FULL PAPER
CURRENT STATUS OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE
IN INDONESIA
A. Hussein S. Kartamihardja
Department of Nuclear Medicine
Faculty of Medicine, UniversitasPadjadjaran
Bandung
INVITED SPEAKER
On
41th Annual Scientific Meeting of
The Australian and New Zealand Society of Nuclear Medicine
Darwin Convention Center
CURRENT STATUS OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE
IN INDONESIA
A. Hussein S. Kartamihardja Department of Nuclear Medicine Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Padjadjaran
Bandung-Indonesia
Presented on
Australian and New Zeland Society of Nuclear Medicine 41st Annual Scientific Meeting
Darwin, Australia 14-18 July 2011
Introduction
Indonesia is the largest archipelago country in the world with 5 big islands
and about 13,466 small islands. It is consist of land area about 39% and sea
area is about 61%. Indonesia is republic country lead by a President elected
every 5 years.1 It is divided into 31 provinces leads by the governor. Number of
population in the year of 2010 is approximately 237 million, which is 3.43% of
world populationwith growth rate about 3.5-4 million people /year.2,3
Health status people in a country depend on several aspects, such as
number health providers with medical facilities, number of man power in health
and medical capabilities and general health system in payment for medical
treatment.
Health care facilities
Number of medical doctors in Indonesia is relatively low compared to
number of population. It is only 19 medical doctors per 100,000 populations. It
is not only problem in number of medical doctor, but also the distribution is not
due to leak of facilities in rural area. Good medical facilities are located in big
hospital.4
Payments for health care can be divided into two systems. Most of people
(more than 85%) should pay by their own expense individually or fee for
servicesystem. Government officials (about 7.8%) are covered by government
health insurance. A number of 6.2% are cover by private health insurance.4
Health and medical services are provided by government and private
companies. There are about 7,243 primary health care and about 873 hospitals
in Indonesia with approximately 120.000 beds, 522 General Hospital belong to
the government and 351 Private Hospitals. Among them, there are 54
Super-specialty hospitals providing tertiary health care.Total annual budget for health
provided by government is about 2.6-2.8% of total national budget.4
In term of human resources, particularly to increase number of medical
doctor, there are 51 medical colleges providing undergraduate medical
education, 11 provide post-graduate medical education for specialist, but only
one institution provides post-graduate medical education in nuclear medicine
specialist.5
Major health problems
Indonesia is a developing country, the 4th largest population country in the
world is facing many problems including in health. Pattern of diseases slightly
different compared to developed country. Infection & Infectious diseases are
still the most health problem in Indonesia, followed by Coronary artery disease,
Nuclear Era in Indonesia
Nuclear technology was introduced in Indonesia in the year of 1965 with
establishing of Triga 2000, 2 Megawatt Reactor, and the first atomic reactor in
Indonesia. This reactor dedicated for research and medical purposes. In 1967,
the first nuclear medicine service was established located in Bandung Atomic
Center, the same place of reactor. In 1982, the second atomic reactor for
research purposes with smaller capacity (300 KW) was established in
Yogyakarta called “Kartini” Reactor.6
In 1988 was the most important moment for developing nuclear technology
in Indonesia when a Multipurpose Atomic Reactor called “Siwabessy”
established in Jakarta with capacity 30 MW.7
Historical Milestones “Nuclear Medicine Era in Indonesia”
The application of nuclear technology in medicine called nuclear medicine
in Indonesia was started in 1967, 2 years after establishment of the first atomic
reactor in Bandung. The regulation of health system stated that all health
services for diagnostic and therapy should be conducted in hospital. Due to this
regulation nuclear medicine services previously provided in Bandung Atomic
Center was stopped.
In 1971 the First Nuclear Medicine Department in hospital was established
in Dr. Hasan Sadikin General Hospital/Faculty of Medicine Universitas
Padjadjaran Bandung – Indonesia.
In1976 a group medical doctor and other scientists from different
educational background were met together to establish a professional
(ISNMB). Recognition of the society by the Indonesian Medical Association is
very important for developing nuclear medicine as an independent medical
specialist, but due to not all member of ISNMB are medical doctor, the
application was not accepted. In 1989 The Indonesian Society of Nuclear
Medicine (ISNM) was established to fulfill requirements to be a professional
organization under the Indonesian Medical Association. Following a long
effort, finally in 1997 the Indonesian Medical Association recognized and
declared ISNM as a independent medical specialty.
Developing of nuclear medicine depends on many aspects, and of them is
quality and number of manpower. In this case, the ability of educational
institution to train doctor to be nuclear medicine specialist is necessary. So in
1997 Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Padjadjaran/Dr. Hasan Sadikin General
Hospital established the first and the only one Center for NM specialty
education program in Indonesia, located in Bandung and in 2011 Master
Degree program in radiopharmacy was established as well. Unfortunately until
now there is no formal training program for nuclear medicine technologists,
technical staff and physicists.
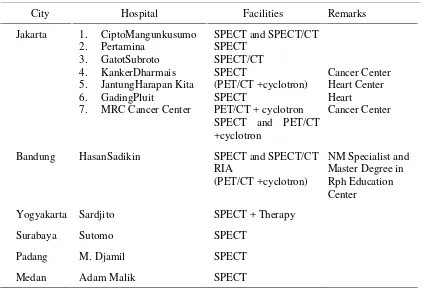
Table 1 showed hospital in Indonesia provide nuclear medicine services
and facilities in every hospital. All hospitals are located in Jawa and Sumatera
Island. Seven out of 12 hospitals are located in Jakarta.5
Equipments
Quality of nuclear medicine services is depending on not only qualified
and competent nuclear medicine physicians and other professional, but also
Number of equipment available in Indonesia are as follow:5
number of population and not well distribution. Most of equipment is located in
several hospitals in Jakarta.
Table 1 : Nuclear medicinefacitities in Indonesia in 20115
City Hospital Facilities Remarks
Jakarta 1. CiptoMangunkusumo
Bandung HasanSadikin SPECT and SPECT/CT
RIA
Yogyakarta Sardjito SPECT + Therapy
small amount of medical doctor chose nuclear medicine as a selected career. By
the middle year of 2011 there are only 31 qualified nuclear medicine
physicians, 30 Nuclear Medicine Technologists, and 4 Nuclear Medicine
Physicists. There are 10 radiopharmacists, but only 2 work in hospital, rest of
them work in atomic energy agency.Number of Nuclear Medicine Resident
who study in faculty of medicine is18 medical doctors.8
Nuclear Medicine Procedure
There are many nuclear medicine procedures can be done using gamma
camera with various radiopharmaceutical, but most of nuclear medicine
procedure in Indonesia related to cardiology, oncology (bone scan), kidney and
thyroid. Other procedures are limited such as infection scan using Tc-99m
cifrofloxacine and ethambutol scan for tuberculosis. The most procedure for
diagnostic is kidney (renogram and GFR) with approximately 500
patients/month, follow by thyroid scan 400 patients/month, bone scan 350
patients/month and myocardial perfusion scan 200 patients/month. Since PET
techology is relatively new, the number of procedure for PET is very limited,
about 20 patients/month. Radioimmunoassay, particularly for detecting thyroid
hormone was done about 550 patients/month.5
Therapy
The role of nuclear medicine on therapeutic is very limited. Most of
therapeutic procedure done to treat hyperthyroidism and well differentiated
thyroid cancer. There are about 75 hyperthyroidsim patients/month and 25
Problems
Development of nuclear medicine in Indonesia is not very good, it is
growing very slow. There are many problems to develop nuclear medicine in
Indonesia, are as follow:
1. Policy
Nuclear medicine is not priority in National Health System, since
infection and infectious diseases still the major health problem in
Indonesia. The government more focus to decrease number of these
diseases. A lot of budget was dedicated to prevent the disease. In this case,
supporting from government is not sufficient to develop nuclear medicine
in appropriate way.
2. Equipment
Problem regarding equipment related to budget not only to buy a new
camera, but also budget for maintenance. By the regulation, It is mostly
impossible to get budget for maintenance, particularly for contract service.
It is very hard to find private sector to infest on nuclear medicine.
3. Radiopharmaceutical
BATAN is a government body, which responsible to develop nuclear
technology has success to develop in house production of
radiopharmaceutical. Unfortunately, the problem was due to the regulation
they could not produce as a commercial product ready in the market. They
stop producing after the research was finished. Other problem is due to
unbalance between demand and high cost of radiopharmaceutical
4. Man power
As mention previously, number manpower in nuclear medicine is very
limited. Appreciation from other medical profession is not sufficient.
5. Appreciation from the community
“Nuclear phobia” is one of problem on development of nuclear
medicine. This situation is understandable, since most of publication
related to nuclear is radiation hazard from radioactive, but less publication
of the benefit of nuclear technology for human being, particularly for
medical purposes.
Concluding remark
Nuclear medicine services in Indonesia has long story with some constrain
in developing.
Nuclear medicine has good opportunity to develop since there is a change
pattern of disease, such increasing number of cardiovascular disease,
degenerative and malignancy.
Referrences.
1. http://us.health.detik.com/read/2011/07/06/155302/1675953/763/pertambah
an-penduduk-ri-terbesar-ke-5-dunia-terbanyak-dari-jabar
2. http://www.unfpa.org/public/world-population-day/
3. Justus M. van der Kroef"The Term Indonesia: Its Origin and Usage".
Journal of the American Oriental Society1951. 71(3):166–171.
doi:10.2307/595186.
5. Masjhur JS. Nuclear Medicine in Indonesia: Yesterday – Today –
Tomorrow. Presented in ARCCNM. Jakarta, September 2003.
6.
http://www.batan.go.id/index.php/kedeputian/fasilitas-nuklir/869-sejarah-reaktor-kartini-yogyakarta
7. http://www.batan.go.id/index.php/home/sejarah.