ITEM ANALYSIS OF ENGLISH SUMMATIVE TEST
OF JUNIOR HIGH SCHOOL
(A Case Study at SMPN 11 Depok)
A Thesis is Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements for The Degree of SI
Advisor:
Drs M. Farkhan, M.pd
By:
Evi Herawati NIM.10201402379
ENGLISH DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF TARBIYA AND TEACHING SCIENCE
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH
STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
Jakarta
ENDORSEMENT SHEET
This “skripsi” entitled “Item Analysis of English Summative Test of Junior High School”, written by name Evi Herawati. Students’ registration number 102014023795 was examined. In the examination session of the faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers Training, Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University Jakarta on 18th of March 2009. The “skripsi” has been accepted and declared to have fulfilled of requirements for degree of S. Pd in English Language Education in The Department of English Education.
EXAMINATION COMMITTEE
CHAIRMAN : Drs. Syauki M.Pd ( ) NIP: 150 246 189
SECRETARY : Neneng Sunengsih ( ) NIP. 150 293 236
EXAMINER I : A M Zaenuri, M.Pd ( )
NIP: 150 182 900
EXAMINER II : Dr. Atiq Susilo, M.A ( )
NIP: 19491122 197803 1001
Acknowledged by:
Dean Tarbiya and Teachers’ Training faculty
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
ITEM ANALYSIS OF ENGLISH SUMMATIVE TEST OF
JUNIOR HIGH SCHOOL
(A Case Study at SMPN 11 Depok)
A “Skripsi”
Presented to the Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers Training In a Partial fulfillment of the requirements
For the degree of S. Pd. (Bachelor of Arts) in English Language Education
Approved by Advisor
Dr. M. Farkhan, M. Pd NIP. 150 299 480
By:
Evi Herawati NIM.10201402379
ENGLISH DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF TARBIYA AND TEACHERS’ TRAINING
STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
ITEM ANALYSIS OF ENGLISH SUMMATIVE TEST OF
JUNIOR HIGH SCHOOL
(A Case Study at SMPN 11 Depok)
A “Skripsi”
Presented to the Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers Training In a Partial fulfillment of the requirements
For the degree of S. Pd. (Bachelor of Arts) in English Language Education
Approved by Advisor
Dr. M. Farkhan, M. Pd NIP. 150 299 480
By:
Evi Herawati NIM.10201402379
ENGLISH DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF TARBIYA AND TEACHERS’ TRAINING
STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
In the name of Allah, the Beneficent, the Merciful
All Praise is to Allah Lord of the worlds who has bestowed upon the writer in completing this skripsi. Peace and blessing be upon to our prophet Muhammad SAW, his families, his companions, and his followers.
In this occasion, the writer wants to say a lot of thanks to her advisor Dr. Farkhan, M. Pd. for his time, guidance, kindness, contributions, and patience in correcting and helping her to finish this paper.
The writer also realized that she would never finish writing this paper without the help of some people around her. Therefore, she would like to give special gratitude to: Prof. Dr. Rosyada., M.A the dean of the faculty of Tarbiyah and
1. Drs. Syauki M. Pd. The head of English Department.
2. All the lectures in English Department faculty of Tarbiyah and teaching science Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University for sharing their knowledge.
3. The librarian of UIN Syarif Hidayatullah, UNIKA Atma Jaya, and UNJ for supporting the writer by allowing her to overview their book collections.
4. Drs. Saidi., M.M. The principal of SMPN 11 Depok for giving the writer an opportunity to carry out the research.
5. The English teacher of SMPN 11 Depok. Mrs. Bekti Sukmawati and all students of SMPN 11, for their motivations to the writer.
6. The writer would like to express her great honor and deepest gratitude to her beloved parents (Abdul Hamid and Rimah Istiqomah), her beloved sisters, Ika Hamidanur and Ela Yustina who always give their love; support, praying, motivations, contributions and moral encouragement to finish her study.
Finally the writer admits that her writing is still far for being perfect, therefore, she hopes some suggestions a critics from the reader for this simple paper and it will have some value for her and for a better thing in their future.
THE TABLE OF CONTENTS
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ... i
THE TABLE OF CONTENTS ... iii
LIST OF TABLES ... v
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION A. Background The of Study ... 1
B. Statement of The Problem ... 3
C. Scope and limitation of Study ... 3
D. Objective of The Study ... 3
E. Method of The Study ... 3
F. The Organization of Study ... 4
CHAPTER II THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK A. Test ... 5
1. Definition of Test ... 5
2. Types of Test ... 6
3. Types of Test Items ... 8
B. Items analysis 1. Definition of Items Analysis ... 14
2. Index of Difficulty ... 14
- Level of Difficulty ... 14
- Discriminating Power ... 15
- the Effectiveness of Distracters ... 15
CHAPTER III RESEARCH OF METHODOLOGY FINDINGS A. Research Methodology ... 17
1. The Purpose of Study ... 17
2. Place and Time of Study ... 17
3. Technique of Sample Taking ... 17
4. Technique of Data Collection ... 17
B. Research of Finding
1. Description of Data ... 20 2. Data Analysis ... 21 3. Alternative of Revision ... 39 CHAPTER 1V CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION
LIST OF TABLES
CHAPTER I
INTODUCTION
A. The Background of Study
English is a tool of communication to get information and it can be used in formal education as academic subject matter. One of the ways to know whether students have learned their lesson at school is by evaluation. Evaluation is one of important aspects in teaching-learning process beside of objective and methods.
Based competence based curriculum 2004 evaluation is a set of activity used to gain, analyze, and interpret the data about student process and learning outcomes that are done systematically and continuously so that result will become meaningful information for decision-making.
Evaluation is defined as a systematically process of determining the extent to which pupils achieve instructional objectives. For the class teacher, it will be useful to know achievement of objective and can motivate the students with pupil achievement.1
The writer considers that the test is one of the instruments that can be used for gathering the information about the students’ strength and the weakness in accepting the lesson.
There are many methods for collecting information for evaluation purposes. One of item is by using a test2. A test in plain word is “A method of measuring a person’s ability or knowledge in a given domain”3. Test are often either used
1
Drs. M. Chabib (ed.), Teknik Evaluasi Pendidikan (Jakarta: P.T. Raya Grafindo Persada, 1996), P.1.
2
Fred Genesse and John A Upshur (eds.), Classroom Based Evaluation, (Melbourne: Cambridge University Press, 1966), P.140.
3
for pedagogical purposes, either as a means of motivating students to study or as a means of reviewing material taught4.
Students usually tend to study harder and be motivated to study with review material when they are going to have an examination or if the teacher announces that they are going to have an examination. As means to measure students’ achievement in learning process, a test should be constructed well so that it is able to distinguish between the students who have studied well and who have not.
Teachers are ones who know the characteristics of their classes. Thus, they are in the best position to construct test items to measure their student achievement and it is not an easy job. Stated by J. Stanley Ahmann and Marvin D. Glock: “Classroom tests are test constructed by classroom teacher for use his particular classes … more of these tests are administered than any other kind. Unfortunately they are carelessly constructed and interpreted”5.
Based on the information above, the writer would like to see the quality of test item by doing item analysis of English Summative Test at second year students of SMPN 11 Depok. The total number of students is 375 students, but the writer took only 85 students. The research is seen from the level of difficulty, discriminating power, and the effectiveness of distracter.
A. Statement of the Problem
Based o the description above, the writer states the problem “Are the English Summative test items tested at the second year students of SMPN 11 Depok qualified as good test items or not that will see from the level of difficulty, discriminating power, and the effectiveness of distracters?
4
Lyle F. Bahman (ed.), Fundamental Consideration in Language Testing,(Toronto: Oxford University Press, 1990), P.22.
5
C. Scope and Limitation of Study
According to Suharsimi Arikunto, “Ada empat cara yang digunakan untuk manilai kualitas soal yaitu dengan meneliti soal yang sudah disusun untuk
mengetahui kejelasan perintah atau bahasa, dengan melakukan analisis soal,
dengan mengadakan checking validitas, dan dengan mengadakan checking
reliabilitas.” (There are four ways to see the quality of test items, they are: by checking the test items that have been arranged to know the clarity of question or using language, by doing item analysis, by checking validity and the last one is by checking reliability)6. But the writer intends to see the quality of test items only by doing item analysis that focuses on three characteristics, they are: level of difficulty, discriminating power, and the effectiveness of distracters. The test item that will be analyzed by the writer is objective test of English Summative Test only that was used at the second year students of SMP 11 Depok.
D. The Objective of Study
The objective of study is to find out the level of difficulty, the discriminating power and the effectiveness of distracter of English summative test items tested at the second year students of SMP 11 Depok
E. The method of Study
To support the discussion, the writer takes field research by observing the English summative test paper and the students answer sheet of the second year of SMP 11 Depok to know the quality of the test items seen from the level of difficulty, discriminating power and the effectiveness of distracters.
F. The Organization of Study
This “Skripsi” consists of four chapters.
The first chapter is introduction; it contains the background of study.
6
The second chapter is theoretical work, which discusses about definition of test, types of test, types of test items, definition of items analysis, kinds of items analysis, and the important of items analysis.
The third chapter, the writer will discuss about the purpose of study, place and time of study, the procedure of research, the technique of data collecting and technique of data analyze.
CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
A. TEST
1. Definition of test
According to Anthony J. Nitko:” Test is a systematic procedure for
observing and describing one or more characteristics of a person with the aid of either a numerical scale or category system”7. While Wayan Murkancana and PPN Sumartana stated that: “Test adalah suatu cara untuk mengadakan penelitian yang berbentuk suatu tugas yang harus dikerjakan oleh anak atau
kelompok anak sehingga menghasilkan suatu nilai tentang tingkah laku atau
prestasi anak tersebut yang dibandingkan dengan nilai yang di capai oleh anak
lain atau dengan nilai standar yang ditetapkan”8 (Test is a technique of measurement which can be a task or correlated tasks which must be done by a learner or a group of learners, in order to yield a norm about his or their achievement and can be compared with score achieved by a learner or a group of learners, or with a standard norm).
Meanwhile Michael t. Nietzel in her book “Introduction to Clinical Psychological” stated that “test is a systematic procedure for observing and describing a person’s behavior in a standard situation”9
Based on the above opinion, the writer can conclude that a test is a procedure designed to elicit score from which one can make inference about certain characteristic of individual.
2. Types of Test
7
Anthony J. Nitko (ed.), Educational Test and Measurement An Introduction, New York Harcourt Brace Jovanovich, Inc, 1983), P. 6
8
Wayan Murkancana and PPN Sumartana (eds.), Evaluasi Pendidikan (Surabaya:PT. Usaha Nasional, 1982), P. 43
9
There are many types of test used to measure student’s achievement. N.E. Gronlund said that the types of test are divided into four types of test, they are placement, formative, diagnostic and summative test10.
a. Placement test
Placement test is a test designed to determine candidate’s place in the teaching program at the beginning of instruction and placement evaluation is concerned with the pupils’ entry performance and the mode of instruction that is most likely to provide option achievement for each pupil.
b. Formative test
The formative test is a test designed to give the student immediate feedback at the end of a unit in the course book or after a lesson designed. Formative test is used to monitor learning progress during instruction 11. The purpose of the formative test is to provide to continuous feedback to both pupil and teacher.
c. Summative test
Summative test is a test intended to show the standard that the students have reached in relation to other students at the same stage and typically comes at the end of a course or unit of instruction. According to Norman E. Gronlund “Summative test is designed to determine the extent to which the instructional objective has been achieved” 12.
d. Diagnostic test
Diagnostic test is a test designed to find out learners’ strengths and weakness with various observational techniques. Diagnostic test is much more comprehensive and detailed because it searches for the underlying causes of learning difficulties and then formulates plan for remedial action.
10
N. E. Gronlund, Measurement and Evaluation in Teaching 3rd ed ( New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., 1985) p. 17
11
N. E. Gronlund, Measurement and Evaluation…, p. 17
12
According to N. E. Gronlund “Diagnostic test is concerned with the persistent or recurring learns of difficulties that are left unresolved by the standard corrective prescriptions of formative evaluation” 13. While a diagnostic test is designed to diagnose a particular aspect of a language.
e. Proficiency test
Proficiency test is a test designed to decide language proficiency of the test-takers. Arthur Hughes in his book “Testing for language teacher” said that the content of proficiency test is not based on the content or objective of language courses that people taking from the test may have followed. Rather, it is based on a specification of what candidates have to be able to do in the language in order to be considered proficiently14. Harold S. Madsen said that “proficiency test can measure overall mastery of English or how well prepared one is to use English in a particular setting such as an auto mechanics course or a university” 15.
f. Achievement test
An achievement test is a test related directly to classroom lessons, units, or even a total curriculum. Achievements tests are limited to particular material covered in a curriculum within a particular time frame and are offered after a course has covered.16
Achievement test is related to what they measure, what the students have learned as a result of teaching.17 The achievement test attempts to measure the extent to which pupil has achieved in various subject area.18
13
N. E. Gronlund, Measurement and Evaluation…, p. 17
14
Arthur Hughes, Testing for Language teacher, (Melbourne: Cambridge University press, 1991), p. 9
15
Harold S. Madsen, Technique in Testing, (New Jersey, Oxford University Press, 1983), p. 8
16
H. Douglass, Teaching by Principles, An Introduction to Language Pedagogy, (San Francisco: Addison Wesley Longman, 2001), p. 384
17
There is an achievement test that is published commercially. But the achievement test will be less interest than proficiency test because achievement test is often prepared to measure progress only in a specific textbook series and most teachers will prepare their own classroom progress tests.19
3. Types of Test Items
a. Subjective test
According to Arthur Hughes: “If no judgment is required on the part of the scorer, then, the scoring is subjective … if judgment is called for, the scoring is said to be objective”.20 It means subjective test is a test where in its scoring requires judgment and evaluation on the field to measure the student ability and knowledge about their receptive and productive skill.
The subjective tests are common used in classroom are essay, short answer and completion:
1. Essay
Essays have been used among teachers for a long time and in answering the question, the students are given freedom to select what they will explain about the question. Essay questions can be classified into two types they are Question and Extended Response Question 21:
• Restricted Response Question
In the restricted response type test, the students are not given complete freedom or restricted in making their response. For example: “State two main
18
Bill R. gearhearts and Ernest P. Wallenberg. Application of pupil assessment Information, (Colorado: Love publishing Company, 194), p. 52
19
Harold S. Madsen, Technique in …, p. 189.
20
Arthur Hughes, Testing for …, p. 19..
21
differences between the simple present tense and simple perfect tense”. The answer of such question is restricted by the scope of topic to be discussed only.
• Extended Response Question
In the extended response, students are given complete freedom in making their responses according to their own words. The question of extended response question is more widely. For example: Describe the strengths of essay questions!”
Thus, the distinctive feature of essay question is freedom of response it provides. The advantages of the essay questions:
There are advantages and disadvantages of the essay’s questions: a. The advantages are:
1. The essay question is useful to measure the students' ability and knowledge to organize, integrate, and express their ideas about the subject.
2. The possibility of guessing is minimized because no options are provided. Thus possibility of receiving score through guessing is eliminated.
3. Constructing essay question is relatively easy
4. Constructing essay question requires less time than the other measurement tool such as true false or multiple choice item.
b. The disadvantages are:
1. The scoring essay question is difficult
It is difficult because involves factors such as handwriting, spelling, and grammatical mistake are influences the scoring. 2. Unreliability of scoring.
2. Short Answer Question
The short answer item consists of a question, which can be answered with a word or short phrase22. For example: a question that can be answered with a word or short phrase is called …(short answer question)
Generally, teachers prefer to use the short answer type of question, probably because they think it has some advantages. It is relatively easy to construct, it also gives the teacher some opportunity to see how well students can express their thought and it is not difficult to score or mark than the essay questions.23
This type of question will be more useful only in testing knowledge of facts and quite specific information.24 However, it is difficult to phrase the short answer question so that only one answer is correct.25
3. Completion
The completion item is a written statement that requires the examinee to supply the correct word or short phrase in response to an incomplete sentence, A question or a word association. Completion test can be used effectively to measure the recall of terms, dates, and names
This type of test can be used at almost all levels. But it is difficult to phrase an incomplete statement so that only one answer is correct, and in making the questions, it may not too many clues are given to answer the questions. Because if too many clues are given, the item will be too easy, and if an insufficient number of clues are presented, the item will be ambiguous and may yield several possibility of correct answer. .26
22
Victor H. Noll, Introduction to Educational Measurements, Bostoin: Houghton Mifflin Company, 1965, p.138.
23
Victor H. Noll, Introduction to Educational…, p.138.
24
Victor H. Noll, Introduction to Educational…, p. 139
25
Wilmar Tinambunan, Evaluation of Students…, p. 62
26
b. Objective Test
An objective test item is any item that there is only a single predictable correct answer.27 The test is scored in such as a manner that subjective judgment is eliminated when determining the correctness of pupil’s answer28. Therefore, whether the item is scored by one teacher or another, today or last week, it will yield the same score.
The objective test items commonly used in classroom test are true false, matching, and multiple choices.
1. True false
True false item refers to alternative response item, the items asks the students to answer with “true” if it conform to the truth or “false” if it essentially incorrect.29
Thus, the item provides the students with a choice of two alternatives, so the students have a possibility to guess the answer and sometimes it will be the right answer. Because of the random guessing to produce the correct answer, the true false test is become less reliable than the other types of test. However, these items are appropriate for occasional use, for example after the students choose the two alternatives between rights and wrong, correct or incorrect, etc. They asked to explain by writing the sentences justifying their response.30
Another advantage of constructing a true false item is that the students are able to respond to more true false items in a given time period than any other selection type items. 31The most common uses of true-false items are:
27
Wilmar, Evaluation of Students…, p. 62
28
Rebecca M. Falette, Modern Language Testing, New York: Harcourt Brace Javanovich Publishers, 1997. p.8
29
Wilmar, Evaluation of Students…, p.70
30
Barbara Gross Davis., Tools for Teaching. (San Francisco: Jersey Bass Publishers, 1993), p. 243
31
1) To measure the ability to identify the correctness of statements of facts, definition of terms and statements of principles.
2) To measure the pupil’s ability to distinguish fact from opinion.
3) To measure aspect of understanding, this is the ability to recognize cause and affect relationship. This type of item usually contains two true propositions in one statement, and the pupil asked to judge whether the relationship between them is true or false.
2. Matching
The matching test item consists of two parallel columns with each word, number or symbol in one column being match to a word, sentence or phrase on the other column.32 This type of item is employed widely in situation where relationships of more or less similar ideas, facts, and principles are to be examined or judged.33 For example:
1. ( ) it is a beautiful day a. noun
2. ( ) beauty is only Skeen deep b. verb
3. ( ) she sing beautifully c. adverb
4. ( ) he beautifies his house before selling it d. adjective
This kind of test is an effective way to test students’ recognition of the relationships between words, definitions, events, dates, categories, example, and so on.34
Matching items are also useful in measuring students’ ability to make association, interpretations or measure knowledge of a series of fact. Besides that, the matching items can be used for a large quality of associated factual
32
Barbara Gross Davis., Tools for…, p. 64
33
Victor H Noll. Introduction to Educational..., p.64
34
material to be measured in small amount of space while the students’ time needed to respond is a relatively short.35
3. Multiple Choice
A multiple choice item consists of one or more introductory sentences followed by a list of two or more suggested responses from which the examinees choose one as the correct answer.36 For example:
Which one of the following is kind of subjective test item? a. short answer
b. true false c. matching d. multiple choice
The multiple choices items can measure both the knowledge and understanding level. Some advantages of using multiple choice items are: the multiple choice items are fast, easy and economical to score, and they can be scored objectively.
The multiple choice items also have disadvantages such as: the technique of the test only by answering the questions with choosing a, b, c, or d based on students’ knowledge, so the students do not have or little opportunity to express their own idea of a problem, pupils have much time to guess the answer and it may effect on their scores, it is difficult to write successful items, and cheating may be facilitated.37
B. ITEM ANALYSIS
1. Definition of Items Analysis
35
Wilmar, Evaluation of Students…, p. 65
36
Anthony J Nitko, Educational Test and …, p. 190
37
According to Anthony J. Nitko :”Item analysis refers to the process of collecting, summarizing and using information about individual test items, especially information about pupils’ responses to items”38. The analysis of student response to objective test items is a powerful tool for test improvement.
Meanwhile J. Stanley Ahmann and Marvin D. Glock said “item analysis is reexamining each test to discover its strength and flaws”39. Item analysis can tell us if an item was too difficult or too easy, how well it discriminated between high and low scores on the test, and whether all the alternatives functioned (useful) as intended or useless.
Each questions needs to function properly: otherwise, it can get a good quality. It is like statement from nana Sudjana “Analysis butir soal atau analisis item adalah pengkajian pertanyaan tes agar diperoleh perangkat
pertanyaan-pertanyaan yang lebih memiliki kualitas yang memadai”.40 (Item analysis is analyzing the test question to get more have good quality for the questions instrument”
2. Index of Difficulty
a. Level of Difficulty
Level of difficulty can be identified by selecting the test with percentage of the correct answer. According to Harold S. Madsen “level of difficulty means the percentage who answers correctly each item”.41
38
Anthony j. nitko. Educational Test and …, P. 284
39
J Stanley Ahmann and Marvin D. Glock, Evaluating Pupil …, P.184
40
Dr. Nana Sudjana, Penilaian Hasil Belajar, (Bandung: PT.Rosde Karya, 1992), P.342
41
It was efficient to compare the student who performed well with larger percentage of the correct answer and those who performed poorly with lower percentage of the correct answer. By analyzing the students’ response to the items, the level of difficulty of each item can be known and the information will be helpful for teacher in identifying concepts to re-teach the study material and giving the students feedback about their learning”42.
b. Discriminating power
“The discriminating power of a test item is an index that shows its ability to differentiate between pupils who have achieved well (the upper group) and those who achieved poorly (the lower group)”43. Students who performed well on the whole test score tend to be high and students who performed badly will get low or upper score.
c. Effectiveness of Distracter
One important aspect affecting the difficulty of multiple choice test items is the quality of distracters. Some distracters, in fact might not be distracting at all, and therefore serve no purpose.44
To know whether the distracters is function or nor, distracter analysis is done that is by comparing the number of students in the upper group and the lower group who select each incorrect alternatives. In addition, if the distracters are not functioned, they should be rewritten or distracter.45
Harold s. Madsen stated in his book, there are three common causes of weak distracter: fist, sometimes an item was drilled heavily in class, so almost everyone has mastered the item, so the answer is obvious. Second, sometimes a
42
Asmawi Zaenul and Noehi Nasution, Penilaian Hasil Belaja,r, (Jakarta: UT, 2001), p. 13.
43
Anthony J. Nitko, op. cit., p. 292.
44
Kathleen M. Bailey, Learning About Language Assessment, (Boston: ITP An International Thomson Publishing Company, 1988), p. 130
45
well recognize pair is used, such as this/these, is/are, etc. even though not everyone has controlled of these yet, and the third cause is the use of obviously impossible distracter, for example: Did he o the work/ A. yes, he did, B. birds eat worms, C. Train cannot fly.46
46
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY AND FINDING
A. Research Methodology
1. The Purpose of Study
The purpose of this research is to know the quality of English summative test items at the second year students of SMPN 11 Depok seen from the level of difficulty, discriminating power, and effectiveness of distracter.
2. Place and Time of Study
The research was held at SMPN 11 Depok that is located at Jl. Murbai Komplek Sukatani Permai Depok. The writer did the research on
August 10th 2007, she took the test paper and the students’ answer sheet to be analyzed.
3. Technique of Sample Taking
The writer took the sample from the second year students of SMPN 11 Depok, and the total number of the students is 375 students that are divided into nine classes. But as a sample, she took only 85 students, they are taken from two classes, they are class II.3 and II.5.
4. Technique of Data Collection.
To collect data based on the topic discussion, she did on observation by visiting the school to ask for the students’ answer sheet and the paper of the English summative test at the second year students of SMPN 11 Depok to be analyzed.
5. Technique of data Analyzing
LD = x 100%
DI =
a. Level of Difficulty Analysis, by using the formula47 WL + WH
nL + nH
Where LD = Level of difficulty
WL = The total number of wrong answer of the lower group WH = The total number of wrong answer of the high group nL = The number of the lower group
nH = The number of the high group With the classification as follows:
LD = 25% - 75% = Good difficulty 25% = Very easy item 75% = Very difficult item
b. Discriminating Power Index by using the formula48: WL + WH
n
Where DI = The discriminating Power Index
n = The number of students in the high group of lower group
With the classification as follows49: DI = 0. 40 = Very good
0. 30 – 0. 39 = Good 0. 20 – 0. 29 = revised 0. 19 = Discarded
47
Wayan Nurkancana dan Sumartana, Evaluasi Pendidikan,(Surabaya: Usaha NAsional,1986), P.136
48
Wayan Nurkancana dan Sumartana, Evaluasi…, P. 136
49
K = 100%
D = (nH + nL)
c. The effectiveness of distracter by using the formula50: (H + L)
nH + nL 25% x 1 2 x nD
Where K = Key answer
H = The number of the high group who choose the option L = The number of the lower group who choose the option nH = The number of the students in the lower group
nL = The number of students in the lower group D = Distracter
nD = The number of distracter With the classification as follows:
Key answer = 25% - 75% / frequency H > frequency L = effective < 25% / frequency H < frequency L = effective > 75% / frequency H = frequency L = ineffective Distracter = 0. 6875 / frequency H < frequency L = effective
< 0. 675 / frequency H > frequency L = ineffective
B. Research Finding
1. Description of Data
The data that the writer used in this study is English summative test, which is Ulangan Umum Semester Genap (II)51 for the second year students of SMPN 11 Depok academic 2007. The total numbers of test items are 45 test items
50
Wayan Murkancana, Evaluasi Pendidikan,h.143
51
No Score 46% 24 30 25 30 26 30 27 29 28 29 29 29 30 29 31 29 32 29 33 28
which consist of 40 multiple choice test items and 5 essay test items52. The multiple choice items consist of 21 reading items, 2 structure, 9 vocabulary items, 2 general knowledge items, 11 language focus items. The test was held on Monday, 14 June 2007 with the given time 90 minutes.
[image:29.612.115.503.165.555.2]2. Data Analysis
Table 1
The Students scores of The English Summative Test Result for 95 Students of the Second Year Students of SMPN 11 Depok academic
year 2007
52
See APPENDIX
No Score 27%
1 39 2 38 3 36 4 36 5 35 6 35 7 34 8 34 9 34 10 34 11 33
H
I
G
H
NO SCORE 27%
The data that will be analyzed is 27% from the upper group and 27% from the lower group and the middle group is ignored.
a. Level of Difficulty
a. Stated Detail Question
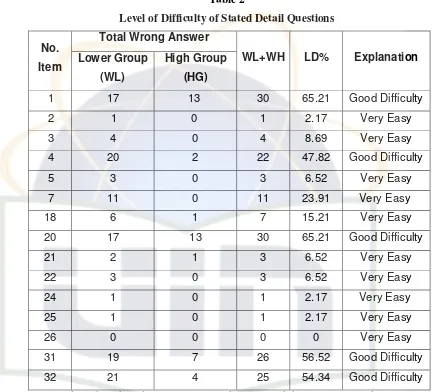
Table 2
Level of Difficulty of Stated Detail Questions
Total Wrong Answer No.
Item Lower Group (WL)
High Group
(HG)
WL+WH LD% Explanation
1 17 13 30 65.21 Good Difficulty 2 1 0 1 2.17 Very Easy
3 4 0 4 8.69 Very Easy
4 20 2 22 47.82 Good Difficulty
5 3 0 3 6.52 Very Easy
7 11 0 11 23.91 Very Easy
18 6 1 7 15.21 Very Easy
20 17 13 30 65.21 Good Difficulty
21 2 1 3 6.52 Very Easy
22 3 0 3 6.52 Very Easy
24 1 0 1 2.17 Very Easy
25 1 0 1 2.17 Very Easy
26 0 0 0 0 Very Easy
31 19 7 26 56.52 Good Difficulty 32 21 4 25 54.34 Good Difficulty
Based on the table above, we can see that in stated detail questions, there are five items having good difficulty with level of Difficulty between 25% - 27%, they are items no.1, 4, 20, 31, and 32. And the others are very easy because the level of difficulty is under 25%, they are items no. 2, 3, 4, 5, 18, 21, 22, 24, 25, and 26.
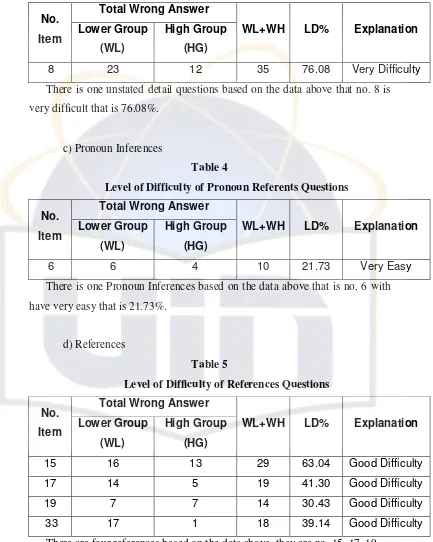
b) Unstated Detail Questions Table 3
Total Wrong Answer No.
Item Lower Group (WL)
High Group
(HG)
WL+WH LD% Explanation
8 23 12 35 76.08 Very Difficulty
There is one unstated detail questions based on the data above that no. 8 is very difficult that is 76.08%.
[image:32.612.115.548.104.646.2]c) Pronoun Inferences
Table 4
Level of Difficulty of Pronoun Referents Questions
Total Wrong Answer No.
Item Lower Group (WL)
High Group
(HG)
WL+WH LD% Explanation
6 6 4 10 21.73 Very Easy
There is one Pronoun Inferences based on the data above that is no. 6 with have very easy that is 21.73%.
d) References
Table 5
Level of Difficulty of References Questions
Total Wrong Answer No.
Item Lower Group (WL)
High Group
(HG)
WL+WH LD% Explanation
15 16 13 29 63.04 Good Difficulty 17 14 5 19 41.30 Good Difficulty 19 7 7 14 30.43 Good Difficulty 33 17 1 18 39.14 Good Difficulty
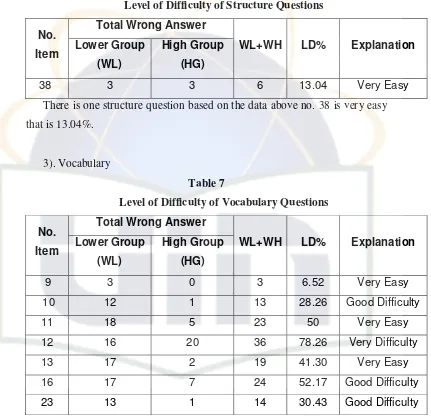
2). Structure
Table 6
Level of Difficulty of Structure Questions
Total Wrong Answer No.
Item Lower Group (WL)
High Group
(HG)
WL+WH LD% Explanation
38 3 3 6 13.04 Very Easy
There is one structure question based on the data above no. 38 is very easy that is 13.04%.
3). Vocabulary
Table 7
Level of Difficulty of Vocabulary Questions
Total Wrong Answer No.
Item Lower Group (WL)
High Group
(HG)
WL+WH LD% Explanation
9 3 0 3 6.52 Very Easy
10 12 1 13 28.26 Good Difficulty
11 18 5 23 50 Very Easy
12 16 20 36 78.26 Very Difficulty 13 17 2 19 41.30 Very Easy 16 17 7 24 52.17 Good Difficulty 23 13 1 14 30.43 Good Difficulty
In vocabulary there are seven items, we can see no. 12 is very difficult item 78.26%. And others are very easy level of difficulty. There are no. 9, 10, 11, 13 16, and 23.
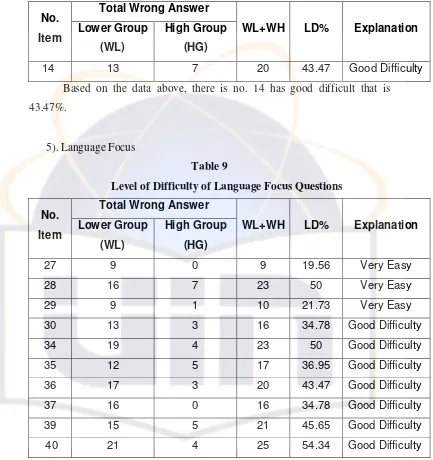
4). General Knowledge
Table 8
Total Wrong Answer No.
Item Lower Group (WL)
High Group
(HG)
WL+WH LD% Explanation
14 13 7 20 43.47 Good Difficulty
Based on the data above, there is no. 14 has good difficult that is 43.47%.
[image:34.612.115.548.105.565.2]5). Language Focus
Table 9
Level of Difficulty of Language Focus Questions
Total Wrong Answer No.
Item Lower Group (WL)
High Group
(HG)
WL+WH LD% Explanation
27 9 0 9 19.56 Very Easy
28 16 7 23 50 Very Easy
29 9 1 10 21.73 Very Easy 30 13 3 16 34.78 Good Difficulty 34 19 4 23 50 Good Difficulty 35 12 5 17 36.95 Good Difficulty 36 17 3 20 43.47 Good Difficulty 37 16 0 16 34.78 Good Difficulty 39 15 5 21 45.65 Good Difficulty 40 21 4 25 54.34 Good Difficulty
There are ten language focus questions based on the data above, there are three items are very easy in level of difficulty they are no. 27, 28, 29. And others have good difficulty they are no. 30, 34, 35, 36, 39 and 40.
b. Discriminating Power Index
1) Reading
Table 10
Discriminating Power Index of Stated Detail Questions
Total Wrong Answer No.
Item Lower Group (WL)
High Group
(HG)
WL+WH DP% Explanation
1 17 13 4 0.17 Discarded 2 1 0 1 0.04 Discarded
3 4 0 4 0.17 Discarded
4 20 2 18 0.78 Very Good
5 3 0 3 0.13 Discarded
7 11 0 11 0.47 Very Good
18 6 1 5 0.21 Revised
20 17 13 4 0.17 Discarded
21 2 1 1 0.04 Discarded
22 3 0 3 0.13 Discarded
24 1 0 1 0.04 Discarded
25 1 0 1 0.04 Discarded
26 0 0 0 0 Discarded
31 19 7 12 0.52 Very Good
32 21 4 7 0.30 Good
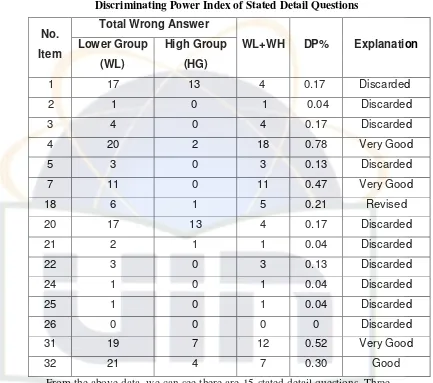
From the above data, we can see there are 15 stated detail questions. Three of them have very good discriminating index, and they are no. 3, 7, and 31 with discriminating power between 0.47% until 0.78%. One of them has a good discriminating power of is 0.30% that is no. 32 and one item has to be revised that is no. 18 with 0.21%. And 10 items must be discarded because their discriminating power are between 0 – 0.17%, they are items no. 1, 2, 3, 5, 20, 21, 22, 24, 25, and 26.
b. Unstated Detail Question
Table 11
Total Wrong Answer No.
Item Lower Group (WL)
High Group
(HG)
WL+WH DP% Explanation
8 23 12 11 0.47 Very Good
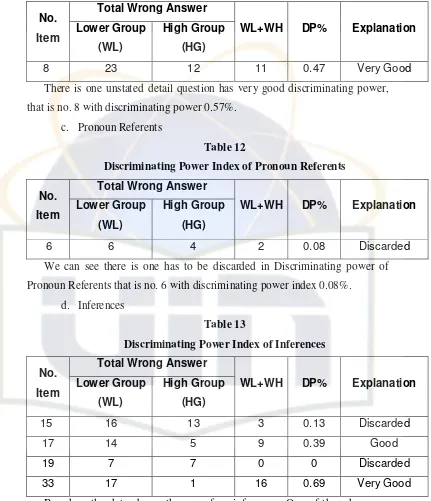
There is one unstated detail question has very good discriminating power, that is no. 8 with discriminating power 0.57%.
[image:36.612.117.548.105.606.2]c. Pronoun Referents
Table 12
Discriminating Power Index of Pronoun Referents
Total Wrong Answer No.
Item Lower Group (WL)
High Group
(HG)
WL+WH DP% Explanation
6 6 4 2 0.08 Discarded
We can see there is one has to be discarded in Discriminating power of Pronoun Referents that is no. 6 with discriminating power index 0.08%.
d. Inferences
Table 13
Discriminating Power Index of Inferences
Total Wrong Answer No.
Item Lower Group (WL)
High Group
(HG)
WL+WH DP% Explanation
15 16 13 3 0.13 Discarded
17 14 5 9 0.39 Good
19 7 7 0 0 Discarded
33 17 1 16 0.69 Very Good
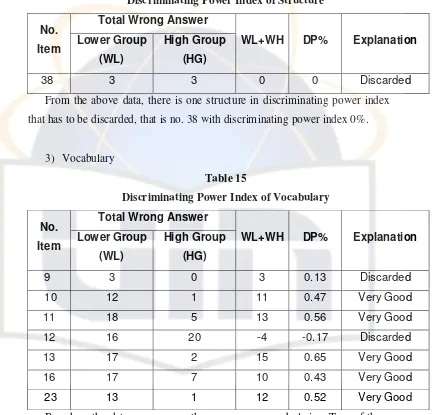
2) Structure
Table 14
Discriminating Power Index of Structure
Total Wrong Answer No.
Item Lower Group (WL)
High Group
(HG)
WL+WH DP% Explanation
38 3 3 0 0 Discarded
From the above data, there is one structure in discriminating power index that has to be discarded, that is no. 38 with discriminating power index 0%.
3) Vocabulary
Table 15
Discriminating Power Index of Vocabulary
Total Wrong Answer No.
Item Lower Group (WL)
High Group
(HG)
WL+WH DP% Explanation
9 3 0 3 0.13 Discarded
10 12 1 11 0.47 Very Good 11 18 5 13 0.56 Very Good 12 16 20 -4 -0.17 Discarded 13 17 2 15 0.65 Very Good 16 17 7 10 0.43 Very Good 23 13 1 12 0.52 Very Good
Based on the data, we can see there are seven vocabularies. Two of them have to be discarded that are no. 9 with 0.13% and no. 12 with -0.17%. But the others have very good discriminating power, they are no. 10, 11, 13, 16 and 23 with discriminating power index from 0.43% – 0.65%.
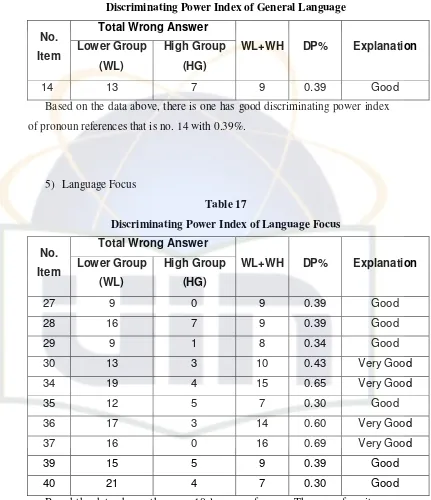
4) General Language
Discriminating Power Index of General Language
Total Wrong Answer No.
Item Lower Group (WL)
High Group
(HG)
WL+WH DP% Explanation
14 13 7 9 0.39 Good
Based on the data above, there is one has good discriminating power index of pronoun references that is no. 14 with 0.39%.
[image:38.612.116.547.106.606.2]5) Language Focus
Table 17
Discriminating Power Index of Language Focus
Total Wrong Answer No.
Item Lower Group (WL)
High Group
(HG)
WL+WH DP% Explanation
27 9 0 9 0.39 Good
28 16 7 9 0.39 Good
29 9 1 8 0.34 Good
30 13 3 10 0.43 Very Good 34 19 4 15 0.65 Very Good
35 12 5 7 0.30 Good
36 17 3 14 0.60 Very Good 37 16 0 16 0.69 Very Good
39 15 5 9 0.39 Good
40 21 4 7 0.30 Good
c. The Effectiveness of Distracter
1). Reading
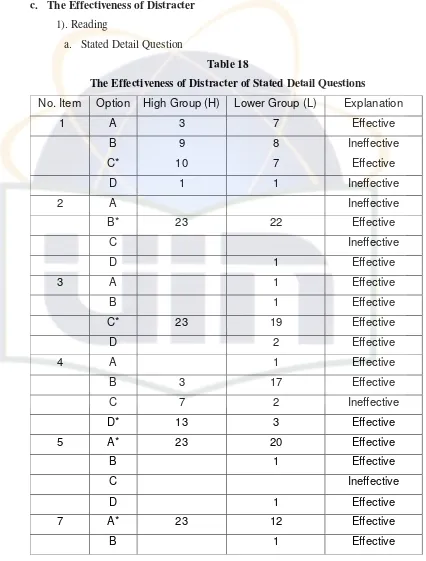
[image:39.612.114.540.147.708.2]a. Stated Detail Question
Table 18
The Effectiveness of Distracter of Stated Detail Questions
No. Item Option High Group (H) Lower Group (L) Explanation
1 A 3 7 Effective
B 9 8 Ineffective
C* 10 7 Effective
D 1 1 Ineffective
2 A Ineffective
B* 23 22 Effective
C Ineffective
D 1 Effective
3 A 1 Effective
B 1 Effective
C* 23 19 Effective
D 2 Effective
4 A 1 Effective
B 3 17 Effective
C 7 2 Ineffective
D* 13 3 Effective
5 A* 23 20 Effective
B 1 Effective
C Ineffective
D 1 Effective
7 A* 23 12 Effective
C 7 Effective
D 3 Effective
18 A 1 5 Effective
B* 22 17 Effective
C 1 Effective
D Ineffective
20 A 9 14 Effective
B 2 3 Effective
C 2 Effective
D* 10 6 Effective
21 A 1 Effective
B 1 Effective
C* 23 21 Effective
D Ineffective
22 A* 23 20 Effective
B Ineffective
C 3 Effective
D Ineffective
24 A Ineffective
B* 23 22 Effective
C Ineffective
D 1 Effective
25 A Ineffective
B 1 Effective
C* 23 22 Effective
D Ineffective
26 A Ineffective
B* 23 23 Ineffective
C Ineffective
31 A 5 11 Effective
B 6 Effective
C* 16 4 Effective
D 2 2 Ineffective
32 A 1 9 Effective
B 1 3 Effective
C* 19 2 Effective
D 2 9 Effective
Based on the above, we can see there are 60 answers key from 15 the answer key of stated detail question items they are 26 answer keys of the effectiveness of distracters and 20 answer keys ineffectiveness of distracters.
b. Unstated Detail Question
Table 19
The Effectiveness of Distracter of Unstated Detail Questions
No. Item Option High Group (H) Lower Group (L) Explanation
8 A 2 6 Effective
B 2 8 Effective
C 8 9 Effective
D* 11 Effective
The table above shows all of the answer keys are effectiveness of distracters.
[image:41.612.114.542.100.579.2]c. Pronoun Referents
Table 20
The Effectiveness of Distracter of Pronoun Referents Questions
No. Item Option High Group (H) Lower Group (L) Explanation
6 A Ineffective
B* 19 17 Effective
D 3 1 Effective
The table show there is one answer key in ineffectiveness of distracter and two answer keys are effectiveness of distracters.
d. Inferences
[image:42.612.113.540.112.569.2]Table 21
The Effectiveness of Distracter of Inferences Questions
No. Item Option High Group (H) Lower Group (L) Explanation
15 A 9 Ineffective
B 1 7 Effective
C 7 9 Effective
D* 6 7 Ineffective
17 A 2 8 Effective
B* 18 9 Effective
C 3 1 Ineffective
D 5 Effective
19 A 1 Ineffective
B 1 1 Ineffective
C* 16 16 Ineffective
D 5 6 Effective
33 A 8 Effective
B* 15 6 Effective
C 6 6 Ineffective
D 2 3 Effective
Based on the data above, we can see that there are 16 answer keys from 4 stated detail question items they are 7 the answer keys of effectiveness of distracter and 5 answer keys of ineffectiveness of distracters.
2) Structure
Table 22
No. Item Option High Group (H) Lower Group (L) Explanation
38 A* 20 20 Ineffective
B Ineffective
C 1 Effective
D 2 3 Effective
From the data above, we can see that there are two the answer keys of effectiveness of distracters and one in ineffectiveness of distracter.
3) Vocabulary
[image:43.612.116.540.201.696.2]Table 23
The Effectiveness of Distracter of Vocabulary
No. Item Option High Group (H) Lower Group (L) Explanation
9 A 2 Effective
B Ineffective
C Ineffective
D* 23 21 Effective
10 A 22 5 Ineffective
B* 1 11 Effective
C 5 Effective
D 2 Effective
11 A 2 6 Effective
B 1 10 Effective
C 2 2 Ineffective
D* 18 5 Effective
12 A 1 7 Effective
B 19 6 Ineffective
C 2 Effective
D* 3 7 Ineffective
13 A 14 Effective
C* 21 6 Effective
D 1 Effective
16 A* 16 6 Effective
B 8 Effective
C 3 7 Effective
D 4 2 Ineffective
23 A 11 Effective
B Ineffective
C* 22 9 Effective
D 1 3 Effective
Based on the data above, there are 28 answer keys from 7 vocabulary items, they are 13 answer keys of effectiveness of distracters and 8 answer keys of ineffectiveness of distracters.
4) General Knowledge
[image:44.612.114.541.104.548.2]Table 24
The Effectiveness of Distracter of General Knowledge
No. Item Option High Group (H) Lower Group (L) Explanation
14 A 7 10 Effective
B 1 Effective
C 2 Effective
D* 16 10 Effective
We can see that all of the answer keys are effectiveness of distracters. 5) Language Focus
Table 25
The Effectiveness of Distracter of Language Focus
No. Item Option High Group (H) Lower Group (L) Explanation
27 A 3 Effective
B 3 Effective
D 3 Effective
28 A 2 5 Effective
B* 16 7 Effective
C 4 Effective
D 5 7 Effective
29 A* 22 14 Effective
B 1 Effective
C 1 7 Effective
D 1 Effective
30 A 2 11 Effective
B 1 Effective
C 1 Effective
D* 20 10 Effective
34 A 1 6 Effective
B 1 4 Effective
C 2 9 Effective
D* 19 4 Effective
35 A 4 Effective
B 2 1 Effective
C* 18 10 Effective
D 3 8 Effective
36 A* 20 6 Effective
B 3 10 Effective
C 6 Effective
D 1 Effective
37 A 3 Effective
B 6 Effective
C* 23 7 Effective
D 6 Effective
B 9 Effective
C* 17 8 Effective
D 6 3 Ineffective
40 A 12 Effective
B* 19 1 Effective
C 4 6 Effective
D 4 Effective
From the data above, there are 40 answer keys from 10 items language focus. There is an ineffectiveness of distracter and others are effectiveness of distracters, those are 29 answer keys.
Revised
There is one item has to be revised that is no. 18 Total Wrong Answer
No.
Item Lower Group (WL)
High Group
(HG)
WL+WH LD% Explanation
18 6 1 7 15.21 Very Easy
Total Wrong Answer No.
Item Lower Group (WL)
High Group
(HG)
WL+WH DP% Explanation
18 6 1 5 0.21 Revised
Total Wrong Answer
No. Item
Option High Group (H)
Lower Group (L) Explanation
18 A 1 5 Effective
B* 22 17 Effective
C 1 Effective
18. The giraffe has two methods of self protection. One of them is … a. Cooking for other giraffes
b. staying to fight with its strong legs c. Hiding in a certain place
d. staying and doing nothing
Based on the data above, No. 18 has 15, 21% level of difficulty, 0, 21% of discriminating power and an ineffectiveness of distracter that is D. There is 0,21% of discriminating power, so it has to be revised in answer key that is in d become d. shouting up.
3. Data Interpretation
Based on the discriminating power index, we can see that there are 14 (35%) items considered very good, they are no. 4, 7, 8, 10, 11, 13, 16, 23, 31, 33, 34, 36, and 37. Moreover, there are 9 (22.5%) good items; they are no. 14, 17, 27, 28, 29, 32, 35, 39, and 40. Then, there is one (2%) that must be revised that is no. 18. The others (40%) are must be discarded they are no. 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 9, 12, 15, 19, 20, 21, 22, 24, 25, 26, 38.
Alternative discarded items
1. What did Dede ride in the zoo? a. monkey
2. What did the big monkey take Dede’s hat? Because … a. It wanted more food
b. Dede was not a happy boy c. Dede fed the monkey d. It wanted play with Dede
3. Why did Mrs. Nafiza give Dede money? a. For a ride on the elephant
b. To bought some monkey’s food c. To bought a hat
d. To bought a ride
5. Who sold International day books? a. Fourth grade
b. Sixth grade c. The writer d. I
6. There were performances in International day. Except … a. food stalls
b. customs c. dance d. display
9.
a. mother b. teacher c. nurse d. friend
a. sold b. cheated c. threw d. made
15. What is the main idea from the third paragraph? a. Camel like Giraffe
b. Source of the water
c. The Giraffe has long time without drinking the water d. The Giraffe eats from threes
19. Why the Dengue Fever is one of the most dangerous diseases in the world? Because …
a. It is rapidly spreads in most tropical urban areas of the world b. It makes many patients get nausea
c. It is caused by virus
d. It is no specific treatment for the disease
20. How the disease is transmitted?
a. The disease rapidly spreads in most tropical urban areas b. The disease cannot spread directly from person to person c. The disease by a virus from bite of mosquito to human d. The endemic in most tropical countries
21. What kind of virus causes Dengue Fever? b. Mosquito
c. Aedes Egypt d. Disease e. Human
a. Nausea b. Rash on arms c. Nomitting d. Headache
24. What did the writer wear for swim? a. Swimsuit and T-shirt to cover b. T-shirt
c. Swimsuit d. Clothes
25. What did the writer do before plunged into the swimming pool? a. walked towards the swimming pool
b. took off the T-shirt on the chair c. change the clothes
d. put the swimsuit on the chair
26. Based on the text the writer enjoyed the water, because … a. It was a funny day
b. It was very hot c. It was very refreshing d. It is my favorite
38. They … have any monkey last night. a. do not
HAPTER IV
CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION
A. Conclusion
Based on the data analysis and interpretation in the previous chapter, the writer would like to conclude that the quality of English achievement test items tested at second year SMPN 11 Depok. Is as follows: there are 14 items (35%) are very good items, they consists of 4 Language focus items, 5 reading items, and 5 vocabulary items. There are 9 items (22.5%) are good, they are 6 reading items, 2 reading items, and 1 general knowledge. Moreover, that is 1 items (2, 5%) must be revised that is no. 18. the last there are 16 items (40%) must be discarded they are 13 reading items, 2 vocabulary items, and 1 structure item.
From the data above the writer concludes that English Summative test Items of Junior High School at SMPN 11 Depok are good, even thought some of the items must be revised and discarded.
B. Suggestion
From the conclusion written above, the writer would like to give some suggestions as follow:
1. More than 50% of discarded items in reading items are very easy, so the writer give alternative discarded items on page 39o 42 inthese scripts. 2. The writer hopes to the teacher should analyze the students’ test result, to
know whether an item given to the students in a good quality or not. Than the items should be revised and discarded to be used for the next evaluation. 3. If the teacher has analyzed the items, they can improve the effectiveness of
REFERENCES
Ahmann, J Stanley and Glock, Marvin D. 1967. Evaluating Pupil Growth, Principle of Test and Measurements. Boston: Allyn and Bacon Inc.
Bahmen, Lyle F. 1990. Fundamental Considerations in Language Testing. Toronto: Oxford University Press.
Bailey, Kathleen M. 1988. Learning about Language Assessment. Boston: ITP an International Thomson Publishing Company.
Baebara, Gross, Davis. 1993. Tool for Teaching. San Francisco: Jersey Bass Publishers.
Douglass, H. 2001. Teaching by Principles, an Interactive Approach to Language Pedagogy. San Francisco: Addison Wesley Longman.
Falette, Rebecca M. 1997. Modern Language Testing. New York: Harcourt Brace Jovenovich Publishers.
Gearhearts, Bill R and Wallenberg, Ernest P. 1974. Application of Pupil Assessment Information. Colorado: Publishing Company.
Genesee, Fred and Upshur, John A. 1996. Classroom Based Evaluation. Melbourne: Cambridge University Press.
Hughes, Arthur. 1989. Testing for Language Teacher. Melbourne: Cambridge University Press.
Madsen, Harold S. 1983. Techniques in Testing. New Jersey: Oxford University Press.
Namara, Tim Mc. 2000. Language Testing. Hong Kong: Oxford University Press.
Nitko, Anthony J. 1983. Educational Test and Measurements, an Introduction. New York: Harcourt Brace Jovanovich Inc.
Nietzel, Michael T. 1998. Introduction to Clinical Psychology. New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
Noll, Victor H. 1965. Introduction to Educational Measurement. Boston: Houghton Mifflin Company.
Nurkancana, Wayan, Drs., and Sumartana, Drs. 1986. Evaluasi Pendidikan. Surabaya: Usaha Nasional.
Mujijo. 1995. Tes Hasil Belajar. Jakarta:Bumi Aksara.
Sujana, Nana, Dr. 2001. Penilaian Hasil Proses Belajar Mengajar. Bandung: Remaja Rosda Karya.
Tinambunan, Wilmar.1988. Evaluation of Students Achievement. Jakarta:Depdikbud.
KEY ANSWERS
1.
C
2.
B
3.
C
4.
D
5.
A
6.
B
7.
A
8.
D
9.
D
10.
B
11.
D
12.
D
13.
C
14.
D
15.
D
16.
A
17.
B
18.
B
19.
C
20.
D
21.
C
22.
A
23.
C
24.
B
25.
C
26.
B
27.
C
28.
B
29.
A
30.
D
31.
32.
33.
34.
35.
36.
37.
38.
39.
40.
ESSAY
41.
There are three different color of water lilies on
the water
42.
2) Once, there were two thin goat
4)
Both of them were hungry
1)
hey wanted to eat the green leaves from two separated bushes
4)
One bush was on the left and the other bush was on the right
2)
They were tied together with a brown rope
43.
“Turn on the lamp, please!”
“Don’t be noisy and silent, please!”
44.
was, went, sat, saw, came, joined.
45.
birthday
Saturday
June 16
thAround 7 – 9 P.M