Increasing interest and increasing skills in teaching-learning earth sciences: A research in Italian schools. Knowledge is often superficial and fragmentary, due to adherence to the ministerial curriculum. But it is necessary to be aware of the discipline to be passionate about it.

Competences and skills
The connection between the impact of the Cixculub meteorite on the Yucatan Peninsula, highlighted by the rich iridium level studied by Alvarez, the Bonarelli level in Italy, and the extinction of the dinosaurs is well known and well documented. The relationship between the formation of the Deccan Traps and the Late Cretaceous Great Extinction is less well known, but may be chronologically more consistent. The authors were vacationing in Switzerland during the cold summer of the "Years without Summer" that followed the eruption of Tambora in 1915.
Epistemology
In the case of the approaches traditionally used in the sciences, inductive and deductive reasoning, in which the rule is given from the beginning, the definition of a law occurs regularly, and with relative ease. In the case of the abductive process, as in the problem-based learning, the ability to synthesize becomes an essential element: to understand why landslides can fall or earthquakes occur, requires a general ability to synthesize [8, 9]. This is the result of an evolution of the process, in which it is sometimes not possible to recognize relationships of cause or effect between the different components, because both are the result of their common history.
Conclusions
Earth sciences, like any scientific discipline, should be based on their epistemology, which is necessary to deal with the foundations of the discipline and to define the conditions that allow the construction of scientific knowledge and the development of methods to achieve this knowledge. The complexity that characterizes the Earth sciences does not allow the recognition of a single formal structure of the discipline and is responsible for its weakness; however, this complexity, due to the presence of so many fields of study that, albeit in different forms, are related to the Earth system, is also its richness [1]. Educators must, of course, be aware of the body of knowledge that makes up the discipline and the myriad interconnections that exist between the various branches of earth science.
Author details
Only clearly defined and shared objectives can bring teachers and geologists, aware of the importance of this discipline, its field of research and its development, for the protection and improvement of the environment, natural or artificial. Finally, it should be a priority for all those interested in the discipline to define a common, coherent and focused epistemological state for the Earth Sciences. But everyone should be equally aware that this knowledge, with its plots and intuitions, is essential to develop the basic skills for the student and for the citizens of today and tomorrow.
This will make it possible to recognize that all the disciplines that make up the Earth sciences are interconnected: only in this way would we be closer to a model and a unified vision of our discipline. Promoting Earth Science teaching and learning in Italian schools: the need for high professionalism of effective educational approaches and extensive collaboration. Recommendation 2006/962/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 18 December 2006 on key competences for lifelong learning.
TOP 1%
Introductory Chapter: Will a Cooperation between Polarized Paradigms in Educational Psychology Be
- Introduction
- Why this book?
- Some explanations regarding the book
- Purposes of the book
- Prospecting future
On the other hand, the contemporary identity of educational psychology is influenced by the challenges of other sciences. This qualitative exegesis supports the idea that the scientific discourse on educational psychology develops under conflicting patterns. The most important problem in the book may include the key question: How to prepare an international course in educational psychology for a globalized society.
A Critical Role of the Psychologist: A Way to Achieve Complexity in Educational Psychology
- Transitions of educational psychology from simplicity to complexity
- Critical thinking as a strategy for the evolution of educational psychology
- A critical educational psychology as a means to achieve a complex educational psychology
- Conclusions
This stamp would remain throughout the twentieth century as part of the professional role. With a discipline inspired by the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries and materialized in the twentieth century, I believe it is only fair that we establish a reflective, innovative, and transformative review of educational psychology at the dawn of the twenty-first century. According to the perspective of a simplified paradigm, psychology as a scientific discipline (as well as traditional pedagogical psychology) would very much belong to this model, since it would represent characteristics that are focused on individual attention (if possible), on the assessment of technical knowledge, on the functionality of pathology, on the standardization of behavior on behavioral standards (norms) and on the hierarchical relationship between areas of knowledge [6].
This acceptance of the scientific position (uncritical and amoral), established a reductionist approach focused on the teaching and learning process as a central object of educational psychology [1]. Through this, it would be possible to channel one of the biggest challenges promoted by the perspective of complexity, i.e. transdisciplinarity [3]. Critical psychology has its roots in the critical theory of the Frankfurt School, with thinkers such as Horkheimer, Adorno, Marcuse or Habermas [14].
Critical and complex educational psychology should evaluate as an educational goal the achievement of conditions that ensure a positive and nourishing quality of life for members of the educational community. In the light of the above, it can be noted that educational psychology presents a history of respected tradition, contributing to the development of educational processes for a little more than 100 years. Traditional educational psychology cannot provide the answers that the educational challenges of the twenty-first century require.
The benefits of this critical and complex educational psychology position are that, on the one hand, there would be conscious and intentional discipline in achieving a quality education, taking care of the development and respect of human values.
Mother-Child Mediated Learning Experience Strategies and Children’s Cognitive Modifiability: Theoretical and
- MLE and cognitive modifiability: theoretical perspective
- MLE strategies
- Dynamic assessment of learning potential
- MLE and cognitive modifiability: research perspective
- Observation of Mediation Interaction (OMI) scale
- Tzuriel’s dynamic assessment approach of learning potential
- The effects of MLE strategies on cognitive modifiability
- In this study [21], we observed a sample of kindergarten children (n = 48) and their mothers in free-play and structured (teaching) conditions and tested the children with the
- Discussion and conclusions
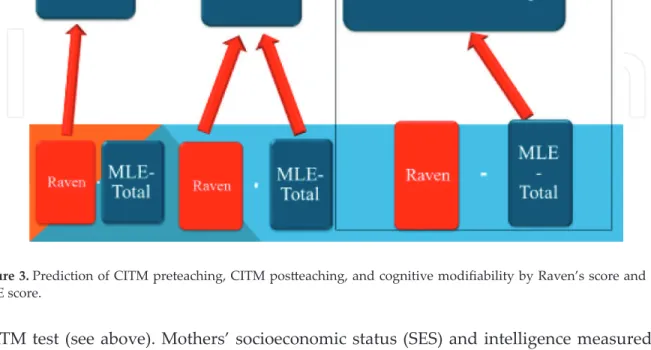
Another aim was to find out which specific combination of MLE strategies predicts children's cognitive modifiability. None of the distal factors of maternal SES or intelligence predicted cognitive modifiability (ie, CATM postteaching). Structural equation model analysis: the effects of distal factors (mothers' socioeconomic level and intelligence) and proximal factors (MLE strategies) on children's cognitive modifiability (copied with permission from Tzuriel and Ernst [ 21 ]).
These results indicate that for children experiencing learning disabilities, the distal factors directly affect the child's cognitive modifiability. It is possible to explain these results by the fact that in samples of children with learning disabilities (eg, ADHD, LD), even adequate mother–child mediation is not sufficient to overcome or “nullify” the power of the distal factors in predicting children's cognitive modifiability. We hypothesize that training mothers to use better MLE strategies in their spontaneous interactions with their children will significantly reduce the effects of the distal factors on children's cognitive modifiability.
Improving MLE strategies is essential to improve the direct effects of distal factors on cognitive modifiability. The distal factors were found to be predictors of the proximal factor of MLE strategies in typically developing children, but they do not predict children's cognitive adaptability. However, in samples of children with learning disabilities, distal factors (unfavorable conditions) were found to directly affect children's cognitive adaptability.
The effects of the distal factors on children's cognitive adaptability would decrease if mothers were trained to mediate.

Acknowledgements
In addition to cognitive aspects, we should consider children's affective and motivational processes as prerequisite factors to determine the nature of MLE processes and children's cognitive modifiability. The dynamic assessment of cognitive modifiability: The learning aptitude assessment unit, theory, instruments, and techniques. Inferential cognitive modifiability of kibbutz young children as a function of mother-child mediated learning experience (MLE) interactions.
Cognitive modifiability of young children's interaction and mother-child mediated learning experience (MLE) in low middle and high SES. Mediation strategies and cognitive modifiability in young children as a function of a peer mediation program with young children (PMYC) and training in analogical versus mathematical tasks. Effects of mother-child mediated learning strategies on cognitive modifiability and psychological resilience of children with learning disabilities.
The effects of mothers' acceptance/rejection attitudes, children's personality, and mothers' mediated learning strategies on cognitive adaptability. Effects of the Bright Start Program in Kindergarten on the Use of Mediated Learning Strategies and Children's Cognitive Adaptability. Mediated sibling learning strategies in Jewish families with many versus few children: the relationship with home support and religious orientation and their effects on cognitive adaptability.
Mediated learning experience (MLE) strategies and discourse quality in mother-child and teacher-child interactions with preschool children: effects on children's cognitive modifiability.
The Importance of Mindfulness in the Achievement of Optimal Functioning: Conceptualization for Research
- The importance of optimal functioning
- Overview of mindfulness
- Mindfulness from an Eastern perspective
- Mindfulness and optimal functioning
- Conclusion and research development for consideration
This theoretical positioning emphasizes a person's achievement of optimal functioning and his/her state of flourishing. Optimal functioning in this case is about maximizing a person's internal state of functioning, be it mental, cognitive, emotional and/or social. For example, optimization of physical function (e.g., a soccer player's goal scoring) may benefit more from psychological (e.g., the use of self-efficacy beliefs to convince the soccer player's determination) and/or psychosocial (e.g., optimization of cognitive function (e.g., a student's academic performance in mathematics).
An effective educational agency (eg the use of an appropriate instructional design) can likewise stimulate intrinsic motivation, effective functioning and expenditure of effort. One interesting facet for consideration is whether and to what extent we can actually 'quantify' the process of optimization. Quantifying optimization, from our point of view, takes into account the extent (or strength) of a person's experience of energy.
In other words, according to our theory, a person's energy is likely to help and result in a level of optimal functioning. It is defined as “the infallible master key of knowing the mind and is thus the starting point; the perfect tool for shaping the mind, and is thus the center; and the sublime manifestation of the attained freedom of the mind, and is thus the pinnacle” [32]. Furthermore, according to our thesis, each major component of mindfulness embraces specific attributes - (i) the psychological component embraces the.
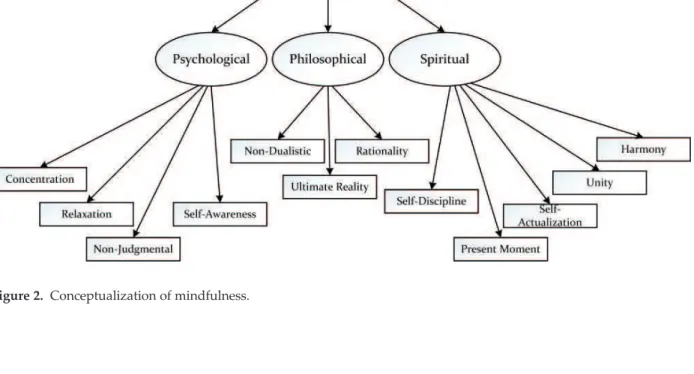
Our proposal of mindfulness is holistic and recognizes the importance of both Western (i.e. the psychological component) and Eastern (i.e. the philosophical component and the spiritual component) ideas and theoretical contributions. In other words, we argue that personal experience of mindfulness can serve to strengthen beyond the actual psychological state of a person's disposition. Some Buddhist nuns and monks would likewise argue that in-depth practice of meditation would also enable some to experience transcendence—the perceived ability of a person to exist in another realm that is beyond the existing time-space realm.
![Figure 1. Optimization and levels of best practice. Adapted from Phan & Ngu [8] and Phan et al](https://thumb-ap.123doks.com/thumbv2/1libvncom/9201196.0/63.918.111.805.882.1189/figure-optimization-levels-best-practice-adapted-phan-phan.webp)


![Figure 2. Example problem from the Children’s Analogical Thinking Modifiability [43] (by permission of the author).](https://thumb-ap.123doks.com/thumbv2/1libvncom/9201196.0/47.918.127.782.926.1210/figure-example-problem-children-analogical-thinking-modifiability-permission.webp)
![Table 1. Studies on MLE strategies and cognitive modifiability: sample characteristics, DA measures, analyses used, and MLE strategies (partially adapted from Tzuriel [5], with permission of the publisher).](https://thumb-ap.123doks.com/thumbv2/1libvncom/9201196.0/49.918.108.818.244.912/strategies-cognitive-modifiability-characteristics-strategies-partially-permission-publisher.webp)
![Figure 4. Structural equation model analysis: the effects of distal factors (mothers’ socioeconomic level and intelligence) and proximal factors (MLE strategies) on children’s cognitive modifiability (copied by permission from Tzuriel and Ernst [ 21]).](https://thumb-ap.123doks.com/thumbv2/1libvncom/9201196.0/51.918.125.804.244.819/structural-equation-socioeconomic-intelligence-strategies-cognitive-modifiability-permission.webp)