i
Andong in the Academic Year of 2013/2014 )
A GRADUATING PAPER
Submitted to the Board of Examiners as a Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Sarjana Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris (S.Pd.I)
in the English Department of Educational Faculty State Institute for Islamic Studies (STAIN) of Salatiga
TIKA RAHMAWATI
11310028
ENGLISH DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATIONAL FACULTY
STATE INSTITUTE FOR ISLAMIC STUDIES (STAIN)
ii
DECLARATION
In the name of Allah, the most gracious and merciful.
Hereby the writer declares that this graduating paper is made by the writer herself. It is not containing materials and written and has been published by other people and other people’s idea except the information from the references.
This declaration is made by the writer, and she hopes that this declaration can be understood.
Salatiga, November 04th 2014 The writer
iii Ruwandi, S. Pd. MA
The Lecturer of Educational Faculty State Institute for Islamic Studies Salatiga
ATTENTIVE COUNSELOR’S NOTE
Case: Tika Rahmawati’s Graduating Paper
Salatiga, November 04th 2014 Dear:
The Rector of State Institute for Islamic Studies of Salatiga
Assalamu’alaikum Wr. Wb.
After reading and correcting Tika Rahmawati’s graduating paper entitled
“THE USE OF SCAFFOLDING TALK TECHNIQUE TO IMPROVE
STUDENTS’ SPEAKING SKILL”, I have decided and would like to propose that if it could be accepted by educational faculty, I hope it would be examined as soon as possible.
Wassalamu’alaikum Wr. Wb.
Counselor
iv
GRADUATING PAPER
THE USE OF SCAFFOLDING TALK TECHNIQUE TO IMPROVE
STUDENTS’ SPEAKING SKILL
(A Classroom Action Research of the Eighth Grade Students of MTSN Andong in the Academic Year of 2013/2014)
CREATED BY: TIKA RAHMAWATI
NIM. 113 10 028
Has been brought to the board of examiners on February 21th, 2014, and hereby considered to completely fulfill the requirements of Degree of Sarjana Pendidikan
Islam (S.Pd.I) in English and Education Department. Board of examiners:
Head : Dr. Sa’adi, M. Ag. Secretary : Ruwandi, M. A. 1st examiner : Setia Rini, M. Pd.
2nd examiner : Ari Setiawan, S. Pd. M. M.
Salatiga, February 21th, 2015 Rector of STAIN Salatiga
v
“
BUILD YOUR DREAMS OR SOMEONE ELSE WILL HIRE YOU TO BUILD
THEIRS, WITH FULL PERSEVERANCE, GREAT WORKS WILL BE
ACCOMPLISHED
”
.
vi This work is sincerely dedicated for:
My beloved husband (Slamet Rohmad Widodo)
My beloved parents, my father (Mat Kasim) and my mother (Siti Rohmatin) who always pray, guide, motivate me to become better person.
My dearest father and mother in law
My sweetest lovely angel (Reyhan Rama Widodo)
My beloved sister (Fajar Istiqomah), my beloved brothers (Irfanul Muslim and Arbain Mahmud) and my big family who fill my life with love and affection.
All of big family MTs N Andong, the head master, all of teachers and students of VIIIB class.
vii
First of all I would like to express my deepest gratitude to Allah SWT , God the almighty for the blessing given to me in completing this thesis as one of requirement to finished study in English Department faculty of States for Institute Islamic Studies.
This thesis would not have been completed without support, guidance and help from individual and institution. Therefore, I would like to express special thanks to:
1. Mr. Dr. Rahmat Hariyadi, M. Pd as the rector of State Institute for Islamic Studies Salatiga.
2. Mrs. Rr. Dewi Wahyu Mustikasari, M. Pd as the head of English Department of States Institute for Islamic Studies (STAIN) of Salatiga and the consultant of this thesis. Thanks for all of your suggestion, recommendation and support for this thesis from the beginning until the end.
viii
for all guidance, knowledge, support, and etc.
6. The craziest friends in D’Phonk (Orin, Chus, Jay, Saras, Fais, Lia, Ria,Atun, Layla, Laely). Thanks for always give me sweet memory, and support.
7. All of my friends TBI ’10 especially A class, thanks for the cheerfull and your togetherness.
8. All of staffs who help the writer in processing of thesis administration. 9. Everybody who has helped me in finishing this thesis. Thanks for all
supports, advice, suggestion and other helps that you all gives. The writer hopes that this thesis will useful for everyone.
Salatiga, 04 Novemberth 2014 The writer
ix
Students’ Speaking Skill (Classroom Action Research of the Eighth Grade Students of MTS Negeri Andong in the Academic Year of 2013/2014 )”. A Graduating Paper. Educational Faculty. English Department. State Institute for Islamic Studies (STAIN). Consultant: Ruwandi, MA.
Keywords: Speaking Skill; Scaffolding Talk technique.
x
DECLARATION ... ii
ATTENTIVE COUNSELOR NOTES ... iii
PAGE OF CERTIFICATION ... iv
MOTTO ... v
DEDICATION ... vi
ACKNOWLEDGMENT ... vii
ABSTRACT ... ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... x
LIST OF TABLES AND FIGURE ... xiii
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION A. Background of Study ... 1
B. Identification of Problem ... 4
C. Research Problems ... 5
D. The Objectives of the Study ... 5
E. Benefits of the Study ... 6
F. Limitation of the Study ... 7
xi CHAPTER II: UNDERLYING THEORIES
A. Speaking ... 10
1. Type of Speaking Performances ... 11
2. Elements of Speaking ... 12
3. The Principle for Teaching Speaking ... 14
4. Teaching Speaking ... 15
5. Technique in Teaching Speaking ... 16
6. Classroom Speaking Aktivities ... 17
7. Characters of Successful Speaking ... 20
B. Scaffolding Talk ... 21
1. Characteristic of Scaffolding Talk ... 23
2. Type of Scaffolding Talk ... 24
3. Procedure of Scaffolding Talk ... 26
CHAPTER III: RESEARCH METHODOLOGY A. The Setting of The Research ... 27
B. The Method of the Research ... 32
C. The Subject of The Research ... 32
xii
G. The Procedure of Research ... 38
H. The Model of Research ... 40
I. Technique of Data Analysis ... 40
CHAPTER IV: DATA ANALYSIS AND DISCUSSION A. Data Presentation ... 42
B. Data Analysis ... 49
C. Discussion ... 53
D. Research Summary ... 74
CHAPTER V: CLOSURE A. Conclusion ... 76
B. Suggestion ... 77 BIBLIOGRAPHY
CURRICULUM VITAE
xiii
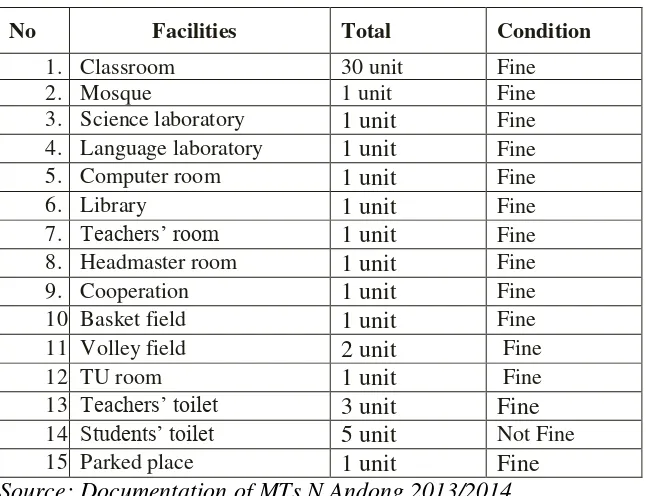
Table 3. 1 Educational Facilities and Tools in MTsN Andong ... 28
Figure 3.1 Figure Cyclical Action Reasearch ... 40
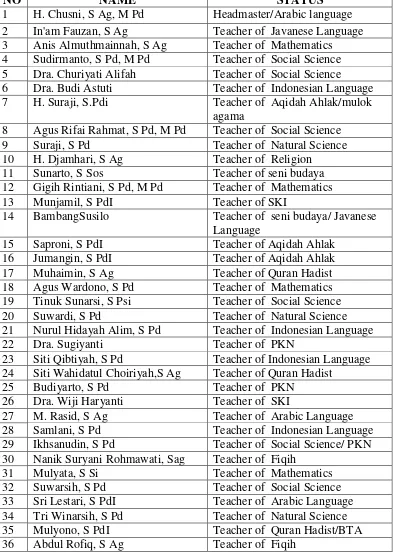
Table 3. 2 List of Teachers (PNS) in MTsN Andong ... 29
Table 3. 3 List of Non Permanent Teachers in MTsN Andong ... 30
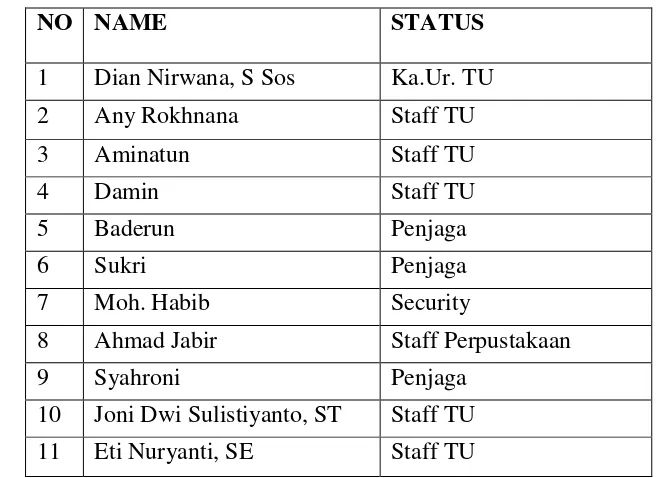
Table 3. 4 List of Staff (PNS and Non Permanent) ... 31
Table 3. 5 The Distribution of the Class of MTsN Andong ... 31
Table 3. 6 The List of VIII B Class Group of MTsN Andong ... 33
Table 3. 7 Students’ Observation Sheet ... 36
Table 3. 8 The Assessment Scale for Oral Ability ... 37
Table 3. 9 The Students’ Achievement ... 38
Table 4.1 The result of pre test ... 42
Table 4. 2 Students’ Observation Sheet ... 44
Table 4.3 The result of post test I ... 45
Table 4.4 The result of post test II ... 46
Table 4. 5 The result of post test I and post test II ... 47
Table. 4. 6 Students’ Observation Sheet ... 48
xiv
Table 4. 10 The Classification of Post test II result ... 51
Table 4. 11 The result of observation cycle II ... 53
Table 4. 12 Type of Scaffolding Talk ... 61
Table 4. 13 Type of Scaffolding Talk ... 67
1 A.Background of Study
There are four language skills which should be mastered by language learners; they are listening, speaking, reading and writing. Speaking is one of the language skills that should be mastered by language learners. To master this skill is not an easy business because there are some language components as the tools for mastering it. Among others are grammar, vocabularies, spelling, pronunciation, fluency etc. Therefore, one will be called skillful in speaking when they are able to make use the component needed to share ideas, feelings and thoughts. However speaking teachers are not so successful in teaching this skill. Brown and Yule (1983: 25) state that “learning to talk in the foreign language is often considered being one of the most difficult aspects of language learning for the teacher to help the students with.” Many of the learners in a speaking class are reluctant speakers. The disability of the students to speak may lead them to be unable to express their ideas, feelings, thoughts even in a simple form of conversation.
increase students speaking skill. The techniques which can be use as Role-plays, Communication games, Discussion, Scaffolding Talk.
An effective and efficient classroom should be organized by an effective efficient teacher as well. To make the classroom effective and efficient, a teacher should deliver and give instructions in English. Teacher need to choose the most effective or efficient technique in speaking class, one of the technique that can be used by teacher in speaking class is Scaffolding Talk. Scaffolding talks is teacher’s talk in the language teaching. It is the communication and interaction between a teacher and students in which teachers give instructions to support the understanding in the language class. It also influences the success of English speaking atmosphere in the classroom (Listyaning S and Zulfa S, 2007:15) because technique belongs to one of the determinants of successful language teaching.
Based on the results of interviews that have been conducted with Mrs. Suhartini and Mr. Heri English teachers at MTs Negeri Andong, the researcher found out some problems related to the instructional activities in there. Those problems are: 1) the students have low speaking ability because they rarely practice English to communicate with the others; 2) students are used to speak Javanese than English language; 3) the students have low grammar, vocabulary and pronunciation mastery; 4) the students have low motivation in learning English; and 5) the teacher still uses monotonous and inappropriate teaching techniques.
Considering the problems faced by the teachers above, it can be said that the English teacher of MTs Negeri Andong still meets some serious problems in teaching and learning process. Above factor entails us to master English, especially speaking skill. There are so many factors, how to students can master speaking ability successfully. The writer tries to suggest that teacher should apply a technique that emphasizes teaching and learning outpace to solve speaking problems. Thus teachers should have good and interesting techniques in teaching to get better interaction with the learners. To solve those problems, from the side of teaching techniques, the researcher thinks that scaffolding talk is a possible way to overcome them because the technique used influence much of the students’ activities in the learning.
developed to describe the type of assistance offered by a teacher or peer to support learning. In the process of scaffolding, the teacher helps the student master a skill that the student is initially unable to acquire it independently.
Based upon the students’ problems, the writer and teacher agree apply this
technique in speaking class. The writer interested to conduct a research entitled
“The Use of Scaffolding Talk Technique to Improve Students’ Speaking Skill (Classroom Action Research of the Eighth Grade students of MTs Negeri
Andong in the Academic Year of 2013/2014 ).
B. Identification of the Problems
Considering the important of the identification problem, the writer is identified the problem as follows:
1. The English teachers do not understand Scaffolding Talk technique well 2. The English teachers do not comprehend that Scaffolding Talk technique
can be used to improve students’ speaking skill.
3. The English teachers are less interested in using Scaffolding Talk technique. 4. The English teachers a lot of times to prepare this technique
5. The English teachers need a lot of energy to prepare and apply this technique.
C.Research Problems
Based on the phenomena above, this research is aimed at giving answers on the following problems:
1. How is the implementation of students’ speaking skill using scaffolding talk technique for the eighth grade students of MTs Negeri Andong in the academic year of 2013/2014?
2. How is the result of the study after using Scaffolding Talk technique in the students’ speaking skill for the eighth grade students of MTs Negeri Andong in the academic year of 2013/2014?
D. The Objectives of the Study
The general purpose of study is to know the degree of Scaffolding Talk technique that is suitable with class condition. The specific objectives of this study are:
1. To find out that the use of Scaffolding Talk technique is able to improve the students’ speaking skill for the eighth grade students of MTs Negeri Andong in the academic year of 2013/2014
E.Benefits of the Study
The researcher viewed that the following benefits may be derived from the study :
1. For the school
To contribute to the MTs Negeri Andong with the new innovation of the Scaffolding Talk technique.
2. For the teacher
The study can be used by the teacher to provide the better technique to improve students’ speaking skill.
3. For the students
motivates the students to study speaking well, foster students' interest in learning. In addition, this model improves students’ knowledge in
speaking skill.
4. To the other researcher
It can lead to future researchers because it will be a good basis to know why students have low performance in speaking skill and its solving. the result of the research can be used as an input in English teaching and learning process.
5. For the writer
F. Limitation of the Study
The writer limits this research dealing with the improvement of students’ speaking skill of the eight grade in MTs Negeri Andong through Scaffolding Talk technique.
G. The Definition of Key Terms 1. Scaffolding Talk
Scaffolding talks is the teacher’s talk in the language teaching. It is the communication and interaction between a teacher and students in which teachers give instructions to support the understanding in the language class. It also influences the success of English speaking atmosphere in the classroom (Listyaning S and Zulfa S, 2007:15).
2. Speaking Skill
Speaking skill is the ability to speak fluently presupposes not only a knowledge of language features, but also the ability to process information and language ‘on the spot’ (Jeremy Harmer, 1988:269).
H.Review of Previous Research
In this research, the writer takes review of related researcher from other thesis as comparative in this research. The previous research is about ‘ The Effect Of Scaffolding On Children’s Reading Speed Reading Anxiety And
In the experiment assessed the effect of scaffolding as a reading intervention. Scaffolding was done by a teacher providing feedback while the child is orally reading. Feedback was given in terms of the decoding (meaning of words), fluency (which involves correct pronunciation, and speed), and modelling (pre practice procedure) while the child is orally reading an unfamiliar story.
The researcher hypothesized that reading intervention through scaffolding improves reading proficiency, increased rate of reading, and reduce reading anxiety. This hypothesis is confirmed by the results in the present study with large effect sizes for each dependent variable. Results show clearly that students benefitted from scaffolding in terms of improving oral reading, faster reading, and reduced reading anxiety.
I. The Graduating Paper Organization
The researcher wants to arrange the graduating paper in order to the reader can catch the content easily. It is divided into five chapters.
Chapter I is Introduction, consist of the background of the study, the research problem, the objectives of the study, the benefits of the study, limitation of study, review of previous research, and outline of graduating paper.
Chapter III discusses about research methodology which consists of Setting of the research, Method of the research, subject of the research, Data collection method, Research Instrument, Evaluation Criteria, the procedure of the research, the model of research, and technique of data analysis.
Chapter IV is Data presentation, Data analysis, Discussion and research summary of cycle 1 and cycle II .
Chapter V the writer states the study in summary that includes of Conclusion and Suggestion.
10 CHAPTER II
UNDERLYING THEORIES
This chapter focuses on giving a theoretical foundation of the study. It aims at giving direction to what extent the study is conducted. This research concern on the use of Scaffolding Talk technique to improve students’ speaking skill.
A.Speaking
Speaking skill is an ability to orally express opinion, thought, and feeling to other people both directly and directly. Speaking is an interactive process of constructing meaning that involves producing, receiving and processing information (Brown, 1994; Burns & Joyce, 1997). speaking is the skill that the students will be judged upon most in real-life situations. It is an important part of everyday interaction and most often the first impression of a person is based on his/her ability to speak fluently and comprehensively. So, as teachers, we have a responsibility to prepare the students as much as possible to be able to speak in English in the real world outside the classroom (Hornby 1995: 37).speaking is the competence to express explain and convey thinking, feeling, and idea. Speaking ability means the ability to think. So it is very important because language is primarily speech. Oral communication is seen as a basic skill so it is needed. Not only serious treatment is needed in teaching but also a great effort in order to be able to master the skill.
term of the ability to carry out conversation in the language (Fauziati 2005: 126). In addition, she asserts that speaking is an interactive process of constructing meaning that involves producing, receiving and processing information.
1. Types of Speaking Performances
Brown (2004: 140) describes five categories of speaking skill area. Those Five categories are as follows:
a. Imitative
This category includes the ability to practice an intonation and focusing on some particular elements of language form. That is just imitating a word, phrase or sentence. The important thing here is focusing on pronunciation. The teacher uses drilling in the teaching learning process. The reason is by using drilling, students get opportunity to listen and to orally repeat some words.
b. Intensive
This is the students’ speaking performance that is practicing some phonological and grammatical aspects of language. It usually places students doing the task in pairs (group work), for example, reading aloud that includes reading paragraph, reading dialogue with partner in turn etc. c. Responsive
requests and comments, giving instructions and directions. Those replies are usually sufficient and meaningful.
d. Interactive
The length and complexity of the interaction which sometimes includes multiple exchange and/or multiple participants.
e. Extensive
Teacher gives students extended monologues in the form of oral reports, summaries, and storytelling and short speeches.
2. Elements of Speaking
The ability to speak fluently presuppose not only knowledge of language features, but also the ability to process information and language on the spot ( Harmer, 2001 : 269 ).
a. Language features
Among the elements necessary for spoken production, are the following:
2) Expressive devices: native speaker of English change the pith and stress of particular parts of utterances, vary volume and speed, and show by other physical and non-verbal (paralinguistic) means how they are feeling(especially in face-to-face interactions).
3) Lexis and grammar: spontaneous speech id marked by the use of a number of commons lexical phrases, especially in the performance of certain language functions.
4) Negotiation language: effective speaking benefits from the negotiator language we use to seek clarification and show the structure of what we are saying. We often need to ask for clarification when we are listening to someone else talks and it is very crucial for students.
b. Mental/ social processing
Success of speaker’s productivity is also dependent upon the rapid
processing skills that talking necessitates.
2) Interacting with others: most speaking involves interaction with one or more participants. This means that effective speaking also involves a good deal of listening, an understanding of how the other participants are feeling. And a knowledge of how linguistically to take turns allow other to do.
3) (on the spot) information processing: quite apart from our response to other’s feelings, we also need to be able to process the information
they tell us the moment we get it.
3. The Principle for Teaching Speaking
Speaking is closely related to listening. The interaction between these two skills is shown in the conversation. There are five principles for teaching speaking as (Nunan, 2003: 54) are:
a. Be aware of the differences between second language and foreign language learning contexts: speaking is learned in two board contexts, foreign language and second language situations. The challenges you face as a teacher are determined partly by the target language context. Learning speaking skill is very is very challenging for students in FL context, because they have very few opportunities to use the target language outside the classroom.
b. Give students practice with both fluency and accuracy: Accuracy is the extent to which students’ speech matches what people actually say when
the language quickly and confidently, with few hesitations or unnatural pauses, false starts, word searches, etc.
c. Provide opportunities for students to talk by using group work or pair work, and limiting teacher talk: pair work and group work activities can be use to increase the amount of time that learners get to speak in the target language during lessons.
d. Plan speaking task that involve negotiation for meaning: it involves checking to see if you have understood what someone has said, clarifying your understanding, and confirming that someone has understood your meaning/by asking for clarification, repetition, or explanations during conversations, learners get the people they are speaking with to address them with language at a level they can learn from and understand.
e. Design classroom activities that involve guidance and practice in both transactional and interactional speaking: interactional speech is communicating with someone for social purpose. Transactional speech involves communicating.
4. Teaching Speaking
a. Pronunciation
(including the segmental features vowels and consonants and the stress and intonation patterns).
b. Grammar
Rules for forming words and making sentences. Grammar and pronunciation has a close relationship. In addition to the sound system learners must be taught by using structure system of language.
c. Vocabulary
Total number of words that make up a language. d. Fluently
Quality or condition of person to speaks a language easily and well. e. Comprehension
For oral communication certainly requires a subject to respond to speech as well as to initiate it (Harris, 1969:81)
Bygate (1987) in Nunan (1991:40) suggest that oral interactions can be characterized in terms of routines, which can either focus on information or interaction. So Teaching speaking is a crucial part of the language learning process. The teacher can use to help themselves expand their knowledge of language and their confidence in using it. These teachers help student learn to speak so that the student can use speaking to learn.
5. Technique in teaching speaking
a. Information Gap
Information gap is a useful activity in which one person has information that the other lack. They must use the target language to share the information. For instance, one student has the direction to a party and must give the information to a classmate.
b. Role Plays
Role plays are also excellent activities for speaking in the relatively safe environment of the classroom. In role play, students are given particular roles in the target language. For example, one student plays the role of a police officer trying to help the tourist file a report. Role plays give learners practice speaking the target language before they must do so in a real environment. c. Simulations
Simulations are more elaborate than role plays. In a simulation, properties and documents provide a somewhat realistic environment for language practice.
6. Classroom Speaking Activities
a) Acting from script
Playing scripts and acting out the dialogues are two kinds of acting scripts that should be considered by the teacher in the teaching and learning process. In the playing scripts, it is important for the students to teach it as real acting. The role of the teacher in this activity is as theatre directors, drawing attention to appropriate stress, intonation, and speed. This means that the lines they speak will have real meaning. By giving students practice in these things before they give their final performances, the teacher ensures that acting out is both a learning and language producing activity. In acting the dialogue, the students will be very helped if they are given time to rehearse their dialogues before the performance. The students will gain much more from the whole experience in the process.
b) Communication games
Games are designed to provoke communication between students. The games are made based on the principle of the information gap so that one student has to talk to a partner in order to solve a puzzle, draw a picture, put a thing in the right order, or find similarities and differences between pictures. Television and radio games, imported into the classroom, often provide good fluency activities.
c) Discussion
highly formal, whole-group staged events to informal small-group interactions. The first is the buzz groups that can be used for a whole range of discussion. For example, students are expected to predict the content of a reading text, or talk about their reactions after reading the text. The second is instant comments which can train students to respond fluently and immediately is to insert ‘instant comment’ mini activities into lessons. This
involves showing them photographs or introducing topics at any stage of a lesson and nominating students to say the first thing that comes into their head. The last is formal debates. Students prepare arguments in favour or against various propositions. The debate will be started when those who are appointed as ‘panel speaker’ produce well-rehearsed ‘writing like’ arguments whereas others, the audience, pitch in as the debate progresses with their own thoughts on the subject.
d) Prepared talks
Students make a presentation on a topic of their own choice. Such talks are not designed for informal spontaneous conversations because they are prepared and more ‘writing like’. However, if possible students should speak
from notes rather than from a script. e) Questionnaires
from questionnaires can then form the basis for written work, discussions, or prepared talks.
f) Simulation and Role play
Simulation and role play can be used to encourage general oral fluency, or to train students for specific situations. Students can act out simulation as them or take on the role of completely different character and express thoughts and feelings as they doing in the real world. Those activities can be used by teachers to teach speaking. Teachers can choose an activity that related to the topic and objective of the lesson. Besides, they must consider the situation, condition of the students and materials that will be taught. For example, they use simulation and role play activities when they teach expressions. Teachers can ask them to write some dialogues and after that they have to act them out in front of the class. It may be used by the teachers in using acting from script. In discussion, teachers can use some pictures or maybe videos in a certain situation. These activities can be used as the way to measure how far students can speak, say and express their feeling in English.
7. Characters of Successful Speaking
a. Learners talk a lot
As much as possible of the period of time allocated to the activity is a fact occupied by learners talk.
b. Participation is even
Classroom discussion is not dominated by a minority of talk active participants. It means that all students get a chance to speak and participate in class.
c. Motivation is high
All students have enthusiasm to speak in class. as Nunan (1991:39) states that the successful in speaking is measured through someone ability to carry out a conversation in the language.
B. Scaffolding Talk
Scaffolding Theory was introduced in the late 1950s by Jerome Bruner, a cognitive psychologist. He used the term to describe children's oral language acquisition that was helped by their parents when they first begins to speak.
Scaffolding as a teaching strategy originates from Lev Vygotsky’s
between what children can do by themselves and the next learning that they can be helped to achieve with competent assistance” (Raymond, 2000: 176).
Inherent in scaffolding from Lev Vygotsky’s (1978) idea of Zone of
proximal development vygotsky suggests that there are two part of learner’s developmental level. 1. The actual developmental level; the zone of proximal development is “the distance between the actual developmental level as determined by independent problem solving. It is the differences between the students actual development level determined by their capability to master the task independently 2. The potential developmental level; as determined through problem solving under the help of teacher, adult guidance or in collaboration with more capable peers (Jauhar 2011: 39). The ability to learn through instruction and help adults make students can understand and do a lot of things than if the students just learning independently.
Scaffolding talks are expressions of the teacher to interact or give instruction to his or her students in the classroom. ‘scaffolding’ was developed to describe the type of assistance offered by a teacher or peer to support learning. In this process of scaffolding, the teacher helps the student master a skill that the student is initially unable to acquire it independently. The teacher offers assistance that is beyond the student’s ability. The teacher
carry out a task, or achieve a goal which would be beyond his or her unassisted efforts”.
The writer conclude that scaffolding talk is teachers’ utterances that accompany his or her action in language classroom to provide guide, support in order to help the students understanding in assigning the students do some task by their instruction. Teacher usually try to use clear and concise words to make students understand what they have to do. Teacher support or assist students in the beginning of the learning and then give opportunity for students to take responsibility independently.
Concerning the definition of scaffolding talk above I want to unfold the characteristic of scaffolding talk according to Bruner in Cameron (2001 : 8) there are six characteristics of scaffolding talk :
a. Provides clear direction and reduces students’ confusion – Educators anticipate problems that students might encounter and then develop step by step instructions, which explain what a student must do to meet expectations,
b. Keeps students on task – By providing structure, scaffolding lesson or research project, provides pathways for the learners. The student can make decisions about which path to choose or what things to explore along the path but they cannot wander off of the path, which is the designated task.
d. Controlling the students frustrating during the task
e. Pointing out what was important to do or showing other way to solve, f. Demonstrating an idealized version of the task given.
Based on the characteristics scaffolding talk given by the expert above I can say that scaffolding talk in English teaching as a support, an assistance, a bridge or a guide provided by the teacher in order that the students are able to accomplish the target language in the ZPD area without any difficulties. There are six types of Scaffolding Talk according to Wood (1998, in Cameron 2001: 9) :
a. Modeling means that the teachers provide clear samples or models before the teachers ask the students to do the tasks and offering behavior for imitation including demonstrations of particular skill.
b. Explaining is necessary for the teachers to help the students to see the connection between things, make links between familiar and unfamiliar knowledge, and bridge gap between students’ previous knowledge and
the new knowledge or experience. Describing, telling and bridging the students to promote students’ understanding.
c. inviting students participation : providing the student to able to participate in the learning process. Teachers provide opportunities to the students to be able to join in the teaching learning process through eliciting, for example: “how do you know and inviting to expand in
meaningful ways, such as: “tell us more about that, “give more details”
d. Instructing: the teacher tells the students what to do or explanation of how something must be done.
e. Questioning
Kind of questioning according Debra, Susan, and Hopper (2006:71) are: 1) Speculative : questions inviting a response with no predetermined answer, often opinions, imaginings, ideas. For example what do you think about Gembira Loka Zoo?
2) Process : questions inviting students to articulate their understanding of learning processes/explain their thinking, like ‘can you explain
why?
3) Procedural : questions relating to the organization and management of the lesson
f. Reinforcing
There are two kinds of reinforcing that is:
1) Verbal reinforcing is a teacher’s comments offering praise and encouragements. providing information regarding the student’s
performance, giving feedback such as yes good, well done, excellent, etc.
2) Gestural reinforcing refers to the teacher’s “smiling, raising eyebrow, clapping hands, signaling O.K, shaking head, etc.”
a. Teacher explain the materials,
b. Giving example of the task to the students related with the materials, c. Modeling, showing students examples of work produce by teacher,
provide assistance, guide, giving clues which provoke the students toward independent learning,
d. Demonstrating, illustrating the procedures from the teacher through work product, supporting the students as they learn and practice procedures,
e. Encourage the students to learn complete their task independently.
27 CHAPTER III
METHODOLOGY OF RESEARCH
In this chapter, the researcher carries out the research methodology, which includes: Setting of the Research, Method of the Research, Subject of the Research, Data Collection Method, Research Instrument, Evaluation Criteria, Research Procedure, The Model of Research and Technique of Data Analysis.
A. The Setting of the Research
1. General situation of MTs N Andong
The research was conducted at Madrasah Tsanawiyah Negeri (MTsN) Andong Boyolali. MTs N Andong is located in Kacangan Andong street Boyolali 57384, phone number (0271)7081585 / 7893064.
The location of the school is near with Traditional Market. In the west of the school there are SMP BK and SD Mojo 1 and In the east of the school is SMK Muhammadiyah 02 Andong. The location of school beside of public transportation. The society surroding MTs N Andong work as a trader and and a lot of store in there.
2. The List of Educational Facilities and Tools
teaching- learning process because all of academicians’ need can be provided. The educational facilities could be seen in the table below:
TABLE 3.1
Educational Facilities and Tools in MTSN Andong in the Academic Year of 2013/2014
No Facilities Total Condition
1. Classroom 30 unit Fine
14. Students’ toilet 5 unit Not Fine
15. Parked place 1 unit Fine
Source: Documentation of MTs N Andong 2013/2014 3. The List of Teacher of MTs N Andong
TABLE 3.2
List of Teachers (PNS) in MTS N Andong of the Academic Year of 2013/2014
NO NAME STATUS
1 H. Chusni, S Ag, M Pd Headmaster/Arabic language 2 In'am Fauzan, S Ag Teacher of Javanese Language 3 Anis Almuthmainnah, S Ag Teacher of Mathematics 4 Sudirmanto, S Pd, M Pd Teacher of Social Science 5 Dra. Churiyati Alifah Teacher of Social Science 6 Dra. Budi Astuti Teacher of Indonesian Language 7 H. Suraji, S.Pdi Teacher of Aqidah Ahlak/mulok
agama
14 BambangSusilo Teacher of seni budaya/ Javanese Language
15 Saproni, S PdI Teacher of Aqidah Ahlak
16 Jumangin, S PdI Teacher of Aqidah Ahlak
17 Muhaimin, S Ag Teacher of Quran Hadist
18 Agus Wardono, S Pd Teacher of Mathematics 19 Tinuk Sunarsi, S Psi Teacher of Social Science
20 Suwardi, S Pd Teacher of Natural Science
21 Nurul Hidayah Alim, S Pd Teacher of Indonesian Language
22 Dra. Sugiyanti Teacher of PKN
23 Siti Qibtiyah, S Pd Teacher of Indonesian Language 24 Siti Wahidatul Choiriyah,S Ag Teacher of Quran Hadist
25 Budiyarto, S Pd Teacher of PKN
26 Dra. Wiji Haryanti Teacher of SKI
27 M. Rasid, S Ag Teacher of Arabic Language
28 Samlani, S Pd Teacher of Indonesian Language
29 Ikhsanudin, S Pd Teacher of Social Science/ PKN 30 Nanik Suryani Rohmawati, Sag Teacher of Fiqih
31 Mulyata, S Si Teacher of Mathematics
32 Suwarsih, S Pd Teacher of Social Science 33 Sri Lestari, S PdI Teacher of Arabic Language 34 Tri Winarsih, S Pd Teacher of Natural Science
35 Mulyono, S PdI Teacher of Quran Hadist/BTA
37 Heri Eko Wardoyo, S Pd Teacher of English language 38 Naimatul Laila Qomariyah, S PdI Teacher of English language 39 Ali Choirudin, S Pd Teacher of Penjaskes
40 Mun Arini, S Pd Teacher of Mathematics
41 Siti Muyasaroh, S Ag Teacher of Indonesian Language 42 Budhi Suwiji, S Sos Teacher of Social Science/ PKN 43 Suhartini, S Pd Teacher of English language 44 Agus Cahyono, S Pd Teacher of Mathematics 45 Siti Alfiyah, S Ag Teacher of Fiqih / SKI
46 Kuwat, S Pd Teacher of Fiqih / PKN
47 Jamal Thoriq, S PdI Teacher of Arabic Language / SKI
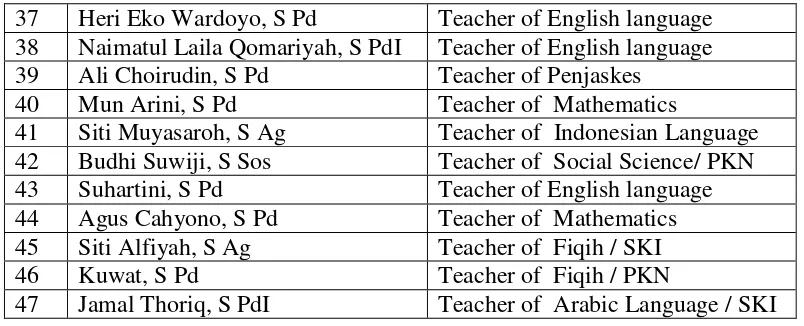
TABLE 3. 3
List of Non Permanent Teachers in MTS N Andong of the Academic Year of 2013/ 2014
NO NAME STATUS
1 Muzazin, S Pd Teacher of Indonesian language
2 Estinigsih Sri Suprapti, S Pd Teacher of English language 3 M. Nur Da'i, S PdI Teacher of English language 4 H. Ali Martono, S Ag Teacher of Arabic Language 5 David Kurniawan, S Pd Teacher of Penjaskes
6 Wiwin Puji Lestari, S Pd Teacher of Natural Science 7 Zakiyah Anawati, S Pd Teacher of Natural Science 8 Widi Astuti, S PdI Teacher of English language
9 Niki Rohmana, S Kom Teacher of TIK
10 M. Ja'farin, S Kom Teacher of TIK
11 Sri Lestari, S E Teacher of Ketrampilan 12 Etik Purwaningsih, SE Teacher of Social Science/
Ketrampilan
13 Agus Setiawan, S Pd Teacher of Penjaskes
TABLE 3. 4
List of Staff (PNS and Non Permanent) in MTS N Andong of the Academic Year of 2013/ 2014
NO NAME STATUS
1 Dian Nirwana, S Sos Ka.Ur. TU
2 Any Rokhnana Staff TU
3 Aminatun Staff TU
4 Damin Staff TU
5 Baderun Penjaga
6 Sukri Penjaga
7 Moh. Habib Security
8 Ahmad Jabir Staff Perpustakaan
9 Syahroni Penjaga
10 Joni Dwi Sulistiyanto, ST Staff TU 11 Eti Nuryanti, SE Staff TU 4. The Distribution of the class
Students are people who like to get something new, not only to get new knowledge, but also other aspects in their life such as; social relation, morality and culture. They learn in school at certain time. The distribution of the class of MTs N Andong could be seen in the table below:
TABLE 3. 5
The Distribution of the Class of MTS N Andong in The Academic Year of 2013/ 2014
No Class Male Female Total
1 First 206 206 412
2 Second 181 177 358
3 Third 161 182 343
B. The Method of Research
The writer uses classroom action research (CAR) in this research. The definition of CAR according to Taggart, 1988: in (Richards, 1994: 12) classroom action research is research typically involves small-scale investigative projects in the teacher’s own classroom and consists of a number of phases, which often recur in cycles. The cycles consist of planning, action, observation, and reflection.
The definition of classroom action research according Iraís, Tlaxcala in (Anne Burns 2009: 16 ) Classroom Action research is carried out by teachers in their context, in their classrooms. Teachers identify a problem or an area they wish to improve and based on theory or experience or a hypothesis they think of an intervention. They document the intervention and results of it. If the results are positive they could lead to the dissemination of the information. If not, the cycle may be started again.
C. The Subject of the Research
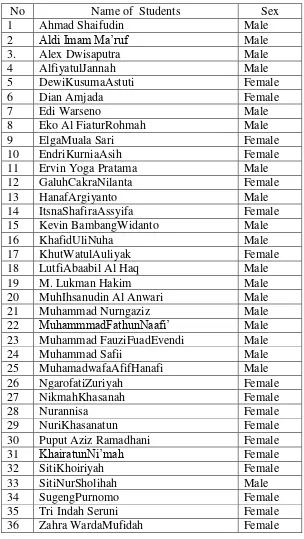
TABLE 3. 6
List of VIII B Class Group of MTs N Andong in the Academic Year of 2013/ 2014
5 DewiKusumaAstuti Female
6 Dian Amjada Female
7 Edi Warseno Male
8 Eko Al FiaturRohmah Male
9 ElgaMuala Sari Female
10 EndriKurniaAsih Female
11 Ervin Yoga Pratama Male
12 GaluhCakraNilanta Female
13 HanafArgiyanto Male
14 ItsnaShafiraAssyifa Female
15 Kevin BambangWidanto Male
16 KhafidUliNuha Male
17 KhutWatulAuliyak Female
18 LutfiAbaabil Al Haq Male
19 M. Lukman Hakim Male
20 MuhIhsanudin Al Anwari Male
21 Muhammad Nurngaziz Male
22 MuhammmadFathunNaafi’ Male
23 Muhammad FauziFuadEvendi Male
24 Muhammad Safii Male
25 MuhamadwafaAfifHanafi Male
26 NgarofatiZuriyah Female
27 NikmahKhasanah Female
28 Nurannisa Female
29 NuriKhasanatun Female
30 Puput Aziz Ramadhani Female
31 KhairatunNi’mah Female
32 SitiKhoiriyah Female
33 SitiNurSholihah Male
34 SugengPurnomo Female
35 Tri Indah Seruni Female
D. Data Collection Method
The researcher will present the act of collecting data as follows: 1)Test.
According Arikunto (2010:226) test is used to measure the basic capabilities and achievements. Especially for learning achievement, tests commonly used in schools can be divided into two general categories:
a) Tests Created by Teacher
Tests made by the teacher with a particular procedure, but no trials have repeatedly then is not yet known features and benefits. b)Standardized Test
Tests that usually already provided in the testing agencies, which are already guaranteed quality. And Standardized Test trials has experienced repeatedly so it can be said to be good.
Researcher prefers tests made by teachers. Because teacher can measures students difficulties in learning English, especially in speaking skill. the writer uses pre-test and post-test. Pre-test is given to students at the very beginning of teaching and learning process then post-test is given after students receiving the method from teacher. Pre and post-test are to knowing the differences of the students ability before and after the teacher use the method.
2)Observation.
In this research, the researcher observes the learning process, notices all the activities related with learning process use check list.
3) Documentation.
Method of documentation that is looking for data about things or variables in the form of notes, transcripts, books, newspapers, magazines, etc.(Arikunto: 2010:274).
In this case, the researcher chooses to use the media to record the activities of students in class so that the data obtained is valid, which is by using cameras and video records.
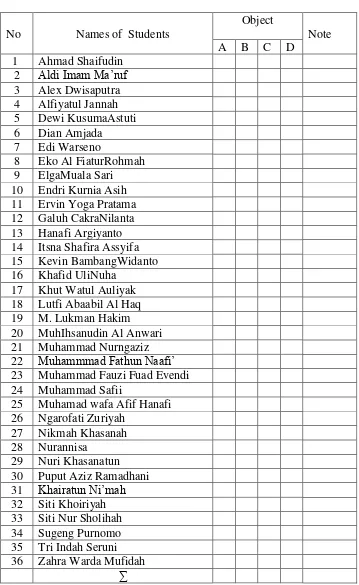
E.Research Instrument
The instrument used to collect the data is observation sheets and test. The writer use pre-test and post-test.
Questions Sheet
Pre-test retell your experience in the past about your holiday! Post-test I Please retell the video about ‘’My Beautiful Holiday at
Balekambang’’ with your own language.
TABLE 3. 7 3 Alex Dwisaputra 4 Alfiyatul Jannah 5 Dewi KusumaAstuti 6 Dian Amjada
7 Edi Warseno
8 Eko Al FiaturRohmah 9 ElgaMuala Sari 10 Endri Kurnia Asih 11 Ervin Yoga Pratama 12 Galuh CakraNilanta 13 Hanafi Argiyanto 14 Itsna Shafira Assyifa 15 Kevin BambangWidanto 16 Khafid UliNuha
17 Khut Watul Auliyak 18 Lutfi Abaabil Al Haq 19 M. Lukman Hakim 20 MuhIhsanudin Al Anwari 21 Muhammad Nurngaziz 22 Muhammmad Fathun Naafi’ 23 Muhammad Fauzi Fuad Evendi 24 Muhammad Safii
25 Muhamad wafa Afif Hanafi 26 Ngarofati Zuriyah
27 Nikmah Khasanah 28 Nurannisa
29 Nuri Khasanatun 30 Puput Aziz Ramadhani 31 Khairatun Ni’mah 32 Siti Khoiriyah 33 Siti Nur Sholihah 34 Sugeng Purnomo 35 Tri Indah Seruni 36 Zahra Warda Mufidah
Explanation :
A: Pay attention
B: Activeness in asking questions C: Activeness in responding questions D: Enthusiasm in doing test
F. Evaluation Criteria
Table 3. 8
The Assessment Scale for Oral Ability
In the oral test, the writer used speaking assessment rubric (http://aguswuryanto.wordpress.com) in the following:
Aspect Score Details
Pronunciation
25 Easy to understand pronunciation and have a native accent 20 Easy to understand though with a certain accent
15 There is a problem of pronunciation that make the listener must concentrate fully and sometimes there are misunderstandings
10 It is difficult to understand because of pronunciation problems, often asked to repeat
5 A serious pronunciation problems that cannot be understood
Grammar
25 No or few grammatical error
20 Occasionally makes grammatical errors but does not affect the meaning
15 Often make grammatical errors which affect meaning 10 A lot of grammatical errors that impede meaning and often
rearranging sentences
20 Sometimes uses inappropriate vocabulary
15 Frequent use of inappropriate vocabulary, conversation is limited due to limited vocabulary
5 A very limited vocabulary so that the conversation is not possible
Content/idea
25 Easy to express ideas although there is repeating in certain part
5 Limited to express ideas communication difficult although in simple dialogue
TABLE 3. 9
The Students’ Achievement
Criteria of Assessment Grade
91-100 Excellent
G. The Procedures of Research
This research used classroom action research and the procedures are follows:
a. Planning
The activities in the planning are:
1)Preparing materials; making lesson plan, and design the steps in doing the action
3)Preparing sheets for classroom observation (to know the situation of teaching learning process when the technique applied)
4)Preparing a test (to know whether students’ speaking skill improve or not).
b. Action
1)Giving pre-test
2)Teaching speaking using Scaffolding Talk Technique
3)Giving opportunity to the students to ask about difficulties or problem.
4)Giving post-test c. Observation
Observing is an observation activity to know how far the action effect have reach target. Observation was conducted by observing and scoring through oral tests to students’ ability in speaking
English. d. Reflection
Reflection was conducted for evaluating all of the actions done in every cycle. The result of the observation is analyzed, it is to remember what occurs that has been written in observation. Reflection seeks to memorize sense of the process, problems and real issues in strategic action. The writer’s reflection is done by
teaching in the first cycle, she will try to solve the problem in the next cycle.
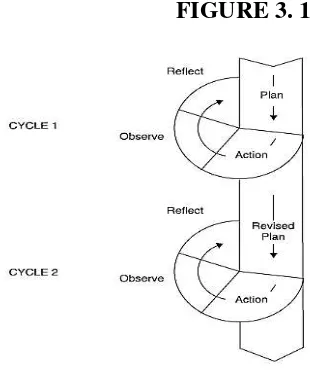
H.The Model of Research
The model which is used in implementation of this research as follow: FIGURE 3. 1
Figure Cyclical AR model based on Kemmis and Mc Taggart (1988) in Anne Burns (2009)
I. Technique of Data Analysis
After collecting the data, the writer will calculate the mean of the students’
score. This method is used to know the students’ score of speaking in each
cycle. The formula according Hadi (1981: 246) is: a.
M =
∑XN
Where,
M : Mean of students’ score
∑X : The sum of students’ score
b. SD (Standart Deviation)
The fisrt step, the writer calculate SD, the formula is:
SDD = √∑ D
SD : Deviasion Standart for one sample t-test
D : Different between pre-test post-test
N : Number of observation in sample c. T-test
After calculating the SD, the writer doing test to know is there any significant differences or not between pre-test and post-test,
to
t0 : T-test for the differences of pre-test and post-test
SD : Deviation Standart for one sample t-test
42
CHAPTER IV
DATA ANALYSIS AND DISCUSSION
This chapter focuses on analyzing the collected data. The researcher gives the details of the findings. In this research, the writer analyzed data collected from thirty six students of the class VIIIB MTs Negeri Andong in the academic year 2013/ 2014. It displays the finding of the collected data since in the beginning until the end of the research. The findings consist of the results of the cycle I, cycle II. The two cycles are treatment of the implementation of the Scaffolding Talk technique in the speaking skill.
A. Data Presentation 1. Cycle 1
a. The result of students’ score of pre-test can be seen in the table as follows:
Table 4.1 The result of pre test
No Names of Students Pre Test
1 Ahmad Shaifudin 60
2 Aldi Imam Ma’ruf 60
3 Alex Dwisaputra 30
4 Alfiyatul Jannah 60
5 Dewi KusumaAstuti 60
6 Dian Amjada 30
7 Edi Warseno 45
8 Eko Al FiaturRohmah 35
9 ElgaMuala Sari 65
11 Ervin Yoga Pratama 40
12 Galuh CakraNilanta 45
13 Hanafi Argiyanto 60
14 Itsna Shafira Assyifa 55
15 Kevin BambangWidanto 30
16 Khafid UliNuha 30
17 Khut Watul Auliyak 45
18 Lutfi Abaabil Al Haq 30
19 M. Lukman Hakim 35
20 MuhIhsanudin Al Anwari 40
21 Muhammad Nurngaziz 50
22 Muhammmad Fathun Naafi’ 35
23 Muhammad Fauzi Fuad Evendi 35
24 Muhammad Safii 65
31 Khairatun Ni’mah 35
32 Siti Khoiriyah 30
Explanation :
A: Pay attention : 15 B: Activeness in asking questions : 3 C: Activeness in responding questions : 4 D: Enthusiasm in doing test : 14
12 Galuh CakraNilanta 75
13 Hanafi Argiyanto 80
14 Itsna Shafira Assyifa 75
15 Kevin BambangWidanto 55
16 Khafid UliNuha 55
17 Khut Watul Auliyak 75
18 Lutfi Abaabil Al Haq 50
19 M. Lukman Hakim 70
20 MuhIhsanudin Al Anwari 55
21 Muhammad Nurngaziz 75
22 Muhammmad Fathun Naafi’ 60 23 Muhammad Fauzi Fuad Evendi 55
24 Muhammad Safii 60
25 Muhamad wafa Afif Hanafi 80
26 Ngarofati Zuriyah 75
28 Nurannisa 80
29 Nuri Khasanatun 55
30 Puput Aziz Ramadhani 75
31 Khairatun Ni’mah 55
32 Siti Khoiriyah 60
12 Galuh CakraNilanta 90
13 Hanafi Argiyanto 85
14 Itsna Shafira Assyifa 80
15 Kevin BambangWidanto 70
16 Khafid UliNuha 65
17 Khut Watul Auliyak 80
18 Lutfi Abaabil Al Haq 65
19 M. Lukman Hakim 85
20 MuhIhsanudin Al Anwari 70
21 Muhammad Nurngaziz 80
22 Muhammmad Fathun Naafi’ 70 23 Muhammad Fauzi Fuad Evendi 50
24 Muhammad Safii 50
25 Muhamad wafa Afif Hanafi 85
26 Ngarofati Zuriyah 75
28 Nurannisa 90
29 Nuri Khasanatun 80
30 Puput Aziz Ramadhani 65
31 Khairatun Ni’mah 75
28 Nurannisa 80 90 10 100
Explanation :
A: Pay attention : 10
B: Activeness in asking questions : 6 C: Activeness in responding questions : 5 D: Enthusiasm in doing test : 15 B.Data Analysis
1. Cycle 1
Moreover, the researcher would like to analyze students’ improvement in speaking skill by calculate the mean of the students’ score of pre test.
The average of the students’ score was calculated as follow:
Mean = the total score =1695 = 47,08 the number of students 36
22 Muhammmad Fathun Naafi’
23 Muhammad Fauzi Fuad Evendi
24 Muhammad Safii
25 Muhamad wafa Afif Hanafi
26 Ngarofati Zuriyah
27 Nikmah Khasanah
28 Nurannisa
29 Nuri Khasanatun
30 Puput Aziz Ramadhani 31 Khairatun Ni’mah
32 Siti Khoiriyah
33 Siti Nur Sholihah
34 Sugeng Purnomo
35 Tri Indah Seruni
36 Zahra Warda Mufidah
TABLE 4. 7
The Classification of Pre-test result Criteria of
Assessment
Frequency Percentile Rank (%)
Grade
91-100 - - Excellent
81-90 - - Very good
71-80 1 2,78 Good
61-70 4 11,11 Fair
51-60 10 27,78 Poor
Less than 50 21 58,33 Very poor
TABLE 4. 8
The result of observation cycle 1
Aspect Total
Pay attention 15
Activeness in asking question 3
Activeness in responding question 4
Enthusiasm in doing test 14
2. Cycle II
a. Mean of post test I
M = ∑XN
M =240036
TABLE 4. 9
The Classification of Post-test 1 result Criteria of
c. SD of post test I and Post test II
From the data above, the teacher calculated SD of post test I and Post test II d. T-test calculation
T calculation is 3,18
TABLE 4. 11
The result of observation cycle 1I
Aspect Total
Pay attention 10
Activeness in asking question 6
Activeness in responding question 5
Enthusiasm in doing test 15
C.Discussion
In this research, the writer acts as the teacher and learning process observed by Mrs. Suhartini is English teacher in there . The writer arranged two cycles, each cycle consist of planning, action, observing and reflection. The whole steps of this research are explained in the description bellow: 1. Cycle 1
a. Planning
Before conducting the research, the writer prepared the instruments of the research, they are as follows:
1) Lesson plan
In order to control the teaching learning process, the writer used the lesson plan as guidance for the writer’s activities in the
2) Material
In the first cycle, the writer used theme about “telling experiences about your last holiday ”. She used several books as a
resource and looking for the material in the internet. 3) Teaching aid
The writer prepared some instrument, such as: blank paper, rubric, and board marker.
4) Sheet for classroom observation
Sheet for classroom observation was prepared in order to know the condition of teaching learning process.
5) Test (pre-test and post test)
Pre-test was a test that was given to the students before the teaching learning process. Meanwhile, post-test was a test that was given to the students after teaching learning process was conducted.
b. Implementation of the action
Teacher : “Assalamu’alaikum wr.wb.” Students : “Waa’aikumussalamw.wb.” Teacher : “Good morning everybody.” Students : “Good morning miss.” Teacher : “How are you today?”
Students : (together) “we are fine, thank you and you?”
Teacher : “I’m fine too thank you. Ok class, let’s start our meeting by say basmalah together.”
Students : (together) “Bismillahirrahmaanirrakhim.” Teacher : “Any one absen today”?
Students : “Nihil miss”(nothing).
Teacher : “Ok, Today we are going to discuss about some materials, but let me introduce myself first, my name is Tika, you should call me Ms. Tika, for the time I’m being the English teacher in this class, any
question?”
Students : “No.”
Teacher : “Thank you, by the way have you ever gone to the zoo?”
Students : (together) “yes.” Teacher : “Where is it?”.
Teacher : “Any volunteer to retell your experience in front of class?”
Students : “Malu miss. Nggak bisa ngomong inggris, pake
bahasa Indonesia saja y miss.”(Shy miss, we can’t
speak in English, use Indonesian language miss) Teacher : “Don’t be shy and afraid if you make a mistake, now
we are going to try speaking English mostly, are you ready?”
Students : “Ready”
Teacher walked around the class and asked a student. Teachers :”what is your name?”
A Student : “Muhammad safii”.
Teacher :”can you tell me what did you do at the last holiday?”
A Student : “pergi ke jogja miss.” (went to jogja miss) Teacher : “in jogja, did you find something wonderful?” A student :” No miss, Cuma pergi ke malioboro.”(just went to
malioboro)
Teacher : “That’s all? How did you go there? By motorcycle or bus?”
Teacher :” now I ask you to retell your experience about your last holiday to your friends in front of class.15 minutes is enough?”
Then the teacher asking to the students to do a pre-test that is by retelling their experience in the past in front of class. The students looked noisy because some students asked to other about their assignment. Most of them could not do their task well, because they felt shy. Other reason is that they lack of vocabularies. When the time was over, the teacher asked the students who want to be the volunteer first? But no one raised their hands finally the teacher pointed one of the students in the class. Then the students pointed by teacher, pointed other friends and so on.
Teacher : (Apakah semuanya sudah maju?) “Has everybody come forward?”
Students : “Yes miss.” (together)
Teacher : “For the next meeting we still discuss the same theme, i hope you study more, Because time is up so enough for meeting today. Let’s say hamdalah together.”
Students : “Alhamdulillahirabbil’alamin” Teacher : “Wassalamu’alaikum Wr. Wb” Students : “Wa’alaikum salam Wr.Wb”
starting the lesson, but that day was different, they looked very happy when we came. After reading holy Qur’an and asmaul husna, the teacher began the lesson. The students had finished the pre-test yesterday. The teacher told the students about the topic that day, and then the teacher asked the students about it. The situation in the class as follows:
Teacher :” Good morning students, how are you today?” Students :” Good morning Miss, we are fine thank you, and
you?”.
Teacher :”Im fine too thank you. Ok class, let’s start our meeting by saying basmalah together.
Students : “Bissmillahhirohmanirrohim.”
Teacher :”Today, we will discuss about recount text, (Pernahkah kalian mendengar tentang recount text?) have you ever heard about recount text?”
Students : ”Yes Miss”.
Teacher : ”Ok, what is recount text itself?
Class became noisy, some of them tried to answer as they know, but the others just silent. Then, the teacher gave explanation about the text.
Teacher : ”(Teks yang menceritakan serangkaian peristiwa
atau pengalaman yang terjadi diwaktu lampau ).
Recount text is a text that tells a series of events or experiences that occurred in the past.
Almost students look confused then the teacher wrote on the white board and explained the generic structure of the text. She also explained about tense used in past tense.
Teacher : “What kind of tense used in recount text? Past tense, present tense, future tense or what?”
A Student : “Past tense, Miss.” Teacher : “Yes, you’re”.
She gave the materials about my holiday and gave vocabulary about it. Teacher :” (Ok, hari ini kita akan membahas tentang liburan,
tapi sebelumnya kalian harus mengetahui kosa kata yang berhubungan dengan liburan). Today we will study about holiday, but before starting it, you have to know the vocabulary about it, Who can mention the vocabulary related with the holiday?”
A Student :” buy souvenir, take a picture
Students mentioned some vocabularies, and then the teacher wrote in the white board She also gave another vocabulary. Then teacher give example about ‘My Holidayat Borobudur Temple’ and give some question related
with the text and ask students to answer it orally.
Teacher : ‘’when did the writer and his friends visit Borobudur Temple?’’
Khoir : ‘’ last holiday miss’’
Nisa : ‘’ taking a picture with a foreign tourist.’’
Teacher : “now we are going to discuss about past tense, if we want to share a story in the previous time, we use past tense. for example Last holiday my friends and I visited Borobudur Temple.
Teacher :” Ok make a sentence, please you!” A student : “ I go to solo yesterday.”
Teacher : “ yes, change into past tense!” A student : “ I went to solo yesterday.”
Teacher : “ very good, i’m going to write some words. Play played played
Go went gone
Buy bought bought
Teacher : “choose one word then please make a sentence, any volunteer first?
Students : silent
Teacher :”siapa yang mau mencoba membuat kalimat didepan kelas saya kasih hadiah(who want to try make a sentence in front of class i will give you reward).”
Teacher : “that good thank you, but remember recount text using past tense, so played not play, do you understand?
Let’s see the form of these verbs above, there are regular verbs and irregular verbs. After giving explanation, she asked them to open the book and shown example of recount text about my holiday in the book and ask some students to read the text and give correct pronunciation then identify generic structure of the text together.
Teacher : ”Now, please open page 9. There is a text about my holiday, read then tried to analyze the generic structure.
After analyzing it the teacher discussed and asked whether any question or not, then she closed the meeting.
TABLE 4. 12 Type of Scaffolding talk
NO (Pernahkah kalian mendengar tentang recount
text?) have you ever heard about recount text?”
2 ”Ok, what is recounttext itself?“
3 Recount text is a text that tells a series of events or experiences that occurred in the past.