The said students have completed their project work titled “A Comparative Study of Color Strength and Color Fastness among Different Cellulosic Fabrics” under my supervision. After obtaining the desired shade and color, we checked the color strength value of the 3 samples with a spectrophotometer. After checking the color strength value, we calculated this value in monk kubelka theory and got that the color strength is better for 100% viscose than 100% cotton and 50/50 cotton viscose fabric.
Color fastness to washing is better for 100% cotton & color fastness to sweat (acid medium) result is better for 100% viscose & color fastness to sweat (alkali medium) result 100% cotton is better. We would like to thank Professor Dr. Mahabubul Haque, Head, Department of Material Design, Daffodil International University, for his appropriate administration and taking important methodology on proposal report. Our deepest gratitude goes to Mr. Shohag, the Deputy Head of Epyllion Group, Rajendropur, Gazipur Dhaka. We are also especially grateful to Mr. Mrs Newton, Assistant General Manager (Carving & Finishing); Mr.Sumon, Senior Executive Officer for giving real help in all organization and specialized issues while working in the business.
We would like to thank our entire classmates at Daffodil International University who participated in the discussion during the completion of the course. Finally, we would like to express our gratitude to our beloved parents and friends for their mental support, strength and help during the writing of the project report.
Introduction
As a manufactured recycled cellulosic fiber, it is neither truly distinctive (like cotton, fleece or silk) nor truly engineered (like nylon or polyester) – it falls somewhere in the middle. If a fiber is produced, it is produced using cellulose or protein. As viscose is produced using inexhaustible plants, it is often referred to as being earth-friendly and economical.
Since thick is produced using cellulose, there is an argument to state that it is a more economical fiber than other manufactured filaments, for example polyester. However, varicose veins can have different properties of cotton depending on how it is manufactured. The way to the uses, the properties and the ubiquity of thick is to stand out it is manufactured.
Despite the fact that it is a characteristic fiber and it is a cellulosic fiber with the goal that receptive color is most regularly used for cotton dyeing. With an increase in the amount of cotton, the K/S values of the fabrics decreased and the L* values of the fabrics increased.
Definition of color & dye
A reactive dye, according to the useful definition of Rys and Zollinger, is a colored compound that has the appropriate collecting power to form a covalent bond between a hydroxyl, amino, or mercapturic carbon atom separate from the substrate. The creation consisted of combining colors containing the receptive gathering, 2,4,6-dichlorotriazinylamino aggregate, which has two labile chlorine molecules triggered by the electron-withdrawing activity of three N particles. In the simplest terms, each individual reactive dye is composed of three essential units, a chromophore, an extender, and a reactive collection(s) (either a haloheteocycle or an established double bond).
These colors are used for coloring cellulose fibers and when connected to a cellulose fiber in a soluble color shower, they form a covalent bond with the fiber's hydroxyl collection by reacting synthetically with the fiber. The covalent bond between the color atom and the fiber makes the color particle part of the fiber particle. It is effortlessly damaged by scratches and will pill on the surface of the material.
Artificially responsive in light of the fact that it is a cellulose fiber, it is damaged by even moderately weak acids. This factory speaks to the beginning of the Modern Revolution of the USA, based on the cotton business system. Cotton is an important product in light of the fact that only about 10% of the raw weight is lost during processing.
The quality, sensitivity, strength and durability of Pima cotton make it one of the main and best types of cotton for clothing, towels and sheets. In the simplest terms, all reactive dyes consist of three basic units, a cormophore, an extender, and a reactive group/assembly (either a haloheteocycle or an activated double bond). These dyes are used to dye the cellulose strands and when these are linked to the cellulose fiber in the base dye shower, they form a covalent bond with the hydroxyl gathering of the fiber by synthetic reaction with the fiber.
The covalent bond framed between the dye atom and the fiber makes the dye particle a piece of the fiber atom. In a reactive dye, a chromophore contains a substituent that is initiated and allowed to react specifically on the surface of the substrate. Therefore, washing and soaping are carried out to remove the hydrolyzed and excess dye to improve the color fastness of the dyed substrate.
The alcohol content should possibly be somewhat higher than for cotton, because of the higher water retention, but also because of the high swelling. There should be as little stress on the texture as could reasonably be expected, given the low wet modulus it will expand effortlessly and dimensional solidity may never be achieved.
Scouring of blends containing viscose
This usually implies slower turnaround times and dye machines with winches to help the texture in the fly, or the stogie-type machines with the texture development in the stream being downstream (like the Gaston County Futura or Hisaka). We found that the wash fastness of the cotton dyed with the cationized dye was better than anything that of the cotton dyed in general. We found that the washing fastness of the cotton dyed with cationized dye and conventional dye was more or less equivalent.
Be that as it may, the best washing speed to recolor was obtained with the Optifix F cationizing operator. Therefore, the second aim of the present study is to develop a rapid method to optimize the number of washes after reactive dyeing to achieve good wash fastness properties, especially for dark and medium shades. Rubbing is done forward and backward, 10 cycles of 10 seconds and the finger weight on the example is 9N.
The adjustment in shading of the sample and the recoloring of the adjacent texture are measured with the dim scales. Color fastness to water is intended to determine the protection against water of dyed, printed or generally tinted fabric yarns and fabrics. The test strategy according to which this test is carried out is ISO 105 E01. The garments that come into contact with the body where sweat is overwhelming can endure actual nearby stains.
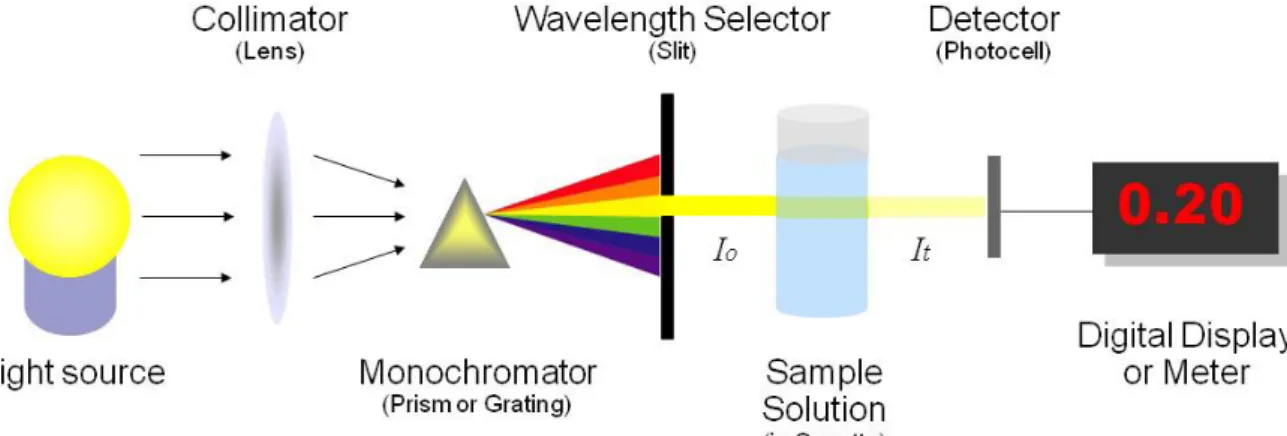
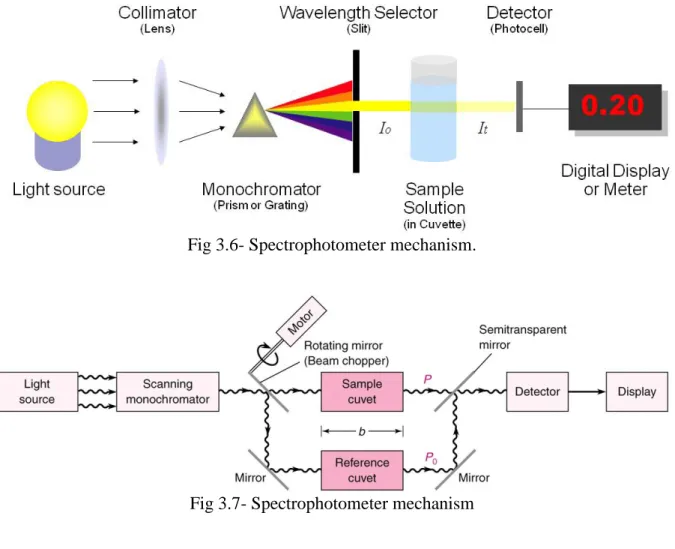
This test is intended for use in evaluating the speed of dyed, printed or generally colored material yarns and textures of various types to the influence of human sweat. Any adjustment in the shading of the samples and re-dyeing of the multifibre is then evaluated with the comparative grayscales for change of shading and re-dyeing. Spectrophotometer examines the vitality of light reflected or transmitted by a sanple. They measure the material's photometric properties in the visible region and create ghostly diagrams of tests.
Colorimetric study is a strategy to determine the convergence of a concocted component or synthetic compound in a response with the guidance of a shade reagent. The technique is generally used in therapeutic research facilities and for mechanical purposes, e.g. examination of water samples regarding mechanical water treatment. Spectrophotometer procedures are used to measure the centralization of solutes in arrangement by estimating the measurement of the light consumed by the arrangement in a cuvette set in the spectrophotometer.[10].

Material
Method
By using spectrophotometer to find out Reflectance values and curves of the colored substances were determined in the visible part of the spectrum (400-700 nm) and the standard illumination was D-65, TL-83/TL-84, A/F with 10° observer. We already knew that if the value of k/s increases, the color intensity will be increased and the shadow will be darker. Here we can see that k/s value is more in 100% viscose fabric, so the color strength of viscose fabric is more than 100% cotton fabric and 50/50 cotton/viscose fabric.
Here we can say that the color fastness to water is excellent for 100% viscose fabric than for 100% cotton and 50/50 cotton/viscose and the grading scale is 4-5. Here we can say that the color fastness to perspiration (acid medium) is excellent for 100% viscose then 100% cotton and 50/50 cotton/viscose and the color fastness to perspiration (alkali medium) is excellent for 100% cotton then 100% viscose and 50/50 cotton/viscose, the grading scale is 4-5. The dry rubbing fastness range of 100% cotton, 100% viscose and cotton/viscose blends is 5.5.5. So the rub fastness of the whole sample is the same result (excellent) and the rub fastness range of wet condition of 100% cotton, 100% viscose and cotton/viscose blend are 4.4 4. So the rub fastness of the whole sample is the same result (good ).
Color fastness to sweat (acid medium) is excellent for 100% viscose fabric than 100% cotton and 50/50 cotton/viscose & color fastness to sweat (alkaline medium) is excellent for 100% cotton fabric than 100% viscose and 50/50 cotton/viscose, its scale is 4-5.