i
ITEMS ANALYSIS ON THE SCORE OF THE ENGLISH
SUMMATIVE TEST
(A Descriptive Study of the Tenth Grade Students of SMK N 3 Salatiga in
the Academic Year of 2013/2014)
A GRADUATING PAPER
Submitted to the Board of Examiners as a Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
for the Degree of Sarjana Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris (S.Pd.I) in the English Department of Education Faculty
SITI MUNADLIROH
NIM. 11310142
ENGLISH DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION FACULTY
STATE INSTITUTE FOR ISLAMIC STUDIES (STAIN)
SALATIGA
v
MOTTO
“Intelligence is not the determinant of success, but hard work is the real determinant of
your success.”
~Alexander Graham Bell~
-
“No surrender term. Winners never give up, because people who give up would never win.”
~Ted Turner~
-
“Life is like to reach the bike, drive as fast as possible.”
vi
DEDICATION
This work is sincerely dedicated for:
1. My beloved parents, my father (Sujadi) and my mother (Siti alfiah) who
always pray, guide, motivate me to become better person.
2. My beloved sisters (Nurul Hikmah and Nana Farida) who fill my life with
love and affection.
3. My beloved uncle and aunt, my uncle (Yaseri) and my aunt (Sujiyem)
who motivate me directly and my big family who fill my life with love,
affection and pleasantness.
4. My closest friends at STAIN Salatiga who always motivate and help me.
Too many memories and impressions together with you and I can’t forget
vii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Bismillahirrahmanirrahim,
In the name of Allah, the most gracious and merciful, the kings of universe
and space. Thank you to Allah because the writer could complete this graduating
paper as one of requirement to finished study in English Department faculty of States
Institute for Islamic Studies.
This graduating paper would not have been completed without support,
guidance and help from individual and institution. Therefore, I would like to express
special thank you to:
1. Mr. Dr. Rahmat Hariyadi, M.Pd as the Rector of State Institute for Islamic
Studies Salatiga.
2. Mrs. Rr. Dewi Wahyu Mustikasari, M.Pd as the head of English Department of
States Institute for Islamic Studies (STAIN) Salatiga and the consultant of this
graduating paper. Thank you for all of your suggestion, recommendation and
support for this graduating paper from the beginning until the end.
3. Mrs. Setia Rini, M.Pd as consultant who has educated, supported, directed and
given the writer advice, suggestion and recomendation for this graduating paper
from beginning until the end. Thank you for your patience and care.
4. All lecturers in English Department Faculty of STAIN Salatiga. Thank you for
ix
ABSTRACT
Munadliroh, Siti. 2014. “Items Analysis on the Students’ Score of the English
Summative Test (Descriptive Study of the Tenth Grade Students of SMK N 3 Salatiga in the Academic Year of 2013/2014)”. Graduating Paper. Educational Faculty. English Department. State Institute for Islamic Studies (STAIN). Consultant: Setia Rini, M. Pd
This research was aimed to give a description for the readers about an items analysis on the students’ score of the English summative test. This research can be used for as an input for the readers; especially for the English teachers, the headmaster, and all people who are involved and responsible in developing good quality of test. The objective of this research was to measure and find out the difficulty level and discrimination index on items of English summative test score of the tenth grade students at SMK N 3 Salatiga in the academic years of 2013/2014. Type of this research was descriptive study. This research was compiled in quantitative method. It was applied purposive sampling technique. The total number of the sample was three classes which were 102 students. The data of this study was taken from observation and documentation which used to obtain the school data like students’ name and general information. The result of this research were as follows, based on the data of difficulty index, there were 21 questions (42%) that placed in the normal position that included to the criteria of moderate question. In the contrary, there were 27 questions (54%) that included to the criteria of easy question and there were 2 questions (4%) that included to the criteria of hard question. Based on the data of discrimination index, there were 24 questions (42%) were in good criteria of discrimination index. Then 17 questions (34%) were in satisfactory criteria of discrimination index. In contrary, the writer found 9 questions (18%) items that were in the poor criteria. It were rejected either due to the difficulty level or discrimination index. It could be concluded that there were 9 questions that must be removed or revised to be good questions.
x
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE i
DECLARATION ii
ATTENTIVE COUNSELOR NOTES iii
PAGE OF CERTIFICATION iv
MOTTO v
DEDICATION vi
ACKNOWLEDGMENT vii
ABSTRACT ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS x
LIST OF TABLES, CHART AND FIGURE xiii
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
A. Background of Study 1
B. Problem Statements 6
C. Objectives of the Study 6
D. Benefits of Study 6
E. Scope Limitation of the Study 7
F. Definition of the Key Terms 7
G. Review of Previous Research 9
H. Research Organization 10
CHAPTER II THEORITICAL FRAMEWORK
A. Language Test 12
B. Test 13
1. Definition of Test 13
xi
C. Summative Test 23
1. Definition of Summative Test 22
2. Purpose of Summative Test 23
3. Advantages of Summative Test 23
4. Assessment Aspect of Summative Test 24
D. The Characteristics of a Good Test 24
2. Rational of Curriculum 2013 Development 36
CHAPTER III METHODOLOGY OF RESEARCH
A. Setting of The Research 37
B. Subject of Research 38
C. Type and Method of the Research 42
D. Technique of Collecting Data 43
E. Technique of Analyzing Data 45
CHAPTER IV DATA ANALYSIS
A. Analysis 49
xii
2. Analysis of the Discrimination Index 53
B. Interpetation of Data 60
C. Finding and Discussion 64
CHAPTER V CLOSURE
A. Conclusions 68
B. Suggestions 69
BIBLIOGRAPHY
CURRICULUM VITAE
xiii
LIST OF TABLES AND FIGURES
Table 3.1 List of X-O2 Students’ Scores of SMK N 3 Salatiga 39 Table 3.2 List of X-W1 Students’ Scores of SMK N 3 Salatiga 40 Table 3.3 List of X-TKR1 Students’ Scores of SMK N 3 Salatiga 41 Table 3.4 Classification of the Difficulty Index 46
Table 3.5 Classification of the Discrimination Index 48
Table 4.1 List of the Difficulty Index on the Test Items 51
Table 4.2 Classification of Discrimination Index 55
Table 4.3 List of Upper and Lower Group based on the Scores 56 Table 4.4 List of the Discrimination Index on the Test Items 58
Table 4.5 List of the Difficulty Index on the Test Items 60 Table 4 6 List of the Discrimination Index on the Test Items 62
Figure 4 1 Item Frequency for each Difficulty Index Range 65
Figure 4.2 Item Frequency for each Discrimination Index
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A. Background of Study
English is a tool of communication to get information and it can be
used in formal education as academic subject matter. In the global era,
English is increasingly needed because it is one of the international languages
mostly used in world.
English as an International language has an important role in any
sphere of activities to be used as a means of communication both written and
spoken, so English language becomes the first foreign language that should be
taught to English students for every level of education in Indonesia. English is
taught as a compulsory subject in elementary, junior and senior high schools,
and as a complementary subject in university.
The purpose of teaching English in Indonesia is to develop the
communication skills especially in oral and written skills (listening, speaking,
reading and writing). To reach the purpose of the instructional activities, the
teachers apply evaluation to measure how far the students understand about
the material.
In education, goals are identified on the basis of students and society’s
need. Based on this needs, educational programs are established so that
2 students’ behaviour is needed as to judge the success of the students in
reaching the goals. Evaluation must be done because education is not
automatically successful. The core of evaluation is then to evaluate the
success of students which is periodically gathered in terms of the objectives.
One of the most important aspects of teaching learning process is
evaluation. It contributes directly to the teaching and learning process used in
classroom instruction. According to Sudijono (1996: 13), the main focus of
classroom evaluation is the students and their learning process. To measure
the students’ competence in the learning process, the teachers need to hold an
evaluation. Evaluation plays an important role in teaching learning activities.
It is an integral part of instructional program.
The measurement of educational achievement is essential to effective
formal education. Formal education is a complex process, requiring a great
deal of time and money and cooperative efforts of many people. Effort must
be directed toward the attainment of specific goals, because education is not
automatically successful. Teachers, students, parents and school officials need
to know periodically how successful their efforts have been, so that they can
decide which practices to continue and which to change (Gronlund, 1982: 9).
Teachers are those who know the characteristics of their classes. Thus,
they are the best position to construct a test to measure their students’
achievement and it is not an easy job. Some teachers make a test carelessly.
teaching-3
learning process. High quality test can give information about how well the
students have comprehended the material, which has been taught by the
teacher. So, teaching learning process will be more effective without any
overlapping.
One of form to evaluate the students’ ability is test. Evaluation can be
done in the form of test. This test could be a teacher-made test or standardized
test. In the teacher-made test, the teachers who make the test should know and
master the principles and the steps that must be done in making the test. By
this knowledge the teachers will get a clear figure about the general
systematic framework of evaluation.
There are numerous types of test. There are placement test,
achievement test, proficiency test and aptitude test. The test which is usually
used by teacher to know how far students have mastered the lessons is the
achievement test. The achievement test is intended to establish how successful
individual students groups of students or the courses themselves have been
achieving objectives of language courses. Then here are two kinds of
achievement test: progress achievement test and final achievement test.
Progress achievements are those intended to measure the progress that
students are making and final achievement tests or summative tests are
intended to measure the students’ achievement at the end of a course of study
4
In order to measure accurately, the teachers should use a good test. It
is not an easy work for them to make it because there are some characteristics
or requirements that must be fulfilled. The characteristics of a good test
include validity, reliability, objectivity and practicality (Sudijono, 1996: 93).
Validity is the most important consideration in test evaluation. The
concept refers to the appropriateness, meaning and usefulness of the specific
inferences made from the score. Test validation is the process of accumulating
evidence to support such inference. The former types of validity are content,
criterion related, and construct (Tinambunan, 1988: 11).
Most of teachers applied test in the multiple choice form in the final
program of teaching learning process. According to Tinambunan (1988: 9),
the summative test is intended to show the standard which the students have
now reached in relation to other students at the same stage.
Item analysis is an important and necessary step in the preparation of
good multiple choice test. Because of this fact; it is suggested that every
classroom teacher who uses multiple choice test data should know something
of item analysis. How it is and what it means. Items analysis provides two
kinds of information on items, there are item difficulty and item
discrimination (Oller, 1979: 254).
In SMK N 3 Salatiga, English summative tests is settled as one of the
most important aspects that can be used as the tools of evaluation to measure
5
not. Since the English summative tests will become the main point of student
ability in English so this test will be very important to be analyzed. If the test
isn’t validwe can say that the test can’t use as the tools of measurement.
The writer focuses the research of the tenth grade students in this
school and focuses on the observation of the English summative tests. As we
know that tenth grade is the beginning class of senior high school where the
teacher can get the general and valid information about the students’ ability.
By knowing the valid information about the students’ ability might help the
teacher to find the suitable steps in treating students in class.
From the reason above the writer concludes that this research is very
important to be done because the English summative tests in SMK N 3
Salatiga is oriented to measure the students’ ability whether the target of
learning has been achieved or not. The teachers in this school also use the
result of the English summative tests in tenth grade as the standing point of
view in treating the students for the next level. If these purposes of this test
can’t give the valid information so the test is also not valid.
Based on the explanation above, it gives an inspiration to the writer to
conducts a research related to how to evaluate the items analysis of the
summative tests score. That is a research entitled “ITEMS ANALYSIS ON
THE SCORE OF THE ENGLISH SUMMATIVE TEST (A Descriptive
Study of the Tenth Grade Students of SMK N 3 Salatiga in the Academic
6
B. Problem Statements
Based on the background described above, this research is aimed at
giving answers on how are the difficulty level and the discrimination index
on items of English summative test score of the tenth grade students at SMK
N 3 Salatiga in the academic years of 2013/2014?
C. Objectives of the Study
The general purpose of the study is to be able to know how the items
analysis on the students’ score of the English summative test at he tenth
grade students at SMK N 3 Salatiga. The specific objectives of this study as
able to measure and find out the difficulty level and discrimination index on
items of English summative test score of the tenth grade students at SMK N
3 Salatiga in academic years of 2013/2014.
D. Benefit of the Study
The result of this study is expected to give a description for the readers
about items analysis of test score toward the summative test. It can be used as
an input for the readers; especially for the English teachers, the headmaster,
and all people who are involved and responsible in developing good quality of
test. In other word, it is useful for all people to know the characteristics of a
7
E. Scope and Limitation of the Study
The discussion of the study will be focused on items analysis on the
students’ score of the English summative tests of the tenth grade students of
SMK N 3 Salatiga. According to Anthony (1983: 284), item analysis refers to
the process of collecting, summarizing, and using information about
individual test items especially information about pupil’s response to items.
According to Widdowson (2000: 60), item analysis usually provides two
kinds of information on items, they are:
1. Item facility (Item difficulty), which helps us decide if the test items are at
the right level for the target group.
2. Item discrimination, which allows us to see if the individual items are
providing information on candidates’ abilities consistent with that
provided by the other items on the test.
F. Definition of Key Terms
1. Validity
Validity is the most important consideration in test evaluation. The
concept refers to the appropriateness, meaning and usefulness of the
specific inferences made from the score. Test validation is the process of
accumulating evidence to support such inference. The former types of
validity (content, criterion related, and construct) are simply considered to
8
of an interpretation but the primary concern for classroom achievement
testing is content validity (Tinambunan, 1988: 11).
Validity is a standard or criterion that shows whether the instrument
is valid or not. A test is valid to the extent that it measures what it claims to
measure (Sukardi, 1987: 173).
2. Items Analysis
According to Anthony (1983: 284), item analysis refers to the
process of collecting, summarizing, and using information about individual
test items especially information about pupil’s response to items.
3. Test
Test is a particular type of assessment that typically consists of a set
questions administered during a fixed period of time under reasonably
comparable conditions for all students (Linn &Gronlund, 1995: 5).
According to Arikunto (2010: 226), to measure is there the object is
analyzed used a test. It’s used to measure the basic competence and
achievement. There are two types of achievement test used in school:
a. Test made by the teacher; that arranged by certain procedure, but it has
not been examined many times so its characteristics and strength has
not been known.
b. Standardized test; a test that usually has been available in a test
9
4. Summative Test
Summative test is final test which is executed after completing
program of teaching learning (Sudijono, 1996: 72).
The summative test is intended to show the standard which the
students have now reached in relation to other students at the same stage
(Tinambunan, 1988: 9). The condition for setting a summative test are that
it covers a much wide range of material than diagnostic test and relates to
be long-term rather than short-term objectives. This brings up problems of
sampling, since what has been learnt, for example in a year, cannot be
assessed in one day, yet the test must reflect the content of the whole
course, and the test must be able to determine the extent to which the
instructional objectives have achieved by the pupils and is used primarily
for assigning course grades of certifying pupil’s mastery of the extended
learning outcomes.
G. Review of Previous Research
In this graduating paper, the writer takes some reviews from other
thesis as a comparative in this research. The first journal is done by Hanik
10
public elementary schools in UDANAWU District, Blitar Regency. They
analyzed the quality of English summative test in terms of the test
construction, content validity, reliability, level of difficulty, level of
discrimination, and the effectiveness of distraction. It was compiled in
descriptive evaluation research.
The second is “Items Analysis of English Formative Test made by English Teacher (A Study of Eleventh Grade Students at SMA N 1 Angkek)”. It is written by Sari S. Octavia, a student of STKIP PGRI Sumatra Barat in the
academic year of 2012. She observed value of the daily tests that have been
achieved by eleventh grade students of SMA N 1 Angkek. Then she observed
how the results of the daily tests given by the English teachers.
H. Research Organization
The writer wants to arrange the graduating paper in order to the reader
can catch the content easily. It is divided into five chapters.
Chapter I is Introduction. It consists of background of study, problem
statements, objectives of the study, benefit of the study, limitation of the
study, definition of key terms, and review of previous research.
Chapter II is Theoretical Framework.This chapter is divided into three
sub chapters. The first sub chapter is talking about language test, which
describes about definition of test, the kind of the test and the characteristics of
11
includes content validity, face validity, construct validity and empirical
validity. The last is talking about items validity.
Chapter III explains about methods of research that consist of setting
of the research, subject of the research, method of the research, procedure of
the research, technique of collecting data and technique of data analysis.
Chapter IV is Findings and Data Analysis. It consists of description of
data, analysis of data, Interpretation of data, finding, discussion, and result.
Chapter V is Closure. The writer states summary of the study includes
12
CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
A. Language Test
Language testing is the practice and study of evaluating the
proficiency of an individual in using a particular language effectively (Brown,
2003: 42). The purpose of language test is to determine a person knowledge
and ability in the language and to discriminate that the persons’ ability from
that of others. Such ability may be of different kinds, achievement,
proficiency or aptitude. Tests, unlike scales, consist of specified tasks through
which language abilities are elicited. The term language test is used somewhat
more widely to include for example classroom testing for learning and
institutional examinations.
Actually there are many ways that use to evaluate the learning process.
One of the ways is test. Generally, test serves to motivate the learner and to
give the unity to portions of the material being studied at different times. It
can be device to prove the skills and abilities in learning.
From explanation above, the writer tries to develop the specific
13
B. Test
1. Definition of Test
There are some definitions about test. Test is a particular type of
assessment that typically consists of a set questions administered during a
fixed period of time under reasonably comparable conditions for all
students (Linn & Gronlund, 1995: 5). According to Tinambunan (1988:
3), test is a set of questions, each of which has a correct answer, that
examinees usually answer orally or in writing. Furthermore, according to
Brown (2003: 3), test is a method of measuring a persons’ ability,
knowledge, or performance in a given domain. Additionally, according to
Griffin and Nix, tests are setting for structured observations and are
expected to provide an efficient source of many types of assessment
information. They also said that test is a formal, systematic procedure
used to gather information about students’ achievement or other cognitive
skill (Griffin and Nix, 1989: 5-6).
In order to know how well the result of learning process, teacher
should evaluate it. By evaluating, teachers can collect information or have
concept whether the teaching and learning activity has successes or not.
Gronlund said that “tests are used as a means to motivate students
to learn or review specific material” (Gronlund, 1982: 6). It means that
test is one motivation of students to learn or review material in their
14
Furthermore Fernandes states that a test as a systematic procedure
for surveying a persons’ behavior and explaining it with the aid of a
numeric scale or a category system (Fernandes, 1984: 1).
In addition, according to Arikunto (2012: 67), test is instrument or
procedure which is used to know or measure a something in the situation
with the methods and rules determined.
Based on the definitions above, the writer concludes that the test
is the particular types of assessment to reinforce learning and to motivate
the students by giving a task or a set of tasks. Through the test, teachers
don’t only measure and motivate the students’ ability but also improve the
lesson in teaching learning process. In order to make a proper decision, the
teacher needs an accurate data. So a good instrument is needed.
2. The Kinds of Test
There are many types of test used to measure students’
achievement. The writer discusses about kinds of test based on two
experts’ opinions. First, According to Tinambunan, there are four types of
15
1) Placement test
A placement test is designed to determine pupil
performance in the beginning of instruction.
2) Formative test
Formative test is intended to monitor learning progress
during the instruction and to provide continuous feedback to both
pupil and teacher concerning learning successes and failures. It is
used at the end of a unit in the course book or after a lesson
designed. The result of this test will give the students immediate
feedback.
3) Diagnostic test
Diagnostic test is intended to diagnose learning difficulties
during instruction. The main aim of diagnostic test is to determine
the causes of learning difficulties and then to formulate a plan for
remedial action.
4) Summative test
According to Sudijono, summative test is final test which is
executed after completing program of teaching learning (Sudijono,
1998: 7-9).
In addition, according to Tambunan (1988: 9), summative
test is intended to show the standard which the students have now
16
Second, according to Brown, tests are divided into three
categories there are achievement test, aptitude test, and proficiency
test. Here, the writer likes to explain more about kind of tests.
1) Achievement test
Achievement test was designed to measure a variety of
learning outcomes, such as knowledge of specific facts, ability to
apply facts and principles (Tinambunan, 1988: 28). A classroom
tests is made by a teacher for his/her students and may or may not
be used again.
According to Gronlund, an achievement test is a systematic
procedure for determining the amount a student has learned.
Although the emphasis is on measuring learning outcomes, it
should not be implied that testing is to be done only at the end of
instruction (Gronlund, 1982: 1).
While, Sudijonos’ opinion (1996: 73), achievement test is
test which is used to reveal the level of attainment or learning
achievement. It is usually a formal examination given at the end of
the school year or at the end of the course, the achievement test
may be written and administered by ministries of education,
17
According to Hughes, achievement tests are directly related
to language course, their purpose being to establish how successful
individual students, group of students, or the courses themselves
have been in achieving objectives. They are two kind of test: final
achievement tests and progress achievement tests.
a) Final achievement tests are those administered at the end of a
course of study.
b) Progress achievement tests, as their name suggests, are
intended to measure the progress that students are making
(Hughes, 2003: 13).
Furthermore, Brown (2003: 47) said that an achievement
test related directly to classroom lessons, units, or even a total
curriculum. Achievement test are limited to particular material
covered in a curriculum within a particular time frame, and are
offered after a course has covered the objectives in question. Then
achievement tests are often summative because they are
administered at the end of a unit or term of study.
In addition, another opinion, an achievement test is
designed to indicate degree of students’ success in some past
learning activities (Tinambunan, 1998: 9). This purpose of
18
aptitude test, where the aptitude test is designed to predict success
in some future learning activities.
In order to have a good achievement test form, a test maker
should consider that achievement test much be constructed well by
paying attention to some following basic principles (Gronlund
1988: 303). They are:
a) Achievement tests should measure clearly defined learning
outcomes that are in harmony with the instructional objectives.
b) Achievement tests should measure an adequate sample of the
learning outcomes and subjects matter content included in
instructions.
c) Achievement tests should include of the tests items, which are
most appropriate for measuring the desired learning outcomes.
d) Achievement tests should be designed to fit the particular uses
to be made of the results.
e) Achievement tests should be made as reliable as possible and
should then be interpreted with caution.
f) Achievement tests should be used to improve student learning.
The content of tests based on the course objectives gives a
number of advantages. The first, it compels course designers to be
explicit about objectives. The second, it makes possible for
19
achieved the instructional objectives. Consequently, the course
designer or teacher should construct a syllabus based on the
instructional objectives and should select books and materials
which are consistent with the course objectives.
Based on the explanation above, the writer concludes that
achievement tests should support and reinforce other aspects of the
instructional process. May they can aid both the teacher and
student in assessing learning readiness.
2) Aptitude test
The second type of test is the aptitude tests. Aptitude tests
are designed to predict, before beginning language study, a
subjects’ capability of acquiring the language (Merry and Sydney,
1993: 7). By looking at “predict” term, it can be recognized that
these tests give some clues as to whether, how well and how
quickly a person is likely to success in learning.
According to Sudijono (1996: 73), the aptitude test is test
which is executed that aim to reveal a basic competence or special
aptitude that students have.
Beside it, Brown states, a language aptitude test is designed
to measures a persons’ capacity or general ability to learn a foreign
20
are considered to be independent of a particular language (Brown,
2001: 391).
Fundamentally, aptitude tests have different features in
nature from achievement test, which has been discussed
previously. Aptitude tests are primarily designed to predict success
in some future learning activities, whereas achievement tests are
designed to indicate degree of success in some past learning
activity (Tinambunan, 1998: 7). From a comparison above, it can
be comprehended that a distinction founded between these two
tests is made in term of the use of the results. It is rather than the
qualities of the tests themselves.
3) Proficiency test
The third type of test is proficiency test. This test is used to
know the proficiency of test-takers. It is hoped after giving this test
the test-taker will know their ability in their ability in language
especially in English language.
According to Hughes (2003: 11), proficiency tests are
designed to measure people’s ability in a language. The content of
proficiency test is based on a specification have to be able to do in
the language in order to be considered proficient.
While Harmer (2001: 321), said that the proficiency tests
21
than measures progress). They are frequently used as stages people
have to reach if they want to be admitted to a foreign university,
get a job, or obtain some kind of certificate. Proficiency tests have
a profound backwash effect since, where they are external exams,
students obviously want to pass them, and teachers’ reputation
sometimes depend (probably unfairly) upon how many of them
succeed.
Appropriate the writers’ experience during the learning,
this test usually consists of the standardized multiple choice items
in structure, reading comprehension, listening comprehension, and
sometimes on writing.
Based on the explanations about the kind of tests above, the writer
concludes that generally test is a systematic and objective procedure to
find out the knowledge and ability of what have been learned from
someone.
C. Summative Test
According to Brown, Summative test has clearly related to summative
assessment. Summative assessment aims to measure or summarize what a
student grasped and typically occurs at the end of a course or unit of
22
and taking stock of how well that student has accomplished objectives. But it
does not necessarily point the way to future progress. Final exams in a course
and general exams are examples of summative assessment (Brown, 2003: 06).
In this part, the writer discusses more about summative test as a follow:
1. Definitions of Summative Test
According to Sudijono, summative test is final test which is
executed after completing program of teaching learning (Sudijono, 1998:
7-9).
In addition, according to Tambunan, summative test is intended to
shows the standard which the students have now reached in relation to
other students at the same stage (Tinambunan, 1988: 9)
2. Purpose of Summative Test
The purpose of summative test is establishes a success learning,
which its result as a substances to fulfill a students’ grade report and
preferment class. So that it is not used to improve a teaching-learning
process, because of all the materials have been extended. If the student
failed, he or she reputed that not pass in a lesson which involved in the
learning (Sutomo, 1985: 20).
3. Advantages of Summative Test
According to Arikunto (2008: 39), there are important advantages
of summative test, they are:
23
b. To be able to know students’ ability in following the next of teaching
programs.
c. To fulfill the progress learning notes that it can be useful to students’
parent, consultant, and mentor in the school.
The main purpose of summative test is determines the point which
symbolize a student success after passing the learning process at certain
time. So that the teacher can determines a student position in the class. It
related to the students condition in following a teaching programs
(Silverus, 1991: 10).
4. Assessment aspect of summative test
According to Sutomo (1985: 20) aspect which is assessed in
summative assessment is all of ability aspect the learning result during the
teaching programs. They are knowledge aspect (cognitive), skill
(psychomotor), and behavior (affective).
Based on the statement above, the writer concludes that the
condition for setting a summative test are that it covers a much wide range
of material than diagnostic test and relates to be long-term rather than
short-term objectives. This brings up problems of sampling, since what
has been learned, for example in a year, cannot be assessed in one day, yet
the test must reflect the content of the whole course, and the test must be
24
achieved by the pupils and is used primarily for assigning course grades of
certifying pupil’s mastery of the extended learning outcomes.
D. The Characteristics of a Good Tests
A test which is good the measuring instrument must meet the test
requirements, namely to have validity, reliability, and usability (Arikunto,
2009: 58). First character of a good test is needed to have validity. Validity
refers to the adequacy and appropriateness of the interpretation made from
tests, with regard to a particular use. An information data can be said is valid
in accordance with actual circumstances. The second characteristic of a good
test is needed to have reliability. A test should be reliable as a measuring
instrument. Reliability is the consistency of assessment results (Linn and
Gronlund, 1995: 48).
If the teachers obtain quite similar scores when the same test
procedure is used with the same students on two different occasions, they can
conclude that their results have a high degree of reliability from one occasion
to another. Similarity, if different teachers independently rate student
performances on the same test task and obtain similar ratings, they can
conclude that tests can be said reliable. If it gives results that remain when a
test is practiced to students for many times, it also conclude that tests can be
25
The third characteristic of a good test is usability in the preparation of
a new test. The term usability, then, refers only to the practically of the
procedure and says nothing about the other qualities percent (Linn and
Gronlund, 1995: 49). The teacher must keep in mind a number of a very
practical consideration which involves economy, ease of administration,
scoring and interpretation of result. How long the administering and scoring
of test will take, choosing a short test rather longer test.
In the writer’s opinion, the practically of a test is important in order
that test materials can be administered well. It must be determined in term of
materials, time, and effort that it requires.
1. Validity
Based on the previous explanation, the writer mentions that one of
a good test characteristic is validity. Test validity is the most critical factor
to be judged in the total of foreign language testing. Validity is the extent
to which a test measures what it is intended to measure (William, 1990:
183). It means validity refers to extent to which the results of an
evaluation procedure serve the particular uses for which they are intended.
For example, if a test is designed to measure oral comprehension, it should
not attend to measure another skill such as reading comprehension. If a
test is intended to measure a persons’ ability to speak the language, it is
valid only if speaking skills and not writing ability are the specific
26 Traditionally, validity has been defined as “the degree to which a
test measures what it claims or purports to be measuring”. According to
Gronlund, the meaning of validity has typically been defined for the
testing profession by a set of standards. In the most recent edition of the
standards, validity has been described as follows: “validity is the most
important consideration in test evaluation. The concept refers to the
appropriateness, meaningfulness, and usefulness of the specific inferences
made from the scores. Test validation is the process of accumulating
evidence to support such inferences. A variety of inferences may be made
from scores produced by a given test, and there are many ways of
accumulating evidence to support any particular inference. Validity,
however, is a unitary concept. Although evidence may be accumulated in
many ways, validity always refers to the degree to which that evidence
support the inferences that are made from the scores. The inferences
regarding specific uses of a test are validated, not the test itself (Gronlund,
1993: 159)”.
The other hand, Tinambunan said that validity refers to the extent
to the results of an evaluation procedure serve the particular uses for
which they are intended. Thus, the validity of a test is extent to which the
test measures what is intended to measure (Tinambunan, 1988: 11).
According to Gronlund, validity refers to the appropriateness of
27
testing, can be clarified further by noting the following general points;
validity refers to the interpretation of test results (not to the test itself),
validity is inferred from available evidence (not measured), validity is
specific to a particular use (selection, placement, evaluation of learning,
and so forth), validity is expressed by degree, for example; high,
moderate, or low (Gronlund, 1982: 126).
In every language, we say that something is valid if it is sound and
meaningful, or well grounded on principles or evidence. For example, we
speak of a valid theory, a valid argument, or valid reason. Validity is the
process of gathering and evaluating validity evidence. Both the test
developer and the test user may play a role in the validation of a test for a
specific purpose (Ronald and Mark, 1988: 175).
In other opinion came from Fernandes, an important characteristic
of a test is its validity. The validity can be viewed as the accuracy of
specified in references made from scores (Fernandes, 1986: 6).
From the definition above, the writer concludes that these are no
differences in the essence of validity, there are only different in the
terminology, such as extent and degree and worth, while all of them intend
to measure the purpose to measure.
There are three types of validity namely content validity, construct
28
a. Content Validity
The principal validity for achievement tests is content validity,
sometimes called content relevance. Content validity talks about
content of test. Febru and Erna said, “Content validity is concerned
with the extent to which the test is representative of a defined body of
content consisting of topics and processes (Febru and Erna, 2011:
167). Therefore, the test should reflect instructional objectives or
subject matters. But it is not expected that every knowledge or skills
will always appear in the test; there may simply be too many things for
all of them to appear in a single test.
According to Hughes a test is said to have content validity if its
contents constitute a representative sample of the language skills,
structure, etc (Hughes, 2003: 11).
The content validity is concerned with how the test measures
the subject matter and behavior under consideration. The test items
must be a representative sample of the domain of possible content or
behavior. Content validity is the most appropriate method for
29
b. Construct Validity
In construct validity, we have to measure the difficulties of the
students toward the test has to be qualified. Terminologically,
according to Anas, achievement test learning can be stated as a test
which it is have a construct validity, if achievement test learning is
exactly reflect a construction in psychology theory with consideration
from composition aspect, design or invention (Sudijono, 1996: 166).
According to Gronlund, construct validity is applicable to both
norm-referenced and criterion-referenced tests, evidence in the latter
case would, it consists of necessity and it can be less dependent on
statistical measures requiring score variability (Gronlund, 1982: 131).
Bachman and Palmer said that construct validity is the
on-going process of demonstrating that a particular interpretation of test
scores is justified and involves, essentially, building a logical case in
support of a particular interpretation and providing evidence justifying
interpretation (Bachman and Palmer, 1984:520).
Beside that Hughes and Porter said that construct validity has
focuses attention on the desirability of basing test construction on an
explicitly recognized theoretical foundation. A possible danger in the
application of construct validity is that may open the way for
subjective, unverified assertions about test validity (Hughes and
30
c. Empirical Validity
Empirical validity is accuracy measure which is basing on
analysis result that has empirical character (Sudijono, 1996: 167).
According to Charles, empirical validity depends on empirical
and statistical evidence as to whether students’ marks on the test are
similar to their marks on other appropriate measures of their ability,
such as their scores on other tests, their self assessments or their
teachers’ rating of their ability (Anderson, 1995: 171).
In order to know whether a test has empirical validity or not, it
can be traced from ways, first is concurrent validity and second is
prediction validity. Concurrent validity applies if data on the two
measures (test and criterion) are collected at or about the same time.
Predictive validity applies if there is an intervening period (e.g., three
or six month) between the time of testing and the collection of data on
criterion. Operationally, this time of criterion data collection is the
distinction between the two types of criterion validity. Specifically, the
question of concurrent validity is whether or not the test scores
estimate a specified present performance; that’s of predictive validity
is whether or not the test scores predict a specified future performance
31 In the writers’ opinion, validity of a test is important to know a
test whether it has a good quality in testing someone’s capability or
not.
2. Reliability
A test should be reliable as a measuring instrument. A test cannot
measure anything well unless it measures consistently. According to
Anderson (1995: 187), a test cannot be valid unless it is reliable. If the test
administered to the same students on the different occasion and there is no
difference to the results. It can be said that the test is reliable.
3. Practicality
The third, characteristics of a good test is practicality or usability
in the preparation of a new test. The teacher must keep in mind a number
of very practical considerations which involves economy, ease of
administration, scoring and interpretation of result. Economy means the
test is not costly. The teachers must take into account the cost per copy,
how many scores will be needed, (for the more personnel who must be
involved in giving and scoring a test, the more costly the process
becomes). How long the administering and scoring of it will take,
choosing a short test rather than longer one. Ease of administration and
scoring means that the test administrator can perform his task quickly and
efficiently. We must also consider the ease with which the test can be
32
According to Heaton (1988: 161), the final point concerns the
presentation of the test paper itself, where possible, it should be printed or
type written and appear neat, tidy and aesthetically pleasing. Nothing is
worse and more disconcerting to the testiest than untidy test paper, full of
miss spellings, omissions and corrections. If it happens, it will be easy for
the students or testiest easy to interpret the test items.
Besides having a good criteria, the other characteristics of the test
that’s more important and specific is the quality of the test items. To know
the quality of the test items, teachers should use a method called item
analysis.
E. Item Analysis
There are several meanings of what item analysis. According to
Anthony (1983: 284), item analysis refers to the process of collecting,
summarizing, and using information about individual test items especially
information about pupil’s response to items.
Item analysis is an important and necessary step in the preparation of
good multiple choice test. Because of this fact; it is suggested that every
classroom teacher who uses multiple choice test data should know something
of item analysis. How it is and what it means (Oller, 1979: 254).
For the teacher made test, the followings are the important uses of
33
back to students about their performance and as a basis for class discussion,
feedback about pupil difficulties, and area for curriculum improvement,
revising the item and improving item writing skill.
According to Widdowson (2000: 60), item analysis usually provides
two kinds of information on items, they are:
1. Item Difficulty (Item Facility)
Item facility, which helps us decide if the test items are at the right
level for the target group. Item facility expresses the proportion of the
people taking the test who got a given item right. According to Arikunto
(1995: 211), item facility refers to item difficulty. Item difficulty is
sometimes used to express similar information, in this case the proportion
that got an item wrong. Where the test purpose is to make distinctions
between candidates, to spread them out in terms of their performance on
the test, the items should be neither too easy nor too difficult. Good test is
items which not too easy or not too difficult. If the items are too easy, then
people with differing levels of ability or knowledge will all get them right,
and the differences in ability or knowledge will not revealed by the item.
Similarly if the items are too hard, then able and less able candidates alike
will get them wrong and the item will not help us in distinguishing
34
2. Item Discrimination
According to Arikunto (1995: 215), analysis of item discrimination
addresses a different target: consistency of performance by candidates
across items. The usual method for calculating item discrimination
involves comparing performance on each item by different groups of test
takers: those who have done relatively poorly. For example, as items get
harder, we would expect those who do best on the vest overall to be ones
who in the main get they right. Poor item discrimination indices are signal
that an item deserves revision.
If there are a lot of items with problems of discrimination, the
information coming out of the test is confusing, as it means that some
items are suggesting certain candidates that relatively better, while order
individuals are better, no clear picture of the candidates’ abilities emerges
from the test. (The scores, in other words, are misleading and not reliable
indicators of the underlying abilities of the candidates) such a test will
need considerable revision (Arikunto, 1995: 216).
F. English Curriculum
The writer would explain about English Curriculum 2013. Based on
module of implementation curriculum 2013 coaching (2014: 2), the
35
1. Concept of Curriculum 2013
Curriculum is one of element which gives contribution to construct
the students’ potential. It is developed based on the competence which is
needed as an instrument. It aims to direct the students to be able to:
a. Quality human who capable and proactive to the God; human who
have good character, skillful human, creative human, and powerful
human.
b. National who democratic and responsibility.
2. Rational of Curriculum 2013 Development
Developing of curriculum 2013 is advance step the curriculum
based on competence which is pioneered in year of 2004. It is advance
step the KTSP (2006) curriculum which include of cognitive competence,
36
CHAPTER III
METHODOLOGY
I. Setting of the Research
This research was conducted in SMK N 3 Salatiga which is located in
Jl. Ja’far Shodiq Rt. 01 Rw. 03 Phone/Fax (0298) 7103119 Salatiga 50744.
The subject of this research was the tenth grade students of SMK N 3 Salatiga
in academic year of 2013/2014.
The existence of SMK N 3 Salatiga has long be expected by
communities especially Salatiga. It was to address the needs of diverse and
quality education. May 21th, 2007, it poured on decree of competence program provider No. 420.5/1510 Head of the Salatiga. The competence program
opened; Mechatronic Technique, Welding technique, Ototronic Technique,
and Agribusiness & Horticulture.
In the face of increasingly fierce competition with public schools, the
management SMK N 3 Salatiga must create educational programs with the
aim to improve services to the stakeholders.
SMK N 3 Salatiga committed to education and training as the
fulfillment of the needs of the labor market by establishing a human resource
37
J. Subject of the Research
In this research, the writer chose SMK N 3 Salatiga as object of the
study especially the tenth grade students. The tenth grade students consist of
twelve classes, but the writer took three classes, they are W1, O2, and
X-TKR1. The numbers of the participants are X-W1 (33 students, all of them are
boys), X-O2 (37 students, all of them are boys), and X-TKR1 (32 students, all
of them are boys). Their native language is Bahasa Indonesia. The average
age of the participants was 16 years old. They have English lesson at least one
meeting in a week which one hour lesson is 45 minutes.
a. Population
According to Arikunto (2010: 173), “population is all respondents of the research subject”. The population of this research was the tenth
grade students of SMK N 3 Salatiga in the academic year of 2013/ 2014.
They are all of tenth grade students of SMK N 3 Salatiga.
b. Sample and Sampling Technique
Sample is part of the representative of population that is observed
(Arikunto, 2010: 174). From the total population of tenth grade students,
the writer took X-W1, X-O2, and X-TKR1 classes as the sample of this
research. It consists of 102 students.
In this research the writer used purposive sampling. According to
Ary, Jacobs and Sorensen (2006: 156),purposive sampling also referred to
38
representative, are chosen from the population. The assumption is that
errors of judgment in the selection will counterbalance one another.
The writer used this sampling technique because of a reason or
purpose in choosing that class as the sample. It was that these classes have
some categories based on the students’ ability in English lesson. They are
X-O2 (as excellent class), X-W1 (as moderate class) and X-TKR1 (as low
class).
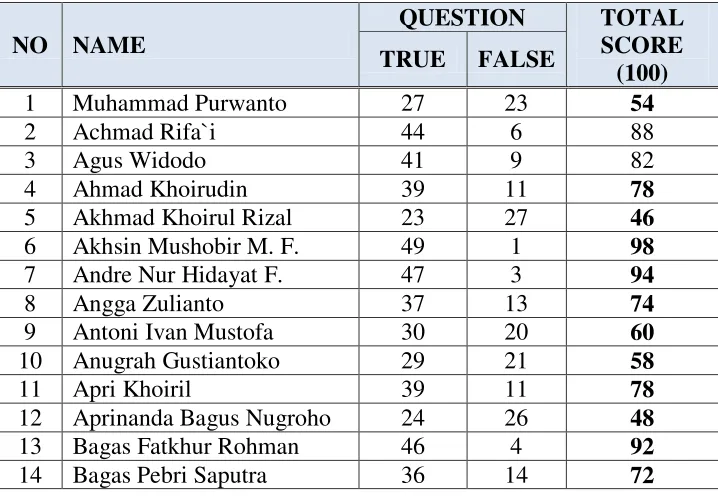
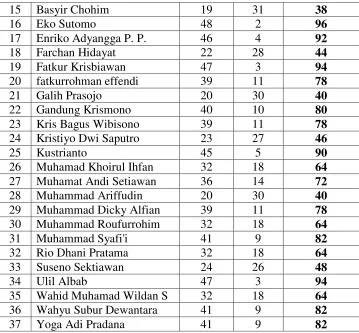
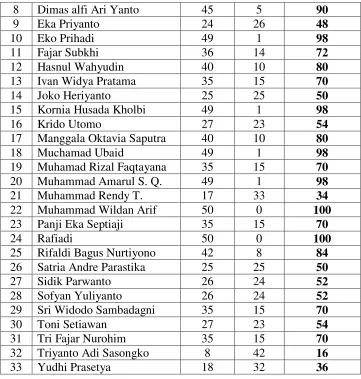
These are the data of X-O2, X-W1 and X-TKR1 students’ English
scores are used as source of the research could be drawn as follows:
40
List of X-TKR1 Students’ Scores of SMK N 3 Salatiga in
41
Stephen and Michael (1982: 46), descriptive study is used in the literal sense
of describing situations events. It is the accumulation of data base that is
42
the facts and characteristics of a given population or area of interest, factually
and accurately.
In this research, the writer described about items analysis on the score
of the English summative tests of the tenth grade students of SMK N 3
Salatiga in the academic year of 2013/2014.
The quantitative method was applied in this study. According to
Lodico (2006: 13), quantitative methods are those which focus on numbers
and frequencies rather than on meaning and experience. Quantitative methods
(e.g. experiments, questionnaires and psychometric test) provide information
which is easy to analyze statistically and fairly reliable. In quantitative
method, the researcher focuses on collecting the data about the statistical
inferences. In addition, quantitative methodology assumes the necessity,
desirability, and even the possibility of applying some underlying empirical
standard to social phenomena (Quinn, 1978: 212).
L. Technique of Collecting Data
According to Muslich (2012: 40) research techniques consists of:
a. Observation
Observation is written note about what is seen, heard, and
experienced in collecting data and reflection toward qualitative data.
Observation is used to get the certain target which is observed. (Sam’s,
43
The writer visited the school, asked for the tests results
(summative test) of English Subject and asked for the question sheet of
English Subject to be analyzed. The writer interviewed with the English
teacher of the tenth grade students of SMK N 3 Salatiga.
b. Documentation
According to Arikunto (2010: 274), documentation is an activity
to look for variable like notes, transcribes, books, newspapers, magazine,
etc. In this method, writer provided a check- list to look for the variable
that had been decided. Whether the wanted variable was rise, then the
writer gave a check (√) in the check- list form.
Documentation means collected the files or data of related
information including the result of tenth grade student’s examination in
even semester. There are two instruments used in this research, they are
English Summative test and English syllabus. The writer came to school,
ask for English summative tests of the tenth grade students of SMK N 3
Salatiga. Then, the writer collected the data about English syllabus,
students’ data profile, students’ English score and the general information
44
M.Technique of Analyzing Data
The writer conducts Items Analysis on the Score of the English
Summative Test (Descriptive Study of the Tenth Grade Students of SMK N 3
Salatiga in Academic Year of 2013/2014. According to Stephen and Michael
(1982: 46), descriptive study is used in the literal sense of describing
situations events. It is the accumulation of data base that is solely descriptive.
The purpose of this approach is to describe systematically the facts and
characteristics of a given population or area of interest, factually and
accurately. In this study, the writer described all of the data and analyzed to
get the result and conclusions.
In analyzing data, the writer uses quantitative approach. Quantitative
approach is summarizing data using numbers. Hypotheses and methods of
data collection are created before the research begins (Lodico, 2006: 6). In
this research, the writer needs to identify, classify, and interpret the data.
Based on the information type that needed of this research, the writer
focuses on collecting the data about the statistical inferences in this research.
The English summative test was consisted of 50 items. It was developed from
the syllabus of curriculum 2013.
Items analysis provides two kinds of information on items, there are
item difficulty and item discrimination. First, the writer measures the
difficulty level that exists in items of the English summative test. According
45
easy called difficulty index. Number of difficulty index between 0.00 until 1.0. It is shows the standard of test difficulty. Test with the difficulty index 0.0
show that the test is too hard, in opposite index 1.0 show that the test is too
easy.
0.0 1.0
Hard Easy
To measure the difficulty index, the writer used the formula bellow:
P = Difficulty Index.
B = Total students that answered correct.
46
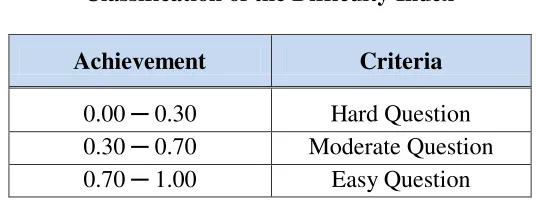
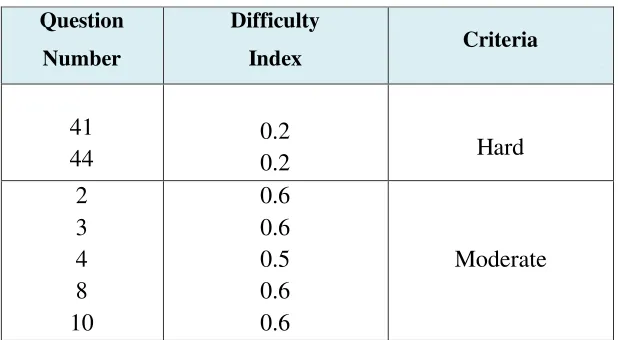
The result would be compared to the classification of difficulty index.
According to Daryanto (1999: 182), the difficulty index is classified as the
criteria bellow:
Table 3.4
Classification of the Difficulty Index
Achievement Criteria
0.00 ─ 0.30 Hard Question
0.30 ─ 0.70 Moderate Question
0.70 ─ 1.00 Easy Question
Second, the writer measures the discrimination index. According to
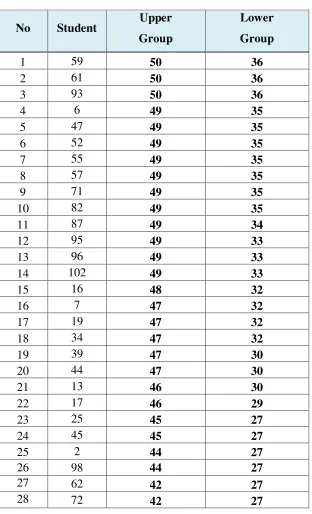
Arikunto (1995: 215), discrimination index is ability of item to discriminate
between high students and low students ability. Number which is show the
discrimination index called difficulty index. It at range 0.00 until 1.00. In
contradiction, the difficulty index not identifies a negative (-) sign and the
discrimination index identifies negative (-) sign.
-1.00 0.00 + 1.00
Discrimination index Discrimination index Discrimination index Negative Low High/Positive
Test item was not good when the item which is answered correctly by the
upper student or lower student because it haven’t discrimination index. Such
46
was same. That item has point D 0.00 because it have not discrimination
index. To measure the discrimination index, the writer used the formula
bellow:
-
= PA – PB
D = Discrimination index
J = Total students
JA = Total of upper group
JB = Total of lower group
BA = Total of upper group who answered correctly
BB = Total of lower group who answered correctly
PA =
= Proportion the total of upper group who answered correctly (P as the discrimination index).
PA =
= Proportion the total of lower group who answered correctly.
According to Daryanto (1999: 189), good item is item that distinguish
between high students and low students. It could be seen from whether able or
unable answered the test. The test items were poor if the test items could be
47
The result would be compared to the classification of discrimination
index. According to Arikunto (1995: 223), the discrimination index is
classified as the criteria bellow:
Table 3.5
Classification of the Discrimination Index
Achievement Criteria
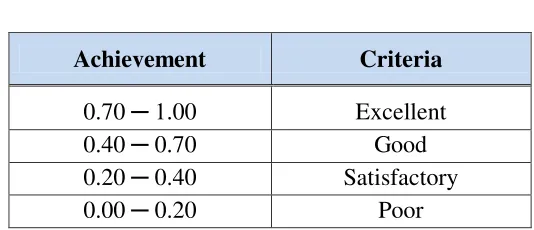
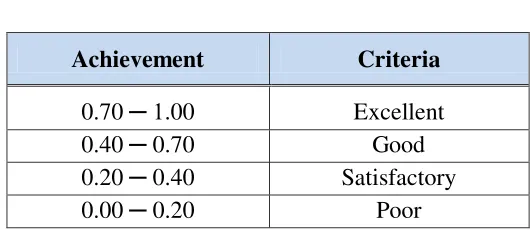
0.70 ─ 1.00 Excellent
0.40 ─ 0.70 Good
0.20 ─ 0.40 Satisfactory
0.00 ─ 0.20 Poor
Moreover classification, According to Aggrawal (1986), items having
negative discrimination is rejected. Items having discrimination index
above 02.00 are ordinarily regarded satisfactory for use in most tests
48
CHAPTER IV
DATA ANALYSIS
This chapter focuses on analyzing the collected data. The writer gives the
details of the findings. This chapter is likely the main discussion of the research
conducted. It displays the finding of the collected data since in the beginning until
the end of the research.
A. Analysis
In this study, the writer provided the whole data analyses of this
research which are explained in the description below:
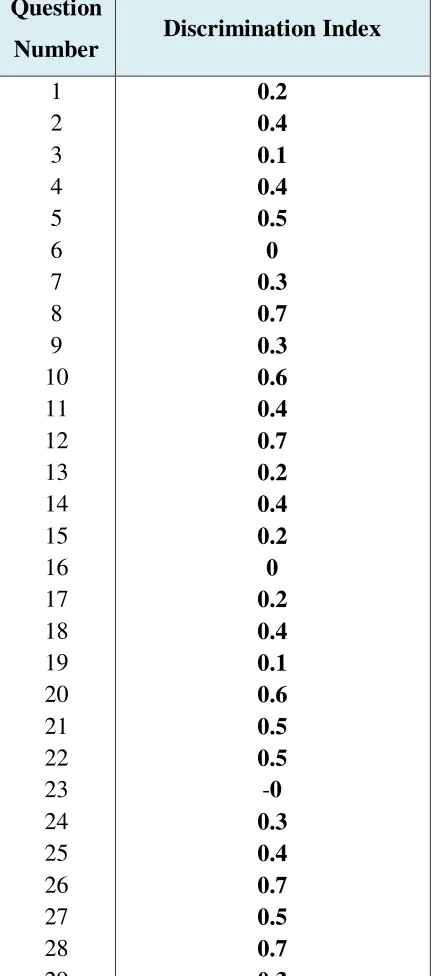
1. Analysis of the Difficulty Index
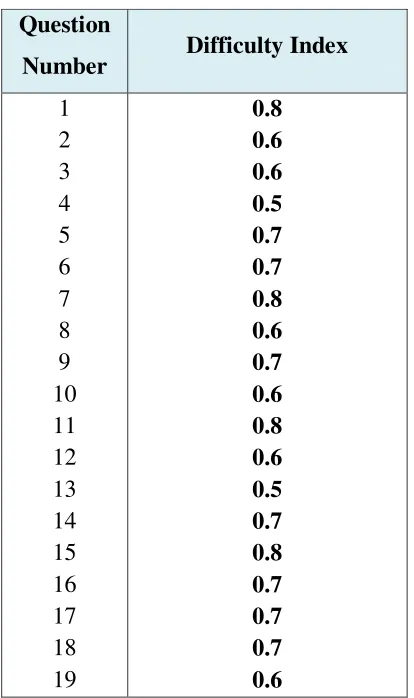
First, the writer measures the difficulty level that exists in items of
the English summative test. According to Arikunto (1995: 212), number
which is indicates the items that difficult or easy called difficulty index. Number of difficulty index between 0.00 until 1.0. It is shows the standard
of test difficulty. Test with the difficulty index 0.0 show that the test is too
hard, in opposite index 1.0 show that the test is too easy.
1.0 1.0