This guideline advises holding a minimum amount of capital in the bank's risk-adjusted assets. Initially, Basel Accord I focused on a bank's credit risk as measured by the cookie ratio.
![Table 1 presents the value of β for each business sector as prescribed by BCBS [5] as follows.](https://thumb-ap.123doks.com/thumbv2/1libvncom/9201131.0/7.918.137.782.878.1281/table-presents-value-business-sector-prescribed-bcbs-follows.webp)
Empirical studies on capital regulation and bank risk
In addition, Islamic banks do not have access to some credit derivatives to mitigate risk, like conventional banks, because they rule according to the Sharia principle. Studies show that BCBS capital regulation fails to address the risk of Islamic banks and misses the point of minimizing the level of risk faced by Islamic banks.
Conclusion
A wide range of financing methods also poses different types of risk to Islamic banking. Since the functioning of Islamic banking differs from conventional banking, the determination of capital requirements also differs [13].
TOP 1%
Introduction
- Basel Committee of Banking Supervision framework for internal control systems
- Thirteen principles of the BCBS internal control framework
- Credit risk
Based on their findings, we propose the use of the BCBS internal control framework to minimize bank credit risk. The chapter attempts to fill these research gaps by analyzing how the internal governance of the BCBS framework of internal controls affects credit risk.
Hypotheses development
- Board functions and activities
- Board structure
- Board monitoring and control
- Control variables
The use of internal controls and credit risk in risk-weighted European banking: The Basel Committee on Banking. We argue that the pursuit of profitability motives in the face of weak internal control systems increases the bank's exposure to credit risk.
Data and methodology
- Internal controls variables
Studying the drivers of credit risk in the Indian banking industry, the authors find a negative relationship between ROA and credit risk [5]. Others use credit risk as explanatory variable and conclude that there is a relationship between credit risk and bank profitability in the US and Asia [26].
Results and discussion
- Internal corporate governance mechanisms and financial crisis of 2008 In the current practices, CBs are not operating alone in the market as IBs have
- Sample
- Measures of variables
- Estimation method and model
CRi,t¼αþβ1The audit committee's expertisei,tþβ2Board policy functioni,t þβ3Number of board meetingsrsi,tþθ1Board diversityi,tþθ2Not. executive memberi,tþθ3Chairman is ex CEOi,t. þδ1 Audit committee independencei,tþδ2Risk-weighted assets in relation to total assets,t þγ1Capital adequacy ratio Tier1i,tþγ2BankSizei,tþγ3Bank rentatiteti,t þεi,t. 6) The chapter uses OLS, fixed effect and random effect estimation techniques. The hypothesis that board supervision reduces bank credit risk is accepted despite the fact that in the case of.
Analysis and findings
- Descriptive statistics
- Correlation
- Diagnostic test
- Hypotheses test
Performance of SSB and IBs in the presence of the financial crisis: two-stage system-GMM estimation. However, studies examining the impact of the 2008 financial crisis in the context of SSBs are very few, and thus this chapter aims to examine the supervisory effect of SSBs on the performance of IBs during the 2008 financial crisis.
Literature review
- Liquidity risk
- Credit risk
- Operational risk
- Research objective and data type
- Data collecting techniques
- Operational definition of observed variables
- Research estimation method
- Research model and analysis method
It is used to determine the short-term or long-term relationship between variables. The cointegration test is performed to establish the existence of the relationship between variables, especially in the long run.
Result and analysis
- Causality test and data instruments .1 Unit root test
- Analysis
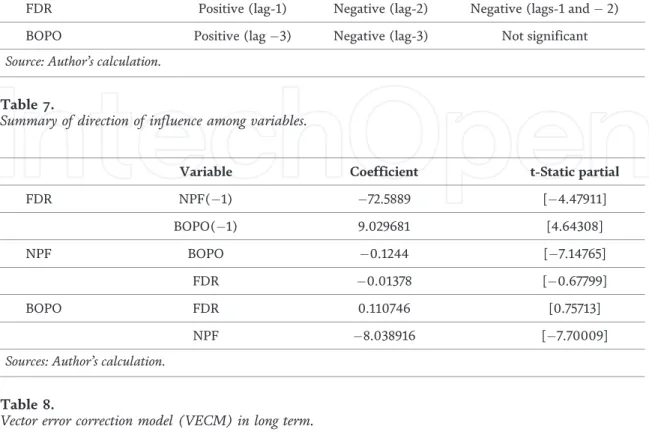
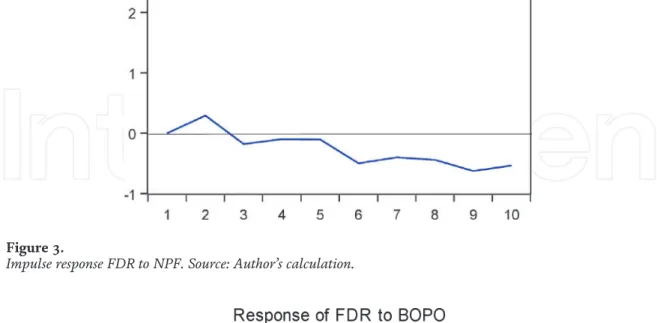
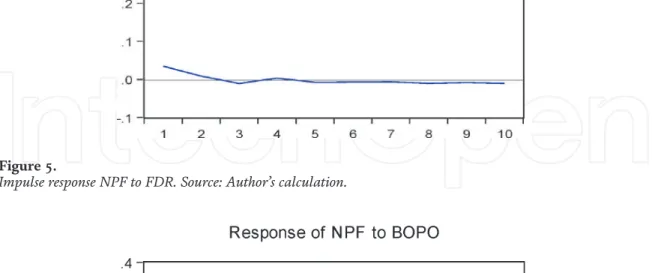
Then the FDR variable is negatively affected by the BOPO in the first lag to the third. This condition indicates that liquidity risk in Islamic banks is only affected by financing risk in the short term and decreases to equilibrium in the long term.

Conclusion, research limitation, and further research
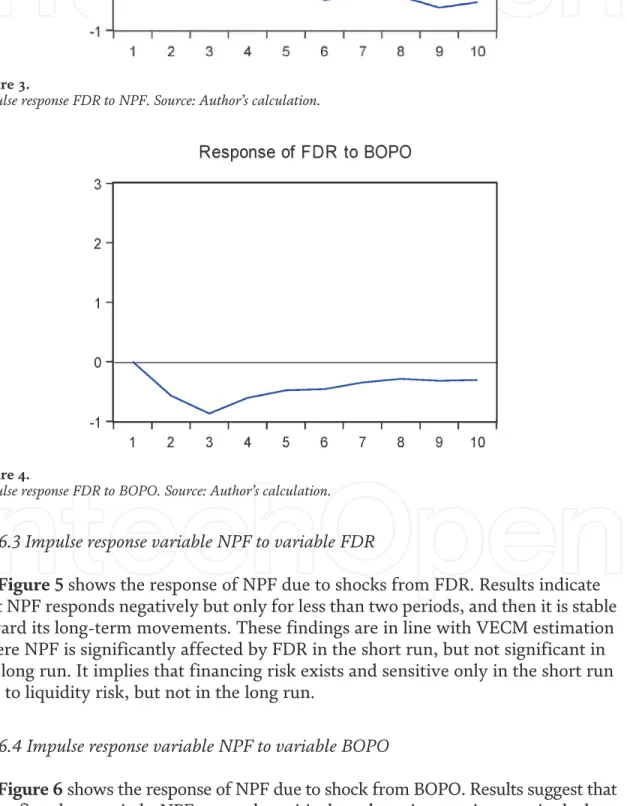
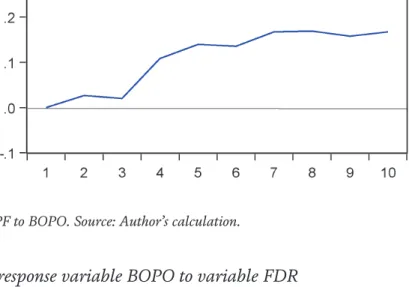
According to the Granger causality test, operational risk exists in Islamic banks where it was influenced by funding risk and liquidity risk. This means that liquidity management in Islamic banks is strong and reliable in mitigating potential shocks due to operational risk.
Scientific uncertainty and climate change
Given the foregoing, that climate change has emerged as one of the major global challenges, it is imperative to explore climate change science and the uncertainties associated with climate change, while at the same time identifying and explaining climate-related risks, the financial aspect of climate change, credit implications of climate change, integration of climate-related risks in credit risk assessment and climate risk management. Because of these interacting sources of uncertainty, studies of climate change and its impacts rarely produce consensus on the distribution of exposure, vulnerability, or possible outcomes.
Climate-related risks
- Physical risks
- Transition risks
- Relationship between physical and transition risks
- Liability risks
Physical risk and transition risks are interrelated because the more transition policies come into effect, the less physical risks are likely to materialize. Organizations are also prone to increased liability risk if they do not manage transition risks well, as envisaged in the polluter pays principle.
Credit risks implications of climate change
36] investigated the relationship between exposure to climate change and credit risk of companies and concluded that exposure to climate risk affects the creditworthiness of loans and bonds issued by companies. 39] found that direct exposures to the fossil fuel sector are small, while aggregate exposures to sectors relevant to climate policy are large, heterogeneous and augmented by large indirect exposures through financial counterparties.
Integrating climate-related risks into credit risk assessment
Counterparty credit scoring requires detailed sectoral and geographic metrics to interpret climate-related risks as an aspect of financial vulnerability, taking into account mitigation measures. The result can also be incorporated into internal and external climate-related risk reporting (Table 1) [43].
Climate change and financial stability
In addition to the climate-related risks affecting financial stability, the secondary effects of climate change (such as food security, social and political unrest and loss of biodiversity) are likely to be non-linear, characterized by tipping points, and material in the long run [48]. In any case, three fundamental reasons can justify this conversion of the financial concept of systemic risk to climate change.
Climate-related risk management
The management information should enable the board to discuss, challenge and take on the financial risks of climate change. Disclosures should be as insightful as possible and reflect the company's changing understanding of the financial risks of climate change (Figure 4) [60].
Conclusion
Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Accommodating the challenges of climate change adaptation and management in conventional risk management: Adaptive Collaborative Risk Management (ACRM).
Methodologies
This chapter is divided into several sections for easy representation of the detail of green banking: the second section will discuss about the methodology used to collect data, the third section explains what green banking is, the fourth section represents its importance, the fifth section elaborates its impact to introduce green business, the sixth section demonstrates the link between green banking, the Islamic summary of banking, the last chapter, Maqas, Shariah, Shariah, and the last chapter.
Definition of green financing, green banking, and green business The green financing concept is an invention of green growth movement and
According to the central bank of Bangladesh-“Green banking is a component of global initiatives by a group of stakeholders to save the environment” [6]; The sustainable banking concept is the result of socially and environmentally oriented banking practices. Green banking is a category of banking practices taking into account all social and ecological factors in order to protect the environment and preserve natural resources.
Importance of green banking
Recently, Bangladesh Bank has integrated "sustainability" into core banking practices through green banking, corporate social responsibility and financial inclusion. Saruti Garg stated that green banking is a nuance that symbolizes practices and policies that help banks to be environmentally, financially and socially responsible.
Impacts of green banking to create green businesses
Therefore, strict regulation, its enforcement and regular follow-up can ensure proper implementation of green banking. The result of green banking is green businesses, and the proliferation of green businesses can move the economy towards a green economy.
Islamic banking, Maqasid Shariah, and green banking
- Islamic banking
- Maqasid Shariah
According to many scholars, Maqasid Shariah serves the well-being of human beings and protects them from harm. Secondly, Maqasid Shariah caters to the interests and needs of every human being as they are extensive.
Conclusion
Concerns about a trade war between the two countries have already led to lower trading in Asian markets in general, with the KLCI (Kuala Lumpur Composite Index) down 0.6% to 1,865.22 points and Hong Kong's Hang Seng Index down 2.5% points after the US and China announced tariffs each. However, this positive sentiment has waned by the second quarter of 2019, with only 63% of Malaysians feeling that their personal finances will be excellent or good in the next year, and 63% having a positive view of their job prospects [5].
Capital and lending
- Brexit and Malaysia
- US-China trade war
- New Malaysia
- Malaysian banking
Economists were quick to believe that the political uncertainty this has created is detrimental to the Malaysian economy [22]. After [30], Malaysia's economic growth is expected to reach 2.5% by the end of the first quarter of 2020.
Conclusion
- Knowledge management
- Knowledge sharing
- Organizational culture
- Hypothesis development
- Conceptual framework
- Implications of the chapter
The purpose of the chapter is to explore the importance of knowledge sharing in bank management along with organizational culture. Furthermore, the results of this study show that there is a positive relationship between organizational culture and knowledge sharing [38].
Conclusions
This study will also contribute to improving the literature related to all the variables of this proposed framework. This assertion is reflected in the views of the banking sector stakeholders in the country and foreign evaluators.
Structure of banks in Nigeria
- Central Bank of Nigeria
- Deposit money banks
- Merchant banks
- Development finance institutions
- Microfinance bank
- Mortgage bank
For example, the cashless policy of the Central Bank of Nigeria has eliminated some of the early challenges of banking services in Nigeria [1]. The Central Bank of Nigeria described microfinance bank as a grassroots financial institution to perform basic banking services for the poor.
Bank services in Nigeria
The roles of microfinance banks are not limited to addressing banking shortages at the grassroots level and providing timely, reasonable, varied and reliable banking services to the poor. Basic services rendered by the commercial bank in Nigeria are the provision of medium and long-term credits, arrangement of syndicated loans, provision of acceptance of credit facilities to their clients, equipment leasing, outreach house function, acceptance of deposits, provision of foreign exchange services, management/advice on portfolio of investment and unit trust management.
Legal and institutional framework of banks in Nigeria
Efficiency of banking services in Nigeria
Seven years later, [9]'s study acknowledged the poor quality of service in the Nigerian banking sector. The introduction of electronic banking in the last two decades brought another twist to banking services in Nigeria.
Challenges undermining bank service delivery in Nigeria
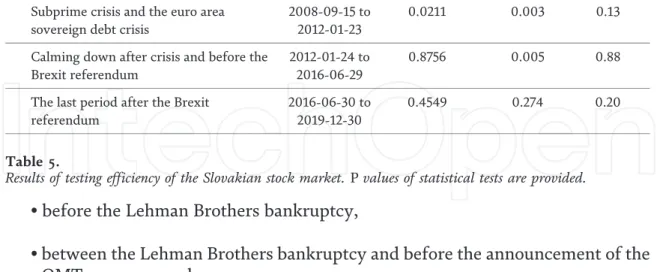
The outbreak of the Eurozone sovereign debt crisis resulted in a slight decrease in the level of correlation between the equity markets of the CEE-4 countries and mature capital markets. The impact of the subprime crisis on the development of the stock markets in the CEE-4 countries has been widely discussed in the economic literature.
Methodology
However, in the case of Slovakia, a significant change was observed shortly before the announcement of the OMT programme. Results of performance testing of the Slovak stock exchange. P values of statistical tests are indicated.
Conclusions
Apart from the above, there are voluminous studies that have covered the predictive power of the yield curve. Although this is significant, the instability of the yield distribution has not affected the movement of growth.
Theoretical framework of yield curve analysis
Similarly, the less steep the yield curve, the lower the subsequent growth rate. It is important to note that early studies on the predictability of recessions from the slope of the yield curve mainly focused on the US economy (see Harvey [16], Stock and Watson [17], Chen [18], Estrella and Hardouvelis [1]), while later research still tended to see an economic extension among other countries, partly focusing on the relationship of future growth and y [19], Davis and Henry [20], Plosser and Rouwenhorst [21], Bonser-Neal and Morley [22], Kozicki [23], Estrella and Mishkin [3], Estrella et al.[24].
Malaysian economy, bond market development and major crises since 1996
Charting the movements of the yield spread over the past two decades, it is evident that the spread turned negative before the two recessions in Malaysia, as shown in Figure 1 below. Whether the inversion of the yield curve can actually indicate future decline in economic output must be proven by the.
Data and methodology
Then, a long-run ARDL shape and bounds test is performed to test the existence of a long-run relationship, which is detected by the F-statistic (Wald test) and should be determined if the F-statistic crosses a critical band of values, see Nkoro and Uko [32]. This is a bound testing procedure created with the ARDL model and is often used in estimating long-run relationships when the properties of the time series data are a mixture of I(0) and I(1).
Estimation results and discussions
- Unit root tests
- Estimation results
The delayed maturity of the yield differential was found to be significant only during the crisis samples (B and C), but not for the entire 20-year period. Zulkhibri and Abdul Rani [10] that return spreads contain little information about the direction of the economy as a whole.
Conclusion
While significant, the instability of the yield spread to influence the movement of growth in this analysis does not support the a priori expectation about the predictive power of the yield curve in Malaysia. In addition, there is an enormous amount of literature on the impact of uncertainty on the economy as a whole and other dimensions of the economy.
Data and methodology
This is the company's net profit (or loss) on the sale at the end of the period. Due to the non-stationary nature and the existence of structural breaks in Figure 1, Rossi and Wang's [42] methodology is the best for analyzing time-varying Granger causality with these data.
Empirical results
Wald Statistics Values of the test, H0: consumer uncertainty does not Granger cause MFA score for exporters. Wald statistic values of the test, H0: consumer uncertainty does not Granger cause MFA score for exporters.
Conclusion
The aim of this chapter is to introduce a new approach for an assessment of the credit risks. The theoretical basis of the presented approach is set out in the metric space of trapezoidal fuzzy numbers.
Essential notions and theoretical background
To accommodate posterior theoretical constructions, we need to introduce the concept of regularization of a finite collection of trapezoidal fuzzy numbers. Theorem 1[7]. In the metric space of trapezoidal fuzzy numbers, R~∗ is the representative of the finite collection of trapezoidal fuzzy numbers, R~j.
Credit risk assessment method
The importance weight for each expert is determined by a function that is inversely proportional to the distance between his assessment and the representative of the final collection of all expert assessments, i.e. the smaller the distance between the expert's assessment and the representative's, the greater the weight of its importance. The section contains important formalisms for determining the importance levels of experts and the result of summing up experts' ratings.
Realization of proposed approach
Condition (b) is also fulfilled: the polar features are "the degree of risk is negligible" and "the degree of risk is extreme." To fulfill condition (c), it is necessary to build a profile, that is, fuzzy set describing the linguistic variable A. Since expert estimates are given in the form of trapezoidal fuzzy numbers, it is first necessary to determine the limits of the scale of.
Since expert estimates are given in the form of trapezoidal fuzzy numbers, first of all, it is necessary to determine the boundaries of the scale of
- Example
- Conclusions
- Literature review 1 Graph model
The limit value of the risk assessment is determined by the manager (group of managers) of the lender. The justification for the presentation of expert credit risk assessments in the form of trapezoidal soft numbers is given.