TUBERCULOSIS HEALTH CARE CADRES IN CURUG VILLAGE, CIMANGGIS, DEPOK: DESCRIPTIVE STUDY
1
Ni Luh Putu Eva Yanti, 2Junaiti Sahar, 2Widyatuti 1
Nursing Study Program, Faculty of Medicine, Udayana University 2
Faculty of Nursing, University of Indonesia Email: [email protected]
Abstract
The establishment of Tuberculosis Health Care Cadres (TB-HHC) aims to help nurses to prevent tuberculosis in community. This study aims to describe the condition of TB-HHC applied tuberculosis control program in Curug Village. The results of the research showed an increase in knowledge of TB-HCC members to control tuberculosis was 11.2% and the attitude was 5.6%. The skills of KKP-TB to provide education was at the mean= 23.5 and a case detection and referral skills were at the mean of=15.4. There are six cadres (from ten cadres) have a case detection and referral skills above average. Tuberculosis Health Care Cadres can strengthen tuberculosis eradication programs in community.
Keywords: health care cadres, tuberculosis control
INTRODUCTION
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease that is still a global burden of disease. WHO data (2013) shows 58% of TB cases occur in Southeast Asia and the Western Pacific. Indonesia get 4th rank highest number of TB cases in the world, after China, India, and South Africa. Data from the Ministry of Health Riskesdas RI (2013), there are five provinces with the highest prevalence of TB in Indonesia. There are West Java, Papua, Jakarta, Gorontalo, Banten and West Papua. West Java occupies the first position with a TB prevalence of 0,7% (the national average of 0,4%).
still low in the discovery of new cases of TB is Depok city. Puskesmas Cimanggis, Curug village is one of the regions with the CDR data is still low.
National strategy TB control strategies implemented by Directly Observed Treatment Short-course (DOTS) across Unit Pelayanan Kesehatan (UPK) including hospitals. This strategy for TB control has been proven as the most effective and economical (Dirjen P2PL Depkes RI, 2009). This strategy is in line with community nurses role such as managers and providers of nursing care for individuals, families, groups, and communities (Allender, Rector, & Warner, 2010). In held nursing care with tuberculosis, nurses require the participation of elements of the community as a form of empowerment and cooperation with the public (Allender, Rector, & Warner, 2010; Helvie, 1998; Hitchcock, Schubert, & Thomas, 1999). Empowering and working with the community in the form of group process through the formation of support groups or social support (Pander, Murdaugh, & Parsons, 2002).
The support group involves the role of health workers in supporting TB control program that includes a treatment supporter (PMO), tracking of TB cases were lost to follow up, and the discovery of TB cases in the community. The support group called Tuberculosis Health Care Cadres (TB-HHC). Support groups effectives help families and TB clients in improving access to TB care and increase the number of findings suspect TB (Solihin, 2014; Rejeki, 2012).
Problem statement this research: how is Tuberculosis Health Care Cadres (TB-HHC) run the
TB control programs. The purpose of this study was to describe the knowledge, attitudes, and skills of TB-HHC in implementing the TB control program.
METHOD
number of respondents who selected 16 people.
Data collection procedures performed by conducting pre-test prior to all the respondents. Instruments used include aspects of knowledge and attitudes about TB disease. Furthermore, respondents receive training on TB-HHC with three topics during three meeting: 1) knowledge of TB signs symptoms, modes of transmission, prevention, and early detection of TB cases; 2) skills of cadres in conducting group counseling and family and how to make referrals; 3) facilitation of health cadres in doing family counseling and group activities in the community. At the four meeting were post-test and evaluation skills of cadres do counseling and early detection through role play activities. Skills evaluation instruments using observation sheet check list.
[image:6.612.72.545.529.700.2]RESULT
Tabel 1. Distribution of knowledge and attitude of TB-HHC before and after training
Item n Pre test Post test Percentage of increasing
pre-post test
Knowledge 16 8,38 9,44 11,2%
Attitude 16 21,06 22,31 5,6%
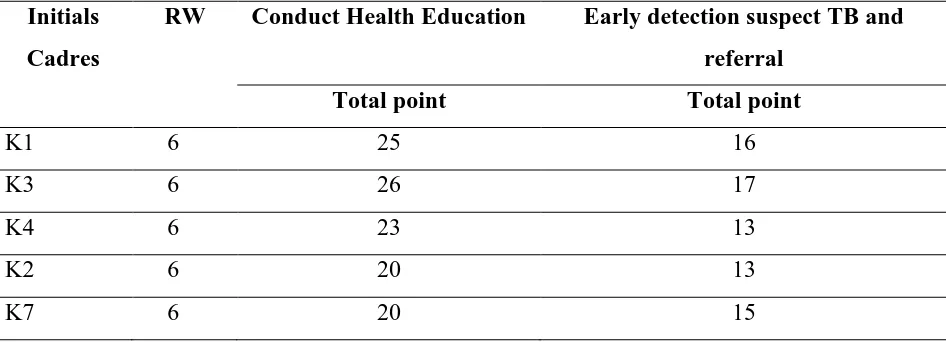
Tabel 2. Distribution of evaluation skill TB-HHC members to conduct health education and early detection suspect TB
Initials
Cadres
RW Conduct Health Education Early detection suspect TB and
referral
Total point Total point
K1 6 25 16
K3 6 26 17
K4 6 23 13
K2 6 20 13
K9 7 27 18
K12 7 24 16
K15 7 20 14
K11 7 25 16
K10 7 25 16
Mean 23,5 15,4
DISCUSSION
TB training to health volunteers have been conducted three meetings during one month. The purpose of training is to teach members about TB-HHC in order to conduct health education to members of the public in their respective areas and can immediately make early detection if it finds the case with TB symptoms. According to Allender, Rector and Warner (2010), methods of health education provided to the public in accordance with the number of lots using the lecture method. Training is one form of health education with the lecture method. This method can measure the cognitive abilities of individuals before and after training. The results indicate an increase in knowledge and attitude of TB-HHC before and after training on TB. The same thing happened on research conducted Pratiwi, Betty, Hargono, Widya (2012), showed 12,5% increase knowledge of health workers and community leaders before and after training on tuberculosis. Training with the lecture method effectively increases the knowledge and attitude of health workers about tuberculosis.
CONCLUSION
There is an increased knowledge and attitudes TB-HHC after training on TB prevention and early detection. The TB-HHC members skill in performing TB health education and early detection still lacking. So the nurse who responsible of TB program needs to conduct guidance and assistance ongoing basis to improve skills in health education, detection and referral of TB cases and conduct home visits in TB treatment monitoring.
REFERENCE
Allender, J.A., Rector, C., Warner, K.D. (2010). Community Health Nursing: Promoting and Proctecting the Public’s Health 7th
Edition. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
Dirjen P2PL Depkes RI. (2009). Pelatihan Penanggulangan TB MDR: Modul 1 Pengantar Pelatihan. Jakarta: Depkes RI
Helvie, C. O. (1998). Advanced Practice Nursing in the Community. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage
Hitchcock, J.E., Schubert, P.E dan Thomas, S.A. (1999). Community Health Nursing: Caring in Action. New York: Delmar Publishers
Kementerian Kesehatan RI. (2013). Riset Kesehatan Dasar 2013. Jakarta: Kemenkes Republik Indonesia
Kemenkes RI. (2013). Petunjuk Teknis Manajemen Terpadu Pengendalian Tuberkulosis Resistan Obat. Jakarta: Kemenkes RI
Pender, N., Murdaugh, C. L., Parsons, M.A. (2002). Health Promotion in Nursing Practice 4rd Edition. New Jersey: Pearson Education, Inc
Pratiwi, N. L., Betty, R., Hargono, R., Widya, N. E. (2012). Kemandirian Masyarakat dalam Perilaku Pencegahan Penularan Penyakit TB Paru. Buletin Penelitian Sistem Kesehatan Vol. 15, No.2; April 2012
Rejeki, H. (2012). Kelompok Pendukung sebagai Bentuk Intervensi Pengendalian TB Berbasis Pemberdayaan Masyarakat di Kelurahan Pasir Gunung Selatan Kota Depok. Karya lmiah Akhir. Tidak dipublikasikan. FIK: UI