www.elsevier.com / locate / bres
Short communication
Expression of AMPA receptors in rat superior colliculus and effect of
orbital enucleation
a,b,c b a,c ,
*
Masahiro Kondo
, Rhyuji Sumino , Haruo Okado
a
Department of Neurobiology, Tokyo Metropolitan Institute for Neuroscience, 2 –6 Musashidai, Fuchu, Tokyo 183-8526, Japan
b
Department of Physiology, Nihon University, School of Dentistry, Chiyoda 101-8310, Japan
c
Core Research for Evolutional Science and Technology(CREST), Japan Science and Technology Corporation, Kawaguchi, Saitama 332-0012, Japan
Accepted 22 August 2000
Abstract
We analyzed the distribution and the morphological characteristics of neurons expressing AMPA-type glutamate receptor subunits (GluR1 and GluR2) in the superficial partition (stratum zonale (SZ), stratum griseum superficiale (SGS) and stratum opticum (SO)) of the rat superior colliculus. GluR1-expressing neurons had round or ovoid somata in SGS and round or fusiform somata and primary dendrites extending tangential or horizontal side in SO. On the other hand, GluR2-expressing neurons mainly corresponded to vertical fusiform cells with vertically oriented dendrites in SGS and medium-sized stellate or ovoid cells with many primary dendrites in SO. The results suggest that the expressions of GluR1 and GluR2 are differentially regulated in individual neurons of the superficial partition. To analyze the effect of retinal deafferentation on the expression of the GluRs, we performed unilateral orbital enucleations in rats within a week after birth. Thirty days after retinal lesioning, lower expression of GluR2 mRNA was observed in the neurons of the contralateral side as compared with that of the ipsilateral side in SO, but not in SGS. These results indicate that GluR2 expression in the SO neurons is regulated by the correct afferentation from the retina. 2000 Elsevier Science B.V. All rights reserved.
Theme: Neurotransmitters, modulators transporters, and receptors
Topic: Excitatory amino acid receptors: structure, function and expression
Keywords: GluR1; GluR2; Calbindin-D28k; Digoxigenin; In situ hybridization; Deafferentation
The superior colliculus (SC) of the rat has a hepta- central nervous system, although there are various regional laminated structure which is divided into two major differences in the distribution [2,11,17]. In situ hybridiza-partitions, a superficial layer (including the stratum zonale tion (ISH) using radioisotope (RI)-labeled oligonucleotide (SZ), stratum griseum superficiale (SGS) and stratum probes [19] and immunohistochemical [18] analysis sug-opticum (SO)) and a deep layer. In the rat visual system, gested that the main subunits of AMPA receptors in the most retinal ganglion cells project contralaterally to the superficial partition of the rat SC were GluR1 and GluR2. superficial partition [15]. It was recently reported that the Very little is known, however, about the expression of the SGS and SO neurons receive direct retinal excitation GluR subunits in individual cells. Therefore, we studied mediated by ionotropic glutamate receptors [7,16]. the expression patterns of GluR mRNAs in the individual On the basis of their pharmacological properties, the neurons of the superficial partition by ISH using digox-ionotropic glutamate receptors are divided into three igenin-labeled RNA probes.
distinct groups, NMDA, AMPA and kainate receptors The products of all RNA probes were constructed and [5,17]. AMPA receptors consist of four subunits (GluR1– ISH was performed according to the technique described in GluR4) and are distributed ubiquitously throughout the Kondo et al. [10] and Ichikawa et al. [6], respectively. The color reaction was performed at RT for 4 h. Under this condition, no signals were detected in adjacent sections *Corresponding author. Tel.: 181-42-325-3881; fax:
181-42-321-which were reacted with GluR1 and GluR2 sense strand 8678.
E-mail address: [email protected] (H. Okado). probes (data not shown). The expression patterns of GluR1
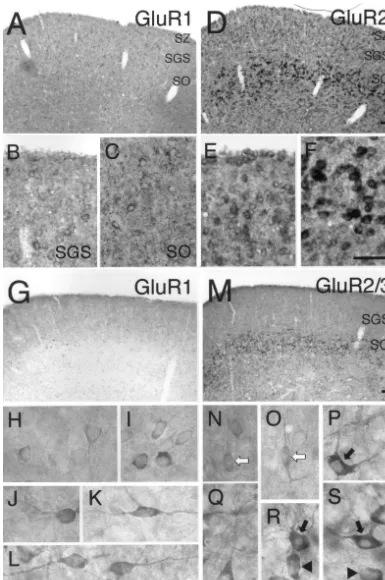
and GluR2 mRNAs showed different laminar distributions of GluR2 mRNA is correlated with increased calcium in the superficial partition. GluR1 mRNA was expressed in permeability of AMPA receptors in the neurons [8]. a few neurons of the SZ, and some neurons of the SGS and Because the cells with round or ovoid somata in the SGS SO (Fig. 1A). The intensity of GluR1 mRNA expression and with ovoid or fusiform somata and tangentially or was weak in individual neurons throughout the SZ to SO horizontally oriented dendrites in the SO showed GluR1 (Fig. 1B,C). On the other hand, GluR2 mRNA was but not GluR2 / 3 immunoreactivity, they might have expressed in many neurons of the SZ to SO (Fig. 1D). The calcium-permeable AMPA receptors. Recently, by whole-intensity was moderate in individual neurons of the SZ and cell patch-clamp recording in SC slice preparations, cal-SGS (Fig. 1E) and strong in the neurons of the SO (Fig. cium-permeable AMPA receptors have been detected in a
1F). few neurons of the superficial partition (personal
com-To determine the morphological characteristics of the munication from Dr. T. Isa). These neurons may corre-GluR subunit-expressing neurons, we next performed DAB spond to the GluR1-positive cells detected in the present immunohistochemical study. The coronal sections (50mm) study.
were first treated in PBS containing 0.4% Triton X-100 for To determine the effect of the removal of retinal input 30 min at RT, and then transferred to PBS containing 5% on the levels of the expression of GluR1 and GluR2 in normal goat serum for 1 h at RT. Sections were then individual neurons of the superficial partition, unilateral incubated with anti-GluR1 or -GluR2 / 3 antibody (2 mg / orbital enucleations of Sprague–Dawley (albino) rats with-ml, Chemicon International) in PBS overnight at 48C. The in a week of birth were performed. The optic nerve was next day, sections were incubated with biotinylated anti- completely transsected at 1–2 mm behind the eyeball using rabbit IgG (1:200 dilution, Vector Laboratories) for 1 h at a microsurgical instrument. Enucleated (n56) and control RT. Sections were incubated with a 1:100 dilution of the (n56) rats were maintained on a regular light cycle for 30 ABC complex (Vector Laboratories) in PBS and then days after eye removal and were then sacrificed.
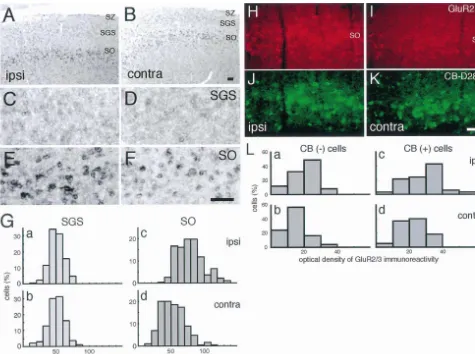
reacted with 0.5 mg / ml 3,3-diaminobenzidine (Sigma) and We could not precisely evaluate the change of level of 0.025% H O in PBS. Sections were mounted on silane-2 2 expression of GluR1 mRNA in any of the experimental coated slides, dehydrated, cleared in xylane and coverslip- groups of rats because the level of expression was low ped with Permount (Fisher Scientific). even in the neurons of the SC of intact rats. The lower It has previously been reported that GluR3 mRNA expression of GluR2 mRNA was observed in the SO of the expression was weak, whereas GluR2 mRNA expression contralateral side compared with that of the ipsilateral side was moderate or strong in the superficial partition [19]. in rats enucleated, although no change of mRNA expres-Therefore, we consider that the GluR2 / 3 immunoreactivity sion was observed in the contralateral SGS (5 out of 6 rats, mainly reflects the expression of GluR2. The patterns of Fig. 2A–G). In addition, the change of GluR2 / 3-immuno-GluR1 and GluR2 / 3 immunoreactivities in each layer were reactivity in the SO was similar to that of GluR2 mRNA similar to those of GluR1 and GluR2 mRNA expression, expression after enucleation (Fig. 2H, I).
respectively (Fig. 1G, M). GluR1-immunoreactive neurons Calbindin-D28k, which belongs to the EF-hand family, of the SGS (Fig. 1H) and the SGS–SO border (Fig. 1I) has high calcium binding activity [1]. Some groups have had mainly round or ovoid somata. In the SO, some reported that orbital enucleation appeared to have no effect GluR1-immunoreactive neurons with round somata and a on the distribution of calbindin-D28k-positive cells in adult few primary dendrites extending horizontally or tangential- rats [12,20]. Under our experimental condition, the dis-ly on the side were observed (Fig. 1J and L). In addition, a tribution of calbindin-D28k-positive neurons in SO did not few neurons with horizontal fusiform somata and horizon- change between the ipsilateral and the contralateral side tally oriented dendrites were observed in the SO (Fig. 1K). (Fig. 2J,K).
On the other hand, most GluR2 / 3-immunoreactive neurons Almost all of the calbindin-D28k-immunoreactive neu-of the SGS had vertical fusiform somata and dorsally rons in the SO project to the lateral posterior nucleus, and / or ventrally projecting dendrites (Fig. 1N, O white although their physiological roles have not been elucidated arrows). In the SO, GluR2 / 3-immunoreactive neurons had [13]. In our morphological study (Fig. 1N–S), a subpopu-various shapes. The neurons included medium-sized stel- lation of GluR2 / 3-immunoreactive neurons resembled the late cells with dendrites oriented in various directions (Fig. cells described previously as calbindin-D28k-expressing 1P, R, S black arrows), pyramidal cells with dorsally neurons [3,4]. Therefore, the correlation between GluR2 / 3 projecting dendrites (Fig. 1Q) and cells with ovoid somata and calbindin-D28k immunoreactivities in the SO neurons and a few dendrites (Fig. 1R, S arrowheads). These results of intact rats was investigated by double fluorescence indicate that GluR1 and GluR2 / 3 were mainly expressed immunostaining [10] using Cy3-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG in morphologically different neurons, which suggests that (1:200 dilution, Jackson ImmunoResearch) and FITC-the expressions of GluR1 and GluR2 are differently conjugated anti-mouse IgG (1:70 dilution, Vector Lab-regulated in individual cells of the superficial partition of oratories). About half (82 / 142) of GluR2 / 3-immuno-the SC as well as o3-immuno-ther forebrain regions. reactive neurons were intensely labeled by
Fig. 2. Effect of unilateral orbital enucleation on the expression of GluR2 in the neurons of the superficial partition of the rat SC. (A–F) Photographs show the change of expression of GluR2 mRNA in the SO at 30 days after enucleation of rats within a week of birth. (A) and (B) show overviews at low magnification. No difference of mRNA expression was observed in the contralateral SGS (D) as compared with the ipsilateral SGS (C). On the other hand, lower expression of GluR2 mRNA was observed in the contralateral SO (F) as compared with the ipsilateral SO (E). (G) Histograms indicate the distribution of the intensities of GluR2 mRNA expressions, were quantified by an image analysis system (NIH Image), in the ipsilateral (a, n5173; c, n5188) and contralateral (b, n5193; d, n5190) sides of the SGS (a, b) and SO (c, d) neurons. (H–K) Photographs show the GluR2 / 3 (H,I) and / or calbindin-D28k (J, K) immunoreactivities at 30 days after surgery in the SO of rats enucleated at P7. Lower immunoreactivity of GluR2 / 3 was observed in the contralateral SO as compared with the ipsilateral (H, I), although no difference of calbindin-D28k immunoreactivity was observed in the SO (J, K). (L) The histograms show the distribution of the level of GluR2 / 3 immunoreactivity, were quantified in terms of mean optical density using NIH Image, in the ipsilateral (a, n550; c, n566) and contralateral (b, n550; d, n576) SO neurons classified on the basis of the calbindin-D28k expression. CB, calbindin-D28k. Scale bar, 100mm.
We next investigated whether there is a difference projections [9]. Recently, several groups demonstrated that between the intensity of GluR2 / 3 immunoreactivity in the the retinal ganglion cells monosynaptically projected to calbindin-D28k-positive and -undetectable neurons after both SGS and SO neurons [14,16]. However, there is little orbital enucleation. In both calbindin-D28k-positive and accurate evidence about the cortico-fugal projection pat--undetectable cells, the distribution curves were similarly terns in each layer. Interestingly, the lower expression of shifted towards lower GluR2 / 3 expression after retinal GluR2 after enucleation was specifically observed in the lesioning (Fig. 2L). The similar changes in different types contralateral SO, but not the SGS. The difference after of cells in the SO suggest that the lower expression of retinal deafferentation may reflect distinct projection pat-GluR2 mRNA seems to occur in most SO neurons, rather terns from the cortex to each layer of the superficial than in only limited projection neurons. These results partition.
suggest that GluR2 expression in the most SO neurons is regulated by the correct afferentation from retina. And they
also indicate that the regulation of GluR2 expression does Acknowledgements
not depend on the calbindin-D28k expression.
[9] H.P. Killackey, R.S. Erzurumlu, Trigeminal projection to the su-Dr. S. Sasaki (TMIN) and su-Dr. T. Isa (National Institute for
perior colliculus of the rat, J. Comp. Neurol. 201 (1981) 221–242. Physiological Sciences) for discussions, and Dr. M.
Hol-[10] M. Kondo, R. Sumino, H. Okado, Combinations of AMPA receptor lmann and Dr. J. Boulter (Salk Institute for Biological subunit expression in individual cortical neurons correlate with Studies) for generously providing the GluR1 and GluR2 expression of specific calcium-binding proteins, J. Neurosci. 17 cDNA clones, respectively. This work was supported by (1997) 1570–1581.
[11] M. Kondo, S. Okabe, R. Sumino, H. Okado, A high GluR1:GluR2
the Ministry of Education, Science, and Culture of Japan 21
expression ratio is correlated with expression of Ca -binding (H.O.), Research Fellowships of the Japan Society for the
proteins in rat forebrain neurons, Eur. J. Neurosci. 12 (2000) Promotion of Science for Young Scientists (M.K.) and 2812–2822.
Japan Science and Technology Corporation (M.K. and [12] R.D. Lane, D.M. Allan, C.A. Bennett-Clarke, R.W. Rhoades,
Dif-H.O.). ferential age-dependent effects of retinal deafferentation upon
calbindin- and parvalbumin-immunoreactive neurons in the superfi-cial layers of the rat’s superior colliculus, Brain Res. 740 (1996) 208–214.
References [13] R.D. Lane, D.M. Allan, C.A. Bennett-Clarke, D.L. Howell, R.W.
Rhoades, Projection status of calbindin- and parvalbumin-immuno-¨
[1] C. Andressen, I. Blumcke, M.R. Celio, Calcium-binding proteins: reactive neurons in the superficial layers of the rat’s superior selective markers of nerve cells, Cell Tissue Res. 271 (1993) colliculus, Vis. Neurosci. 14 (1997) 277–286.
181–208. [14] X. Li, A. Hallqvist, I. Jacobson, O. Orwar, M. Sandberg, Study on [2] F. Conti, R.J. Weinberg, Shaping excitation at glutamatergic the identity of the rat optic nerve transmitter, Brain Res. 706 (1996)
synapses, Trends Neurosci. 22 (1999) 451–458. 89–96.
[3] R.J. Cork, S.Z. Baber, R.R. Mize, CalbindinD28k- and parvalbumin- [15] R. Linden, V.H. Perry, Massive retinotectal projection in rats, Brain immunoreactive neurons form complementary sublaminae in the rat Res. 272 (1983) 145–149.
superior colliculus, J. Comp. Neurol. 394 (1998) 205–217. [16] F.-S. Lo, R.J. Cork, R.R. Mize, Physiological properties of neurons [4] B. Dreher, D.A. Barker, M.R. Bath, K.A. Keay, Spatiotemporal in the optic layer of the rat’s superior colliculus, J. Neurophysiol. 80
pattern of ontogenetic expression of calbindin-28 / kD in the re- (1998) 331–343.
tinorecipient layers of rat superior colliculus, J. Comp. Neurol. 376 [17] S. Ozawa, H. Kamiya, K. Tsuzuki, Glutamate receptors in the (1996) 223–240. mammalian central nervous system, Prog. Neurobiol. 54 (1998) [5] M. Hollmann, S. Heinemann, Cloned glutamate receptors, Annu. 581–618.
Rev. Neurosci. 17 (1994) 31–108. [18] R.S. Petralia, R.J. Wenthold, Light and electron immunocytochemi-[6] T. Ichikawa, K. Ajiki, J. Matsuura, H. Misawa, Localization of two cal localization of AMPA-selective glutamate receptors in the rat
cholinergic markers, choline acetyltransferase and vesicular acetyl- brain, J. Comp. Neurol. 318 (1992) 329–354.
choline transporter in the central nervous system of the rat: in situ [19] K. Sato, H. Kiyama, M. Tohyama, The differential expression hybridization histochemistry and immunohistochemistry, J. Chem. patterns of messenger RNAs encoding non-N-methyl-D-aspartate Neuroanat. 13 (1997) 23–39. glutamate receptor subunits (GluR1-4) in the rat brain, Neuroscience [7] T. Isa, T. Endo, Y. Saito, The visuo-motor pathway in the local 52 (1993) 515–539.
circuit of the rat superior colliculus, J. Neurosci. 18 (1998) 8496– [20] R. Schmidt-Kastner, D. Meller, U.T. Eysel, Immunohistochemical
8504. changes of neuronal calcium-binding proteins parvalbumin and
[8] P. Jonas, N. Burnashev, Molecular mechanisms controlling calcium calbindin-D28k following unilateral deafferentation in the rat visual entry through AMPA-type glutamate receptor channels, Neuron 15 system, Exp. Neurol. 117 (1992) 230–246.