THE APPLICATION OF INFORMATION GAP TECHNIQUE TO IMPROVE SPEAKING SKILL AT THE SECOND GRADE OF SMA N 4
BANDAR LAMPUNG
(A Script)
By
Cintia Arinanda Prima Putri
FACULTY OF TEACHER TRAINING AND EDUCATION UNIVERSITY OF LAMPUNG
i ABSTRACT
THE APPLICATION OF INFORMATION GAP TECHNIQUE TO IMPROVE SPEAKING SKILL AT THE SECOND GRADE OF SMP NEGERI 4 BANDAR
LAMPUNG
By
Cintia Arinanda Prima Putri
Speaking is one of difficult subjects for students in learning language because it has many elements such as pronunciation, vocabulary, grammar, fluency, comprehension and accurancy used to carry out a communication among the people. Some problems in speaking are still experienced by the students of Junior High School. They still look hesitate to interact with their friends and their teacher by using English. This might happen because they are shy or afraid of making mistakes in their prnounciation and grammar.
The aim of this research was to find out the application of Information Gap technique in improving students’ speaking skill escpecially in terms of pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar from the analysis of quantity and quality of speaking. Information gap technique has many various of tasks, but in this research the researcher only gave three different tasks of information gap activity to the students and tried to analyze quantity and quality of speaking. The research was conducted at SMPN 4 Bandar Lampung. The sample was the students of eighth grade ( class 8.L) in academic year of 2014/2015.
This study used quasi experimental design with repeated measured deisgn. To collect the data, speaking test applied that was administered three different topics with three treatments in each meetings. There were two raters to judge the students’ speaking performance. Repeated Measure T-Test was used to analyze the data and the hypothesis testing at the significant level of 0,05.
ii
mean score was 66,58 and students’ mean score in the second topic that was finding difference topic was 67,64 while in topic 3 that was giving direction topic,
student’ mean score was 68,37. And the analysis of Repeated Measure T-test shows that there is significant difference and significant improvement of students’ speaking skill in every topics. Moreover in analysis of quantity and quality of speaking, there was a significant difference in three topics, and topic which has better pronounciation, vocabulary, and grammar and could produce more time of speaking and turn taken was topic three (giving direction topic).
In according with the results, it is suggested that is one of the weak aspect of speaking was pronunciation and also grammar. To improve these two elements, teacher should apply more effective strategies is dealing with these, for example
THE APPLICATION OF INFORMATION GAP TECHNIQUE TO IMPROVE SPEAKING SKILL AT THE SECOND GRADE OF SMA N 4 BANDAR
LAMPUNG
By
CintiaArinanda Prima Putri
A Script
Submitted in a Partial Fulfillment of The Requirement for S-1 Degree
in
The Language and Arts Department of Teacher Training and Education Faculty
FACULTY OF TEACHER TRAINING AND EDUCATION UNIVERSITY OF LAMPUNG
iii
CURRICULUM VITAE
The researcher, Cintia Arinanda Prima Putri was born on Januari 20th 1994 in Bandar Lampung. She is the only child of a wonderful couple, Defrizal and Dra. Kemala Sari. She started her study from Kindergarden at TK kartini in 1998 and graduated in
1999. In the same year, she was registered at Elementary School of SDN 1 Rawa Laut and graduated in 2005. She continued her study at SMP Negeri 5 Bandar Lampung and graduated in 2008. She continued at SMA Negeri 1 Bandar Lampung and
graduated in 2011. In the same year in 2011 the reseacher was given a chance to come into English Education Study Program, Language and Art Education
v
MOTTO
“ A person who never made a mistake never tried anything new”
iv
Dedication
with love and appreciation, this script is proudly dedicated to :
The greatest inspirations in my life “MAMI PAPI’’
My beloved Grand Mother
My big family
My special love
My brotherhood and sisterhood in English Department 2011
vi
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Alhamdulilahirabbil ‘alaamiin
,
The writer would like to acknowledge her deepest praise to the almighty Rabb , the most merciful and the most gracious, ALLAH SWT for tremendous blessing that enable her to accomplish this script entitled “The application of Information Gap technique to improve speaking skill atThe Second Grade of SMP N 4 Bandar Lampung’’ is submitted as a compulsory
fulfilment of the requirement for S-1 degree at Department of Language and Arts of Faculty of Teacher Training and Education, University of Lampung.
The researcher would like to express her gratitude to all persons who helped and supported the researcher until the completion of this research.Firstly, thewriter would like to dedicate her since gratitude and respect to Drs. Hery Yufrizal M.A., Ph.D., as the first advisor for his willingness to give assistance, ideas, encouragement, constructive idea and scientific knowledge within his time during the research writing process. She also wants to extend his gratitude to Drs. Basturi Hasan, M.Pd., as the second advisor, for his kindness, suggestion, and patience in guiding the writer in finishing this script. Her thankfulness is also addressed to Drs. Sudirman, M.Pd., as the examiner for his invaluable suggestion, criticism, and gave knowledge to make the script more valuable. And for all the lectures of English Department of study program.
vii
The researcher would like to express her spesial gratitude and respect to her beloved big family of English Departement 2011 especially for her best friends Kinanti, Cahyati Sri W, Novaliana Citra A. Thanks you so much for being such a great companion during our togetherness at campus. And also for my beloved best friends in senior high school Pristiani A, Ivat Rachmawaty, Dani Syahfitri for their support and motivated reseacher during this script writing process. And for my spesial love, M.Sacha Wijaya thank for your support, warmth, care, and for coloring my life. The researcher also thank to my close friends in PPL Ayu Mayasari, Melani Novrita, Ismah Fatimah, Isti Khoiriyah, Doddy Ferdiansyah, M.Panji W, Putri Ratna S, Rika Emilda, Ahmad Wahyudi for your motivation for me.
The gretest honour and appreciation would be finally dedicated to her beloved mother and father to all their greatest love, cared, spirit motivation. Her sincere thanks are also dedicated to her beloved cousins, Desria Monica, Arin Ferlina, Ria Anggraini, Nurma Puspita, Jeta Desia, Jesica Aprilia , Rahmi Novia, Jenisa Tri Oktavia, Sylvia Trinanda and all his family without any exception.
Finally, the writer realizes that this script still has some weakness. Therefore, critics and suggestions are invited for its improvement. Hopefully, this script cangive benefit to the readers or those who want to carry out futher research.
Bandar Lampung, September 2015
The writer
viii
2.2.Aspects ofSpeaking ... 10
2.3.Types of Speaking ... 15
2.4.Technique of Teaching Speaking ... 21
2.5.Concept of Information Gap Technique ... 21
2.6.Teaching Speaking by Information Gap ... 23
2.7.Type of Information Gap Activities ... 24
2.8.Procedure of Teaching Speaking through Information Gap ... 26
2.9.The Advantages of Information Gap ... 29
2.10.The Disadvantages of Information Gap ... 30
2.11. Theoritical Assumption ... 31
2.12. Hypothesis ... 31
III. METHOD 3.1.Design ... 32
3.2.Subject of The Research ... 33
3.3.Data Collecting Technique ... 33
3.4.Research Procedure... 34
ix
3.6.Validity and Reliability of Instrument ... 36
3.6.1 Validity of the Instrument ... 37
3.6.2 Reliability of the Instrument ... 37
3.7.Scoring Data ... 39
3.8.Data Analysis ... 41
3.9.The Schedule of The Research ... 42
IV. RESULT AND DISCUSSION 4.1.The Classroom Activities ... 43
4.2.Result of Speaking Task ... 48
a. Validity of Speaking Task ... 49
b. Reliability of Speaking Task ... 49
4.3.Analyzing Quantity and Quality of Speaking ... 51
4.3.1 Quantity of Speaking ... 51
4.3.2 Quality of Speaking ... ... 55
4.3.3 Result of Hypothesis Testing ... 60
4.4.Analysis aspect of speaking ... 62
4.5.Discussion of the finding ... 64
4.5.1 The application of Information Gap ... 64
4.5.2 Evaluating The Tasks ... 66
4.5.3 Evaluating Learning Process ... 71
V. CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION 5.1.Conclusions ... 76
5.2.Suggestions ... 78
REFERENCES ... 80
xii
5 Table of Score Inter-Rater Reliability of 2nd Topic... 86
6 Table of Score Inter-Rater Reliability of 3rd Topic ... 88
7 The Score of Each Aspect in the 1stTopic ... 90
8 The Score of Each Aspect in the 2nd Topic ... 91
9 The Score of Each Aspect in the 3rd Topic... 92
10 The Comparison of Each Topic, 1st Topic, 2nd topic, 3rd Topic .. 93
11 The Analysis of Quantity of Speaking and Quality of Speaking 94 a. Analysis Time of Speaking ... 94
b. Analysis Turn Taking ... 95
c. Analysis Aspect of Speaking (Pronunciation) ... 97
d. Analysis Aspect of Speaking (Vocabulary) ... 98
e. Analysis Aspect of Speaking (Grammar) ... 99
12 Lesson Plan 1 (Finding Missing Information Topic) ... 101
13 Speaking Task of 1st Topic ... 105
14 Students’ Voice Transcription In Evaluating 1st Topic ... 109
15 Lesson Plan 2 (Finding Difference Topic) ... 113
16 Speaking Task of 2nd Topic ... 117
17 Students’ Voice Transcription In Evaluating 2nd Topic ... ... 121
18 Lesson Plan 3 (Giving Direction Topic) ... 125
19 Speaking Task of Topic 3 ... 129
xi
LIST OF CHART
Chart Title Page
x
LIST OF TABLE
Table Title Page
2.1 Procedure of Teaching Speaking ... 26
3.1 Scoring Data from Aspect of Speaking Test ... 39
3.2 Rating Sheet Score ... 40
3.3 Schedule of The Research ... 42
4.1 Pair Sample T-test (Time of Speaking) ... 52
4.2 Pair Sample T-test (Turn Taking) ... 54
4.3 Pair Sample T-test (Pronunciation) ... 55
4.4 Pair Sample T-test (Vocabulary) ... 57
4.5 Pair Sample T-test (Grammar) ... 58
4.6 The Mean of Students’ Score in Quantity of Speaking ... 67
I.INTRODUCTION
This chapter present about the background of the research, the research
question(s), objective of the research, uses of the research, scope of the research, and definition of term.
1.1Background of the problem
English is taught in every level of education from kindergarden to university. The English knowledge will help people to be easier to current issue and to get better
in life. The demand in English curriculum of SMA states that SMA/MA students should be able to use language in informational level. Arriving at informational level means that the students are expected to be able to access knowledge and
information from the target language (English) by their language skills. There are four skills of language should be taught by English teacher of SMA/MA, i/e., listening, speaking, reading, and writing (Depdiknas, 2006:307). After the
students mastering listening, they will try to read and after that they will start to speak.
Recently, many students especially in Indonesian students think that to
2
exchange information and ideas namely oral ability or in other words is speaking
skill.
Speaking is one of important language skills for students in learning language because speaking is one of the ability to carry out a conversation in language. Speaking is communication or conversation, between two people are exchanging
information or they have a communication or conversation needs (Doff, 1987). As we know that speaking or oral ability is specific ability to give a speaker chance
to express ideas and opinion with other. Speaking is also called productive skill. Everything which has been read and listened can be expressed through speaking.
Moreover, it is useless to master a number of vocabulary items and grammar if the students can not be implemented in communicating and interacting with others. It
implies how essential speaking in communication. During writer’s experince for teacher training pratice (PPL) in SMP N 1 Lumbok Seminung Lampung Barat for three months, it indicated students are difficult to produce language and express
their ideas in English orally, students did not get used to speak English in their daily English class. There are some factors why that problem occured. First,
students had difficulty to speak the English word. Mostly, they are still influenced by their mother tounge. The second, the students were not fluent in speaking, because they usually have problem in grammar and pronunciation in speaking.
3
feel nervous and afraid when they are asked to speak English, they are shy to
speak to the other people because lack of oral ability.
Unfortunately, during the observer’s observation in SMP N 4 Bandar Lampung,
the observer has found that there were many students show up in the classroom without having developed a confident to speak in English. In fact, some junior
high school students found also some difficulties to speak in English. To be more concrete, Nugraha’s research (2010) also found that some students were not able
to communicate orally well because they were lack of vocabulary and not confident while speaking in English, and also they needed more practice. Relating
to the problems faced by the students above, teachers have to teach to speak English to overcome those problems.
In addition, another factor that causes this problem is related to the teacher. There are some teachers do not have motivation in learning process, this make students feel secured to study in English class. Not only that but also the teacher does not
have time to their students in classroom interaction. Teacher only explains the lesson but they do not give chance to the student to practice their English. The
teacher frequently never uses new method or new way jot suitable to teach students. Therefore the students will be unmotivated, bored, and difficult in
learning speaking.
In fact, there are many techniques appropriate to teach English skill, which is
4
technique which make students or learners interest, motivate, and active in
learning process. It depends to the teacher’s choice of what technique would be suitable with the lesson that the teacher is going to teach, although, as we know
that each technique has each strength and weakness.
So in this research, the researcher used information gap activity as media in
teaching speaking. In the usage of this technique, it could help students to speak actively in the class by using a conversation, so information gap should be done in
a pair or group work. According to Neu and Reeser (1997) in information gap activity, one person has certain information that must be shared with others in
order to solve problem, gather information or make decisions. By applying information gap technique, the students will be comfortable to speak everything, teacher only gives simple explanation about the activity and give example
vocabulary needed for this activity. Then, the students can get opportunity to develop their speaking ability and they will have easier and succeed in their study. Information gap technique has many various of task such as finding difference,
finding missing information, discovering idential pairs, and giving direction. But in this research the writer tried to analyze quantity and quality of speaking based
5
1.2Formulation of the problem
From the description in the background of study, the problem arise are as follows: 1. Is there any differences of students’ achievement in speaking skill
especially in terms of pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar when they were given three different topics ?
2. In terms of Quantity of speaking, which tasks of information gap
technique could produce more time of speak and turn taken ?
3. In terms of Quality of Speaking such as prononciation, grammar, and
vocabulary, which tasks of information gap technique could produce better pronounciation, grammar, and vocabulary ?
1.3Objective of The Research
Basically, the objectives of the research are as follows:
1. To find out whether will be any differences of students’ achievement in speaking skill especially in terms of Pronunciation, Vocabulary, and Grammar.
2. To find out which task of information gap technique to improve speaking skill based on Quantity of Speaking.
3. To find out which task of Information Gap technique can improve speaking skill based on Quality of Speaking, pronounciation, Grammar, and Vocabulary.
1.4Uses of The Research
6
There are two important types in this research, these uses can be described as
follows:
1.4.1 Theoretically
The result of this research can be used to give information and knowledge to the readers about the application of information gap to improve speaking skill in teaching learning process and it will give contribution to successful teaching
learning English especially speaking skill. For the other researcher, this might be can be used as a reference who will concentrate on student’s speaking ability .
1.4.2 Practically
The result of this research can give positive effect of teacher’s knowledge about using new method in teaching learning process. It is also to encourage English
teacher to seek of the student’s difficult in speaking skill. It can be motivate the
students to improve their interest in speaking and students get significant result.
This technique is able to make the students enjoy when they speak and they do not feel bored. So the students can be comfortable to speak English.
1.5Scope of The Research
This research was intended to find out quantity and quality of speaking by given
three different tasks of Information Gap. This research is a qualitative research and has been conducted at SMP N 4 Bandar Lampung. The researcher has
choosen the class by Purposive Random Sampling through lottery drawing and it was intend to find out whether there is a significant improvement between three different topics given by teacher and to see which topic get the highest gain from
7
student’s oral ability used three aspects namely pronunciation, vocabulary, and
grammar.
1.6Definitions of Terms
There are in terms needed to be defined in order to avoid misunderstanding and ambiguity, they are :
Speaking
Speaking is oral communication. It is two ways process between speaker and listener and involves productive and reactive skill of understanding (Byrne, 1984)
speaking is an activity which is done by one speaker to one listener or more in many different contexts using speech organ, in order to get some information
which can be presented through ideas, thoughts, opinion, and feeling orally.
Information Gap
Information gap activity is the process of completing the information through exchanging the information with their friends by asking and talking each other in order to get complete information.
That was introduction of the research, in includes the explanation about the background, research problem, objectives of this research, use of the research,
8
II. LITERATURE REVIEW
The fundamental study should be undertaken based on some relevant theoretical
reviews. The study would be conduct based on reviews and discussions of some theories. There are the following theoretical reviews: (1) concept of speaking
skill, (2) type of speaking, (3) concept of teaching speaking by information gap (4) the advantages and disadvantages of teaching speaking through information
gap, and (5) Hypothesis testing. Those are the literature reviews that will be discussed in this sub chapter.
2.1 Concept of Speaking Skills
Speaking is very important ability in doing daily activities because people can react to other person and situation and express our ideas, thought, and feeling
through spoken language. (Pollard, 2008) says that one of the most difficult aspects for students to master is speaking. It is difficult when learners have to
consider and think about their ideas, what to say, language, grammar, vocabulary, pronunciation in one time and how to react with a person who communicates with them.
According to Haris (1974) said that speaking is encooding process whereby, we
9
language. So we can produce spoken message to someone. So, here speaking
situation involves a speaker who puts a message with words or someone that has content and a listener. Meanwhile, Byrne (1984) state that speaking is oral
communication. It is a two way process between speaker and listener and involve productive and reactive skill of understanding. Based on this idea it is understood that through speaking someone can communicate or express what she or he wants
in order to understand one another.
In addition, (Brown, 2004) says that speaking is a productive skill that can be directly and empirically observed, those observations are in variably colored by the accuracy and effectiveness of the test-takers listening skill, which necessarily compromises the reliability and validity of an oral production test. Moreover, he divides speaking skill into two, namely: micro and macro skills of speaking. The micro skills refer to producing the smaller chunk so language such as phonemes, morphemes, words, collocations, and phrasal units. The macro skill simply the speaker’s focus on the larger elements: fluency, discourse, function, style, cohesion, nonverbal communication and strategic options.
In relation to this, Lado (1976: 240) stated that speaking as an ability to converse or to express a sequence of ideas fluently. Its means that in the process of
speaking there must be at least two people, one is the speaker and one other as the listener. In communication or speaking process, the speaker must be able to share
10
can express her or his idea, emotions and reactions to other or situation and
influence other person. Furthermore, someone can communicate or express what he or she wants from other and response to other speaker. It means that in order to
express someone’s ideas, the speaker must also attend the aspect of speaking, in
order that the massage is understandable to the listener.
Tarigan (1982: 18) refers to speaking as the ability to produce articulation, sounds or words to express, to say, to show, and to think about ideas, taught and feeling.
In summary, speaking skill is the ability of the students or people to communicate their ideas orally. In other words, the listener can receive the message and reacts
communicatively to the speaker by producting the sound and by using correct pronunciation, the listener will be able to understand or catch the ideas and the meaning communicate by the speaker.
2.2 Aspects of Speaking Skill
There are basically six components of these skills they are :
1. Pronounciation refers to be the person’s way of pronounciation words. Someone who learns English as foreign language must be able to use English
pronounciation as well as other skills (Oster,1985: 431). To be concrete below is pronunciation have various aspect and would be desrcibe below based on (Kenwothy, 1987) :
a. Combination of sound
All learners expect English to have new and different sounds, in fact they
11
the „th’ sound in „the’ and „three’. Sometimes sounds occurs in groups.
Two consonants occur at the end of the word „salt’. When this happens within a word it is called a consonant cluster.
b. Word strees
In words have more than one syllable, one of these is made to stand out more than the other(s). This is done by saying the syllable slightly louder,
holding the vowel a little longer, and pronouncing the consonant very clearly these features combine to give that syllable prominence or stress.
For example in „table’, „isn’t’, and „any’ the first syllable are stressed.
When speaking, it is important to put the stress on the correct syllable.
Otherwise, it would sound unnatural, and might even be difficult to understand. Here are some example of the word stress of some common word (the stress part is bold)
-water : wa’ ter -potato: po’ta to -together: to’geth er -before: be’fore
c. Rhythm
Having been introduced to word stress, learners will be ready to move on to the rhythm of English. There are group of syllables, just like bars
music, and within each group there are strong and weaker beats. There is a tendency in English for the strong beats to fall on nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverb (word that carry a lot of meaning) and for the weak
12
da Da da da da Da da da Da da
The following short sentence has the rhythm weak-weak, strong-weak-weak:
What do you think of it?
Da da da Da da da
So, it actually has a “waltz rhythm”
d. Intonation
Intonation is the name given to sentence stress, or what is sometimes
called the „music of the language’. Speech is also like music in that it
uses changes in pitch, speaker can change the pitch of their voice as they
speak and they can make it higher or lower. They can even jump up suddenly in pitch. So pitch has a melody called intonation. Speaker use pitch to send various message. For example, if A had said „there isn‟t any salt on the table‟ B might have repeated the same words but with
gradually rising pitch and this would have had the effect of sending
message such as „Are you sure –I‟m amazed –I was sure I put it there”
The correct use of the following features will determine the pronunciation grade are combination of sound, word strees, rhythm, and intonation. I have evaluated
them in this research.
2. Grammar which is the rule of study of language inflection. It is a system of
units and patterns of language (Lado, 1969: 221). In relation to contexts, a speaker should consider the following criteria:
13
b. Who the audience is
c. Where the communication takes place
d. What communication takes place before and after a sentence in question
e. Implied versus Literal Meaning f. Styles and Registers
The utility of grammar is also to learn the correct way to gain expertise in a
language in oral and written form. The students are intended to speak English which is grammatically true. However, the students often make some mistakes in
putting to be and putting verb in sentence. For example: I‟m sit in my class. The sentence should be I am sitting in my class. They sometimes wrong to use to be
and verb with adjective, not with verb. The other example is : you was my friend. The sentence should be you were my friend. The students sometimes wrongly choose to be in subject.
3. Vocabulary refers to the words used in language. Phrases, clauses, and sentence are built up by vocabulary. In short, vocabulary is very important because without words we can not speak at all (Wilkins, 1983: 111). Vocabulary is divided into two parts, close class and open class. The close category is so called because it does not easily accept new word. Its mean that members are fixed and do not change. Close category/class consist of preposition, pronoun, and conjuction. Here are the example of close class : 1). I like dancing and singing (Conjuction)
2). What is your favorite food?(pronoun)
3). My home is beside the market (preposition)
14
Noun is a part of speech that identifies a person, place, thing, or idea. Here are the example of noun.
1). I love playing game (noun)
2). My hobby is reading story book (noun)
Verb is a word that express action or a stated of being. Here are the example of verb:
1). Rudi is playing football with his brother. (verb)
2). Shinta makes a cup of coffee for her father. (verb)
Adjective is a kind of word that modifies a noun. Here are the example of adjectives:
1). Kinan is a good singer (adjective)
2). I always bored if i am stay at home alone (adjective)
Adverb is
1). He study english everyday (Adverb of time)
2). My mother is cooking in the kitchen (adverb of place)
4. Fluency refers to the one who express quickly and easily (Oster, 1985: 210).
It means that when a person making a dialogue with another person, the other person can give respon well without difficulty. Fluency refers to the
smoothness of flow which sounds, syllables, words, and phrases are joined together when speaking. In the classroom, the students often speak English
with pause, they often say “ums” or “a”. They not pluent speak English in
classroom. Based on Thornbury (2005: 8) people can be said as fluent speakers if they fulfill the following features:
a. Pauses maybe long but not frequent b. Pauses are usually filled
c. Pauses occur at meaningful transition points
15
5. Comprehension denotes the ability of understanding the speaker’s intention
and general meaning (Heaton, 1991: 35). It means that if person can answer or express well and correctly, it shows that he comprehends or understand
well. For example : the students that given a question from teacher, they can answer question correctly. It means that they comprehend what teacher said. They are correct to speak and the audience can understand what they said.
6. Accurancy is related to the closeness of a measurement, within certain limits, with the true value of the quantity under measurement. Accuracy is relative.
A child in early primary isn’t capable of the same level of accuracy as an
adult. Teachers who concentrate on accuracy help their students to produce grammatically correct written and spoken English.
However, since this research focused on these aspect of speaking skill, therefore
only three elements that is pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar are deeply analyzed.
2.3 Types of Speaking skill
Brown (2001: 250) said that much of our language teaching is devoted to instruction in mastering English conversation. He classifies the types of oral
16
1. Monologue
Planned Unplanned
2. Dialogue
Interpersonal Transactional
The meaning of Monologue is the oral language involves only one people in it. There is only one person who speaks as in lectures, news casting, radio broadcast, etc. monologue can be divided into two types, planned monologue and
unplanned monologue. Planned monologue is the person who speaks use monolog which has prepared a note or text to help him or her to speak fluently. The unplanned monologue is the person who speaks in monologue does not use
any notes or texts. All words spoken emerge from the speaker’s mind naturally and spontaneously.
The meaning of dialogue is the oral language involves two or more speaker in it. Based on the function dialogue can be divided into two types, interpersonal and transactional. Interpersonal dialogue is functioned to promote social relationship
17
information.
Brown also provides type of classroom speaking performance, they are : a. Imitative
A very limited portion of classroom speaking time may legitimately be spent
generating “Human tape-recorder” speech, where for example, learner practice an
intonation contour or try to pinpoint a certain vowel sound. Imitation of this kind
is carried out not for the purpose of meaning full interaction but for focusing on some particular element of language form. For example Students listen to the
teacher and repeat the pronunciation of English words and expressions such as:
Words: Bus Terminal, police station, desk clerk, information counter, downtown
b. Intensive
Intensive speaking goes one-step beyond imitative to include any speaking performance that is design to practice some phonological or grammatical aspect of
the language. Intensive speaking can be self-imitative or it can even from part of
some pair work activity, where learners are “going over” certain forms of
language. For example directed response tasks, reading aloud, and dialogues
such as, reading aloud, When doing a read-aloud, it is best if all students have a copy of the text so that they can follow along, usually taking notes as they listen.
The teacher or a volunteer can begin reading the text, reading a few lines or a whole paragraph.
c. Responsive
A good dealt of student speech in the classroom is responsive short replies to teacher-or-student-initiated questions or comment. These replies are usually
18
authentic. For example students doing question and answer about giving
intructions and directions, and paraphrasing. Such as, “Can you tell me where is the post office in this area, please?” The answer is: “Yes, Sure, post office is
behind this restaurant.”
d. Transactional (dialogue)
Transactional dialogue, which is carried out for the purpose of conveying or exchanging spesific information is extend form of responsive language.
Conversation for example may have more of a negotiate nature to them than does responsive speech. For example Role plays, Oral interview, Discussions, and Conversation. Such as, Role-playing can be thought of as unstructured drama
(Dallman-Jones et al., 1994). In these exercises, a student looks at the topic from
the perspective of a character, who will affect and be affected by the topic. e. Interpersonal (dialogue)
Interpersonal dialogue carried out more for maintaining social relationship than for the transmission of the facts and information. The conversations are little trickier for learners because they can involve some or all of the following factors:
1.A casual register
Casual register is the informal language of a broader but still well defined
19
2.Colloquial language
Colloquial language is informal language that is not rude, but would not be used in formal situations. For example, when someone said “a soft drink”,
they called “pop”.
3.Emotionally charged language
Emotionally charged means using language that stirs the reader in some form. 4.Slang
Slang can be divided into four different types; country slang, urban slang, gay slang and common slang. Country slang is used by those who are in the rural parts of a country, while urban slang is spoken by those from the city or by
African-Americans. Gay slang is used by gays, bisexual, homosexuals or transsexuals. Common slang is used by almost everybody. Every culture and
every region has its own slang. Some of these include American slang, Costa Rican slang, Spanish slang and South African slang. English regions such as Wales, Ireland and Scotland also have their own slang. (Literary device) for
example Y‟all, wanna, gonna, and so on. 5.Ellipsis
An ellipsis proves to be a handy device when you're quoting material and you want to omit some words. The ellipsis consists of three evenly spaced dots (periods) with spaces between the ellipsis and surrounding letters or other
marks. The ellipsis can also be used to indicate a pause in the flow of a sentence and is especially useful in quoted speech. For example "I'm
20
6. Sarcasm
Sarcasm is an ironic or satirical remark that seems to be praising someone or
something but is really taunting or cutting. Sarcasm can be used to hurt or offend or can be used for comic affect. Example “I work 40 hours a week to be this poor”, “Is it time for your medication or mine”.
f. Extensive (monologue)
Finally, students at intermediate to advanced level are called on to give extended
monologues in the form of oral reports, summaries, or perhaps short speeches. In this the register is more formal and deliberative. This monologues can be planned or impromptu. For example oral persentations, story telling, retteling story, or
news event.
Information Gap is an activity where the learners should complete the missing information by talking each other. So the purpose of information gap technique is
to create a conversation or dialogue that can convey spesific information to complete the missing information. From those explanations, information gap is more suitable to used the transactional dialogue. Because transactional dialogue
which is carried out for the purpose of conveying or exchanging spesific inforamtion is extend form of responsive language. So the researcher considers to
used transactional dialogue in constructing the student’s conversation through
21
2.4. Technique of Teaching Speaking
Teaching speaking means teaching how to use language for communication, for
transferring ideas, thought, over felling to other people. Rivers(1978: 6) states that speaking is developed from the first context with the language. Thus, we have to introduce speaking with the language that we learn, because by speaking we can
transfer our ideas or thoughts to other people. Classroom activities that develop
student’s ability to express themselves through speech would therefore seem as in
important component of a language course.
It is clear that communication through language is very important to other people.
We cannot only teach what will be spoken but also the situation that we deal with. The teacher teaches speaking by carrying out students to certain situation.
For instance, the topic is “sport”, the teacher carries out to involve students’ activities in this situation. The topic here must be familliar to the students, so that the ideas and their organization are clear and the learners have an oral command
of the language need to be described the topic. It is clear that speaking is the ability to express ones though and it is one of suitable forms of communication.
There are several ways of teaching speaking that the teachers can use during teaching learning process. One of them is Information Gap Technique.
2.5. Concept of Information Gap Technique
As human being, we need to communicate and interact with other people. We
22
Therefore we share information. So, to develop the students’ speaking skills, the
researcher uses Information gap technique. The idea of the information gap technique as an organizing concept for a speaking activity is that one person has
information that another lacks. It means that the students must use English to share that information in order to accomplish a task.Information gap technique is
a technique where the students usually working in pairs, each has accessed to some information (Watcyn. J, 1995). By working together they try to solve the
whole.
Afterwards, there are three definitions of information gap. The first by Neu &
Reeser (1997) he states in information gap activity, one person has certain information that must be shared with others in order to solve a problem, gather
information or make decisions. The second is by Harmer who writes information gap is where two speakers have different bits of information, and they can only
complete the whole pictures by sharing that information because they have different information, there is a „gap’ between them. The third is by Dorit Sasson who defines that information gap activities are those in which students
exchange information in order to complete a required lesson plan activity. Most information gap activities are done in pairs, with each student having a part of the
information.
According to (Littlewood, 1981), information gap means a type of activity which
23
language to convey information known to them but not to their speaking partners
(Bailey:191). Beside that, (Sasson, 1991) state that in information gap activity, students are supposed to be working in pairs. One student will has the information
that other partner does not has and the partners will share their information. Information gap activities served many purposes such as solving a problem or collecting information. Also, each partner plays an important role because the
task cannot be completed if the partners do not provide the information the others need. These activities are effective because everybody has the opportunity to
talk extensively in the target language.
2.6.Teaching Speaking by Information Gap
One way of getting student to practice speaking is by conducting Information Gap activity in the classroom. Harmer (2007: 129) say that an Information Gap where
two speaker have different bits of information, and because they have different
information, there is „Gap’ between them. In this activity, students work in pair.
One student have information that other parther does not have and the partner will
share their information. According to Wood (2005: 47) the aim of information gap activity is to get the students to use the language they are learning to interact in
realistic and meaningful way. Besides that information gap activity also have many purposes such as solving problem or collecting information.
On the other hand, Hayriyekayi (2013) states that in information gap, each partner plays an important role because the task can not be completed if the partner do not
24
everbody has the opportunity to tal extensively in the target language. Actually
information gap gives the students opportunity to practice where there is a task to complete and speaking is the way to complete it.
Meanwhile Harmer (2007) say that the example of activities in where the information gap exists are Describe and Draw activity and find the difference. The procedure of this activity are in describe and draw, there are two students in which
each of them has different task, one as the instructor who describe the original picture to his/her partner, and the other one act a artist who draw the picture based
on his/her partner instruction. While in find the differences, two students are given to very similiar picture, then each of them will ask to share information to find the
difference between their picture.
2.7.Types of Activities Which Are Based on Information Gap
The teacher should design the speaking activity so as provide an opportunity for learners to produce language that they had recently learn. The principle underlying communicative activities is that the teacher structure the situation so
that learners have to overcome an information gap or solve a problem. Speaking activities based on information gap principle can be divided into some categories,
25
a. Discovering Idential Pairs
There are four, five, or six picture given to student A for example and student B hold a duplicate of these picture. He/she must ask question to the other to
discover which student has the picture idential to his own. b. Finding differences
The students devided into two group, students A and students B. Each students
has picture which look the same but actually they have differences. The students must discuss the picture in order to discover what the difference are.
c. Giving Direction
Student A and B have idential map but only student A has a complete map and
the other has incomplete one. Student A know the extaxt location of some bulding or othe features. He/she must direct to student B to the correct spot. d. Complementing the crossword
Students devided into two group. Two students have the same crossword in which some of the boxes are the blank. The procedure of this activity is student A ask student B and student B should ask student A in order to get word which
he/she need. When student A or student want to get word they must should explain them. They forbidden to say the words.
e. Finding Missing Information
Two student, student A and B have same text, tabular, or picture. But each student has missing information. Student A has the information needed by the
26
From those type of activities in Information gap technique, the researcher
considers to use the finding missing information, finding difference, and giving direction in her research. Because three of activities in information gap is more
easy to understand by students and does not spends much time to create the real situation and conversation by using information gap technique.
2.8.Procedure of Teaching Speaking through Information Gap Technique
Teaching speaking by using information gap technique is done by dividing the
students into pairs and they work orally with their partner to complete a given task, so the students in the class are involved directly in communicative activity. In this research, the writer made the procedures of teaching speaking through
Information Gap technique as follow:
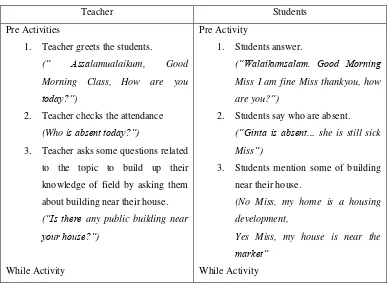
Table 2.1. Procedure of Teaching Speaking through Information Gap
Teacher Students
Pre Activities
1. Teacher greets the students.
(“ Assalamualaikum, Good Morning Class, How are you
today?”)
2. Teacher checks the attendance
(Who is absent today?”)
3. Teacher asks some questions related to the topic to build up their
2. Students say who are absent.
27
1. Teacher explain the topic
(“Well students, do you know what is it ?. Here, we can learn how to
give direction to the other people by
asking and answers questions”, for
2. Teacher explain the sentence pattern related to the topic (Asking direction and Preposition) (“Before
you doing the tasks, i will explain
you about preposition used in the
sentences, For example : beside,
behind, in front of, near, and etc).
Teacher asks the students to
someone to show the way, you must
ask clearly, so someone else can
understand what do you want. In the
other hand, if you want to give the
right direction to someone, you must
also explain it clearly, so the others
can get the right information”). Do
you know how to ask and answer
when you want to ask and help
people to show the way?
3. Teacher makes sure that the
1. Students respond the topic
(“ it is a map miss” )
28 the tasks, with divided the class into pairs and gives them handout and remind them not to look each other.
(“Oke next, to check your
understanding about the topic which
has been explained before, i want
give you task, first please choose
your partner individually. I will give
you direction)
5. Teacher asks the students to sit face to face on their desk and students B answer and after that changed so they have take turn asking for information.
(“oh ya, for students A you may
asked first after that students B
answered and then changed, do you
understand?”)
7. Teacher makes sure that the instruction have been clearly understood by everyone in the class
And the teacher asks them to do their task
(Okey class, do you undestand well
? Doing your tasks now”)
8. While the students are complete the
understand about this
topic”).
29
task, the teacher moves around the class listening unobsively and giving help if they have found some difficult.
9. When the students have completed the task, teacher asks them to see their partner task to check whether their answer is correct or not. (“ to
make sure your tasks is correct, the
next step you may check your
2. The teacher closes the meeting.
(“Okey thankyou for today students,
see you next time.
Wassalamualaikum)
The students check their partner’s answer
Post Activities
1. The students give example of asking and giving direction about some building
2.9. The Advantages of Information Gap to Improve Speaking Skill
The advantages of teaching speaking in information gap are student will have
active in role in the classroom. Both group work and pair work students is suitable
in conducting Information gap. Scrivener said that by creating classroom activities that include such information gap, we can provide activities that mimic this reason for communication, and this maybe more motivating and useful for language
30
conducting information gap in the classroom, the teaching of speaking will be
more meaningful since we can give the opportunity to the students to use the target language because they have the reason/purpose to do so.
Morever, Lan Son (2009) states that the advantages of using information gap are it
can improve student’s motivation in learning speaking because information gap
technique gives student a reason to talk, keep them thinking, and represent the real communication and factual learning. It is also can built student’s confidence.
Because this technique give less than persenting in front of class, comportable, casual and non threatened atnosphere and free interaction with peers.
2.10. The Disadvantages of Information Gap to Improve Speaking Skill
According to (weir, 1990) see that there are some problem which might appear
when information gap used in the classroom. He state that there will be have problem if in a pair work information gap, one of the participant dominates the interaction as his/her partner may have more limited opportunity to demostrate
communicate potensial. Besides that pair work in information gap is not easy to be to be administered, since in one class consist of a number of pair and each pair
cannot be paid attention at the same time, therefore noise and indiscipline such as
the use of students’ native language is difficult to be controlled.
The disadvantages of information gap in teaching speaking also is this technique spend much time, because the teachers have to make a good preparation in their
31
are appropriate in their different background. The teachers also should be able
give motivation and modeling the technique to the students in teaching learning process because information gap technique is difficult to understand by the
students.
2.11.Theoretical Assumption
From the frame of theory and explanation above, it could be assumed that applying Information gap technique in teaching speaking can give positive effect
in improving students’ speaking skill and it can also increase three aspects of
speaking; pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar. Information gap technique
can give the students easier to communicate. By utilizing information gap activity , it is assumed that students can create the interaction with others and able to communicate some information. Thus, the students would be able to communicate
well. As the result, students’ speaking ability can be increased.
2.12. Hypothesis
Concerning the theories and the assumption above, the hypothesis could be formulated as follows:
H1 : There is a significant difference in students speaking ability especially in terms of pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar among three topics which are tested for the application of Information Gap Technique. The criteria is H1 is
accepted if alpha level is lower than 0.05
Ho : There is no difference in students’ speaking ability especially in term of pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar among three topic which is tested for the application of information gap technique. The criteria is H0 is accepted if alpha
32
III. METHODS
This chapter discusses about the research methods that use in this study, such as: design, data, data source, instruments, procedure, data analysis, and hypothesis testing describe here.
3.1 Design
This research applied a Quasi-experimental design that involved periodic
measurements on the dependent variable for a group of test units. This was a quasi- experiment design, because there was no randomization of test units to treatments, and the timing of treatment presentation, as well as which test
units are exposed to the treatment, may not be within the researcher’s control (Gay, 2006). The researcher used Quasi-experimental design to identify the application of using three types of information gap technique to the students’
speaking skill. The researcher has given different topic or activity for each treatment in every test. In this research, the researcher analyzed quality of
33
The research design will be describe as follows:
X1 T1 X2 T2
X3 T3
Note: X1 : Treatment 1 (Finding Missing Information) T1 : Speaking Test 1 X2 : Treatment 2 (Finding Difference) T2 : Speaking Test 2
X3 : Treatment 3 ( Giving Direction) T3 : Speaking Test 3
The researcher has given three treatments that is teaching speaking by using information gap technique to the students which has given three different topics
and three different tasks. After that, the researcher analyzed how the implementation of information gap in improved speaking skill in term of quality of speaking and quantity of speaking.
3.2 Subject of The Research
Subject of this research was the second year students of SMP N 4 Bandar
Lampung in academic year of 2014/2015. The researcher used one class as the subject of the research. The class was 8L that consist of 27 students.
3.3 Data Collecting Technique
34
time of speaking and turn taking. In collecting the data, the researcher would be
the following steps:
1. Recording
The researcher recorded the students’ speaking skill during treatment in each topic by using voice recorded as the recording tool.
2. Transcribing
The researcher transcribed the students’ speaking skill from the audio
recording that has been conducted in order to investigate the quality of
speaking and quantity of speaking to find which topic of information gap is the most effective to improve speaking skill.
3.4Research procedure
In collecting the date, the researcher follows the following steps:
1. Determining the subject
In this research, the researcher has conducted at SMP N 4 Bandar Lampung as the population. The subject was class VIII L, there were 26
students. The researcher only choose one class as the subject of the research.
2. Finding and Selecting Materials
The researcher has choosen some of the materials from the students’ book based on the syllabus. The materials were about finding missing
35
three treatments in each meetings. in finding the effect of information gap
technique to improve students’ speaking skill. 3. Conducting treatment by using Information Gap
In this research, the treatments were administered in three meetings in which 90 minutes that conducted three different topics in every meeting.
The topic used in the first treatment was about “Finding Missing
Information” , the second topic was about “Finding Different”, and the
third topic was about “Giving Direction”. In every treatment, the
researcher asked the question related to the topic. 4. Analyzing the task Result
After scoring the students’ performance, the researcher compared the
result of each topic, to see the improvement of students’ speaking skill
from 1st topic until 3rd topic in each aspects of speaking that was pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar.
5. Analyzing the quality and quantity of speaking
After scoring students’ work and transcribing the students speaking, the
researcher analyzed quality of speaking in terms of pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar and quantity of speaking in terms of time of
speaking and turn taking using SPSS Repeated measure T-Test or Paired Sample Test. The researcher analyzed the mean of every task by compare from each topic to find which task of information gap is more suitable to
36
3.5 Instrument of The Research
To gain the data, the researcher applied one kind of instrument:
Speaking Task
The instrument of this research was speaking task. The researcher conducted speaking task to find out how are the aplication of information gap to improve
speaking skill. In conducting the task, the researcher provided three topics in three meetings. First, the researcher asked the students to divided class into two, group A and group B, after that they have choosen their partner. Then, the reseracher
gave handout to each pairs and asked them to completed the task by doing conversation orally. Before their doing the tasks, the researcher asked students to
put their mobile phone in their desk so the researcher could evaluated students by
listened students’ voice in voice recording during their doing the tasks, and the
researcher gave 10 minutes to the students to completed the task and record it.
The researcher asked students to speak clearly since the students’ performance is being record during the test.
3.6. Validity and Reliability of the Instrument
In fulfilling the criteria of a good test, validity and reliability of the test should be consider. They are as follows:
3.6.1. Validity of the Instrument
The test can be said valid if the test measures the objective to be measured and
37
quality or not. There are several types of validity but in this research the
researcher only use two type of validity, they are constract validity and content validity.
1. Content Validity
Content validity means that the test is good reflection of what has been taught and of the knowledge that the researcher wants her students to know,
Here, the researcher correlated the test with syllabus and curriculum for Junior High School. If the table represents the material that the researcher
wants to test, it can be said that it has content validity (Shohamy, 1985:74).
2. Construct Validity
Construct validity is concern with whether the test is actually in line with the theory of what it means to know the language (Shohamy, 1985: 74)
that is being measured, it will examine whether the test questions actually reflect what it means to know a language. Its means that the test would measure certain aspect based on the indicator. The researcher examined it
by reffering the aspect that would be measured with the theories of those aspects (Pronunciation, Vocabulary, and Grammar).
3.6.2 Reliability of the Instrument
In this research, reliability is defined as the stability or consistency of the test. One
of the reliabilies purposed by Harris (1974:14) is reliability of the scoring of the test. Since the speaking test was a subjective test meaning the scoring process
38
subjectively in judging the students’ speaking skill. The ratters were the
researcher herself and the second ratter was English teacher at that school. The raters worked collaboratively to judge students’ performance. To know how
reliable the scoring is the researcher used Spearman Rank The statistical formula is:
After finding the cooeficient between raters, the researcher would analyzed the cooeficient of realibity with the standart of reliability according to Slamet
(1998:147) as follow:
The standard of reliability
39
B. a low reliability ranges from 0.20 to 0.39
C. an average reliability ranges from 0.40 to 0.59
D. a high reliability ranges from 0.60 to 0.79
E. a very high reliability ranges from 0.80 to 0.100
In ensuring the reliability of the scorer, the writer used inter rater reliability that was by taking the scorer from two scorer. So, there are two scorer on each
students’ draft.
For example:
Pronunciation Vocabulary Grammar Total
Scorer 1 25 20 15 60
Scorer 2 20 25 15 60
120:2
So, the students’ scorer is 60
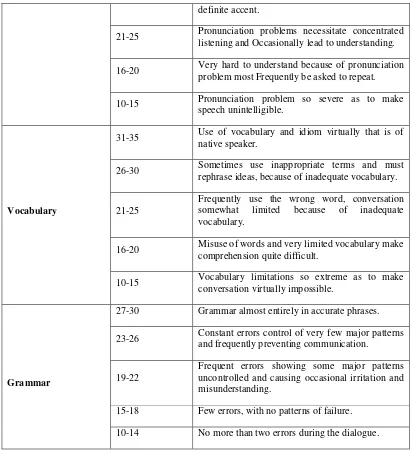
3.7 Scoring Data
Three aspects that would be evaluated by the researcher: pronunciation, grammar, vocabulary. The researcher used computation as follows:
Table 3.1 Scoring Data from Aspect of Speaking Test
Aspects of speaking Rating scales Description
Pronunciation
31-35 Speech is fluent and effortless as that native speaker.
26-30
40
definite accent.
21-25 Pronunciation problems necessitate concentrated listening and Occasionally lead to understanding.
16-20 Very hard to understand because of pronunciation problem most Frequently be asked to repeat.
10-15 Pronunciation problem so severe as to make
rephrase ideas, because of inadequate vocabulary.
21-25
Frequently use the wrong word, conversation somewhat limited because of inadequate vocabulary.
16-20 Misuse of words and very limited vocabulary make
comprehension quite difficult.
10-15 Vocabulary limitations so extreme as to make conversation virtually impossible.
Grammar
27-30 Grammar almost entirely in accurate phrases.
23-26 Constant errors control of very few major patterns and frequently preventing communication.
19-22
Frequent errors showing some major patterns uncontrolled and causing occasional irritation and misunderstanding.
15-18 Few errors, with no patterns of failure.
10-14 No more than two errors during the dialogue.
41
3.8. Data Analysis
Data analysis has been done for the learning product, the researcher used speaking task to collect the data. There were some steps used to analyze the data got from
the test
a. Transcribing the students’ utterance
After the teacher recorded the students’ utterance, the researcher
transcribed the record into the written form. This is very useful in order to know how much time and word which is produce students and to give
scores to the students and also to know the error mostly made by the students during speaking.
b. Scoring the students’ speaking ability
Based on the transcription, the researcher could decide the score for the
students’ speaking test. The reseacrher used the Analytic Rating Scale
proposed by Shohamy (1985)
c. Tabulating the result of the test and finding the difference mean of each topic. The mean was calculating by appying Repeated Measured t-test or
Pair Sample T-test by SPSS
d. Testing the Hypothesis
The hypothesis of this research is:
H1 : There is a significant difference in students’ speaking skill in term of Pronunciation, Vocabulary, and Grammar among three topic which are tested for application of Information Gap Technique
The hypothesis was statistically analyzed by using Repeated Measure
42
significance as the value of significance. We can draw the conclusion
(Setiyadi, 2006:172). The researcher used significant level of 0,05. It means that the probability of errors in the hypothesis is only 5% from
100%, and the hypothesis was approved if p< 0,05.
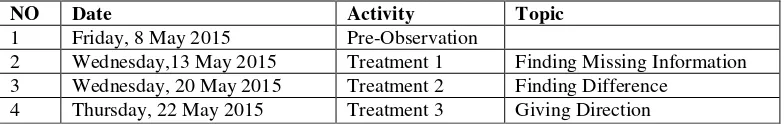
3.9. The Schedule of the Research
Practically, the observation during finished this research is about 1 month and conducted 4 meetings. The table below shows the schedule of the research.
Table 3.3 Schedule of the Research
NO Date Activity Topic
1 Friday, 8 May 2015 Pre-Observation
2 Wednesday,13 May 2015 Treatment 1 Finding Missing Information
3 Wednesday, 20 May 2015 Treatment 2 Finding Difference