
31
Brown (2004: 186-187) proposes three types of reading, namely academic
reading, job-related reading, and personal reading.
Genres of reading that belong to academic reading are textbooks,
theses, essays, papers, reference material, editorials and the like.
Types of reading which are job-related reading are such as memos,
applications, schedules, letters/emails, reports, and so forth.
Genres of reading that belong to personal reading are such as
newspapers, magazines, invitations, novels, short stories, etc.
3. Reading Skill
Reading involves a complex process. According to Spratt et al. (2005: 22), when people read, there are some activities involved in the
brain such as understanding the text at the level of letters, words and sentence, understanding cohesion and coherence, understanding various
kinds of text, relating the text to the knowledge of the world, making sense of the text and using appropriate sub skill. Based on this explanation, it is
clear that reading is an active activity.
Reading is an activity done by everyone for certain aim or purpose. Spratt, et al. (2005: 22) said that the reason why people read can affect
their way to read or which reading sub skill they will employ. There are some sub-skills of reading that can be used for different reasons of
32
gist or skimming, reading for detail, extensive reading and intensive
reading.
A good reader needs to master reading skills to achieve different
purpose in reading. According to Brown (2004: 187-188), there are two elements of reading skill, namely micro skills and macro skills. These are
micro skills and macro skills of reading stated by Brown as below:
a. Micro skills
1) Discriminating among the distinctive graphemes and orthographic
patterns of English,
2) Retaining chunks of language of different lengths in short-term memory,
3) Processing writing at an efficient rate of speed to suit the purpose, 4) Recognizing a core of words, and interpreting word order patterns
and their significance,
5) Recognizing grammatical word classes (noun, verbs, etc.), systems (e.g. tense, agreement, pluralization), patterns, rules, and
elliptical forms,
6) Recognizing that a particular meaning may be expressed in
different grammatical forms,
7) Recognizing cohesive devices in written discourse and their role
in signaling the relationship between and among clauses.
33
1) Recognize the rhetorical forms of written discourse and their
significance for interpretation.
2) Recognize the communicative functions of written texts,
according to form and purpose.
3) Infer context that is not explicit by using background knowledge.
4) Infer links and connections between events, ideas, etc., deduce causes and effects, and detect such relations as main idea, supporting idea, new information, given information,
generalization and exemplification.
5) Distinguish between literal and implied meanings.
6) Detect culturally specific references and interpret them in a context of the appropriate cultural schemata.
7) Develop and use battery of strategies, such as scanning and
skimming, detecting discourse markers, guessing the meaning of words from context, and activating schemata for the interpretation
of texts.
In the context of teaching and learning process of reading, the teacher should introduce and teach the students those skills in order to
train the learner to be a good reader.
4. Model of Reading Process
34
are two common models of reading process. They are bottom-up approach
and top-down approach.
Bottom-up approach show when the reader starts by knowing the
printed word, then recognizing the sound, interpreting the words, and after that decoding the meaning of the words. In other words, before readers come to the level of understanding the meaning of the words, they should
learn from the level of recognizing the letters first. In addition, Salmi (2011: 702) state that in this model, readers begin with the lowest level,
from which the symbols are identified.
In top-down processing model, the readers need to contribute their
knowledge in the process of receiving the new information from the text. The readers can understand the meaning of the text not through recognizing from all small part of the written symbol but through by
maximizing the use of their existing and activating their knowledge. In Salmi (2011: 703) state that in top-down processing model, readers do not
read every word, but see through the text in order to be able to guess the meaning of the words or phrases.
B. Teaching Reading
Teaching is guiding and facilitating learning, enabling the learner to learn, setting the condition for learning (Brown, 2000: 7). Therefore, to
35
The teacher also play roles which are necessary to improve student‟s reading
ability in teaching reading practice.
The teachers need to guide the students in teaching reading activity to
gain knowledge and skills of reading. Furthermore, through giving tasks and activities, the teachers also need to facilitate learning which can make students interact with the reading material, the teacher and other students. By giving appropriate materials, it will support student‟s learning process.
1. Principles of Teaching Reading
According to Nation (2009: 6-8), there are four principles of the teaching reading. They are meaning-focused input, meaning-focused
output, language-focused learning and fluency development.
The first principle is meaning-focused input. It means that in a reading course, it is important to determine practice with a range of
reading purposes such as reading to search for information, reading to learn, reading for fun, reading for integrating information, reading to
critique text, and reading to write. Besides, the reading text should be appropriate with the language proficiency level of the students and the reading activity should be used to develop language proficiency.
The second principle is meaning-focused output. It means that a reading course should be involved with other language skills such as
36
activities, for example in a reading class, there will be integration between
four skills, it might include a pre-reading discussion on the topic to activate schemata, listening to a lecture about the topic of a passage to be
read, a focus on a certain reading strategy such as scanning, skimming, etc., writing summary of the passage.
The third principle is language-focused learning. It means that a
reading course should be able to help the students to develop their reading skills and knowledge for effective reading. The teaching of reading should
be done based on the micro skills of reading and the language features needed to read including phonemic awareness, phonics, spelling practice, vocabulary and grammar. The learners should be given the reading
strategies including previewing, setting a purpose, predicting, posing questions, connecting to background knowledge, paying attention,
guessing meaning from context, etc. besides reading skills and language features. Then, the teachers give training and practice for students in
integrating a range of strategies like reciprocal teaching or concept-oriented reading. The students also should be familiar with the structure of the texts used in reports, stories, recount and so on.
The last principle is fluency development. There are three main points in this principle. First, the teaching process of reading should help
37
to stories, independent reading, and shared reading. Third, the learners
should read a lot.
The teachers have to consider the purpose of reading, the
complexity of the texts, and the development of reading skills and strategies of reading skills.
2. Creating Condition for Teaching Reading
In order to be successful in teaching reading, it is necessary to create good condition in reading learning process. In Johnson (2008: 11-13), there are some tips to keep in mind as teacher create good reading
conditions as below:
a. Help children fall in love with books
Reading is a pleasurable act. There are wonderful stories and interesting characters found in books. Everyone can experience magic, adventure, romance, moral dilemmas, comedy, tragedy, triumph, failure, or success. A teacher‟s or tutor‟s number one job is to help
students fall in love with books.
b. Create a space every day for sustained, silent reading
Just like learning to play a musical instrument, children who
are learning to read get better at it by practicing.
38
Choice is important in helping readers grow. Reading is more
pleasurable when we are able to make choices about what we read. Children need to be able to make the same kinds of choices about their
reading material, not all the time, but much of the time. (Choice doesn‟t mean total choice all the time.)
d. Connect reading pleasure to reading practice
A simple behaviorist principle is that if we find something to be enjoyable (a positive reinforcement), we are more likely to do that
thing again. If we find something to be boring, frustrating, or meaningless (an aversive conditioner), we are less likely to do that
thing again.
In the same way, if the act of reading is linked to instruction that students find unpleasant or disagreeable, they will be less inclined
to engage in future reading behavior e. Keep instruction simple
Good teachers make things seem as simple as possible. In this way they are like gymnasts. Gymnasts are able to perform complicated moves and make them look simple. Circus performers make simple
moves look difficult. As teachers we want to be gymnasts, not circus performers.
f. Include talk and other forms of social interaction
39
to each other about what they‟re reading and share their ideas and
insights with others. In this way, the stories come to life, students gain insight and ideas from others, and language learning is enhanced.
3. Teaching Reading for Junior High School Students
Teaching reading in Junior High School is one of the important things that have to be done well. Teaching and learning process of English in the Junior High School is expected to make the students reach the
functional level, that is, to communicate written and orally to solve daily problems (BSNP, 2006). English is one of the compulsory subjects that
has to be taught for Junior High School level.
Students expect to comprehend written text to reach the functional
level including the ability of comprehending many kinds of short functional texts, procedure texts, descriptive texts, recount texts, and report texts in the area of teaching reading for Junior High School. In the
forms of descriptive, recount and narrative texts for the eighth year students, the students can develop their reading skills through short
functional texts and simple essays
In the first semester, to interact with the society, the students expect to have reading skills which deal with reading aloud and
40
learn the materials of functional texts and simple essays in forms of
narrative and recount texts.
In this study, the researcher will select the material about
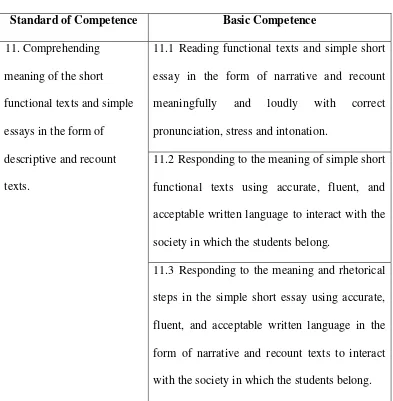
descriptive texts because it is one of the appropriate materials that should be taught in the first semester. The expected reading competences from the junior high school students of the eighth grade in the first semester are
displayed below.
Table 2.1
Standard of Competence and Basic Competencies of Reading Standard of Competence Basic Competence
11. Comprehending meaning of the short
functional texts and simple essays in the form of
descriptive and recount texts.
11.1 Reading functional texts and simple short essay in the form of narrative and recount
meaningfully and loudly with correct pronunciation, stress and intonation.
11.2 Responding to the meaning of simple short
functional texts using accurate, fluent, and acceptable written language to interact with the
society in which the students belong.
11.3 Responding to the meaning and rhetorical steps in the simple short essay using accurate, fluent, and acceptable written language in the
41 C. Background Knowledge Strategy
1. Definition of Background Knowledge Strategy
Bartlett in Eileen (2008: 2) theorizes that when readers read, they
tend to interpret their texts according to their own background knowledge. Rosenblatt in Moreillon (2007:19) told that developed a theory of reading as a transaction among the reader, the text, and the
intention of the author. She posited that each reader brings his own feelings, personality, and experiences to the text and that each reader is
different each time he revisits a particular text.
Background knowledge is what the reader brings to the reading event. Each reader‟s interpretation and each reading of the text are
potentially unique. This theory helps explain our individual responses to literature, art, and music and can be applied more broadly to our
generalized responses in all areas of learning (Moreillon, 2007:19). Furthermore, Knuth and Jones in Yuksel (2012: 1197) defined prior knowledge as some life experience, either real or vicarious, previous
works read and experience with language. According to Jonssen and Gabrowski in Yuksel (2012: 1198), they defined prior knowledge as
knowledge, skills, or ability that students bring to the learning process. According to Rumelhart et al in Eileen (2008: 2), the text does not in itself carry meaning but rather depends on the individual‟s pre-existing
42
In summary, background knowledge is what the reader brings to
the reading activity which might come from their experience or from reading process.
2. Making Connection Types in Background Knowledge Strategy
Keene and Zimmermann in Moreillon (2007:21) suggest that readers make three types of connections. They are self,
text-to-text, and text to world. Readers can use each of these frames to identify the source of their prior knowledge connections.
Questions related to each of these types of connection provide teachers with tools to engage students in active reading. Connections help
everyone remember what they read. Connections also give value to literacy events in which the reader engage. Building connections not only supports comprehension, it also enriches reader‟s literate lives by giving
deeper significance to literacy experiences.
There are three types of connections based on Keene and
Zimmermann in Moreillon (2007:21-24):
a. Text-to-Self Connections
Text-to-self connections require that educators know the children in their care and be familiar with student‟s home lives and
local communities. Posing and answering questions can be an
43
knowledge accessible to students. These sample questions center on
three areas of text-to-self connections such feelings, experiences, and ideas:
1) Have you ever felt like the character in this story? Describe what happened and how you felt.
2) Have you a similar experience? Compare your experience to
that of the character.
3) Have you heard or read this information before? What does this
information mean to you?
4) How does connecting a story or information to your own life experiences help you better understand it?
b. Text-to-Text Connections
Learner can be guided to make connections between text when teachers make effective connections between children‟s home
and school lives. In a broad sense, a text can be any communication from which a person makes meaning. This includes all forms of
paper-based documents as well as oral communication, visual images, and electronic resources. This view of a text offers learners
a wide range of possible sources for making connections.
The following sample questions center on making text-to-text connections. They can be used to guide teacher‟s and student‟s
44
1) Have you ever read another book or seen a movie in which the
characters have feelings or experiences similar to the ones in this story? Describe how they are the same.
2) Have you ever read another book or seen a movie in which a story element (setting, plot, conflict, theme, or style) is similar to the one in this story? Describe how they are same.
3) Have you read another book or seen a movie in which the writer used language or text structure similar to that in this
story? Describe how these texts are similar.
4) How does making connections to familiar texts help you
comprehend the new text? c. Text-to-World Connections
With text-to-world connections, readers stretch their
thinking beyond the particulars of what they read, hear, and view to connect story themes with larger life issues. These are some questions that can be used to guide educator‟s or student‟s thinking:
1) What do you think the author‟s message or purpose was in writing this story or presenting this information?
2) Did the author suggest a message that connects with bigger ideas about the way things are in the world? What do you already know about these?
45
4) How does making connections to larger issues help you
comprehend this text?
3. Kinds of Background Knowledge Activation Strategies in Reading Comprehension
In order to activate background knowledge, there are some strategies. In Yuksel (2012:1198) there are reflection and recording
strategy, brain storming, small group discussion, K-W-L strategy, concept map, contact-2, and PKTandD. These strategies have some advantages
and disadvantages with respect to each other as following below:
a. Reflection and Recording Strategy
Teachers can ask the students “what do you know”, to know
what their students have already known. They asked the answers
orally or in written format.
b. Brain Storming
According to Porter in Yuksel (2012:1199), brain storming simply is that the teacher begins by introducing a problem or a new
topic. The students tell all the possible answers, ideas and words. The teacher can write the student‟s sayings on the board. By doing
46
about a topic. It provides teachers with observing the misconceptions related to topic in some degree. However, to assess the student‟s
prior knowledge one by one is really hard at this strategy.
c. Small Group Discussion
According to Schmidt, small group discussion can be another way to activate student‟s prior knowledge. In this strategy, teachers
give a problem, a situation or a topic to their students to discuss in small groups. After discussion, groups share their ideas and findings with whole class. By doing that, teachers can observe student‟s prior
knowledge related to the topic.
d. K-W-L Strategy
K-W-L strategy is developed by Ogle. K-W-L strategy is a strategy that it aims to unite prior learning and new learning together.
At this strategy, with the beginning of the lesson, a prepared sheet separated into three columns is given to each student. Then, in before
learning phase, students are asked to write what is known about the topic and this part forms the K (Known?) of K-W-L strategy. At second phase, students write their questions about what they want to
learn related to the topic in second column W (Wanted?). Lastly, after learning new topic, students fill the third column L (Learned)
47
comprehension and summarizing abilities, increase their motivation
and focus on attention to the lesson. It can be used as an assessment tool for teachers.
Developed by D. Ogle in Fengjuan (2010:78), KWL is an instructional scheme that develops active reading of expository texts by activating learner‟s background knowledge. KWL strategy
provides a structure for recalling what learners know about a topic, writing what they want to know, and finally make a list for their new
information. There is KWL instructional scheme as an instructional reading strategy as follow:
Table 2.2 The experience expected
to use:
48
It is multifunctional tool that can be used in summarizing the
topic, introducing the topic, assessment as well as prior knowledge activation tool. Concept maps may show student‟s misconceptions
about a topic and help both teacher and students connect prior knowledge in visual format.
f. CONTACT-2 (Computer-Assisted Activation)
Overall the strategies above are carried out by face to face discussions or paper and pencil. However, CONTACT-2 which was
developed by Biemans and Simons, is a computer-assisted approach. It provides students with searching for preconceptions, comparing and contrasting these preconceptions with new information and
formulating, applying and evaluating new conceptions.
g. PKT and D (Prior Knowledge Test and Diagnosis) Model
PKTandD is anoher computer-based method developed by Lin, Lin and Huang. It was designed to diagnose and strengthen prior
knowledge of students before new topics.
In this system, there is an item bank related to topics and the instructor selects some related items from item bank before new
49 D. Reading Comprehension
1. Definition of Reading Comprehension
According to Torgesen in Westwood (2008:33), reading
comprehension is both a cognitive and an affective activity. Good readers are „active‟ in the sense of becoming involved cognitively and emotionally
in what they are reading. They are often keen to use text as a way of
obtaining new information, acquiring new ideas, solving problems, and as a source of enjoyment.
Furthermore, Snow (2002:33) states that reading comprehension is the process of simultaneously extracting and constructing meaning through interaction and involvement with written language. The words extracting
and constructing isto emphasize both the importance and the insufficiency of the text as a determinant of reading comprehension. Comprehension
entails three elements below:
a. The reader who is doing the comprehending
b. The text that is to be comprehended
c. The activity in which comprehension is a part.
Therefore, teacher not only should help students how to read but
50 2. Components of Comprehension
A study by Davis (in Alderson, 2000:9) is generally regarded as the significant attempt to delineate separate comprehension skills. His
analysis showed the following eight comprehension skills:
a. recalling word meaning (vocabulary knowledge)
b. drawing inferences about the meaning of word in context
c. finding answers to questions answered explicitly or in paraphrase d. weaving together ideas in the content
e. drawing infers from the content
f. Recognizing a writer‟s purpose, attitude, tone and mood g. identifying a writer‟s technique
h. following the structure of a passage
Those eight elements are the most important in the comprehension
in reading. It can be the measurement or indication of comprehension in issued or not. Such as knowledge in word meaning, if a student reads a text or information, he or she has to know the meaning of every single
word and the knowledge of the word in that context (passage).
The writer will take five components of comprehension to make score of the students reading comprehension that consist of vocabulary knowledge, drawing inferences, recognizing a writer‟s purpose, finding the answers of
51 3. Levels of Comprehension
Readers may engage in different types or levels of thinking in constructing the meaning of text. In constructing the meaning of a text,
readers may engage in different types or levels of thinking. According to Dallmann (1982:25), there are three levels of comprehension are typically
identified: literal, interpretative, and critical.
a. Literal Comprehension
Literal comprehension is an understanding the ideas and
information explicitly state in the passage. The abilities are:
1)Knowledge of word meaning
2)Recall of details directly stated and paraphrased in own words.
3)Understanding of grammar clues-subject, verb, pronouns, conjunction, and so forth.
4)Recall of main idea explicitly stated.
5)Knowledge of sequence of information presented in passage.
b. Interpretative comprehension
Interpretative comprehension is an understanding of ideas and
information not explicitly stated in passage. The abilities are:
52
2) Infer factual information, main ideas, comparisons, cause-effect
relationship not explicitly stated in the passage. 3) Summarization of story content.
c. Critical Comprehension
Critical comprehension includes analyzing, evaluating, and personally reacting to information presented in the passage. The
abilities are:
1. Personal reacting to information in a passage indicating its meaning
to the reader.
2. Analyzing and evaluating the quality of written information in terms
53
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A. Time of the Research
This research was conducted in SMP Muhammadiyah 2 Sawangan Magelang in the academic year 2015/2016. There were some steps that the
writer did to conduct this research. They were preparation, implementation, analysis the data, and report the result of the research. Those steps described briefly as follows:
a. Preparation
1) Proposal Draft Consultation : November 2015
2) Observation : November 2015
b. Implementation
1) Data Collection : November 2015 - Desember 2015
a) Pre-Test
Experimental Class : November 2015
Control Class : November 2015 b) Treatment
Experimental Class : November 2015 –
54 c) Post-Test
Experimental Class : December 2015
Control Class : December 2015
2) Analysis the Data : December 2015
B. Object of the Research 1. Population
Population is all subject intended to be investigated (Hadi,
1990:20). The population of this research is the entire second year students of SMP Muhammadiyah 2 Sawangan in the academic year 2015/2016. There are 96 students, consist of 51 female students and 45
male students.
2. Sample and Sampling Technique
The population of the study was 96 students from the second year students of SMP Muhammadiyah 2 Sawangan, which consist of
three classes. The sample was taken in term of purposive sampling technique. In purposive sampling technique, who will take as a sample selected with particular consideration based on the purpose of the
research (Sukandarrumidi, 2004:65)
The writer used purposive sampling technique because it is in line with the method of the research. The writer chose a sample by
55
purposive sampling, the researcher choose the sample according to the
English teacher‟s recommendation.
The writer took two classes of SMP Muhammadiyah 2
Sawangan. There were VIII A as the control class and VIII B as the experimental class. Mrs. Zumanah, the English teacher, said that both of classes considered as appropriate classes to be researched. Mrs.
Zumanah recommended VIII B CLASS as the experimental group because some of students in that class have difficulties in
comprehending their understanding in English text. The teacher recommended using that class as the experimental group with hope that Background Knowledge Strategy can help the students to improve student‟s reading comprehension. Besides, the teacher recommended
VIII A as the control group because some of students have same
reading comprehension with VIII B.
Furthermore, the samples of this research were VIII B as the experimental group and VIII A as the control group. There were 30
students in VIII B class and 30 in VIII A Class. The experimental class was given treatment using Background Knowledge Strategy and the
control class was given treatment using traditional strategy.
The detail data of students in this research presented on the
56
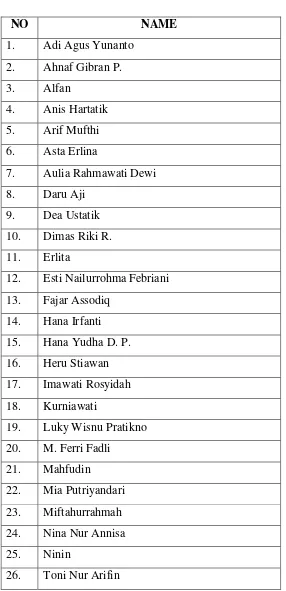
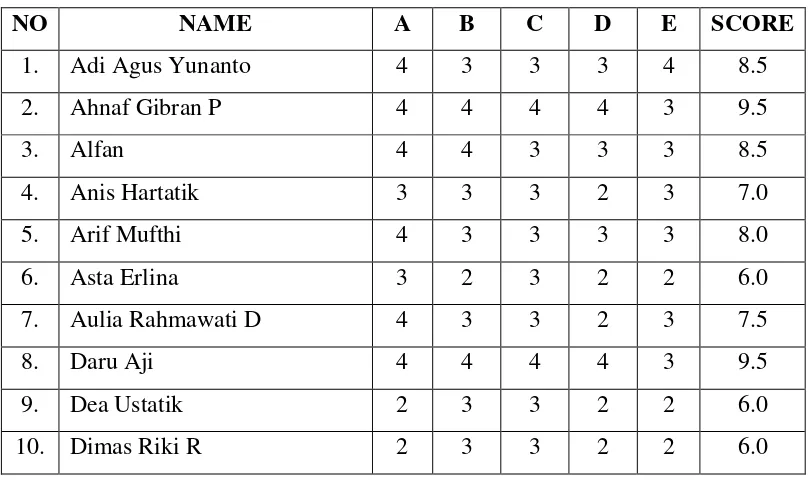
Table 3.1
List of VIII B Class as EXPERIMENTAL CLASS
NO NAME
7. Aulia Rahmawati Dewi 8. Daru Aji
9. Dea Ustatik 10. Dimas Riki R. 11. Erlita
12. Esti Nailurrohma Febriani 13. Fajar Assodiq
14. Hana Irfanti 15. Hana Yudha D. P. 16. Heru Stiawan 17. Imawati Rosyidah 18. Kurniawati
19. Luky Wisnu Pratikno 20. M. Ferri Fadli
21. Mahfudin
22. Mia Putriyandari 23. Miftahurrahmah 24. Nina Nur Annisa 25. Ninin
57 27. Wahyu Nur R. 28. Graciela Veronika D. 29. Ihsan Abdurrozaq 30. Widya Ega Rahayu
Table 3.2
List of VIIIA as CONTROL CLASS
NO NAME 7. Dhifa Kurniawan 8. Dini Setyawati 9. Dodi
10. Erwanto
11. Liya Maesarotul Hasanah 12. Nifa Istiningsih
13. Nova Ella S. 14. Nur Indah Sari 15. Paryanto
58 22. Tanti Sugiyanti 23. Vita Agustiningrum 24. Wahyu Putri Setyorini 25. Watini
26. Winarni
27. Ichsan Rodzikin 28. Renfila Ningsih 29. Isti Hasanah 30. Alviani
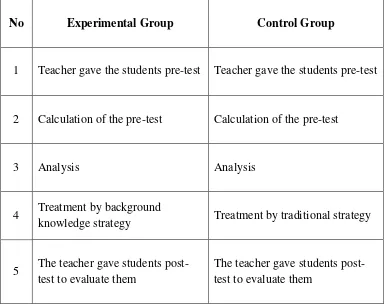
C. Research Design
Table 3.3
The Differences between Experimental and Control Group
No Experimental Group Control Group
1 Teacher gave the students pre-test Teacher gave the students pre-test
2 Calculation of the pre-test Calculation of the pre-test
3 Analysis Analysis
4 Treatment by background
knowledge strategy Treatment by traditional strategy
5 The teacher gave students post-test to evaluate them
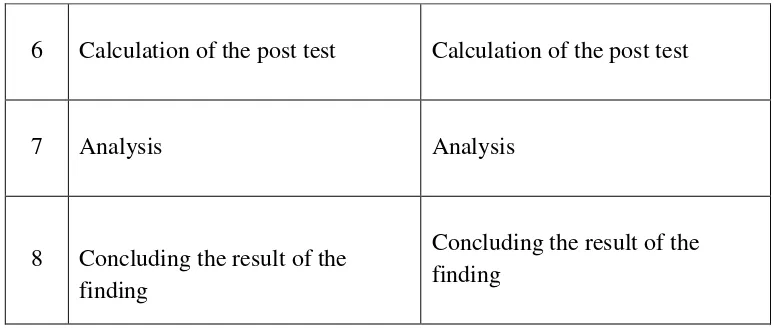
59
6 Calculation of the post test Calculation of the post test
7 Analysis Analysis
8 Concluding the result of the finding
Concluding the result of the finding
D. Instrument
The instrument used in this research is a test. There was a written test to measure the student‟s reading comprehension. In the written test the writer
use rubric to evaluate the student‟s reading comprehension. The rubric is:
Table 3.4
60
Employs two kind of data collection namely pre-test and post-test is used to know the student prior ability of the two groups by using the different material and the same level of difficulty, and post-test is given after giving different
treatment to know the result of the different treatments for the calculation of the score total is by using formula:
S
=
Where is:
S = score
R = number of right answer
61 E. Research Methodology
Method of the research used in this study are: 1. The setting of Research
The research was submitted at SMP Muhammadiyah 2 Sawangan. SMP Muhammadiyah 2 Sawangan is located in Krogowanan village. Sub-district of Sawangan.
2. Subject of the Study
The subjects of the research were the students of class VIII A and VIII B of SMP Muhammadiyah 2 Sawangan. Class of VIII A consisted of
30 students. Class of VIII B consisted of 33 students. The researcher selected 30 students from VIII B to measure with VIII A. They were
selected as the subjects of the research based on the discussion with the English teacher. There were some considerations of choosing the students
of class VIII A and VIII B of SMP Muhammadiyah 2 Sawangan. First, it was related to the student‟s reading ability. According to the English
teacher, both of class have some same ability in reading comprehension.
Second, during the learning process, the students interaction and motivation not optimal in the teaching activities. Therefore, based on the
62
students were from various areas with various cultural background
families.
3. Data Source
Data source is subject where the data acquired (Arikunto, 1998:114). In order to know whether there are significant differences between students who taught using building background knowledge
strategy and those who not taught without building background knowledge strategy. Sukandarrumidi (2004:44) also states that data source means all
information whether is real thing, abstract things, phenomenon or indication with quantitative and qualitative.
In order to know whether there are significant differences between
students who were taught using Background Knowledge Strategy and those who were not. The writer used the data sources both from primary
and secondary data that described as follows: a. Primary
The primary data sources of this research were taken during pre-test and post-pre-test both from experimental and control class students pre-test.
b. Secondary
63 4. Research Type
b.Experimental Research
In this research, the writer conducted experimental research
method. According to Gay in Emzir (2008:63) that is an experimental research method is one of the precise methods to examine correctly the hypothesis concern with the cause and effect because of the fact,
instruction toward a group and experimental sample. In experimental study, the researcher manipulate at least one variable, control other
relevant variable, and observe the effect or influence toward one or more related variable.
Experimental and control group were investigated. The first is experimental group and the second group is as control group. Experimental group consist of student teach by background knowledge
strategy and the second group that consist of student teach without background knowledge strategy.
Both of groups given different treatment that might related with the performance of the dependent variable. Each group given treatment for some periods of time then the writer administers a test to dependent
64
c. Characteristics of Experimental Research
According to Emzir (2008:68) there are three essential characteristics of experimental research as follow:
1)Manipulation
Direct manipulation from the researcher toward at least one independent variable is one of characteristics that make experimental
research different with other research methodology. 2) Control
Control refers to removing or minimizing the influence of such variables by several methods. According to Gay in Emzir (2008:67) that control refers to research‟s effort to remove the influences of
such variables (except independent variable) which can give affect on dependent variable. In other word, the researcher propose same
group condition, therefore the main difference among them put on independent variable. It is the difference that caused by the
researcher. 3) Observation
Observation necessary to know whether there is an effect of
manipulation on independent variable toward dependent variable in experimental research. The researcher did observation on the
65 d.The Procedure of the Research
Basically, procedure in experimental study has same procedures with other research. In this research the writer uses some ways, as
Emzir (2008:69) state. There are six steps as follow: 1) choose and formulate the problems
2) choose the subject and instrument measurement
3) choose the research design 4) performing the procedure
5) analysis the data
6) formulate the conclusion
e. Data Collection Techniques
There are three methods of collecting data in this study as follow:
1) Observation
The writer observed the location and the population before
doing the research. The research was done by interviewed the English teacher to know the problems in teaching English, expecially in student‟s reading comprehension. Observation on the
research site was done at Monday, July 6
, 2015.
Observation is one of instrument in collecting the research data. Besides doing the test, the writer did class observation.
66
phenomenon on the research. It also applied to know the condition
and situation in learning process (Sukandarrumidi, 2004:69).
Observations were conducted to know what happens in the
classroom when the strategy is implemented. The researcher observed the learning process of reading to obtain the information about the success of the strategies and the problems that occurred
during the implementation of the strategy. 2) Test
A test is a series of questions or other instruments, which is used measure individual or group skills, knowledge, intelligence,
capability, or talent (Arikunto, 1998:139). The writer used test to find out the effectiveness of using building background knowledge to improve student‟s reading comprehension.
Tests (including pre-test and post-test) were used to compare the student‟s reading comprehension before and after taught by
using building background knowledge strategy. It showed whether there will be improvement of student‟s reading comprehension or
not by the implementation of the strategies.
The pre-test and post-test in this research were in the form of multiple choice consisting of 5 items, essay consist of 5 items, and