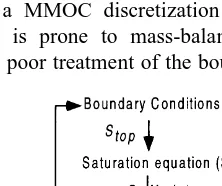
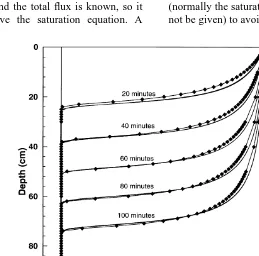
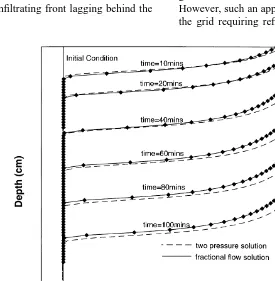
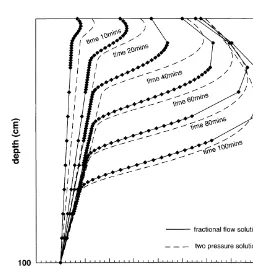
Directory UMM :Data Elmu:jurnal:A:Advances In Water Resources:Vol22.Issue5.1999:
Teks penuh
Gambar
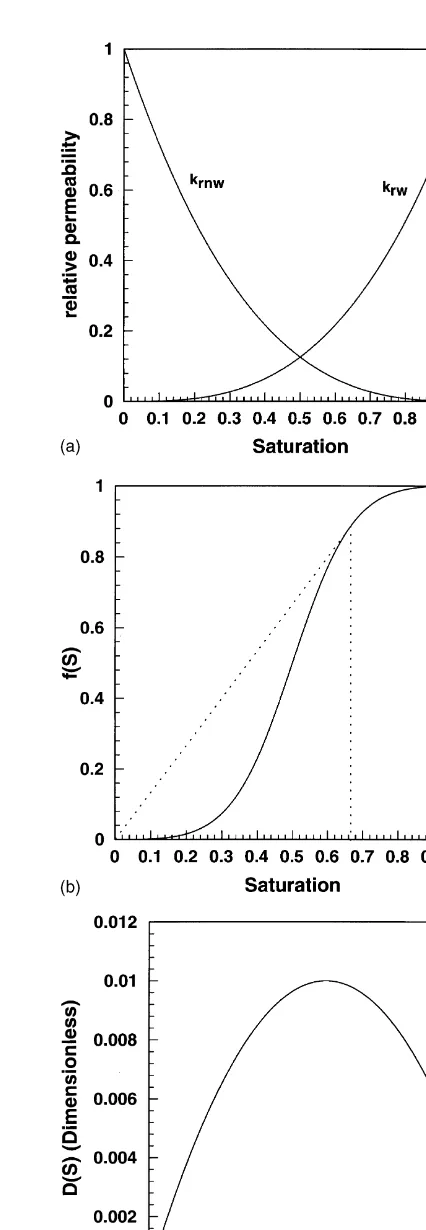
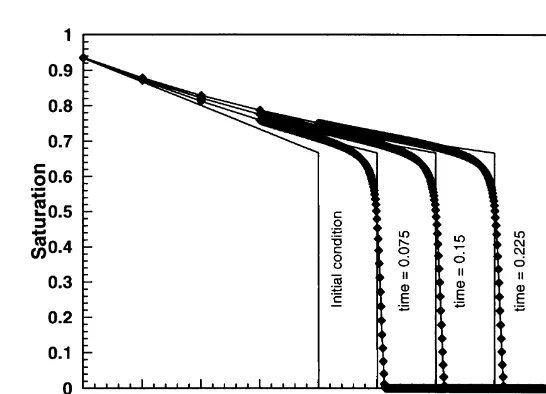
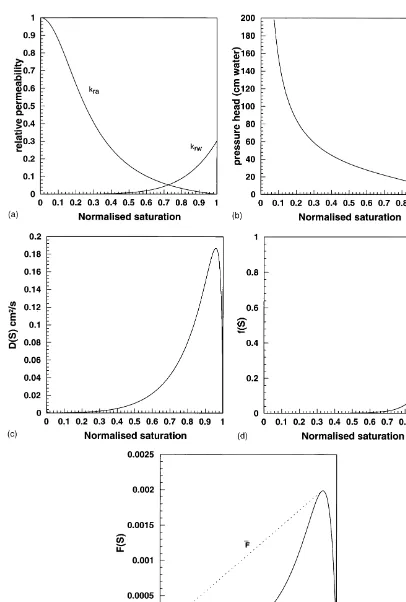
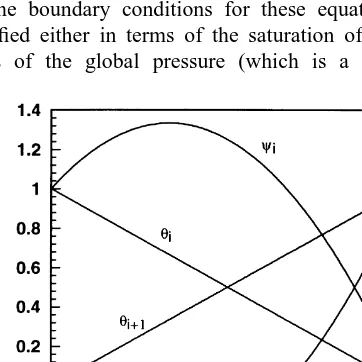
Dokumen terkait
Following the simulation of numerous continuous hourly rainfall time-series, the GLUE procedure is also used to identify behavioural model simulations (which consist of acceptable
In this section we describe numerical experiments which we use to compare the Runge±Kutta characteristic methods developed in this paper (using both forward- and back-tracking)
In this paper we analyze a model for brine transport in porous media, which includes a mass balance for the fluid, a mass balance for salt, Darcy’s law and an equation of state,
The equation describing the ensemble-average solute concentration in a heterogeneous porous media can be developed from the Lagrangian (stochastic–convective) approach and from a
The analytical solution (solid line) is compared with numerical solutions obtained by integrating the covariance function by rules of second-order (dashed line), third-order
Herein, the model 1DS2DSS is used to study the error in the prediction of the outflow hydrograph using a one-dimensional simulation of the subsurface flow for the case of a
A flexible first-order numerical model is developed to study the sensitivity, the head variance, and cross-correlation functions of f and h (and h and a) for transient flow in
Firstly, to derive closed solutions of the flow equation at very large length scale, i.e., to derive the velocity field, the flow pattern and the residence time of a fluid particle,