SMP JOANNES BOSCO SCIENCE TE
ACHERS’
PERCEPTION ON THE IMPLEMENTATION
OF BILINGUAL EDUCATION
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Kresentia Yosta Dhinda Aprillia
Student Number: 081214015
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
i
SMP JOANNES BOSCO SCIENCE TE
ACHERS’
PERCEPTION ON THE IMPLEMENTATION
OF BILINGUAL EDUCATION
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Kresentia Yosta Dhinda Aprillia
Student Number: 081214015
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
iv
“Everyone has a right to
CHOOSE but only successful
people who can choose
THE BEST CHOICE
.”
I dedicate this thesis to:
My Beloved Jesus
My Self
My Parents
My Sisters and Brother
vii
ABSTRACT
Aprillia, Kresentia Yosta Dhinda. 2012. SMP Joannes Bosco Science Teachers’
Perception on the Implementation of Bilingual Education. Yogyakarta: Sanata Dharma University.
The implementation of bilingual education in SMP Joannes Bosco, Yogyakarta started in 2009. Subjects which are delivered bilingually to SMP Joannes Bosco students are Science and Math. Bilingual teachers in SMP Joannes Bosco are in learning process to conduct an effective bilingual teaching-learning activity for the students. According to Adeyanju (as cited in Adeyanju, 2003), learning will occur as a result of perception.
Therefore, the researcher was inspired to analyze the SMP Joannes Bosco
Science teachers’ perception on the implementation of bilingual education. There
were two problems formulated by the researcher in this study: 1) What is SMP Joannes Bosco Science teachers’ perception on the bilingual education implementation? 2) How is the bilingual education for Science class at SMP Joannes Bosco implemented?
To answer the research problems, survey research was conducted in this study by holding an interview to Science teachers in order to obtain Science
teachers’ perception on the bilingual education implementation. Moreover, the researcher also administered a questionnaire to Science teachers and conducted some observations in Science (Physics, Biology, and Chemistry) class of the seventh grade students who were in the second semester in SMP Joannes Bosco to obtain the implementation of bilingual education in SMP Joannes Bosco.
The research findings showed that the SMP Joannes Bosco Science teachers had a positive perception on the implementation of bilingual education. It was shown from the responses given in the interview that according to the Science teachers, bilingual education was very important for improving the students’ even
the Science teachers’ English skill in order to improve Indonesian education.
However, the bilingual education at SMP Joannes Bosco had not been
implemented yet as the Science teachers’ understanding. It was shown from the questionnaire and observation results regarding the Science teachers’ language in the bilingual teaching-learning activity. The teachers used English and Indonesian simultaneously only for giving a command and asking a question to the students. In general, SMP Joannes Bosco Science teachers had a good perception regarding the purpose of the bilingual education implementation.
viii
ABSTRAK
Aprillia, Kresentia Yosta Dhinda. 2012. SMP Joannes Bosco Science Teachers’
Perception on the Implementation of Bilingual Education. Yogyakarta: Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Pelaksanaan pendidikan bilingual atau dwibahasa (Bahasa Indonesia dan Bahasa Inggris) dimulai pada tahun 2009 di SMP Joannes Bosco, Yogyakarta. Mata pelajaran bilingual untuk siswa di SMP Joannes Bosco adalah Sains dan Matematika. Guru bilingual di SMP Joannes Bosco sedang berada dalam proses pembelajaran untuk menerapkan kegiatan pembelajaran bilingual yang efektif bagi para siswa. Menurut Adeyanju (seperti dikutip dalam Adeyanju, 2003), pembelajaran akan terjadi sebagai akibat dari persepsi.
Oleh karena itu, peneliti terinspirasi untuk menganalisa persepsi guru Sains di SMP Joannes Bosco mengenai penerapan pendidikan bilingual. Ada dua masalah yang dirumuskan oleh peneliti dalam penelitian ini: 1) Bagaimana persepsi guru Sains SMP Joannes Bosco pada pelaksanaan pendidikan bilingual? 2) Bagaimana pendidikan bilingual untuk kelas Sains di SMP Joannes Bosco dilaksanakan?
Untuk menjawab rumusan masalah tersebut, peneliti melaksanakan penelitian survei dengan mengadakan wawancara kepada guru Sains untuk mendapatkan persepsi guru Sains terhadap penerapan pendidikan bilingual. Selain itu, peneliti juga memberikan kuesioner untuk guru Sains dan melakukan beberapa pengamatan di kelas Sains (Fisika, Biologi, dan Kimia) khususnya pada siswa kelas tujuh yang berada di semester kedua di SMP Joannes Bosco untuk mengetahui penerapan pendidikan bilingual di SMP Joannes Bosco.
Hasil dari penelitian menunjukkan bahwa guru Sains di SMP Joannes Bosco memiliki persepsi positif terhadap pelaksanaan pendidikan bilingual. Hal ini terlihat dari respon yang diberikan dalam wawancara bahwa menurut guru Sains, pendidikan bilingual sangat penting untuk meningkatkan kemampuan Bahasa Inggris para siswa maupun guru Sains dengan tujuan meningkatkan kualitas pendidikan di Indonesia. Namun pendidikan bilingual di SMP Joannes Bosco masih belum berjalan sesuai dengan pemahaman guru Sains di SMP Joannes Bosco. Hal ini terlihat dari hasil kusioner dan pengamatan mengenai bahasa yang digunakan guru Sains dalam kelas bilingual. Guru Sains menggunakan Bahasa Inggris dan Bahasa Indonesia secara seimbang hanya untuk memberikan perintah dan mengajukan pertanyaan kepada siswa. Secara umum, guru Sains di SMP Joannes Bosco memiliki persepsi yang baik mengenai tujuan dari diterapkannya pendidikan bilingual di sekolah.
ix
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
First of all, I would like to dedicate my greatest gratitude to dear Jesus Christ for His amazing love, bless, guidance and everything that always be given to encourage me every day. He always supports and gives me strength, health,
positive mind, passion, and happiness during the process of conducting this thesis.
Then I would like to express my greatest appreciation to Caecilia Tutyandari, S.Pd., M.Pd., my beloved sponsor who always gives me her best guidance, advice, suggestion, patience, and smile from the beginning of
conducting the research until the accomplishment of this thesis. I also would like
to express my great appreciation to Sr. Margareth for her willingness in checking and correcting the grammar mistakes in my thesis patiently.
I feel so proud and grateful to my beloved father, BapakSuprabowo, S.H. and my beloved mother, IbuJovita Budi Kristiani who always teach me how to face every problem that I have, support my effort, and take care about my health
during the process of accomplishing this thesis. I feel grateful also to my oldest
sister, Priscilla Yosti Nanda Ariesta S.Kom., my younger brother, Norbertus Dhendy Restu Prayogo, and my youngest sister, Yustina Violieta Prabawati for giving spirit and supporting me.
I would like to give my gratitude to Dra. C. Bekti Susilowati, for giving me permission to do the survey research at SMP Joannes Bosco, Yogyakarta. I
also thank Asterina Saptiyani, S.Pd. as the coordinator of bilingual team in SMP Joannes Bosco, who is very kindly supporting and giving advice for my thesis. I
x
willingness to become my interviewees, fill the questionnaire patiently, and
become the participants of my observation in the Science class. I also thank all of
the seventh grade students year academic 2011/2012 of VII Freedom class for their willingness to become my participants in conducting the observation.
I thank my best friends forever, Irine Puji Telisadewi, Monika Asri Lestari, Levyn Gracia Hanardi, and Stefanus Brian Dwi Nugroho for the great moments, the friendship, and the solidarity during the first until the last semesters
in Sanata Dharma University.
My gratefulness also goes to all of lecturers, staff, and my friends in the
English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University, for the
wonderful lessons, experiences, and moments. I also appreciate all people who
help and support me during the process of conducting this thesis, but I could not
mention their names one by one. God always be with us.
Kresentia Yosta Dhinda Aprillia
xi
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
TITLE PAGE ... i
APPROVAL PAGES ... ii
DEDICATION PAGE ... iv
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY ... v
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI ... vi
ABSTRACT ... vii
ABSTRAK ... viii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ... ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... xi
LIST OF TABLES ... xv
LIST OF APPENDICES ... xvi
CHAPTER I. INTRODUCTION A. Research Background ... 1
B. Research Problems ... 3
C. Problem Limitation ... 3
D. Research Objectives ... 3
E. Research Benefits ... 4
xii
CHAPTER II. REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
A. Theoretical Description ... 6
1. Perception ... 6
a. Definition of Perception ... 6
b. A Four-stage Sequence of Perception ... 7
c. Factors Affecting Perception ... 8
d. Teachers’ Perception ... 9
2. Bilingual Education ... 10
a. Definition of Bilingual Education ... 10
b. The Implementation of Bilingual Education ... 11
B. Theoretical Framework ... 14
CHAPTER III. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY A. Research Method ... 16
B. Research Setting ... 17
C. Research Participants ... 17
D. Instruments and Data Gathering Technique ... 17
E. Data Analysis Technique ... 20
xiii
CHAPTER IV. RESEARCH RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
A. Science Teachers’ Perception on the Implementation of
Bilingual Education ... 27
1. Interview Results towards the Science Teachers’ Perception on the Implementation of Bilingual Education ... 27
a. Description of Science Teachers’ Past Experience, Expectations, and Thought on Bilingual Education ... 28
1) Science Teachers’ Past Experience ... 28
2) Science Teachers’ Expectations ... 29
3) Science Teachers’ Thought ... 31
b. Science Teachers’ Perception on Bilingual Class ... 33
B. The Implementation of Bilingual Education ... 38
1. Questionnaire Results towards the Bilingual Education Implementation ... 39
a. Science Teachers’ Teaching Motivation ... 39
b. Science Teachers’ Language ... 41
1) Science Teachers’ Language in Providing Learning Material ... 41
2) Science Teachers’ Language in Providing Learning Media ... 41
3) Science Teachers’ Language in Class Activity ... 42
xiv
a. Observation Results in Physics Class ... 45
1) First Observation at Physics Class ... 45
2) Second Observation at Physics Class ... 47
b. Observation Results in Biology Class ... 48
1) First Observation at Biology Class ... 48
2) Second Observation at Biology Class ... 50
c. Observation Results in Chemistry Class ... 51
1) First Observation at Chemistry Class ... 51
2) Second Observation at Chemistry Class ... 52
d. Observation Results in Science Class ... 54
CHAPTER V. CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS A. Conclusions ... 55
B. Recommendations ... 58
1. Recommendations for Bilingual Teachers ... 58
2. Recommendations for Future Researchers ... 59
REFERENCES ... 60
xv
LIST OF TABLES
Page
Table
1.1 Blueprint of the Interview Guideline ... 20
1.2 Blueprint of the Questionnaire ... 22
2.1 Questionnaire Results of Science Teachers’ Teaching Motivation ... 39 2.2 Questionnaire Results of Science Teachers’ Language in Class
xvi
LIST OF APPENDICES
Page
APPENDIX A Surat Permohonan Izin Penelitian ... 63
APPENDIX B Interview Guideline ... 64
APPENDIX C Kuesioner ... 65
APPENDIX D Observation Sheet ... 67
APPENDIX E Raw Data of Interview Results ... 70
APPENDIX F Questionnaire Results ... 77
APPENDIX G Raw Data of Observation Results ... 80
APPENDIX H Sample of Presentation used by Biology Teacher ... 96
APPENDIX I Sample of Handout used by Biology Teacher ... 97
APPENDIX J Sample of Chemistry Final Test ... 98
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter presents six sections. They are the research background,
research problems, problem limitation, research objectives, research benefits, and
definition of terms.
A. Research Background
SMP Joannes Bosco is one of the potential schools in Yogyakarta which is
in process to be a bilingual school or Rintisan Sekolah Bertaraf Internasional
(RSBI). There is a bilingual team at SMP Joannes Bosco that always has a
monthly meeting in order to monitor the improvement of the implementation of
bilingual education in SMP Joannes Bosco. The bilingual team consists of
Science, Math, and English teacher.
When having a teaching practice at SMP Joannes Bosco, the researcher
joined a monthly meeting of bilingual team at SMP Joannes Bosco on Thursday,
August 25th, 2011. At the meeting, the coordinator of bilingual team stated that
teaching-learning activities at SMP Joannes Bosco especially for Science
(Physics, Biology, and Chemistry) and Math classes have to be taught in two
languages (English and Indonesian) and the teachers should improve the students’
English vocabulary items related to Science and Math subjects.
Based on a theory from Brown (2007) regarding content based learning, in
2
and curriculum in order to complement each other. In implementing bilingual
education, the teachers and the students in a bilingual school are exposed to learn
some English vocabulary items related to Science in order to understand the
Science subject which is delivered in two languages. Based on an article in
National Capital Language Resource Center from Keatly and Kennedy (2003),
language learning is a process of developing learners’ competence when using the
language for a specific purpose and teachers should facilitate the students'
development of language skills.
Bilingual teachers in SMP Joannes Bosco are still in learning process to
implement an effective bilingual education for Science and Math class. Based on
Adeyanju (as cited in Adeyanju, 2003), learning will occur as a result of new
skills, knowledge, perceptions, facts, beliefs, and new information. Moreover,
Adeyanju (2003) concludes that teacher has an important role of the effectiveness
in teaching-learning activities.
Therefore, the researcher would like to focus on SMP Joannes Bosco
bilingual teachers’ perception on the implementation of bilingual education. The
bilingual teachers’ perception would like to be analyzed as the factors that can
affect the learning process in the bilingual class at SMP Joannes Bosco. Science
class is recommended for the researcher by the coordinator of bilingual team in
SMP Joannes Bosco. Moreover, the researcher also would like to focus on the
implementation of bilingual education for Science class at SMP Joannes Bosco
B. Research Problems
Relating to the research background, there are two problems formulated by
the researcher. The research problems are:
1. What is SMP Joannes Bosco Science teachers’ perception on the bilingual
education implementation?
2. How is the bilingual education for Science class at SMP Joannes Bosco
implemented?
C. Problem Limitation
The focus of this research will be on the SMP Joannes Bosco Science
teachers’ perception on the bilingual education implementation. The researcher
also focuses on the implementation of bilingual education in Science (Physics,
Biology, and Chemistry) classes of seventh grade students who are in the second
semester at SMP Joannes Bosco.
D. Research Objectives
As it has been stated in the research problems, the objectives of this
research are to investigate the answer to the research problems. The research
objectives are:
1. To determine the SMP Joannes Bosco Science teachers’ perception on the
bilingual education implementation.
2. To describe the implementation of bilingual education in Science class for
4
E. Research Benefits
Hopefully, this research gives some beneficial contributions in some
educational fields such as:
1. Bilingual teachers
This research gives detailed description regarding some factors that can
affect the implementation of bilingual education for bilingual teachers who are
going to implement an ideal bilingual teaching-learning activity for the students at
school.
2. SMP Joannes Bosco
This research discusses the Science teachers’ perception on the bilingual
education implementation and the implementation of bilingual education
especially for Science class at SMP Joannes Bosco. This research is a feedback of
the teaching-learning activities in Science class as a bilingual class at SMP
Joannes Bosco.
3. Other researchers
This research is expected to be helpful for everyone especially other
researchers who want to conduct a further research on the similar or same topic
with the researcher.
F. Definition of Terms
There are some definitions that should be defined in order to lead the
1. Bilingual Education
According to Hamers and Blanc (1990), the definition of bilingual
education is a system of school education in which, for a verifying amount of
time, simultaneously or consecutively, the instruction when teaching is planned
and given in more than one language or at least two languages. The researcher
focuses on the language used by Science teachers in teaching Science (Physics,
Biology, and Chemistry) at SMP Joannes Bosco especially for students who are in
seventh grade.
2. Perception
Based on Altman, Valenzi, and Hodgetts (1985), perception is the way of
stimuli by a person to meaningfully interpret the reality. In this research, the
perception is about the evaluation of SMP Joannes Bosco Science teachers
(Physics, Biology, and Chemistry) in perceiving bilingual education when
teaching Science for seventh grade students.
3. Teaching Implementation
According to Vio (2002), implementation is the carrying out, execution, or
practice of a plan, a method, or any design in order to do something. In this
research, it is about SMP Joannes Bosco Science teachers’ practice in using two
languages (English and Indonesian) in teaching Science.
6
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
This chapter presents the review of related literature of this study. This
theoretical writings divided into two sections. The first section is theoretical
description that consists of some theories related to the study. The second section
is the study matter as the theoretical framework.
A. Theoretical Description
The theoretical description discusses two sections. The first section is
perception and the second section is bilingual education.
1. Perception
In describing the theories of perception based on some experts, the
researcher describes the definition of perception, four stages sequence of
perception, factors affecting perception, and teachers’ perception.
a. Definition of Perception
According to Ponty (2005), physiology of perception begins by
recognizing an anatomical path leading from a receiver through a definite
transmitter to a recording station. Whereas Kreitner and Kinicki (2008) explain
that perception is a cognitive process to interpret and understand the surroundings.
Besides, Altman, Valenzi, and Hodgetts (1985) acknowledge that perception is the
Perception comes from a person into the meaningful interpreting through the
selected stimulation.
b. A Four-stage Sequence of Perception
Kreitner and Kinicki (2008) reveal that perception involves a four-stage
information processing sequence as follows:
1) Selective attention/comprehension
Attention is the process of becoming consciously aware of something or
someone. Based on a research by Kreitner and Kinicki (2008), people tend to pay
attention to salient stimuli. Something is salient when it stands out from its
context.
2) Encoding and simplification
Encoding is required, raw information is interpreted or translated into
mental representations. The perceivers establish cognitive categories to complete
the mental representation. The information of animals, objects, people, or events
is evaluated by comparing their characteristics in schemata. According to Kreitner
and Kinicki (2008), a schema represents a person’s mental picture or a summary
of particular events or type of stimulus.
3) Storage and retention
The information of animals, objects, people, or events also passes the three
categories of storage and retention. They are event memory, semantic memory,
8
4) Retrieval and response
People retrieve information from their judgments and decisions. The
judgments and decisions based on the process of drawing, interpreting, and
integrating categorical information stored in a long-term memory or retrieving a
summary of the judgments.
c. Factors Affecting Perception
In fact, there are four factors that can affect a person’s perception
according to Altman, Valenzi, and Hodgetts (1985). The factors are selection of
stimuli, organization of stimuli, the situation, and self-concept.
1) The selection of stimuli
It is known as a sensory adaption. In perceiving things, people select some
specific things through the process of selection. Each person has different
processes of selection so that people usually perceive things differently depending
on their own process of selection.
2) The organizing of stimuli
After some specific things or information have been selected through the
selection of stimuli, they must be arranged to become meaningful. In the
organizing of stimuli the mind arranges the information by selecting specific item
and identifying the information in a meaningful way. Based on Altman, Valenzi,
and Hodgetts (1985), there are three principles of organizing of stimuli. The
3) Situation
A situation that person’s familiarity with, expectations about, or past
experience is another factor affecting the perception. Perceiving a situation is
related to how people perceive their behavior and attitude in a specific situation.
Different situations affect people in perceiving their behavior. Science teachers
who basically are not familiar with English may have different perception with
English teachers in improving students’ English vocabulary items through the
bilingual class.
4) Self-concept
The way people perceive their selves affecting the perception of the world.
A self-concept is important for people in order to create a mental image of
something.
d. Teachers’ Perception
As stated in Chapter I, the focus of this study is on the teachers’
perception. According to Muijis and Reynolds (2011), there are three main types
of perception that matter to teach. The perceptions are an evaluation on an
effective teaching, students’ behavior in learning, and situation around the school
itself. The three main types of perception occur from the SMP Joannes Bosco
Science teachers’ perception on the implementation of bilingual education in
teaching-learning activities for Science class. Three types of teachers’ thought that
can have an impact on teaching are identified by Clark and Petersen (as cited in
Muijis & Reynolds, 2011): teacher planning, teacher thought processes, and
10
2. Bilingual Education
In this section, the researcher describes the theories about bilingual
education. This section includes the definition of bilingual education and the
implementation of bilingual education.
a. Definition of Bilingual Education
According to Hamers and Blanc (1990), the definition of bilingual
education is a system of school education in which, for a verifying amount of
time, simultaneously or consecutively, the instruction when teaching is planned
and given in more than one language or at least two languages. Hamers and Blanc
(1990) also describe that most programs of bilingual education are divided into
three categories. The first category is that the instruction is given in both
languages simultaneously. The second category is that the instruction is given first
in L1 until such time when the students are able to use L2 as the means of learning.
The last category is that the largest part of instruction is given in L2, and L1 is
introduced at larger stage as an introductory language.
Based on Bax (2010), many nations in Asia including Indonesia have
meant a radical re-assessment of what they consider to be ineffective approaches
to English language education. One response has been a move towards what is
perceived as more innovative solutions involving bilingual and immersion
approaches and the teaching of content subjects such as Math and Science through
the English.
Hymes describes “bilingual education is a sociolinguistic subject that
successful of their communities in characteristic of contemporary life” (1985).
Whereas Ogletree (1978) concludes that bilingual education is a vehicle for
cultural pluralism. Bilingual education gives the non-English speaking child an
opportunity to learn his own language and culture which can affect their
self-concept development, helps to maintain the linguistic and cultural heritage of the
ethnic group, and develops educational change by giving an assumption that the
most suitable curriculum for children is an English based curriculum.
Based on a current research by Ogletree (1978), bilingual education is still
in the developmental process. Like another innovation, bilingual education has a
high unrealistic expectation with unplanned implementation and limited
evaluation. Ogletree (1978) notes that:
Whether bilingual-bicultural education will become a change agent and secure equal status with other programs, as a desirable and essential aspect of the American educational process is still a question. Like all socio-political issues, its future depends upon the attitudes and belief of the populace. Failure to nurture it may doom thousands of non-English speaking children to academic failure.
b. The Implementation of Bilingual Education
Teachers’ knowledge is potentially important for an effective teaching
-learning activity. There are three main types of teachers’ knowledge that matter to
the effective teaching-learning activities according to Muijis and Reynolds (2011).
The first knowledge is teachers’ subject knowledge. It is about the teachers’
understanding on the subject that they have to teach. The second is teachers’
pedagogical knowledge. It is about the teachers’ understanding on an effective
teaching. The last is pedagogical subject knowledge. It is about the teachers’
12
the three main types of knowledge, they would be able to fully apply an effective
teaching-learning activity. It is obvious that teachers have to know what they have
to teach. Bilingual teachers not only have to know the subject that they have to
teach but also the language that they have to use in a bilingual teaching-learning
activity. Mcneil and Wiles (1990) generate that in an effective teaching-learning,
teachers possess an assumption about how the students learn. The teachers’ theory
reflects a basic assumption about how students learn and teachers’ role in the
teaching-learning activity.
There is a list of effective classroom practices through bilingual education
for the bilingual teachers according to Finocchiaro (1985):
1) Teachers adapt and modify the existing textbook, making additions and
deletions when necessary and changing the sequence of material presentation
where logical.
2) Teachers teach vocabulary that the students need immediately because it is
related to places or happenings in their homes and community and it enables
the students to talk about the elements in their environment.
3) Teachers use the same listening comprehension passage at three different
levels of difficulty during the semester.
4) Teachers vary the types of participation – larger group, smaller group, and pair
practice.
5) Teachers engage in role-playing, problem-solving or community learning
activities.
According to Crawford (1998), English as a second language (ESL) in
bilingual education is best taught in natural situations, with the second language
for meaningful contexts rather than in repetition of grammar and vocabulary.
Moreover, according to Mcneil and Wiles (1990), an effective teaching-learning
depends on the use of media as the learning tool. Teachers who are able to use
media effectively in teaching-learning activity can become the designer and the
manager of the teaching-learning activity. The media helps the teachers to control
and enhance the teaching-learning activity in the classroom. Moreover, Slavit and
Mulhern (2003) describe that bilingual textbooks play an important role as the
media in supporting ESL students’ language and literacy learning in bilingual
class. Students who learn to read in their native language do not need to relearn to
read in English since many of the processes involved in decoding text and
understanding print relationships transfer from the L1 into English.
Slavit and Mulhern (2003) also describe that there are some strategies in
teaching through bilingual textbooks. The strategies are introducing topics,
supporting transfer of reading in L1 to L2, supporting independent reading, using
L1 version as a preview, using L1 version as a review, reading two versions for
self-assessment, comparing and contrasting cognates, improving home-school
connections, supporting family literacy programs, raising all children’s awareness
of multiculturalism, helping teachers learn another language, and encouraging
14
B. Theoretical Framework
This is a study of SMP Joannes Bosco Science teachers’ perception on the
implementation of bilingual education. This research is also about the
implementation of bilingual education especially for Science class at SMP
Joannes Bosco.
Perception theory according to some experts as stated in the first main
point helps the researcher to understand the meaning of perception in order to
answer the first research problem. By using the theory stated by Altman, Valenzi,
and Hodgetts (1985) regarding some factors that can affect the perception, the
researcher would like to analyze the factors which can affect the data toward
Science teachers’ perception on bilingual education at SMP Joannes Bosco.
Science teachers can have different perceptions in perceiving the bilingual
education for SMP Joannes Bosco students.
There are three types of teachers’ thought are identified by Clark and
Petersen (as cited in Muijis & Reynolds, 2011). This theory helps the researcher in
identifying the Science teachers’ understanding of bilingual education.
While in answering the second research question, the researcher uses the
theory of bilingual education stated by Hamers and Blanc (1990) in order to
explain the teachers’ language at Science class activities. The researcher also uses
the theories of the bilingual education implementation in teaching-learning
activities stated by McNeil and Wiles (1990) about media as the learning tool.
Another theory used by the researcher is about teachers’ knowledge stated by
These theories help the researcher to understand the fact of the bilingual
education implementation that may occur in SMP Joannes Bosco as one of the
potential schools which is developing to be a bilingual school. The theory of the
bilingual education implementation also helps the researcher in identifying a
practical teaching strategy in Science class that has to be observed at SMP
16
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This chapter is divided into six sections. They are the research method,
research setting, research participants, instruments and data gathering technique,
data analysis technique, and research procedure.
A. Research Method
In order to find out the answers to the research questions stated in Chapter
I, an appropriate way for the researcher to gain such data was a survey research.
The purpose of the survey research was to describe a characteristic of a
population. The researcher would like to investigate Science teachers’ perception
on the implementation of bilingual education for Science class at SMP Joannes
Bosco. The researcher used a qualitative method in order to gain the detailed
description. According to Babbie (1973), survey research can use a qualitative
(e.g. ask open-ended questions) or a quantitative method.
Fraenkel and Wallen (2009) describe that the survey research had three
major characteristics. The major characteristics were collecting information from
a group of people in order to describe some characteristics, collecting information
through asking some questions, and collecting information from a sample rather
than from every member of the population. Covering the population at SMP
Joannes Bosco as the research participants and the limited time for doing the
research. The population of this research was all of the bilingual teachers in SMP
Joannes Bosco and the sample of this research was the Science teachers in SMP
Joannes Bosco who taught the seventh grade students.
B. Research Setting
This research was conducted at SMP Joannes Bosco, Jl. Melati Wetan
No.51, Yogyakarta. The collecting data started when the seventh grade students
(VII Freedom) of SMP Joannes Bosco year academic 2011/2012 were in the
second semester.
C. Research Participants
The participants of this research were three Science teachers who taught
seventh grade students at SMP Joannes Bosco. Science teachers at SMP Joannes
Bosco were the teachers who taught Physics, Biology, and Chemistry. VII
Freedom class is recommended for the researcher to do the observation when the
Science teachers were teaching Science in that class.
D. Instruments and Data Gathering Technique
There were three instruments used by the researcher. The types of the
instruments used in this survey research were an interview guideline, a
18
1. Interview Guideline
The first instrument was an interview guideline. Based on Borg and Gall
(1983), the collection data through an interview in survey research was a unique
method to obtain more data which involved direct verbal interaction between
individuals. Babbie (1973) describes that the interviewer in survey research
should be a neutral medium in holding the interview so that the interviewer’s
presence would not affect the respondents’ perception of the given questions.
Before holding the interview, the researcher arranged an interview guideline
which consisted of questions that have to be asked to the Physics, Biology, and
Chemistry teachers in SMP Joannes Bosco. The interview was about the Science
teachers’ past experience related to bilingual education, Science teachers’
expectations on bilingual education, Science teachers’ understanding on bilingual
education, and Science teachers’ perception on Science teaching-learning
activities as a bilingual class. The purpose of the interview was to determine the
answer to the first research question as stated in the Chapter I. The first research
problem was about the Science teachers’ perception on the bilingual education
implementation.
2. Questionnaire
The second instrument was the questionnaire. The questionnaire was
administered to Physics, Biology, and Chemistry teachers. The form of the
questionnaire was a close-ended form. Borg and Gall (1983) reveal that the
possible answer to a close-ended questionnaire is known and few in number. The
by Borg and Gall (1983). The participants answered the questionnaire by giving a
check sign under the phrase that described their opinion. The answer to the
questions of the questionnaire was in the phrase; Sangat Tidak Setuju (STS) for
strongly disagree, Tidak Setuju (TS) for disagree, Setuju (S) for agree, and Sangat
Setuju (SS) for strongly agree.
The questionnaire for the Science teachers was conducted in a rating scale
in order to assess how the Science teachers’ teaching motivation in the bilingual
teaching-learning activity, Science teachers’ language in providing learning
material and media for the students, and Science teachers’ language in the
bilingual teaching-learning activity. The purpose of the questionnaire for Science
teachers was to investigate the answer to the second research question as stated in
Chapter I. By administering the questionnaire, the researcher would like to
describe how the bilingual education is implemented in the teaching-learning
activity for Science class at SMP Joannes Bosco.
3. Observation Sheet
Borg and Gall (1983) note that by only using the questionnaire and
interview for a survey research, the respondents tend to bias the data they offer
about their selves. Therefore the researcher needed an observation to overcome
this problem.
Besides the questionnaire, in order to answer the second research question
as stated in Chapter I, the researcher conducted some observations so that the
bilingual teaching-learning activity in the Science could be observed naturally.
20
was that the natural observation could be used in natural setting. Natural
observation also was often used in educational research to study classroom
behavior. The observation focused on the Science teachers’ implementation of
bilingual education in teaching-learning activities. The implementation was about
the teachers’ language in the bilingual teaching-learning activity such as in
greeting, opening, asking previous topic, introducing material, closing, explaining
the material, giving reinforcement, giving instructions for the assignment or
discussion, giving a command and asking a question to the students.
E. Data Analysis Technique
The first step in analyzing the data was analyzing the interview results.
The researcher analyzed the positive answer to the interview from the bilingual
teachers at SMP Joannes Bosco as the positive teachers’ perception on the
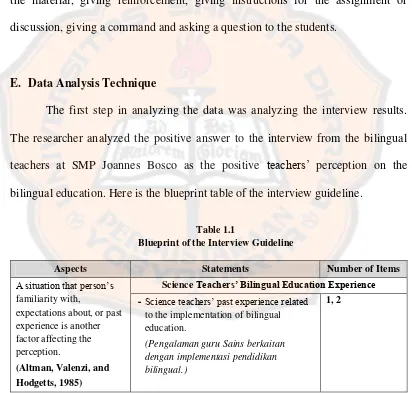
bilingual education. Here is the blueprint table of the interview guideline.
Table 1.1
Blueprint of the Interview Guideline
Aspects Statements Number of Items
A situation that person’s familiarity with,
expectations about, or past experience is another factor affecting the perception.
(Altman, Valenzi, and Hodgetts, 1985)
Science Teachers’ Bilingual Education Experience
- Science teachers’ past experience related
to the implementation of bilingual education.
(Pengalaman guru Sains berkaitan dengan implementasi pendidikan bilingual.)
Science Teachers’ Expectations on Bilingual Education
- Science teachers’ expectation on the
implementation of bilingual education for every school in Indonesia.
(Ekspektasi guru Sains terhadap penerapan kelas bilingual di seluruh Indonesia.)
6
- Science teachers’ expectation on the
importance of bilingual education for students’ future.
(Ekspektasi guru Sains terhadap kelas bilingual bagi masa depan para siswa.)
11
Science Teachers’ Thought on Bilingual Education There are three types of
teachers’ thought are identified that can have an impact on teaching:
- Science teachers’ understanding of
bilingual education generally.
(Pemahaman guru Sains terhadap pendidikan bilingual secara umum.)
3
- Science teachers’ opinion about an
effective implementation of bilingual
Science Teachers’ Perception as Evaluation on Bilingual Class There are three main types
of perception that matter to teaching. They are the
- Science teachers’ perception on the
positive and negative factors which can influence the effectiveness of teaching-learning activity in the bilingual class.
(Persepsi guru Sains terhadap hal-hal positif maupun negatif yang
mempengaruhi keefektifan kegiatan belajar-mengajar di kelas bilingual.)
8
- Science teachers’ perception on the
advantages and disadvantages of the bilingual class.
(Persepsi guru Sains terhadap manfaat dan kerugian dari adanya kelas bilingual.)
5
- Science teachers’ perception on the
students’ behavior and motivation in the bilingual class.
(Persepsi guru Sains terhadap keaktifan, minat dan motivasi anak dalam kelas bilingual.)
22
- Science teachers’ perception on the
facilities which can support the teaching-learning activity in the bilingual class.
(Persepsi guru Sains terhadap sarana-prasarana di sekolah yang mendukung kegiatan belajar-mengajar di kelas bilingual.)
7
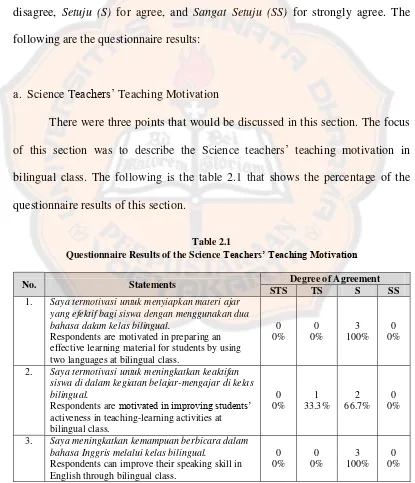
The second step was analyzing the result of the close-ended questionnaire
for the Science teachers at SMP Joannes Bosco. The questionnaire results showed
the percentage of the Science teachers’ response on their implementation of the
bilingual education in the teaching-learning activities. Here is the blueprint table
of the questionnaire.
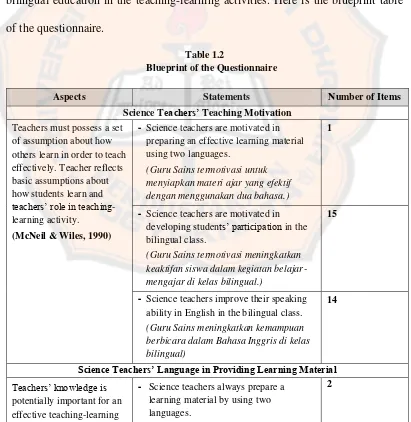
Table 1.2
Blueprint of the Questionnaire
Aspects Statements Number of Items
Science Teachers’ Teaching Motivation
Teachers must possess a set of assumption about how others learn in order to teach effectively. Teacher reflects
- Science teachers are motivated in
preparing an effective learning material using two languages.
(Guru Sains termotivasi untuk menyiapkan materi ajar yang efektif dengan menggunakan dua bahasa.)
1
- Science teachers are motivated in
developing students’ participation in the bilingual class.
(Guru Sains termotivasi meningkatkan keaktifan siswa dalam kegiatan belajar-mengajar dikelas bilingual.)
15
- Science teachers improve their speaking
ability in English in the bilingual class.
(Guru Sains meningkatkan kemampuan berbicara dalam Bahasa Inggris di kelas bilingual)
14
Science Teachers’ Language in Providing Learning Material Teachers’ knowledge is
potentially important for an effective teaching-learning
- Science teachers always prepare a
learning material by using two languages.
activity.
(Muijis and Reynolds, 2011).
(Guru Sains selalu menyiapkan materi ajar dengan menggunakan dua bahasa.)
Science Teachers’ Language in Providing Learning Media Media as the learning tool
in the classroom can control and enhance the teaching-learning activity in the class.
(McNeil & Wiles, 1990
- Science teachers use interesting and a
variety of learning media by using two languages.
(Guru Sains menggunakan media
pembelajaran bilingual yang menarik dan bervariasi menggunakan dua bahasa.)
6, 7
Science Teachers’ Language in Class Activity Most programs of
bilingual education fit into one of three categories: 1) Instruction is given in
both languages simultaneously. 2) Instruction is given first
in L1 and the pupil is taught until such time when he is able to use L2 as a means of learning. 3) The largest part of
instruction is given through L2 and L1 is introduced at larger stage, first as a subject and later as a medium of instruction.
(Hamers and Blanc, 1990)
- Science teachers deliver the material easily
in two languages.
(Guru Sains bisa menyampaikan materi bilingual kepada siswa dengan mudah.)
8
- Science teachers speak in English when
opening and closing the teaching-learning activity in the bilingual class.
(Guru Sains membuka dan menutup kelas bilingual menggunakan Bahasa Inggris.)
3, 13
- Science teachers speak in English when
explaining material and some specific vocabulary items.
(Guru Sains berbicara dalam Bahasa Inggris ketika menjelaskan materi ajar dan beberapa kosakata tertentu.)
4, 5
- Science teachers use two languages in giving
homework, assignment, and test for the students.
(Guru Sains memberi pekerjaan rumah, tugas individu atau kelompok maupun ulangan harian kepada siswa dalam dua bahasa.)
9, 10, 11
- Science teachers ask the students to speak in
two languages in discussion.
(Guru Sains mengajak siswa berdiskusi dengan menggunakan dua bahasa.)
24
The next step was analyzing the result of the observations. The
observation results showed the natural situation of teaching-learning activities in
Science class as the implementation of bilingual education by the Science teachers
at SMP Joannes Bosco.
F. Research Procedure
There were some steps in this survey research employed by the researcher
as the research procedure according to Ary, Jacobs, and Sorensen (2010). They
were:
1. Preparation
The preparation started from asking permission from the headmaster of
SMP Joannes Bosco to conduct this research. After having the permission, the
researcher arranged a meeting with the bilingual team at SMP Joannes Bosco in
order to explain and discuss the topic of the research about the Science teachers’
perception on the bilingual education and the implementation of bilingual
education at SMP Joannes Bosco. Then, the researcher arranged the schedule for
holding an interview with the Science teachers, administering a questionnaire to
the Science teachers, and then conducting some observations at VII Freedom for
subject Science (Physics, Biology, and Chemistry). Based on Borg and Gall
(1983), before gathering data through the instruments, the research had to field
test the instruments to identity ambiguities and misunderstanding or any problems
2. Gathering Data
The second step was gathering data through the interview guideline,
questionnaire, and observation sheet. Firstly, the researcher held the interview
with the Science teachers at SMP Joannes Bosco. The interview was held on
Saturday, May 5th, 2012 from 10 a.m. – 12 p.m. with the Physics and Biology
teachers, and on Wednesday, May 19th, 2012 at 8 a.m. with the Chemistry teacher.
Secondly, after holding the interview with the Science teachers, the researcher
directly administered the questionnaire to the Science teachers.
Thirdly, the last gathering data technique was the observation. The
researcher filled in the observation sheet with pre-activity, whilst-activity, and
post-activity at VII Freedom class in order to describe the implementation of
bilingual education for Science class at SMP Joannes Bosco. The researcher
conducted the observation six times for a month, two times for each subject when
the Science teachers (Physics, Biology, and Chemistry) were teaching at VII
Freedom class. The observation started on Monday, May 7th, 2012 until Friday,
May 25th, 2012. The observations at VII Freedom class for Physics subject were
done on Monday, May 7th, 2012, and on Wednesday, May 19th, 2012. Then the
observations at VII Freedom class for Biology subject were done on Thursday,
May 10th, 2012 and on Thursday, May 24th, 2012. While the observations at VII
Freedom class for Chemistry subject were done on Friday, May 11th, 2012 and on
26
3. Processing Data
The last step was analyzing the data gathered through the interview
guideline, questionnaire, and observation sheet in order to draw the conclusion.
The processing data included coding data, interpreting the results, and then finally
27
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
This chapter presents detailed description regarding data gathered on this
study. The data is gathered from holding an interview, administering a
questionnaire, and conducting some observations. This chapter shows whether
Science teachers have a positive or negative perception on the implementation of
bilingual education. This chapter also reveals the implementation of bilingual
education for Science class of seventh grade students at SMP Joannes Bosco.
A.Science Teachers’ Perception on Bilingual Education
In order to answer the first research question of this study as stated in
Chapter I, the researcher held an interview with Science (Physics, Biology, and
Chemistry) teachers at SMP Joannes Bosco. The researcher asked some
open-ended questions to Science teachers at SMP Joannes Bosco about Science teachers
past experience, expectations, and thought related to bilingual education.
Moreover, Science teacher asked about Science teachers’ perception on the
implementation of bilingual education.
1. Interview Results towards the Science Teachers’ Perception on Bilingual Education
The purpose of holding the interview with Science teachers was to find out
28
thought on bilingual education and to find out Science teachers’ evaluation as the
Science teachers’ perception on bilingual class at SMP Joannes Bosco. Science
teachers are expected to have some experiences related to bilingual education and
a positive expectation and understanding of bilingual education implementation so
that the Science teachers will have a positive perception on bilingual class. The
following are the interview results:
a. Description of Science Teachers’ Past Experience, Expectations, and Thought
on Bilingual Education
Before finding the Science teachers’ perception on the implementation of
bilingual education, the researcher would like to describe how Science teachers’
past experience related to bilingual education, Science teachers’ expectations on
bilingual education for Indonesian education and students’ future, and Science
teachers’ thought on bilingual education based on the interview results. The
1) Science Teachers’ Past Experience
The first respondent had joined a training course about bilingual education
before teaching a bilingual class. The second respondent also had joined a seminar
about bilingual education at Gadjah Mada University Yogyakarta about two years
ago.
“Kalo seminar gitu udah..di UGM. Mungkin uda berapa taun yang lalu
ya..uda lupa e mbak..lebih dari dua taun yang lalu kayaknya.”
“I have joined a seminar in UGM. I joined the seminar about two years ago if I am not mistaken.”
While the third respondent had an experience related to bilingual education
when taking an ESP course in Yogyakarta for six months.
“Memang ada..dulu pernah mengikuti kelas English for special purpose..
pernah ikut disitu satu semester..6 bulan. Belajar mengenai bagaimana mengajar dalam Bahasa Inggris dengan bilingual.”
“I have joined a course about English for special purpose for one semester…six months. I have studied about how to teach at a bilingual class.”
(Respondent 3, Appendix E)
According to Altman, Valenzi, and Hodgetts (1985), perception can be
influenced by past experiences. It could be seen from the interview result of this
section that all of the Science teachers in SMP Joannes Bosco had experience
related to bilingual education in order to gain more description regarding bilingual
education.
2) Science Teachers’ Expectations
Besides the past experiences, Altman, Valenzi, and Hodgetts (1985)
describe that an expectation is one of the factors that can affect a perception. In
order to find out Science teachers’ expectations on bilingual education, the
researcher asked about Science teachers’ opinions on the importance of the
bilingual education implementation in every school in Indonesia and the
importance of bilingual education for the students’ future. For the importance of
the bilingual education implementation in every school in Indonesia, the second
respondent said that it would be great but impossible because of the difference on
the range of facilities in every school in Indonesia.
“Setiap daerah punya perbedaan sendiri-sendiri..kondisi geografisnya ya
30
pendukungnya tidak secepat kita yang berada di Jawa kan. Jadi ya
memang tidak bisa disamaratakan itu tidak bisa.”
“Every region is not the same. For example, facilities in Java are more complete and modern than in the other regions.”
(Respondent 2, Appendix E)
While the third respondent said that teachers’ understanding of English
was very important before deciding to implement the bilingual education at a
school. Bilingual education was very important for every school but it could be
implemented successfully only in a school where teachers and students who were
familiar with English.
“Tergantung ya..kalau sekolah itu siap ya gapapa tapi kalau sekolah itu
tidak siap ya tidak bisa..harus persiapan dulu. Siap dalam hal gurunya bisa Bahasa Inggris.”
“It depends on the school itself whether the school especially the teachers are ready or not for the implementation of bilingual education at class.”
(Respondent 3, Appendix E)
The importance of bilingual education for the students’ future, according
to the first respondent, bilingual education was very important for students who
were going to continue their study abroad.
“Kalau dilihat dari banyaknya sekolah internasional yang masuk ke
Indonesia..saya kira bilingual juga penting ya untuk mengantarkan mereka ke sekolah-sekolah internasional atau bahkan ke luar negeri.”
“Bilingual is important for students who are going to continue their study to international school or even study abroad.”
(Respondent 1, Appendix E)
The second respondent said that the students could develop their English
vocabulary items related to Science through bilingual learning at school.
“Saya kira penting ya mbak. Mereka jadi anak-anak yang mempunyai
wawasan dua bahasa ditambah materinya yang bersangkutan.”
“I think it is important for students in improving their knowledge and vocabulary items related to the subject.”
Science teachers expected that the bilingual education could be
implemented on every school in Indonesia in order to improve Indonesian
education. However, the school had to consider about the facilities at school, the
students’ competence, and the teachers’ competence before deciding to implement
a bilingual education. Science teachers also expected that by learning through
bilingual education, students could improve their English so that they could
continue their study abroad.
3) Science Teachers’ Thought
Based on Clark and Petersen (1986), there are three types of teachers’
thought as perception that affect on teaching. They are teachers’ plan, teachers’
thought process, and teachers’ theories and beliefs. In order to find Science
teachers’ thought on bilingual education, the researcher asked about Science
teachers’ understanding on a bilingual education generally and teachers’ opinions
about an effective implementation of bilingual education. According to the first
respondent, learning through bilingual education meant that students could
improve their English vocabulary items directly through teaching-learning
activities.
“Jadi ya menurut saya pendidikan bilingual itu ya menambah kosakata
anak..membantu memperkaya perbendaharaan anak dan langsung diterapkan dalam kehidupan sehari-hari kan kalau lewat pembelajaran.”
“In my opinion, bilingual education can improve students’ English vocabulary items then it will be used at students’ daily activity directly through the learning.”
32
While according to the third respondent, the meaning of bilingual
education was using two languages in teaching-learning activities.
“Pendidikan bilingual menurut saya itu membelajarkan suatu materi..ya
misalkan kimia..dalam dua bahasa..Bahasa Inggris dan Bahasa
Indonesia.”
“In my opinion, bilingual education is using two languages in teaching. For the example, I teach Chemistry by using English and Indonesian.”
(Respondent 3, Appendix E)
Besides the Science teachers’ understanding on bilingual education, the
researcher also asked Science teachers’ opinions regarding an effective
implementation of bilingual education. The first respondent said that an effective
way to start a bilingual class was by introducing some English vocabulary items
to the students at the beginning of the class.
“Penetrapannya menurut saya ya langkah pertama ya hanya pengenalan
kosakata gitu..tapi kalau dua-duanya siap antara siswa dan guru ya
paling bahasa campuran dulu ya bilingual.”
“In my opinion, the first step on the implementation of bilingual education is by introducing the English vocabulary items. However if both the students and the teachers are good in English then they can speak using two languages.”
(Respondent 1, Appendix E)
The third respondent said that his strategy for an effective teaching at
bilingual class was by translating his explanation from English into Indonesian or
translating his explanation from Indonesian into English.
“Dalam mengimplementasikan pendidikan bilingual saya sendiri ketika
menyampaikan materi terkadang saya sampaikan dalam Bahasa Inggris kemudian saya terjemahkan atau dalam bahasa Indonesia lalu saya terjemahkan dalam Bahasa Inggris.”
“In the implementation of bilingual education, I explain the material in English then I will translate it in Indonesian or I will explain in Indonesian then I will translate it in English.”
It could be seen from the interview results of this section that the meaning
of bilingual education according to the Science teachers’ perception was a
teaching technique by using two languages at the same time (English and
Indonesian) in order to improve students’ English vocabulary items related to the
subject. Two effective teaching techniques in bilingual class according to the
Science teachers’ perception were introducing the English vocabulary items
related to the subject at beginning of the class and by translating teachers’
explanation from English into Indonesian and vice versa.
b. Science Teachers’ Perception on Bilingual Class
This is the main answer result of the interview. In this section, after
finding out the description of Science teachers past experience, expectations, and
thought on bilingual education, the researcher would like to find out detailed
description regarding SMP Joannes Bosco Science teachers’ perception as their
evaluation on the implementation of bilingual education at SMP Joannes Bosco.
There are three main types of perception as the evaluation that matter to teach
based on Muijis and Reynolds (2011). They are the perceptions on an effective
teaching, students’ behavior in learning, and the situation around the school itself.
In order to find out the Science teachers’ perception on the effective
teaching at the bilingual class, the researcher asked about Science teachers’
perception on the positive and negative factors which could influence the
34
asked about Science teachers’ perception on the advantages and disadvantages of
bilingual class.
For the positive factor which could influence the effectiveness of
teaching-learning activities at bilingual class, the first respondent said that students’ and
teachers’ understanding in English could influence the teaching-learning activities
at bilingual class. If the teachers and students could understand English well, then
the teaching-learning activities at the bilingual class could become more effective.
“Kemampuan guru dan siswa..kalau siswa dan guru mampu berbahasa
Inggris yang baik ya itu bisa jadi faktor positif yang mempengaruhi
keefektifan pembelajaran bilingual.”
“If the teachers and the students have a good ability in English, it can be a positive factor which influences the bilingual teaching-learning activities.”
(Respondent 1, Appendix E)
The second respondent said that some interesting learning media and
learning sources such as bilingual textbooks and presentation through PowerPoint
by using English and Indonesian could be the positive factors for an effective
bilingual class.
“Faktor positifnya ya media-media yang menarik seperti buku bilingual,
PowerPoint itu.”
“The positive factors are some interesting media such as bilingual textbook and presentation through a PowerPoint.”
(Respondent 2, Appendix E)
While the third respondent said that students’ willingness in learning some
English vocabulary items was one of the positive factors at bilingual
teaching-learning activities.
“Untuk faktor positif, siswa ada sedikit kemauan untuk menambah ilmu
mengenai istilah-istilah dalam Bahasa Inggris.”
“For the positive factor, some students have a willingness to improve their knowledge in English vocabulary items.”