ANALYSIS AND DESIGN
4.1 Analysis
4.1.1 Collecting Data
1. Data Test
Test data obtained from web questionnaires that have been made
before by the author. The questionnaire data from the web is stored
as a txt file.
Example :
Table 4.1: Table Test Data
Data Angket Status
@dosen sering hadir tidak tepat waktu sehingga mahasiswa sering untuk menunngu dahulu...
?
2. Data Training
Training data was taken from randomly collecting data from
BMSI server Unika Soegijapranata. The data collected is 1092 data
(questionnaire). Then the data will be selected again by the author.
200 data were taken for training data, with details of 100 data with
negative opinion and 100 data with positive opinion. The selected
data is only data that has a number of letters above 50 and the
determination of negative and positive opinions is determined
manually by the author. Then the questionnaire data is stored in the
txt file.
Example :
Table 4.2: Table Data Training
Data Angket Status
Jangan telat terus Pak kalau kuliah pagi! dan mohon konfirmasi ketidakhadiran sebelum hari perkuliahan...
Negative
@Dosen memulai perkuliahan tidak tepat waktu. Negative
cara pengajaran yang santai, tidak terburu buru, sehingga mudah di ikuti dan di pelajari oleh siswa siswa nya.
Positive
Tidak ada karena semuanya sudah berjalan dengan baik. Sehingga mahasiswa dapat menerima mata kuliah tersebut dengan puas.
Positive
4.1.2 Prepare Data
In the next process, training data and test data will be processed by Text
Preprocessing method. Preprocessing stage prepares data in the form of
unstructured text into structured data which is ready to be used for the next
process. Preprocessing stages used in this study include :
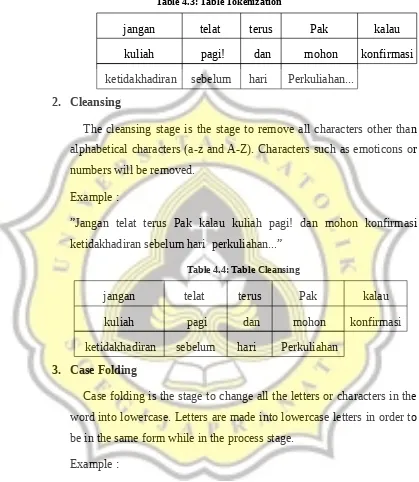
1. Tokenizing
Tokenizing stage is the stage to cut text questionnaire into each word
contained. This word piece is called a token or term.
Example :
”Jangan telat terus Pak kalau kuliah pagi! dan mohon konfirmasi
Table 4.3: Table Tokenization
jangan telat terus Pak kalau
kuliah pagi! dan mohon konfirmasi
ketidakhadiran sebelum hari Perkuliahan...
2. Cleansing
The cleansing stage is the stage to remove all characters other than
alphabetical characters (a-z and A-Z). Characters such as emoticons or
numbers will be removed.
Example :
”Jangan telat terus Pak kalau kuliah pagi! dan mohon konfirmasi
ketidakhadiran sebelum hari perkuliahan...”
Table 4.4: Table Cleansing
jangan telat terus Pak kalau
kuliah pagi dan mohon konfirmasi
ketidakhadiran sebelum hari Perkuliahan
3. Case Folding
Case folding is the stage to change all the letters or characters in the
word into lowercase. Letters are made into lowercase letters in order to
be in the same form while in the process stage.
Example :
”Jangan telat terus Pak kalau kuliah pagi! dan mohon konfirmasi
Table 4.5: Table Case Folding
jangan telat terus pak kalau
kuliah pagi dan mohon konfirmasi
ketidakhadiran sebelum hari perkuliahan
4. Stopword Removal / Stoplist
Stopword removal is the stage to eliminate words that usually appear
in large numbers and are considered to have no meaning. Usually
omitted words are people's pronouns or connecting words. Stopword
data used in this research is stopword by Tala, F. Z. which amounts to
759 words.
Table 4.6: Table Stopword
dan, atau, tetapi, tapi, akan tetapi, jika, kalau, karena, walau, walaupun, juga, jadi, maka, sehingga, supaya, agar, hanya, lagi, lagipula, lalu, sambil, melainkan, namun, padahal, sedangkan, demi, untuk, apabila, bilamana, sebab, sebab itu, karena itu, bilamana, asalkan, meskipun, biarpun, biar, seperti, daripada, bahkan, apalagi, yakni, adalah, yaitu, ialah, bahwa, bahwasannya, kecuali, selain, misalnya, untuk itu
Example :
”Jangan telat terus Pak kalau kuliah pagi! dan mohon konfirmasi
ketidakhadiran sebelum hari perkuliahan...”
Table 4.7: Table Stopword Removal
telat kuliah pagi mohon konfirmasi
5. Stemming
Stemming is a stage for finding a root word or process to change a
word that has a suffix, prefix and / or a confix to a basic word. The
basic word used in this study is the basic word from Bahtera
(https://bahtera.org/). Bahtera is the Indonesian dictionary that became
the reference according to the Kamus Besar Bahasa Indonesia (KBBI).
The basic word in Bahtera is 28,526 words.
The algorithm used for stemming in the research is the algorithm
Nazief & Adriani. The steps of Nazief & Adriani algorithm are as
follows:
A) Search for words that will be compared with basic word
dictionaries. If found then it is assumed that word is root word. So
the algorithm stops.
B) Inflection suffix.
- remove Particle (P), which includes: "-lah", "kah", "tah" and
"any".
- remove Possessive pronoun (PP), which includes: "me", "- you"
and "it".
C) Derivation suffix.
Eliminate the word with the suffix "-i", "-kan", and "-an".
D) Derivation prefixes
- remove prefixes that can be morphological ("be", "be-", "pe-" and
"te").
- remove non-morphological prefix ("di-", "ke-" and "a").
E) If all the above processes fail, then the algorithm returns the
Example :
”Jangan telat terus Pak kalau kuliah pagi! dan mohon konfirmasi
ketidakhadiran sebelum hari perkuliahan...”
Table 4.8: Table Stemming
telat kuliah pagi mohon konfirmasi
kuliah
4.1.3 Word / Term Weighting
Weighting of terms or words is the stage to give the weight (value) to
each word in the document. In text mining, a technique commonly used to
give weight to a word is TF-Idf.
Tf-Idf is a combination of Term Frequency and Inverse Document
Frequency.
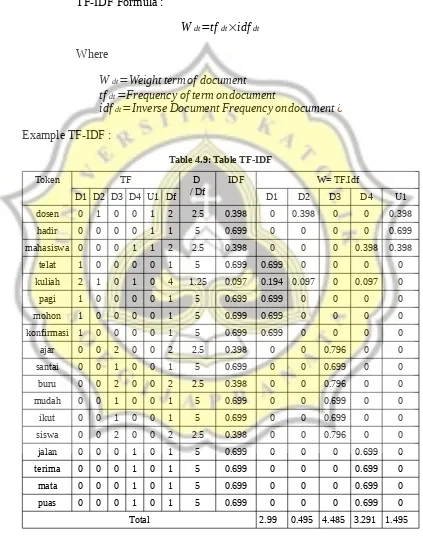
1. Term Frequency (TF)
TF (Term Frequency) is the frequency of occurrence of a term / word
in the document concerned.
2. Inverse Document Frequency (IDF)
IDF (Inverse Document Frequency) is a calculation of many terms /
words that are widely distributed on each processed document.
IDF Formula :
idf=log(N/df)
Where :
N=amount of all data
3. TF-IDF
TF-IDF Formula :
Wdt=tf dt×idfdt
Where
Wdt=Weight term of document
tfdt=Frequency of term on document
idfdt=Inverse Document Frequency on document¿
Example TF-IDF :
4.1.4 Process Data
K Nearest Neighbor algorithm is an algorithm that calculates the
similarity or distance between two documents. Neighboring determination
in K-Nearest Neighbor is usually calculated based on Euclidean Distance.
For classifying text, Euclidean distance determination can use Cosine
Similarity. Cosine similarity can calculate the similarity between two
documents in text form.
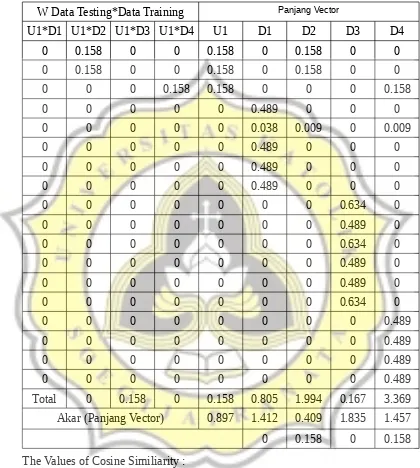
The formula used to calculate cosine similarity is:
cos(∅QD)=
cos(∅QD)=Similarity between documents Q¿D
Table 4.10: Table Cosine Similarity
W Data Testing*Data Training Panjang Vector
U1*D1 U1*D2 U1*D3 U1*D4 U1 D1 D2 D3 D4
Total 0 0.158 0 0.158 0.805 1.994 0.167 3.369
Akar (Panjang Vector) 0.897 1.412 0.409 1.835 1.457
0 0.158 0 0.158
The Values of Cosine Similiarity :
Table 4.11: Table Value Cosine Similarity
D1 D2 D3 D4
The next step is to re sequencing the level of the resemblance of the data were
obtained:
Table 4.12: Table Sequence Cosine Similarity
D2 D4 D1 D3
0.431 0.121 0 0
4.1.5 Classifying Data
After obtaining the value of similarity between test documents and
training documents. The next stage is to determine the value of parammeter
K in k nearest neighbor. The value of K is the number of nearest neighbors
or the number of how much data of similarity comparison between
documents is taken.
Then sort the object into the group that has the value of similarity
between the highest documents. By using the nearest neighbor category
with the highest level of similarity it can be predicted the final result or the
decision of the calculated data.
Example :
Value K = 3
Once the sequence is known from the level of similarity. Then take as
much as the value of K (n) tested. Training documents with the highest
level of similarity with the Test document will be selected. The result:
Table 4.13: Table KNN
D2 D4 D1
0.431 0.121 0
Data Test after Test with System :
Table 4.14: Table KNN Result
Data Angket Status
@dosen sering hadir tidak tepat waktu sehingga mahasiswa sering untuk menunngu dahulu...
Negative
The test document is categorized as a questionnaire with a negative
opinion. Because it has a high level of similarity with training documents
that have a negative opinion.Desain
4.2.1 Use Case Diagram
Based on the picture above, the program will get input from the
user (input file). After that, the data will go into the process of
pre-processing and tf-idf to get the weight or value contained therein.
After getting the value or weight, the data will be calculated the level
After obtaining the result of the similarity level between
documents, the data will be classified with K-Nearest Neighbor into
data with negative and positive opinion. This project is based on the
similarity level between test documents and training documents. The
high level of similarity between data, it will be selected. The result of
system process will be saved as history.
4.2.2 Flowchart System
In this system there are 5 processes that will be done. The first process, the
user inputs a questionnaire file to be tested. The second process is preprocessing
where the data will be processed so it is ready for use in the next process. In
addition to preprocessing test data, training data will also be processed
preprocessing. The next process is TF-IDF, where the data will be processed and
then given the weight value of the document. The fourth process is Cosine
Similarity, where data will be searched the level of similarity between data. The
final process of the system will classify the data with K Nearest Neighbors