INDEPENDENT LAB WORK MODULE DESIGN OF GEOMETRIC
OPTICS ABOUT CONVEX LENS USING PHET SIMULATION
(PHYSICS EDUCATION AND TECHNOLOGY)
“GEOMETRIC OPTICS“
Oleh,
MarianusAmaKii
NIM: 192013012
TUGAS AKHIR
Diajukankepada Program StudiPendidikanFisika,
FakultasSainsdanMatematikagunamemenuhisebagiandaripersyaratanuntukmemperolehg
elarSarjanaPendidikan
Program StudiPendidikanFisika
FAKULTAS SAINS DAN MATEMATIKA
UNIVERSITAS KRISTEN SATYA WACANA
SALATIGA
Independent Lab Work Module Design of Geometric Optics about
Convex Lens Using PhET Simulation (Physics Education and Technology)
“Geometric Optics“
M. A. Kii
a), D. N. Sudjito
b)*, D. Noviandini
Department of Physics Education, Faculty of Science and Mathematics Universitas Kristen Satya Wacana
Jl. Diponegoro 52-60 Salatiga 50711, Jawa Tengah-Indonesia
E-mail: a) [email protected] b) [email protected](corresponding author)
ABSTRACT
In learning geometric optics, most of students were difficult to determine the position of real image, whether in front of the lens or behind the lens. The study of geometric optics about convex lens in a real laboratory can not present all of the parameters, such as lens curvature radius, refractive index of lens material, and lens diameter, so it needs virtual laboratory of simulation to support the learning process. This research investigated how to design the independent lab work module of convex lens using PhET simulation “Geometric Optics” and the effectiveness of the module in helping students to understand convex lens. All collected datafrom modules, observation sheets, questionnaires, and evaluation tasks were analyzed using the descriptive qualitative method. Respondents of this study were 10 freshmen of Physics and Physics Education of UKSW batch 2016. Based on the observations, all students did the lab work well. Questions led to the module were successfully answered well by students with a minimum score of 70%. Based on the evaluation, 70% of students managed to get a minimum score of 70%. The questionnaire results showed that students gave positive responses ≥80% towards the questionnaire. So, the independent lab work module of geometric optics about convex lens using PhET simulation “Geometric Optics” is effective in helping the students to understand convex lens.
Keywords: independent lab work module, PhET simulation,convex lens
1.
Introduction
Physics is a subject that is taught specifically to students ranging from junior high school to senior high school, as well as undergraduate students who majored in Physics and its application (engineering).However, students and even students who take Physics courses often have difficulty in studying Physics. One of the Physics materials often misunderstood by students is geometric optics [1]. This is stated by research conducted by Arlilla Anugrahini which shows that many students have difficulties in understanding the material of geometric optics, especially about refraction by a lens. Most of them are still difficult to determine the position of the real image, whether in front of the lens or behind the lens. When practicum activities take place, they also still have trouble distinguishing real and virtual images [2].
methods is good, the class becomes more orderly and takes place in a relatively short time because the teacher relates and explains all the material learned. But this method is only appropriate if it is applied to abstract physics materials, such as relativity, electromagnetic waves, etc. Where it is limited to observe the concrete phenomenon for the material. It should be learned for materials such as geometric optics presented by showing concrete phenomena related to matter [3]. This can be done with activity-based learning. The research of Siska Murki revealed that the application of activity -based learning can improve students' cognitiveand psychomotor abilities on the body's anatomical material (which is concrete) [4].
Lab activity integrated to learning is better than learning done by lecture method for geometric optics. However, to study geometric optics about convex lenses, not all parameters can be presented in the real laboratories, such as the radius of lens curvature, refractive index of lens material, and lens diameter, so that visual laboratory simulation or animation is needed to support learning.
Currently developing visual media as a representation of the material presented in formal schools. One of it is PhET simulation (Physics Education and Technology). PhET is an interactive simulation that is very suitable to be applied in education. PhET was created in order to provide virtual laboratory based simulations that facilitate teachers and students in learning in the classroom or independently.
Previously many studies have suggested that PhET simulation is very effective and helps students understand the concept of Physics, for example research by Retna Wuryaningsih et al [5], Pujiyono et al [6], Lusi Indriyani et al [7], Yuafi MED et al [8] Mubarrok MF et al [9], Sumargo Eko et al [10], Wiwit et al [11], Setiadi Rahmat et al [12], Nurhayati et al [13], Afifah RMA et al[14], Satriya Ary Hapsara et al [15], Maria Dinavalentine et al [16], and Prihatiningtyas et al [17]. Therefore, PhET simulation will be used in this research.
The PhET simulation used in this research is Geometric Optics. The simulation shows how to form an image by a convex lens. The parameters that can be varied are the radius of lens curvature, refractive index of lens material, and lens diameter. If we want to vary all of these parameters in order to study the image formation by convex lens, it takes longer time and needs an additional time out of the class. This requires students to study independently out of the class. However, in order to students' independent learning can be more focused and the learning objectives are achieved, guidance is needed in the form of independent modules.
There are many indicators that can be made from PhET Geometric optics, but in this study only limited to two indicators: 1) to investigate factors that affect the focal length of the convex lens, and 2) to investigate factors affect that the nature of the image generated by a convex lens.
2.
Materials and Methods
2.1 PhET simulation
PhET Simulation (Physics Education and Technology) is one example of a virtual simulation created by the University of Colorado that contains physics, biology, and chemistry simulations for the benefit of classroom teaching or individual learning. PhET simulations emphasize the relationship between real-life phenomena with the underlying science, supporting an interactive and constructivist approach, provide feedback, and provide creative workplaces [17].
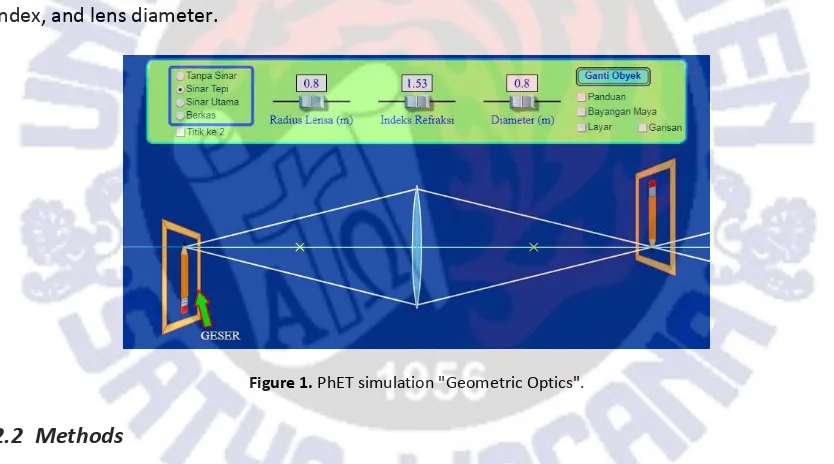
PhET is freeware, so it can be downloaded for free, and it can be operatedonline or offline. To operate PhET offline, the program must be downloaded first at http://PhET.colorado.edu [16]. In the web address, one of the existing physics simulations is the Geometric Optics simulation, which is a simulation of image formation by convex lensthat can be used to deepen fundamental physics material. The advantage is to know the ray diagrams of the lens (marginal rays or principal rays) simply by shifting the location of objects, to measure the distance of objects and the distance of the image from the lens, and thus we can determine the nature of the image. Figure 1 shows the PhET simulation display "Geometric Optics". Physical variables that can be altered in the simulation are lens radius, lens refraction index, and lens diameter.
Figure 1. PhET simulation "Geometric Optics".
2.2
Methods
The research method used in this research is the Descriptive Research. Respondents of this study were 10 freshmen of Physics and Physics Education of UKSW batch 2016. The research instruments used are independent lab work module of geometric optics about convex lens using PhET Geometric Optics simulation, observation sheet, evaluation tasks, questionnaire, and interview questions. The observation sheet is used to record the process of running the independent lab work using independent lab work module of convex lens with PhET simulation. The evaluation tasks are used to find out students' understanding of convex lens after using the independent lab work module with PhET simulation. The questionnaire
sheet is used to record students’ responses to the independent lab work module. Interview
The students are required to follow and do all steps in the lab work module using PhET simulation. While they do, the observation sheet is filled by the observer. After completing the lab work with the module, the evaluation task is done by the students. Further questionnaires were filled by students. In the final activity conducted the interview.
All data obtained from students 'answers to the questions in the module, observation sheet, evaluation tasks, questionnaire, and interview were analyzed descriptively qualitatively in order to determine the effectiveness of the module on students' conceptual understanding of convex Lens.
This module is effective if (1) all students can do at least 70% of activity correctly as the guidance, (2) all students give positive response toward at least 70% statements of independent lab work module based on the observation and questionnaire, and (3) at least 70% students get the minimum evaluation score of 70.
3.
Results and Discussion
Before the independent lab work begins, students are required to install Physics Education and Technology (PhET) software on their 14-inch laptops according to the instructions given in the independent lab work module. After PhET Geometric Optics simulation is ready for use as shown in Figure 1, the students are given introductory material from the module which contains the meaning of convex lens as well as the parts of the lens. It is to make students easily run the steps on the independent lab work. After the introductory material is given, the independent lab work activity begins.
4.1 Observation sheet
In the independent lab work module, there are two indicators of learning. To achieve the first indicator, there are 3 activities that discuss the influence of the radius of lens curvature, lens refraction index, and lens diameter to the focal length of the lens. To achieve the second indicator, there are two activities that discuss the effect of change of position of object and lens diameter to the image properties produced by a convex lens. During the lab work, the observer fills in the observation sheet to record the process of the independent lab work using a PhET simulation. To calculate the percentage of successful experiments (PSE) can use the following formula:
number of activities performed correctly
PSE 100
total number of activities
The result of the observations during the practicum can be seen in Table 1. There are 2 kinds of assessment criteria for the percentage of the successful experiments (PSE), i.e. 1) the students did not ask during the process of independent lab work activities took place, and 2) the student can do 10 items of assessment of the total 5 activities that exist in the lab work module.
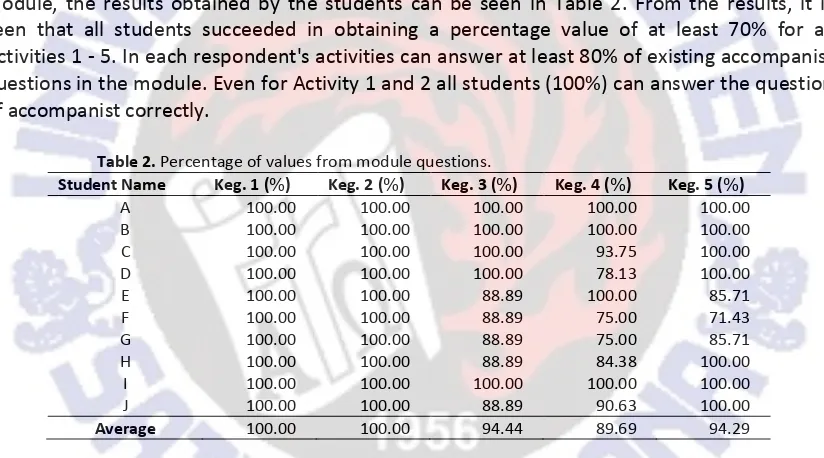
Based on Table 1, six out of ten students get a 100% PSE which means that they can meet all assessment criteria. Students who get 90% PSE only meet the first criterium, and in the second criterium, students only do 9 of 10 items. Two students who achieved the PSE of 80% fulfilled the first criterium, and in the second criterium, they only worked on 8 of 10 items. One student got the PSE of 70% because he asked once and only worked on 8 out of 10 items.
activity has been going well. The independent lab work module successfully guides students to Activities 1 - 5. In each respondent's activities can answer at least 80% of existing accompanist questions in the module. Even for Activity 1 and 2 all students (100%) can answer the question of accompanist correctly.
Table 2. Percentage of values from module questions.
Student Name Keg. 1 (%) Keg. 2 (%) Keg. 3 (%) Keg. 4 (%) Keg. 5 (%)
With this result, it can be said that all students successfully answered more than 70%of the accompanist questions that exist in the module self-contained independently correctly. This shows that the independent lab work module with PhET simulation succeeds in making the students understand the materials or concepts that exist in each activity.
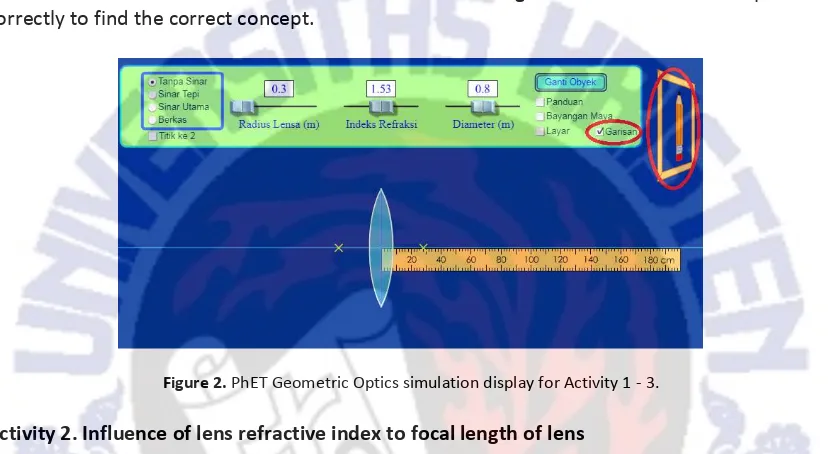
Activity 1. Effect of lens radius on focal length of lens
practicum module. There are 6 questions for this activity. However, the core of this activity or other activities lies in the question accompanist draw conclusions.
After conducting the experiment, students were asked questions to draw the conclusion "does the radius of the lens affect the focal length of the lens? If so how will it affect? ". All students correctly answer that the radius of the lens affects the focal length of the lens. The greater the radius of the lens, the greater the focal length of the lens.
Based on the observation, all students are able to correctly answer the accompanist questions that exist in Activity 1. Students have been working on the practicum in accordance with the instructions contained in it. So this module has guided the students to experiment correctly to find the correct concept.
Figure 2. PhET Geometric Optics simulation display for Activity 1 - 3.
Activity 2. Influence of lens refractive index to focal length of lens
After students do a practicum about the effect of the lens radius on the lens focal length, Activity 2, students are invited to investigate how the lens refractive index impacts the focal length of the lens.
To see the effect of the lens refraction index on the focal length of the lens, experiments were performed by adjusting the circumstances in which the radius of the lens always remained at 0.4 m, and the diameter of the lens also fixed with a value of 0.8 m. After that, the students run the simulation and observe what happens to the focal length of the lens when the lens refraction index is changed to become larger. The students write the value of the focal length of the lens as measured by the simulated ruler into Table 2 provided on the lab work module. There are 6 questions for this activity.
After this second experiment, students were given the same question as Activity 1 to get the conclusion "does the lens refraction index affect the focal length of the lens? If so, how will it affect? ". All students correctly answer that the refractive index affects the focal length of the lens. The greater the lens refraction index, the lesser the focal length of the lens.
refraction index on the lens focal length. This indicates that the steps written in the module are clear and can guide the student in conducting the experiment.
Activity 3. Effect of lens diameter on focal length of lens
After the students knew the effect of lens refraction index on the lens focal length, in Activity 3 students were assigned to investigate how the effect of lens diameter on the lens focal length.
To see the effect of lens diameter on the focal length of the lens, an experiment was conducted by setting the circumstances in which the magnitude of the lens radius always remained at a value of 0.74 m, and the magnitude of the lens refraction index was also fixed with a value of 1.53 m. After that, the student runs the simulation and observes what happens to the focal length of the lens when the lens diameter is changed to become larger. The student writes the value of the focal length of the lens as measured by the simulated ruler into Table 3 provided on the lab work module. There are 9 questions for this activity.
After conducting the experiment, students are given a question to get the conclusion: "does the diameter of the lens affect the focal length of the lens? If so, how will it affect? ". All students correctly answer that the lens diameter does not affect the focal length of the lens. The greater the diameter of the lens, the magnitude of the focal length of the lens is always fixed. Before entering the accompanist question draws a second conclusion, a brief material on the equation is given to calculate the focal length of the lens and a description of the variables used in the formula. The second question is "Try to calculate the focal length of the lens by using one of the data in each of Tables 1 and 2. Then compare the results obtained with the experimental results, whether it is same or different?". Eight of ten students have come to the conclusion that the lens focal length of the experimental results is the same as the lens focal length of the calculation results. But there are two students who do not carefully perform the calculation so that the data obtained in the experiment is not the same as the results of calculations, but the formula used is correct.
Based on the observation, students can follow the instructions in the module correctly. This indicates that the instructions in the module are sufficiently clear to guide the student in the experiment. The independent lab work module using PhET simulation helps them learn how the lens diameter influences the focal length of the lens.
Activity 4. The effect of change the position of the object on the nature of the image produced by the convex lens
the laptop used should be 14 inches so that all student answers can be equalized when making measurements using a real ruler. After the circumstances fit, the students run a PhET simulation and observe what happens to the image properties when the distance of the object is altered increasingly away from the lens.
Figure 4. PhET simulation to investigate the effect of position change on image properties.
The experimental results are written into Table 4 which is present in the independent lab work module. As for the results that need to be noted is the distance of the image (s ) and the i image properties that concern the image orientation of the object, the size of the image of the object, and the type of image. There are 32 questions for this activity.
After the experiment was done, the module was given a question to draw the conclusion, namely, "Does the change of the position of the object affect the nature of the
image produced by the convex lens?”. All students can correctly answer that the change of the
position of the object affects the image properties generated by the convex lens. Students are given additional questions "Group the same image properties into Table 5 and re-record the distance of the object and the distance of its image." Seven out of ten students can group the exact same image properties. While the three students gave a less precise answer.The reason given when conducting an interview is that they do not understand the intent of the given question. Therefore, the question needs to be changed into a simpler (easier to understand) question such as "The same image properties are grouped into Table 5 and re-record the distance of the object and the distance of its image?". When the question was asked back to the three students, it turns out their better understandingof the purpose of the question. Then the students are given more questions "Based on the grouping, determine the location of the object space and the image space and the sum of the two? And is the sum of the object space + the image space of each grouping equal in value? ". This question was answered correctly by nine students, while one student answered incorrectly. This is because the student who answered incorrectly did not read the description of the division of the object space and the
image space on the convex lens so that he can’t correctly answer the given question. At the
end of Activity 4, students are asked the question "what is the relationship between lens focal length f, object distance (so), and distance of image (si)? Write in the form of equations ". All students correctly answer that the relation f,so, and si is 1/f = 1/so + 1/si.
activity are clear enough and make the students understand about the effect of position change on the nature of the image.
Activity 5. Effect of lens diameter on the image properties generated by the convex lens
In Activity 5, students are assigned to investigate how the effect of lens diameter on the image properties. Prior to starting this experiment, students were asked to make a state where the object distance of 6 cm was measured using a real ruler, a lens radius of 0.8 m, and a refractive index of 1.5. During the experiment, the variable was fixed. Students are asked to write down the image properties formed when the lens diameter is made larger into Table 7 provided in the module. Questions for this activity amounted to 14.
After the experiment done, the students were given 3 questions to draw the conclusion: "when the lens diameter is enlarged, is the image property associated with the image orientation, the image size, and the type of image formed change? If not, are there other image properties that seem to be changing? If there are other image properties that undergo changes, how will they affect the change in lens diameter? ". Eight of ten students correctly answer that when the lens diameter is enlarged, the image properties associated with the image orientation, the image size, and the type of image formed does not change. The changing nature of the image is the dim light of the image, where the larger the diameter of the lens, the lighter the image is formed. Two students answered incorrectly for lack of careful reading of instructions. Then the students are assigned to investigate why when the diameter of the lens is enlarged, the images generated become brighter. Before answering the question, students are instructed to activate the "many rays" icon in PhET Geometric Optics simulation in order to know the way the rays beam is. Students write down the number of rays that enter the lens and what about the brightness of the images when the diameter of the lens is made greater.
After conducting the experiment, students were asked questions to draw the conclusion "Why when the diameter of the enlarged lens will affect the dim light of the image formed?". Nine students answered correctly that when the lens diameter is enlarged, the amount of light entering the lens increases so that the resulting image becomes brighter. Based on interviews conducted on students who answered wrongly, it turns out he was not paying close attention to the questions given, even though he has obtained the correct observations on this experiment.
Students have done PhET experiment quite well and the guidance given in Activity 5 is well followed. Thus the experimental steps and the accompanist questions help the student understand the effect of lens diameter on the image properties.
4.2 Questionnaire Sheet
work module encourages them to seek further information related to the material in the module. Item 9 - 10 on the appropriateness of the learning materials with the practicum module and whether the overall learning packaging is interesting with the PhET simulated help module.
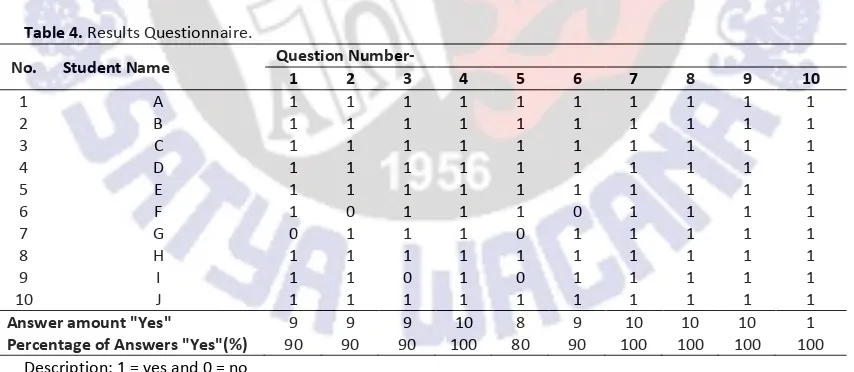
Questions in the questionnaire sheet are arranged so that students who respond positively will answer yes, and if the negative response will answer no. Percentage of student appraisal (P) to module obtained by: seen in Table 4.Based on the data in Table 4, it can be seen that the positive response given by
the students to the questionnaire questions is ≥80%. This means that students enthusiastically
conduct independent practicum using PhET simulations and state that PhET simulations are helpful in understanding material quickly. This is because learning with PhET simulations involves the student's sense of vision, and makes students interested in experimenting with PhET apps so they become actively involved in learning.
For module assessment, it appears that the font type, font size, and color images in the module are easy and interesting to read. The contents of the module also provide clear information and implementation instructions and use easy-to-understand sentences. Students also stated that the material described in the module is not boring, encouraging them to seek further information related to the material, and there is a correspondence between the learning materials and the independent lab work module, as well as the simulated PhET module making the overall packaging of learning more interesting.
4.3 Evaluation tasks
After the independent lab work was done, students are given a matter of evaluation to know their understanding of image formation by convex lens by using PhET simulation media. The formula used to obtain the evaluation value of the student (NE) is as follows:
Number of values earned
NE 100
total amount of value
The list of evaluated results can be seen in Table 3. From the evaluation results, it is known that seven of ten students score above 70, even one student gets 100. However, three students get the score below 70. After interviewing the three students, which is stated among others, lack of careful reading of independent lab work manual so that there are concepts that are not understood, in a hurry to work on the module so that the impact is less understanding some evaluation questions, and forget about the results or conclusions of experiments obtained when working on independent practicum module so that not all the questions of evaluation can be done correctly.
Table 3. Results for the Evaluation task
No. Student Name Value of Evaluation Results
1 A 100.00
2 B 93.33
3 C 80.00
4 D 86.67
5 E 73.33
6 F 26.67
7 G 33.33
8 H 53.33
9 I 93.33
10 J 86.67
Average 72.67
Seven out of ten students (70%) get scored above 70 with an average grade of 72.67. This shows that the independent lab work module PhET successfully enables students to understand about the materials that have been given.
4.
Conclusion and Remarks
Based on the observations, all students did the lab work well. Questions led to the module were successfully answered well by students with a minimum score of 70%. Based on the evaluation, 70% of students managed to get a minimum score of 70%. The
questionnaire results showed that students gave positive responses ≥80% towards the questionnaire. So all indicators are achieved. Thus it can be concluded that the independent lab work module of geometric optics about convex lens using PhET
simulation “Geometric Optics” is effective in helping the students to understand convex
References
[1] Kaltakci, D.,& Erylmaz,A. 2009. Source of Optic Misconceptions. Contemporray Science Education Research: Learning and Assesment.
[2] Anugrahini, A., Sutopo., & Asim. 2013. Remidiasi pemahaman konsep siswa kelas x tentang pembentukan bayangan oleh pembiasan pada permukaan datar dan lensa menggunakan pertanyaan socratik.
[3] Sulasiah.,Ramalis, A.R., &Wiendartun. 2009. Upaya Meningkatkan Prestasi Belajar Siswa SMA Melalui Penerapan Model Pembelajaran Kooperatif Tipe Student Teams Achievement Division (STAD).
[4] Murti, A., Muhibbuddin., & Nurmaliah, C. 2014. Penerapan Pembelajaran Berbasis Praktikum untuk PeningkatkanKemampuan Kognitif Dan Psikomotorik pada PerkuliahanAnatomi Tumbuhan.Jurnal Biologi
Edukasi Edisi 12, 6(1).
[5] Wuryaningsih, R., & Suharno. 2014. Penerapan Pembelajaran Fisika dengan Media Simulasi PhET pada Pokok Bahasan Gaya untuk Meningkatkan Hasil Belajar Siswa Kelas VIIIA SMPN 6 Yogyakarta.
[6] Pujiyono., Sudjito, D. N., & Sudarmi, M. 2014. Desain pembelajaran dengan menggunakan media simulasi PhET (Physics Education and Technology) pada materi medan listrik.
[7] Indriyani, L., &Rohandi. 2017. Pengaruh penggunaan simulasi PhET dengan model problem solving terhadap minat belajar siswa pada pembelajaran tentang Hukum Boyle dan Gay Lussac di Kelas XI IPA SMA Negeri 1 Prambanan dan SMA Negeri 2 Klaten.
[8] Yuafi M.E.D., & Endryansyah. 2015. Pengaruh penerapan media pembelajaran PhET simulation terhadap hasil belajar siswa kelas X TITL pada standar kompetensi mengaplikasikan rangkaian listrik di SMKN 7 Surabaya. Jurnal Pendidikan Teknik Elekro, 4(2), 407-414.
[9] Mubarrok M.F, & Mulyaningsih, S. 2014. Penerapan pembelajaran fisika pada materi cahaya dengan media PHET simulation untuk meningkatkan pemahaman konsep siswa di SMP. Jurnal Inovasi Pendidikan Fisika,
3(1).
[10] Eko, S., & Yuanita, L. 2014. Penerapan media laboratorium virtual (PhET) pada materi laju reaksi dengan model pengajaran langsung. Unesa Journal of Chemical Education, 3(1) pp 119-133
[11] Wiwit., Ginting, S. M., & Firdaus, M. F. 2013. Penerapan pembelajaran kimia dasar menggunakan media powerpoint 2010 dan PhET simulation dengan pendekatan modification of reciprocal teaching berbasis konstruktivisme. Jurnal Exacta, 11(1).
[12] Rahmat, S., & Muflika, A.A. 2012. Eksplorasi pemberdayaan courseware simulasi PhET untuk membangun keterampilan proses sains siswa SMA. Jurnal Pengajaran MIPA, 17(2), 258-268.
[13] Nurhayati., Fadilah, S., &Mutmainnah. 2014. Penerapan metode demonstrasi berbantu media animasi software PhET terhadap hasil belajar siswa dalam materi listrik dinamis kelas X Madrasah Aliyah Negeri 1 Pontianak. Jurnal Pendidikan Fisika dan Aplikasinya, 2(4).
[14] Afifah R.M.A., Masjkur, K., &Sutarman. 2014. Pengaruh Pembelajaran Guided Inquiry Berbantuan PhET Terhadap Kemampuan Berfikir Tingkat Tinggi dan Tanggung Jawab Siswa Kelas XI IPA Pada Materi Teori Kinetik Gas.
[15] Hapsara, S. A., Sudjito, D. N., & Noviandini, D. 2016. PhET (Physics Education Technology) Virtual Laboratoryas Physics Learning Media about Factors that Influencethe Number of Emitted Electrons in Photoelectric Effect.
[16] Dinavalentine, M., Sudjito, D. N., & Noviandini, D. 2017. Desain modul praktikum mandiri tentang pembiasan cahaya menggunakan simulasi PhET “Bending Light” untuk mahasiswa.