SKILL AND CONCEPT COMPREHENSION IN LEARNING ECOSYSTEM FOR SECONDARY
Research Paper
Submitted as partial requirement to obtain degree of Sarjana Pendidikan in International Program
on Science Education study program
Arranged by:
Frilia Rizky Amalia 1002530
INTERNATIONAL PROGRAM ON SCIENCE EDUCATION FACULTY OF MATHEMATICS AND SCIENCE EDUCATION
EFFECT OF PROBLEM-BASED LEARNING ON STUDENTS’ PROBLEM SOLVING SKILL AND CONCEPT COMPREHENSION IN LEARNING ECOSYSTEM FOR
SECONDARY
Oleh
Frilia Rizky Amalia
Sebuah skripsi yang diajukan untuk memenuhi salah satu syarat memperoleh gelar Sarjana pada Fakultas Pendidikan Matematika dan Ilmu Pengetahuan Alam
© Frilia Rizky Amalia 2014 Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia
Juli 2014
Hak Cipta dilindungi undang-undang.
Frilia Rizky Amalia, 2014
Effect Of Problem-Based Learning On Students’ Problem Solving Skill And Concept Comprehension In Learning
Ecosystem For Secondary
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
EFFECT OF PROBLEM-BASED LEARNING ON
STUDENTS’ PROBLEM SOLVING SKILL AND CONCEPT COMPREHENSION IN LEARNING ECOSYSTEM FOR SECONDARY
Frilia Rizky Amalia
Indonesia University of Education International Program on Science Education
ABSTRACT
Aims of this study to examine effect of problem-based learning toward students’ problem solving skill and concept comprehension in learning ecosystem in one of private school in West Bandung. Data is gained by concept comprehension test, problem solving test, observation sheet and questioner. The observation sheet is adapted from Gok. The observation sheet consist of indicators of problem solving skill; identifying the fundamental principle(s), solving and checking. The result of data analysis shows that there are improvements in concept comprehension in experimental class with normalized gain 0.5 which categorized into medium improvement. In other hand in control class is obtained -1.1. For problem solving skill in experimental class is obtained 0.31 which is categorized into medium improvement, while in control class is obtained 0.14 which is categorized into low improvement. From observation sheet can be described that problem solving skill profile in experimental class is higher than control class. Mostly students gave positive attitude in learning through problem-based learning.
Frilia Rizky Amalia, 2014
Effect Of Problem-Based Learning On Students’ Problem Solving Skill And Concept Comprehension In Learning
Ecosystem For Secondary
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
EFFECT OF PROBLEM-BASED LEARNING ON
STUDENTS’ PROBLEM SOLVING SKILL AND CONCEPT COMPREHENSION IN
LEARNING ECOSYSTEM FOR SECONDARY
Frilia Rizky Amalia Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia International Program on Science Education
ABSTRAK
Tujuan dari penelitian ini untuk menguji pengaruh pembelajaran berbasis masalah terhadap keterampilan memecahkan masalah siswadan pemahaman konsep dalam pembelajaran ekosistem di salah satu sekolah swasta di Bandung Barat. Data diperoleh dengan tes pemahaman konsep, tes pemecahan masalah , lembar observasi dan skala bertingkat. Lembar observasi diadaptasi dari Gok. Lembar observasi terdiri dari indikator keterampilan pemecahan masalah; mengidentifikasi prinsip dasar, pemecahan dan mengevaluasi. Hasil analisis data menunjukkan bahwa ada perbaikan dalam pemahaman konsep di kelas eksperimen dengan normalisasi gain 0,5 yang dikategorikan ke dalam perbaikan menengah. Di sisi lain di kelas kontrol diperoleh -1.1. Untuk keterampilan pemecahan masalah di kelas eksperimen diperoleh 0.31 yang dikategorikan ke dalam perbaikan menengah, sementara di kelas kontrol diperoleh 0.14 yang dikategorikan ke dalam perbaikan rendah. Dari lembar observasi dapat digambarkan bahwa profil keterampilan pemecahan masalah di kelas eksperimen lebih tinggi dari kelas kontrol. Sebagian besar siswa memberikan sikap positif dalam belajar melalui pembelajaran berbasis masalah.
Frilia Rizky Amalia, 2014
Effect Of Problem-Based Learning On Students’ Problem Solving Skill And Concept Comprehension In Learning Ecosystem For Secondary
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
CONTENTS
CHAPTER II LITERATURE REVIEW
A. Problem-Based Learning………...
B. Problem Solving Skill ………..
C. Concept Comprehension………...
D. Ecosystem ………
E. Relevant Research ………
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
viii
Frilia Rizky Amalia, 2014
Effect Of Problem-Based Learning On Students’ Problem Solving Skill And Concept Comprehension In Learning Ecosystem For Secondary
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
G. Data Processing ...
H. Research Procedure ...
CHAPTER IV RESULT AND DISCUSSION
A. Results of Concept Comprehension
B. Discussions of Concept Comprehension
C. Results of Problem Solving Skill
D. Discussions of Problem Solving Skill ...
CHAPTER V CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS
A. Conclusions…….………..……….……….
B. Recommendation ………...……….……...
REFERENCES...………..………....
APENDICES...………..……….....
22
26
27
30
31
35
41
41
43
Frilia Rizky Amalia, 2014
Effect Of Problem-Based Learning On Students’ Problem Solving Skill And Concept Comprehension In Learning Ecosystem For Secondary
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION A. Background
Education is a fundamental aspect of life toward national development of a
country. In its implementation, education at schools is involving teachers as educators
and students as learners, realized by the interaction of teaching and learning or the
learning process. In this context, teachers are required to establish a systematic planning
of learning activities based on the curriculum. On its implementation in the field, there is
still a learning process that implements many conventional methods. By this method
students only listen to the material presented by the teacher, students are passive.
Meanwhile, the current curriculum requires that students take an active role in building
the self-concept. Krajcik (in Brown, Lawless and Boyer, 2013) stated that within a
classroom, scientific inquiry involves student-centered projects that actively engage
students observing, questioning, information gathering, data analysis, explanation and
communication of the results. According to the curriculum that centered on student
learning, teacher as motivator and facilitator in it so that the classroom atmosphere come
alive.
In the 21st century, competition in many areas of life, including education,
especially science education is very rigorous. We are faced with the demands of the
importance of quality human resources that are able to compete. Qualified human
resources, which are produced by a qualified education, can be a main strength to
overcome the problems encountered. One of the ways to be taken is through improving
the quality of education. There are five preliminary definition of 21st century skills;
adaptability, complex communication/social skills, non-routine problem-solving,
self-management or self-development, systems thinking (National Research Education, 2010).
Levy and Murnane (in National Research Education, 2010) stated that one of them is
non-routine problem solving, a problem solver should uses expert thinking in recognize
patterns and narrow the information to reach a diagnosis of the problem.
Now globalization has been developed, students who are able to deal to
Frilia Rizky Amalia, 2014
Effect Of Problem-Based Learning On Students’ Problem Solving Skill And Concept Comprehension In Learning Ecosystem For Secondary
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
solve problems as well. Therefore education system must be able to make condition how
students can become good problem solvers. Education system must be able to provide
facilities for students to develop themselves, especially to solve problem. So, it is not
enough that students can only work on the problems that exist in the textbooks.
Many theories and educational research experts suggest that learning will be
successful when students are actively participating in the learning process. Student Active
Learning Method (CBSA) is coming as a new method. One approach that accommodates
learning CBSA is Problem Based Learning (PBL).
Problem-based learning (PBL) intends to provide the space for free thinking to the
researcher interest to take research about how problem-based learning can improve
problem solving skill in cases environment.
B. Research Problems
The research problem of this research is “How is the effect of problem-based
learning toward students’ problem solving skill and students’ understanding toward
ecosystem?”
From the research problem above, researcher attempt following questions:
1. How is the effect of problem-based learning on students’ problem solving
3
Frilia Rizky Amalia, 2014
Effect Of Problem-Based Learning On Students’ Problem Solving Skill And Concept Comprehension In Learning Ecosystem For Secondary
2. How is the effect of problem-based learning on students’ concept
comprehension of ecosystem?
3. How is students’ impression in learning ecosystem by problem-based
learning?
C. Limitation of the Problem
The problems that are going to be researched is limited in some aspects as follow:
1. Problem-based learning syntax that presented in this learning is according to
Arends (2008).
2. Problem solving skill that will be measured is fundamental principle of problem
solving according to Gok (2010) those are Identifying the Fundamental
principle(s), solving, and checking or reflecting.
3. Concept comprehension that will be measured is cognitive domain based on
Benjamin Bloom Taxonomy of Educational Objectives, for this occasion is
limited in knowledge (C1), comprehension (C2), applying (C3), and analyzing
(C4).
D. Research Objectives
According to problem that formulated in the research problem, the research is
intended to:
1. To analyze students’ problem solving in science learning through implementation of
problem-based learning.
2. To analyze students' understanding of concepts on the topic of ecosystem.
3. To analyze students’ attitude in learning by problem-based learning.
E. The Significant of Research
This research hopefully may give some benefits. Such as:
1. For students
a. Students should be able to relate concepts and knowledge they have gained to
Frilia Rizky Amalia, 2014
Effect Of Problem-Based Learning On Students’ Problem Solving Skill And Concept Comprehension In Learning Ecosystem For Secondary
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
c. Students should be able to build concepts and knowledge through learning
experience with problem-based learning.
2. For Teacher
Teachers should be able to develop creative ideas in science instruction.
3. For Researcher
As a precious experience that can be developed in the future for better science.
4. For next researcher
Frilia Rizky Amalia, 2014
Effect Of Problem-Based Learning On Students’ Problem Solving Skill And Concept Comprehension In Learning Ecosystem For Secondary
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
CHAPTER III METHODOLOGY A. Location and Sample/Population
The population of this research was seventh grade in one of Islamic Bilingual
School in West-Bandung. Researcher conducted in one class that learning the topic with
problem-based learning, as the experiment class. One class as control class, that learns
the topic without problem-based learning as treatment.
B. Research Design
The design for this research that used was two groups pretest-posttest design.
Between the treatment there are pre-test and post test. Firstly, students would be given
pre-test (O1) before treatment to know students’ prior knowledge about the topic and
problem solving skill, then the next step students would be given problem-based learning
model as treatment (X), then after treatment students would be given post-test regarding
to topic and problem solving skill in experimental and control class. Therefore, the
differences between pre-test and post-test assumed as the effect of problem-based
learning.
Table 3.1 Research Design
Group Pre-test Treatment Post-test
Experimental O1 X O2
Control O1 - O2
Description:
O1 : test before treatment
X : treatment (problem-based learning) O2 : test after treatment
Frilia Rizky Amalia, 2014
Effect Of Problem-Based Learning On Students’ Problem Solving Skill And Concept Comprehension In Learning Ecosystem For Secondary
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
C. Research Method
Research method that already used in this research was quasi experimental
method. Since it has not met the requirements of the scientific experiment (Arikunto,
2010). This method was carried out on two class in Secondary school. Firstly, researcher
prepared lesson plan, learning material, problem that would be posed, and instrument of
this research that needed. Then, researcher implements problem-based learning in
experimental class, in other hand control is given lecturing.
D. Operational Definition
In order for getting the expected goals and also to avoid misunderstandings in the
interpretation of existing terms in this study, would require an explanation of some terms,
those are:
1. Problem-based learning is a learning model that begins with a problem and the
teacher as a facilitator. The syntax of problem-based learning by Arends (1997) that
consist of: (1) presenting orientation about problem to students, (2) organize students
to observe, (3) help individual investigation and group, (4) develop and present the
works, and (5) analyze and evaluate the process to overcome the problem. From that
syntax, teacher can measure the quality of problem-based learning.
2. Problem solving is an activity of making a way out so that there is a match between
the expected results. Problem solving involves comparing things, but always intended
to come to a solution. The fundamental principle of problem solving can be as the
assessment, those are: are identifying the fundamental principle(s), solving, and
checking or reflecting. Learning will be conducted and assessed by observation sheet
of problem solving skill that adapted according to Gok (2010) and pre-test and
post-test.
3. How students understand the concepts that have been studied, also classify objects
18
Frilia Rizky Amalia, 2014
Effect Of Problem-Based Learning On Students’ Problem Solving Skill And Concept Comprehension In Learning Ecosystem For Secondary
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
choices and essay. Concept comprehension already conducted by pre-test and
post-test
E. Research Instrument
Table 3.2 Blueprint of Students’ Concept Comprehension (multiple choices)
Indicator C1 C2 C3 C4 Total
Table 3.3 Blueprint of Students’ Impression to Learning by Problem-based Learning
Nu. Indicator Item
1. Students’ response toward problem-based learning 1, 8, 15
2. Students ability to solve problem 2, 12, 14
3. Students’ response toward the topic that learned by problem-based learning
4, 6, 7
4. Students’ concept comprehension 3, 9, 10, 13 5. Indicates students that interest in learning science 5, 11
Table 3.4 Blueprint of Students’ Problem Solving Skill (Essay)
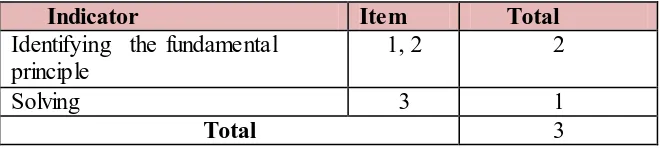
Indicator Item Total
Identifying the fundamental principle
1, 2 2
Solving 3 1
Frilia Rizky Amalia, 2014
Effect Of Problem-Based Learning On Students’ Problem Solving Skill And Concept Comprehension In Learning Ecosystem For Secondary
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
Table 3.5 Blueprint of Observation Sheet Indicator problem solving 2 = if students understand and cannot interpret the problem.
3 = if students understand the problem and can interpret the half problem. 4 = if students understands the problem and can interpret the problem perfectly.
Solving 1. Choosing some solution of these sub-problems and making decision to solve problem.
2 = if students are able to choose some useful sub-problems, carrying out the solution of these sub-problems but poor in making decision to solve problem. 3 = if students are able to choose some useful sub-problems, carrying out the
solution of these sub-problems and making decision to solve problem imperfectly.
4 = if students are able to choose some useful sub-problems, carrying out the solution of these sub-problems and making decision to solve problem.
Checking/reflecting 1. Check the
20
Frilia Rizky Amalia, 2014
Effect Of Problem-Based Learning On Students’ Problem Solving Skill And Concept Comprehension In Learning Ecosystem For Secondary
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu satisfactory
Validation, discriminating power, level of difficulty, reliability using Anates that used
to analyze the instrument.
1. Validation
A good assessment the data should accordance to reality. The instrument
of research should be valid, in order to get valid result (Arikunto, 2012). Validity
that will be used is content validity. Content validity is used to measure particular
purpose which is parallel with the material given. So, formula that will be used is
correlation product moment equation.
Frilia Rizky Amalia, 2014
Effect Of Problem-Based Learning On Students’ Problem Solving Skill And Concept Comprehension In Learning Ecosystem For Secondary
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu The formula to find difficulty level as follow:
P : difficulty level
B : number of students who answer correctly JS : Total number of students
(Arikunto, 2012)
For multiple choices by using Anates software, there are sixteen items test
that categorized into very easy. Two items test is easy. Nine items test is
categorized to medium level. Two is categorized to difficult item test and one is
very difficult. For essay, three items test is categorized to medium level, two
items test is easy level and one is categorized to difficult level.
3. Reliability
Arikunto (2012: 100) stated that a test can be said to have good that if
such tests can provide consistent of results.
“A reliable measure in one that provides consistent and stable indication of the characteristic being investigated.”
(Anderson in Arikunto, 2012: 101)
The formula that will be used to determine reliability in objectives test is alpha
formula:
r11 = Instrument reliability
22
Frilia Rizky Amalia, 2014
Effect Of Problem-Based Learning On Students’ Problem Solving Skill And Concept Comprehension In Learning Ecosystem For Secondary
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu = Amount of Varian score in each item
= Varian total
(Arikunto, 2012)
For reliability result is written in appendix.
4. Discriminating Power
Discriminating power is the ability of question to distinguish between
high-ability students with low ability students (Arikunto, 2012: 226).
Discriminating power is
indicated by the discrimination index. The discrimination index ranges between
0:00 to 1:00 (Arikunto, 2012). It is same with difficulty level). The formula to
determine discrimination index is as follow:
DP : Discriminating Power
The classification of discrimination power
Frilia Rizky Amalia, 2014
Effect Of Problem-Based Learning On Students’ Problem Solving Skill And Concept Comprehension In Learning Ecosystem For Secondary
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
obtained 66.67% for index discriminating power. For more detailed can be seen in
appendix.
G. Data Processing
By using statistics, data is processed. The explanation of data processing, as follow:
1. Pre-test and post-test analysis
Pre-test and post-test results would be gained by the result of normalized
gain. The process to get normalizes gain, as follow:
a. Scoring Process
In this research, there are 15 items of multiple choice for pre-test and
post-test. Score one will be given if the answer is correct, and zero for incorrect
answer. Also, there are three essays. For scoring the essay, the range is from 1 – 5
depending of the criteria. For scoring result is attached in appendix.
b. Calculating Gain Score
Gain value could be obtained from the differences between pre-test and
post-test result. By using this formula, gain was obtained:
G = Sf - Si Description:
G = gain
Sf = post-test
Si = pre-test
(Hake, 1999)
For concept comprehension item test, the experimental class obtained 17.7
as the gain score and -10.1 is gain score in control class. in other hand, for
problem solving skill in experimental class is 23.47 and 13.04 for control class.
24
Frilia Rizky Amalia, 2014
Effect Of Problem-Based Learning On Students’ Problem Solving Skill And Concept Comprehension In Learning Ecosystem For Secondary
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
The gain score would be used to determine normalized gain score. The
effectiveness of problem-based learning toward students’ problem-solving skill
and concept comprehension would be seen by result of normalized gain.
Normalized gain of each student <g> defined as following formula:
Frilia Rizky Amalia, 2014
Effect Of Problem-Based Learning On Students’ Problem Solving Skill And Concept Comprehension In Learning Ecosystem For Secondary
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu Formula to find deviation:
∑x2
d = ∑d2 –
Then, see the significance in table t.
(Arikunto, 2010)
Testing hypotheses of problem solving skill by SPSS software is obtained
1.757, it means H0 is rejected automatically H1 is retained. For concept
comprehension testing hypotheses is obtained 0.0 it also means H0 is rejected
automatically H1 is retained.
2. Likert Scale Analysis
Percentages of questioner would be obtained by:
P = x 100 %
Description:
P : Percentage
F : Frequency of the answer N : Total of response
(Sugiyono, 2011)
The result of likert scale is mostly students give positive attitude in learning.
3. Observation Sheet Analysis
For analyzing the observation sheet
Score =
x 100 %
(Kunjaraningrat, 1993)
The observation sheet result shows that experimental class obtained 8.91
26
Frilia Rizky Amalia, 2014
Effect Of Problem-Based Learning On Students’ Problem Solving Skill And Concept Comprehension In Learning Ecosystem For Secondary
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
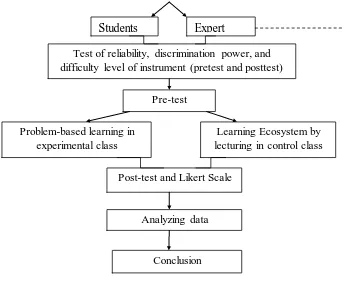
H. Research Procedure
I.
J.
K.
L.
M.
N.
Seminar proposal
Making research instrument (pretest, post test, observation sheet, and questionnaire.)
Revision Instrument validation
Problem Identification and Research objective
Literature study of problem-based
learning
Literature study of students’ problem solving skill and
understanding
Analyzing Indicator of students’ problem solving
skill and understanding concept Literature study of
Frilia Rizky Amalia, 2014
Effect Of Problem-Based Learning On Students’ Problem Solving Skill And Concept Comprehension In Learning Ecosystem For Secondary
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
Figure 3.1 Research Procedure
Pre-test
Test of reliability, discrimination power, and difficulty level of instrument (pretest and posttest)
Problem-based learning in experimental class
Post-test and Likert Scale
Analyzing data
Conclusion
Learning Ecosystem by lecturing in control class
Frilia Rizky Amalia, 2014
Effect Of Problem-Based Learning On Students’ Problem Solving Skill And Concept Comprehension In Learning Ecosystem For Secondary
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
CHAPTER V
CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATION
A. Conclusion
Based on result that already obtained and discussed, can be drawn conclusion.
First, through problem-based learning students’ concept comprehension is better than
traditional teaching. It clearly noticed by the differences of normalized gain in
experimental and control class. In experimental class is obtained 0.5 that included to
medium improvement. In other hand, in control class is obtained -1.1 that included to low
category. So, there is significant different on students’ concept comprehension in
experimental class through problem-based learning.
The students’ problem solving skill is also improving. It can be seen by the normalized gain in experimental class that learnt through problem-based learning is
higher than control class that learnt by lecturing. The experimental class obtained 0.31 as
the normalized gain. It is categorized medium improvement. Meanwhile, control class
obtained 0.14 as normalized gain. It included to low improvement. The result of
observation sheet also presents that students’ problem solving skill in experimental class
is better than students in control class.
Majority of students in experimental class, give positive attitude toward the
implementation of problem-based learning. Based on indicators of likert scale, majority
of students gave positive attitude toward concept comprehension and problem solving
skill also mostly of students gave positive of learning through problem-based learning.
B. Recommendations
After conducting this research and finding and processing the result, there are
some recommendations for further researcher that interest to problem-based learning and
also for teacher as following:
Frilia Rizky Amalia, 2014
Effect Of Problem-Based Learning On Students’ Problem Solving Skill And Concept Comprehension In Learning Ecosystem For Secondary
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
Problem-based learning can be as the alternative model to encourage students to be
active learner. It is better for students to be active learner in order to improve
students’ concept comprehension and others skill. 2. For further researchers
For further researcher can use and develop problem-based learning in other concept to
measure other skills, to find out the weakness of problem-based learning, in order to
give solution in developing problem-based learning. Also suggested for further
Frilia Rizky Amalia, 2014
Effect Of Problem-Based Learning On Students’ Problem Solving Skill And Concept Comprehension In Learning Ecosystem For Secondary
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
REFERENCES
Anderson, L.W and Krathwohl, D. R. (2001). A Taxonomy for Learning, Teaching and Assessing. NewYork: Longman.
Arends, R.I. (2008). Learning to Teach. Yogyakarta: Pustaka Pelajar.
Arikunto, P. D. (2012). Dasar-Dasar Evaluasi Pendidikan. Jakarta: Bumi Aksara.
Arikunto, P. D. (2010). Prosedur Penelitian. Jakarta: Rineka Cipta.
Brown, Lawless and Boyer. (2013). Promoting Positive Academic Dispositions Using a Web-based PBL Environment: The GlobalEd 2. In Interdisciplinary Journal of Problem-Web-based Learning [Online], 23 pages. Available: docs.lib.purdue.edu/cgi/viewcontent. [August 24 2013]
Cenkseven-Önder, F., and Çolakkadioğlu, O. (2013). Decision-making and problem-solving as a well-being. In academicjournals [Online], --. Available: www.academicjournals.org [October 1 2013]
Chamberlin, S.A., and Moon, S.M. (--). How Does the Problem Based Learning Approach Compare to the Model-Eliciting. Seminar Nasional Pendidikan MIPA.
Gijbels, D., Dochy, F., Van den Bossche, P., and Segers,M. (2005). Effects of Problem-Based Learning: A Meta-Analysis From the Angle of Assesment. In Review of Educational Research [Online], --. Available: sagepub.com/journal [October 1 2013]
Gok, T. (2010). The General Assessment of Problem Solving Processes and Metacognition. In Eurasian Journal of Physics and Chemistry Education [Online] , --. Available: EurasianJournal.com [October 1 2013]
Hallinger, P., and Lu, J. (2011). Assessing the instructional effectiveness of problem-based management education in Thailand: A longitudinal evaluation. In Management Learning [Online], --. Available: sagepub.com [October 1 2013]
Hake, R.R. (1999). Analyzing Change/Gain Score. Woodland Hill:---
Hirça, N. (2011). Impact of Problem-based learning to students and teacher. In Asia-Pasific Forum on Science Learning and Teaching [Online], 19 pages. Available: egitim.bartin.edu [October 1 2013]
Frilia Rizky Amalia, 2014
Effect Of Problem-Based Learning On Students’ Problem Solving Skill And Concept Comprehension In Learning Ecosystem For Secondary
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
Irvani, A. I. (2013). Hubungan Kemampuan Self-directed Learning dan Problem Solving Siswa SMP melalui Pembelajaran Berbasis Masalah. Research Paper of Biology Education UPI. Bandung: Not published.
Jo, S. and Ku, J. (2011). Problem Based Learning Using Real-Time Data in Science Education for the Gifted. In Gifted Education International [Online], --. Available: gei.sagepub.com [October 1 2013]
Koentjaraningrat. (1993). Metode-Metode Penelitian Masyarakat. Jakarta: Gramedia.
Masitoh, I. (2013). Kemampuan Memecahkan Masalah dan Penguasaan Konsep Siswa melalui Project-based Learning pada Materi Daur Ulang Limbah. Research Paper of Biology Education UPI. Bandung: Not published.
McGraw-Hill Higher Education. (2003). Retrieved 10 31, 2013, from Research Method in
Psycology:
http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072494468/student_view0/chapter11/learning_objectives.html
Musilawati, Y. (2013). Implementasi Model Pembelajaran Problem-based Instruction untuk Meningkatkan Pemahaman Konsep Fisika Siswa. Research Paper of Physics Education UPI. Bandung: Not published.
National Park Service. (2014). National Park Service. Retrieved 02 21, 2014, from Golden Gate National Recreation Area: http://www.nps.gov/goga/naturescience/climate-change-causes.htm
National Research Education. (2010). Exploring the Intersection of Science Education and 21st Century Skills: A Workshop Summary. Washington (DC): National Academies Press .
Ningsih, I. W. (2010). Upaya Meningkatkan Pemahaman Konsep dalam Matematika Siswa melalui Model Siklus Belajar (Learning Cycle) dengan Media LKS di SMP Negeri 2 Depok Sleman. Research Paper of Mathematics Education UNY. Yogyakarta: Not published.
OECD. (2005). First Results of the Adult Literacy and Life Skills Survey. Ottawa: OECD Publishing.
Pramono, J. & Ghofur, M.A. (2013). Biologi. Sidoarjo: Masmedia.
45
Frilia Rizky Amalia, 2014
Effect Of Problem-Based Learning On Students’ Problem Solving Skill And Concept Comprehension In Learning Ecosystem For Secondary
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
Queen's University Belfast. (2013). Problem-based learning [Online],-- Available: http://qub.ac.uk/ [October 5 2013]
Sari, D. D. (2012). Penerapan Model Problem Based Learning (PBL) untuk Meningkatkan Kemampuan Berpikir Kritis Peserta Didik pada Pembelajaran IPA Kelas VIII SMP Negeri 5 Sleman. Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta. Yogyakarta: Not published.
Setyawardani, D., Rusilowati, A., and Hartono. (2012). Pengembangan Alat Evaluasi Proposition Generating Task untuk Mengukur Struktur Kognitif Siswa di SMA. In Journal of Innovative Science Education [Online], --. Available: journal.unnes.ac.id [October 5 2013]
Slameto. (2003). Belajar dan Faktor-Faktor yang Mempengaruhinya. Jakarta: RinekaCipta.
Sugiono. (2011). Metode Penelitian Kuantitatif Kualitatif dan R&D. Bandung: Alfabeta.
The Pennsylvania State University. (2013). PBL-protocols: Guiding and Controlling Problem Based Learning Processes in Virtual Learning Environments. Retrieved 07 01, 2014, from http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/
Tim Matrix Media Literata. (2008). Biologi SMP. Jakarta: Grasindo.