http://www.southjournals.com
South Journal of Educational Psychology and Counseling
http://southjournals.com/ojs-2.4.5/index.php/sjepc
Structural Equation Modeling Relationship between Organizational Culture, Job Motivation and Mediation Role of Psychological Empowerment
H. Hosseiniravesh1*, M.R. Ismaeelzadeh2
1. Department of Physical Education and Sport Science, Islamic Azad University, Zabol Branch, Zabol, Iran
2. Department of Physical Education and Sport Science, Islamic Azad University, Mashhad Branch, Mashhad, Iran
*Corresponding author:H. Hosseiniravesh
To cite this paper: Hosseiniravesh, H. & Ismaeelzadeh, M.R. (2017). Structural Equation Modeling Relationship between Organizational Culture, Job Motivation and Mediation Role of Psychological Empowerment. South journal of Educational Psychology and Counseling, 4, 1, 19-25.
Abstract
The purpose of the research was to design and fit the structural pattern of casual relationship between organizational culture and job motivation, whit mediation role of psychological empowerment. This was a cross- sectional descriptive study. The participants in this study included 226 employees of Islamic Azad university of Zabol who were selected through multistage random sampling. 3 questionnaires, include Organizational Culture Survey, Psychological Empowerment, Work Motivation, and were used, and confirmatory factor analysis and structural equation modeling through AMOS-16 software were used for data analysis. The structural equation modeling analysis supported model fitting to the data. The results showed that the organizational culture was positively and indirectly related to work motivation, through psychological empowerment. It is recommended that managers support a culture where teamwork is encouraged, information is distributed fairly, decision- marking is shared, communication is open, rewards fit functions and meetings are effective in order to empower employees. Such a culture will increase, work motivation.
Introduction
Organizational culture is a set of assumptions, values and norms shared by symbols such as stories, myths, and legends and anecdotes passed to employees and is approved by them [1]. Organizational culture has been studied in six areas that include: teamwork, collaboration in the activities, honesty, support, conflict resolution. Teamwork, refers to cooperation with partners and group communication. The moral atmosphere, is determined with good labor relations, respect for employees, fairness, trust and organizational character. The flow of information: this dimension known with enough information to do a job, a stable relationship and communication with other areas of work and part. Involvement is the extent to which employees express their ideas and participate in decision-making, and to provide their ideas are encouraged by managers. Curated, are related with the value and clarity of feedback provided by supervisors about performance. Meetings; the extent to which meetings, effective and useful and people can freely in meetings, to raise their opinions and ideas [2].
Organizational culture effect on all aspects of the organization, including mission and goals, determine strategies, organizational structure, communication, attitude-free, wonderful, performance, innovative practices and management staff and the organizational effectiveness. Among the important cultural implications of organizational, is psychological empowerment [3, 4]. Blanchard et al, have defined empowerment as employees' perceptions of the ability to adapt to events, situations and staff who work with them at work [5]. Thomas, argued that empowerment is a multidimensional concept and it cannot be explained with a concept [6]. So psychological empowerment divided into four components which are: meaningful; an opportunity that people feel important and pursue valuable goals [7]. Merit: merit or efficacy of refers to the conviction or belief about their ability to perform skilled work activities [8]. Autonomy, refers to the sense and perceptions of independence and planning to start business activities [9]. Effectiveness: refers to the extent of being able to affect individuals' perception of job strategies, performance or results [10]. Yet different patterns, were examined antecedents and consequences of psychological empowerment. Among these variables, organizational culture is one of the most important predictors of psychological empowerment [4, 11, 12]. On the other hand, organizational culture and psychological empowerment, impact either directly or indirectly the majority on organizational outcomes. One of the important organizational outcomes, is job motivation. Job motivation is a variable that causes direction, severity and duration of job behavior [13]. Pinder knows Job motivation the set of energetic forces that emanate from within and outside the person, to initiate work-related behavior, and shape, direction, intensity and persistence [14].
Great deal of research has been done in this area. Many researchers in studies on motivation and psychological empowerment had undergone a significant positive correlation was found between them. Also showed a significant relation between psychological empowerment and innovative practices show. Some researchers also found a significant positive relationship between psychological empowerment of and enthusiasm for the job. In fact, this study seeks to answer the question of whether organizational culture indirectly through psychological empowerment is effective on the consequences or not.
The study sample included all staff and faculty members of Islamic Azad University of Zabul who were working in 1395. Sample of validation phase consisting of 50 and to 46 people responded to the questionnaire and sample of hypothesis testing stage was 226. As well as to collect data from three questionnaires were used as follows. Organizational culture questionnaire of Glaser et al. (1987) Questionnaire whit 6 subscales and 36 items that include teamwork (8 items), ethical climate (7 items), information flow (4 items), participation (4 items), director (8 Gubeh) and meetings (5 items). The reliability of the questionnaire in this study whit Cronbach alpha and split-half, in the range of 0.73 to 0.97 calculated, and which represents a favorable credit. As well as to determine the validity of the two methods of convergent validity (with the Denison organizational culture questionnaire) and confirmed factor analysis used and the results show the high validity of the questionnaire. Goodness of fit indices organizational culture are presented in Table 1.
Spreitzer psychological empowerment questionnaire (1995). The questionnaire included four sub-scales that are meaningful, competence, autonomy and effectiveness. The questionnaire consists of 12 items and the reliability of the questionnaire in this study, the Cronbach's alpha and split-half, in the range of 0.66 to 0.99 confirmed and shown that represents a good reputation. As well as to determine the validity, using confirmatory factor analysis of the results indicate the validity of the questionnaire respectively. Goodness of fit indices of psychological empowerment, have been presented in Table 1.
Job Motivation questionnaire Robinson (2004) includes a 11-item Cronbach's alpha coefficient and split-half reliability of the questionnaire, 0.74 and 0.82 respectively, reflecting a favorable credit this is the questionnaire.
Table 1. The indices confirmed the fitness factor analysis
Variables X2 X2/d CFI RMSEA
Organizational Culture 1167.1 2.01 0.9 0.067
Psychological Empowerment 74.02 1.54 0.98 0.049
Job motivation 339.46 2.95 0.91 0.093
To analyze the data, structural equation model which combines the factor analysis, multivariate regression analysis is used. This model can examine the causal relationships between latent variables and observed variables measuring in non-experimental research methods. In this study, each of the relationships mediated by Baron and Kenny and the three regression model were tested. Seville test to determine significant independent variable on the dependent variable indirect routes through the mediator was used.
Results
Table 2 describes the view of some variables. According to the Table 2 among the psychological empowerment, the significance and merit, and in the dimensions of organizational culture, the guardianship have gained the highest score.
Table 2. Descriptive information of variables for all subjects
Variables Lower Higher Mean Standard Deviation
Psychological Empowerment 20 60 47.9 6.6
Meaningful 4 15 13.1 2
Merit 6 15 13.1 1.7
Autonomy 3 15 10.27 2.6
Effectiveness 3 15 11.45 2.4
Organizational Culture 48 177 128.75 27.8
Teamwork 8 40 30.16 6.6
Ethical climate 7 35 24.76 7.2
Flow of information 4 20 12.59 3.4
Partnership 4 20 13.57 3.8
Supervision 12 40 30.44 6.9
Meetings 5 25 17.21 5.2
Job motivation 27 55 44.86 6.1
Table 3. Fit the proposed model based on scattering
Diffusion index X2 X2/d RMSEA GFI AGFI CFI IFI F N NFI
Proposed Model 310.19 3.07 0.09 0.9 0.81 0.91 0.91 0.87 0.9 0.9
As you can see in Table 3, square X2 was 310.19, the ratio X2 / d was 3.07, root mean square error of approximation RMSEA was 0.09, goodness of fit index GFT was 0.9, adjusted goodness of fit index was AGFI 0.81, fitness index increased IFI 0.91, comparative fit index CFI 0.91, and Bentler-Bonnet indicator or an index softened fitness (NFI) to test the effects directly on the model was used and to determine their significance, Baron and Kenny and questions test was used.
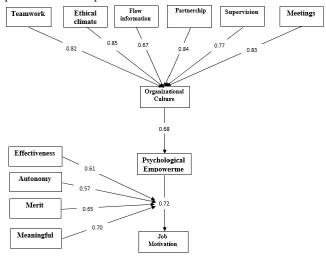
According to Table 3, it can be concluded that Proposed Model without the taking of corrective, has goodness of fit and acceptable. Figure 1 illustrates the analysis of the Proposed Model with path.
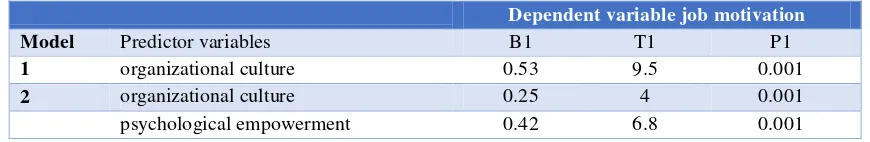
Table 4. The regression coefficients organizational culture, psychological empowerment, job motivation
Dependent variable job motivation
Model Predictor variables B1 T1 P1
1 organizational culture 0.53 9.5 0.001
2 organizational culture 0.25 4 0.001
psychological empowerment 0.42 6.8 0.001
In the proposed model and determine their significance Sobel test and Baron and Kenny method was used. As indicated in the model to the organizational culture has been used as the only predictor of job motivation. Organizational culture to job motivation path coefficient was (0.53) and was significant. The model suggests that organizational culture and psychological empowerment, both at the same time as predictors of the dependent variable in the regression equation. As set out in Schedule suggest that psychological empowerment as a predictive variable when the organizational culture is added to the regression coefficient of the predictor variables (organizational culture) of 0.53 dropped to 0.25 with job motivation. It approved the mediating effect of psychological empowerment. The results showed that all paths through the relationship of organizational culture on job motivation, psychological empowerment have a significant and positive, thus these three hypotheses were confirmed.
Conclusion
The findings show that organizational culture indirectly through psychological empowerment has significant positive relationship with job motivation and that culture is an essential component of work teams, have enough information to do the jobs of its employees, proper and respectful working relationships among the staffs, All employees are involved in decisions related to their jobs, managers and supervisors give clear feedback of subordinates and meetings, are effectiveness and useful, led to a heightened sense of significance, competence, autonomy and effectiveness in employees and these emotions, increase their job motivation.
motivation and have been reluctant to carry out activities. Generally if an organization's culture, make meaningful sense, competence, autonomy and created effects on employees, the psychological empowerment are created, and that their intrinsic motivation to perform job assignments are increases. A culture that encourages supervisors, who provided additional information to employees, makes employees feel empowered and effective, and successfully coordinated with their managers and managers trust them, and gives them autonomy and greater freedom to get things done, which makes the to provide staff without fear of punishment, penalties and mistakes innovative ideas and creative functions of their work. Cultures that in many ways, increase employee participation in decision-making related to the task or the entire organization is likely that employees feel more empowered. Collaborative cultures that employees are capable, creativity, gratitude and is also more freedom to employees [18]. Scott and Jaffe (2009) said, in organizations with strong cultures, the leader provides an environment that allows each individual to learn and share. In such cultures, their employees want to learn and develop their abilities and talents and their skills, to believe in themselves and their sense of competence [19]. This means that they should be faced with continuous set of challenges. In fact employees empowerment-based organizations, employ a variety of mechanisms necessary for growth and learning opportunities employees. Capable human resource, while also working to increase the content of the work, and develop their skills, trying to spirit along with ingenuity, coordinate with others, and do their job tasks and formidable force to reach that level decide whit awareness. In short organizational culture encourages employees to start work supervisors, and allows them sufficient autonomy that their skills and abilities, freely and without fear of error, mistake and punishment appeared to raise and in this way they feel competent and by creating conditions that employees can see their results, they created a sense of influence and can be sure that in this culture, innovative and creative behaviors among employees spread significantly. This means that organizational culture by creating a significant sense of, competence, autonomy and integral, leads the employees, has a great passion to their jobs, so that their work be so absorbed, that even not feel the passage of time, and were trying to do their job duties. The most important aspect of their organization with a weak culture, the hierarchy of authority in the vertical direction, and almost all the power is concentrated in the top echelons of the organization. But in organizations with strong cultures, it is impossible to managers do all that is necessary to achieve the organization's vision and mission. Delegating authority makes increase organizational strength, and each member of the organization will have more power. This would motivate employees. When given to the employees feel that they can be effective and having the power to perform tasks, they motivated and do more passion for their work.
When the reward to be distributed in the proper way, an opportunity to strengthen the interdependence between managers and employees will be provided. These dependence makes the supervisors trust to subordinates, and the get right of decision and granted participation to them, and therefore their feeling of autonomy and influence will increase.
References
2. Davodi H. Bahari F. Mirzajani M. (2012). Relatedness of organizational culture and job
motivation with teachers’ job satisfaction. Quarterly Journal of Career & Organizational Counseling, 4(13): 127-139.
3. Campbell S L, Fowles E R, Weber B J. (2004). Organizational structure and job satisfaction in public health nursing, Public Health Nursing, 21(6), 564-571.
4. Colagar S, Khaddam H. (2007). The relationship between leadership styles of nurse managers and job satisfaction of nurses, Journal of Gorgan University of Medical Sciences, 9 (3): 68-65.
5. Bhatnagar, J. (2007). Predictors of organizational commitment in India: strategic HR roles, organizational learning capability and psychological empowerment. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 18 (10), 1782-1811
6. Bitmis, M. G., Ergeneli, A. (2011). Contingency approach to strategic management: a test of the mediating effect of leader member exchange on the relationship between psychological empowerment and job satisfaction in 21st century workplace. Procedia Social and Behavioral Sciences, 24, 1143-1153.
7. Chang L. C., Shih C. H., Lin S. M. (2010). The mediating role of psychological empowerment on job satisfaction and organizational commitment for school health nurses: A cross-sectional questionnaire survey. International Journal of Nursing Studies, 47, 427-433. 8. Egan, T. B, Yang, B., Bartlett, K. R. (2004). The effects of organizational learning culture and
job satisfaction on motivation to transfer learning and turnover intention. Human Resource Development Quarterly, 15 (3), 279-301.
9. Fock, H., Chiang, F., Au K. Y, Huid, M. K. (2011). The moderating effect of collectivistic orientation in psychological empowerment and job satisfaction relationship. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 30(2), 319-328.
10. Kim S. Y. (2013). Exploring the relationships among leader-member exchange, employee empowerment and Job satisfaction in public organizations. Indiana University Bloomington School of Public and Environmental Affairs; Paper presented at the 12th Public Management Research Conference, Madison, Wisconsin, June 20-22.
11. Wang, G., Lee, P. D. (2009). Psychological empowerment and job satisfaction an analysis of interactive effects. Group & Organization Management, 34 (8), 271-296.
12. Weichun Zhu, Sosik, John J., Riggio, Ronald E. & Yang Baiyin (2012), Relationships between Transformational and Active Transactional Leadership and Followers’ Organizational Identification: The Role of Psychological Empowerment, Institute of Behavioral and Applied Management, pp. 186-212.
13. Raja, V., Bhavani, D. &Ramaprabou, V. (2015). The Demographical Study on Job Satisfaction and Emotional Intelligence of White Collar Employee at Puduchery, Indian Streams Research Journal, Vol. 5, Issue 7. pp. 1-7.
14. Organ, D, & Greene, C.N. (2006) .Role ambiguity, Locus of control and work satisfaction .Journal of applied psychology. 5:101-112.
15. Zimmerman. M. A, (2004). “Empowerment theory: psychological, organizational and
community levels of analysis”, Inrappaport j, seidman e, Eds, Handbook of community
psychology. New York, kluwer academic/ plenum publishers, PP 43–63.
16. Zand, D.E. (2007). Trust and managerial problem Solving. Administrative Science Quarterly. 17: 229 – 239
17. Kahn W.A. (2005). Psychological Conditions of personal engagement and disengagement at work. Academy of Management journal .33:692– 724
18. Jose, Joby, (2015). The Influence of Job Satisfaction on Organizational Culture and its Dimensions in it Industry, Golden Research Thoughts, vol. 4, issue 10, pp. 1-10.
19. Jain. Ajay K. Giga, Sabir I. Cooper, Cary L. (2008). “Employee wellbeing, control and