Directory UMM :Data Elmu:jurnal:E:Ecological Economics:Vol36.Issue3.Mar2001:
Teks penuh
Gambar

Dokumen terkait
Sections 2–4 explore, respectively, the case of zero, positive and negative income elasticity of leisure demand in a simple general equilibrium model with endogenous growth..
An increase in the profit tax rate from 0 to 0.10 would increase the domestic output and market share of the host firm, and lower the on-site production of the MNC such that the
In a homogeneous goods model all firms face the same price which is determined by a twice continuously differentiable inverse demand function P(Q ) where Q is the total
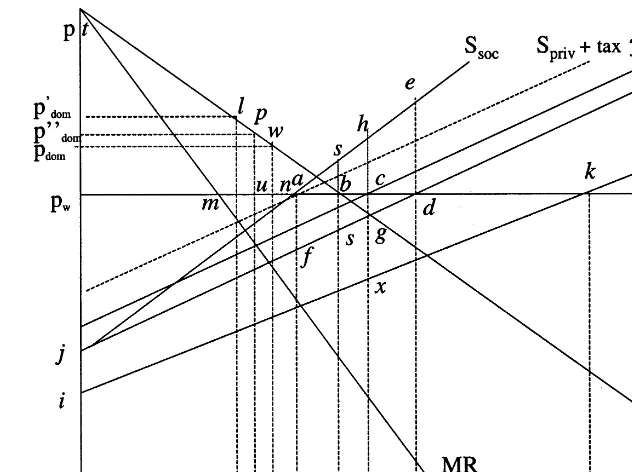
1 illustrates a market for a specific class of labor services both before and after a rightward shift in the demand curve, where the demand curve shifts due to increased
Market Price Response of World Rice Research, 3 (1989) 333 Demand for food in Myanmar (Burma), 11 (1994) 207.
On condition that both household members work on the family farm, estimation of the labor supply functions (6) can be done by substituting the marginal product of family farm labor
66 4-2 Demand 67 4-2a The Demand Curve: The Relationship between Price and Quantity Demanded 67 4-2b Market Demand versus Individual Demand 68 4-2c Shifts in the Demand Curve 69
66 4-2 Demand 67 4-2a The Demand Curve: The Relationship between Price and Quantity Demanded 67 4-2b Market Demand versus Individual Demand 68 4-2c Shifts in the Demand Curve 69