A SET OF ANALYTICAL EXPOSITION TEXT SPEAKING
MATERIALS USING VIDEOS TO DEVELOP STUDENTS’
CRITICAL THINKING FOR 11
thGRADER OF LANGUAGE
DEPARTMENT OF
SMA STELLA DUCE 2 YOGYAKARTA
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By Asri Purnamasari Student Number: 071214129
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TEACHER TRAINING AND EDUCATION SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
i
A SET OF ANALYTICAL EXPOSITION TEXT SPEAKING
MATERIALS USING VIDEOS TO DEVELOP STUDENTS’
CRITICAL THINKING FOR 11
thGRADER OF LANGUAGE
DEPARTMENT OF
SMA STELLA DUCE 2 YOGYAKARTA
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By Asri Purnamasari Student Number: 071214129
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TEACHER TRAINING AND EDUCATION SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
iv
I dedicate this thesis to:
My Jesus Christ and Mother Marry
v
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY
I honestly declare that this thesis, which I have written, does not contain the work or parts of the work of other people, except those cited in the quotations and the references, as a scientific paper should.
Yogyakarta, 7th December 2011
The Writer
vi
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN
PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIAH UNTUK KEPENTINGAN AKADEMIS
Yang bertanda tangan di bawah ini, saya mahasiswa Universitas Sanata Dharma: Nama : Asri Purnamasari
NIM : 071214129
Demi pengembangan ilmu pengetahuan, saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma karya ilmiah saya yang berjudul:
A SET OF ANALYTICAL EXPOSITION TEXT SPEAKING MATERIALS
USING VIDEOS TO DEVELOP STUDENTS’ CRITICAL THINKING FOR
11th GRADER OF LANGUAGE DEPARTMENT OF SMA STELLA DUCE 2
YOGYAKARTA
beserta perangkat yang diperlukan (bila ada). Dengan demikian saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma hak untuk menyimpan, mengalihkan dalam bentuk media lain, mengelolanya dalam bentuk pangkalan data, mendistribusikan secara terbatas, dan mempublikasikannya di internet atau media lain untuk kepentingan akademis tanpa perlu meminta ijin dari sayameupun memberikan royalti kepada saya selama tetap mencantumkan nama saya sebagai penulis.
Demikian pernyataan ini yang saya buat dengan sebenarnya. Dibuat di Yogyakarta
Pada tanggal: 7 Desember 2011
vii
ABSTRACT
Purnamasari, Asri. 2011. A Set of Analytical Exposition Text Speaking Materials Using Videos to Develop Students’ Critical Thinking for 11th Grader of Language Department of SMA Stella Duce 2 Yogyakarta. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
In learning English, especially learning an analytical exposition text speaking materials, students often find difficulties to build and share their opinion and arguments about some cases in their speaking activity. This problem happens because the students lack media to support them to find background information about the case or topic of speaking activities. In fact, in this present English learning in teenagers especially in senior high school, teachers attempt to provide modern and creative learning English activity using effective media in the classroom. Knowing the fact that speaking skill in analytical exposition is important, the researcher does this research in order to design more appropriate set of Analytical Exposition Text speaking materials using videos to develop students’ critical thinking for 11th Grader of Language Department of SMA Stella Duce 2 Yogyakarta.
This research was carried out to answer two research questions: (1) how is a set of Analytical Exposition Text speaking materials using videos to develop students’ critical thinking for 11th Grader of Language Department of SMA Stella Duce 2 Yogyakarta designed? and (2) what does a set of designed Analytical Exposition Text speaking materials using videos to develop students’ critical thinking for 11th Grader of Language Department of SMA Stella Duce 2 Yogyakarta look like?
viii
To answer the second research question, the researcher presented the final version of the speaking materials after conducting some revisions based on comments and suggestions from the post-designed respondents. The material consists of four units. Every unit of the designed materials includes two stages, and in every stage there are four sections, namely Let’s Start, Let’s Focus, Let’s Practice, and Let’s Review.
ix
ABSTRAK
Purnamasari, Asri. 2011. A Set of Analytical Exposition Text Speaking Materials Using Videos to Develop Critical Thinking for XI Grade of Language Department of SMA Stella Duce 2 Yogyakarta. Yogyakarta: Program Studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Dalam membelajari Bahasa Inggris, khususnya mempelajari teks Ekposisi Analitis, siswa sering menghadapi kesulitan dalam membangun dan menyampaikan pendapat serta argumentasi mereka mengenai topik pembicaraan dalam ketrampilan berbicara. Permasalahan ini terjadi karena siswa kekurangan media untuk mendukung mereka dalam menemukan informasi mengenai permasalahan dan topik pembicaraan tersebut. Pada kenyataannya, dalam proses pembelajaran Bahasa Inggris bagi para remaja saat ini khususnya di sekolah menengah atas, guru mencoba untuk menyediakan aktivitas modern dan kreatif dalam pembelajaran Bahasa Inggris dengan menggunakan media yang efektif di dalam kelas. Berdasarkan kenyataan bahwa pentingnya kemampuan berbicara dalam Teks Ekposisi Analitis, peneliti melakukan penelitian ini untuk membuat set materi pembelajaran berbicara Teks Ekposisi Analitis dengan menggunakan videos untuk mengembangkan pemikiran kritis siswa kelas 11 jurusan bahasa di SMA Stella Duce 2 Yogyakarta.
Penelitian ini dilaksanakan untuk menjawab 2 masalah penelitian: (1) bagaimana set materi pembelajaran berbicara Teks Ekposisi Analitis dengan menggunakan videos untuk mengembangkan pemikiran kritis siswa kelas 11 jurusan bahasa di SMA Stella Duce 2 Yogyakarta dirancang? dan (2) seperti apakah set rancangan materi pembelajaran berbicara Teks Ekposisi Analitis dengan menggunakan videos untuk mengembangkan pemikiran kritis siswa kelas 11 jurusan Bahasa di SMA Stella Duce 2 Yogyakarta tersebut?
x
hasil menunjukkan bahwa nilai tengah dari tiap pernyataan berkisar antara 3.6 sampai 4.6 dari skala 5. Maka dapat disimpulkan bahwa set materi pembelajaran berbicara Teks Ekposisi Analitis dengan menggunakan videos untuk mengembangkan pemikiran kritis siswa kelas 11 jurusan Bahasa SMA Stella Duce 2 Yogyakarta tersebut baik dan dapat diterima.
Untuk menjawab pertanyaan kedua dalam rumusan permasalahan, penulis menyajikan versi akhir dari materi pembelajaran setelah mendapat komentar dan masukan dari responden. Materi pembelajaran berbicara terdiri dari 4 unit yang dalam setiap unitnya mempunyai 4 bagian yaitu Let’s Start, Let’s Focus, Let’s Practice, and Let’s Review.
xi
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
My greatest gratitude goes to my One, Jesus Christ, for His marvelous grace, everlasting love and endless guidance throughout my life. Without Him, I could not have passed the hard times in completing my thesis. I would like to express my thankfulness to Mother Mary for wonderful mercy and prayer.
I am particularly indebted to Agustinus Hardi Prasetyo, S.Pd., M.A. as my advisor, who has been willing to devote his valuable time to read, correct and give suggestions on my thesis patiently. Without his help, I would not be able to finish my thesis.
I owe a great debt to Gregorius Punto Aji, S.Pd., M.Hum., Fidelis Chosa Kastuhandani, S.Pd., M.Hum. and Adesti Komalasari, S.Pd., M.A. for their invaluable assistance to evaluate my designed materials. I also thank all of the secretariat staff of English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University and all librarians who have assisted me during the completion of my thesis. I also address my deepest gratitude to all English Language Education Study Program lecturers who kindly and patiently teach me from the first semester as the beginner in English language education until now, I can finish my thesis and I can get much knowledge which is very useful for my everlasting life. Hope that all of them might get the best blessing from Jesus Christ for the whole dedications as lecturers in Sanata Dharma University and I will always pray for all of them.
xii
responded and became the participants for the whole steps of finishing this thesis. I also thank my beloved Stero Debate Club students who have given me inspiration, support and spirit to finish my thesis.
My deepest gratitude goes to my beloved parents Yohanes Wasana Minarta and Nanik Haryati Anyuk for the endless love and prayer for me. I owe my beloved little sister Emerensiana Jayati Wahastuti who always gives me support and spirit in my life, especially in finishing my thesis. I give my best gratitude to Wiliyanto Djung who loyally accompanies me in every struggle of my life, moreover in doing my thesis and along my journey of learning in English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University. I thank them all for their unconditional love and support. They have taught me how to value life in wonderful way. I love them all.
I address my gratitude to my other families for their support both spiritually and financially to Maryati Steiner and families, Yuliani Steiner and families, Romo Andalas, Pak Lek Gunarto and families, and all of my families. I thank them for all prayers and blessing in the whole process of finishing my thesis.
My special thanks go to my beloved friends. I thank them for coloring my life, sharing, laughs and loves. I thank the Class C of English Language Education Study Program of year 2007 students who become the friends from the first semester, give wonderful friendship and give many meaningful value of life during the togetherness in learning. I also address my gratitude to Lala, Bre, Popon, Asty, Haya, Dei, Raras, Yusak, Seto and Icha for the togetherness and friendship during my study at Sanata Dharma University since the first semester. I thank the Edulight members (Yohanes Heri Pranoto, S.Pd., Nidya Kusuma P. S.Pd., Susana Tri Cahyani, Asep Nugroho, Wendy Rahmad Biyadi, Bretya and Gloria) for the hard work and companionship. For my best friends, Dwi Yulianto Nugroho, S.Pd., Susana Tri Cahyani, Lidwina Widawati, who always understand and give me support in every parts of my life.
xiii
precious moments during these 4 years and the most special one Sr. Benedicte for caring and loving me. The last, I also give my deepest gratitude to all the people whose name I cannot mention one by one for their practice, friendship and attention. I thank you very much for the whole people around.
xiv
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
TITLE PAGE... i
APPROVAL PAGES……… ii
DEDICATION PAGE……….. iv
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY………. v
PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI……….. vi
ABSTRACT……….. vii
ABSTRAK……….. ix
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS………. xi
TABLE OF CONTENTS………. xiv
LIST OF TABLES………... xviii
LIST OF FIGURES………. xix
LIST OF APPENDICES………. xx
CHAPTER 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1Research Background……….... 1
1.2 Research Problem……….. 7
1.3Problem Limitation……… 7
1.4Research Objective……… 8
1.5Research Benefits……….. 9
1.6Definition of Terms……… 11
CHAPTER 2. REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE 2.1 Theoretical Description……… 19
2.1.1 Material Design Models……… 20
2.1.1.1 Instructional Design Model……… 21
2.1.1.1.1 Kemp’s Model………. 22
xv
2.1.1.1.3 Davies’ Model………. 26
2.1.1.2Interactive Design Model for the Videos Design… 30 2.1.2 Tyler’s Approach……… 32
2.1.3 English Standard and Basic Competence 2006 for Senior High School………. 33
2.1.4 Material Adaptation……….. 34
2.1.5 English Analytical Exposition Text……….. 36
2.1.6 Teaching Speaking Skill………. 38
2.1.7Videos and English Language Teaching……….. 38
2.1.7.1 Videos as an Audiovisual Aid in English Language Teaching……….. 38
2.1.7.2Videos Application In English Language Teaching 40 2.1.7.3The Potential and Limitations of Videos………….. 40
2.1.7.4The Visual Element in Communication…………... 41
2.1.7.5Teaching with Videos………. 42
2.1.7.6Using Videos in Language Teaching……….. 45
2.1.8 Critical Thinking……….. 46
2.2 Theoretical Framework……… 48
CHAPTER 3. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY 3.1Research Method………. 53
3.2Research Setting………. 66
3.3Research Participants……….. 67
3.3.1 Research Participants of the Pre-design Study……… 67
3.3.2 Research Participants of the Post-design Study…… 68
3.3.3 Research Subject……… 69
3.4 Instruments and Data Gathering Technique……… 69
3.4.1 Instruments………...70
3.4.1.1Questionnaire………. 70
3.4.1.2Interview and Observation……… 71
xvi
3.4.2.1Schedule……… 72
3.4.2.2Technique of Selecting The Respondents…………. 73
3.5 Data Analysis Technique………. 74
3.5.1 Data Analysis Technique of the Pre-design Study 74 3.5.2 Data Analysis Technique of the Post-design Study 75 3.6 Research Procedures……….. 78
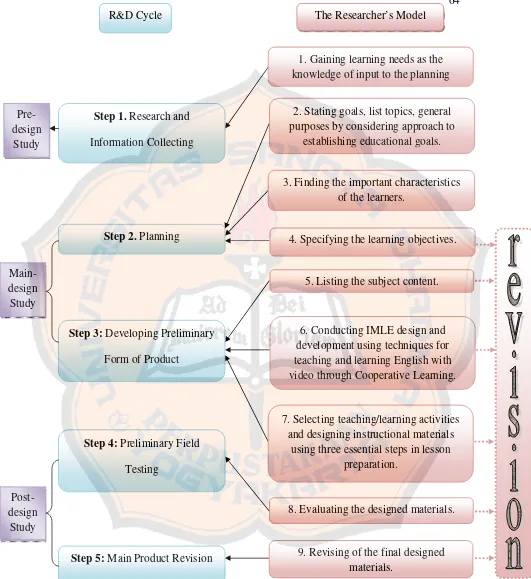
CHAPTER 4. RESEARCH RESULTS AND FINDINGS 4.1 The Result of Elaboration of the Steps of the Researcher’s Model Taken from Kemp’s Instructional Design Model to Design A Set of Analytical Exposition Text Speaking Materials Using Videos to Develop Students’ Critical Thinking for 11th Grader of Language Department of SMA Stella Duce 2 Yogyakarta………... 83
4.1.1 Gaining knowledge of inputs to the planning process: learning needs……….. 84
4.1.1.1 The Result and Analysis of the Questionnaire……. 85
4.1.1.2 The Result and Analysis of Interview the Students 94 4.1.1.3The Result and Analysis of Interview the Teachers 104 4.1.2 Considering Goals, Listing Topics, Stating the General Purposes………. 112
4.1.2.1Goals……….. 112
4.1.2.2Topics………... 114
4.1.2.3General Purposes……….. 115
4.1.3 Enumerating the Important Characteristics of the Learners……… 117
4.1.3.1Academic Factors………. 117
4.1.3.2Social Factors……… 118
xvii
4.1.5.1 Activities to Know the Students’ Knowledge
(Pre-Activities)………. 123
4.1.5.2 Activities to Give the Students Knowledge (Main-Activities)……….. 123
4.1.5.3 Activities to Explore the Students’ Achievements (Post-Activities)……… 125
4.1.6 Choosing the Appropriate Videos for the Topic of Learning……… 125
4.1.7 Selecting Teaching/Learning Activities and Designing Instructional Materials……….... 128
4.1.7.1 Teaching/Learning Patterns……….. 128
4.1.7.1.1 Group Presentation………. 128
4.1.7.1.2 Individualized Learning………. 129
4.1.7.1.3 Interaction between Teacher and Students……. 130
4.1.7.2 Instructional Resources……….. 130
4.1.7.2.1 Selecting Media (Videos)………... 130
4.1.7.2.2 Making the Final Decision on Media (Videos)… 131 4.1.8 Evaluating the Designed Materials……….. 131
4.1.9 Main Product Revision………. 142
4.2 The Brief Description of A Set of Analytical Exposition Text Speaking Materials Using Videos to Develop Students’ Critical Thinking for 11th Grader of Language Department of SMA Stella Duce 2 Yogyakarta……… 144
CHAPTER 5. CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS 5.1Conclusions………. 149
5.2Recommendations………. 151
5.2.1 For Senior High School English Teachers……… 152
5.2.2 For Future Researchers………. 153
REFERENCES………. 154
xviii
LIST OF TABLES
Table Page
1.1 Students Speaking Skill Activities Rubric………. 15
3.2 The Blueprint of the Results of the First Part of the Post-Design Questionnaire……… 77
4.1 The Result of the Questionnaire for 24 Students……… 85
4.3 General Purposes of the Designed Material……… 115
4.4 The Objectives of the Designed Material……… 120
4.5 The Description of the Respondents……… 132
xix
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure Page
2.1 The Kemp’s Instructional Model……… 24
2.2 Borich’s Stages of Planning Process………... 25
2.3 Davies’ Preliminary Steps in Lesson Planning………... 27
2.4 Davies’ Main Steps in Lesson Planning……….. 28
2.5 Davies’ Final Steps in Lesson Planning……….. 30
2.6 A Schematic Overview of the Principle Factors in IMLE Design and Development……….. 31
2.7 Tyler’s Approach to Establish Educational Goals……….. 33
2.8 A Model of Cooperative Learning………... 48
2.9 The Steps Used to Design the Set of Instructional Material in This Study………. 52
xx
LIST OF APPENDICES
APPENDICES………... 157
APPENDIX A: Surat Ijin Penelitian………... 158
APPENDIX B: The Observation Checklists………...160
APPENDIX C: The Lists of Questionnaire & Interview Questions…... 164
APPENDIX D: The Post-design Questionnaire………... 173
1
CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION
This thesis is conducted to design a set of Analytical Exposition Text Speaking Materials for 11th Grader of Language Department of SMA Stella Duce 2 Yogyakarta using Videos to Develop Students’ Critical Thinking. In this chapter, the researcher would like to discuss six major points. Those include research background, research problem, problem limitation, research objectives, research benefits, and definition of terms to avoid misunderstanding in this study. The further discussion about every part will be shown below.
1.1 Research Background
of important cases. To criticize some cases, students need to know the background knowledge that is needed to analyze the cases and then share their critical thinking about the cases. Therefore, students need media to help them find their critical thinking about some cases in their life. An Analytical Exposition Text unconsciously proposes the students as the speakers to criticize a problem in their real life. It is because in Analytical Exposition Text, the students are given some cases and then the students should give their arguments to criticize the cases, whether they agree or disagree with the thesis statement held by the cases. To criticize the thesis from the case, the students should be able to deliver their critical thinking about the case in oral language. Therefore, the students are proposed to be the speaker in using Analytical Exposition Text. Learning Analytical Exposition Text is important because students will use this kind of text in many kinds of speaking activities in school, debate or speech competition and many others. Moreover, in this globalization era, the students are demanded to master English, especially in speaking ability so that they can communicate effectively with many people around the world.
There are many kinds of media that are effectively used in learning English activity to help teachers and students achieve their learning goals. Gerlach and Donal (1973) states that media have four general purposes:
1. media can help to simplify the teaching process,
2. media are machines that allow the teachers to practice the principle of object teaching and illustration,
3. media help the students to reduce the use of their mother tongue, and 4. media are the instruments of motivation to stimulate the teaching and
learning process (p.241).
One of the important media to support creative and effective English learning activity in the classroom is videos. Boyle (1997) stated that videos provide a very powerful resource for learning. To obtain the full benefits of videos for learning, the videos should be used as an active resource. The learners should not just view the videos, they should use it. The use of videos needs to be functionally integrated into the overall learning context. Therefore, in this research, the videos are used as the media to help students think about the cases given. By watching the videos, students can grasp background knowledge on the case and then they can analyze the thesis statement based on the background knowledge they get in the videos. In this case, to learn an Analytical Exposition Text speaking materials, students need media which can help them to gain enough information about the topic, so that they can build and share their critical thinking about the topic in some speaking activities.
activities. By using videos, students can also have fun and enjoy situation in learning activity to improve their speaking ability, so that they will not be bored. Besides, the students can also find new idea and new vocabularies after watching the videos. The students can also learn correct pronunciation, speaking style and also speaking techniques by watching the videos.
Stempleski (1987) stated that videos can be used in a variety of instructional setting such as in classroom, in self study and in evaluation situation. Therefore, to help the students to learn Analytical Exposition Text speaking materials, the students need a successful speaking activity which is supported by the videos.
The characteristics of a successful speaking activity are:
1. Learners talk a lot. As much as possible of the period of time allotted to the activity is in fact occupied by learner talk. This may seem obvious, but often most time is taken up with teacher talk or pauses. 2. Participation is even. Classroom discussion is not dominated by a
minority of talkative participants: all get a chance to speak, and contributions are fairly evenly distributed.
3. Motivation is high. Learners are eager to speak; because they are interested in the topic and have something new to say about it, or because they want to contribute to achieving a task objective.
4. Language is of an acceptable level. Learners express themselves in utterances that are relevant, easily comprehensible to each other, and of an acceptable level of language accuracy.
something, to negotiate or solve a particular problem, and to maintain social relationship and friendship. By watching a videos the students can get information of the issues through their audio and visual ability of learning. As the result, the students can have the background knowledge of the issues that are needed to criticize issues and they can easily construct their idea about the issues.
For 11th Grader of Language Department of SMA Stella Duce 2 Yogyakarta, English is one of the major subjects that has 8 hours per week. Since there are 8 hours per week for students to learn English, they should have great ability in written and spoken English. One of the learning topics that are learned in English subject according to Standard Competency and Basic Competency for Senior High School in the first semester is about an Analytical Exposition Text. An analytical exposition becomes one of texts used as the materials for their progress and final test.
is to promote a particular point of view about something and through arguments which are supported by some facts.
Through the observation phases in SMA Stella Duce 2 Yogyakarta, the researcher found that many students were difficult to develop their critical thinking just by using their imagination about some important issues. Therefore, by using videos to show the clear background knowledge and status quo of the issues, the students are really helped to develop their critical thinking. They can digest the stimulus that is served by the videos and then they can easily think about their opinion and perception of the certain important issues. If they have built their critical thinking about some topics or issues, they would have easily shared their arguments through speaking skill. Moreover, in SMA Stella Duce 2 Yogyakarta, the students can access internet easily and quickly so that it can really support them to access videos which are related to the topic of learning to support them in teaching and learning English process.
and fun in the classroom, so that they would not be bored and they would learn enthusiastically.
Knowing the fact that speaking skill is important in learning and using Analytical Exposition Text, the researcher does this research in order to design more appropriate and effective media as set of English Analytical Exposition Text speaking materials for 11th Grader of Language Department of SMA Stella Duce 2 Yogyakarta using videos to develop the students’ critical thinking.
1.2 Research Problem
In this research there are two main problems to be solved based on the problems elaborated in the background of the research, they are:
1. How is a set of Analytical Exposition Text speaking materials for 11th Grader of Language Department of SMA Stella Duce 2 Yogyakarta using videos to develop students’ critical thinking designed?
2. What does a set of designed Analytical Exposition Text speaking materials for 11th Grader of Language Department of SMA Stella Duce 2 Yogyakarta using videos to develop students’ critical thinking look like?
1.3 Problem Limitation
students’ English speaking skill which is supported by some aspects of learning, such as learners’ characteristics, learning style and the effective learning strategy in SMA Stella Duce 2 Yogyakarta is videos. The focus of learning that is improved in these materials is students’ critical thinking of some issues in the use Analytical Exposition Text through their speaking skill.
There are 25 students of 11th Grader of Language Department of SMA Stella Duce 2 Yogyakarta who become the participants of the research. They are about 16-17 years old. One reason why the researcher only focuses on the use of videos to develop students’ critical thinking in speaking an Analytical Exposition Text is because this kind of text needs appropriate media to give the students background knowledge about the topic of learning. The ability of using speaking skill fluently in students’ English competency is really important and demanded in this modern and globalization era. Using videos to improve the students’ critical thinking in speaking an Analytical Exposition Text will support the students in using great spoken English appropriately and fluently. Through learning these materials, the students can also improve their English information in general.
1.4 Research Objectives
The research objectives of this research are to answer the identified problem formulations, they are:
2. To present a set of designed Analytical Exposition Text speaking materials for 11th Grader of Language Department of SMA Stella Duce 2 Yogyakarta using videos to develop students’ critical thinking.
1.5 Research Benefits
This research has benefits for both formal and informal education. In formal education, it will be useful for Senior High School teaching and learning English activity. The teachers and also the students will get the benefits of the designed materials. Then for informal education, this research will be useful for debate club, speaking conversation club, speech club, English speaking course, and many others. The research will be useful also for the researcher and also for the further researchers. The benefits of this research, therefore, can be clarified as follows:
1. For students of 11th Grader of Language Department of SMA Stella Duce 2 Yogyakarta
2. For the English teacher
The English teacher would also be provided with well developed Analytical Exposition Text materials, which are suitable to the students’ need in modern teaching and learning activity at this modern and computer based learning era. Therefore, the teacher who is willing to teach English speaking skill class using videos can use the effective, appropriate and suitable materials to achieve the goals of English teaching activities, especially in teaching Analytical Exposition Text.
3. For the researcher
4. For Future Researchers
The researcher hopes that this research can be useful for everyone who wants to conduct a research or study related to the use of videos in developing the materials for teaching and learning English activity, especially the Analytical Exposition Text materials for English speaking skill. Moreover, this research is needed the further research in order to evaluate, reprogram, update and reconstruct the designed materials.
5. For Debate Club, Speaking Conversation Club, Speech Club, and English Speaking Course.
The designed materials will be useful for the non formal education like debate club, speaking conversation club, speech club, English speaking course, and many others. As it is stated before, Analytical Exposition Text is useful for many kinds of speaking activities, especially in debate and speech activities. This designed materials support the implementation of Analytical Exposition Text in the speaking activities by using videos to develop critical thinking. Therefore, the non formal education will find the fun way of learning Analytical Exposition Text speaking materials by using this set of materials designed.
1.6 Definition of Terms
terms used in this research easily. The keywords and also the phrases will be defined related to the research. Therefore, in this section, it is important to define the following terms.
1. Design
Design is the general arrangement or planning. Design is as “a developed plan to guide educational activity in a situation” (Houle, 1978:230). In designing for multimedia learning, as it is explained by Boyle (1997:3), conceptual design is concerned with a three issues, they are:
- Content structuring
- The structuring of interactivity
- Creating a coherent compositional frame
Kemp (1997:8) stated that in instructional design plan, there are three questions to be answered as the essential elements of instructional technology: 1. What must be learned? (objectives)
2. What procedures and resources will work best to reach the desired learning levels? (activities and resources)
2. Analytical Exposition Text
Analytical Exposition Text is a text that relies on arguments, so sometimes it is called an argumentative text and its social function is to persuade the reader or listener that something is a case, so sometimes it is called a persuasive text (Sudarwati, & Grace, 2007).
An analytical expositiontext is a sort text which is meant to persuade the readers or listeners that something is the case or important. In persuading the readers or listeners, some supporting ideas or arguments on why the researcher’s opinion is important, are presented. Since analytical exposition is popular among scientists, academic community and educated people then you can find this type of text in scientific books, journals, magazines, newspaper articles, academic speech or lectures, research report etc (Cantiqa, Analytical Exposition Text, Thursday, May 5th, 2011).
In this study, Analytical Exposition Text is a kind of argumentative texts whose the purpose is to promote a particular point of view about something and the arguments proposed are supported by the facts to strengthen their arguments, so that the listener will be confined by the speakers’ idea.
3. Speaking
teachers should come on to what the problems are presently to create an effective speaking activity.
Iberri-Shea (2009) states that there are several clear advantages of using public speaking such as presentation and debate tasks in English Language Teaching; 1) practice with all four language skills (listening, speaking, reading, and writing; 2) development of critical thinking skills; 3) improved learning. While preparing for public speaking assignments such as presentation and debate, students are asked to develop a position, explore beliefs and theories, analyze arguments, evaluate the credibility or bias of a source, and distinguish between relevant and irrelevant information.
In this study, the word speak means stating arguments with the supporting facts or idea about something (certain issue) in the form of an Analytical Exposition Text through speech, conversation, discussion and debate.
4. Materials
Most accounts of materials development describe processes which are spontaneous and which rely on an intuitive feel for activities which are likely to ‘work’. However Bell and Gower (1998) start by articulating the principles which they want to guide their writing and Hall (1995) starts by articulating his theories of language learning.
5. Speaking Materials
In this study, the term speaking materials is defined as set of property that is needed to conduct a process of saying arguments with the supporting facts or idea about something in the form of an Analytical Exposition Text through speech, conversation, debate and discussion in the teaching and learning English activity in the classroom.
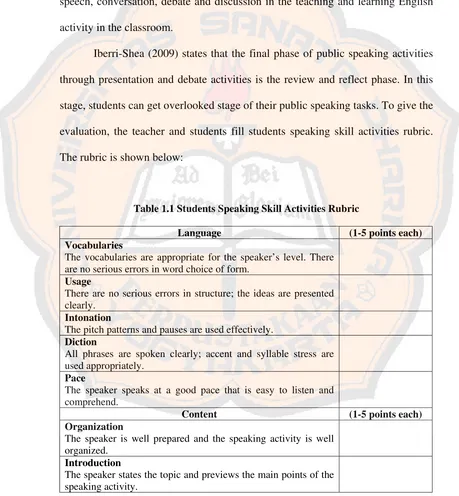
Iberri-Shea (2009) states that the final phase of public speaking activities through presentation and debate activities is the review and reflect phase. In this stage, students can get overlooked stage of their public speaking tasks. To give the evaluation, the teacher and students fill students speaking skill activities rubric. The rubric is shown below:
Table 1.1 Students Speaking Skill Activities Rubric
Language (1-5 points each)
Vocabularies
The vocabularies are appropriate for the speaker’s level. There are no serious errors in word choice of form.
Usage
There are no serious errors in structure; the ideas are presented clearly.
Intonation
The pitch patterns and pauses are used effectively. Diction
All phrases are spoken clearly; accent and syllable stress are used appropriately.
Pace
The speaker speaks at a good pace that is easy to listen and comprehend.
Content (1-5 points each)
Organization
The speaker is well prepared and the speaking activity is well organized.
Introduction
Content (1-5 points each) Body
There is enough supporting information to fulfill the assignment. The information is relevant to the topic.
Conclusion
The speaking activity includes a summary statement and a review of the main points.
Taken from: Using Public Speaking Task in English Language Teaching,
by Iberri-Shea, Gina (2009:36)
6. Designing Speaking Materials
In this study, the term designing speaking materials means creating a new whole arrangement plan of a set of property that is needed to conduct a process of saying arguments with the supporting facts or idea about something in the form of an Analytical Exposition Text through speech, conversation discussion, and debate in the teaching and learning English activity in the classroom.
7. Videos
Dave Willis (1983:17) also adds that videos offers the possibility of showing still or moving pictures in black and white, or at higher costs, in color with or without accompanying sound. Stempleski (1987) stated that the importance of using videos as media of language teaching and learning are; 1) to motivated students to learn, 2) to provide authentic look, 3) to facilitate better comprehension of the intended message.
In this study, the word videos means recorded audio visual file about certain issues as the topic of learning which really helps the students have unconscious learning which is effective for the students to learn naturally. The videos are applied by showing the short movie or show about some issues that are spoken as the topic of the Analytical Exposition Text speaking activity.
8. Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is proposed to attempt to persuade by giving good reasons using arguments, and how to distinguish attempts to persuade in which the speaker or researcher intends to put forward an argument from those in which their intention is to persuade people by some means other than argument. Critical thinkers should primarily be interested in arguments and whether they succeed in providing people with good reasons for acting of believing (Bowell, Tracy and Kemp, Gary, 2002:2).
9. The 11th Graders of Language Department of SMA Stella Duce 2 Yogyakarta The 11th grade students of Language Department are the students of SMA Stella Duce 2 Yogyakarta who are in the 11th level of Language Department of senior high school.
19
CHAPTER 2
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE REVIEW
This chapter includes a discussion of the related literature review. This chapter presents theoretical research which consists of two main parts, namely theoretical description and theoretical framework. Theoretical description discusses some theories related to the study which are needed to design the materials. It consists of brief discussions of basic theories of Instructional Design, Learning Approach, English Standard and Basic Competence 2006 for Senior High School, Senior High School Students, English Analytical Exposition Text, Speaking Skill Materials, Teaching with Videos, and Critical Thinking.
The theories discussed will be used as the basis to establish the theoretical framework of this research and development. Theoretical framework discusses major relevant theories which help the researcher design a set of Analytical Exposition Text speaking materials using videos to develop students’ critical thinking for 11th graders of Language Department of SMA Stella Duce 2 Yogyakarta.
2.1 Theoretical Description
do this research. The second part is Learning Approach as the basis for the activities in the designed materials. The third part is English Standard and Basic Competence 2006 for Senior High School. In this part, the researcher is explaining a brief basic rule of English Competence for Senior High School Students, 11th Grader. The fourth part is the theory about Senior High School Students. In this part, the researcher is going to share the theory about learner characteristics, learning style, and learners’ ability as Senior High School students. The fifth part is English Analytical Exposition Text. This is the main part of the product that the researcher will create. The researcher will give the theory about Analytical Exposition Text as one part of teaching and learning process in the Senior High School. The sixth part is about Videos and English Language Teaching. The seventh part is about Teaching Speaking Skill which is the real skill to be developed through this product. In this part, the researcher explains brief theory about the use of videos in developing students’ critical thinking. The eighth part is the theory about Critical Thinking. In this part, the researcher will explore a brief theory about Critical Thinking itself and also explain about how the use of videos could develop students’ critical thinking. Then, based on those theories, it will be created the theoretical framework to design the materials.
2.1.1 Materials Design Models
and guide the researcher to design the materials well. The models are divided into two main areas, the first one is designing materials in general for instructional design model and the second one is designing materials using videos as the media. The further explanation about those kinds of materials design models will be discussed in the next section.
2.1.1.1Instructional Design Model
Designing materials in teaching English for Senior High School Students is not an easy thing to do. Teacher needs a good preparation and plan to conduct an effective teaching and learning activity. When the teacher plans the materials, the teacher needs to follow some steps in creating them. According to Kemp (1977), there are three major elements which support the successful innovation in education:
1. teachers who are deeply concerned with their teaching effectiveness and who are motivated by the desire for improvement,
2. administrators who willingly encourage and support those teachers, and
3. a carefully designed plan for developing improved instructional practice. These all elements will give the good result for the third, the instructional design plan (p. 4)
videos to develop students’ critical thinking for 11th grader of Language Department of SMA Stella Duce 2 Yogyakarta. The more explanation about each model will be discussed below.
2.1.1.1.1 Kemp’s Model
Kemp (1977) explains that the instructional process in designing materials needs development of an overall plan incorporating the interrelated parts in a sequential pattern. Kemp (1977) adds that this process is called system approach to problem-solving which is based on the method of scientific inquiry. In this process, there are some steps like recognizing problem, forming hypothesis, conducting experiments, data gathering from them which lead to a conclusion about the accuracy of the hypothesis. The correct result will be used to produce or improve the products.
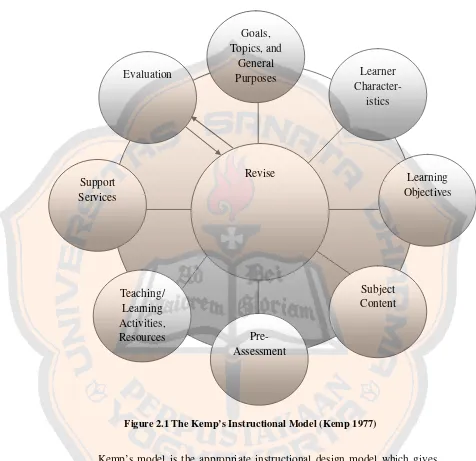
According to Kemp (1977), an Instructional Design is a very common and applicable for every level of education, from elementary, secondary, or collage. Since the researcher would like to design the English materials for Senior High School students, this model is very appropriate to be applied. Kemp (1977) states that there are three questions as the essential elements of the Instructional Design that are answered by the use of this model, they are:
1. What must be learned? (Objectives)
3. How will we know when the required learning has taken place? (evaluation)
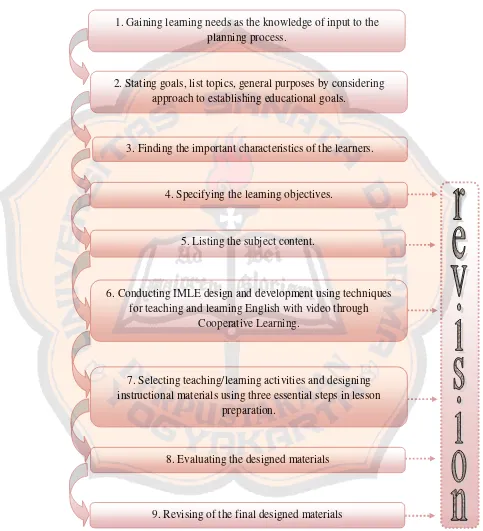
There are eight steps in this model as a plan to design the materials of teaching and learning activities. The steps in this model are flexible process which is interdependent in among the eight elements. The researcher could start with whichever element that is chosen as the starting point of the plan and the decisions related to one may affect others. The researcher could also move back and forth to the other steps.
The eight steps in Kemp’s instructional design model are stated below: 1. Consider goals, and then list topics, stating the general purposes for
teaching each topic.
2. Enumerate the important characteristics of the learners for whom the instruction is to be designed.
3. Specify the learning objectives to be achieved in terms of measurable student’s behavioral outcomes.
4. List the subject content that supports each objective.
5. Develop pre-assessments to determine the students’ background and present level of information about the topic.
6. Select teaching/learning activities and instructional resources that will treat the subject content so students will accomplish the objectives.
7. Coordinate such support services as budget, personnel, facilities, equipment, and schedules to carry out the instructional plan.
8. Evaluate students’ learning in terms of their accomplishment of objectives, with a view to revising and reevaluating any phases of the plan that need improvement.
Figure 2.1 The Kemp’s Instructional Model (Kemp 1977)
Kemp’s model is the appropriate instructional design model which gives the clear steps of designing materials for the teaching and learning process in this research. Since the steps in this plan are flexible process and there is an independence among the eights elements whose decisions relating to one may affects others, the researcher can start the step from whichever steps and then
Revise Goals, Topics, and
General Purposes
Pre-Assessment
Learning Objectives Support
Services
Learner
Character-istics Evaluation
Subject Content Teaching/
move back and forth to the other steps. The researcher can also choose the sequence and the order of the steps.
2.1.1.1.2 Borich’s Model
Planning is the systematic process of deciding what and how your students should learn. Teachers make such decision on the average of every two minutes while they are teaching, according to an estimate, by Clark and Peterson (1986). Borich (1996:111) states that in the planning process of designing materials, the researcher needs to gain and record information from five inputs. The five inputs that need to be gained and recorded are aims and goals, information of learner’s characteristics, information of subject matter, information of teaching methods, and tacit information acquired from classroom experience. This is the figure of part of planning process according to Borich (1996:113).
Add new data about Expend set of Revise match, as needed. inputs, as needed. alternatives, as
needed.
2.1.1.1.3 Davies’ Model
According to Davies (1981) there are three essential steps in lesson preparation. The whole steps are seen as interrelated activities. The three essential steps are Preliminary Steps, Main Steps, and Final Steps.
Davies (1981) explained that in lesson planning, there are a number of preliminary steps that must be taken before the main activities of lesson planning occur in a teaching and learning activity. These preliminary steps of lesson planning are all concerned with the content of the lesson. They are:
1. Choose the topic of the lesson.
2. Take steps to gather the materials and examples. 3. Decide on the aim and the objectives of the lesson. 4. Identify what the learners know and believe. 5. Select the materials to be included in the lesson. The main purposes in these preliminary steps are to:
1. Identify the nature of the task.
2. Identify what the learners know already. 3. Determine what has to be taught in the lesson.
Evaluation
Evaluation Evaluation
Evaluation
Figure 2.3 Davies’ Preliminary Steps in Lesson Planning (Davies 1981:83)
The next step that is explained by Davies (1981:89) is The Main Steps in Lesson Preparation. The main steps can be undertaken after the preliminary steps in lesson preparation have been completed. In the main steps in lesson preparation, there are three activities that make up the stages of the development part of the lesson. The main steps include:
1. Identify an appropriate instructional method. 2. Arrange the teaching points into a logical sequence.
Write the final lesson
plan
Prepare class handouts and audiovisual
aids Prepare the
instructional setting
Refer to lesson plan,
3. Choose appropriate learning activities and experiences. 4. Decide how learning is to be assessed.
Here is the figure of the main steps that is explored by Davies.
Evaluation
Evaluation Evaluation
Figure 2.4 Davies’ Main Steps in Lesson Planning (Davies 1981:90)
The purposes of the main steps are:
1. Identify how the materials are to be taught. 2. Identify how the materials will be sequenced. 3. Determine how learning will be assessed.
The last essential step in the lesson preparation is the Final Steps in lesson planning (Figure 2.5 on page 30). These steps are started when the preliminary
Identify how the material
will be taught
Determining how learning will
be assessed
Identify how the material
and also the main steps are completed which mean that the principal tasks have been accomplished. The steps include:
1. Write the final version of the lesson plan. 2. Prepare class handouts, audiovisual aids, etc. 3. Refer to the lesson plan and refresh your memory. 4. Prepare the classroom, or either instructional setting. The purposes of these Final Steps are:
1. Record the final version of the plan on paper, in a form that is usable in the instructional setting.
Evaluation
Evaluation Evaluation
Evaluation
Figure 2.5 Davies’ Final Steps in Lesson Planning (Davies 1981:94)
2.1.1.2 Interactive Design Model for the Videos Design
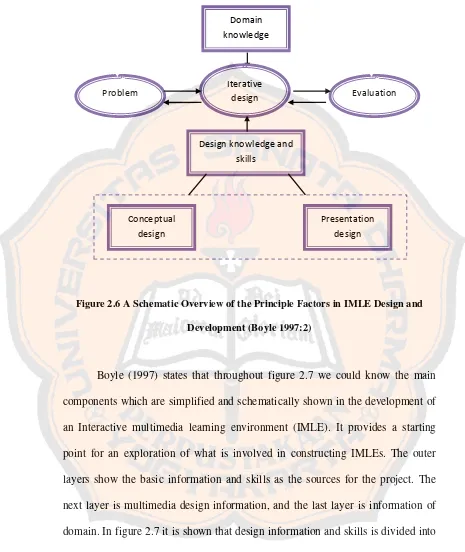
Designing materials in this research needs some understanding on the designing for multimedia learning. According to Boyle (1997), there is a schematic overview of the principle factors in Interactive Multimedia Learning Environment (IMLE) design and development (Figure 2.6 on page 29).
Write the final lesson
plan
Prepare class handouts and audiovisual
aids Prepare the
instructional setting
Refer to lesson plan, and refresh your
Figure 2.6 A Schematic Overview of the Principle Factors in IMLE Design and
Development (Boyle 1997:2)
Boyle (1997) states that throughout figure 2.7 we could know the main components which are simplified and schematically shown in the development of an Interactive multimedia learning environment (IMLE). It provides a starting point for an exploration of what is involved in constructing IMLEs. The outer layers show the basic information and skills as the sources for the project. The next layer is multimedia design information, and the last layer is information of domain. In figure 2.7 it is shown that design information and skills is divided into two main areas. They are conceptual design and presentation design. The conceptual design creates the deep learning architecture of the system which is structuring interactive option for the learner. Presentation design is the realization
Conceptual design
Presentation design Iterative
design Domain knowledge
Problem Evaluation
of the system as a computer based artifact. In this area, the issues are about screen layout, color schemes and the individual media detailed used.
Boyle (1997:1) shares more about the central layer is the process in designing a multimedia project. It is a kind of iterative design model. The design features of the system are evaluated and this formative feedback will guide the process turn into the next stage of the project development. There are the process of design, implementation and evaluation which are dynamically interwoven in a productive spiral. The process of this productive spiral is implemented in the process of project development.
2.1.2 Tyler’s Approach
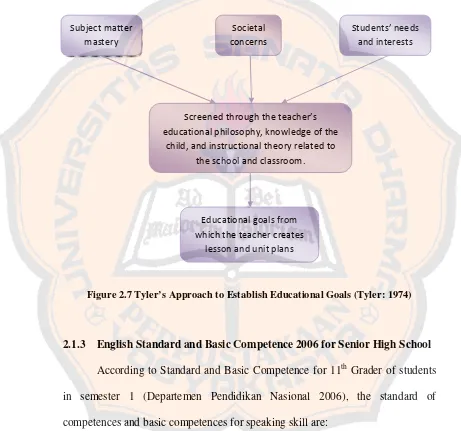
Tyler (1974) states the important thing in developing a teaching and learning process is educational goals. Educational goals tell the learners, the parents, and the community why the teacher teaches the planned lessons, and then energizes and motivates the students to become actively engaged in and committed to the learning process.
To formulate instructional goals and plan, Tyler (1974) develops several approaches. In Tyler’s Goal Development Approach, there are five factors to consider when establishing priorities for what students should learn. Firstly, the goals must include:
1. the subject matter we know enough about to teach (subject matter mastery),
2. social concerns, which represent what is valued in both the society at large and the local community, and
Secondly, these goals must be refined to match:
4. your school’s educational philosophy and your community’s priorities, and
5. what instructional theory and research tells us can be taught.
Here is the illustration of Tyler’s approach to establishing educational goals:
Figure 2.7 Tyler’s Approach to Establish Educational Goals (Tyler: 1974)
2.1.3 English Standard and Basic Competence 2006 for Senior High School
According to Standard and Basic Competence for 11th Grader of students in semester 1 (Departemen Pendidikan Nasional 2006), the standard of competences and basic competences for speaking skill are:
3. Expressing the meaning of formal and sustained transactional and interpersonal conversation in daily life.
Subject matter mastery
Educational goals from which the teacher creates
lesson and unit plans Screened through the teacher’s educational philosophy, knowledge of the
child, and instructional theory related to the school and classroom.
Students’ needs and interests Societal
3.1 Expressing the meaning in formal and sustained transactional (to get things done) and interpersonal (to socialize) conversation using spoken language accurately, fluently, and understandably in the form of expressing and asking opinions, expressing satisfaction and dissatisfaction.
3.2 Expressing meaning in formal and sustained transactional (to get things done) and interpersonal (to socialize) conversation using spoken language accurately, fluently, and understandably in the form of giving advice, warning, accepting request, and expressing relief, pain, and pleasure feeling.
4. Expressing the meaning of short functional text and a monologue in the form of report, narrative and analytical exposition in daily life.
4.1 Expressing the meaning of formal and informal short functional spoken text accurately, fluently, and understandably in daily life.
4.2 Expressing the meaning of a monologue using spoken language accurately, fluently, and understandably in the form of report, narrative, and analytical exposition in daily life.
2.1.4 Materials Adaptation
1. The teaching environment (national, regional, institutional, cultural, etc), e.g., the materials have not been designed for the cultural and ethnic diversity of your class.
2. The learners (age, language level, prior learning experience, learning styles, etc), e.g., the materials favor analytical leaning style.
3. Their own preferences (personality, teaching styles, beliefs about language learning and teaching), e.g., the materials offer a lot of communicative activities but a teacher fears she or he will lose control of the class by doing them.
4. The course objectives (syllabus, institutional targets, etc), e.g., the materials focus on teaching grammar but the course objectives focus on helping learners to develop communication strategies.
5. Materials (texts, tasks, activities), e.g., the text is interesting but the activities are boring and do not seem to fully exploit the text.
These all factors must be considered well by the teachers before designing the materials of teaching and learning activities.
There are some procedures of materials adaptation that are explored by Tomlinson and Masuhara (2004). The sequence of materials adaptation may be described as:
1. Profiling of teaching context 2. Identifying reasons for adaptation 3. Evaluating
4. Listing objectives 5. Adapting
6. Teaching 7. Revising
2.1.5 English Analytical Exposition Text
a. Definition of Analytical Exposition
James (2006) explains that Analytical Exposition Text is a text that elaborates the researcher‘s idea about the phenomenon surrounding. Its social function is to persuade the reader that the idea is important matter and to promote a particular point of view about something.
b. Generic Structure of Analytical Exposition
The structure of a simple analytical exposition has three sections:
1. Introduction (Thesis): Introducing the topic and indicating the researcher’s position or saying what the topic is about.
2. Main Section: Stating what the main points are, or explaining the arguments to support the researcher’s position. It may include evidence or reasons to support the researcher’s views.
3. Conclusion (Reiteration): Restating the researcher’s position c. Language Features of Analytical Exposition
• It is written in third person • It uses relational process • It uses internal conjunction • It uses causal conjunction
readers or listeners, some supporting ideas or arguments on why the researcher’s opinion is important, are presented. Since analytical exposition is popular among scientists, academic community and educated people then you can find this type of text in scientific books, journals, magazines, newspaper articles, academic speech or lectures, research report, etc.
Both analytical exposition and hortatory exposition are grouped as argumentative essay. Both present arguments to support the thesis, but actually the difference is on the generic structure. Analytical exposition ends with paragraph to strengthen the thesis or reiteration while hortatory makes a recommendation for the readers. The social function of Analytical Exposition Text is to persuade the readers or listeners that something is the case or important.
2.1.6 Teaching Speaking Skill
Ur (1999) said that speaking skill is the intuitively the most important of all the four skills which are listening, speaking, reading and writing. A speaker of a language is identically the person who knows a language. In other words, speaking includes all other kinds of knowing; and many foreign language learners are interested in learning to speak.
The characteristics of a successful speaking activity according to Ur, Penny (1999, p.120) are:
1. Learners talk a lot. Teacher uses as much as possible of the period of activity to occupy the learner to talk.
2. Participation is even. In the speaking class, the discussion is served to the whole students get chance o speak and evenly distributed.
3. Motivation is high. The learners are eager to speak because they are interested in the topic and have something new to say about it, or because they need to talk more in order to achieve their objectives of learning. 4. Language is of an acceptable level. The learners are freely to express
themselves in utterances that are relevant, easily comprehensible to each other, and of acceptable level of language accuracy.
The teacher has to notice these points to conduct successful speaking activity.
2.1.7 Videos and English Language Teaching
2.1.7.1Videos as an Audiovisual Aids in English Language Teaching
Videos are one of the audiovisual aids in English language teaching and learning activity. According to Davies (1981), there are some characteristics of effective aids. He states that audiovisual are most effective when they are:
1. Simple and to the point.
3. Essential and necessary. 4. Interesting and challenging. 5. Saving in effort and time.
Davies (1981) explores that the audiovisual aids fill a number of roles in education process. They are:
1. Aids to instruction, assist the teacher to communicate more efficiently and take over the operating role of instruction to the teachers.
2. Aids to learning, help the students to learn more efficiently, promote understanding that the old saying “A picture is worth a thousand words” help the students to grasp meaning. The audiovisual aids also assist in the transfer of teaching and learning activity.
In using audiovisual aids, according to Davies (1981) in teaching and learning activity, there are a number of benefits. Aids can be interesting to watch, challenging and reinforcing. To select the audiovisual aids, in this research is to select the videos, the teacher has to consider some aspects according to Davies (1981):
1. Objectives to be realized.
2.1.7.2Videos Application In English Language Teaching
According to Brumfit (1983) “videos is perceived as a useful time shift extension of television and is acquired particularly for the access it gives to specialized interest off-air recording” (p.2). Videos is also obtained in order to expand aspects of the curriculum, especially teacher training and specific English programmers after which its use is frequently extended to general interest courses. Videos are commonly introduced to give a lift to methodology on term of interest and motivation, to extend the range of teaching techniques available.
Brumfit (1983) states that the potential of videos is far from being realized and it is capable of more functions that is generally fulfilled, particularly those of a more strictly linguistic nature. In terms of skills videos is used most to develop the listening skill in isolation, often more as an extended audiotape than as the means of giving a more complete idea of language in action in the framework of a complete situation. Despite interest in videos and frequent references to its potential, there is an uncomfortable gap between actual and ideal use. Institution generally acknowledges that videos are not used as much or as constructively as it should be.
2.1.7.3The Potential and Limitations of Videos
videos particularly when it is relatively new to them. It carries an aura of entertainment which can keep students quiet and relatively contended whether they are learning or not.
Videos offers the possibility of showing still or moving pictures in blacking white, or, at higher cost, in color with or without accompanying sound.
2.1.7.4The Visual Element in Communication
Dave Willis (1983:20) states that the teachers have to consider how the visible context supports or modifies the production or comprehension of verbal message. This proof can be discussed under four headings, they are:
1. Contextualized Reference
Common visual context is use to share information when writing and speaking.
2. Information Weighting
To emphasize certain aspects of message, people use both verbal and non-verbal devises. Paralinguistic features, like movements of the head and hands, are commonly used to indicate the importance attached to a particular utterance or part of an utterance. It shows that using visual aids especially videos, help the verbal understanding of information.
3. Attitudes
teacher can really help the learners to learn new information of grammatical and phonological subjects.
4. Discourse Structure
Gesture is commonly used to mark or reinforce transitions in discourse in which the visual contributes immediately and directly to communication. There are also aspects of cultural familiarization which can be made easier by a visual presentation, Dave Willis (1983).
2.1.7.5Teaching with Videos
Rice (1993) stated that there are five techniques for teaching and learning English with videos. They are Freeze Frame, Silent Viewing, Sound Only, Jigsaw Viewing, and Normal Viewing. It is also stated that teaching with videos can help the students learn conversation, culture, grammar, listening, pronunciation and intonation, vocabularies, and writing.
Frame really useful for pronunciation and grammar practice. By stopping the videos on the certain intonation pattern, grammatical structure, or idiom that the students have to know. The teacher can also rewind slightly to make the important points clearer.
3. Sound Only involves listening for aural clues to the action. To use this technique, the teacher can turn the brightness control down until the screen goes dark or minimize the screen. In this technique, the students can just listen to the sound and conversation of the videos, then the students can make prediction about what is happening: who and where the people are and what they are doing. They can also give the characteristics of the people and also the events in the videos through the sounds. The major advantage of this method is that the students can positively confirm and evaluate their guess (or laugh at their mistakes) by viewing the accompanying videos section (Alison 1993:28). Sound only is a good technique to make the students pay close attention to a small piece of dialogue while avoiding the destruction in the action of the screen.
ways to divide the students into different group of understanding the videos through different techniques.
5. Normal Viewing as an educational sense is a technique that is used when the teacher is going to give the students the visual and verbal information that the students need to complete the task. In this normal viewing, the teacher combines both the visual and audio tracks. Using both audio and visual tracks supplies overwhelming information, therefore it is important just to show the short track for the students’ short-term memory. In using normal viewing, the teacher needs to conduct very structured task such as activities that focus on ordering events, checking off things that they see, listening for paraphrases, and gathering impressions that can lead into writing assignments. Through this normal viewing that is usually used in the second or third step in teaching with videos, the students can recall their vocabularies or language exchanges that they have already got on their teaching and learning activities.
2.1.7.6Using Videos in Language Teaching
speak as well as the real speaker. The videos can give the stimulus to speak, so that they will enjoy the speaking activities from the stimulus or input from the videos. They also can learn vocabularies from the moving pictures shown.
Videos can be used as valuable aid in the learning process, according to Zuber-Skerritt (1984). Using videos enables the teacher to maintain the learning process as learner-centered learning. The learners develop through a broad range of possible activities and sensitivity to the critical or pertinent elements of communication. Using videos allows the learners to be interested in the classroom as a stepping stone to fun and communicative activities. Therefore, the researcher in this study uses communicative language teaching through the cooperative language learning in the designed materials. Fun learning will raise the students’ motivation to follow the lesson and thus create relaxed atmosphere which leads the students to learn easier.
2.1.8 Critical Thinking
Warnick & Inch (1994) stated that there are two large groups of skills in the skills for the critical thinking. The first group is the skill of discovery and the second group is the skill of justification. The first group is generally made up of receptive skills. They are identifying evidence, evaluating arguments, and judging relevance of evidence and reasoning, and understanding how inferences work. The second group is made up of skills and arguer must have to successfully defend a position, select the best possible evidence to support one’s position, choose the best solution from many alternative solutions, anticipate and counter objections to one’s view, and employ sound reasoning.
Figure 2.8 A Model of Cooperative Learning (Borich 1996:425)
2.2 Theoretical Framework
In this part, the researcher would like to implement the Kemp’s model of instructional design which is supported by Tyler’s approach to establish educational goals. Borich’s model of planning process is also implemented in this research in order to make the process of designing the materials more effective. In listing the subject content, the researcher considers the materials adaptation from Tomlinson and Masuhara. Next, to choose appropriate media and videos, the researcher applies principle factors in Interactive Multimedia Learning Environment (IMLE) design and development from Boyle. Then, to select teaching/learning activities and instructional resources that will treat the subject
forms attitude
and values
provides models of prosocial behavior
improved
presents alternative collaborative skills perspectives and
Cooperative Learning viewpoints Result in better self‐esteem
builds a coherent and increased integrated identity achievement