AN ITEM ANALYSIS ON THE DIFFICULTY LEVEL OF AN
ENGLISH SUMMATIVE TEST FOR SECOND GRADE OF SMP
MUHAMMADIYAH 29 CINANGKA- SAWANGAN DEPOK
A”Skripsi”
Presented to the Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers Training
In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
For the Degree of S.Pd (Bachelor of Arts) in English Language Education
By:
LIA ANDRI ANI
NIM. 103014027001
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
THE FACULTY OF TARBIYAH AND TEACHERS TRAINING
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
JAKARTA
AN ITEM ANALYSIS ON THE DIFFICULTY LEVEL OF AN
ENGLISH SUMMATIVE TEST FOR SECOND GRADE OF SMP
MUHAMMADIYAH 29 CINANGKA- SAWANGAN DEPOK
A”Skripsi”
Presented to the Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers Training
In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
For the Degree of S.Pd (Bachelor of Arts) in English Language Education
Approved by
Advisor
Dr. H. M. Farkhan M.Pd
NIP. 19571005 198703 1 003
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
THE FACULTY OF TARBIYAH AND TEACHERS TRAINING
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
JAKARTA
ENDORSEMENT SHEET
The examination committee of the Faculty of Tarbiyah certifies that the “Skripsi”
(scientific paper) entitle “ An Item Analysis on the Difficulty Level of an English
Summative Test for Second Grade of SMP Muhammadiyah 29 Cinangka- Sawangan
Depok” written by Lia Andri Ani, students’ registration number: 103014027001, was
examined by the committee on February 28
th, 2011 and was declared to have passed
and, therefore, fulfilled one of the requirements for academic title of ‘S.Pd.’
(Bachelor of Arts) in English Language Education at the Department of English
Education.
Jakarta, February 28
th, 2011
Examination Committee
CHAIRMAN
:
Drs. SYAUKI, M.Pd.
( ___________________)
NIP. 19641212 199103 1 002
SECRETARY
:
NENENG SUNENGSIH, S.Pd
.
(___________________)
NIP. 19730625 199903 2 001
EXAMINER 1
:
SUNARDI KARTAWISASTRO, Dipl. Ed.
NIP. 19440719 196510 2 001
( ___________________)
EXAMINER 2
:
Drs. AM. ZAINURI, M.Pd.
( ___________________)
NIP. 19530304 197903 1 003
Acknowledge by:
Dean of Tarbiyah and Teacher’s Training Faculty
Prof. Dr. DEDE ROSYADA, MA.
i
ABSTRAK
Lia Andri Ani
. 2010, An Item Analysis on the Difficulty Level of an English
Summative Test for Second Grade of SMP Muhammadiyah 29,, Skripsi,, Jurusan
Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris. Fakultas Ilmu Tarbiyah dan Keguruan, Universitas Islam
Negeri Syarif Hiidayatullah Jakarta.
Pembimbing: Dr. H. M. Farkhan M.Pd
Kata Kunci
: Item Difficulty Level, Summative Test
Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk mendeskripsikan kondisi objektif tentang analisis
tingkat kesulitan butir- butir soal test sumatif bahasa inggris di SMP Muhammadiyah
29 Sawangan Depok. Penelitian ini diharapkan bahwa setiap guru harus memahami
dengan jelas kualitas sebuah soal sumatif dan dapat mengetahui tingkat kesukaran
butir- butir soal tersebut.
Penelitian ini termasuk dalam penelitian kuantitatif, karena penelitian menggunakan
beberapa data numerik yang dianalisis secara statistik. Penelitian ini dikategorikan
sebagai deskriptif evaluatif karena penelitian ini menggambarkan kondisi objektif
tentang tingkat kesukaran tes sumatif pada ujian semester genap kelas dua SMP
Muhammdayah 29. Penelitian ini juga merupakan sebuah analisis karena penulis
menganalisa lembar ujian test sumatif . subjek dari penelitian ini adalah siswa kelas
8-1 SMP Muhammadiyah 29. Dan teknik yang di pakai dalam penelitian ini adalah
sebuah tes.
ii
kesulitan soal tes sumatif bahasa inggris untuk siswa kelas dua semester genap SMP
Muhammadiyah 29 Sawangan Depok memiliki tingkat kesulitan sedang.
iii
ABSTRACT
Lia Andri Ani
. 2010. An Item Analysis on the Difficulty Level of an English
Summative test for Second Grade of SMP Muhammadiyah 29 Cinangka- Sawangan
Depok, Skripsi, English Education Department, the Faculty of Tarbiyah and
Teacher’s Training, Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University Jakarta.
Advisor: Dr. H. M. Farkhan M.Pd
Key words
: Item Difficulty Level, Summative Test.
This study is aimed at describing the objective condition about analyzing of the item
difficulty level of an English summative test at Muhammadiyah Junior High School
29 Sawangan Depok. Through this study, it is hoped that the teacher can get clear
description about the quality of English summative test item. So, it can be known
which one of the test items is too easy, moderate, and difficult. Therefore, they can be
used for the next evaluation.
This study is included in quantitative research, because the researcher used some
numerical data which is analyzed statistically. Also, this study is categorized as
descriptive evaluative because it is intended to describe the objective condition about
the difficulty level of student’s summative test at second semester of second grade
student of SMP Muhammadiyah 29. This study was also called an analysis because it
tries to analyze as objectively as about how difficult the English summative test
paper. It will describe difficulty level of each item in Muhammadiyah Junior High
School’s summative test. The subject of this study was second grade of SMP
Muhammadiyah 29. The techniques are used in collecting data is test.
iv
summative test item for second grade of second semester of students’ at
Muhammadiyah Junior High School 29 Sawangan Depok belongs to the test items
which have moderate level of difficulty.
v
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
In the name of Allah, the Beneficent, the Merciful.
All praises be to Allah, Lord of the worlds, who gives guidance and blessing to the
writer in completing this “skripsi”. Peace and blessing upon our final prophet in the
world Muhammad peace be upon Him, his family, relatives, and all of his followers.
This “skripsi” is presented to the English Departement the faculty of Tarbiya and
Teacher’s Training, State Islamic University Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta as a partial
fulfillment of the requirements for the Degree of Strata 1 (S1) in English Language
Education. This “Skripsi” could not be completed without a great deal of help of
many people, especially of her heartfelt gratitude of course goes to her beloved
parents (Mr. Yanto and Mrs. Marsanih) who have given support spiritually and
materially. Her beloved husband and son (Jamal Abdillah and Fahish Huwaida
Abdillah), who Always give support, motivation and encouragement to finish her
“skripsi”.
The writer would like also to express her greatest thanks and gratitude to:
1.
Mr. Dr. H. M. Farkhan M.Pd. as my advisor, who gives valuable help,
guidance, comments, corrections, and suggestions for the completion this
“skripsi”.
2.
Mr. Drs. Syauki, M.Pd. and Mrs. Neneng Sunengsih S.Pd as the Head and
Secretary of English Education Department
3.
Mr. Prof. Dr. Dede Rosyada, MA. as the Dean of faculty of Tarbiya and
Teachers Training.
4.
All lecturers of English Education Department for their guidance to the writer
during her study at faculty of Tarbiya and Teachers Training at UIN Syarif
Hidayatullah Jakarta
vi
6.
Reni Oktaviani, Syahrul Bachtiar and Ridwan Maulana as my brothers and
sister
7.
All her inspiring teachers of SMP Muhammadiyah 29 Cinangka Sawangan
and friends in a class of English Education Department from academic 2003
who inspire her to learn a lot, and to any person who cannot be mentioned
one by one for their any contributions to the writer during finishing her
‘skripsi”.
May Allah, the Almighty bless them all, so be it.
Finally, the writer realizes that she would never finish writing this “skripsi” without
the help of some people around her and the writer realizes that this “skripsi” is still
far from being perfect. Any positive and contributive comments are welcome.
Jakarta, March, 2011
vii
TABLE OF CONTENTS
COVER
APPROVAL SHEEET
ENDORSMENT SHEET
ABSTRACT
………..
i
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
………
v
TABLE OF CONTENTS
………. vii
LIST OF TABLE
………..
ix
LIST OF FIGURE
……….
x
LIST OF APPENDIXES
………..
xi
CHAPTER I : INTRODUCTION
……….
1
A.
Background of the Study ………..
1
B.
Limitation and Formulation of the Problem ………
3
C.
Objective of the Study ………..
3
D.
Method of the Study ……….
3
CHAPTER II :THEORITICAL FRAMEWORK
………
4
A.
Test ………
4
1. Definition of the Test ………..
4
2. Purpose of Test ……… ..
4
3. Types of Test ……….
5
B.
Types of Test Item ……….
7
1.
Subjective Test ……….
7
2.
Objective test ………. ..
10
C.
Categories of Good Test ……….
13
1.
Validity ……….
13
2.
Reliability………. 15
3.
Practically ……….
15
viii
1.
Definition of Item Analysis ………
16
2.
Kind of Item Analysis ………
17
E.
Importance of Item Analysis ………
21
CHAPTER III : THE PROFILE OF THE SCHOOL
………
24
A.
Background of School ………..
24
B.
Vision and Mission of School ………..
24
C.
Organization of School ……….
25
D.
Subject Teacher’s Data ……….
25
E.
Data of Students ………
26
F.
Learning Facility ………..
27
G.
Supporting Activities ………
27
CHAPTER IV : RESEARCH METHODOLOGY AND FINDINGS
…
28
A.
Research Methodology ………
28
1.
Purpose of Research ………...
28
2.
Place and Time of Research ………...
28
3.
Technique of Sample Taking ……….
28
4.
Technique of Data Collecting ………
29
5.
Technique of Data Analysis ………..
29
B.
Research Findings ………
30
1.
Description of Data ………
30
2.
Analysis of Data ……….
34
3.
Interpretation of Data ……….
40
CHAPTER V : CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS
………..
43
A.
Conclusions ……….
43
B.
Suggestions ……….
43
BIBLIOGRAPHY
………
44
ix
[image:12.612.119.541.54.455.2]LIST OF TABLES
Table 2.1
Rank Scale of Difficulty Level ……….…
19
Table 4.1
Index of Difficulty ……….
30
x
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure
Diagram of Student of Score ………
33
[image:13.612.121.541.53.454.2]
xi
LIST OF APPENDIXES
Appendixes 1 Soal Ujian Semester Genap SMP Muhammadiyah 29 ………….. 46
Appendixes 2 Laporan Nilai Test ………
62
Appendixes 3 Surat Pengajuan Judul ………
65
Appendixes 4 Surat Bimbingan Skripsi ………
66
Appendixes 5 Surat Pernyataan Karya Sendiri ……….. 67
Appendixes 6 Surat Permohonan Izin Penelitian ………..
68
Appendixes 7 Surat Keterangan Penelitian dari Sekolah ………..
69
1
INTRODUCTION
A. Background of the Study
Learning is an important process that helps student to fulfill society’s demand for educated workers. Learning process is aided by a teacher. A good teacher is one who knows what to teach, how to teach as well as how to
evaluate. The teacher has to evaluate student progress on the mastery of academic skills which are being taught in a certain period of time. And the result of evaluation will provide information about the quality of the teacher’s instruction and the student’s abilities.
Evaluation is a very important aspect in teaching and learning
activities. Evaluation plays an important role in some activities, especially in terms of education. The information gained through this evaluation will be very useful to make improvement in the future.
Evaluation in English language teaching is so important. It can tell the teacher the effectiveness of instruction, the student’s progress, strengths, and
weakness. In the teaching learning process, evaluation can be done in the form of achievement test. The teachers, who make achievement test, should know and master the principles and the steps that must be done in making the test. This test can be a teacher-made test or standardized test. By this knowledge teachers will get a clear describing about systematic frame work
of evaluation.
Evaluation is defined as, “ The systematic gathering of information for the purpose of making decisions.”1
1
2
The more reliable and relevant the information, the better the likely hood of making the correct decision connecting with students and the instruction.
Evaluation is an integral part of instructional program. It contributes directly to the teaching and learning process. The evaluation result is useful to improve students learning by providing information to overcome learning difficulties, to asses and to improve instruction by judging the appropriateness and attainability of instructional objectives and also the effectiveness of instructional method.2
There are many methods for collecting information for evaluation purposes. One of them is by using a test.3
A test in plain words is “ A method of measuring a person’s ability or knowledge in a given domain.”4 Tests are often used for pedagogical purposes, either as a means of motivating students to study or as a means of reviewing material taught.5
The writer considers that the test is one of the instuments which can be used for gathering the information about the strengths and the weaknesses in acception the lesson by the students.
As a means to measure students’ achievement in learning process, a
test should be constructed well. So that it was able to distinguish between the students who have studied well and those who have not.
Based on the reality above, the writer would like to analyze the difficulty level of summative test items tested at second level students of
SMP Muhammdiyah 29 Sawangan, Depok.
2
Wilmar Tinambunan, Evaluation of Students Achievement, ( Jakarta : depdikbud, 1998), p. 3
3
Fred genesse and John A. Usphur, Classroom Based Evaluation, ( melboutne : Cambridge University Press, 1996), p. 140
4
H. Douglass, Teaching by Principles, An Interactive Approacch Pedagogy, ( Sn Fransisco Addison Wesley Longman, 2001), p. 384
5
B. Limitation and Formulation of the Problem
To make this writing easier to understand, the writer limits the study as follow:
a. The research was focused only on the difficulty level of English Summative test of the second semester 2009/ 2010
b. The test which is analyzed was English Summative test of the second semester 2009/ 2010 academic year
c. The research was focused only on the second grade student of at SMP Muhammadiyah 29 Sawangan Depok
In this writing, the writer formulates the problem:” Are the English summative test items tested at the second year students of SMP Muhammadiyah 29 Sawangan Depok qualified as good items or not?”
C. Objective of the Study
The objective of the study is to know the difficulty level of English summative test items tested at the second grade of SMP Muhammadiyah 29 in 2009/ 2010 academic year.
D.Method of the Study
4
BAB II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
A. Test
1. The Definition of Test
According to Anthony J. Nitko :” Test is a systematic procedure for observing and discribing one or more characteristics of a person with the
aid of either numerical scale or category system.”1 And another definition is “ a test is a systematic procedure for observing and discribing a person’s behavior in a standard situation.”2 A test is a standardized situation that provides an individual with a score.”3
Based on the above opinions, we can conclude that a test is a procedure designed to elicit score from which it can make inference certain characteristics of individual.
2. Purpose of Test
As a means of evaluation, test has some functions of course. According to Penny Ur:” Test has some functions, namely:
a. Give the teacher information about where the students are at the moment to help decide what to teach next
b. Give the students information about what they know, so that they also have an awareness of what they need to learn or review.
c. Assess for some purpose external to current teaching d. Motivate students to learn or review specific material e. Get a noisy class to keep quiet and concentrate
1
Anthony J. Nitko, Educational test and measurement an Introduction, (New York : Harcourt Brace Jovanovich, Inc, 1983), p. 6
2
Michael T. Nietzel, Introduction to Clinical Psychology, (New Jersey : Prentice Hall, 1998, p. 159
3
f. Provide a clear indication that the class has reached a ‘station’ in learning. Such as the end of unit, thus contributing to a sense of structure in the course as a whole.
g. Get students to make effort (in doing the test itself), which is likely to lead to better result and feeling of satisfaction.
h. Give students tasks which themselves may actually provide useful review or practice, as well as testing
i. Provide students with a sense of achievement and progress in their learning.4
From the description above, test has some important functions to make the education getting better.
3. Types of Test
There are many types of test used to measure students’ achievement. However, most specialists have agreed on the names of achievement, proficiency, diagnostic and aptitude tests for the types of test most frequently given.5
a. Achievement Test
In second language instruction, “The achievement test is similar to progress test. However, achievement tests are usually not built around one part of teaching material but are designed for use with students from variety of different schools and program”.6
According to Andrew Harrison, “An achievement test (also called an attainment or summative test) looks back over a longer period of learning that the diagnostic test, for example a year’s work, or a whole course, or even a variety of different courses. It is intended to show the standard which the students have now reached in relation to other students at the same stage”7
4
Penny Ur, A Course in Language Teaching : Practice and Theory, ( Londan : Cambridge University Press, 1996), p. 34
5
Mary Finnnachiaro and Sydney sako, Foreign Language Testing, a Pragmatical Approach, (New York: Regents Publishing Company, Inc, 1983), p. 15
6
Rebecca M. Falette, Modern Language Testing, (New York: Harcourt Brace Jovanocich Publishers, 1997), p. 5
7
6
In addition, a quote by Harold S. Madsen states that, “There is an achievement test that published commercially. But the achievement test can make us less interested in proficiency test because achievement tests are often prepared to measure progress only in specific textbook series and most teachers will prepare their own classroom progress tests”.8
b. Proficiency Test
“Proficiency tests are designed to measure people’s ability in language regardless of any training they may have had in that language. The content or objective of language courses that people taking to the test many have followed. Rather, they based on a specification of what candidates have to be able to do in the language in order to be considered proficient”.9
In addition, proficiency tests are often global measures of ability in a language or other content area. They are not necessary in developing or administered with reference to some previously experienced course of instruction. These measures are often used for placement or selection, and their relative merits lies in their ability to spread students out according to ability on a proficiency range within the desired area of learning.10
The proficiency test usually consists of standardized multiple-choice items on grammar, vocabulary, reading comprehension, oral comprehension, and sometimes on writing.
c. Diagnostic Test
The results of evaluation are intended to find the appropriate way to improve learning and instruction.
Thus, diagnostic test is much comprehensive and detailed because
it searches for underlying cause of learning difficulties and then formulate a plan for remedial action.
8
Harold S. Madsen, Techniques in Testing, (New York: Oxford University Press; 1983), p.189
9
Arthur Hughes, Testing for Language Teacher, (Melbourne; Cambridge University Press, 1991), p.9
10
d. Aptitude Test
According to H. Douglas Brown in his book “Aptitude test is designed to measure a person’s capacity or general ability to learn a foreign language and to apply someone to the classroom learning of any language”.11
It is usually used to:
1. Determine readiness for instructional program
2. Classify or place individuals in appropriate language classes 3. Diagnose the individual’s specific strength and weakness 4. Measure aptitude for learning
The opinion above is supported by Grant Henning, in his book “Aptitude tests are often used to measure the suitability of a candidate for specific program of instruction or particular kind of employment. For this reason these tests are often synonymously with intelligence test or screening test”.12
Thus, these tests are given before the students begin to study and to select them in section appropriate to their ability.
B. Types of Test Item
Based on the manner of scoring, the type of test item is divided into
two general types.
1. Subjective Test
Subjective test is a test where in its scoring requires judgment and evaluation of the scorer. In this type of test, the answer usually is in a form of composition where the students are given a freedom to relate in their
11
H. Douglas Brown, Language Assessment: Principles and Classroom Practices, (New York: Pearson Education, Inc. 2004), p.43
12
8
own words. The subjective tests that are common used in classroom are essay, short answer and completion.
a. Essay
The essay item is the most complex of supply type item. It demands that the students compose a response, often extensive to a question for which no single response or pattern of response can be cited as correct to the exclusion of all the answer.13
The essay test usually consisted of questions beginning with or including such directions as discuss, explain, outline, evaluate, define, compare, contrast, and describe.14
Example: Explain the definition of item analysis!
Thus, the distinctive feature of essay question is freedom of response it provides. Meanwhile, there are some advantages of essay item, namely:15
a) The essay question is useful for measuring the pupil ability to
organize, integrate, and express their idea. b) Constructing essay question are relative easy c) The possibility of guessing minimized.
d) Constructing essay question require less time than the other measurement tool such as true false or on multiple choice items.
Beside the above advantages, the essay items have few disadvantages, namely:
a) Scoring essay question is difficult b) Unreliability of scoring
13
Drs. Wilmar Tinambunan, Evaluation of Students Achievement, (Jakarta: depdikbud, 1998), p.86
14
Victor H. Noll, Introduction to Educational, Measurement ( Boston, Houghton Mifflin Company, 1965), p.131
15
c) Judgment of students; responds requires much time d) Limited sample of total instructional content
b. Short answer question
The short answer item consists of a question, which can be answered with a word or short phrase.16
Example of instructions to answer the short answer question:
“Warm - blooded animals that are born alive and suckle their young are called …. (Mammals) “
Generally, teachers prefer to use the short answer type of question, probably because they think it has some advantages. It is relatively easy to construct, it also gives the teacher some opportunity to see how well students can express their thought and it is also not difficult to score or mark than the essay question.17 However, it is difficult to phrase the short answer question so that only one answer is correct.18 And this type of question will be more useful only in testing knowledge of facts and quite specific information.19
Thus, when teachers are going to know the border description about something, they are better to use the essay form.
c. Completion
The completion item is a written statement that requires the examinee to supply the correct word or short phrase in response to an incomplete sentence, a question, or a word association. Completion test
16
Victor H. Noll, Introduction to Educational Measurement (Boston: Houghton Mifflin Company, 1965), p.138
17
ibid
18
Drs. Wilmar Tinambunan, Evaluation of Students Achievement, (Jakarta: depdikbud, 1998), p.62
19
10
can be used effectively to measure the recall of terms, dates, names and generalizations.20
For example: There are five continents in the world. They are …,
Africa, …, Australia and Europe. Asia is … continent in the world. …. One is Australia.
This type of test can be used at almost all levels. But it is extremely difficult to phrase the question or incomplete statement. So, it only one answer correct, and in making the questions, it may not too many clues are given to answer the questions. If too many clues are given, the items will be too easy, and if an insufficient number of clues are presented, the item will be ambiguous and may yield several possibility of correct answer.21
2. Objective Test
An objective test item is any item that there is only a single predictable correct answer.22 The test is scored in such a manner that subjective judgment is eliminated when determining the correctness of a pupil’s answer.23
Therefore, whether the item is scored by one teacher or another,
today or last week, it will yield the same score.
The subjective test items commonly used in classroom testing are true false, matching and multiple choices.
20
Drs. WilmarTinambunan, Evaluation of Students Achievement, (Jakarta: depdikbud, 1998), P.81
21
Drs. WilmarTinambunan, Evaluation of Students Achievement, (Jakarta: depdikbud, 1998), p.61
22
Rebecca M. Valette, Modern Language Testing, (New York: Harcourt Brace Jovanocich Publishers, 1997), p.8
23
a. True false
True false item is referred to alternative response item the items asks the student to answer with the “true” if conform to the truth or “false” if it essentially incorrect.24
For example: “(T)/ (F) Photosynthesis is the process by which leaves make a plant’s food “
Thus, the item provides the student with a choice of two alternatives, so the student have a possibility to guess the answer and sometimes it will be the right answer. Because of the random guessing to produce the correct answer, the true false tests become less reliable than the other types of test. But these items are appropriate for occasional use, for example: After the students choose the alternatives between right and wrong, correct and incorrect, etc. They are asked to explain by writing the sentences justifying their response.25
Another advantage of constructing a true false item is that the students are able to response to more true false items in a given time period than any other selection type items.26
The most common uses of true false items are:
a) To measure the ability to identify the correctness of statements of
facts, definition of terms and statements of principles.
b) To measure the pupil’s ability to distinguish fact from opinion to measure aspect of understanding, that is the ability to recognize cause and affect relationship. This type of item usually contains
two true prepositions in one statement, and the pupil asked to judge whether the relationship between them it true or false. c) To measure the simple aspect of logic as illustrated in the
example.
24
Drs. Wilmar Tinambunan, Evaluation of Students Achievement, (Jakarta: depdikbud, 1998), p.70
25
Barbara Gross Davis, Tools for Teaching, (San Fransisco: Jersey Publisher, 1993), P. 243
26
12
b. Matching
The matching test item consists of two parallel columns with each word, number, or symbol in on column being matched to a word, sentence, or phrase on the other column.27This type of item is employed widely in situation where relationship of more or less similar ideas, facts, and principles are to be examined or judged.28
For example:
(B) 1. Invented the telephone A.Christopher Columbus
(A) 2. Discovered Amerika B. Alexander Graham Bell (C) 3. First president of the Uniited Stated C. George Washington
This kind of test is an effective way to test students’ recognition of the relationships between words, definitions, events, dates, categories, example, and so on.29
Matching items are also useful in measuring students’ ability to make association, interpretations or measure knowledge of a series of fact. Besides that, the matching items can be used for a large quantity of associated factual material to be measured in a small amount of space while the students’ time needed to respond is relatively short.30
c. Multiple choices
A multiple choice item consisted of one or more introductory sentences followed by a list of two or more suggested responses from which the examinee chooses one as the correct answer.31
27
Ibid, p.64
28
Victor H. Noll, Introduction to Educational Measurement, (Boston: Houghton Mifflin Company, 1965), p.64
29
Barbara Gross Davis, Tools for Teaching, (San Fransisco: Jersey Publisher, 1993), p.243
30
Drs. WilmarTinambunan, Evaluation of Students Achievement, (Jakarta: depdikbud, 1998), p.190
31
For example:
1. Who was the first United States astronaut to orbit the earth in space?
a. Scott Carpenter b. John Glenn c. Virgil Grissom The multiple choices item can measure a variety of learning outcomes from simple to complex, and it is adaptable to most type of subject matter content.
C. Categories of a Good Test
Based on Nourman E. Gronlund in his book; Measurement and Evaluation in Teaching, he said that, “The most essential of characteristics a good test can be classified into three main aspects, they are: Validity,
reliability, and practically. 1.Validity
J.B. Heaton says, “ The validity of a test is the extent to which it measures what it is supposed to measure and nothing else.”32
The validity of a test must be considered in measurement in this case
there must be seen whether the test used really measures what are supposed to measure, briefly. The validity of a test is the extent to which the test measures what is extended to measure. there are four types validity:
a. Face Validity
Face validity means the way the best looks to the testiest, teachers, moderator, and administrator. Therefore. It is useful to show a test to
32
14
colleagues or friends in order to discover obsurdities and ambiguities of a test.
b. Content Validity
Content validity is concerned with the materials that the students have learned. The test should cover samples of the teaching materials given. To fullfil this teacher should refer his consideration to the teaching syllabus.
J. B. Heaton says, “ Content validity depends on careful analysis of the language being tested and of the farticular course objectives, the test should be so constructed as to certain a representative sample of the course.”33
c. Construct Validity
Construct validity deals with construct and underlying theory of the language learning and testing.
J. B. Heaton stated, “ If the test has construct validity it is capable of measuring certain specific characteristics in accordance with a theory of language and behavior and learning.”34
d. Empirical Validity
There are two kinds of empirical validity; they are concurrent validity and predictive validity which depend on whether the test scores are correlated with subsequent or concurrent criterion measures. If we use a test of English as a second language to screen university applicants and than correlate test score s with grade s made at the end of the first semester, we are attempting to determine predictive validity of the test. On the other hand, we follow up the test immediately by having an English teacher rate each student’s English proficiency on the basis of his class performance during the first week and correlate the two
33
J. B. Heaton, Writing, Writing English Language Test, (Longman: 1998), p. 154- 155
34
measures, we are seeking to establish the concurrent validity of the test.35
2.Reliability
A test should be reliable as a measuring instrument. A test cannot measure anything well unless it measures consistently. According to J. Charles Anderson Claphan and Diannae Wall, “ A test cannot be valid unless it is reliable.”36
3. Practically
The third characteristics of a good test is practically or usability in the preparation of a new test. The teacher must keep in mind a number of very
practical considerations which involves economy, ease of administration , scoring and interpretation of result.
Economy means the test is not costly. The teacher must take into account the cost per copy, how many scores will be needed. ( for the more personnel who must be involved in giving and scoring a test, the more
costly the process becomes). How long the administering and scoring of it will take, choosing a short test rather than longer one.
Ease of administration and sccoring means that the test administrator can perform his task quickly and efficiently. We must also consider the
ease with which the test can be administrated.
Ease of interpretation and aplication J. B. Heaton states,” The final point concerns the presentation of the test paper it self.” 37
Where possible, it should be printed or type written and appear neat, tidy and aesthetically pleasing. Nothing is worst and more disconcerting to
35
J. B. Heaton, Writing ..., pp. 154- 155
36
J. Charles Anderson Claphan and Dianne Wall, Language Test Construction and Evaluation ( British : Cambridge University Press, 1995), p. 187
37
16
the testiest than untidy test paper, full of miss spellings, omissions, and corrections. “if it happens, it will be easy for the students or testiest are easy to interpret the test items.”38
Beside having a good criteria, the other characteristics of the test that’s more important and specific is the quality of the test items. To know the quality of the test items, teachers should use a method called item
analysis.
D. Item Analysis
1. The Definition of Item Analysis
An item analysis is a systematic procedure by which the teacher can get some information about the quality of the test item. According to J. Stanley Ahmann and Marvin D. Glock, “Item analysis is reexamining each test item to discover its strength and flaws.”39
While Anthony J. Nitko, in his book stated that, “Item analysis refers to process of collecting, summarizing and using information about individual test items, especially information about pupil’s response to item”.40
Meanwhile, Harold S. Madsen explains that the selection of appropriate language item is not enough by itself to ensure a good test. Each question needs to function properly. Otherwise, it can weaken the exam. Fortunately, there are some rather simple statistical ways or checking individuals’ item. This procedure is called item analysis.41
38
J. Charle Anderson, Caroline Claphan and Dianne Wall, Language Test Construction and Evaluation (British: Cambridge University Press, 1995), p. 161
39
J. Charles Anderson, Caroline Claphan and Dianne Wall, Language test Construction and Evaluation (British: Cambridge University Press, 1995), p.184
40
Anthony J. Nitko, Educational Test and Measurement an Introduction, (New York: Harcourt Brace Jovanovich, Inc., 1983), p. 284
41
2. Kinds of Item Analysis
There are three characteristics usually considered in the field of test and measurement; they are level of difficulty, discriminating power and
effectiveness of distracter. a. Level of Difficulty
According to Lyle F. Bachman “Item difficulty is defined as the proportion of test takers who answered the item correctly, and the item difficulty index, p, values can be calculated on the basis of test takers response to the item”.42
The percentage is inversely related to the difficulty because the
larger the percentage of correct answer, the easier the item and the more difficult the item is, the fewer will be the student who select the correct option.
A good test item should have a certain degree of difficulty it may
not too difficult because the tests that are too easy or too difficult will yield score distribution that make it hard to identify reliable in achievement between the pupil who have done well and those who have done poorly.
According to Lyle F. Bachman in her book; Statistical Analyses for Language Assessment, said that “To analyze the level of difficulty in large group the writer has to prepare for the item analyses, first score the entire test. Then arrange them in order from the one with the highest score to one with the lowest. Next, divided the paper into three groups; those with the highest scores in one stack and lowest in another. The middle groups can be put aside for a while. It can be stated below”43
42
Lyle F. Bachman, “Statistical Analyses for Language Assessment, (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2004), p. 151
43
18
P = RU+ RL = PU+ PL 2n 2
In which:
P: Index of difficulty
RU: The number of students in the upper group who got the item right RL: The number of students in the lower group who got the item right PU: The proportion of students in the upper group who got the item right
PL: The proportion of students in the lower group who got the item right
N: The number of students’ in the upper/ lower group, assuming that the two groups are equal in size
In addition, Lyle F. Bachman in her book: Statistical Analyses for Language Assessment, explained that “In small group, the researcher can easily calculate the item difficulty that using all the test paper. It can be stated below”.44
P = R N In which:
P: Index of difficulty
R: The total number of person who got the item correct N: The number of students’ who took a test
Based on the technique previously, the writer is going to find out the difficulty level of all items in the English summative test by using this formula:
44
P = R a
N n which:
P: Index of difficulty
R: The total number of person who got the item correct N: The number of students’ who took a test
Score of P can be ranged from 0- 1. If P is 0.00 it means there are
no students who can answer the item test correctly. These items belong to very difficult one. And if P is 1 means that all the students can answer the item correctly. These items belong to very easy one.
[image:33.612.149.539.54.572.2]To make clear the writer will give the table of difficulty level range as follow:
Table 2.1
The range scale of level of Difficulty
DIFFICULTY LEVEL P
Difficult 0- 0.14
Moderate 0.15- 0.85
Easy 0.86- 1.00
20
b. The Discriminating Power
A good test item should have a discriminating power. The discriminating power of test item is an index that shows its ability to differentiate between pupils who have achieved well (the upper group) and those who have achieved poorly (the lower group).45
If the test items are given to the students who have students who have studied well, the score will be high and if they are given to those who have not, the score will be low. On the contrary, if good test item. The tests that do not have discriminating power will not yield the proper description of the students’ ability as stated by Nana Sudjana in his book:”… tes yang tidak memiliki daya pembeda tidak akan menghasilkan gambaran yang sesuai dengan kemampuan siswa yang sebenarnya.”46
(“… The tests that do not have discriminating power will not yield the proper description of the students’ ability”)
Therefore, it is very important to measure the discriminating power test item to produce good test items.
c. The Effectiveness of Distracter
One important aspect affecting the difficulty of multiple choice test items is the quality of distracter. Some distracter, in fact, might not be distracting at all, and therefore serve no purpose.47
A good distracter will attract more students who have not studied
well (the lower group) than the upper group. On the contrary, a weak distracter will not be selected by any of the lower achieving students.
45
J. Stanley Ahmann and Marvin D. glock, Evaluating Student Progress: Principles of the Test & Measurement, (Boston: allyn & Bacon, Inc., 1981) , p.187
46
Nana Sudjana, Penelitian Hasil, p.141
47
There are three common causes of weak distracter; first, sometimes an item was drilled heavily in class, so almost everyone has mastered the item, so the answer is obvious. Second, sometimes a
well recognized pair is used, such as this /these, is/is, etc. even though, not everyone has controlled of these yet, students know that one’s of the two is the right answer, no other seems likely, and the third, cause is the use of obviously impossible distracters.
For example : Did he do the work?
A. Yes, he did. B. Birds eat worms. C. Train cannot fly. In a good test item, the distracters must function effectively, if the distracters do not function, they should be rewritten or discarded. And to know whether the distracters do function or not, distracter analysis is done that is by comparing the number of students in the upper group and the lower group who select each in correct alternatives.48
3. The Importance of Item Analysis
Item analysis is an important and necessary step in the preparation of good multiple choices tests. Because of this fact, it is suggested that every classroom teacher who uses multiple choice. Test data should know something of item analysis, how it is and what it means.49
According to Anthony J. Nitko in his book; Educational Test and Measurement an Introduction, stated that “For the teacher who make test, the following are the important uses of item analysis: determining whether an item functions as teacher intents, feedback to the students about their performance and as a basis for class discussion, feedback to the teacher about pupil difficulties, area for curriculum improvement, revising the item and improving item writing skills.50
48
Drs. Wilmar Tinambunan, Evaluation of Students Achievement, (Jakarta: depdikbud, 1998), p.141
49
John. W. Oller, Language Testing at School, A Pragmatic Approach, (London: Longman, 1979), p. 245
50
22
a. Determining whether an item functions as teacher intends
The item will function well if the test item tested is able to distinguish those who master the learning objectives from those who do
not. To differentiate between them, the test item should have certain level difficulty, discriminating power and the effectiveness of distracters. Therefore, item analysis should be done.
b. Feedback to students’ performance and as a basis for class discussion
After knowing the students’ responds to the item, the students’ performance can be known and students’ error can be corrected and the test items that are felt difficult for most of them can be discussed in their class.
c. Feedback to the teacher about pupils’ difficulties
The result of item analysis will be useful for teachers to know the major types of pupils’ difficulties. So they know the study requiring material additional instruction.
d. Area for curriculum improvement
By item analysis, it can be known what kind of items which are felt
difficult by students. If certain kinds of item are repeatedly difficult for students or certain errors occur often, may be the item is not compatible to be taught in a school program. So, curriculum may be needed to be revised.
e. Revising the items
f. Improving item writing skills
After the teachers know what kinds of test items have to be discarded, they will try to make new test items and it will improve their
24
BAB III
THE PROFILE OF THE SCHOOL
A. Background of School
SMP Muhammadiyah 29 Sawangan was established in July, 1st 1985. It is located in jalan Abdul Wahab No. 29 Cinangka Sawangan Depok. SMP Muhammadiyah 29 Sawangan is located in a strategic area, free from traffic
jam and far a way from a crouded.
As a private educational institution, 29 Junior High School strives to a
maximum increase student achievement. Also trying to complete the orderly
administration and school facilities and infrastructure required.
From these efforts that can be seen from most of its graduate’s
students who remained well in his new school.
29 Junior High School has 14 permanent classrooms. Science lab
(complete lab multimedia: laptop, LCD, and other supporting media), the
library and it means that the more complete and better.
B.Vision and mission of School
Formation of a pious Muslim students, morality, superior, proficient believe
C. Organization of School
Principal : Abdul Kadir, S.Pd. Students’ Consultant : Yatie Ervayanty, S.Pd.
Curriculum Consultant : Marwadi Irawan, S.H. Teacher Class VII.1 : Dinar Suhartini, S.Pd. Teacher Class VII.2 : Edi Zulkarnain, S.Pd. Teacher Class VII.3 : Robby Maula, S.Pd.
Teacher Class VII.4 : Dini Amalia Permana, S.Pd. Teacher Class VIII.1 : Nurdin Abdullah
Teacher Class VIII.2 : Windawati, S.Pd. Teacher Class VIII.3 : Wardih HB
Teacher Class VIII.4 : Siti Rahmah, S.Ag.
Teacher Class VIII.5 : Abu Hayat Teacher Class IX.1 : Mahmud, SE
Teacher Class IX.2 : Syaiful Kurniawan, SKM Teacher Class IX.3 : Sufri Helmi, Amd. Teacher Class IX.4 : Achmad Fachrudin
Teacher Class IX.5 : Yatie Ervayanty, S.Pd.
Administration Staff : Suganda Hermawan and Mahmud Joy
D.Subject Teachers’ Data
1. English : Supri Helmi, Amd., dan Windawati, S.Pd.
2. Indonesian : Drs. Namud, Yatie Ervayanty, S.Pd dan Sofyan Hadi, S.pd
26
5. Science : Dra. Suhana, Nurdin, BA. Dinar Suhartini, S.Pd. 6. Social : Marwadi Irawan, S.Pd. dan
Robby Maula, S.Pd.
7. Gymnastic : Sudirman, S.Pd. dan Wardih
8. Art : Dedy Mudayis HS., dan Suaib
9. Computer : Ahmad Fahrudin
E.Data of Students
Class VII.1 : Total: 37 students Class VII.2 : Total: 37 students Class VII.3 : Total: 37 students
Class VII.4 : Total: 37students Class VII. 5 : Total: 36 students Class VIII.1 : Total: 43 students Class VIII.2 : Total: 42students Class VIII.3 : Total: 42 students
Class VIII.4 : Total: 42 students Class IX.1 : Total: 36 students Class IX.2 : Total: 36 students Class IX.3 : Total: 36 students Class IX.4 : Total 36 students
F.Learning Facilities
The school has some rooms to support the teaching and learning activities, there are: Fourteen classrooms, one library, a laboratory, a
lab-computer, and also, a multimedia room.
In the office there are: Principal’s room, Co Principal’s room, teacher’s room, Administration’s room, rest room, and guest room.
G. Supporting Activities
The school has some supporting activities, like scouting, life skill activities and sports like basketball, volleyball and football.
a. Name of school : SMP MUHAMMADIYAH 29
CINANGKA SAWANGAN
b. Address : Jl. Abdul Wahab No. 29 Cinangka
Sawangan- Depok c. School Statistic Number : 204020517177
d. School Type : Junior High School
e. Phone/ fax : 021 74708650
f. School Status : State- owned
g. Founding Status : Potencial
h. Principal : Abd. Kadir S. Pd
i. Principal’s Latest Education : Scholar j. Principle’s Work Period : 2009- 2010
28
BAB IV
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY AND FINDINGS
A.Research Methodology
1. The Purpose of Research
The purpose of this study is to know the difficulty level of each item of English summative test items of the second semester in the second
grade students of SMP Muhammadiyah 29 in 2009/ 2010 academic year.
2. Place and Time of Research
The research was held at SMP Muhammadiyah 29 which it located on Jalan Abdul Wahab, kecamatan Cinangka, Sawangan- Depok. While the
time for the research was for four months, namely from March 2010 until June 2010. And the test was given on June 9th, 2010.
3. Technique of Sample Taking
In this research, the writer took the population from the second year
students of SMP Muhammadiyah 29 Sawangan, Depok Academic year 2009/ 2010. The population of the second class is 169 students, which is divided into four classes.
Because the population is homogenous, the sample is taken only one
4. Technique of Data Collecting
To collect data based on the topic of discussion, the writer did an observation by visiting the school to ask for the students’ answer sheet and
the test paper of the English summative test at SMP Muhammadiyah 29 to be analyzed.
In the process of writing this paper, the writer uses the following steps:
a) Collect the students’ English summative test items and the answer sheets.
b) Arrange all testers’ answers in order from the highest score to the lowest score.
5. Technique of Data Analysis
The writer used quantitative method to analyze the difficulty level by using the formula: 1
P = R/ N
In which :
P = Index of difficulty
R = The total number of person who got the item correct N = The number of students’ who took a test
The criteria that used :
1
30
Table 4.1
DIFFICULTY LEVEL P
Difficult 0- 0.14
Moderate 0.15- 0.85
Easy 0.86- 1.00
B. Research Findings
1. Description of Data
The data that the writer used in this study is the English summative
test for “final test of the second semester” the second graders of SMP Muhammadiyah 29 Junior High School academic year 2009/ 2010. The total numbers of test items are 40 test items. The test was held on June 9th, 2010 with the given time 120 minutes. which the writer focused to analyze only in multiple choice item.
Table 4.2
The Students’s Score in the Second Semester SMP Muhammadiyah 29
Sawangan Depok
Academic year 2009/ 2010
Classification of Student
Ranking Name Score
1 Student 1a 76
2 Student 2a 73
3 Student 3a 71
4 Student 4a 70
5 Student 5a 70
[image:44.612.163.479.549.698.2]7 Student 7a 66
8 Student 8a 66
9 Student 9a 66
10 Student 10a 66
11 Student 11a 66
12 Student 12a 65
13 Student 13a 65
14 Student 14a 65
15 Student 1b 63
16 Student 2b 61
17 Student 3b 61
18 Student 4b 60
19 Student 5b 60
20 Student 6b 60
21 Student 7b 60
22 Student 8b 58
23 Student 9b 56
24 Student 10b 56
25 Student 11b 56
26 Student 12b 56
27 Student 13b 56
28 Student 14b 56
29 Student 15b 55
30 Student 1c 55
31 Student 2c 53
32
33 Student 4c 53
34 Student 5c 51
35 Student 6c 51
36 Student 7c 50
37 Student 8c 50
38 Student 9c 48
39 Student 10c 46
40 Student 11c 45
41 Student 12c 43
42 Student 13c 38
43 Student 14c 36
From the table above, it can be seen that the number of students in that class forty three. The highest score of this class is 7.6, whereas the lowest
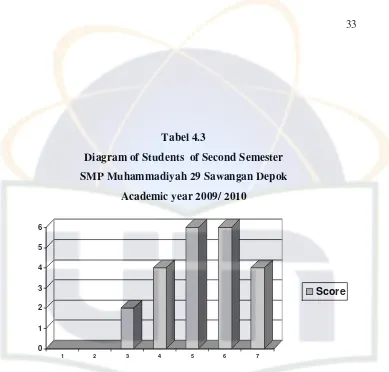
Tabel 4.3
Diagram of Students of Second Semester
SMP Muhammadiyah 29 Sawangan Depok
Academic year 2009/ 2010
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Score
The diagram above shows that the English summative test scores are from 1- 10 and the total number of students is forty three students. Also,
most students in that class who got the score 56 are six Students. The student who got 76 is one, the student who got score 71 is one, the students who got 70 are two, the student who got 68 is one, the students who got 66 are five, the students who got score 65 are three, the student who got 63 is
one, the students who got 61 are two, the students who got 60 are four, the student who got 58 is one, the students who got 55 are two, the students who got 53 are three, the students who got score 51 are two, the students who got score 50 are two, the student who got score 48 is one, the student who got score 46 is one, the student who got score 45 is one, the student
34
2. Analysis of Data
From the data above, the students were divided into three groups
based on the score : upper, middle, and lower group to find level of difficulty.
In the following table, it will be shown the data of students’ response or answer in English summative test. It is tested on June 9th, 2010 with the
given time 120 minutes.
1. Number 1 is a good item, because there are 15 students from 28
students who can answer correctly. The difficulty level of this item is 0.54. It means that it is range 0.15 to 0.85 that belongs to moderate items.
2. Number 2 is a good item, because there are 11 students from 28 students who can answer correctly. The difficulty level of this item is
0.39. It means that it is range 0.15 to 0.85 that belongs to moderate items.
3. Number 3 is an easy item, because most students can answer it correctly. There are 27 students from 28 students who can answer correctly. The difficulty level of this item is 0.96. It means that it is
range 0.86 to 1.00 that belongs to easy item
4. Number 4 is a difficult item, because there are only 3 students from 28 students who answer it incorrectly. The difficulty level of this item is 0.11. It means that it range 0.00 to 0.14 that belongs to difficult item.
6. Number 6 is a difficult item, because there aren’t students who answer correctly. The difficulty level of this item is 0.00. It means that it range 0.00 to 0.14 that belongs to difficult item.
7. Number 7 is a difficult item, because there are 3 students from 28 students who answer correctly. The difficulty level of this item is 0.11. It means that it range 0.00 to 0.14 that belongs to difficult item.
8. Number 8 is a difficult level, because there are 4 students from 28
students who can answer it correctly. The difficulty level of this item is 0.14. It means that it range 0.00 to 0.14 that belongs to difficult item.
9. Number 9 is a good item, because there are 12 students from 28 students who can answer it correctly. The difficulty level of this item
is 0.43. It means that it range 0.15 to 0.85 that belongs to moderate item
10. Number 10 is a good item, because there are 17 students from 28 students who can answer it correctly. The difficulty level of this item is 0.61. It means that it range 0.15 to 0.85 that belongs to moderate
item.
11. Number 11 is a good item, because there are 20 students from 28 students who can answer it correctly. The difficulty level of this item is 0.71. It means that it range 0.15 to 0.85 that belongs to moderate
item
36
13. Number 13 is a good item, because there are 18 students from 28 students who can answer it correctly. The difficulty level of this item is 0.64. It means that it range 0.15 to 0.85 that belongs to moderate
item.
14. The number 14 is good item. Because there are 13 students from 28 students who can answer it correctly. The difficulty level of this item is 0.46. It means that it range 0.15 to 0.85 that belongs to moderate
item
15. The number 15 is difficult item. Because, there are 4 students from 28 students who can answer it correctly. The difficulty level of this item is 0.14. It means that it ranges 0.00 to 0.14 that belongs to difficult item.
16. The number 16 is a good item. Because, there are 5 students from 28 who answer it correctly. The difficulty level of this item is 0.18. It means that it ranges 0.00 to 0.14 that belongs to a moderate item. 17. The number 17 is a good item. Because, there are 11 students from
28 students who can answer it correctly. The difficulty level of this
item is 0.39. It means that it ranges 0.15 to 0.85 .that belongs to a moderate item.
18. The number 18 is a good item. Because, there are 11 students from 28 students who can answer it correctly. The difficulty level of this item is 0.39. It means that it range 0.15 to 0.85 that belongs to a
moderate item.
19. The number 19 is a good item. Because, there are 18 students from 28 students who can answer it correctly. The difficulty level of this item is 0.64. It means that it ranges 0.15 to 0.85 that belongs to a
20. The number 20 is an easy item. Because, there are 23 students from 28 students who can answer it correctly. The difficulty level of this item is 0.82. It means that it ranges 0.86 to 1.00 that belongs to an
easy item.
21. The number 21 is a good item. Because, there are 16 students from 28 students who can answer it correctly. The difficulty level of this item is 0.57. It means that it ranges 0.15 to 0.85 that belongs to a
moderate item.
22. The number 22 is a good item. Because, there are 21 students from 28 students who can answer it correctly. The difficulty level of this item is 0.75. it means that it range 0.15 to 0.85 that belongs to a moderate item.
23. The number 23 is a good item. Because, there are 5 students from 28 students who can answer it correctly. The difficulty level of this item is 0.18. It means that it range 0.00 to 0.14 that belongs to a moderate item.
24. The number 24 is a good item. Because, there are 19 students from
28 students who can answer it correctly. The difficulty level of this item is 0.68. It means that it range 0.14 to 0.85 that belongs to a moderate item.
25. The number 25 is a difficult item. Because, there aren’t students who can answer it correctly. The difficulty level of this item is 0.00.It
means that it ranges 0.00 to 0.14 that belongs to a difficult item. 26. The number 26 is an easy item. Because all of students who can
38
27. The number 27 is a good item. Because, there are 9 students from 28 students who can answer it correctly. The difficulty level of this item is 0.32. It means that it range 0.15 to 0.85 that belongs to a moderate
item.
28. The number 28 is a good item. Because, there are 13 students from 28 students who can answer it correctly. The difficulty level of this item is 0.46. It means that it range 0.15 to 0.85 that belongs to a
moderate item.
29. The number 29 is a good item. Because, there are 7 students from 28 students who can answer it correctly. The difficulty level of this item is 0.25. It means that it range 0.15 to 0.85 that belongs to a moderate item.
30. The number 30 is a difficult item. Because, there are 2 students from 28 students who can answer it correctly. The difficulty level of this item is 0.07. It means that it range 0.00 to 0.14 that belongs to a difficult item.
31. The number 31 is a good item. Because, there are 22 students from
28 students who can answer it correctly. The difficulty level of this item is 0.79. It means that it range 0.15 to 0.85 that belongs to a moderate item.
32. The number 32 is a good item. Because, there are 13 students from 28 students who can answer it correctly. The difficulty level of this
33. The number 33 is a good item. Because, there are 6 students from 28 students who can answer it correctly. The difficulty level of this item is 0. 21. It means that it range 0.14 to 0.85 that belongs to a moderate
item.
34. The number 34 is a difficult item. Because, there aren’t students who can answer it correctly. The difficulty level of this item is 0.00. It means that it range 0.00 to 0.14 that belongs to a difficult item.
35. The number 35 is a difficult item. Because, there are 2 students from 28 students who can answer it correctly. The difficulty level of this item is 0.07. It means that it range 0.00 to 0.14 that belongs to a difficult item.
36. The number 36 is a good item. Because, there are 10 students from
28 students who can answer it correctly. The difficulty level of this item is 0.36. It means that it range 0.15 to 0.85 that belongs to a moderate item.
37. The number 37 is an easy item. Because, there are 27 students from 28 students who can answer it correctly. The difficulty level of this
item is 0.96. It means that it range 0.86 to 1.00 that belongs to a n easy item.
38. The number 38 is a good item. Because, there are 11 students from 28 students who can answer it correctly. The difficulty level of this item is 0.39. It means that it range 0.14 to 0.85 that belongs to a
moderate item.
39. The number 39 is a good item. Because, there are 8 students from 28 students who can answer it correctly. The difficulty level of this item is 0.29. It means that it range 0.15 to 0.85 that belongs to a moderate
40
40. The number 40 is a good item. Because, there are 19 students from 28 students who can answer it correctly. The difficulty level of this item is 0.68. It means that it range 0.15 to 0.85 that belongs to a
moderate item.
From the explanation above, we can see that there are 9 Items belongs to the difficult item. They are items 4, 6, 7, 8, 15, 25, 30, 34, 35. Which are it ranges 0.00 to 0.14. Furthermore, 3 items belong to the easy item. They are 3, 26, 37.Which is in range 0.86 to 1.00. The other, 28 items that belongs to the average items. They are 1, 2, 5, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 16, 17,
18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 27, 28, 29, 31, 32, 33, 36, 38, 39, and 40. Which are it ranges 0.15 to 0.85.
3. Interpretation of Data
Based on the data of item analysis result in difficulty level above, those are 40 items from second grade students of SMP Muhammadiyah Junior High school 29 can be broken down into subcategories easy, moderate, and difficult. Also, she can see that from 40 items there are 28 items regarded as good test items because they have already fulfilled their
criteria of a good level of difficulty, with the range of difficulty level from 0.15 to 0.79, they are items number 1, 2, 5, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 16, 17, 18,
19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 27, 28, 29, 31, 32, 33, 36, 38, 39, 40 . Beside that, there are 3 items which belong to the test item having low level of difficulty that
For whole items, the writer can interpret that the difficulty level of English summative test for second grade in Junior High School, belongs to the test items which have moderate level of difficulty, ranging from 0.15 to
0.79, it is 0.69. So, these test items are moderate. In other word, the test has a good difficulty level.
In addition, the writer would like to discribe the table above by the diagram which showed the percentage of difficulty level of the second
grade students of second semester at SMP Muhammadiyah 29 Sawangan Depok.
Tabel 4.4
Diagram of Difficulty Level
Percentage of English Summative Test
Easy 3 8% Difficult
9 23%
Moderate 28 69%
Easy Moderate Difficult
42
For whole items, the writer can say that the difficulty level of English summative test item for second grade of second semester of students’ at SMP Muhammadiyah 29 Sawangan Depok belongs to the test items which
43
CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION
A. Conclusion
The study shows that the easy level which belong to the test item having low level of difficulty that range from 0.86 until 1.00 is 8 percent, moderate level which belong to the test items having moderate level of
difficulty that range from 0.15 until 0.85 is 69 percent, and difficulty level which have high level of difficulty that range from 0.00 until 0.14 is 23 percent.
The difficulty level of English summative test item for second grade of second semester of students’ at SMP Muhammadiyah 29 Sawangan Depok
belongs to moderate level of difficulty ranging from 0.15 until 0.85. Therefore, these test items are average. In other word, the test has a good level of difficulty.
B. Suggestion
In the end of this writing, the writer would like to give some suggestion for the teachers of SMP Muhammadiyah 29:
1. To know whether an item given to student is good quality or not, the teacher should analyze the students’ test result.
2. The items that fulfill the criteria of good items can be used for the future
evaluation.
3. The items that do not fulfill the criteria should be revised so that they can be used for the next evaluation.
44
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Ahmann, J. Stanley and Marvin D. Glock, Evaluating Student Progress:
Principles of the Test & Measurement, Boston: Allyn & Bacon, Inc.
1981.
Anderson, J. Charles, Caroline Claphan and Dianne Wall, Language Test
Construction and Evaluation, British: Cambridge University Press,
1995.
Bachman, Lyle F., Fundamental Consideration in Language Testing, Toronto: Oxpord University Press, 1990.
Bachman, Lyle F., Statistical Analyses for Language Assessment, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2004.
Bailey, Kathleen M., Learning about Language Assessment: Dilemmas, Decisions, and Direction, London: Heinle & Heinle Publisher, 1998.
Brown, H. Douglas, Teaching by Principles, an Interactive Approach Pedagogy, San Fransisco: AddisonWesley Longman, 2001.
Brown, H. Douglas, Language Assessment: Principles and Classroom Practices, New York: Pearson Education, Inc.2004.
Davis, Barbara Gross, Tools for Teaching, San Fransisco: Jesrey Publishers, 1993.
Falette, Rebecca M., Modern Language Testing, New York: Har