PROBLEM BASED LEARNING TO ENHANCE STUDENTS’ CRITICAL
THINKING SKILLS AND CONCEPT COMPREHENSION IN
POLLUTION CONCEPT
Research Paper
Submitted as fullfilment of the requirement
for degree of Sarjana Pendidikan in International Program on Science Education
Prepared by:
Mitha Hardianni 0902182
Mitha Hardianni,2013
Problem Based Learning To Enhance Students’ Critical Thinking Skills And Concept Comprehension In Pollution
Concept
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu 2013
PROBLEM BASED LEARNING TO ENHANCE STUDENTS’ CRITICAL
THINKING SKILLS AND CONCEPT COMPREHENSION IN
POLLUTION CONCEPT
Oleh Mitha Hardianni
Sebuah skripsi yang diajukan untuk memenuhi salah satu syarat memperoleh gelar Sarjana Pendidikan pada Fakultas Matematika dan Ilmu Pengetahuan Alam
© Mitha Hardianni 2013 Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia
Juli 2013
Hak Cipta dilindungi undang-undang.
Mitha Hardianni,2013
Problem Based Learning To Enhance Students’ Critical Thinking Skills And Concept Comprehension In Pollution
Concept
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
AUTHORIZATION PAGE
PROBLEM BASED LEARNING TO ENHANCE STUDENTS’ CRITICAL THINKING
SKILLS AND CONCEPT COMPREHENSION IN POLLUTION CONCEPT
by:
Mitha Hardianni
Registration Number: 0902182
Approved and authorized by:
First Supervisor
H. Hayat Sholihin, M.Sc. Ph.D NIP: 195711231984031001
Second Supervisor
Dr.Yayan Sanjaya, M.Si. NIP: 197112312001121001
Head of
Study Program of International Program on Science Education
DECLARATION
I declare that this research paper with tittle ” PROBLEM BASED LEARNING TO
ENHANCE STUDENTS’ CRITICAL THINKING SKILLS AND CONCEPT COMPREHENSION IN POLLUTION CONCEPT ” is my own work. There is no plagiarism or work of other inside this research paper and i do not do plagiarism or citation that is not
accordance with the prevailing scientific ethics. This reserach paper is submitted as partial fulfillment of the requirement for Sarjana Pendidikan degree.
Bandung, June 2013
Mitha Hardianni,2013
Problem Based Learning To Enhance Students’ Critical Thinking Skills And Concept Comprehension In Pollution
Concept
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
PROBLEM BASED LEARNING TO ENHANCE STUDENTS’ CRITICAL THINKING SKILLS AND CONCEPT COMPREHENSION IN POLLUTION CONCEPT
Mitha Hardianni 0902182
Supervisor I : H. Hayat Sholihin, M.Sc.Ph.D
Supervisor II : Dr.Yayan Sanjaya, M.Si.
International Program on Science Education FPMIPA UPI 2013
ABSTRACT
This research paper which entitled “Problem Based Learning to Enhance Students’ Critical
Thinking Skills and Concept Comprehension in Pollution Concept” is conducted due to
traditional learning which is more focus on students’ academic achievement rather than the
process of contructing the knowledge and students’ thinking skill in solving their problem. Thus, the main objectives of this research are to investigate the enhancement of students’ critical
thinking skill and concept comprehension trough Problem Based Learning approach also to investigate students response toward Problem Based Learning. Research method that used in this reserach is quantitative descriptive method with one group pretest and posttest design. Population of this research are 10 grade of high school students in one of international school in Tanggerang. While the sample of this reseach are choosen by using purposive sampling method. the sample chosen are 10 grade students in lower achievement class. According to the result of this reseach indicates that there is enhancement of students’ critical thinking skill with normalized gain index value is as much as 0.33 which include in medium category. Students enhancement of concept comprehension in this reseach are analyed in each subtopic and each cognitive domain. The subtopic that most reached by students is soil pollution with normalized gain index value is 0.75 which include in high category. Meanwhile, the highest enhancement in cognitive domain are understanding aspect (C2) and evaluating aspect (C5) with normalized gain index value is 0.57 which include in medium category. Furthermore in students response, mostly students gave positive response toward science and Problem Based Learning.
TABLE OF CONTENT
CHAPTER II PROBLEM BASED LEARNING, CRITICAL THINKING SKILL AND CONCEPT COMPREHENSION IN POLLUTION CONCEPT
Mitha Hardianni,2013
Problem Based Learning To Enhance Students’ Critical Thinking Skills And Concept Comprehension In
Pollution Concept
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A. Population and Sample ... B. Research Method ... C. Research Design ... D. Operational Definition ... E. Research Instrument ... F. Validation of Instrument ... G. Collecting Data Technique ... H. Data Analysis Techniques ... I. The Result of Trial Test Instruments ... J. Research Procedure ... K. Research Scheme ...
CHAPTER IV RESULT AND DISCUSSION
A. Implementation of Problem Based Learning ... B. Students’ Concept Comprehension ... C. Students’ critical thinking skills ... D. Questionnaire of students’ response ... E. Interview Result ...
CHAPTER V CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATION
APPENDICES ... 68
TABLE LIST
2.1 Step of problem based learning………
2.2 Six cognitive domains……….. 2.3 Definition of critical thinking………... 2.4 Critical thinking ability based on experts……….... 2.5 Indicators of critical thinking skill……… 2.6 Critical thinking skill that can be seen through problem based learning………..
3.1 One group pre test and post test design………
3.2 Interpretation of validity of test item………
3.3 Interpretation of reliability………
3.4 Interpretation of discriminating power………. 3.5 Category of student score……….
3.6 N-gain index category………..
3.7 Percentage of learning implementation category……….
3.8 Recapitulation of validity concept comprehension test ………... 3.9 Recapitulation of discriminating power concept comprehension test ………
3.10 Recapitulation of difficulty level concept comprehension test ……….
3.11 Recapitulation of validity critical thinking skills test ……… 3.12 Recapitulation of discriminating power critical thinking skills test ………
3.13 Recapitulation of difficulty level critical thinking skills test ……… 4.1 Average percentage of teacher activity………
4.2 Average percentage of student’s activity……….. 4.3 Blueprint question of concept comprehension………. 4.4 Improvement recap of students’ concept comprehension……… 4.5 Result of students’ concept comprehension test in each subtopic……… 4.6 Improvement recap of concept comprehension in each cognitive domain………
Mitha Hardianni,2013
Problem Based Learning To Enhance Students’ Critical Thinking Skills And Concept Comprehension In
Pollution Concept
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
4.7 Blueprint of critical thinking test……….. 4.8 Improvement of students’ critical thinking skills in each indicator………
4.9 Questionnaire of students’ response through problem based learning……… 4.10 Result of students’ response in each indicator………
4.11 Interview result………..
52 53
FIGURE LIST
2.1 Aspect of Problem Based Learning……… 2.2 Old and new revision of Bloom’s taxonomy……….. 2.3 Global warming……….. 2.4 Acid rain……….
2.5 Water pollution………...
3.1 Research Scheme ………... 4.1 Implementation percentages of teacher activities………... 4.2 Percentage of students’ activity during Problem Based Learning……….. 4.3 Pretest and Posttest comparison in concept comprehension test……… 4.4 Pretest and posttest result of students’ concept comprehension in each subtopic…….. 4.5 Result of students pretest and posttest in each cognitive domain………... 4.6 Normalized gain index of students’ concept comprehension in each cognitive
domain………...
4.7 Result of pretest and posttest critical thinking skills……….. 4.8 N-gain of critical thinking skill in each indicator………...
4.9 Result percentage of students’ response through Problem Based Learning…………...
Mitha Hardianni,2013
Problem Based Learning To Enhance Students’ Critical Thinking Skills And Concept Comprehension In
Pollution Concept
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu APPENDIX LIST
A.1. Lesson Plan………...
A.2. Worksheet……….. A.3. Reflection sheet………. B.1 Concept comprehension test………..……... B.2 Recap instrument analysis of concept comprehension test………... B.2.1 Instrument analysis of concept comprehension test……….………...
B.3 Critical thinking skills test……….
B.4 Recap instrument analysis of critical thinking test………
B.4.1 Instrument analysis of critical thinking test……….
C.1 Blueprint of concept comprehension……….
C.2 Concept comprehension test……….. C3. Blueprint of critical thinking test………..
C.4 Critical thinking test………..
C.5 Observation sheet of teacher’s activity……….
C.6 Observation sheet of student’s activity……….
C.7 Questionnaire of students’ response ……….…
C.8 Interview sheet………..
D.1 Observation analysis of teacher’s activities ……….
D.2 Observation analysis of students’ activities ……….…….
D.3 Normalized gain analysis of concept comprehension………... D.4 Data distribution of concept comprehension pretest………. D.5 Data distribution of concept comprehension posttest………... D.6 Normalized gain analysis of critical thinking………... D.7 Data distribution of critical thinking pretest……….
D.8 Data distribution of critical thinking posttest………
D.9 Questionnaire analysis………...
E.1 Permission letter of instrument trial………...……….
E.2 Implementation research letter ………...………... E.3 Judgment validation sheet ……….
E.1 Picture of research implementation………
E.2 Biography ………..…………
140 141
Mitha Hardianni,2013
Problem Based Learning To Enhance Students’ Critical Thinking Skills And Concept Comprehension In Pollution Concept
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION A. Background
Nowadays, traditional or conventional learning is more focus on students’ academic achievement. Parents also more concern to their children test score rather than the students self concept and learning strategies. Also today traditional learning more focuses on memorizing information, conducting the experiment and performing mathematical calculation to solve problem in book. Knowledge is not attained but constructed (von Glasersfeld, 1989 in Kim, 2005). Based on that statement it can be evaluated whether current traditional teaching learning can make students construct their own knowledge or not. Based on study that carried by Colburn(2000 in Daniel, O.I and Bimbola, Oludipe, 2010 ) in lecture hall setting, it is found that only 20% of students still remember what lecturer discuss because they were too busy taking notes and internalize the information also, when the lecture conducted after eight minutes, only 15% of students who pay attention. This kind of traditional teaching and learning can arise some question about the ability of students to perform their creative and critical thinking to solve some problem that occur on their environment. Educators should invite learners to explore the world
experiences, encourage them to have critical thinking and challenges them to solve the problem not only focus on academic achievement score.
approach to another approach that facilitate students to foster their critical thinking skills and ability to solve problem.
As human there are many problems that face in everyday situation. These problems arise from process of interaction both of our physical and the environment and our problem will be more complex by day. So, as human we have to be ready to face problem and issues in our life. Every people should have right knowledge, skill and competencies that required handle and solve problem. Based on that fact, we can conclude that education definitely has an obligation and function to equip the learners to deal with problems and urgent matter to fulfill their own life. That is why
it becomes challenge for educators to build up students’ ability and
capability to deal with fast dynamic world and their unknown future. Education can use as tools to perfectly provide critical thinking and skills that will be needed students to face problem and issues in their environment. Adeyemi (2012) stated that person who tries to solve problem without having appropriate knowledge, skills and abilities often tend not only to behave irresponsibly and erratically, but also in ways that damage their own future and the human condition in the society.
Problem Based Learning is interactive learning process that using real life problem. Torp and Sage (2002, in Hmelo-silver,2004) described
problem Based Learning as focused, experiential learning organized around the investigation and resolution of messy real world problems (in Sahin & Yorek, 2009). In this learning process students assume as problem solver who investigate problem and find out information that be needed to solve the problem, so students becoming self directed learners. Through Problem Based Learning approach student involve in collaborative groups to identify what they need to learn to solve problem which made them engage in self directed learning then apply their knowledge to solve the problem.
Mitha Hardianni,2013
Problem Based Learning To Enhance Students’ Critical Thinking Skills And Concept Comprehension In Pollution Concept
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
include in higher order thinking. Critical thinking becomes so important because critical thinking plays role in science education as science
fundamental reasoning. Scriven and Paul define “the intellectually disciplined process of actively and skillfully conceptualizing, applying, analyzing, synthesizing, and/or evaluating information gathered from, or generated by observation, experience, reflection, reasoning, or
communication as a guide to belief and action’’ (in Ebiendele, 2012). Hence, it means that critical thinking has an importance role in science learning.
Based on problem that explain above researcher interested to take research on how learning process using Problem Based Learning approach
toward students’ critical thinking skills and concept comprehension.
B. Research Problem
Research problem for this research is “How is the enhancement of
students’ critical thinking skills and concept comprehension in pollution concept trough Problem Based Learning approach?” To make it clearly the problem above elaborate into following questions:
1. How is the enhancement of students’ critical thinking skills in pollution concept through Problem Based Learning approach?
2. How is the enhancement of students’ concept comprehension in pollution concept through Problem Based Learning approach?
3. How is the students’ response toward implementation of Problem Based Learning approach?
C. Research Focus
Authors limit the issues in this research in order to focus research as follows:
1. Learning process that will be conducted is using Problem Based
2. Students’ critical thinking skills based on indicator of critical thinking
that state by Ennis are basic clarification, decision, inference, advanced
clarification and supposition and integration. To analyze the absence of
students’ critical thinking will be test by essay test item.
3. Students’ comprehension will be test by multiple choice tests which
are made based on Bloom’s taxonomy cognitive aspects such as remembering (C1), understanding (C2), analyzing (C4) and evaluating (C5).
D. Research Objectives
The main purpose of this paper is:
1. To investigate the enhancement of students’ critical thinking in pollution concept through problem based learning approach.
2. To investigate the enhancement of students’ concept comprehension in pollution concept through problem based learning approach.
3. To investigate students response toward implementation of Problem Based Learning approach.
E. Significance of Research
1. For teacher, this research can be used as inspiration to develop learning
process in classroom.
2. For students, this research is expected to make students become active
learner and enhance students’ critical thinking skills
Mitha Hardianni,2013
Problem Based Learning To Enhance Students’ Critical Thinking Skills And Concept Comprehension In
Pollution Concept
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A. Population and Sample
Populations in this research are grade 10 high school students in one of international school in Tanggerang. Number populations in this school are seven classes with 278 students. The sampling method that be used in this study is purposive sampling method. Purposive sampling method is used because researcher
wants to know improvement of lower achiever students‟ critical thinking skill and
concept comprehension. Sample of this research are 18 students in 10B class.
B. Research Method
In this research students‟ critical thinking skill and concept comprehension
will be dependent variable while the independent variable is Problem Based learning. The method that be used in this study is quantitative method. Quantitative used to collect and analyze numerical data obtained from formal instruments. This quantitative method is using type of descriptive. Descriptive is used to describe of identified variable or phenomena (Arikunto, 2002).
C. Research design
Table 3.1 One group pre test and post test design
Pre test Treatment Post test
O1 X O2
O1 = Pre test of students concept comprehension and critical thinking skill.
X = Problem Based Learning model
O2 = Post test of students concept comprehension and critical thinking skill.
Steps to implement the research first time students be given pre test (O1) to know students‟ prior concept comprehension and critical thinking skill then gave treatment(X) which used Problem Based Learning approach and the last gave post test (O2) to students. Thus, it can be obtained the differences between pretest and
posttest which assumed as the effect of treatment.
D. Operational Definition
To avoid misconception in this research, so there is explanation about the
terms that are used in this research, as follow: 1. Problem Based Learning
Mitha Hardianni,2013
Problem Based Learning To Enhance Students’ Critical Thinking Skills And Concept Comprehension In
Pollution Concept
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
2. Concept comprehension
Concept comprehension in this research based on cognitive domain of Bloom‟s
taxonomy new revision. The aspects that use in this research are remembering aspect (C1), understanding aspect (C2), analyzing aspect (C4) and evaluating aspect (C5).
3. Critical thinking skill
According to Ennis critical thinking is process to make decision based on what believe and what to do. There are six aspects that include in critical thinking skills but in this research just take five aspect of critical thinking skills as indicator because the sixth aspect only asses students behavior. So to make test
item for students‟ critical thinking researcher use five indicators such as
clarification, decision, inference, advanced clarification, supposition and
integration. The result of students‟ test will be scored by scoring guide.
E. Research Instrument
To collect the data there are some instrument that be needed: 1. Students‟ concept comprehension test
To measure Students‟ concept comprehension test item that be used is multiple choice. Researcher made 34 multiple choice test items then would be
eliminated based on analysis result of trial instrument. Total question number that be used for pre test and post test are 15 questions of multiple choice which each multiple-choice item is given a numeric value of one for correct answer and zero for incorrect. Blue print for this multiple choice is made based on
2. Students‟ critical thinking skills test
To measure students‟ critical thinking test item that be used is essay.
Researcher choose essay test item because more efficient to asses critical thinking. The number of question that be used are five questions which used range score from three until zero. Critical thinking skills indicator is used to make blueprint of critical thinking skills test as shown on appendix C.3.
3. Observation sheet
There are two kinds of observation sheets that will be used in this research such as:
a. Teacher‟s observation sheet
This observation sheet is advantageous to investigate whether process of Problem Based Learning run well or not. This observation sheet can be seen on appendix C.5
b. Students‟ observation sheet
This observation sheet is advantageous to investigate students‟ activities during learning process is appropriate or not with problem Based Learning. This observation sheet can be seen on appendix C.6
4. Questionnaire of students‟ response
This questionnaire is used to know students‟ response toward Problem based Learning process. Students must fulfil the questionnaire by give mark on scale
number which presents their agreement for option “YES” and disagreement for option “NO”. The interview guideline used to know teacher point of view as additional information about learning process through Problem Based Learning
Mitha Hardianni,2013
Problem Based Learning To Enhance Students’ Critical Thinking Skills And Concept Comprehension In
Pollution Concept
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
5. Teacher interview
The interview carried with biology teachers who teach in class that were used
as research subjects. This interview is intended to find out teachers' opinions toward Problem Based learning.
F. Validation of Instruments
To validate the instrument in this research, there are some steps were done as follow:
1. Instruments judgment
After made the instrument, the instruments were reviewed and judged by the experts. The experts are lecturer of biology and pedagogy who expert in assessment. Based on judgment researcher got some suggestions and revision for instrument.
2. Instruments trial
Before the instruments are used for research implementation, the instruments were tested to students that already learn about pollution. In this case researcher chose grade XI as trial instruments participants.
3. Instruments Analysis
The instruments that are used in this research were judge and trial to other students. The result from instrument trial analyzed to get its validity, Reliability, difficulty level and discriminating power.
a. Validity
Based on Scarvia B. Anderson and friends “a test is valid if it measures what it
researcher makes” (Fraenkel et al., 2012:147). To measure the validity of instruments researcher used software. Software calculation actually uses
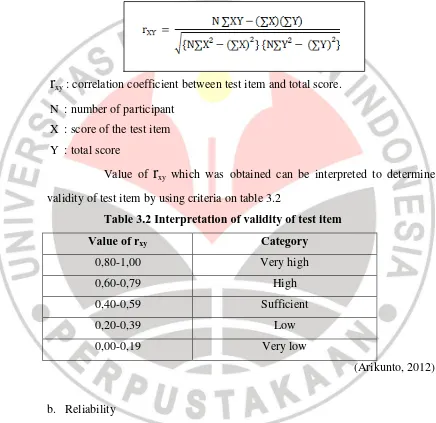
product moment correlation formula as follow (Arikunto, 2012:87):
rxy
: correlation coefficient between test item and total score.N : number of participant X : score of the test item Y : total score
Value of
rxy
which was obtained can be interpreted to determinevalidity of test item by using criteria on table 3.2
Table 3.2 Interpretation of validity of test item
Value of rxy Category
0,80-1,00 Very high
0,60-0,79 High
0,40-0,59 Sufficient
0,20-0,39 Low
0,00-0,19 Very low
(Arikunto, 2012)
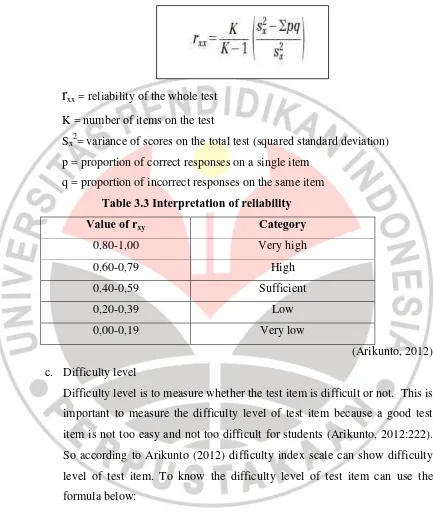
b. Reliability
Reliability is the provision of a test when retested to the same subject. To know this provision essentially can be seen from alignment of the result (Arikunto, 2012:104). To measure test item reliability researcher used
Mitha Hardianni,2013
Problem Based Learning To Enhance Students’ Critical Thinking Skills And Concept Comprehension In
Pollution Concept
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
rxx
= reliability of the whole testK = number of items on the test
Sx2= variance of scores on the total test (squared standard deviation)
p = proportion of correct responses on a single item q = proportion of incorrect responses on the same item
Table 3.3 Interpretation of reliability
Value of rxy Category
0,80-1,00 Very high
0,60-0,79 High
0,40-0,59 Sufficient
0,20-0,39 Low
0,00-0,19 Very low
(Arikunto, 2012) c. Difficulty level
P = difficulty level
B = amount of student who answer question with the right answer JS = total amount of students who undertakes the test
d. Discriminating power
Discriminating power is ability to distinguish between lower and higher achiever from the result of test item (Arikunto, 2012:226). The formula that can be used as follows:
D = discriminating power JA = amount of high achiever JB = amount of low achiever
BA= amount of high achiever who answers question with the right answer BB= amount of low achiever who answers question with the right answer PA = proportion of high achiever who answers question with the right answer
PB = proportion of low achiever who answers question with the right answer Table 3.4 Interpretation of discriminating power
Discriminating power interval Category
Negative Test item is not appropriate
0.00 < x ≤ 0.20 Poor
0.21 < x ≤ 0.40 Sufficient
0.41 < x ≤ 0.70 Good
0.71 < x ≤ 1.00 Excellent
(Arikunto, 2012)
P =
Mitha Hardianni,2013
Problem Based Learning To Enhance Students’ Critical Thinking Skills And Concept Comprehension In
Pollution Concept
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu G. Collecting Data Technique
To collect data some steps done the steps are including gave pre test first
before implementation of Problem Based Learning then analyze the result of pretest, gave treatment by using Problem Based Learning during that process data were taken based on observation sheet, gave post test then analyze the result of posttest, gave questionnaire to students and the last had interview with Biology teacher.
H. Data Analysis Techniques
1. Scoring
Gave score to students‟ concept comprehension and critical thinking skill test. For concept comprehension test gave score 1 for right answer and 0 for false answer while for critical thinking skill test used scoring guide. The formula used to convert score into percentage as follow:
After percentage of students‟ score were obtained, it can be classified based on score percentage category according to Arikunto as follow:
Table 3.5 Category of student score
Percentage (%) Category
76-100 Good
56-75 Sufficient
40-55 Poor
0-39 Very poor
(Source: Arikunto, 2012)
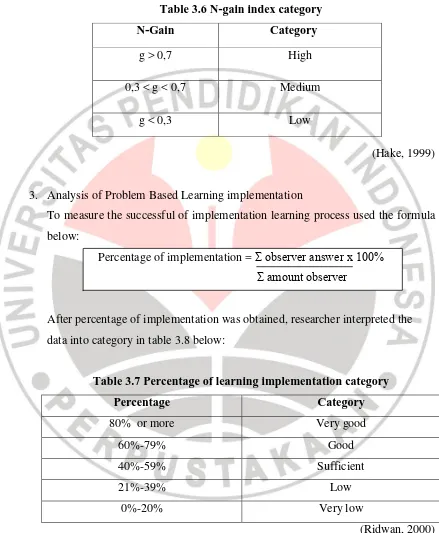
2. Gain and Normalized Gain
To find out the difference between pretest and posttest score can use gain formula. The formula which is used to calculate the gain value is:
(Hake, 1998) With:
= gain
= post test score
= pretest score
To see the improvement of students‟ concept comprehension and critical
thinking skill used normalized gain as it shown as formula below:
(Hake, 1999) With:
< > = normalized gain
= posttest score
= pretest score
Mitha Hardianni,2013
Problem Based Learning To Enhance Students’ Critical Thinking Skills And Concept Comprehension In
Pollution Concept
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu Table 3.6 N-gain index category
(Hake, 1999)
3. Analysis of Problem Based Learning implementation
To measure the successful of implementation learning process used the formula below:
Percentage of implementation = Ʃ observer answer x 100% Ʃ amount observer
After percentage of implementation was obtained, researcher interpreted the data into category in table 3.8 below:
Table 3.7 Percentage of learning implementation category
Percentage Category
80% or more Very good
60%-79% Good
40%-59% Sufficient
21%-39% Low
0%-20% Very low
(Ridwan, 2000)
N-Gain Category
g > 0,7 High
0,3 < g < 0,7 Medium
4. Students response analysis
To analyzed students response in learning process through Problem based
Learning used formula as following:
Percentage of students‟ response = Ʃ students who answer „yes‟ x 100% Ʃ amount students
5. Interview analysis
Analyze interview result of teacher‟s opinion toward Problem Based Learning
I. The Result of Trial Test Instrument
The instruments were tested before it is used in this research. It is tested to grade XI of senior high school at one international school in Tanggerang who already learned the same topic. There are two kinds of test that are used those are multiple choice containing 34 items and essay containing 18 items.
From trial instrument result, researcher analyzed the result to get validity, reliability, difficulty level and discriminating power. For concept comprehension test item were analyzed by using ANATES pilihan ganda Version 4.1.0, meanwhile critical thinking test were analyzed by using ANATES uraian Version 4.0.7. The recap result of validity, discriminating power and difficulty level of concept
comprehension can be seen on table below.
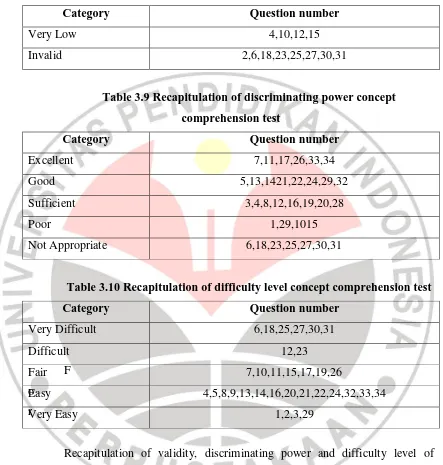
Table 3.8 Recapitulation of validity concept comprehension test
Category Question number
High 5,7,11,17,22,24,26,32,33,34
Sufficient 13,20,29
Mitha Hardianni,2013
Problem Based Learning To Enhance Students’ Critical Thinking Skills And Concept Comprehension In
Pollution Concept
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
Category Question number
Very Low 4,10,12,15
Invalid 2,6,18,23,25,27,30,31
Table 3.9 Recapitulation of discriminating power concept comprehension test
Category Question number
Excellent 7,11,17,26,33,34
Good 5,13,1421,22,24,29,32
Sufficient 3,4,8,12,16,19,20,28
Poor 1,29,1015
Not Appropriate 6,18,23,25,27,30,31
Table 3.10 Recapitulation of difficulty level concept comprehension test
F o
r
Recapitulation of validity, discriminating power and difficulty level of critical thinking skills illustrated in the following table below.
Table 3.11 Recapitulation of validity critical thinking skills test
Category Question number
High 2a,2b,6a,6b
Category Question number
Very Difficult 6,18,25,27,30,31
Difficult 12,23
Fair 7,10,11,15,17,19,26
Easy 4,5,8,9,13,14,16,20,21,22,24,32,33,34
Very Easy 1,2,3,29
Category Question number
Sufficient 2d,3,4a,5b,7b,7c
Low 2c,4b,7a
Very Low 1a,1b,1c,5a
Invalid -
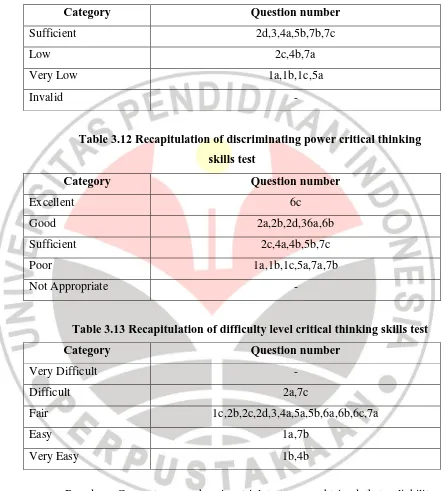
Table 3.12 Recapitulation of discriminating power critical thinking skills test
Category Question number
Excellent 6c
Good 2a,2b,2d,36a,6b
Sufficient 2c,4a,4b,5b,7c
Poor 1a,1b,1c,5a,7a,7b
Not Appropriate -
Table 3.13 Recapitulation of difficulty level critical thinking skills test
Based on Concept comprehension trial test were obtained that reliability
value of instruments is as much as 0.81 which include as very high category. Meanwhile in critical thinking skills test reliability value is 0.75 which include as
high category. Thus, it showed that those test are qualified to be used.
Category Question number
Very Difficult -
Difficult 2a,7c
Fair 1c,2b,2c,2d,3,4a,5a,5b,6a,6b,6c,7a
Easy 1a,7b
Very Easy 1b,4b
Mitha Hardianni,2013
Problem Based Learning To Enhance Students’ Critical Thinking Skills And Concept Comprehension In
Pollution Concept
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu J. Research Procedure
There are many steps that are done during this research which classified into
three stages of research procedure. Three stages are preparation stage, implementation stage and final stage which are explained in detail below:
1. Preparation stage
In preparation stage first researcher did some literature review from both digital media and printed media. after got an idea about research topic researcher made research proposal which already presented in proposal seminar then researcher done some revision which given by judges. Based on consultation with supervisor and teacher in the school, researcher made research instrument and designed lesson plan for implementation Problem Based Learning. Instruments and lesson plan that made were judged by expert in this research expert were lecturer and teacher. Researcher also revised instruments based on judgment after revision the instruments tried to upper grade students then analyzed the result to find validity, reliability, discriminating power and difficulty level test item that qualified for students.
2. Implementation stage
In implementation stage first gave pretest to students before implementation of Problem Based Learning then implemented Problem Based Learning in pollution
concept. After implementation students were given posttest and questionnaire.
The last interviewed biology teacher to know teacher‟s response about Problem
Based Learning model.
3. Final stage
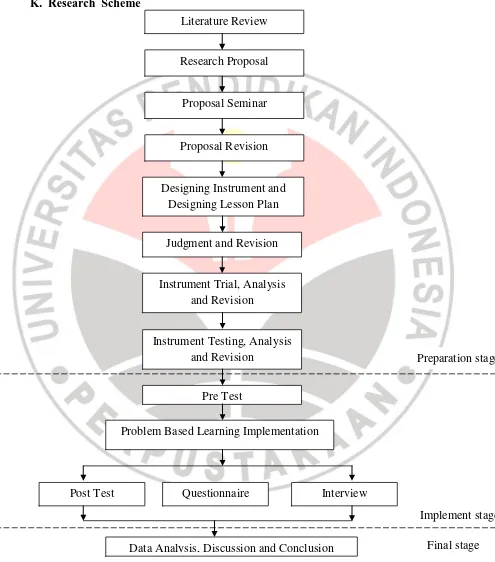
K. Research Scheme
Literature Review
Research Proposal
Proposal Seminar
Proposal Revision
Designing Instrument and Designing Lesson Plan
Judgment and Revision
Instrument Trial, Analysis and Revision
Instrument Testing, Analysis
and Revision Preparation stage
Pre Test
Problem Based Learning Implementation
Post Test Questionnaire Interview
Data Analysis, Discussion and Conclusion
Implement stage
Mitha Hardianni,2013
Problem Based Learning To Enhance Students’ Critical Thinking Skills And Concept Comprehension In
Pollution Concept
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu CHAPTER V
CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATION
A. Conclusion
Based on research result of implementation Problem Based Learning in pollution concept can be concluded as follow:
1. After implementation of Problem based Learning, result of students test show that there is enhancement of students’ critical thinking skill with value 0.33 which include into medium category. Enhancement of critical thinking skill also can be identified in each indicator of critical thinking skill. Advance clarification indicator obtained the highest enhancement among the other indicators with normalized gain value is 0.53 which include in medium category.
2. Problem Based Learning can enhance students concept comprehension with average normalized gain value 0.42 which is include in medium category. From students concept comprehension result also can be analyzed enhancement in each subtopic and cognitive domain. In subtopic, the subtopic that most reached by students is soil pollution with normalized gain index value is 0.75 which include in high category. While, the highest enhancement in cognitive domain are understanding aspect (C2) and evaluating aspect (C5) with normalized gain index value is 0.57 which include in medium category.
B. Recommendation
There are some suggestion can be considered related with implementation of
Problem based Learning toward students’ concept comprehension and critical thinking skill as follows:
1. For further researcher it is suggested to do literature review more deeply about Problem Based Learning and critical thinking
2. further researcher who want to implement Problem Based Learning in class should make sure that problem given are easily understood and exist around students
3. For further researcher is recommended to add another class as control group so it can measure more clearly the role and influence of Problem Based Learning in improving students concept comprehension and critical thinking skill
4. Further researcher also need to look another kind of critical thinking test which appropriate with students
Mitha Hardianni,2013
Problem Based Learning To Enhance Students’ Critical Thinking Skills And Concept Comprehension In
Pollution Concept
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu REFERENCES
Adeyemi, S. (2012). Developing Critical Thinking Skills in Students: A Mandate for Higher Education in Nigeria. European Journal of Educational Research. 1, (2), 155-161.
Akçay, B. (2009). “Problem-based learning in science education”. Journal of Turkish Science Education. 6, (1)
Akinoǧlu, O & Tandoǧan, R.Ö. (2007). The effect of problem based learning in science
education on students’ academic achievement, attitude and concept learning. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science & Technology Education. 3, (1), 71-81.
Andi (2012). [Online]. Available at:
http;///andinurdiansah.blogspot.com/2012/05/pemahaman-konsep.html. [May, 12th 2013]
Angeli, C. (2002). Teacher’s Practical theories for The Design and Implementation of Problem-Based Learning. Sci. Educ.Int
Arikunto, S. (2010). Prosedur Penelitian Suatu Pendekatan Praktik. Jakarta: Rineka Cipta.
Arikunto, S. (2012). Dasar-Dasar Evaluasi Pendidikan. Jakarta: Bumi Aksara
Bailin, S. (2002). Critical Thinking and Science Education. Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publisher.
Barrett, T. (2005). Understanding Problem-Based Learning. [Online]. Available at: http://www.nuigalway.ie/celt/pblbook/ [March, 19th, 2013]
Binulal. (2013). Effects of Select Instructional Practices on Improving The Achievement of Low Achievers. International Journal of Scientific and Research publications.
CatN.(2003). Water Pollution Guide. [online]. Available at: http://jj49z6.vc.c3.catn.com/ [March 19th, 2013]
Cheong, F. (2008). Using a Problem Based Laerning approach to Teach an Intellegent Systems Course. Journal of Information Technology Education. 7.
Cinar, D. and Bayraktar, S. (2006). The Effect of The Problem Based Learning Approach on Higher Order Thinking Skills in Elementary Science Education. Turkey: Selcuk University
Daniel, O.I and Bimbola, O.(2010). Effect of constructivist-based teaching strategy on academic performance of students in integrated science at the junior secondary school level. Educational Research and Review. 5,(7).
Dogru, M & kalender, S. (2007). Applying the Subject “Cell” Through Constructivist
Approach during Science Lessons and the Teacher’s View. Journal of environmental & science education. 2, (1), 3-13.
Duron, R. et al. (2006). Critical Thinking Framework for Any Discipline. [online]. Available at: http://www.isetl.org/ijtlhe . [March, 19th, 2013]
Ennis, R.H. (2011). Nature of Critical Thinking: An Outline of Critical Thinking Disposition and Abilities. University of Illinois.
Ennis, R.H. (2011). The Nature of Critical Thinking: An Outline of Critical Thinking
Dispositions and Abilities.[Online]. Available at:
http://faculty.education.illinois.edu/rhennis/documents/TheNatureofCriticalThinkin g_51711_000.pdf [March, 7th 2013]
Farid, Sajid. et al (2012) Water pollution: Major issue in urban areas. [Online]. Available at: http://www.academicjournals.org/IJWREE [March, 3rd 2013]
Fraenkel, J.R. et al (2011) How to Design and Evaluate Research in Education. San Francisco:McGraw-Hill
Fung, et al. (2009). Lower secondary Science Matters. Singapore: Marshall Cavendish Education.
Gijbels, D and Loyens, S. (2008). Understanding The Effect of Constructivist Learning Enviroment: Introducing a Multi-Diractional Approach. [Online]. Available at: Springerlink.com [March, 3rd 2013]
Harrison, Bob. (2007). What is Problem Based Learning?.[Online]. Available at: http://www.siera-training.com. [February, 21st 2013].
Mitha Hardianni,2013
Problem Based Learning To Enhance Students’ Critical Thinking Skills And Concept Comprehension In
Pollution Concept
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
Khalid, Abida & Azeem, M. (2012). Constructivist Vs Traditional: Effective Instructional Approach in Teacher Education. International Journal of Humanities and Social Science.. 2, (5)
Kim, J.S. (2005). The Effects of a Constructivist Teaching Approach on Student Academic Achievement, Self-concept, and Learning Strategies. Asian Pacific Education Review. 6, (17)
King, FJ. et al. (2000). Higher Order Thinking Skills. Center for Advancement Learning and Assessment.
Lai, Emily R. (2011). Critical Thinking: A Literature Review. [Online]. Available at: http://www.pearsonassessments.com/research. [February 27th, 2013]
Lai, Emily. (2011). Critical Thinking: A Literature review. Pearson
Liuda. (2002). The Educating of Students’ Decision Making Competence in The Problem Based Learning Context: Facing The Perspective of The Contemporary Knowledge
Society. [online]. Available at:
http://www.leeds.ac.uk/educol/documents/00003289.htm. [July, 17th 2013]
Masek, Alias & Yamin, Sulaiman. (2011). The effect of problem based learning on critical thinking ability: a theoretical and empirical review. International Review of Social Sciences and Humanities. 2, (1)
Nandal, S. (2011) Effectiveness Analysis of Problem Based learning VS Traditional Lecture Method. Journal of Applied Management & Computer Science.
Purvis, C. (2009). Factors That Influence The Development Of Critical Thinking Skills In Associate Degree Nursing Students. Thesis of University of Georgia: unpublished
Richardson, Virginia. (2003). Constructivist Pedagogy. Teacher Collage Record. 105, (9)
Ridwan, Sa’ada. (2000). Identifikasi dan Penanggulangan Kesulitan belajar Siswa dalam
Mempelajari Konsep Cahaya di Kelas II G SLTPN 12 Bandung. Postgraduate Thesis, UPI Bandung: unpublished
Shashank Nakate.(2011). Types of Air Pollution. [Online]. Available at: http://www.buzzle.com/articles/types-of-air-pollution.html. [March 19th , 2013]
Sugiyono. (2008). Metode Penelitian Kuantitatif, Kualitatif dan R&D. CV.ALFABETA
Sungur, S., Tekkaya, C., & Geban, Ö. (2006). Improving Achievement through Problem-Based Learning. Educational Research. 40, (4)
Swan, Karen. 2005. A Constructivist Model for Thinking about Learning Online. Research Center for Educational Technology.
Ujwal Deshmukh.(2012). Soil Pollution Causes and Effects. [Online]. Available at: http://www.buzzle.com/articles/soil-pollution-causes-and-effects.html [March 19, 2013]
Volkwyn, Roy. (2006). Pollution. [Online]. Available at:
www.bcb.uwc.ac.za/sa_ed/grade10/ecology/conservation/poll.htm#intro [March 19, 2013]