i
(A case Study at the Third Year of SMP Puspita Bangsa Ciputat)
A “Skripsi”
Presented to the Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers’ Training
In a Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
for the Degree S.Pd. (Bachelor of Arts) in English Language Education
By
Linda Maisari
203014001572
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF TARBIYAH AND TEACHERS’ TRAINING
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
JAKARTA
ii
DEPARTEMEN AGAMA UIN JAKARTA
FITK
Jl. Ir. H. Juanda No. 95 Ciputat 15412 Indonesia
FORM (FR)
Saya yang bertanda tangan di bawah ini, Nama : Linda Maisari sendiri dan saya bertanggung jawab secara akademis atas apa yang saya tulis. Pernyataan ini dibuat sebagai salah satu syarat menempuh Ujian Munaqasah.
Jakarta, 28 Februari 2011 Mahasiswa Ybs.
Linda Maisari
vi
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
In the name of Allah, the beneficent and the Merciful. All praise be to Allah Lord of the world, who has blessed the writer in completing this paper. Peace and blessing be upon the prophet Muhammad SAW, his family, his companions, and to all his followers.
On this great occasion, the writer would like to say her great honor and deepest gratitude to his beloved parents: my father, Zakaria. A.Ma.ed (alm) and my mother, Sarkiyah A.Ma.ed, Her sister, Lianah Dwi A.Ma.ed and her brother, M. Agus Salim A.Md, and whole family who gave her huge motivation and moral encouragement to finish the paper.
Her gratitude also goes to:
1. All lecturers of English department who have taught the writer during his study.
2. Drs. Syauki, M.Pd. as the head of English Department.
3. Mrs. Neneng Sunengsih, M.Pd. as the secretary of English Department. 4. Prof. Dr. Dede Rosyada, MA as the Dean of Tarbiyah Faculty.
5. Dr. Fahriany, M.Pd. as the writer’s advisor for her sincerity in guiding the writer carry out this work from beginning to the end.
6. All staffs and officers of the library of UIN Jakarta who have given permission to use and copy their books for her paper.
vii
Rupedih, S.Ag, Arif Rahman Tanjung, S.Pd, Moh. Cahyono Adhi Nur, S.Pd, Nandang Sunandar said, Ade Cahyati, Erma lina, S.Pd, Inayah, S.Pd, Mira delima, Juweria, Herlinawati, S.Pd and Leni) who always help and give the writer inspiration and remind her in accomplishing this “skripsi”
May Allah SWT guides and gives them all happiness through out theirs live. Amin.
Finally, the writer realizes that this “skripsi” is not perfect; therefore, the writer would like to accept any constructive critic and suggestion to make this
“skripsi” better.By all modesty, the writer hopes this „skripsi’ would be useful for
the writer and especially who interested in English education.
Jakarta, February 28, 2011
viii
ABSTRACT
MAISARI, LINDA. 2011 Some Difficulties Faced by the Students in Learning the Present Perfect Tense (A Case Study at the Third year of SMP Puspita Bangsa Ciputat), Skripsi, English Department, The Faculty
of Tarbiya and Teachers’ Training, Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic
University Jakarta.
Advisor: Dr. Fahriany, M.Pd.
Key words: LearningDifficulties, Present Perfect Tense
The purpose of this study is to describe the students’ difficulties in learning Present Perfect tense at the third year students of Puspita Bangsa junior High School Ciputat, it includes what kind of difficulties faced by the students of SMP Puspita Bangsa in learning Present Perfect Tense.
The aim of the research is to analyze about what kind of difficulties faced by the third year students of SMP Puspita Bangsa in learning present perfect tense. Sample of the research are as 36 third year students. This research is using case study method by collecting data from observation, test and questioner.
The finding of study state that the third year students of SMP Puspita Bangsa Ciputat still find difficulties in learning present perfect tense, because the students have not mastered yet the form of present perfect tense: the use of have/has, regular and irregular verb-form of past participle, especially the form of past participle. Besides, the students still confuse using the time expression of present perfect tense.
The writer suggested that the teacher should explained about the form and the use of present perfect tense in clear way in other to make students understand, the teacher should give more exercises related to the present perfect tense. For the students, they must learn individually about present perfect tense and should pay
ix
MAISARI, LINDA. 2011, Some Difficulties Faced by the Students in Learning the Present Perfect Tense (A Case Study at the Third year of SMP Puspita Bangsa Ciputat), Skripsi, pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Fakultas Ilmu Tarbiyah dan keguruan, Universitas Islam Negeri Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta.
Pembimbing: Dr. Fahriany, M.Pd.
Kata kunci: Kesulitan belajar, Present Perfect tense
Tujuan dari penelitian ini adalah untuk menggambarkan kesulitan-kesulitan siswa dalam belajar present perfect tense pada kelas tiga siswa SMP puspita Bangsa Ciputat. Tujuan tersebut untuk mengetahui jenis kesulitan apa yang siswa SMP Puspita Bangsa hadapi dalam belajar present perfect tense.
Selain itu tujuan penelitian ini adalah untuk menganalisa kesulitan-kesulitan siswa dalam belajar perfect tense pada kelas tiga siswa SMP Puspita Bangsa Ciputat. Siswa yang termasuk dalam penelitian ini berjumlah 36 siswa. Penelitian ini menggunakan metode studi kasus dengan mengumpulkan data-data observasi, test dan questioner.
Berdasarkan hasil penelitian ini, menyatakan bahwa siswa kelas tiga SMP Puspita Bangsa Ciputat masih mengalami kesulitan dalam belajar present perfect tense, karena siswa belum menguasai bentuk present perfect tense: penggunaan Have/has, perubahan bentuk kata kerja ke tiga baik kata kerja yang beraturan atau yang tidak beraturan. Selain itu siswa masih bingung kapan waktu menggunakan present perfect tense.
x
CHAPTER II : THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK A. Tense ... 7
xi
CHAPTER III : RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A. The Object of the Research ... 28
B. Place and Time ... 28
C. Method of the Study ... 29
D. Population and Sample ... 29
E. Instrument of Research ... 29
F. Technique of Data Collecting ... 30
CHAPTER IV : RESEARCH FINDINGS A. Data description ... 32
B. Data Analysis ... 33
C. Data Interpretation ... 39
CHAPTER V : CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION A. CONCLUSION ... 41
B. SUGGESTIONS ... 41
BIBLIOGRAPHY ... 43
xii
LIST OF TABLES
Table Page
Table 4.1 Present Perfect Tenses and Its Distribution in the Test item ... 32
Table 4.2 Student’s Score of Test Result ... 35
Table 4.3 The Classification of Scores by S. Arikunto ... 37
Table 4.4 Frequency of the Difficulty in Present Perfect Tense ... 38
xiii
Page
Appendix 1 English test ... 45
Appendix 2 Answer key of students’ test ... 47
Appendix 3 Questioner guide for English teacher ... 48
Appendix 4 Questioner transcript from teacher ... 49
Appendix 5 Questioner guide for students ... 53
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A. Background of the Study
English is a foreign language in Indonesia that has been taught from Elementary School as a Local Content, and Junior High School until Senior High School as a compulsory subject, up to University. People realize that teaching English became very important now and needs much concern. In Learning English, there are four skills (listening, speaking, reading, and writing) and complements, they are: grammar, pronunciation, and Vocabulary for supporting the development of those skills. Besides the four skills, Grammar also should be mastered by students. Grammar is needed even in communication, without the proper knowledge of grammar the students will find many problems to build up the sentences and express their idea for communication activities, lf the grammar is good, they will be confident in speaking English with other people. According to Penny Ur, “there is no doubt that a knowledge-implicit of grammatical rule is essential for the mastery of language: you cannot use words unless you know how they should put
together”1
Without the proper knowledge of the students grammar will find
1
many problems to build up the sentences and express their idea for communication activities.
Now English is the most common language used throughout the world. A distinction is often made that depends on how the language is learned: as a native language (or mother tongue) or as a foreign language.2 English is as a foreign language in Indonesia. Many schools in Indonesia, English is determined as a compulsory subject in national curriculum. The curriculum that progresses now what it is called A Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan Pendidikan (KTSP) or issued in 2006 curriculum. In this curriculum, grammar is one of the point in teaching learning English for junior high school. The grammar focus for the third year students in second semester are about simple present, simple past, the present prefect and future.
In this English curriculum of KTSP, each skill has Standar Kompetensi (SK) and Kompetensi Dasar (KD). Standar Kompetensi (SK) become the global explanation and Kompetensi Dasar (KD) as the specific explanation of Standar Kompetensi and Matery (pokok / Pembelajaran).
“Dalam konteks pendidikan, bahasa Inggris merupakan alat untuk berkomunikasi secara lisan & tulis. Berkomunikasi adalah memahami & mengungkapkan informasi, pikiran, perasaan, dan mengembangkan ilmu pengetahuan, teknologi, dan budaya. Kemampuan berkomunikasi dalam
2
3
pengertian yang utuh adalah kemampuan berwacana, yakni kemampuan memahami dan menghasilkan teks lisan & tulis yang direalisasikan dalam empat keterampilan berbahasa, yaitu mendengarkan, berbicara, membaca, & menulis. Ke empat keterampilan inilah yang digunakan untuk menanggapi atau menciptakan wacana dalam kehidupan bermasyarakat.”3 (on the educational context, English is means to communicate orally and written. Communication is to understand and to express informasi, thought, feeling and to develop knowledge, technology and culture. Ability in communication and able to understand the text.
Actually, many Junior Hight School students have some difficulties in learning English language skills and English language complements. According to their. These problems can be known from the result of the
students’ achievements and the teacher evaluation. So the teacher role is very
important to make the students be creative to solve their problems.
The writer chooses SMP Puspita Bangsa as a case study because the writer did the research about Some Difficulties Faced By The Students in Learning Present perfect Tense. To measure the ability and to get the data of
the students’ score in SMP Puspita Bangsa, so the writer decided to give the
test and Questioner. The teacher use book Stepping more, Junior High School
3
grade IX, Firmansyah Diyata. Chapter V, page 126, and The Bridge English Competence for SMP Grade IX, page 84.
Some writers believe that in learning English as a foreign language or second language the learner should, first of all, master the grammar structure system, the basic structural patterns of the present perfect tense items.
Grammar is one of the language aspects which are taught to every language learner. It has an important role in understanding the English language. As said by W. Stannard Allen in living English structure stated:
“English has three main divisions, past, present and future…..”.4
Absolutely,
the verb in English influenced by the “time”, when it happens or will happen
(past, present, or future). So a verb should be concord or related with the time. Accoring to Raymond Murphy: We use the present perfect (have been/ have played/ have done etc.) when we talk about a time from the past until now-for example, your life: I’ve seen that women before but I can’t remember when.5
In this skripsi, the writer will not discuss grammar in general. She will write about tense. Tense is one of discussions of grammar in general. According to Laurie Bauer said tense is usually defined as relating to the time
4
W. Stannard Allen, Living English Structure (London: Logman, 1987), p.75
5
5
or an action, event or state. 6 The time of the action is commonly expressed by the verb. Almost all verbs can show the difference between the past and present by a change in the verb form. With tense students can know when the action occur, and understand the correspondence between the form of the verb and their concept of time.
According to Richard Viet, “Tense is frequently described as the
property that relates to the time a verb’s action is performed”7
. some grammarians said that English has a great variety of tenses. This is one of reasons why the Indonesia students have difficulties in understanding tenses, because there are no tenses in Indonesia language. Present perfect tense is one tense that should be mastered by students.
When the students want to tell a verb that “used to indicate an action that took place at an indefinite time or over a period of time in the past, but
still has relevance in the present”.8
We call it the present perfect tense.
Eventhough the third grade students of Junior High School have learned it, they still find difficulty in learning present perfect tense, especially in using forms and usages.
6
Laurie Bauer, English word formation (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1983), p. 157.
7
Richard Viet, Discovering English Grammar, (Boston Houghton Mifflin Company 1986), p. 149
8
This is the reason, why the writer is interested in writing about the problems in grammar test in Present Perfect Tense for the third year students of SMP Puspita Bangsa Ciputat.
B. Limitation of the Study
The writer limits the study error or difficulties at the third year of SMP Puspita Bangsa Ciputat. These errors are taken from the test focused on Perfect tense, either the forms or the usages.
C. Statement of the Problem
Based on the writer formulates the problem as follows: WHAT KIND OF DIFFICULTIES FACED, BY THE STUDENTS OF SMP PUSPITA
BANGSA IN LEARNING THE PRESENT PERFECT TENSE?
D. Objective of the Study
The purpose of the study is to find out the difficulties in learning grammar, especially present perfect tense of the students at the third year of SMP PUSPITA BANGSA Ciputat in terms of forms or the usages, and then can use in their daely life.
7
CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
This chapter contains the description of the theoretical framework of relevent theories concerning by the students in learning present perfect tense.
A. Tense
Definition of English Tense
One of The important things in learning grammar is tense. Marella Frank
defines, “tense is special verb ending or accompanying auxiliary verb signal
the time an event takes place”1 Almost all verbs can show the differences between the present, past and future time by changing in the verb form. From
this, can be also defined as „tenses is an actual usage, refers consistently only
to grammatical forms2. So time, as Lyons say, tense is “grammaticalizes the relationships which held between the time up the situation that is being
describe and the temporal zero point of the deictic context”3
Based on the explanation above, the writer can conclude that tense is a verb form or series of verb Forms used to express a time relation. Tenses may also indicate whether an action, activity or state is past, present or future.
1
B. Kinds of Tense
Based on Longman Grammar of Spoken and Written English defines,
“from structural point of view, English verbs are inflected for only two tense: present and past”4
In her book “Modern English: A Practical Reference Guide” Marcella
Frank points out, “there are three past tenses and two future tenses. Note further that the past perfect is tied in time to the past tense, the present perfect to the present tense, and the future perfect to the future tense”.5
So, if simple and compound tense are mixed together, there are twelve kinds of tenses. They are: simple present, simple past, simple future, present progressive, past progressive, future progressive, present perfect, past prefect, future perfect, present perfect progressive, past perfect progressive, and future perfect progressive.
C. Present Prefect Tense
1. The Meaning of Present Prefect tense
Present perfect tense, in Oxford Learner’s Pocket Dictionary defined as verb which expresses an action done in a time period up to the present, formed in English with have/has and past participle.6
Raymond Murphy said: “When we talk about a period of time that
continues up to the present, we use the present perfect”.7
4
Douglas Biber, et.al., Longman Grammar of Spoken and Written English, (Harlow: Pearson Education limited, 1999), P.453
5
Marcella Frank, Modern English: A Practical Reference Guide, P.66
6 Oxford Learner’s Pocket Dictionary, (New York: Oxford University Press, 2009), new ed., p. 347
7
9
From two definitions above, the writer concludes that present perfect tense can be defined as an action occurred in the past which are completely finished but still have connection to the present or future.
2. The Form of the Present Perfect Tense.
There are many tenses in English grammar; one of them is present perfect tense. There are some definitions about present perfect tense such as follows:
According to Betty Schrampfer Azar in Fundamentals of English Grammar pointes out that “The basic form of the present perfect: have or has + the past participle. Use have with I, you, we, they, or plural noun (e.g., Students). Use has with she, he, it, or a singular noun (e.g., Jim). With pronouns, have is constructed to apostrophe + ve („ve) and has to apostrophe + s („s)”.8
a. Affirmative
To make affirmative statement, we use the following formula :
S + have/has + Past participle + …
Example:
8
Subject Have / has Past participle
I Have Watched The movie
We Have Played Volleyball
They Have Eaten
Sarkiyah Has Finished Her study
Zakaria Has moved Since 1 p.m.
To make an affirmative statement, we use the following formula : S + have/has + been + Past participle + …
Example:
Subject Have/has been
I Have been At school Since & a.m.
We Have been here For three day
They Have been To Malaysia This weekend Sarkiyah Has been To museum This holiday Zakaria Has been In hospital Since thursday
According A.J. Thomson and A.V. Martinet said: “the present perfect tense is formed with the present tense of have + the past participle”9.
9
11
Present perfect tense is formed by using the auxiliary verb have/has and the present participle form of the main verb (have/has+ regular or
irregular verb) and it’s commonly accompanied by definite time words
such as since and for. b. Negative
To make a negative statement, we use the following formula
S + have/has + not + Past participle + …
Example:
Subject Have/has Not Past
participle
I Have Not Watched The movie
We Have Not Played Volleyball
They Have Not Eaten
Sarkiyah Has Not Finished Her study
Zakaria Has Not moved Since 1 p.m.
To make a negative statement, the verb be, we use the following formula:
Example:
Subject Have/has not been
I Have Not been At school Since & a.m.
We Have Not been here For three day
They Have Not been To Malaysia This weekend Sarkiyah Has Not been To museum This holiday Zakaria Has Not been In hospital Since thursday
c. Interrogative
To make an interrogative statement of verb other than be we put have/has before the subject. The following formula:
Have/has + Subject + Past participle +…?
Example:
Have/has Subject Past participle
Have I Watched The movie?
Have We Played Volleyball?
Have They Eaten Meatball?
Has Sarkiyah Finished Her study?
13
To make an interrogative statement of verb be, we use the formula:
Have/has + Subject + ...?
Example:
Have/has Subject been
Have I been At school Since 7 a.m.
Have We been here For three days?
Have They been To Malaysia This weekend? Has Sarkiyah been To museum This holiday? Has Zakaria been In Hospital Since Thursday?
To make an interrogative statement of verb other than be, we use the formula:
Haven’t/hasn’t + Subject + past participle + ...?
Example:
Have/has Subject Past participle
Haven’t I Watched The movie?
Haven’t We Played Volleyball
Haven’t They Eaten Meatball
To make an interrogative negative statement of verb be, we put has before the subject. The formula is:
Have/has + Subject + Past participle + ...?
Example:
Have/has Subject not been
Have I Not been At school Since 7 a.m.?
Have We Not been here For three
days?
Have They Not been To Malaysia This weekend? Has Sarkiyah Not been To museum This holiday? Has Zakaria Not been In Hospital Since May?
3. The Usage of Present Perfect tense
Betty S. Azar, “the present perfect expresses the idea that something happened (or never happened) before now, at an unspecified time in the past. The exact time it happened is not important. If there is a specific mention of time, the simple past is used. 10 (e.g., I have been here
since seven o’clock). we can conclude the diagram as follow:
10
15
(Time?)
She also said, “The present perfect also expresses the repetition of
an activity before now. The exact time of each repetition is not important”. (e.g.: I have met many people since I came here in June).
The present perfect also, when used with for or since, expresses a situation that began in the past and continues to the present. In the example, notice the difference between since and for: since + a particular time, for + duration of time.
E.g.:
1) I have beenhere since seven o’clock
2) We have been here for two weeks
In a Practical English grammar, A.J. Thomson and A. V. Martinet state that this tense may be said to be sort of mixture of present and past, it is always implies a strong connection with the present and is chiefly used in conversation, letter, newspaper, and radio reports”. 11
Michael Swan said “when we want to talk about action or
situations, which started in the past and have continued up to the present, we often use the present perfect to show the connection between past and
present”.12
11
A.J. Thomson and A.V. Martinet, Op.cit, p.166 12
The present perfect is very often used with since and for. Since is used to say when something started; it is followed by a reference to a point of time (e.g. Since April 27th). For is used to say how long something has been going on; it is followed by reference to a period of time (e.g. for three months).
Based on those statements above, it can be concluded that the present perfect tense is used to express:
a. An action which happened at some unknown time in the past. Examples:
I have already seen that film. I don’t want to see it again
(It doesn’t matter when I saw it)
Have you ever been to Germany?
(It doesn’t matter when you went, I just want to know whether you
have been there or not).
b. An action or activity happened in the past and was repeated over a period of time.
Examples:
I have eaten Chinese food several times. She has visited Bali Island twice.
c. An action happened in the past and the result of the action continues to or is still true at present.
Examples:
17
(The result of the action continues to the present, i.e. now the door is still close)
d. An action or state happened in the past and continues to the present. Examples:
I have lived in Jakarta for twenty two years.
(I started to live in Jakarta twenty two years ago and I still live in Jakarta now.
He has worked at the Bank since 2004.
(He started to work at the Bank in 1994, and he is still work there now) e. These adverbs are frequently used in present perfect tense: ever,
already, yet, just, never.13 1. Ever means „at any time’
For example: Have you ever been to the British Museum? 2. Already means „before now’
For example: Have you already been to the British Museum? 3. Yet means „up to now’
For example: Have you visited the British Museum yet? 4. Just refers to the very recent past
For example: I have just visited that Museum. 5. Never means „not any time’
For example: I have never visited that Museum.
13
The time signal for present perfect tense are indicated by since, for, this week, up to now, so far, not yet, already, often, once, twice, three times, etc.14
From the discussion above the present perfect tense focused on the action that happened in the past but related to the present moment. It is used commonly to show that the action has just been completed, or at least the effect of the action is still felt at the moment if speaking.
D. Learning Difficulty
Some students have difficulties in their learning. It can be showed by their low/bad scores or achievement in several subject matters. Abu Ahmadi
and Widodo Supriyono defines, “Dalam keadaan dimana anak/siswa tidak
dapat belajar sebagaimana mestinya, Itulah yang disebut dengan kesulitan
belajar”. (The condition where the students cannot learn normally is called learning difficulty).15
There are some factors which caused learning difficulties. According to Abu Ahmadi and Widodo Supriyono, there are two factors: internal and external factors, as follows:16
a. Student’s internal factors
The student’s internal factors are divided into two aspects, as follows:
14
Team of five, Improving Reading Skill in English (Jakarta: Darul Ulum press. 2001), p. 64
15
Abu Ahmad and Widodo Supriyono; Psikologi Belajar, (Jakarta: PT. Rineka Cipt, 1991), p.74 (translated by the writer).
16
19
1) Physiological Aspect, this aspect is about the condition of students’ body from every part of the body.
2) Psychological Aspect, this aspect emphasizes on the inside
conditions of the students. It consists of students’ intelligence, talent,
interest, motivation, mental health and special type of learner. b. Students external factors
Student’s extern factors cover all situations and condition around
environment that do not support student’s learning activity. Environment
factors cover as follows:
1) Social Environment, the social environment here is the human environment outside students who have contact directly with them such as family, in their school, neighbors and mass media.
2) Nonsocial Environment, the factors which include the nonsocial
environment are the location of student’s house, the school’s
building, learning instruments, curriculum, and school timing. All
these factors are though could be the influences for student’s
achievement.
In addition, Syaiful Bahri Jamarah made it more specific divisions the cause of learning difficulties into student’s factor,
school’s factor, family’s factor, and society’s factor.17
a. Students Factor
Some factors that make students difficult in learning
17
1. Lack of intelligence
2. Lack of talent and not suitable with lesson which learning or given by teacher
3. Unstable emotion 4. Lack of study activity 5. Lack of healthy
6. Not having motivation in learning 7. Etc.
b. School’s Factor
1. Personal of teacher is not good 2. Teacher does not have quality
3. Unharmonious relationship between teacher and students 4. Teacher is unskilled to diagnosis student’s difficult in
learning
5. The way teacher teach is lack of good 6. Media is not complete
7. Condision of school is not graffiti 8. Indiscipline
9. Etc. c. Family’s Factor
21
1. Lack of tools of study for students in home 2. Less education fee that parents prepared 3. Family’s healthy is less of good
4. Lack of parents attention
5. Children too much helping parents 6. Etc.
d. Society’s Factor
Some factors in society that makes students difficult in learning are:
1. Commotion, noise, dispute, fight, robe that often happen in society
2. Electronic media like television that often showing properly programs like immoral, pornograhic, etc.
3. Drugs
4. Slum area, dirty environment 5. Etc.
E. Difficulties in Learning Present Perfect Tense
As it mentioned above that present perfect tense is one of the subject in grammar that most of the students usually find the difficulties in learning it. Martin Parrot in his book Grammar for English Language Teachers said
that “learners generally have far more difficulty in using present tense correctly than in understanding them. Even if they don’t know or are unclear about the difference in meaning between different tense, in most cases there is plenty of information in the context to help them understand whether, for example, an action is temporary or not.18 He also made some list of typical difficulties for learners when they study the present perfect tense, they are: form and meaning, the use of how long with for and since, and over-use of present perfect forms.19
In English subject, some students have some difficulties in learning tense, especially present perfect tense. Based on the description above, the writer divided the two main difficulties in learning present perfect tense, they are: the difficulty in form of present perfect tense and the difficulty in the use of present perfect tense.
a. Difficulty In Form of Present Perfect Tense
The form of present perfect tense is have/has + past participle. Have used for subject I, we, they, you while has used for subject he, she,
it. Raymond Murphy state, “we form the present perfect tense with
have/has + past participle. Uses have with I, we, they, you. Use has with
18
Martin parot, Grammar for English Language Teachers, p. 162 19
23
he, she, it”.20
But in fact, there are some students still have difficulty in understanding the form of present perfect tense.
Here are the examples of mistakes made by students: I has lost my chance to study abroad.
She have finished her homework.
The above sentences are wrong because the students use “has” for
subject I and use “have” for subject she. The correct answers for examples
above are:
I have lost my chance to study abroad. She has finished her homework.
It proved that there are some students who still have difficulties in understanding the form of present perfect tense, especially in putting have/has for subject.
As it is mentioned above the form of present perfect tense is have/has + past participle. But from the form above, there are some students who also still have difficulties in using verb-form which is either regular or irregular verbs of past participle.
Martin Parrot in Grammar for English Language Teachers, explained about several reasons why learners may make mistakes in the use of regular and irregular forms. They may:
1. (consciously or unconsciously) have learnt the wrong form of a particular verb.
20
2. be quessing the form because they don’t know what it is.
3. over-generalize ruler (for example, ignoring irregular forms or using past forms in questions or infinitives)21
Here is the explanation about regular and irregular verbs, while past, and past participle) are the same. For example: hit
b) With other irregular verbs, the simple past is the same as the past participle (but different from the base form). For example:
tell – told
c) With other irregular verbs all three forms are different. For example: break - broke – broken.22
An irregular verb is one of verb-forms that do not end in – ed to show past action. Therefore, to increase knowledge about irregular verbs, students must be learned individually and must memorize the irregular
21
Martin Parrot, Grammar for English Language Teachers, (Cambridge: Cambridge Press, 2004), p. 192
22
25
forms. According to Robert Krohn, “Many verbs, however, have irregular
forms. These forms must learn individually”.23
Because the irregular verbs must be memorized, therefore there are many students who still get difficulties in learning present perfect tense. Although there are some students who have already memorized the irregular verbs, they still get difficulties in putting these verbs in sentence. Here are the examples of student’s difficulties in past participle:
Andy has knew Liza for a long time.
I have meeted many people since I came here in June. The correct answers for example above are:
Andy has known Liza for a long time. (The irregular verbs all three forms are different: know-knew-known
I have met many people since I came here in June. (The past participle is same with simple past: meet-met-met)
The above example proved that there are some students who still do not know of irregular verbs. They are still confused, when they should use the first, the second or third verbs in their own sentences.
b. Difficulty in the Use of Present Perfect Tense
Some grammarians said that English has a variety of tense. This is one of the reasons why the Indonesia students have difficulties in understanding tense, because there are no tenses in Indonesia language.
23
But in learning English, especially tenses, the students must be able to distinguish every tense in English, especially between present perfect tense and simple past tense. These tense are interrelated. They are used in the past time. Some students are still confused to distinguish the use.
Wishon and Julie M. Burks said, “ the past tense is used for
activities that occurred over a period of time in the past, but are now
finished, or that occurred at intervals in the past, but don’t occur now”.24
While the present perfect tense is used to express the activity that happened in the past but still related to the present moment of speaking.
According Betty Schrampfer Azar in Understanding and Using English Grammar defined, “The present perfect expresses the ideas that something happened (or never happened) before now, at an unspecified time in the past. The exact time it happened is not important”.25
That statement has been supported by Elaine Kiln and Darcy Jacks
who said, “The present perfect tense refers to an event that happened at an unknown or unspecified time in the past. No specific time is given in a present perfect statement or question. (If we use past time expression such
as yesterday or last week, we use the past tense)”.26
But in fact, there are many students who still make mistakes in distinguishing the use of present perfect tense and simple past tense. This
is the example of student’s mistake: she has lived in Jakarta last year.
24
George E. Wishon and Julia M. Burks, Let’s write English revised edition, p. 195 25
Betty Schrampfer Azar, Understanding and Using English Grammar, p. 29
26
27
28
This chapter presents the description of the research method used in this research, includes the objective of study, place and time of research, method of the study, population and sample, instrument of research, and technique of data collecting.
A. The Object of the Research
The object of the research is the third year student of SMP Puspita Bangsa Ciputat. First grade consists of 120 students which divided into three classes; second grade consists of 136 students which divided into three classes. Third grade consist of 121 students. So the write just consist third grade A consist of 36 student.
In the field research, to make the writer easier in analyzing the data. The writer did the observation, by giving the test and questioner to find out some difficulties face by students in learning present perfect tense.
B. Place and time
29
C. Method of the Study
This paper is written based on case study and field research: In this case the writer took SMP Puspita Bangsa Ciputat Tangerang as place for investigation to be discussed. In field research the writer observed some difficulties and problem of SMP Puspita Bangsa Ciputat the third year student in learning process of Present Perfect tense after collecting and processing the data the writer did the observation and gave the test to the students by giving the question to find out some data from the students. The would like to offer an alternative to solve the problem.
D. Population and Sample
In this research the writer took the population of the third year students of SMP Puspita Bangsa Ciputat consisting of 3 classes (3a, 3b and 3c). The total population is about 121 students.
In sample. The writer did not take all the population. The writer took one class as a sample that is in the third class A of 36 students when the writer was doing the research.
E. Instrument of the research
In this study, the writer used instruments to get the data needed, they are :
textbook that used by teacher and students, English teaching-learning process included the problem faced by students in understanding the English lesson, especially present perfect tense.
b. Test. The test helps to the teacher understand, the students, plan learning experiences for them, and determine the extent to which the instructional objectives are being achieved.
c. Questioner. The data of this study is also collected by using questioner, such as the reasons why the students find difficuties in learning present perfect tense.
F. Technique of Data Collecting
To get objective data based on the correctness that happened in the field, the writer used some techniques of data collecting, they are:
1. Observation. It is the main technique in collecting data about teaching English in the classroom. It was conducted from January 27th up to February 24th 2010. In this case, the writer acted as an observer who observed the teaching learning process without being involved in the process. Without being invplved in the present.
2. Test. In the research, the writer used test as the instrument to get the data.
It is given to find out students’ difficulties in learning present perfect tense
and got the students’ test score. She made the test that covered present
31
16, 19, 22, 25), regular verb (number of the item are 2, 5, 11, 14, 17, 20, 23), and irregular verb (number of the items are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24). So, every correct item gets 2 points. Finally, the total score for the test is got from the total correct answers in part multiple-choice them divided by 5.
32
In line with the research problems, technique of data collecting present finting as follow it presents technique of data collecting presents finding as follows: (1) Data description (2) Data Analysis (3) Data Interpretation.
A. Data description
The writer got the results from the English test score about present perfect tense. She gave the test to the thirty six students of third which consists of 25 items which is asking about has/have, regular verb, and irregular verb. The instrument of the test can be seen in appendix I, page 34.
The following tables are the students’ score and the present perfect
tense and its distribution.
Table 4.1
Present Perfect Tenses and Its Distribution in the Test item
No Difficulty Number of Item
1. has/have 1, 4, 7, 10, 13, 16, 19, 22, 25 2. regular verb 2, 5, 8,11, 14, 17, 20, 23 3. irregular verb 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24
33
test is a multiple choice. This test consists of 25 items which is asking about the difficulties in present perfect tense. This test consists of 25 items which are divided into three main aspects, they are has/have (number of item are 1, 4, 7, 10, 13, 16, 19, 22, 25), regular verb (number of the item are 2, 5, 11, 14, 17, 20, 23), and irregular verb (number of the items are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24). So, every correct item gets 2 points. Finally, the total score for the test is got from the total correct answers in part multiple-choice then divided by 5.
B. Data Analysis
The data analysis is conducted by arranging the data obtained systematically. This is done to make easier for the writer to write the research report. The data gained from observation consist of two types, field-notes and observation sheets. Then the data are analyzed to answer research questions.
The data gained from test dealing with what the difficulties are faced by students in learning present perfect tense.
The writer also used the formula that purposed by Anas Sudijono 2004, such as:
M = TS N
M = Mean Score
Besides the formula above, the writer also used the percentage the test formula, as follow:
P = f x 100 % 1 N
P = Percentage
f = Frequency of error made.
N = Number of sample which is observed
After having percentage and frequency, the writer looked for the average by using the formula:
p = f x 100 % N x n
P = Percentage F = Frequency
N = Number of the Students n = Number of item test
To know the test result, the writer shows table as follow:
1
35
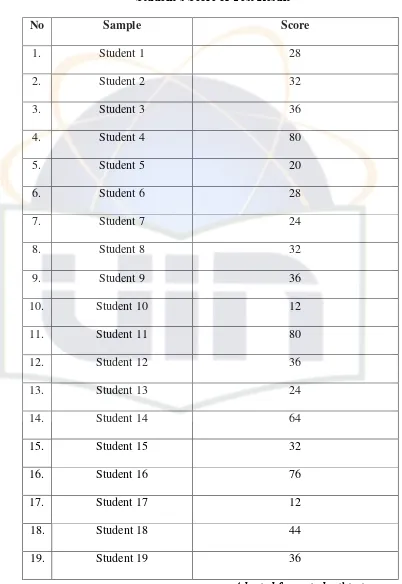
Table 4.2
Student’s Score of Test Result
No Sample Score
1. Student 1 28
2. Student 2 32
3. Student 3 36
4. Student 4 80
5. Student 5 20
6. Student 6 28
7. Student 7 24
8. Student 8 32
9. Student 9 36
10. Student 10 12
11. Student 11 80
12. Student 12 36
13. Student 13 24
14. Student 14 64
15. Student 15 32
16. Student 16 76
17. Student 17 12
18. Student 18 44
19. Student 19 36
20. Student 20 36
21. Student 21 40
22. Student 22 72
23. Student 23 36
24. Student 24 28
25. Student 25 40
26. Student 26 26
27. Student 27 52
28. Student 28 28
29. Student 29 64
30. Student 30 28
31. Student 31 24
32. Student 32 36
33. Student 33 32
34. Student 34 24
35. Student 35 32
36. Student 36 36
Total 1366
The writer uses formula to find the mean, as follow: M = TS
N
= 1366
37
= 37.9
According to the data above, it is found out that the mean score is 37.9
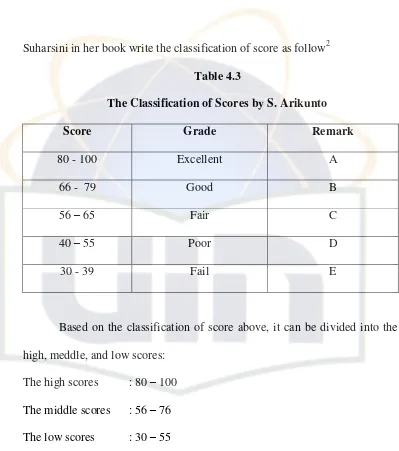
Suharsini in her book write the classification of score as follow2
Table 4.3
The Classification of Scores by S. Arikunto
Score Grade Remark
80 - 100 Excellent A
66 - 79 Good B
56 – 65 Fair C
40 – 55 Poor D
30 - 39 Fail E
Based on the classification of score above, it can be divided into the high, meddle, and low scores:
The high scores : 80 – 100 The middle scores : 56 – 76 The low scores : 30 – 55
Futhermore, the writer will determine the percentage of the score by using formula below: P = F x 100 %
N x n
2
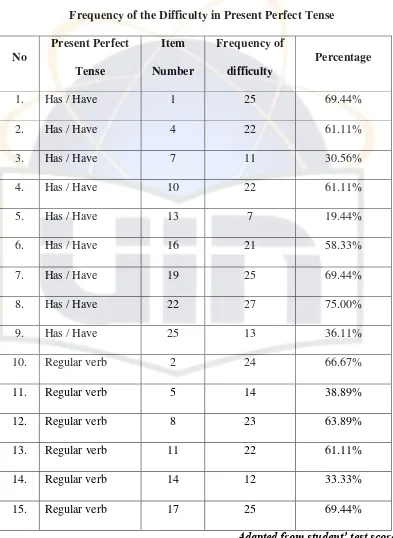
The frequency of difficulty of present perfect tense, could be seen to the following table:
Table 4.4
Frequency of the Difficulty in Present Perfect Tense
No
39
16. Regular verb 20 27 75.00%
17. Regular verb 23 18 50.00%
18. Irregular verb 3 10 27.88%
19. Irregular verb 6 13 36.11%
20. Irregular verb 9 29 80.56%
21. Irregular verb 12 28 77.78%
22. Irregular verb 15 30 83.33%
23. Irregular verb 18 28 77,78%
24. Irregular verb 21 29 80.56%
25. Irregular verb 24 30 83.33%
Total 25 535 59.44%
To find out the whole average is using the formula: P = F x 100 %
N x n
= 535 x 100 % 36 x 25
= 535 x 100% 900
= 59.44 %
C. Data Interpretation
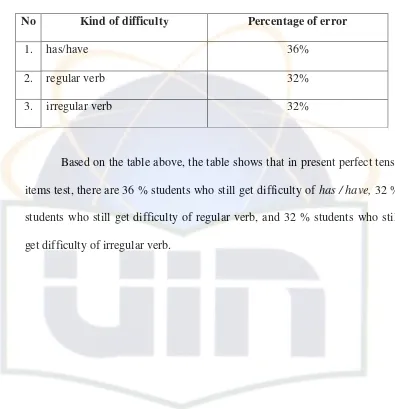
Table 4.5
Kind and percentage of difficulty in present perfect Tense
No Kind of difficulty Percentage of error
1. has/have 36%
2. regular verb 32%
3. irregular verb 32%
Based on the table above, the table shows that in present perfect tense items test, there are 36 % students who still get difficulty of has / have, 32 % students who still get difficulty of regular verb, and 32 % students who still get difficulty of irregular verb.
41
CHAPTER V
CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION
This chapter present about conclusions and suggestions of the writer which done at SMP Puspita Bangsa Ciputat.
A. CONCLUSION
The writer concluded that many students are still confused in the form and the usage of present perfect tense. It shows from the result of the research
in the frequency of students’ error made in the form and the usage of present
perfect tense. The writer concluded that the students still get difficulty in understanding present perfect tense. For this case, the students should know more when and how to use present perfect tense correctly.
B. SUGGESTIONS
There are some suggestions that can be given in relation to the writer’s
conclusion. The suggestions are as follows:
1. It is hoped that the teacher can give more attention in teaching present perfect tense because the student have understoont yet correctly.
3. It is hoped that the teacher should explane the present perfect tense clearly way in order to the students understand it easily.
43
Azar, Betty S. Understanding and Using English Grammar. New Jersey: Prentice Hall, Inc., 1989.
Allen, Stannard W. Living English Structure. London: Logman, 1987.
Arikunto, Suharsimi. Dasar-Dasar Evaluasi Pendidikan. Jakarta: Bumi aksara, 2003.
Bauer, Laurie. English word formation. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1983.
Djamarah, Syaiful Bahri Drs., Psikologi Belajar, Jakarta : Rineka Cipta, 2008. Departemen Pendidikan Nasional. Kurikulum 2006 Standar Kompetensi. Jakarta:
Departemen Pendidikan Nasional, 2006.
Frank, Marcella. Modern English: A Practical Reference Guide. New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
Greenbaum, Sidney and Quirk, Randolph. A Student’s Grammar of the English Language. English Longman, 1990
Himpunan Perundang-undangan RI, Sistem Pendidikan Nasional. Bandung: Nuansa Aulia, 2008.
Kirn, Elaine rt. al., Interactions 1 Grammar 4thEdition. New York: Mc Graw-Hill Companies, 2002.
Parrott, Martin, Gramer for English Language Teachers, Cambridge University Press, 2010.
Murphy, Raymond. English Grammar in Use With Answer. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1985.
Oxford Learner’s Pocket Dictionary. New York: Oxford University Press, 2009. new ed.
Pedoman Penulisan Karya Ilmiah, Skripsi, Tesis dan Disertasi. Jakarta: CeQDA, 2007.
Sudijono, Anas. Pengantar Statistik Pendidikan. Jakarta: PT Raja Grafindo Persada, 2004.
Swan, Michael. Practical English Usage. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1987. Team of five, Improving Reading Skill in English. Jakarta: Darul Ulum press.
2001).
Thomson, A.J. and Martinet, A.V. A Practical English Grammar. London: Oxford University Press, 1986.
Ur, Penny. Grammar Practice Activities. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1998.
Viet, Richard. Discovering English Grammar. Boston Houghton Mifflin Company, 1986.
45
Appendix 1
RESEARCH INSTRUMENT
Name/Class : ________________ Date : ________________
Choose the correct answer to fill in the blank the sentence below by crossing A,B,C,D, or E use only present perfect tense!
1. ……… you ever visited Mexico?
a. are b. have c. had d. were
2. I have (write) …………my wife a letter every other day for the last two weeks.
a. written b. wrote c. writen d. wratten
3. I (attend, not)………any parties since I came here.
a. hasn’t attended c. hadn’t attended
b. haven’t attended d. has attended
4. How long. ……….. Anna lived here?
a. is b. Did c. have d. has
5. In her whole lifetime, Anna (see, never)…………. Snow.
a. has never seen c. has never see
b. have never seen d. have never been seen 6. I (Finish) ……… my Work. I finished it two hour ago.
a. finished c. has finished
b. have finished d. have finishing
7. Up to now, Professor Williams…….. given our class five tests.
11. We have (be) ………. here for two weeks.
a. was b. did c. were d. been
12. I have (like) ……….. cowboy movie ever since I was a child
a. liked b. liking c. look d. likes
13. We …….. had four tests so far
a. are b. have c. has d. were
14. I have (know)…… him for many years
a. knew b. knowed c. known d. knowing
15. They have (move)……… into a new apartment.
a. moved b. moving c. moven d. been moven
16. Mr. Parker travels to Washington, D.C., frequently she……… flown there many time.
a. has b. have c. does d. is
17. Have you even (eat)………….. at that restaurant?
a. eaten b. ate c. eating d. have eaten 23. I have……… this same pair of shoes for three years.
a. have b. having c. has d. had
24. Our younger brother hasn’t …………the window.
a. open b. opening c. opened d. opens
25. They ……… done their homework
Appendix 3
Questioner
Hari\Tanggal : Rabu, 24 Februari 2010 Nama : Ibu Setiana S.W Sitepu S.Pd. Jabatan : Guru Bahasa Inggris
Tempat : Ruang Guru
A. Pertanyaan :
1. Metode apa yang Ibu gunakan dalam pengajaran bahasa Inggris khususnya tentang present perfect? Dengan cara menghapal rumus atau dengan cara yang lain?
2. Kesulitan apakah yang menjadi kendala Ibu ketika mengajarakan materi present perfect?
3. Apakah siswa mendapat kesulitan dalam menerima materi tersebut? 4. Bagaimanakah Ibu mengatasi kendala tersebut?
5. Bagaimana antusiasme siswa terhadap mata pelajaran Grammar khususnya present perfect?
6. Apakah siswa dapat membentuk kalimat positif dalam present perfect? 7. Apakah siswa dapat membentuk kalimat negative dalam present perfect? 8. Apakah siswa dapat membentuk kalimat interrogative dalam present
perfect?
9. Apakah siswa dapat menguasai perubahan verb ketiga?
10.Apakah yang Ibu lakukan ketika siswa tidak mengerti tentang pelajaran grammar khususnya present perfect?
11.Apakah siswa mendapatkan kesulitan membentuk kalimat positif dalam present perfect?
12.Apakah siswa mendapatkan kesulitan membentuk kalimat negative dalam present perfect?
49
Appendix 4
Hasil Questioner
Hari\Tanggal : Rabu, 24 Februari 2010 Nama : Ibu Setiana S.W Sitepu S.Pd. Jabatan : Guru Bahasa Inggris
Tempat : Ruang Guru
A. Pertanyaan :
1. Metode apa Ibu gunakan dalam pengajaran bahasa Inggris khususnya tentang present perfect?
Jawaban: Dengan cara menghapal rumus atau dengan cara yang lain? Metode yang saya gunakan adalah metode komunikatif sesuai dengan kurikulum KTSP yang lebih menekankan kepada bagaimana cara siswa aktif berinteraksi di dalam kelas dengan menggunakan bahasa Inggris. Ya, terkadang saya menyuruh mereka menguasai materi grammar dengan cara menghafal namun kadang juga dengan cara menganalisa bacaan yang terdapat materi gammar yang hendak dipelajari.
2. Kesulitan apakah yang menjadi kendala Ibu ketika mengajarakan materi present perfect?
Jawaban: Kendala yang sering saya temukan adalah kurangnya keterampilan beberapa siswa dalam hal vocabulary terkadang mereka kurang memahami konteks, karena mereka tidak mengerti kosa kata yang dimaksud. Selain itu, Murid juga terkadang masih mengalami kesulitan untuk membedakan kata kerja.
3. Apakah siswa mendapat kesulitan dalam menerima materi tersebut?
4. Bagaimanakah Ibu mengatasi kendala tersebut?
Jawaban: Untuk mengatasi kesulitan-kesulitan tersebut, saya memperbanyak latihan tentang materi grammar dalam bentuk menjabarkan rumus-rumus yang mudah dalam setiap materi grammar khususnya materi present perfect dan dalam perubahan past participle.
5. Bagaimana antusiasme siswa terhadap mata pelajaran Grammar khususnya present perfect?
Jawaban: Mereka merespon, walaupun tidak semua siswa merespon hanya sebagian siswa karena meraka merasa bosan ketika belajar grammar khususnya present perfect. Mereka harus menghafal rumus dan perubahan kata kerja.
6. Apakah siswa dapat membentuk kalimat positif dalam present perfect?
Jawaban: Bisa, karena hanya menggikuti rumus yang ada, sehingga siswa dapat membentuk kalimat positif berdasarkan pola.
7. Apakah siswa dapat membentuk kalimat negative dalam present perfect?
Jawaban: Bisa, karena hanya menggikuti rumus yang ada, sehingga siswa dapat membentuk kalimat negative berdasarkan pola.
8. Apakah siswa dapat membentuk kalimat interrogative dalam present perfect?
Jawaban: Bisa, karena hanya menggikuti rumus yang ada, sehingga siswa dapat membentuk kalimat intorrogative berdasarkan pola.
9. Apakah siswa dapat menguasai perubahan verb ketiga?
Jawaban: Tidak semua siswa menguasai perubahan kata kerja ketiga hanya sebagian siswa.
10.Apakah yang Ibu lakukan ketika siswa tidak mengerti tentang pelajaran grammar khususnya present perfect?
51
11.Apakah siswa mendapatkan kesulitan membentuk kalimat positif dalam present perfect?
Jawaban: Tentu saja ada siswa yang menggalami kesulitan dalam membentuk kalimat positif khususnya dalam perubahan kata kerja ketiga dikarenakan kemampuan siswa berbeda-beda. Namun tidak semua siswa, karena sebagian dari mereka adalah siswa-siswa yang memiliki kemampuan akademis yang baik yang juga ditunjang dengan mengikuti belajar bahasa Inggris di luar jam sekolah seperti kursus. Dan bagi mereka yang kurang dapat berdiskusi belajar bersama dengan teman yang mampu ketika menemui kesulitan.
12.Apakah siswa mendapatkan kesulitan membentuk kalimat negative dalam present perfect?
Jawaban: Tentu saja ada siswa yang menggalami kesulitan dalam membentuk kalimat negative khususnya dalam perubahan kata kerja ketiga dikarenakan kemampuan siswa berbeda-beda. Namun tidak semua siswa, karena sebagian dari mereka adalah siswa-siswa yang memiliki kemampuan akademis yang baik yang juga ditunjang dengan mengikuti belajar bahasa Inggris di luar jam sekolah seperti kursus, dan bagi mereka yang kurang dapat berdiskusi belajar bersama dengan teman yang mampu ketika menemui kesulitan.
13.Apakah siswa mendapatkan kesulitan membentuk kalimat interrogative dalam present perfect?
yang kurang dapat berdiskusi belajar bersama dengan teman yang mampu ketika menemui kesulitan.
Tangerang, 24 Februari 2010
53
Appendix 5
Questioner
Hari\Tanggal : Rabu, 24 februari 2010
Nama :
Jabatan : Siswa
Tempat : Dalam Kelas
A. Pertanyaan :
1. Apakah Anda menyukai pelajaran Grammar Khususnya Present Perfect? 2. Apakah Anda bisa mengikuti dan memahami penjelasan guru Anda
tentang Present Perfect?
3. Apakah sebelumnya anda pernah mempelajari grammar terutama Present Perfect?
4. Apakah Anda mengalami kesulitan dalam mempelajari Present Perfect dalam perubahan verb (kata kerja ketiga)?
5. Apakah Anda mengalami kesulitan membentuk kalimat positif?
6. Apakah Anda mengalami kesulitan dalam membentuk kalimat negatif? 7. Apakah Anda mengalami kesulitan dalam membentuk kalimat
interrogative?
8. Apakah yang Anda lakukan ketika anda tidak mengerti tentang pelajaran grammar khususnya present perfect?
9. Dimanakah letak kesulitan Anda dalam mempelajari grammar terutama present perfect?
Appendix 6
Hasil Questioner
Hari\Tanggal : Rabu, 24 Februari 2010
Nama :
Jabatan : Siswa
Tempat : Dalam Kelas
A. Pertanyaa :
1. Apakah Anda menyukai pelajaran Grammar Khususnya Present Perfect? A. Ya, karena pelajarannya tidak terlalu sulit.
B. Ya, Sempet suka, Susah sempet pusing. C. Tidak.
D. Ya, karena cukup mudah.
E. Saya tidak terlalu menyukainya karena terlalu menyulitkan perubahan kata kerjanya.
F. Tidak.
G. Ya, pelajaran itu tidak terlalu sulit. H. Ya, pelajaran itu tidak terlalu sulit. I. Tidak, karena baru kali ini.
J. Ya, karena pelajaran yang menyenangkan, mudah dipahami dan bisa menambah pengetahuan.
K. Ya, karena soalnya mudah.
L. Lumayan, karena engga susah-susah banget. M. Suka, karena mudah dimengerti.
N. Ya, saya menyukainya, karena saya menyukai pelajaran bahasa Inggris.
O. Tidak, karena baru kali ini. P. Yah, tapi sedikit sulit.
Q. Yah, karena agak mudah dimengerti. R. Ya, karena saya ingin bisa.
S. Yah saya sangat menyukainya, tetapi saya masih banyak belum memahaminya.
T. Ya, karena agak mudah dimengerti. U. Tidak, karena saya belum terlalu bisa. V. Ya, saya cukup menyukainya.
W. Ya, karena gurunya menjelaskan secara detail. X. Yah, lumayan mudah.
Y. Yah, gurunya menyampaikan secara mudah, sehingga saya suka. Z. Tidak, karna tidak tau.
2. Apakah Anda bisa mengikuti dan memahami penjelasan guru Anda tentang Present Perfect?
A. Ya, karena pelajarannya tidak membosankan.
55
C. Yah, karena mudah dipahami.
D. Bisa karena guru menjelaskannya dengan sangat jelas.
E. Saya memahaminya tetapi ketika sudah keluar dari pembahasan itu, saya akan lupa.
F. Yah, karena mudah dipahami.
G. Ya, karena pelajarannya tidak membosankan. H. Ya, karena mudah memahaminya.
I. Ya, karena mudah dipahami. J. Ya, karena mudah dipahami. K. Ya, karena mudah dipahaminya.
L. Ya, karena guru menjelaskannya dengan jelas. M. Tidak, karena tidak terlalu sulit.
N. Saat guru menjelaskan saya mengerti dan bisa mengikutinya, tetapi mudah lupa jika tidak dipelajari lagi.
O. Yah, karena mudah dipahami.
P. Ya, karena pelajarannya mudah dipahami. Q. Ya, saya dapat memahaminya.
R. Saya kurang bisa tetapi, saya berusaha untuk memahaminya. S. Semoga saja, saya bisa memahaminya.
T. Ya, saya dapat memahaminya. U. Sedikit binggung
V. Insya Allah saya bisa memahaminya. W.Ya, karena gurunya tidak membosankan. X. Bisa, karena gurunya asik.
Y. Yah, karena gurunya menjelaskannya mudah dipahami. Z. Sedikit-sedikit.
3. Apakah sebelumnya Anda pernah mempelajari grammar terutama Present Perfect?
A. Belum, karena baru kali ini. B. Tidak pernah mempelajarinya. C. Yah.
D. Tidak, saya belum pernah mempelajarinya, baru sekarang ini.
E. Pernah, sewaktu saya SD, sebelumnya saya pernah belajar present perfect tense.
F. Ya, gampang.
G. Belum, karena baru kali ini. H. Tidak, karena baru kali ini. I. Ya.
J. Belum pernah, karena memang belum diajari. K. Tidak, karena baru kali ini.
L. Belum, baru kali ini.
M. Belum, hanya di sekolah saja. N. Belum, baru saat ini ajah.
Q. Ya, waktu saya masih SD saya pernah mempelajarinya. R. Belum.
S. Belum pernah, baru kali ini saya mempelajarinya. T. Yah, waktu saya SD, saya pernah mempelajarinya U. Belum pernah
V. Belum, baru kali ini. W.Tidak, baru kali ini.
X. Belum, sebelumnya kita belum pernah mempelajarinya. Y. Tidak, karena baru kali ini.
Z. Belum dipelajari.
4. Apakah Anda mengalami kesulitan dalam mempelajari Present perfect dalam perubahan verb (kata kerja ketiga)?
A. Tidak, karena mudah dipahami. B. Sulit banget, tadi ajah engga ngerti. C. Tidak, karena sudah paham.
D. Ya, karena ada yang beraturan dan ada yang tidak beraturan. E. Iya, karena saya kesulitan menghafalkan rumusnya.
F. Tidak, karena sudah paham. G. Tidak, karena mudah dipahami.
H. Ya, karena verb kata kerja ketiga sangat sulit. I. Ya, karena tidak mengerti.
J. Ya, karena mengubah bentuk kata menjadi verb 3 itu sangat sulit. K. Tidak, karena sudah paham.
L. Lumayan, karena masih kurang paham dalam perubahan verb. M. Ya, perbedaan kata yang cukup rumit.
N. Ya, binggung.
O. Yah, sungguh sangat sulit.
P. Ya, perubahan kata yang membuat saya sangat sulit. Q. Ya, menggalami kesulitan.
R. Ya, untuk penempatan verb ( kata kerja) S. Yah, karena ini sulit untuk dipahami. T. Ya, menggalami kesulitan.
U. Yah, saya belum terlalu bisa.
V. Yah, perubahan katanya membuat saya terkecoh.
W.Yah, karena menggunakan perubahan verb 3 (kata kerja ketiga). X. Yah, karena saya belum bisa merubah verb3 (kata kerjanya) Y. Tidak, karena cara guru menjelaskan membuat saya paham. Z. Yah, karena belum mengerti.
5. Apakah Anda mengalami kesulitan membentuk kalimat positif? A. Tidak, karena mudah.
57
J. Tidak terlalu sulit, karena soalnya tidak terlalu sulit. K. Tidak, karena mudah.
L. Tidak, karena sudah paham. M. Tak, karena mudah dimengerti. N. Tidak, jika sudah tahu verbnya. O. Yah, karena sangat sulit. P. Masih binggung.
Q. Tidak, karena hanya mengikuti kata yang sudah ada. R. Tidak, karena saya sudah mempelajarinya terlebih dahulu. S. Sedikit.
T. Tidak, karena hanya mengikuti pola yang sudah ada. U. Yah, karena binggung.
V. Yah.
W.Iyah, karena rumusnya tidak hapal.
X. Iya. Karena masih binggung dengan kalimat present perfect. Y. Tidak, hanya mengikuti rumus.
Z. Yah, susah sekali.
6. Apakah Anda mengalami kesulitan dalam membentuk kalimat negatif? A. Tidak, karena tingal ditambah kata not.
B. Orang jarang di pelajari, gimanah mau bisa kalau gituh. C. Yah.
D. Tidak kerena cukup mudah.
E. Tidak terlalu sulit karena sebelumnya saya pernah mempelajarinya. F. Yah, sudah ngerti.
G. Tidak, karena tinggal di tambah kata not saja. H. Tidak, karena mudah.
I. Ya, susah dipahami
J. Tidak terlalu sulit karena hanya menambah kata not. K. Tidak, karena hanya ditambah not saja.
L. Tidak, karena sudah paham.
M. Tak, karena tinggal ditambah not saja. N. Tidak, jika sudah tahu verbnya.
O. Yah, membentuk kalimat negative tuh sangat sulit. P. Sedikit mengerti.
Q. Yah, saya masih binggung dalam perubahan katanya.
R. Tidak, karena saya sudah dapat memahami cara penempatan kata. S. Saya hanya sedikit memahaminya.