i
By:
ARETA WULAN DARI
109014000082
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TARBIYAH AND TEACHERS TRAINING
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
JAKARTA
ii A “Skripsi”
Presented to the Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teacher’s Training In a Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
For the Degree of S. Pd. (Bachelor of Art) in English Language Education
By:
ARETA WULAN DARI 109014000082
Approved by the Advisor
Dr.H.M.Farkhan, M.Pd Teguh Khaerudin, M.App.Ling
NIP: 150 299 480 NIP: 19811031 201101 1 006
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TARBIYAH AND TEACHERS TRAINING
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
JAKARTA
iii
Training certifies that the “Skripsi” (Scientific Paper) entitle “AN ANALYSIS ON THE CONTENT VALIDITY OF ENGLISH SUMMATIVE TEST ITEMS AT THE EVEN SEMESTER OF THE SECOND GRADE OF JUNIOR HIGH SCHOOL”. Written by ARETA WULAN DARI, student’s registration number 109014000082 was examined by the Committee on April,
10th 2014. The “skripsi” has been accepted and declared to have fulfilled one of the requirements for the degree of “S.Pd” (Bachelor of Art) in English Language
Education at the English Education Department.
Jakarta,April, 10th 2014
EXAMINATION COMMITTEE
CHAIRMAN : Drs. Syauki, M.Pd. ( )
NIP. 19641212 199103 1 002
SECRETARY : Zaharil Anasy, M.Hum. ( )
NIP. 19761007 200710 1 002
EXAMINERS : 1.Dr. Fahriany, M.Pd ( )
NIP. 19700611 199101 2 001
2.Atik Yuliyani, MA.TESOL ( )
Acknowledged by:
Dean of Tarbiyah and Teachers’ Training Faculty
iv
ABSTRACT
Areta Wulan Dari (NIM: 109014000082). An Analysis on the Content Validity of English Summative Test Items, Skripsi of English Education Department at Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers’ Training of State Islamic University Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta, 2014.
v
ABSTRAK
Areta Wulan Dari (NIM: 109014000082). An Analysis on the Content Validity of English Summative Test Items, Skripsi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Fakultas Tarbiyah dan Keguruan Universitas Islam Negeri Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta, 2014.
vi
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Praised be to Allah, Lord of the world, who has given the writer His love
and compassion to finish the last assignment in her study. Peace and salutation be
upon to the prophet Muhammad SAW, his family, his companion, and his
adherence.
It is a pleasure to acknowledge the help and contribution to all of lecturers,
institutions, family and friends who have contributed in different ways hence this “skripsi” is processed until it becomes a complete writing which will be presented to the Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers’ Training in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of S.Pd (Bachelor of Art) in English Language
Education.
In this occasion, the writer would like to say her great honor and deepest
gratitude to her beloved parents: Mr. Arkat Sarim and Mrs. Entin and her sisters,
Neng Dia and Riri Atika. Special thanks for Berry Efendi who always accompany
the writer and give his love, support, motivation, and advices in accomplishing
her study.
The writer also would like to express her sincere gratitude to her advisors,
Mr. Dr.M.Farkhan, M.Pd and Mr. Teguh Khaerudin, M.AppLing who have
patiently given their valuable helps, guidance, suggestions, and critical remarks
have enabled the writer to refine this “skripsi”.
The writer also realizes that she would never finish writing this “skripsi”
without the help of some people around her. Therefore, she would like to say a lot
of thanks to:
1. Drs. Syauki, M. Pd., the Head of English Department
vii
3. All lecturers of English Department for all the knowledge they given to the
writer.
4. Mrs. Nurlena Rifa’i, MA., Ph.D., the Dean of the Faculty of Tarbiyah and
Teachers’ Training Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University Jakarta.
5. Mr. Oman Rochmanudin, M.Pd the head master of Al-Amanah Junior
High School.
6. Mr. Shodikin Nizan S.Pd and Mrs. Deasy Maryatul S.pd as the English
Teachers of Al-Amanah Junior High School.
7. All her friends in “B class” of English Education Department 2009.
Finally, the writer does realize that this “skripsi” cannot be considered perfect
without critiques and suggestions. Therefore, it is such a pleasure for her to get
critiques and suggestions to make this “skripsi” better.
Jakarta, April 2014
viii
TABLE OF CONTENT
TITLE ... i
APPROVAL ... ii
ENDORSEMENT SHEET ... iii
ABSTRACT... iv
ABSTRAK ... v
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ... vi
TABLE OF CONTENT ... vii
LIST OF TABLES ... x
LIST OF APPENDICES ... xi
CHAPTER I : INTRODUCTION ... 1
A.Background of the Study... 1
B.Identification of the Problem... 4
C.Limitation of the Problem ... 4
D.Formulation of the Problem ... 5
E. Objective of the Study... 5
F. Significance of the Study ... 5
CHAPTER II : THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK ... 6
A.Language Test ... 6
1. The Definition of the Test ... 6
2. The Types of the Test ... 7
a. Proficiency Test ... 7
b. Achievement Test ... 8
1) Final achievement Test ... 8
2) Progress achievement Test... 8
3) Diagnostic Test ... 9
4) Placement Test ... 9
3. The Characteristics of a Good Test... 9
ix
1. Content Validity ... 12
2. Face Validity... 13
3. Construct Validity ... 14
4. Criterion-Related Validity ... 15
C.Material,Syllabus and Curriculum ... 15
D. Relevant Studies... 20
CHAPTER III : RESEARCH METHODOLOGY... 23
A. Time and Place of The Study ... 23
B. The Object of the Study ... 23
C. Method of the Study ... 23
D. Instrument of the Study ... 24
E. Technique of Data Collecting ... 24
F. Technique of Data analysis ... 24
CHAPTER IV : RESEARCH FINDINGS ... 26
A.Data Description ... 26
B.Data Interpretation ... 43
CHAPTER V : CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION ... 49
A. Conclusion ... 49
B. Suggestion ... 49
BIBLIOGR APHY... 51
x
LIST OF TABLES
Table 2.1 Standard Competence and Basic Competence of Reading, Writing, Listening and Speaking Aspect ... 17
xi
LIST OF APPENDICES
Appendix 1 English syllabus of Second grade students at even semester of
Al-Amanah Junior High School ... 56
Appendix 2 English summative test for the second grade students at even semester academic year 2012-2013 ... 61
Appendix 3 Data Card ... 65
Appendix 4 The description of the conformity between the summative test item and the syllabus ... 74
Appendix 5 The description of the inconformity between the summative test item and the syllabus ... 86
Appendix 6 Surat Pengesahan Proposal Skripsi... 95
Appendix 7 Surat Bimbingan Skripsi ... 96
Appendix 8 Surat Izin Penelitian... 97
1
In teaching and learning process, evaluation is one of the important things
to be paid attention especially by a teacher. Teaching and evaluation cannot be
separated because evaluation is a tool to measure the teaching and learning
process has been achieved or not. Moreover, it contributes some information to
teaching and learning process, especially for a teacher.
Evaluation plays an important role in education activities. It is because
education has goals that need to be reached. Like Gronlund stated that “evaluation
is a systematic process of determining the extent to which instructional objectives
are achieved by pupil”.1 It can be understood that by giving evaluation, teachers can know whether the students reach the education’s goal or not. Moreover, evaluation draws how well students achieve the materials after teaching learning
process has done. The information of evaluation will be very useful to make
judgments of the students, either about their progress in learning the goals or
about their overall achievement.
There are many techniques for collecting information for evaluation
purposes. One of them is by using a test. Test is a tool or procedure used to
measure and appraise. By testing, the teachers can get information related to students’ achievement or the effectiveness of their performance in teaching. In other word, the teacher can get information about how well students have
mastered the courses that they have just learned.
There are numerous types of test. First is a placement test. It provides
information that will help to place students at the stage (or in the part) of the
teaching program most appropriate to their abilities. Second is a proficiency test.
It measures people’s ability in the language. Third is a diagnostic test, to identify
learners’ strengths and weaknesses. The last is an achievement test, to establish
how successful individual students, groups of students, or the courses themselves
1
have been in achieving objectives of language courses. The test that is usually
used by teachers in order to know how far students have mastered the lessons is
the achievement test.2
According to Hughes there are two types of achievement tests, the first is final
achievement test and the last is progress achievement test.3 This statement gives an understanding that in the achivement test there are two kinds test which can
used in measuring the student ability, the first is final achievement test which is
usually well known as the summative test, and the last test is progress
achievement test or it is said as the formative test.
Based on the writer’s experience when she did a teaching practice at
Al-Amanah Junior High School, she corrected students’ answer sheet on the summative test. She found that many students answered incorrectly on the same
certain numbers of summative test questions. Based on students’ confession, it
happened because the test items’ materials that existed on the summative test have
not explained yet by their teacher. Therefore, students have not got some
knowledge needed. It will make student cannot be able to answer the question in
the test. It showed that there was a problem in that test.
Most of the items that written by the teachers for summative test was
inappropriate with the characteristic of a good test.There were some inadequacies
in the summative test especially in the content of instruction; the themes, the type
of texts, and the indicators, therefore there are some item contents which disagree
with syllabus that provided in the indicators. In other word, the test has a poor content validity. Consequently, the test that is designed to measure the students’ ability is not appropriate.
In order to measure the student’s ability accurately, the teachers should use a
good test. It is not an easy work to construct a good test, because there are some
characteristics or requirements that must be fulfilled. The characteristics of good
2
Athur Hughes, Testing for Language Teacher, (Great Britain: Cambridge Univercity Press.,1995), p.11
3
test include validity, reliability, and practicality.4 From the statement above, it can measure a competence or student’s ability.
Commonly, there are three kinds of validity. There are content,
criterion-related (concurent and predictive) and construct are used in the educational and
psychological exam.6 From the three kinds of validity, content validity has the important roles in interpretating the test as a tool of evaluation, so that the teacher
can measure student’s ability effectively.
Content validity depends on careful analysis of the language being tested and (Boston:Allyn and Bacon, 1990), p.183.
6
Charles D. Hopkin and Richard L. Antes, Classroom Measurement and Evaluation, (Illionis: F.E Peacocok Publishers, Inc., 1990), p. 328.
7
students cannot demonstrate skills that they posses if they are not tested. Second,
irrelevant items are presented that the students will likely answer incorrectly only
because the content was not taught. The effect of that are lower test scores
because there is no relation between test item with material learnt to achieve
instructional objective. Therefore, the writer would do an analysis on the content
validity on the research title “An analysis on Content Validity on Student’s English Summative Test Items”.
B. Identification of the Problem
Based on the background of the study, the writer identifies some problems:
1. There are problems on the test item materials existed on the summative
test that have not been taught yet.
2. There are problems on most of the question items written by the teachers
for summative test which are inappropriate with the characteristic of a
good test.
3. The test is not measure what supposed to be measured.
4. A Test, which does not have content validity, complicates the students to
answer the test questions.
C. Limitation of the Study
To make this writing easier to be understood, the writer limits the study as
follow:
a) The research focused only on the content validity of English final test
(summative test) of the even semester at the second grade academic year
of 2012/2013.
b) The research focused only on reading and writing skills because the
summative test consists of multiple choice and essay items.
c) The test to be analyzed is the English summative test for the second grade
students at Junior High School of “Al-Amanah”.
d) The syllabus to be used is the syllabus which was made by the teacher
D. Formulation of the Study
Based on the background of the study, the writer formulated the problem
whether each test items of the summative test for the second grade students of
Junior High School of “Al-Amanah” represent the indicators as suggested its
syllabus as an indicator of the content validity.
1. Is the English final test in line with the syllabus that is constructed by
Al-Amanah school?
a. How appropriate is the English final test with the indicator of the
syllabus?
b. How is the distribution of the indicator of the syllabus in the test?
E. Objective of the Study
The objective of this study is to find out whether each test items of the
summative test for the second grade students of Junior High School of
Al-Amanah represent the indicators as suggested its syllabus as an indicator of the
content validity.
F. Significance of the Study
The result of this study is expected to give a description for the readers
about an analysis of the content validity toward the summative test. It also can be
used as an input for the readers; especially for the English teachers, the
headmaster, and all people who are involved and responsible in developing
quality of education. In other word, it is useful for all people to know the
characteristics of a good test and for the researchers as the basic for conducting
6
individual action is got, and scored using the basic standard.2
While, Nitko stated in his book, Educational test and measurement an
Introduction, Test is systematic procedure for observing and describing one or
more characteristics of person with the aid of either a numerical of category
Norman E. Gronlund and Robert L. Linn, Measurement and Evaluation in Teaching 6Th Edition, (New York: MacMillan Publishing Company, 1990), p. 5.
2
Cecil R. Reynolds. et al, Measurement and Assesment in Education, (New Jersey: Pearson Education Inc., 2009), p. 3.
3
Anthony J. Nitko, Educational Test and Measurement An Introduction, (NewYork: Harcourt Brace Jovanovic, Inc.,1983), p. 6.
4
Based on the definitions above, the writer can conclude that test is a set of
proficiency tests, achievement tests, diagnostic tests, and placement tests. 6 1. Proficiency test Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan, 1988), p. 7.
6
Arthur Hughes, Testing for Language Teachers Second Edition, ( Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1989), P. 11.
7
Tim McNamara, Language Testing, (Hongkong: Oxford University Press, 2000), p. 7. 8
From some opinion above, the writer conclude that proficiency test is
designed to measure individual’s general ability in a language. it usually used
English for specific purposes.
2. Achievement test
Achievement test are directly related to language course, their purpose
being to establish how succesful individual student, groups of students, or the
course themselves have been in achieving objectives. While, Cecil Reynolds
stated that achievement test are designed to assess the knowledge or skills of
an individual in a content domain in which her or she has received
instruction.9 From the statement mentioned clearly states that the achievement test is tested after the examinee received the course.
A test that used by the teacher to measure a success level of student
in learning teaching proccess is the achievement test. Arthur Hughes divided
the achievement test in two parts, final achievement test and progress
achievement test10.
1. Final achievement test
Final achievement tests are those administered at the end of a course of
study. The content of final achievement test should be based directly on a
detiled course syllabus or on the books and other materials used, this has
been reffered to as the syllabus content approach
2. Progress achievement test
Progress achievement test as their name suggest are intended to
measure the progress that students are making.
Final achievement and progressachievement test basically have a same understanding that is to measure student’s ability about the materials that learned, but the diference between final and progress are the final
9
Cecil R. Reynolds. et al, Measurement and Assesment in Education, (New Jersey: Pearson Education Inc., 2009), p. 5.
10
achievement examined in the end of the course but the progress
achievement examined in the part of the course.
3. Diagnostic test
A diagnostic test is used to identify learners’ strengths and weakness.
According to Wilmar Tinambunan a diagnostic test is intended to diagnose
learning difficulties during instruction.11 This definition gives an understanding that the diagnostic test is constructed to know the learning
difficulties of the student during the instruction, usually this test used in the
first sections before the course is began.
4. The placement test
Placement tests intended to provide information that will help to place
student at the stage ( or in the part )of the teaching programme most
appropriate to their abilities. While, JB. Heaton said that a placement test
enables us to sort students into groups according to their language ability at
the begining of the course.12 It can be understood that this test describes someone to entered in the group based their ability or competence in the
begining of the course.
3. The Characteristic of a Good Test
A test can be regarded as a good one, if it fulfills some of characteristic of a
good test. Harris in his book Testing english as a second language stated all good
test possess three qualities; validity, reliability, practicality.13 Therefore, the test will be good if the test contains three elements, they are validity, reliability, and
practicality, if in the test lack of them means the test need observed again.
11
Wilmar Tinambunan, Evaluation of Student Achievement, (Jakarta: Departemen Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan, 1988), p. 8.
12
JB. Heaton, Classroom Testing, ( New York: Longman Inc., 1990), p. 15 13
The first characteristic of a good test is validity. Validity is the extent to student’s grammar without concern in another aspect.
Test validity is the most critical factor to be judged in the total program of
consistent result and give consistent information.
The third characteristic of a good test is practicality. The test practicality
H.Douglas Brown, Teaching by Principle an Interactive Approach to Language Pedagogy, (New York: Addison Wesley Longman, Inc., 2001), p. 86.
that need to thought, like financial, time, scoring administration so the teacher will
classifies validity into four: content validity, face validity, construct validity, and
criterion-related validity.19
processes.20 Moreover, the test should reflect instructional objectives or subject matters. But it is not expected that every knowledge or skill will
always appear in the test; there may simply be too many things for all of them
to appear in a single test.
Wiersma divided content validity into two parts, content validity of
teacher-constructed tests and content validity of published tests.21 Content validity of teacher-constructed test essentially depends on the sampling of
items. If the test items adequately represent the domain of possible items, the
test has adequate content validity. When a test is not content valid, there are
two consequences. First, the students cannot demonstrate skills that they
possess if they are not tested. Second, irrelevant items are presented that the
students will likely answer incorrectly only because the content was not
taught. Both of these consequences tend to lower the test scores; as a result,
the test score is not an adequate measure of student performance relative to the
content covered by instruction.
Most teachers are quite familiar with the content they cover during
instruction, and, to a large extent, teacher-constructed tests have an inherent
content validity. However, in planning a test, teachers can use a
straightforward procedure that tends to improve content validity.
The second part is content validity of published tests. Teachers may, at
least on occasion, use published tests, some of which accompany curriculum
materials. The tests constructed for a specified textbook or set of materials
usually have high content validity if the materials are used as intended for
instruction. Sometimes materials are used as supplementary and are only
partially covered, in which case any accompanying tests would at least need to
be reviewed for content validity.
20
William Wiersma and Stephent G Juts, Educational Measurement and Testing, (Boston: Allyn & Bacon, 1990), p.184
21
According to Wilmar, content validity may be defined as the extent to
Wilmar Tinambunan, Evaluation of Student Achievement, (Jakarta: Departemen Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan, 1988), p. 12.
23
Arthur Hughes, Testing for Language Teachers 2nd Edition, ( Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1989), pp. 22-23.
24
J. Charles Alderson, et. al. Language Test Construction & Evaluation, (Cambridge: Cambridge University,1995), p. 172.
25
William said that construct validity is concerned with the psychological
constructs that are reflected in the scores of a measure or test.26 It means, the result of testing which has done will be desribed in the form of scores.
Construct validity deals with construct and underlying theory of the
language learning and testing. J.B. Heaton states that if the test has construct
validity it is capable of measuring certain specific characteristics in
accordance with a theory of language and behavior and learning.27 The statment mentioned gives a describing that the test made by teacher where it
has construct validity otomaticaly it can measure certain specific characteristic
accordence theory language.
While, Kenneth said that construct validity is the systematic analysis of
tests score designed to assess whether there is a basis for validity.28 This statment explain that it should be basis, in this case the theory of language and
behavior that sistematic in designing the construct validity
4. Criterion-Related Validity
concurent validity and last is predictive validity. Concurent validity is
constanted when the test and standarisation are arranged at about same time,
26
William Wiersma and Stephent G Juts, Educational Measurement and Testing, (Boston: Allyn & Bacon, 1990), p.193
27
JB. Heaton, Writing English Language test, (London and New York, Longman1998), p. 161.
28
Kenneth D. Hopkuns, Educational and Psychological Measurement and Evaluaton, (Boston: Allyn & Bacon, 1998), p. 99.
29
while the predictive validity is focuss the level when a test can guess
examinee’s future action.30
C. Material, Syllabus and Curriculum
The materials are the important parts of the teaching learning process that
should be mastered by the teacher and should be passed to the students. The
materials that given by the teacher must agree with the syllabus and it will be
better if suit with the context learning. James D. Brown said that materials is
defined as any systematics description of the technique and exercises to be used
in clasroom teaching.31 It is mean that a description of teaching and learning technique that used by a teacher and a lot of exercises that given to the student as
a tool of test must arranged systematicaly, so that materials that taught in the
classroom can be achieved effectively.
Richard and Rodgers stated that materials designed on the assumptions that
learning is initiated and monitored by the teacher must meet quite different
requairements from those designed for student self-instruction.32 It can be understood that materials that constructed for student must effective and
systematic,because the teacher still a task to extend the material clearly to control
learning process when the student do the task from the materials.
From the statements above, the writer can conclude that materials is the
descriptions of learning object that given to the students in the classroom by
considering the approach, syllabus, technique, and exercises so that the learning
purpose can be achieved effectively.
A syllabus is designed based on school program and students degrees. Besides
that, when a teacher constructs the syllabus, it must be suitable with students’
30
Arthur Hughes, Testing for Language Teachers Second Edition, ( Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1989), pp. 27-29.
31
James D Brown, The Elemen of Language Curriculum: A Systematic Approach to Program Development, (New Jersey:Heinle & Heinle Publisher.,1995), p.139.
32
ability and relevant to early situation. It is hoped in other to the indicators that
depeloved in the syllabus can be achieved.
According to Richards, a syllabus is a specification of the content of a course
of instruction and list what will be taught and tested.33 from the definition mentioned, syllabus is a tool of instruction or reference and a lot of materials that
will be taught to the student and finaly will be tested also to measure student’s
understanding about the material that has learned based syllabus reference. In the
content of syllabus indicator plays an important part, because indicator describing
competence that has to mastered by the students.
While, Brown said that syllabus are predominantly concerned with the choices
necessary to organize the language content of a course or program.34 It can be understood that when the teachers will teach the materials in the classroom, they
can choice a lot of courses and organize the materials that needed. Whole must
concerned to the syllabus so the materials or course not lateral.
Syllabus is not separated with the curriculum, because the instructions or the
content in the curriculum will be developed into syllabus based on the
competency standard and basic competence. Posner said that curriculum is the set
of instructional startegies teacher plan to use.35 It means that curriculum hold the important role, that is the instructional strategies for the teacher where curriculum
be basic reference in teaching and learning process.
From the statements, the writer concludes that curriculum is the planned
learning experiences of an educational system with attention to the elements of
program of studies, program of activities and program of guidance.
33
Jack C. Richards, Curriculum Development in Language Teaching, (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2001), p. 2.
34
James D Brown, The Elemen of Language Curriculum: A Systematic Approach to Program Development, (New Jersey:Heinle & Heinle Publisher.,1995), p.141.
35
The government decided competency standard and basic competence in the
curriculum. The competency standard and basic competence based on the latest
English syllabus for the second grade of Junior High School are states as follow:
Table 2.1
Standard competence and Basic Competence of Listening, Speaking, Reading and
Writing in School-Level Curriculum
Standard Competency Basic Competence
Mendengarkan
1. Memahami makna dalam
percakapan transaksional dan
interpersonal resmi dan berlanjut
(sustained) dalam konteks
kehidupan sehari-hari
1.1 Merespon makna dalam percakapan
transaksional (to get things done)
dan interpersonal (bersosialisasi)
resmi dan berlanjut (sustained)
secara akurat, lancar, dan berterima
yang menggunakan ragam bahasa
lisan dalam konteks kehidupan
sehari-hari dan melibatkan tindak
tutur: menyampaikan pendapat,
meminta pendapat, menyatakan
puas, dan menyatakan tidak puas
1.2 Merespon makna dalam percakapan
transaksional (to get things done)
dan interpersonal (bersosialisasi)
resmi dan berlanjut (sustained)
secara akurat, lancar, dan berterima
yang menggunakan ragam bahasa
lisan dalam konteks kehidupan
sehari-hari dan melibatkan tindak
tutur: menasehati, memperingatkan,
meluluskan permintaan, serta
dan pleasure
2. Memahami makna teks fungsional
pendek dan monolog berbentuk
reports, narrative, dan analytical
exposition dalam konteks kehidupan
sehari-hari
2.1 Merespon makna yang
terdapat dalam teks lisan
fungsional pendek resmi dan tak
resmi secara akurat, lancar dan
berterima dalam berbagai konteks
kehidupan sehari-hari
2.2 Merespon makna dalam teks
monolog yang menggunakan ragam
bahasa lisan secara akurat, lancar dan
berterima dalam konteks kehidupan
sehari-hari dalam teks berbentuk:
report, narrative, dan analytical
exposition
Berbicara
3. Mengungkapkan makna dalam teks percakapan transaksional dan
interpersonal resmi dan berlanjut
(sustained) dalam konteks kehidupan
sehari-hari
3.1 Mengungkap-kan makna dalam
percakapan transaksional (to get things
done) dan interpersonal (bersosialisasi)
resmi dan berlanjut (sustained) dengan
menggunakan ragam bahasa lisan
secara akurat, lancar dan berterima
dalam konteks kehidupan sehari-hari
dan melibatkan tindak tutur:
menyampaikan pendapat, meminta
pendapat, menyatakan puas, dan
menyatakan tidak puas
3.2 Mengungkap-kan makna dalam
percakapan transaksional (to get things
done) dan interpersonal (bersosialisasi)
menggunakan ragam bahasa lisan
secara akurat, lancar dan berterima
dalam konteks kehidupan sehari-hari
dan melibatkan tindak tutur:
menasehati, memperingatkan,
meluluskan permintaan, serta
menyatakan perasaan relief, pain, dan
pleasure
4. Mengungkapkan makna dalam teks
fungsional pendek dan monolog yang
berbentuk report, narrative dan
analytical exposition dalam konteks
kehidupan sehari-hari
4.1 Mengungkap-kan makna dalam
teks lisan fungsional pendek resmi dan
tak resmi secara akurat, lancar dan
berterima dalam berbagai konteks
kehidupan sehari-hari
4.2 Mengungkap-kan makna dalam
teks monolog dengan menggunakan
ragam bahasa lisan secara akurat, lancar
dan berterima dalam konteks kehidupan
sehari-hari dalam teks berbentuk:
report, narrative, dan analytical
exposition
Membaca
5. Memahami makna teks fungsional pendek dan esei berbentuk report,
narrative dan analytical exposition
dalam konteks kehidupan sehari-hari
dan untuk mengakses ilmu
pengetahuan
5.1 Merespon makna dalam teks
fungsional pendek (misalnya banner,
poster, pamphlet, dll.) resmi dan tak
resmi yang menggunakan ragam bahasa
tulis secara akurat, lancar dan berterima
dalam konteks kehidupan sehari-hari
5.2 Merespon makna dan langkah
retorika dalam esei yang menggunakan
ragam bahasa tulis secara akurat, lancar
sehari-hari dan untuk mengakses ilmu
pengetahuan dalam teks berbentuk:
report, narrative, dan analytical
exposition
Menulis
6. Mengungkapkan makna dalam
teks esei berbentuk report, narrative,
dan analytical exposition dalam
konteks kehidupan sehari-hari
6.1 Mengungkap-kan makna dalam
bentuk teks fungsional pendek
(misalnya banner, poster, pamphlet,
dll.) resmi dan tak resmi dengan
menggunakan ragam bahasa tulis secara
akurat, lancar dan berterima dalam
konteks kehidupan sehari-hari
6.2 Mengungkap-kan makna dan
langkah retorika dalam esei dengan
menggunakan ragam bahasa tulis secara
akurat, lancar dan berterima dalam
konteks kehidupan sehari-hari dalam
teks berbentuk: report, narrative, dan
analytical exposition
Content Standard for English Syllabus of Junior High School 2006, adapted from “Kemendikbud”
D. Previous Studies
The research about content validity has already been done by
several researchers. There are at least eight researchers who conducted their
research related to content validity. The following are the summary of the research
that the writer read.
The eight researches that the writer has read had the same background of
the study. They stated that their researches were based on the fact that the test
characteristic of a good test. the same fact that the writer also found. By stating
that, they meant that the test should be constructed well. That made them held the
research in order to solve those problems.
All eight studies using summative test paper as their main data source and
they use working table as their instrument. They focused on the content validity of
summative test item and by comparing teaching syllabus with the English
summative test.
Like Nofiyanti did in her research, she used qualitative method as her
technique data analysis for content validity on English summative test. The result
of her study was 90% of English summative test that hold in SMPN 87 Jakarta
was in line with English curriculum. Furthermore, English summative test item in
SMPN 87 Jakarta has reached a good content validity.
Etika found the empirical evidence of the English summative test content
validity made by the professional team for the odd semester of the first year
students. The finding of the research prove that the test items of English
summative test for the odd semester of the first grade students in SMA Dua Mei
have bad content validity. It is showed through the percentage and the content
analysis. Based on the percentage, she found that the English summative test is
72% valid in terms of its conformity with the indicator. Suminar found that SMP
Al-Zahra Indonesia at even semester 2010/2011 did not have a good content
validity because only 40% of the test items that conformed to the English
syllabus. In other words, the test did not represent the learning objectives of the
even semester because many materials were not included in the test.
The same research was found by Yahyudin in SMA Nurul Falaah.
Summative test items did not have a good content validity because there are 53%
indicators which are not assessed by the test. Another same research has been done by Fauzi in “MTs.Salafiyah”. The English summative test items have bad content validity, they cover only 48%. Sulaeman found the summative test items
sufficient. Rosita did a research in Senior High School Ciledug. She did her
research by observation and documentation. She analyzed the data by using a
formula and described the result by using descriptive analysis method. The result of her study is the validity of the test is in the level of “badness” because there are 18% which is must be revised, 18% has enough quality, 24% has low quality and
40% has lowest quality.
The last relevant study is from Hanik and Fachrurozy. They did a research
in 6th grade of elementary school in the public elementary school in Uduwanu district. The finding is the content validity of materials being tested do not cover
all the basic competences of School-Based Curriculum, the three test format are
reliable, the level of difficulty of each test format is fair, the level of
discrimination for the three formats are very good, and the distracters in the
multiple-choice format is mostly effective.
The writer sum up that mostly the researchers use same method in their
research. The result presentation of their research mostly same by using the
descriptive analysis technique, but the results are different. Mostly the validity of
the summative test items is not good. Therefore, the writer wants to analyze the
23
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A. Time and Place of the Study
To carry out this study, the writer decided to choose Junior High
School of Al-Amanah. It is because there has not been a similar study
here. Al-Amanah is located at Jl. AMD Babakan Setu-Tangerang Selatan.
The research is conducted on May up to June 2013. It was conducted at
the second grade students of Junior High School of Al-Amanah academic
year 2012/2013.
B. The Object of the Study
The object of the study is the test items of English summative test
for the second grade students of SMP Al-Amanah Serpong academic year
2012/2013.
C. Method of Study
In this study, the writer collected the data and then the writer
analyzed the test items, whether each test items of the summative test for
the second grade students of SMP Al-Amanah represent the indicators as
suggested in its syllabus. The test is measured adaptable with the syllabus
and indicators especially from reading and writing skills.
So based on the data and types of information needed of this
research, the writer used qualitative research. Also, this study is
D. Research Instrument
The research instruments which was used by the writer in
collecting the data is documentation. The documents are:
1. Paper/ test booklet
The writer asked the English summative test paper from the
school. The test which is analyzed is the English summative test for
the second grade student at the even semester. The total items are 45
items English summative test. It is 40 items of multiple choice and 5
items of essay.
2. English syllabus and indicators for the second grade students of Junior
High School
The writer analyzed the English summative test items, and then
conform it to the English syllabus and the indicators. The English
syllabus which is made by the teacher should be based on the Standard
competency and basic competence.
E. Technique of Data Collection
The writer collected the data from an English teacher in SMP
Al-Amanah Tangerang Selatan. Then, the writer asked for the syllabus and
the summative test of the English subject on the even semester 2012/2013
academic year in the second grade of Al-Amanah Junior High School.
F. Technique of Data Analysis
To examine the item test, the writer identifyed each of the item in
the summative test and made a data card by identifying the components of
the test. The writer categorized the components of the test. Next, the writer
compared the components of the test with the materials which are
represented in syllabus and counted the percentages of each component.
To make the percentage, the writer uses the formula:
F
P = x 100%1
P = Percentage of Content Validity
f = Frequency of item appearance
n = Number of sample
Moreover, to measure the conformity level of the English summative
test items, the writer adopts the conformity level criteria by Arikunto:
Table 3.1
The Criteria of the Conformity Level2 81% - 100% Very good
61% - 80% Good
41% - 60% Fair
21% - 40% Poor
0 – 39% Very poor
1
Anas Sudiyono, Statistik Pendidik an, (Jakarta: PT. Raja Grafindo Persada, 2006), p. 43. 2
26
Akhir Semester Sekolah Menengah Pertama ( SMP ) Tahun Pelajaran 2012/2013
for the second grade students of SMP Al-Amanah. The total numbers of test items
The conformity between the English final test items (Summative test) and the syllabus
langkah retorika dan
lancar dan berterima yang
berkaitan dengan
lancar dan berterima yang
berkaittan dengan
Basic Competence Based on The Iindicators of Writing
bahasa tulis secara akurat,
makna dan langkah
retorika dalam esei
pendek sederhana dengan
menggunakan ragam
bahasa tulis secara akurat,
lancar dan berterima
The Description of the Test Items
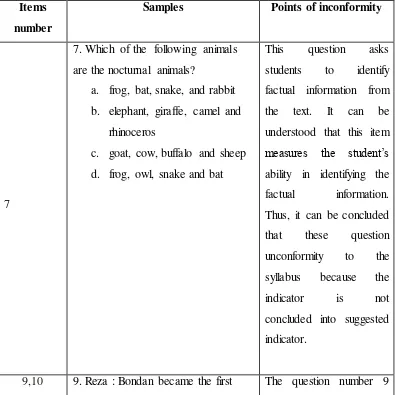
Items
number Samples Points of conformity
14,25,31 Once upon a time the jungle,
students to identifiying the
felt relieved that Rox just saved
understood that these items
we returned home. We were very
c. to describe the animals
d. to describe the zoo in general
who,where, or what written
in a letter
the reorientation in narrative text,
then the question number 16 asks
student to identify part of
narrative text. It can be
understood that these items
measure the rhetoric steps or
language features in
story
16. After reaching his home. Beauty’s father told her the truth. Beauty loved her father very much, so she didn’t refuse what her father asked. She went to the Beast’s castle and lived there only with the beast.
Her gloomy life began since then.
She often tried to run away but the
Beast always successfully stopped
The next day I taught Zacky
how to play volleyball. It took three
days for him to be able to do the
service well.
We spent the last two days by
visiting museums in our city.
Ronggowarsito nd Mandala Bakti
Museums. We learned a lot from the
things displayed in the museum.
1. The writer felt … when he knew
Zacky didn’t have any plan either.
a. Sad c. Haappy
b.Sorry d. Guilty
2. The true statement according to
the text above is …
a. The writer went around the
city by bicycle
b. Zacky learned how to play
volleyball from the writer.
c. The writer and Zacky visited
three museums during the
holiday.
d. The things displayed at the
museums were boring.
32,34 Elegant architecture, finest
material
EXECUTIF
This questions ask students to
identify the purpose of the text. It
KALIURANG VILLAS
b. to describe about Kaliurang
b. to explain the readers the
The underlined statement is the expression to …
Grand Opening Special offer
50% off All items
students to identify the expression
of the underlined statement, and
the question number 41 asks
students to identify the
information from that functional
text. It can be understood that these items measure students’ ability in identifying functional
text. Thus, these items conform to
the recommended indicator
namely “mengidentifikasi teks
c. what is offered in the text
above?
d. when will the discount be
ended?
Table 4.3
The inconformity between the English final test item (Summative test) and the syllabus
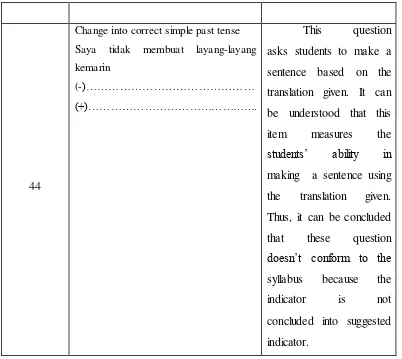
Items number
Samples Points of inconformity
7
7. Which of the following animals
are the nocturnal animals?
a. frog, bat, snake, and rabbit
b. elephant, giraffe, camel and
rhinoceros
c. goat, cow, buffalo and sheep
d. frog, owl, snake and bat
This question asks
students to identify
factual information from
the text. It can be
understood that this item measures the student’s ability in identifying the
factual information.
Thus, it can be concluded
that these question
unconformity to the
syllabus because the
indicator is not
concluded into suggested
indicator.
winner in science competition. Do
you know that?
Adi : are you sure? As far as I know
he becomes the second winner.
Adi’s response shows the expression to … information.
a. Little rabbit was relieved
b. Rox saved a little rabbit’s life
ability in identifying the
Dialogue for number 17-19
a. Excuse me
b. this is my seat
c. What’s wrong
d. Wow
24. Tommy : what about my recount text about “Having Dinner at The Restaurant?”
Grace : It is excellent
Tommy : Return back my text Grace : … I still check it up because your text is too long
Tommy : all right
a. I’m sorry, wait a minute
b. Don’t mention it. Get it
c. It’s very excellent. Here you
are
d. It is very good. thanks
26
26. Where do usually read this
notice?
a. in the Bank
c. in the canteen
b. in the bus station
d. in the class
This question asks
students to identify the
place of the notice where
it is usually put. It can be
understood that this item measures the student’s ability in finding the
factual relation about the
concluded that these daughter”. The word underline refers to …
a. Elizabeth and Mr. Michael b. the bride and Mr. Michael c. Mr. and Mrs. Albert Evans d. Elizabeth and her parents
concluded that these you that I can’t go to the bookstore with you today. dinner in the restaurant. Any message? Isaac : No, thanks. I’ll contact his hand phone. Nice talking to you
38,39,40
38. I was walking a long the main street
about 10.a.m. when I saw this blue car
robber had everyone in the bank lying on
the floor. At this point, hurried to the
Read and complete Putri’s letter with the correct conjunction
This question asks
January 13th 2013
Dear Siska,
I gt your invitation tody. I’m really sorry I can’t come to your party, … (a) my parents are going to be out of town. There’s no one to take care of my sisters … (b) I have to stay at home with them.
Make the sentences from these sign !
44
Change into correct simple past tense
Saya tidak membuat layang-layang
kemarin
(-)………
(+)……….
This question
asks students to make a
sentence based on the
translation given. It can
be understood that this
item measures the
students’ ability in
making a sentence using
the translation given.
Thus, it can be concluded
that these question doesn’t conform to the syllabus because the
indicator is not
concluded into suggested
indicator.
B. Data Interpretation
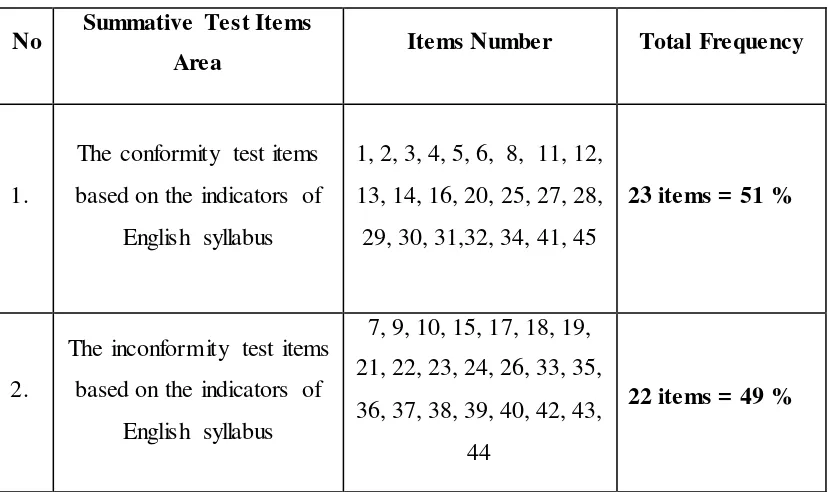
The following table describes the total frequency of the conformity and the
inconformity of English final test items to the syllabus based on the data of item
analysis result above. Based on the data of item analysis result, we can see the
Table 4.4
The Analysis Result of the Conformity and the Inconformity of English Final Test Items at Even Semester for the Second Grade Students of
Junior High School of “Al-Amanah”
No Summative Test Items
Area Items Number Total Frequency
1.
The conformity test items
based on the indicators of
The inconformity test items
based on the indicators of
items. The calculations are explained bellow.
F : Frequency of conformity
N : Number of sample
F
P = ── × 100% N
23
P = ── × 100% 45
P = 51.11 %
So, based on the calculation above the English final test which is
administrated in the second grade students of junior high school of “
Al-Amanah” is 51.11% valid in terms of its conformity with the indicators.
While, based on the data of the inconformity items number, the writer
analyses:
P : Percentage
F : Frequency of inconformity
N : Number of sample
F
P = ── × 100% N
22
P = ── × 100% F
45
P = 48.89%
Table 4.5
The indicators represented by the test items 1. Mengidentifikasi berbagai makna teks narrative/recount
2. Mengidentifikasi tujuan komunikatif teks narrative/recount
3. Mengidentifikasi langkah retorika dan ciri kebahasaan teks
narrative/recount
4. Mengidentifikasi berbagai informasi dalam teks fungsional
5. Mengidentifikasi tujuan komunikatif teks fungsional
6. Mengidentifikasi teks fungsional
Table 4.6
The indicators aren’t represented by the test items
1. Membaca nyaring dan bermakna teks essai berbentuk narrative/recount
2. Mengidentifikasi ciri kebahasaan teks fungsional
b. Content Analysis
Based on the tables and the explanation of the data above, we know that
some indicators are not suggested in the syllabus but they are included in the
test items whereas the indicators are still suggested in the standard
competence and basic competence. On the contrary, there are some indicators
While, there are indicators which dominate the test items. We can see that
the indicator “mengidentifikasi berbagai informasi dalam teks fungsional”
represented 8 items number, and the indicator “Mengidentifikasi berbagai
makna teks narrative/recount” represented 3 items number. On the other
hand, there are some indicators which only have few items number. Instead
they just have two items number.
Ideally, it will be proportional if every indicator represented equally.
There are 8 indicators suggested in the syllabus, and they have to be
represented by 45 items number. So, every indicator should represent 5 or 6
items number.
According to the item analysis above, the writer concludes that the
English summative test which is administrated in the second grade students
of the junior high school of ”Al-Amanah” represent almost the whole
indicators from the syllabus of the even semester.
Therefore, it can be understood that the test designer has not understood
enough to construct the test item. It is shown through the 51% of indicators
suggested in the test items are not suggested in the syllabus. She recognized
that the english final test must be in line with the recommended curriculum
and the English syllabus. But in the application, the writer still found some
inadequacies in the English final test (summative test) especially in the
49
CHAPTER V
CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION
A. Conclusion
In this research the writer analyzed the conformity of the test item with
syllabus, the writer found that the English summative test item which was
administered in the second grade students of Junior High School of Al-Amanah
are 51.11% valid in terms of its conformity with the indicators. The items tests
that represent the suggested indicators in the syllabus are 23 items and the
inconformity items are 22 items. So, based on Arikunto’s opinion, it means fair,
because the percentage falls into the level of 41% - 60%.
Therefore, the writer concluded that the English summative test of the even
semester on the second grade students of Al-Amanah Junior High School for the
first point of view is 51.11% valid in terms of the conformity of the test items
with the syllabus. On the other words, the English summative test of the even
semester on the second grade students of Junior High School of Al-Amanah has
bad content validity. It means that almost 49% indicators in the test items are not
suggested in the syllabus, besides that the indicator of reading dominate almost all
the items and the indicator of writing only one item in essay form.
B. Suggestion
Based on what the writer found, it can be understood that there is still found
the teacher or the test designer who cannot reconstruct the good test items. So,
before making a test, the test designer has to understand how to write a good test
in term of validity. Therefore, it will be better if the test designer/teachers make
the test items by considering a conformity between the test items and the
indicators which is provided in the syllabus because syllabus is the important
guide for teachers about the materials that have to be taught in the classroom.
In constructing the test items, teachers also have to consider about the
fairly. It is better if there are not indicators which are dominate each other because
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Arikunto, Suharsimi, Dasar-dasar Evaluasi Pendidikan, Jakarta: Bumi Akasara.
Arikunto, Suharsimi, Manajemen Penelitian. Jakarta: PT. Rineka Cipta, 2005.
Brown, Douglas. Principles of Language Learning and Teaching. Third Edition. Boston: Prentice Hall Regents, 1994.
Brown, James Dean. Testing in Language Programs. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall Regents, 1996.
Creswell, John W. Educational Research. Boston: Pearson Education, 2012.
Gay, L.R. Educational Evaluation and Measurement: Competencies for Analysis and Application, 2nd Ed. Singapore: Macmillan Publishing Company, 1991.
Gronlund, Norman E. and Robert L. Linn. Measurement and Evaluation in Teaching, 6th Ed. Singapore: McMillan Publishing Co., 1990.
Gronlund, Norman E., Measurement and Evaluation in Teaching, 4th Ed, Singapore: McMillan Publishing Co., 1990.
Harris, David P. Testing English as a Second language. New Delhi: Tat Mc Graw-Hill Publishing Company, Ltd.
Heaton, J.B. Writing English Language Test. New Edition. New York: Longman Inc. New York, 1990.
Hopkins, Kenneth D., Educational and Psychological Measurement and Evaluation, 8th ed, Boston: Allyn and Bacon, 1998.
Hughes, Arthur. Testing for Language Teachers. Great Britain: Cambridge, 1989.
Kubiszyn, Tom and Gary Borich, Educational Testing and Measurement: Classroom Application and Practice, Ninth Edition. River Street: John Wiley and Sons, Inc, 2010.
Nasution, S. Asas-asas Kurikulum. Jakarta: Bumi Aksara, 1995.
Nitko, Anthony. J. Educational Test and Measurement an: Introduction. New York: Hancourt Brace Jovanivich, Inc., 1983.
Reynolds, Cecil R. et al. Measurement and Assessment in Education. 2nd Ed.Upper Saddle River: Pearson Education, Inc., 2009.
Richards, C. Jack & Rodgers, S. Theodore, Approaches and Methods in Language Teaching, (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1986
Richards, C. Jack, Curriculum Development in Language Teaching, (UK: Cambridge
University Press, 2001
Sudijono, Anas. Pengantar Evaluasi Pendidikan. Jakarta: PT. Raja Grafindo Persada, 2005.
Sudiyono, Anas, Statistik Pendidikan. Jakarta: PT. Raja Grafindo Persada, 2006.
Sukardi, H.M., Evaluasi Pendidikan: Prinsip & Operasionalnya, Jakarta: PT. Bumi Aksara, 2011.
Thoha, M. Chabib, Teknik Evaluasi Pendidikan. Jakarta: PT. Raja Grafindo Persada, 1991.
The Items that Conform to the Syllabus
Based on the item analysis, there are 23 items that represent the
suggested indicators by the syllabus
No item The question
1
Text 1
The following text is for question 1 to 3
The holiday had come. At first, I had no idea to spend my free time. I had no plan because I knew my parents were very busy. My father was finishing his project. While my mother had to take care of my little sister. She was just five months.
Luckily, one of my friends Zacky didn’t have any plan either. So, he came to my house nearly every during the holiday. We did a lot of things.
The next day I taught Zacky how to play volleyball. It took three days for him to be able to do the service well.
We spent the last two days by visiting museums in our city. Ronggowarsito nd Mandala Bakti Museums. We learned a lot from the things displayed in the museum.
The writer felt … when he knew Zacky didn’t have any plan either.
a. Sad c. Happy
b. Sorry d. Guilty
This question asks students to identify the specific information from the
recount text. It can be understood that this item measures the student’s ability in
identifying specific information in the text. Thus, this item conforms to the
recommended indicator namely, “mengidentifikasi informasi tertentu dari teks
fungsional pendek”.
No item The question
2
The true statement according to the text above is … a. The writer went around the city by bicycle
b. Zacky learned how to play volleyball from the writer. c. The writer and Zacky visited three museums during the
holiday.