Professor PK Ramdial from the Department of Anatomic Pathology for histological input in this study. Consultants from the Department of Medicine for their assistance in patient recruitment, with special thanks to Dr. Halema Dawood and Dr. Aditya Maney 7.
LIST OF TABLES
INTRODUCTION
DISCUSSION
In patients with proteinuria
CHAPTERl INTRODUCTION
Global impact of HIV/AIDS
Sub-Saharan Africa remains the worst affected region in the world with 25.4 million people living with HIV at the end of 2004 [UNAIDS/WHO, 2004] (Figure 2). Just under two-thirds (64%) of all people infected with HIV are in sub-Saharan Africa, as are more than three-quarters (76%) of all women living with HIV.
Characteristics of HIV
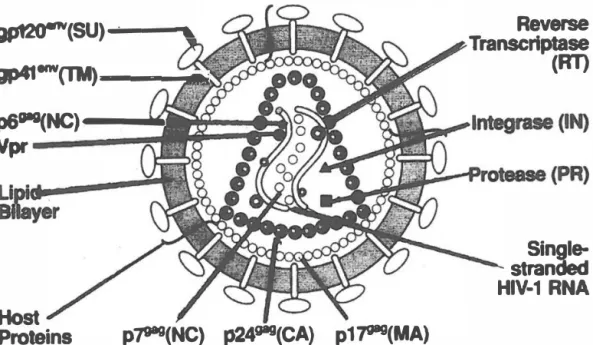
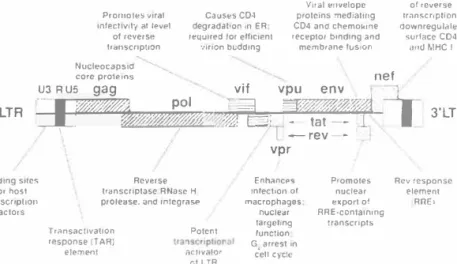
The capsid protein forms the major component of the inner shell of the virion, whereas the myristylated matrix protein is associated with the inner surface of the lipid bilayer and probably stabilizes the outer and inner components of the virion. This core also contains two copies of the single-stranded IIlV-1 genomic RNA associated with the various preformed viral enzymes, including reverse transcriptase, integrase, and protease (Figure 6).
Host
HIV-I subtypes
Reverse Transcriptase
HIV-1 RNA
Laboratory Testing for HIV-1
- HIV Antibody Tests
- Standard Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
- Western Blot (WB)
- Radioimmunoprecipitation Assay (RIPA)
- Indirect Immunofluorescence Assay (IFA)
- Other Anti-HIV-1 Antibody Tests
- Viral Culture Techniques
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell Co-culture for HIV-1 isolation
- Quantitative Cell Culture: This technique measures the relative amount of viral load within cells. The culture technique is the same as the previous method
- Quantitative Plasma Culture: This is the measurement of free infectious virus in the plasma. This is done through quantitative plasma culture techniques
- Ultrasensitive Cell Culture: This method provides the optimal culture condition for tissue reservoirs ( such as resting memory CD4+ T lymphocytes) for
- P24 Antigen Assays .1 HIV p24 Antigen test
- Acidified p24 Antigen Procedure
- Quantitative Viral RNA and DNA Assays
However, these test results must be confirmed using confirmatory tests such as p24 antigen tests. This is an ELISA-based test that detects the presence of free IIlV-1 np24 antigen in the patient's serum.
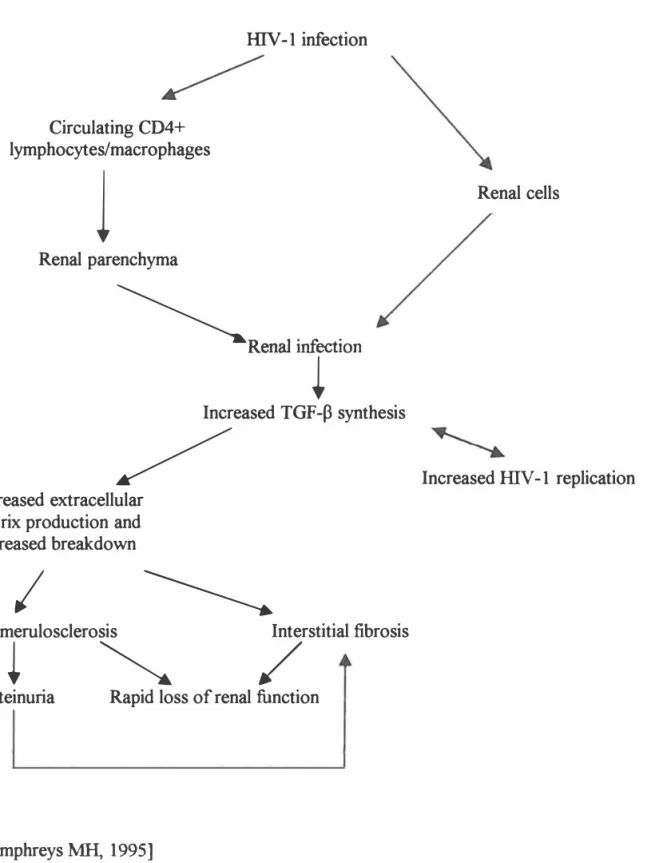
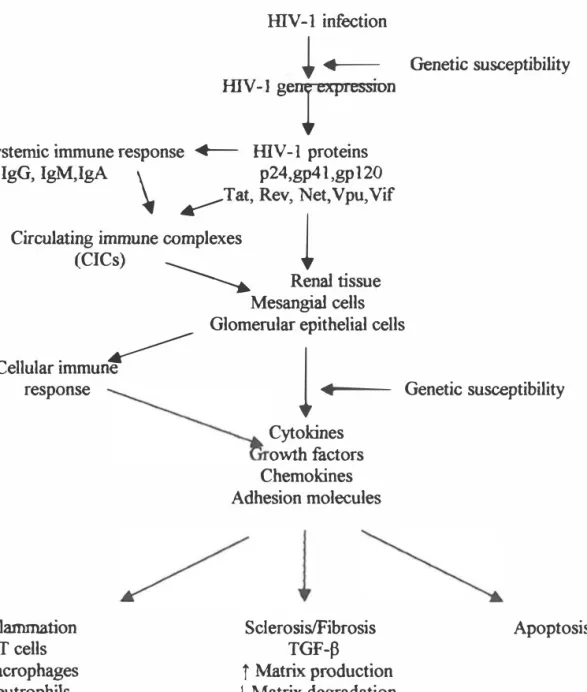
HIV and Renal Disease
- Fluid-electrolyte and acid-base disturbances
- Acute renal failure
- HIV-associated immune complex renal disease (HIVICD)
- HIV-associated thrombotic microangiopathy (HIV-TTP/HUS)
- Immunotactoid glomerulopathy (ITG)
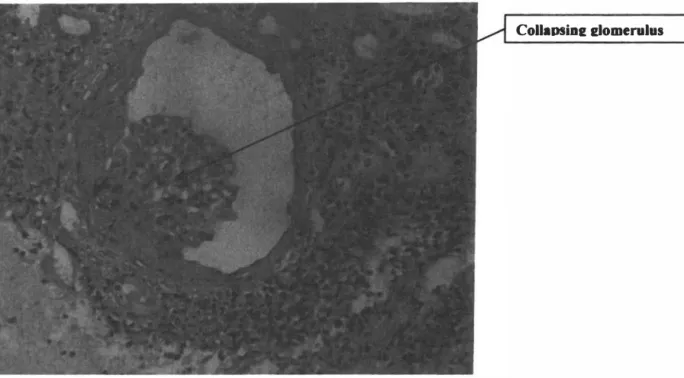
- HIV-associated nephropathy (HIV AN)
- Definition
- Prevalence
- Racial Predilection of HIV AN
- Pathogenesis
- Clinical features
- Treatment
Tubular urate deposits have been found to induce ARF in AIDS-related lymphoma [Ogea Garcia et al., 1989]. The prevalence of ngalflV infection among patients with TTP/HUS varies widely, ranging as high as 36% [Berns et al., 1995]. In contrast, microangiopathic hemolytic anemia predominates in HUS and renal failure may be extensive [Berns et al., 1995].
24-hour protein excretion may be in the nephrotic range [Charasse et al., 1991; Meisenberg et al., 1988]. Another recent theory proposes that tactoid formation is localized to the podocyte [Schwartz et al., 2002]. Ahuja et al (1999) examined 557 IDV-l infected patients and reported that the prevalence of HIV AN was 1.
Bruggeman et al (2000) reported a series of twenty HIV-1 seropositive patients with renal disease who underwent renal biopsies. This also applied when comparing the kidneys of HIV-infected patients without HIV AN [Yamamoto et al., 199.9]. Ifudu et al (1997) studied 23 HIV-infected patients with proteinuria; 5 of them had biopsy proven HIV AN.
However, in the HAART era, Ahuja et al (2000) conducted a retrospective study involving 22 HIV-infected patients initiated on maintenance. Stock et al (2003) studied 14 IDV-infected patients who had kidney transplantation (10 patients) and liver transplantation (4 patients).
CHAPTER2
HYPOTHESIS AND OBJECTIVES
As discussed in the previous chapter, the incidence of HIV infection in South Africa varies from 16 to 20% according to population-based and clinic studies. The true prevalence of kidney disease in the HIV-infected population in Africa and South Africa is unknown, as there is a lack of data in this regard. Therefore, approximately 880,000 South Africans will present with HIV AN during the course of HIV infection.
The actual disease rate reported in the early studies is likely to be higher than 10%. Thus, it is important to look for the prevalence and pattern of renal involvement among the HIV-infected South African population. This study therefore attempts to detect early-stage renal disease in HIV-positive patients, especially HN AN.
The other objective of this study is to determine the efficacy of ACE inhibition in preventing the progression of renal disease in HIV-infected patients from an early stage of renal involvement. Currently, due to limited resources, HIV-infected patients are not considered for renal replacement therapy if they develop ESRD. Therefore, if ACEI can be proven to be beneficial in the early stage of HIV-related renal disease, these patients will benefit from such therapy financially.
CHAPTER3 METHODOLOGY
- Ethical app1-oval and patient consent
- Patient profile
- J Inclusion criteria
- Exclusion criteria
- Investigations
- Urine
- Blood
- Renal biopsy
- GFR/Creatinine clearance
- Statistical Analysis
Standard urine dipstick tests using UriCheck 9 (RapiMed Diagnostics, Sekunjalo Health Care, Sandton, South Africa) were performed on all patients at initial examination. Those with a positive test for proteinuria went on to have a 24-hour urine collection to quantify the amount of protein in the urine, which was done in the chemistry laboratory at King Edward VIII Hospital using the time-end point method. Patients with two positive tests for microalbumin at least one month apart were selected as patients with persistent microalbuminuria and asked to complete a 24-hour urine collection for microalbumin quantification using the same timed endpoint method mentioned above.
All patients with > 1 gm/24 h proteinuria were treated with Perindopril and followed long-term. All kidney tissue samples were immediately immersed in the appropriate fixatives and sent to the Anatomical Pathology Laboratory at the Albert Luthuli lnkosi Central Hospital. IMF studies were not done on 21 samples that were submitted in the initial part of the study.
The Wilcoxon test was used for statistical analysis of paired data from the same patients at entry and end of follow-up. Mann-Whitney U test was used for statistical analysis of unpaired data between patients in different groups. To evaluate the effect of follow-up time, repeated measures ANOV A test was used, which looked for the time effect on data independent of group.
CHAPTER4
RESULTS
- Demographics of study population
- Proteinuria
- Microalbuminuria
- CD4 count
- Creatinine Clearance
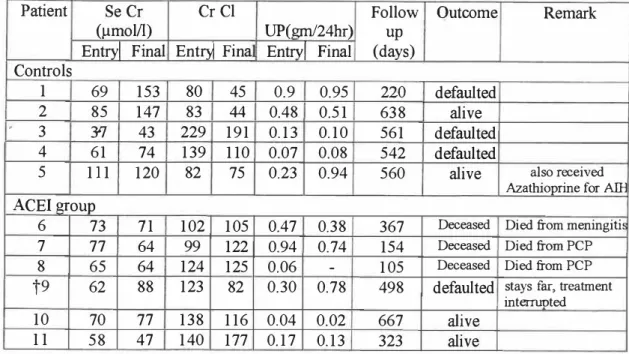
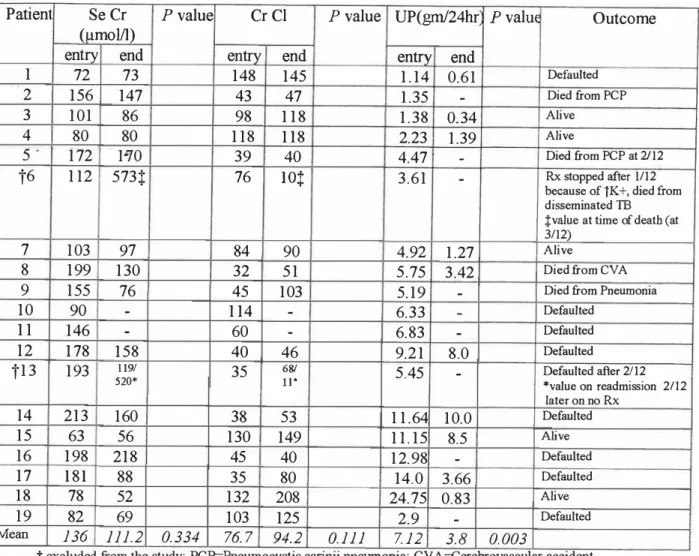
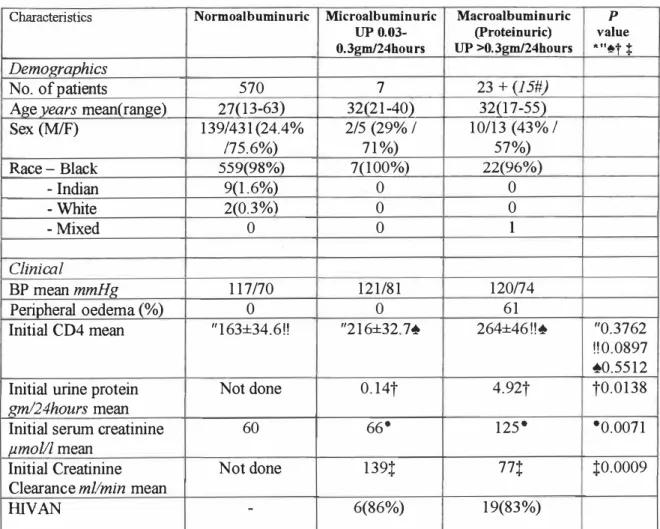
Characteristics of patients with proteinuria > lgm/24 hours Patient Age Sex Race CD4 Renal biopsy ACEI Group. Characteristics of patients with microalbuminuria were shown in Table 2 and Table 7. Characteristics of patients with microalbuminuria. Creatinine clearance (Cr Cl) was both measured and calculated at study entry to assess the correlation.
CrCl was better preserved in patients with > 1 g proteinuria/24 hours receiving ACEI, although this was not statistically significant (p=0.111) (Figure 16). The effect of ACEI therapy in slowing disease progression was assessed by comparing the percentage of patients whose CrCl was halved at the end of the study. In no group of patients with proteinuria < lgrn/24 hours who received ACEI therapy was CrCl halved, while.
Percentage of patients with halved creatinine clearance at the end of the study (group with proteinuria
Patients with proteinuria < lgm/24hours
Patients with proteinuria > lgm/24hours
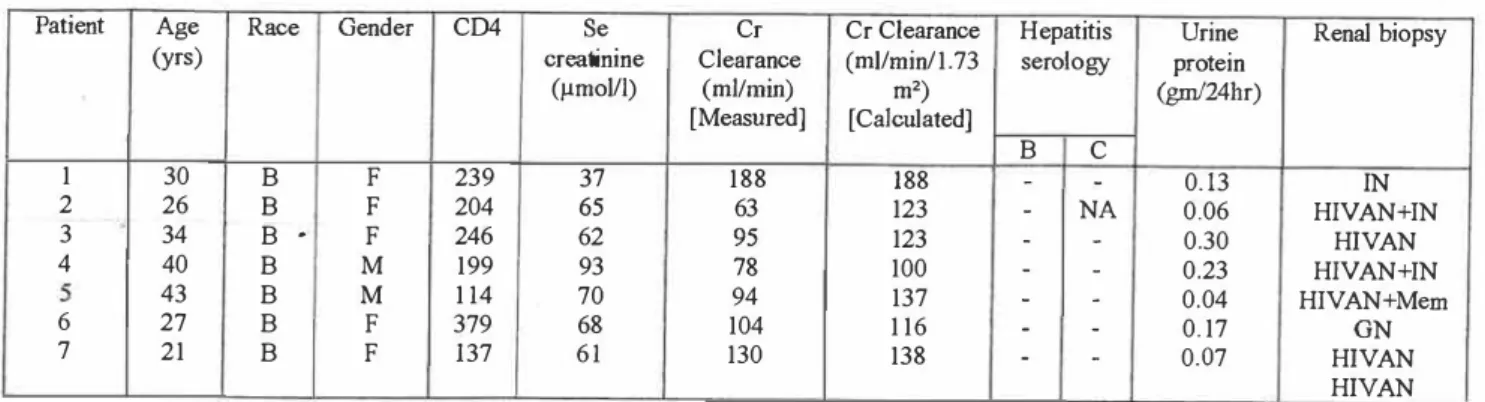
Patient Age Race Sex CD4 Serum Cr Clearance Hepatitis Urine. yr) creatinine (ml/min) serological protein.
CHAPTERS DISCUSSION
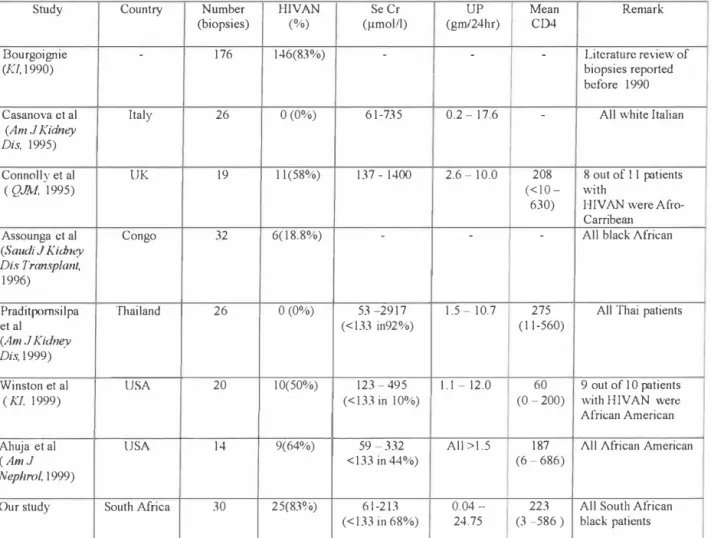
Pantanowitz et al (1999) reported renal biopsies of black HIV-infected patients from Johannesburg, which showed FSGS in 62%;. Diallo et al (1997) studied 33 HJV-infected black African patients with nephrotic syndrome in Abidjan over a 7-year period, and HIV-related nephropathy was found in 5 (15%). There are different subtypes of HIV-I; subtype B is most common in the United States, North America, and Europe, while subtype C is responsible for the vast majority of infections in Africa [Quinn et al., 1998].
Casanova et al (1995) did a biopsy study in white Italian HIV-positive patients, but HIV AN was not detected. Wei et al (2003) recently demonstrated the sustained long-term gene protective effect of ACEI in patients with lllV AN. Human immunodeficiency virus proteases may have activity in the rennin-angiotensin cascade, and serum ACE levels have been shown to be elevated in IIIV-infected patients [Ouellete et al., 1992].
ACEs are protease inhibitors and this inhibition can have a salutary effect at the tissue level [Kimmel et al., 1996]. Kanauchi et al (2001) also performed renal biopsies in 23 type 2 diabetic patients with microalbuminuria; 13 (57%) had typical diabetic glomerulosclerosis and 10 (43%) revealed atherosclerotic nephropathy without evidence of diabetic glomerulopathy. Two other studies showed the prevalence of renal albuminuria in HIV-infected outpatients without clinical evidence of renal disease to be 29.8% and 25%, respectively [Kimmel et al., 1993; Kabanda et al., 1996].
CHAPTER6
CONCLUSION
The number of people living with HIV has increased in most regions, and South Africa remains the worst affected region in the world. As the IIIV-infected population grows, so will the number of patients with varying degrees of renal involvement, which will ultimately pose a threat to currently overburdened renal services in the region. Preventive measures still need to be strengthened in an attempt to reduce the number of new cases.
Care for already infected patients should be optimized, including the provision of anti-retroviral therapy on a wider scale. Those with overt proteinuria and renal impairment should have histological diagnoses established at an early stage of the disease. ACEI therapy should be started as soon as possible in patients with HIV AN and all proteinuric nephropathies in HIV-infected patients, which is the only promising therapy currently widely available for our patient population.
Renal biopsy may be a consideration in individuals with persistent microalbuminuria to diagnose HIV AN at an early stage and to obtain the maximum benefits of ACE inhibition.
Babut-Gay ML, Echard M, Kleinknecht D, et al: Zidovudine and nephropathy with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection [letter]. Bruggeman LA, Ross MD, Tanji N, et al: Renal epithelium is a previously unrecognized site of HIV-1 infection. Burns GC, Paul SK, Toth IR, et al: Effect of inhibition of angiotensin-converting enzyme in HIV-associated nephropathy.
Carbone L, D' Agati V, Cheng JT, et al: Course and prognosis of human immunodeficiency virus-associated nephropathy. Ifudu 0, Rao TK, Tan CC, et al: Zidovudine is useful in human immunodeficiency virus-associated nephropathy. 011iz C, Meneses R, Jaffe D, et al: Outcome of patients with human immunodeficiency virus on maintenance hemodialysis.
Ray PE, Bruggeman LA, Weeks BS, et al: bFGF and its low-affinity receptors in the pathogenesis of HIV-associated nephropathy. Roy J, Paquette JS, Tremblay JF, et al: The immunosuppressive rapamycin suppresses replication of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Wali RK, Drachenberg CI, Papadimitriou JC, et al: HIV-I-associated nephropathy and response to highly active antiretroviral therapy [letter].