Proposed by:
Proposed By:
ARI PUJI LESTARI 208014000114
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TARBIYAH AND TEACHERS’ TRAINING SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
A "Skripsi"
Presented to the Faculty ofTarbiyah and Teacher's Training in a Partial Fulfillment of the Requirement for the Degree of S.Pd. (S-1) English Language
Education
By: Ari Puji Lestari
208014000114
Approved by the Advisor \
\
L
/
Drs. S uki M.Pd. Atik Yuliani,MA TESOL.
NIP:1964121 199103 1 002 NIP: 19840410 201503 2 003
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TARBIYAH AND TEACHER'S TRAINING
SYARIF HIDA YA TULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
JAKARTA
2015 L
OF THE ENGLISH SUMMATIVE TEST (A Case Study at The Second Year Students of SMP PGRI 2 Ciputat), written by Ari Puji Lestari, student's registration number 208014000114 was examined by the Commitee on 06 July, 2015. The "Skripsi" has been accepted and declared to have fulfilled one of the requirements for the degree of "S.Pd" (S-1) in English Education at the Department of English Education.
CHAIRMAN
SECRETARY
EXAMINER I
EXAMINER II
EXAMINATION COMMITTEE
: Dr. Alek, M.Pd.
NIP. 19690912 200901 1 008 : Zaharil Anasy, M.Hum.
NIP. 197 61007 200710 1 002 : Drs. Nasifuddin Djali, M. Ag
NIP. 19560306 199003 1 002 : Dr. Ratna Sari Dewi, M.Pd
NIP. 19720501 199903 2 013
iii
Jakarta, 06 July 2015
SURAT PERNYATAAN KARYASENDIRI
Saya yang bertanda tangan di bawah ini,
Nama : Ari Puji Lestari
Tempat, Tanggal Lahir : Jakarta, 22 Mei 1990
NIM : 208014000114
Jurusan : Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris
Bahwa skripsi yang berjudul: AN ANALYSIS ON THE CONTENT VALIDITY OF THE ENGLISH SUMMA TIVE TEST (A Case Study at Second Year Students of SMP PGRI 2 Ciputat) adalah benar basil karya ilmiah saya sendiri di bawah bimbingan dosen:
1. Nama Pembimbing NIP
: Drs. Syauki, M.Pd : 19641212 199103 1 002 Jurusan/Program Studi: Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris 2. Nama Pembibing : Atik Yuliani,MA.TESOL.
NIP : 19840410 201503 2 003
Jurusan/Program Studi: Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris
Saya bertanggung jawab secara akademis atas semua yang saya tulis dalam skripsi ini serta siap menerima segala konsekuensi apabila terbukti bahwa skripsi ini bukan basil karya ilmiah saya sendiri.
Demikian surat pemyataan ini saya buat dengan sesungguhnya sebagai salah satu syarat menempuh Ujian Munaqasah.
Jakarta, June 30th2015 Mahasiswa Yhs.
Ar'i Puii Lestari NfM.208014000114
Semester 2013/2014(A Case Study at the eight Students of SMP PGRI 2 Tangerang Selatan), "Skripsi", Department of English Education, Faculty of Tarbiya and Teachers' Training, "Syarif Hidayatullah" State Islamic University Jakarta.
Advisor: Drs. Syauki, M.Pd
Atik Yuliani, MA.TESOL
Key Words: summative test, content validity, English syllabus, analyzes.
The objective of this study is to analyze the empirical evidence whether or not the English Summative Test for the second grade students of SMP PGRI 2 has good content validity and in line with syllabus.
The method of this research was content analysis. It was collected the English Summative Test question paper for the grade students of SMP PGRI 2 in odd semester 2013/2014, and then examined the content of test items in order to judge what the test measures, and also analyzed on both of the relevance and coverage of content of the syllabus used by the school in relation to the test content to know their degree.
The finding of this research showed that the level of content validity of the English summative test for the second grade students of SMP PGRI 2 in the odd semester of the 2013/2014 academic year fell into the level 40-55%, which meant
less good level.
L
Semester 201312014(A Case Study at the eight Students of SMP PGRI 2 Tangerang Selatan ), Pendidikan Bahasa lnggris, Fakultas Ilmu Tarbiyah dan Keguruan, Universitas Islam Negeri Jakarta.
Pembimbing : Drs. Syauki, M.Pd
Atik Yuliani, MA.TESOL
Kata kunci : tes summative, validitas isi, silabus bahsa inggris, analisa.
Studi ini bertujuan untuk menganalisa bukti empiris apakah tes summative bahasa inggris SMP PGRI 2 memiliki validitas isi yang baik dan sesuai dengan silabus sekolah tersebut atau tidak.
Metode studi ini adalah menganalisa isi, yaitu mengambil soal bahasa inggris siswa kelas SMP PGRI 2 Tangerang Selatan pada semester ganjil 2013/2014, kemudian memerikasa item tes untuk menilai ukuran tes tersebut untuk mengetahui tingkat validitas isi tes tersebut.
Hasil dari penelitian ini menunjukan bahwa level validitas isi dari tes summative bahasa inggris SMP PGRI 2 Tangerang Selatan pada semester ganjil tahun pelajaran 2013/2014 berada dalam level 40-55% yang berati memiliki validitas isi yg kurang bagus.
-\
セIャセIiaゥャセ@
In the name of Allah, the Most Gracious, the Most Merciful
Praise be to Allah, Lord of the worlds, for His blessing, love and mercy given to the writer, so she can complete the last assignment in her study. Then, peace and salutation be upon the prophet Muhammad, his family, companion and his adherences.
This "skripsi" is presented to the Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers' Training in a partial fulfi111ment of requirements for the Degree of S.Pd (S-1) in English Education Department.
In arranging this skripsi, a lot of people had given motivation, support, advice and even remark to helped the writer. In this oppotunity, the writer would like to express great honor and gratitude to all of them.
First of all, the writer would like to express her deepest gratitude to her beloved parents, to her beloved husband Lukman Mansur, her brother Fajar Riyadi, her little sisters Habibah Pratiwi, and the only little brother Ichsan Adi Nugroho, and the whole family who always give prayer, support, motivation and moral encouredgment to finish her study. Also, she expresses great honor and deepest appreciation to her advisor, Drs. Syauki, M.Pd and Atik Yuliani, MA, TESOL., who have given suggestions and critical remarks in the process of completing this skripsi.
Her appreciation and thank also goes to:
1. All of the lectures of English Education Department 2. Dr. Alek, M.Pd., the Head of English Education Department
3. Zaharil Anasy, M.Hum., the secretary of English Education Department 4. Prof. Dr.Ahmad Thib Raya, M.A., the Dean of Faculty of Tarbiyah and
Teachers' Training SyarifHidayatuflah State Islamic University Jakarta.
I
5. Her beloved best friends in PBI who always support the writer.
Finally, the writer hopes this "skripsi" is useful for the writer particularly and all the readers, and she realized that this skripsi is far from being perfect. Therefore, the writer would like to welcome any suggestion and critism to make this paper better.
viii
Jakarta, 30 June 2015
The Writer
ix
B. Limitation of the Study ... 3
C. Formulation of the Problem ... 4
... D. Purpose of the Study ... 4
E. Significant of the Study ... 4
CHAPTER II : THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK ... A. Language Test ... 6
1. Definition of Test ... 6
2. Type of Test ... 6
3. Characteristic of a good test ... 9
B. Validity ... 10
1. Content Validity ... 11
2. Face Validity ... 11
3. Construct Validity ... 12
4. Criterion-Related Validity ... 12
C. Material, Syllabus and Curriculum ... 13
CHAPTER III : RESEARCH METHODOLOGYAND FINDINGS ... 19
A. Time and Place of the Study ... 19
B. Method of Study ... 19
C. Research Instrument ... 19
D. Technique of Data Collecting ... 20
E. Technique of Data Analysis ... 20
CHAPTER IV : RESEARCH FINDING AND DISCUSSION ... 22
A. Description of the Data ... 22
x
Table 4.2 The Distribution of Writing ... 23 Table 4.3 The Conformity between the Summative Test Items and the English Syllabus ... 26 Table 4.4 The Unconformity Between the Summative Test Items and the English Syllabus ... 28
L
xi
_\
1
English is a foreign language in Indonesia. It has an important role in any sphere of activities especially in the term of education. Because of that, English language becomes the first foreign language that should be taught to students in every level of education in Indonesia. The government and private institution are struggling to enhance teaching and learning process of English in Indonesia.
In education, one of the important fields, which should be paid attention to, is an evaluation. It is considered that between teachings and evaluation is like two sides of a coin, which cannot be separated. Obviously, it contributes some information to the teaching and learning process, especially for a teacher.
Norman E Gronlund explains that evaluation is the systematic process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting information to determine the extent pupils are achieving instructional objectives1. Based on the statement above, evaluation has to be arranged systematically and has to be based on the curriculum so that we
can get obvious and comprehensive analysis of the student’s achievements.
But Mimin Haryati assumed in her book Model dan Tingkat Penilaian Pada Satuan Pendidikan ,evaluation is the identification of activities to see whether a planned program that has been achieved or not, valuable or worthless, and can also be to look at the implementation level of efficiency.2
Anas Sudjiono assumed that an evaluation is a process to measure something.
And it’s needed an instrument to do it. One of the evaluation instruments is a test.3 In other word based on the statement above test is measure of instrument. Test as
1
Norman E Gronlund, Measurement and Evaluation in Teaching, sixth edition, (New York: Mcmillan Publishing co,1985),p.5
2
Mimin Haryati, Model danTeknik Penilaian Pada Satuan Pendidikan, (Jakarta: Gaung Persada Press, 2009), p.15
3
an instrument should have a good quality, because the quality of the test will be influenced of the result.
There are numerous types of test. There are placement test, to provide information that will help to place students at the stage of the teaching program
most appropriate to their abilities, proficiency test, to measure people’s ability in the language, diagnostic test, to identify learners’ strengths and weaknesses, and
achievement test, to establish how successful individual students, groups of students, or the courses themselves have been in achieving objectives of language courses. The test which is usually used by teachers to know how far students have mastered the lessons is the achievement test.4
There are two kinds of achievement test: progress achievement tests and final achievement tests or summative tests. Progress achievement tests are those administreted at the end of a course of study. They may be written and administreted by ministtries of education, official examining boards, or by members of teaching institution. Clearly the content of these tests must be related to the courses with which they are concerned, but the nature of this relationship is matter of disagreement among language testers. And the content of a final achievement test referred to as syllabus content approach.intended to measure the progress that students are making, and final achievement tests or summative tests
are intended to measure the students’ achievement at the end of a course of study.5
In order to measure accurately, the teachers should use a good test. It is not an easy work for them to make it because there are some characteristics or requirements that must be fulfilled. The characteristics of good test include validity, reliability, comprehensiveness, and practicality. Zainal Arifin said, if a test can give information and can be used to achieve the goal, then the test is valid.6
4
Athur Hughes, Testing for Language Teacher, (New York: Cambridge University Press.,1995), p.11
5
Ibid., p.13.
6
Norman E. Gronlund said, “Validity is concerned with the interpretation and use of assessment result. For example, if we infer from an assessment that students have achieved the intended learning outcomes, we would like some assurance that our tasks provided a relevant and representative measure of the outcomes”7.
“The validity has three types of validation are important in your role as a classroom, those are content validity, face validity, and construct validity”.8A test may be valid if it covers all of the three types it, but the most important and the primary concern of test used in the classroom instruction is content validity.
“Content validity it can claim if a test actually sample the subject matter about which conclusion are to be drawn, if it requires the test-taker to perform the behavior that is being measured”.9
Content validity is concerned with the materials that the students have learned. The test should cover samples of the teaching materials given. To fulfill this, the teacher should refer his consideration to the teaching syllabus.
Based on the writer experienced in the Language Testing subject at 2011th, she found that there were some inadequacies in the summative on SMP PGRI 2 Ciputat test especially in the content of instruction; the themes, the type of texts, and the indicators. Consequently, the test which is designed to measure the
students’ proficiency is not appropriate.
Because of the importance of content validity in a test, the writer tries to know whether the test items are in line with the syllabus or not. The English syllabus that is used here is the latest one recommended by national education department. The summative test which will be studied is taken from SMP PGRI 2 Ciputat for the first level students, academic year 2013 – 2014. The summative test is named:
“UlanganUmum Semester GanjilTahunPelajaran 2013 – 2014.”
7
Norman E. Gronlund , Assessment of Student Achievement, (New Jersey : Person, 1985), p. 46
8
H. Douglas Brown, Teaching by Principles an interactive Approach to Language Pedagogy, (Longman: Sanfransisco State University, 2001), p. 388
9
Therefore based on that problem, the writer tries to analyze and interpret it under the title: “An Analysis on the Content Validity of the Summative Test at Odd Semester for the Eight Students of SMP PGRI 2 Ciputat.”
B. Focus on The Reasearch
To make this writing easier to understand, the writer limit the study as follow: a. The writer focused only on the content validity of English summative test
of the odd semester at second grade academic year of 2013/2014and writer focused only on readingand writing skills.
b. The test to be analyzed is the English summative test for the tenth grade students at SMP PGRI 2 Ciputat.
c. The syllabus to be used is the syllabus which was made by the teacher referenced to the latest curriculum 2013-2014.
C. Reasearch Questions
To make the study easy to understand, the writer formulates the problem whether each test items of the summative test for the second grades students of
SMP PGRI 2 Ciputat represent the indicators as suggested its syllabus as an
indicator of the content validity. The writer breaks down into two formulate:
1. How many indicators represent on the syllabus?
2. Is the English summative test having a good content validity?
D. Purpose of the Study
is useful for all people to know the characteristics of a good test and for the researchers as the basic for conducting further research.
E. Significance of Study
The results of the study are expected can contribute to all people in developing quality of English evaluation such as test designers, teachers, headmasters, and further researchers.
For the test designer, it can be reference to measure content validity of English summative test. This study can give contribution or a useful input and feedback as bases for improving English summative test to the English teacher who join the test designer group. The teacher can take advantages from it as information about the effectiveness or failure of a method, and
also students’ achievement in measuring the lesson.
The results of this study are useful for the English teacher at SMP PGRI 2 Ciputat to know how far their students have understood the material that the teachers have already taught. It is also important to provide better insight and how to make the better English summative test to be used in evaluation activity. It is hoped to enrich the teachers to knowledge of analysis English summative test.
For the headmasters, it is useful to check how well the English summative test which is designed by the teachers who join test designers group. It is
also important to monitor their students’ progress in learning English.
6
A.
Language Test
1.
The Definition of Test
In order to know how well the result of teaching learning processes is, a teacher must evaluate it. One of the evaluation instruments is a test. There are many definitions of test. Dr. T.Swarupani said that Tests are tools or instrument of measurements and measurements guide us in evaluation.1
In other hand Grounlund said in his book, Measurement and Evaluation in
Teaching, “Test is an instrument or systematic procedure for measuring a sample
of behavior.”2
Then according H. Douglas Brown in his book, Teaching by Principles an
Interactive Approach to Language Pedagogy, “Test is an instrument or
proceduredesigned to elicit performance from learner with the purpose of measuring their attainment of specific criteria”.3
Based on the definition above the writer can conclude that test is an instrument and measure instructional. In addition, a test forms a systematic instrument to measure specific criterion.
2.
The Type of Test
There are many types of test used to measure students’ achievement. A test can be categorization according to the types of information they provided. This categorization will useful both in deciding whether an existing test is suitable for a specific category and in writing appropriate tests where these are necessary.
1
Dr. T. Swarupa Rani, Mrs. J. R. Priyadarsaini, and Digumarti Bhaskara Rao(ed.), Educational Measurement and Evaluation, ( New Delhi: Discovery Publishing House, 2004), p.124
2
N.E. Groundlund, Measurement and Evaluation in Teaching, (New Jersey : Mc. Millan Publishing Company, 1985). p. 5
3H. Douglas Brown,
Generally classified in term of their functional role in classroom instructional is placement, formative, diagnostic, and summative test.4
a. Placement Test
Placement test is concerned with the pupil’s entry performance and typically focuses on questions. Such as: “Does the pupil possess the knowledge and skills needed to begin the planned instruction?” .The goal of placement test is to determine pupil performance at beginning of the instruction.5
b. Formative Test
Formative test is used to monitor learning progress during instruction. It purpose to provide continues feedback to both pupil and teacher concerning learning successes and failure.6 In other words formative test is test which can give feedback about a weakness and success between students and teacher the goal of formative test.
c. Diagnostic test
Diagnostic test is highly specialized procedure. It is concerned with the persistent or recurring learning difficulties that are left unresolved by standard corrective prescription of formative evaluation7. The main aim of diagnostic evaluation is to determine the causes of persistent learning problems and formulate a plan for remedial action.
d. Summative Test
It is designed to evaluate achievement at the end of instruction. It is design to determine instructional objective have been achieved and is used primarily for assigning course grade or for certifying pupil mastery of the intended learning outcomes. Although the main purpose of summative evaluation likes that, it also provides information for judging the appropriateness of the course
4
Norman E Gronlund and Robert L, Linn, Measurement and Evaluation in Teaching , ( New York: Collier Macmillan Publisher,1990), p. 12
5
Brown, op.cit , p.390
6Norman E Gronlund and Robert L.Linn,
loc. cit.
7
objectives and the effectiveness of the instruction.8 Implies summative test means evaluate achievement which doing in the end of course and the purpose
it to know whereas a student’s was understand about the objectives which
appropriate or not.
According to H.Douglas Brown explain kinds of tests in his book are only for the purpose of help to identify and differences among types, not to serve as a manual for designing such tests: proficiency, diagnostic, achievement, and aptitude tests.9
a. Proficiency Test
These test aim to assess the general ability of a person at a given time. Its scope is governed by a reasonable expectation of what abilities learners of a given status should possess. It is not restricted by considerations of the areas covered in any specific course objectives or syllabus as in the case of achievements tests. While the usual end of course examination in a school or college may be taken as a typical example of an achievements test, a national level selection or admission test for candidates coming from different states and university jurisdictions can be taken as a typical example of a proficiency test.10 A proficiency test is not intended to be limited to any one course, curriculum, or single skill in the language.11
b. Diagnostic Test
Diagnostic test is designed to diagnose a particular aspect of a language. A diagnostic test in pronunciation might have the purpose of determining which
8
Ibid.
9
Brown, op.cit , p.390
10Rani,
loc.cit .
11
phonological features of English are difficult for a learner and should therefore become a part of a curriculum12.
c. Aptitude tests
They identify the prerequisite characteristics which are essential for one to be competent to perform given task. Presenting items on such sub skills which may eventually be developed into expert complex skills, these test identify those who can do well in a field of study or a profession and those who cannot. These tests are generally used while selecting people for special course.13 According H. Douglas aptitude test is designed to measure a
person’s capacity or general ability to learn a foreign language and to be successful in that undertaking.14
d. Achievement tests
Achievements test is related directly to classroom lesson, units, or even a total curriculum. Test are limited particular material covered in a curriculum within a particular time frame, and are offered after course has covered the objectives in question. It can serve as indicators of features that a student needs to work on in the future, but the primary role of an achievement test is to determine acquisition of course objectives at the end of a period of instruction.15 The aim of achievements test depend on the unit,
3.
The Characteristic of a Good Test
While a design of test needed to recognize the various test of each case depending on purpose, time, subject, and the most characteristic of a good test. As
12
Brown, loc.cit.
13
Rani, loc.cit.
14Brown,
op.cit , p.391
15
we know that test a test can be said as a good test if it has certain qualifications of four characteristics, those are validity, reliability, predictability and objectivity.16
a.
Validity
Norman E Gronlund and Robert L.Linn said “validity is concerned with the interpretation and use of assessment result. For example, if we infer from an assessment that students have achieved the intended learning outcomes, we would like some assurance that our tasks provided a relevant and representative measure of the outcomes”17. “The attribute of validity is arguably the most important quality of an assessment. Validity is concerned with the appropriateness or meaningfulness of an assessment target. In other word validity is concerned with whether a test or performance assesses what intended it to assess.18
There are some different ways, in which validity can be established. Most writers differ from each other in approaching and classifying validity. For the more detailed explanation of validity, the writer will discuss in the next subchapter.
From the previous explanation that one of characteristics of a good test is validity. Validity test is the most critical factor to be judged in the total of a foreign language testing. A test is valid when it measures effectively what it is intended to measure.
Validity really is not a simple concept; however, the concept of validity reveals a number or aspect, each of which deserves our attention. Rani etc. classifies validity into four: content validity, face validity, construct validity, and criterion-related validity.19
16
Dr. T. Swarupa Rani, Mrs. J. R. Priyadarsaini, and Digumarti Bhaskara Rao(ed.),
Educational Measurement and Evaluation, ( New Delhi: Discovery Publishing House, 2004),p. 306
17
Norman E.Gronlund and C.Keith Waugh, Assessment of StudentAchievement, (Upper Saddle River,New Jersey Columbus,Ohio: Person Education,2009),p.46
18
Chistoper R. Gareis and Leslie W. Grant, Teacher Made Assessments, (Depot Way West, Larchmont: Eye On Education,2008),p.34
19
1) Content Validity
Content validity is the most important criterion for the usefulness of a test/ tool. It is especially important in the case of an achievement test.20Then if a test actually samples the subject matter about which conclusion are to be drawn, if it requires the test taker to perform the behavior that is being measured, it can claim content validity. 21
Moreover, the test should reflect instructional objectives or subject matters. From statement above, it is implied that content validity is a tool which important to measure achievement test.
Christoper R. Garies and Leslie W. Grant said, “Content validity is concerned with how adequately an assessment samples the intended learning out comes, standards, or objectives of an instructional unit”22. In other words content validity is made purpose of instructional unit concerned with assessment which appropriate.
2) Face Validity
Face validity is a concept is very closely related to content validity on the face of it, appear from the learner’s perspective. To test what it is designed test to achieve performance on a test, a learner needs to be convinced that the test is indeed testing what it clam to test. 23
While Robert and Tracy said “the statement that we do not care what a test looks like is not entirely true. What a test looks like may be of importance in determining its acceptability and reasonableness to those who will be tested. This appearance of reasonableness is often called face validity”.24
20
Ibid.
21
H. Douglas Brown, op.cit. , p.388
22
Cristhoper Garies, op.cit., p. 37
23
H.Douglas Brown,loc.cit.
24Robert M. Thorndike and Tracy Thorndike-Christ,
Substantially, there is no different view among definition above. They would like to elaborate that a test is considered having face validity, if its appearance is acceptable, it is clearly readable, and it has a clear instruction in answering the test.
3) Construct Validity
Christopher said “Construct validity is concerned with how accurately an assessment aligns with the theoretical framework of the intended learning outcomes, standards, or objective of the instructional
unit. In other word, validity asks”, “Does the assessment measure what it purpose to measure?”25.
H. Douglas Brown said a third category of validity that teachers must be aware of in considering language tests is construct validity. One way to look at construct validity is to ask question“Does this test actually tap
into the theoretical construct as it has been defined?” “Proficiency is a construct”.26
4) Criterion-Related Validity
Criterion validity implies the extent to which a tool performance is related to some other valued measure of performance.27 While according Norman E Gronlund and C. Keith Waugh on book assessment of student achievement. There are two types of studies used in obtaining criterion related evidence of validity. These can be explained most clearly using test scores, although they could be used with any type of assessment result. The first type of study concerned with the use test performance to predict future performance on some other value measure called a criterion. For example, we might use scholastic aptitude test scores to predict course grade. For obvious reason, it is called a predictive study.
25
Cristhoper Garies, loc.cit.
26H.Douglas Brown,
op.cit.,p. 389
27
The second type of study is concerned with the use of test performance to estimate current performance on some criterion. With the procedure both measure test and criterion are obtained at approximately the same time, type of study is called a concurrent study.28
b.
ReliabilityThe second characteristic of a good test is reliability. Reliability is the consistency or dependability of the result assessment.29It is implies how consistent result test from one measurement to another. Therefore, to be considered reliable, a language test must obtain consistent result and give consistent information. So reliability needed to measure of difficulties of item test, because the consistent will given good result information about test which is want to measure on the difficulties items test.
c.
PredictabilityThe third characteristic of a good test is predictability means the test should be such as can give a forecast of the possibilities of the future achievement of the students. Symbolic focus head, heart, and hand.30 The purpose of predictability is used to predict some possibilities of the future achievement of students to be realization and relevant.
d.
ObjectivityThe fourth characteristic of a good test is objectivity. Objectivity refers to the extent the opinion or judgment of the scorer is eliminated from the scoring process. Objectivity is high in most of the standardized tests achievement, aptitude, creativity and intelligence. The test items are objective type fill in the
28
Norman E. Gronlund and C. Keith Waugh, op. cit., p. 50
30
blanks, multiple choice, and true false.31 The objectivity concerned to wide, opinion about scorer.
B. Material, Syllabus and Curriculum
Focus on the use of language use the possibility teachers to realize the underlying principles of teaching. They found the materials not suitable with either the objective or instructional unit. In this situation, teachers have to develop their instructional material or the objectives of teaching
Before discussing about material on language use we should know is a material. According Yohanes Mujiono said on his paper “The material is instructional when it informs the learners about the language. It is experiential when it provides exposure to language in use, eliminative when it stimulates
language use, and exploratory when it seeks discoveries about language use”.32 Its means material is an instructional when the information on it can be subject matter in teaching.According to Yohanes Mujiono on his paper Tomlison summarized there are at least sixteen principles would agree to be basic principles of SLA relevant to the materials development for teaching languages.
1. Materials should achieve impact.
2. Materials should help learners to feel at ease.
3. Materials should help learners to develop confidence.
4. What is being taught should be perceived by learners as relevant and useful?
5. Materials should require and facilitate learner self-investment. 6. Learners must be ready to acquire the points being taught.
7. Materials should expose the learners to language in authentic use.
8. The learners’ attention should be drawn to linguistic features of the input. 9. Materials should provide the learners with opportunities to use the target
language to achieve communicative purposes.
31
Ibid.,p. 306
32Yohanes Mujiono,I paper “Tips Developi g Materials for the 2006 Curriculu ,
10.Materials should take into account that the positive effects of instruction are usually delayed.
11.Materials should take into account that learners differ in learning styles. 12.Materials should take into account that learners differ in affetive attitudes. 13.Materials should permit a silent period at the beginning of instruction. 14.Materials should maximize learning potential by encouraging intellectual,
an esthetic and emotional involvement which stimulates both right and left brain activities.
15.Materials should not rely too much on controlled practice. 16.Materials should provide opportunities for outcome feedback.33
Those all on statement above are the principles and procedures of design, implementation, and evaluation of language teaching material. So teaching materials can be developed by evaluating learning material.
The world curriculum is used interchangeable with syllabus. A syllabus is a reference of the courses a teacher teaches or intends to teach. Penny Ur stated that
“syllabus is a document which consists, essentially, of a list”.34
The syllabus is the content, the list of topics/concepts to be taught, whereas the curriculum is a consideration of the objectives, the content, methods chosen to achieve those objectives. It could/should contain a consideration of the kind of assessment one will use to check progress35.
From the statements above, the writer can conclude that syllabus is a specific plan of what is to be applied and a teacher applying into activities in the classroom. Syllabus is the program was designed by the schools. Then, it is used to be realization planning in teaching.
33
Yohanes Mujiono, op.cit., p.2
34
Penny Ur, A Discourse in Language Teaching: Practice and Theory, (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1996), p. 176
35
A syllabus is designed based on school program and students degrees. Besides
that, the content of the syllabus must be suitable with students’ condition and
relevant on the situation.
To make sure that learning process will run effectively, it’s needed for a
syllabus designer to include the kind of student learning experiences, and the brief of material in the syllabus. Characteristic of a syllabus:
1. Consist of comprehensive of list of:
a. Is ordered (easier, more essential items first)
b. Has explicit objectives (usually expressed in the introduction) 2. Is a public document
3. May indicate a time schedule
4. May indicate a preferred methodology or approach 5. May recommend materials36
Syllabus is part of curriculum but excluding the element of curriculum evaluation. According George A. Beauchamp expand in his book Akhmad sudrajat said Kurikulum & Pembelajaran dalam Paradigma Baru said,
“Curriculum is a written document which may contain many ingredients, but basically it is plan for education of pupils their enrollment in given school”.37
David Nunan states that “curriculum is a large messy concept which can be looked at in a number of ways. A very broad definition is that it includes all of the
planned learning experiences of an educational system.”38Richards describes a curriculum as follow:
An educational program which states:
1. the educational purposes of the program (the ends);
36
Penny Ur, op.cit.,p. 177 37
Akhmad Sudrajat M.Pd, Kurikulum&Pembelajaran dalam Paradigma Baru, (Yogyakarta: Paramitra, 2011), p.1
38
David Nunan, Teaching English as a Second Foreign Language: Syllabus Design,
2. the content, teaching procedures and learning experiences which will be necessary to achieve this purpose (the means);
3. Some means for assessing whether or not the educational ends have been achieved.39
From the statements, the writer concludes that curriculum is the planned, designed, purposes and procedure or concept teaching which role given from schools.
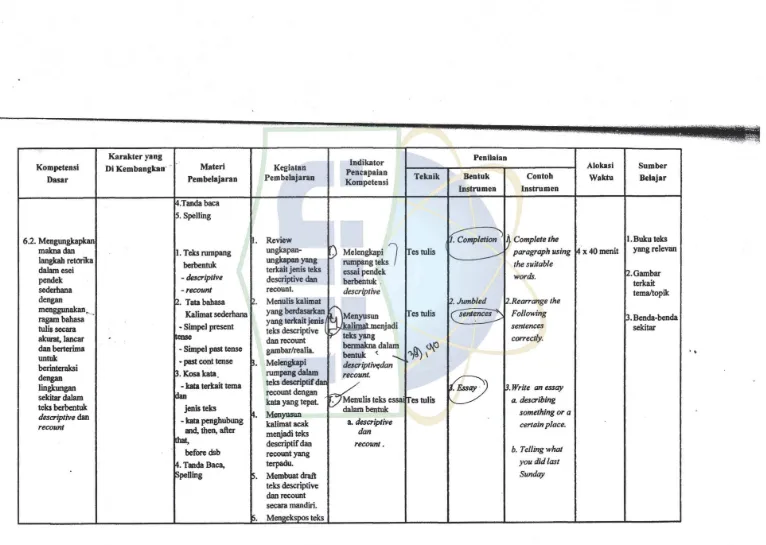
The government decided competency standard and basic competence in the curriculum. The competency standard and basic competence based on the latest English syllabus for the second grade of Junior High School are state as follow:
Standard competence and Basic Competence of Listening, Reading and Writing in School-Level Curriculum
Adapted from content Standard of SMP PGRI 2 CIPUTAT English Syllabus
Mendengarkan
Standar kompetensi
1. Memahami makna dalam percakapan transaksional dan interpersonal pendek sederhana untuk berinteraksi dengan lingkungan sekitar.
Indikator
a. Merespon makna yang terdapat dalam percakapan transaksional (to get thing done) dan interpersonal (bersosialisasi)
b. Merespon makna yang terdapat dalam percakapan transaksional (to get things done) dan interpersonal (bersosialisasi) sederhana secara akurat, lancer, dan beretrima lingkungan sekitar yang melibatkan tindak tutur; mengundang, menerima, dan menolak ajakan, menyetujui/tidak menyetujui, memuji, dan memberi selamat.
39
2. Memahami makna teks fungsional pendek dan teks monolog sederhana bentuk descriptive dan recount untuk berinteraksi dengan lingkungan sekitar.
a. Merespon makna yang terdapat dalam teks lisan fungsioinal pendek sederhana secara akurat, lancer, dan berterima untuk berinteraksi dengan lingkungan sekitar.
b. Merespon makna yang terdapat dalam monolog pendek sederhana secara akurat, lancer, dan berterima dengan lingkungan sekitar dalam teks berbentuk descriptive dan recount.
Membaca
Standar komptensi
1. Memahami makna tes tertulis fungsional pendek dan esai sederhana berbentuk descriptive dan recount yang berkaitan dengan lingkungan sekitar.
Indikator
a. Membaca nyaring bermakna teks tulis fungsional dan esai berbentuk descriptive dan recount pendek sederhana dengan ucapan, tekanan dan intonasi yang berterima berkaitan dengan lingukngan sekitar.
b. Merespon makna dalam teks tulis fungsional pendek sederhana secara akurat lancer dan berterima yang berkaitan dengan lingkungan sekitar:
teks fungsional pendek berupa undangan dan pesan singkat.
tata bahasa : request
kosakata : kata terkait, tema dan jenis teks
ungkapan baku : don’t be late! & don’t miss it!
Menulis
Standar kompetensi
1. Mengungkapkan makna dalam teks tulis fungsional pendek dan esai sederhana berbentuk descriptive dan recount untuk berterinteraksi dengan lingkungan sekitar.
Indikator
a. Mengungkapkan makna dalam bentuk teks tulis fungsional pendek sederhana dengan menggunakan ragam bahasa tulis secara akurat, lancer, dan berterima dengan lingkungan sekitar.
20
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A. Time and Place of the research
To carry out this study, the writer decided to choose PGRI 2 Ciputat. This is located at Tegal rotan Desa Pondok Aren, Kec. PondokAren, Tangerang Selatan.SMP PGRI 2 Ciputat academic year 2013/2014.
B. Method of Study
In this research the writer used comparative descriptive method. She compared summative test in the syllabus,whether each test items of the summative test for the first year students of SMP PGRI 2 Ciputat the indicators as suggested its syllabus on the content validity.The test was measured with the syllabus and indicators especially from reading, writing, and speaking skills. She calculates the result based on the formula of the test analysis.
So based on the data and types of information needed of this research, the writer used qualitative research categorized as descriptive analysis. It described the conformity and unconformity of the SMP PGRI 2 Ciputat summative test with the syllabus and indicators.
C. Research Instrument
The research instruments are used by the writer in collecting the data were:
1. Paper/ test booklet
The writer ask the English summative test paper from the school. The test items which multiple choice are 30 items number and the items in essays are 5 items.
The writer analyzed the test items on the summative test and then conform it to the English syllabus and the indicators.
C. Technique of Data Collecting
The instruments used in collecting the data they are English summative test and English syllabus of the odd semester for the first year students of SMP PGRI 2 Ciputat. The English summative test was held on December 2013. The writer focused on reading,writing, and speaking skills because the summative test consists of multiple choice items, essays, and there are some dialogues represent the indicators of reading and writing.
D. Technique of Data Analysis
To describe the data, the writerdescribes the information about the kinds of the test item which conform to the syllabus and indicators. Then collected the data are analyzed used qualitatively and quantitatively used to determine whether the items of the test have represented to the functional skills.
While, the qualitative analysis used to measure the percentage of conformity between content of the test with the functional skills. Quantitative, the data are calculated using the formula:
P : Percentage
F : Frequency of unconformity
N : Number of sample
It is used to find how many percent the test items represent the indicators from the syllabus, and how many indicators represented by the test items.
F
In addition, the writer also compares the percentage with the criteria adopted
from Arikunto’s opinion:
76 – 100 % = Good
56 – 75 % = Sufficient
40 – 55 % = Less good
< 40 % = Bad1
Beside, the writer compared the result of the analysis, whether it has content validity or not, to the result of the interview from the team teachers who made the summative test, if there is relation to the result found.
1
23
1.
The Description of the DataThe writer analyzes the test materials whether they conform to the English syllabus of SMP PGRI 2 Ciputat. The data was a written test and the instrument was a syllabus. The English test was made by an English teacher of SMP PGRI 2 Ciputat. The data used in this study is the English summative test for odd semester, which is called Ulangan Umum Semester Ganjil Tahun Pelajaran 2013/2014 for the Second Grade students of SMP PGRI 2 Ciputat. The total numbers of reading and writing test items are 35 items which consist of 30 multiple choice items and 5 essays. The data analyzed measured only two skills. They were reading and writing. The analyze start from number 11-40 multiple choice and 5 essays. The test was held on Tuesday, 3th December 2013 with the given time 120 minutes.Having investigated the summative test items, the writer is able to describe the data as follows:
Table 4.1
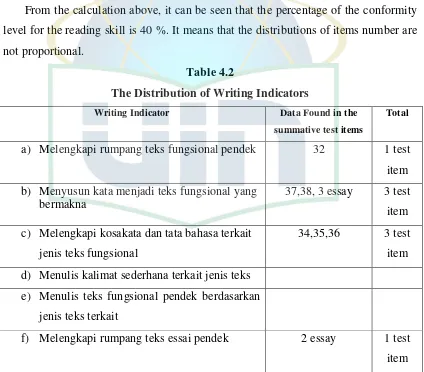
The Distribution of Reading Indicator
Reading Indicator Data Found
in the
Summative
test items
Total
a) Membaca dengan nyaring dan bermakna teks
fungsional pendek berupa descriptive dan recount
0
b) Mengidentifikasi berbagai informasi dalam teks fungsional pendek berupa descriptive dan recount teks.
14,15,21, 22, 28,
5 test items c) Mengidentifikasi fungsi social teks fungsional
pendek berupa undangan, pesan singkat
0
d) Mengidentifikasi ciri kebahasaan teks fungsional pendek berupa undangan, pesan singkat
0
e) Merespon makna gagasan dalam esei pendek
sederhana
23, 30 2 test
item f) Merespon makna tekstual dalam teks descriptive dan
recount
16, 24, 31 3 test item g) Merespon langkah retorikateks descriptive dan
recount
0
h) Merespon pertanyaan tentang tujuan komunikatif teks descriptive dan recount
13, 29,33 3 test item i) Merespon ciri kebahasaan teks descriptive dan
recount
0
j) Membaca nyaring teks descriptive dan recount 0
Total 4 indicators 13 test
items
F
P = ──× 100% N
4
P = ──× 100% 10
P = 40 %
P = percentage of content validity for the indicator of reading skill F = frequency of reading skill indicator appearance in the test items N = total of reading skill indicator required in the English syllabus
[image:36.612.110.534.320.692.2]From the calculation above, it can be seen that the percentage of the conformity level for the reading skill is 40 %. It means that the distributions of items number are not proportional.
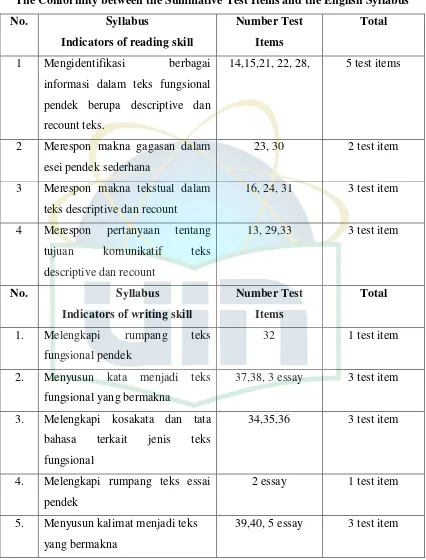
Table 4.2
The Distribution of Writing Indicators
Writing Indicator Data Found in the
summative test items
Total
a) Melengkapi rumpang teks fungsional pendek 32 1 test
item b) Menyusun kata menjadi teks fungsional yang
bermakna
37,38, 3 essay 3 test
item c) Melengkapi kosakata dan tata bahasa terkait
jenis teks fungsional
34,35,36 3 test
item d) Menulis kalimat sederhana terkait jenis teks
e) Menulis teks fungsional pendek berdasarkan jenis teks terkait
f) Melengkapi rumpang teks essai pendek 2 essay 1 test
g) Menyusun kalimat menjadi teks yang bermakna
39,40, 5 essay 3 test
item h) Menulis kalimat dalam bentuk descriptive
dan recount
4 essay 1 test
item
Total 6 indicators 12 test
items According to the table above, there are 8 indicators of writing. However, the English summative test fulfilled only 6 indicators and they are developed into 12 test items. The percentage of the conformity level for the writing skill can be calculated as follow:
F
P = ──× 100% N
6
P = ──× 100% 8
P = 75 %
P = percentage of content validity for the indicator of writing skill F = frequency of writing skill indicator appearance in the test items N = total of writing skill indicator required in the English syllabus
From the calculation above, it can be seen that the percentage of the conformity level for the writing skill is 75 %. It means that the distributions of writing are almost proportional.
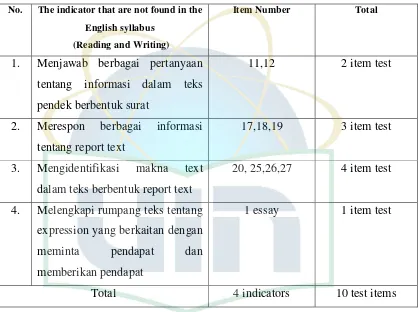
Table 4.3
The Conformity between the Summative Test Items and the English Syllabus
No. Syllabus
Indicators of reading skill
Number Test Items
Total
1 Mengidentifikasi berbagai
informasi dalam teks fungsional pendek berupa descriptive dan recount teks.
14,15,21, 22, 28, 5 test items
2 Merespon makna gagasan dalam
esei pendek sederhana
23, 30 2 test item
3 Merespon makna tekstual dalam teks descriptive dan recount
16, 24, 31 3 test item
4 Merespon pertanyaan tentang
tujuan komunikatif teks
descriptive dan recount
13, 29,33 3 test item
No. Syllabus
Indicators of writing skill
Number Test Items
Total
1. Melengkapi rumpang teks
fungsional pendek
32 1 test item
2. Menyusun kata menjadi teks
fungsional yang bermakna
37,38, 3 essay 3 test item
3. Melengkapi kosakata dan tata
bahasa terkait jenis teks
fungsional
34,35,36 3 test item
4. Melengkapi rumpang teks essai pendek
2 essay 1 test item
5. Menyusun kalimat menjadi teks yang bermakna
6. Menulis kalimat dalam bentuk descriptive dan recount
4 essay 1 test item
Total the conform indicator are 10 indicators 25 test items
From the table above, it can be seen that there are 4 indicators of reading and 6 indicators of writing skill which are appropriate to the English syllabus at second grade of odd semester. There are 5 indicators about specific information, 2 indicators about main idea, 3 indicators about meaning of text, 3 indicators about purpose of communicative of text, 1 indicators about complete the text, 3 indicators covering arranged word into good sentence, 3 indicators covering complete the verb refer the text, 1 indicators covering complete the suitable word, 3 indicators covering arranged sentence to be good paragraph, 1 indicators covering write an essay.
The percentage of the conformity between the summative test items and the English syllabus can be calculated as follow:
F
P = ──× 100% N
10
P = ──× 100% 18
P = 55,5 %
P = percentage of indicators reading and writing
F = frequency of indicators reading and writing Appearance in the Test Items N = Number of indicators
based on the indicators in the English syllabus is 55, 5 %. Based on the Arikunto’s
[image:40.612.115.533.234.546.2]criteria, the percentage above fell into level of 40%-55% which meant that the distribution was less good.
Table 4.4
The Unconformity between the Summative Test Items and English Syllabus
No. The indicator that are not found in the
English syllabus
(Reading and Writing)
Item Number Total
1. Menjawab berbagai pertanyaan
tentang informasi dalam teks pendek berbentuk surat
11,12 2 item test
2. Merespon berbagai informasi
tentang report text
17,18,19 3 item test
3. Mengidentifikasi makna text
dalam teks berbentuk report text
20, 25,26,27 4 item test
4. Melengkapi rumpang teks tentang expression yang berkaitan dengan
meminta pendapat dan
memberikan pendapat
1 essay 1 item test
Total 4 indicators 10 test items
2. The Analysis of the Data
Based on the table and descriptions before, the writer found, that some indicators are not suggested in the syllabus but they are included in the test items. For the example answering some questions about specific information form on letter and determining meaning text form of report text. In fact, the material of letter and report text has been taught in the last section of even semester material.
Besides, some development of some syllabus requirements in the test items was not proportional. There were some learning activities which had many item numbers. In contrast, there were some learning activities which had few item numbers develop in the test. For example, according to the learning activities of reading, particularly for determining rhetorical steps of the texts in the form of descriptive test and recount text, and mentioning characteristic of short functional text in the form of invitation, there were not test items represent them. It also happened to the learning activities of writing.
Based on the explanation above, the writer assumed that some possibility reason why there were some materials of the learning activities suggested in the syllabus did not appear or did not develop in the test. It could happen because the test maker assumed that it would be too easy for the students to answer them. Moreover, it could happen because of the limitation of time. There were so many test items which needed so much time to answer, especially for the writing components. So, the test maker defined the limitation of the improvement or the development of the learning activities in the test items.
3. The Interpretation of the Data
The following describe the level of the conformity of summative test items to the syllabus. We can see as follow:
F
10
P = ──× 100% 18
P = 55,5 %
P = percentage of indicators reading and writing
F = frequency of indicators Appearance in the Test Items N = Number of Indicators
In addition, the writer also compares the percentage with the criteria adopted
from Arikunto’s opinion:
76 – 100 % = Good
56 – 75 % = Sufficient
40 – 55 % = Less good
< 40 % = Bad1
The total numbers of reading and writing test items are 35 items which consist of 30 multiple choice items and 5 essays. The data analyzed measured only two skills. They were reading and writing. The analyze start from number 11-40 multiple choice and 5 essays.From the interpretation of the data above, the percentage validity level of the English summative test for the second year students of SMP PGRI 2 Ciputat, in the odd semester 2013/2014 academic year was 55, 5%. According Arikunto’s meant of conformity level, which percentage fell into level of 40%– 55 % is less good. The percentage 55,5% adopted from indicators of reading represent by syllabus only 4
indicators, and only 6 indicators represent with syllabus. The total numbers’ of
indicators of reading and writing 10 indicators, while the total indoctor on the syllabus 18 indicators.
1
Then, the writer was able to see the table 4.7 the total percentage of reading skills are 40% and total percentage of writing skills are 70%. But the total number percentage of indicators reading and writing skills are 55.5%. So, the English summative test for the second year students of SMP PGRI 2 Ciputat in the odd semester of the 2013/2014 academic year had less good content validity.
No. Number Of Indicators Items Number that
Represent the
Indicators
Total Frequency
1. Reading Skills that conform with the syllabus
14,15,21, 22, 28, 23, 30, 16, 24, 31, 13,
29,33
F
P = ──× 100%
N 4
P = ──× 100%
10 P = 40 % 4 Indicators
2. Writing Skills that conform with the syllabus
32, 37,38, 3 essay, 34, 35, 36, 2 essay, 39, 40, 5 essay,
4essay
F
P = ──× 100%
N 6
P = ──× 100%
8 P = 75 % 6 Indicators
Total of
Indicators
that
Represent
with
Syllabus
18 Indicators 10 items F
P = ──× 100%
N 10
P = ──× 100%
33
A. Conclusion
In this research the analyzed the test items, whether each test items of the summative test for the eight students of SMP PGRI 2 represent the indicators as suggested its syllabus as an indicator of the content validity. Also, this research is categorized as descriptive analysis. It described the conformity and unconformity of
the SMP PGRI 2’s summative test with the indicators.
In this research the writer analyzes based on two points of view. First, related to the percentage, the writer found that the English summative test which is administrated in the second year students of junior high school of PGRI 2 is 55, 5% valid in terms of its conformity with the items test. The items tests that represent the suggested indicators in the syllabus are 25 items and the unconformity items are 10
items. So, based on Arikunto’s opinion, is means sufficient because the percentage
level of 40%-55%.
Therefore, the writer concludes that the English summative test of the odd semester on the eight students of SMP PGRI 2 Ciputat has less good content validity. Although based on the percentage of its conformity with the indicators is 55, 5% valid.
B. Suggestion
indicators must be appropriate with the syllabus. And the writer would like to suggest the test designer to:
edition
, (New York: Mcmillan Publishing co,1985)
Haryati, Mimin,
Model danTeknik Penilaian Pada Satuan Pendidikan,
(Jakarta: Gaung Persada Press, 2009)
Sudijono, Anas,
PengantarEvaluasiPendidikan
, (Jakarta: PT:Grafindo
Persada,2008)
Hughes, Athur,
Testing for Language Teacher,
(New York:
Cambridge Univercity Press.,1995)
ArifinM,Pd,
Drs.
Zaenal,
EvaluasiPembelajaran
,(Bandung:
PT.Remaja Rosdakarya,2009)
E. Gronlund, Norman,
Assessment of Student Achievement,
(New
Jersey: Person, 1985)
Brown, H. Douglas,
Teaching by Principles an interactive Approach
to Language Pedagogy
, (Longman: Sanfransisco State University,
2001)
Swarupa,
Rani,
T.,
R.
Priyadarsaini,
J,
and
Rao,
DigumartiBhaskara(ed.),
Educational Measurement and Evaluation
,
New Delhi: Discovery Publishing House, 2004
Gronlund, Norman E and Robert L, Linn,
Measurement and
Evaluation in Teaching
, New York: Collier Macmillan Publisher,
1990
Arikunto, Suharsimi,
Dasar
–
DasarEvaluasiPendidikan Ed. Revisi,
Cet5
. Jakarta: BumiAksara, 2010
Thorndike, Robert M. and Tracy Thorndike-Christ,
Measurement and
Gareis, Chistoper R. and Leslie W. Grant
, Teacher Made Assessments,
(Depot Way West, Larchmont: Eye On Education,2008
)Mujiono, Yohanes,
In paper “Tips Developing Materials for the 2006
Curriculum
, (Jakarta: Unika ATMAJAYA)
Ur, Penny,
A Discourse in Language Teaching: Practice and Theory
,
1
item
11.
Text for question number 11-12
January, 24th, 2011 Dear Susan,
Thank you for your suggestion going to Bunaken. I had a great time on my holidays last month. I went to Bunaken. I went there with some friends.
I departed from Jakarta on Wednesday afternoon and arrived there on Thursday morning. When we arrived in the hotel, we took a rest a while.
In the afternoon, we went to dive in Bunaken Sea. I was amazed by the scenery under the sea. It was a really beautiful place that I have ever visited.
I spent a week there and went home on Tuesday.
Sincerely, MelaniAditya
How many days did Melani spend her holiday in Bunaken? Five days
These questions ask students to identify the question how many days. It
can be understood that this item measures the student’s ability in responding about
days the invitation and announcement text. Thus, these items conform to the recommended indicator namely, “Mengidentifikasi fungsi social teks fungsional pendek berupa: undangan dan pesan singkat”.In addition the text used is invitation and announcement text. Thus, it also conforms to the suggested text.
No item
The question
12
“When we arrived in the hotel, we took a rest for while.” (line 9)
The word “we” refers to ….
a.Susan and Melani b.Susan and her friends c.Melani and her friends d.Melani and the guide
These questions ask students to identify the purpose of the text. It can be
understood that this item measures the student’s ability in responding the
invitation and announcement text. Thus, these items conform to the recommended
indicator namely, “Mengidentifikasi fungsi social teks fungsional pendek berupa:
undangan dan pesan singkat”.In addition the text used is invitation and
announcement text. Thus, it also conforms to the suggested text.
No item
The question
13
Text for question number 13-14
Announcement To : All Basketball Team
We will have technical meeting for the next match. Please do come to school on Sunday 12that 09.00 a.m.
What is the purpose of the short functional text above? ... a. To tell about the match
b. To inform about technical meeting c. To amuse the readers about meeting d. To invite the students to join the match
These questions ask students to identify the purpose of the text. It can be
understood that this item measures the student’s ability in responding the
invitation and announcement text. Thus, these items conform to the recommended
indicator namely, “Mengidentifikasi fungsi social teks fungsional pendek berupa:
undangan dan pesan singkat”.In addition the text used is invitation and
announcement text. Thus, it also conforms to the suggested text.
No item
The question
14
To whom this announcement announces? a.Basketball team
b.Students c.Teacher
d.The team coordinator
These questions ask students to identify the purpose of the text. It can be
understood that this item measures the student’s ability in responding the
invitation and announcement text. Thus, these items conform to the recommended
indicator namely, “Mengidentifikasi fungsi social teks fungsional pendek berupa:
undangan dan pesan singkat”.In addition the text used is invitation and
No item
The question
15
Text is for question 15-16
To : Emmy Suliatiningsih
I will be glad if you want to come to my 14th birthday party. It will be held:
Date : February 28th2014 Time : 5.00 p.m
Place : Jl. Raya Baruga No. 26, Makassar
Sincerely yours Rahmi
Which of the following statement is TRUE according to the text? a. Emmy invites Rahmi to her birthday
b. Emmy lives in Jl. Raya Baruga No.26 c. Rahmi is Emmy’s twin sister
d. Rahmi was born on October, 28th 2000
This question asks the students to show which is not true about text. It can
be understood that question tries to measure the students’s ability in
understanding factual information from the short functional text. Therefore, it
conforms to the suggested indicator
“mengidentifikasiberbagaiinformasidalamteksfungsionalpendek”. In addition the
text used is descriptive and recount text. Thus, it also conforms to the suggested text.
No item The question
The underlined word has the same meaning with ….
a. Satisfied
b. Sad
c. Happy
d. Grateful
These questions ask students to identify the purpose of the text. It can be
understood that this item measures the student’s ability in responding the
invitation and announcement text. Thus, these items conform to the recommended
indicator namely, “Mengidentifikasi fungsi social teks fungsional pendek berupa:
undangan dan pesan singkat”.In addition the text used is invitation and
announcement text. Thus, it also conforms to the suggested text.
No item
The question
Text for 17-20
Singapore
Singapore is an island city of about 4 million people. It’s a beautiful city with lots of parks and open spaces. It’s also a clean city.
Most of the people live in high-rise flats in different parts of the island. The business district is very modern, with lots of tall new office building. Singapore also has some nice older sections. In china town there are rows of hold shop houses. The government buildings in Singapore are very beautiful. They are date from the colonial days.
Singapore is famous for its shops and restaurants. There are many
good shopping centers. Most of the goods are free. Singapore’s
restaurants sell Chinese, India, Malay, and European food, and the price are quite reasonable.
(Source: Dit. PSMP, 2006) How is the city in Singapore?
17 b. It’s dirty city. c. It’s clean city. d. It’s crowded city.
The question of number17 asks students to identify how is Singapore. It
can be understood that this item measures the student’s ability in responding recount text. Thus, these items conform to the recommended indicator
namely,“Mengindentifikasi berbagai informasi dalam teks fungsional pendek”, In addition the text used is descriptive and recount text. Thus, it also conforms to the suggested text.
No item The question
18
These statements are true based on the text, EXECPT ….. a. Singapore has lots of parks and open spaces
b. The business district is very old
c. There are old shops in Chinatown in Singapore d. The price of the restaurants in Singapore is reasonable
This question asks the students to show which is not true about text. It can
be understood that question tries to measure the students’s ability in
understanding factual information from the short functional text. Therefore, it
conforms to the suggested indicator
“mengidentifikasiberbagaiinformasidalamteksfungsionalpendek”. In addition the
text used is descriptive and recount text. Thus, it also conforms to the suggested text.
No item The question
19
What does last paragraph tell about? It tells about ….
a. Singapore and it’s condition
c. The food in Singapore
d. The shops and restaurants Singapore
This question asks students to determine tells about of the parahraph. It
can be understood that this item measures the student’s ability in identifying the topic from the text. Thus, this item conforms to the recommended indicator
namely, “mengindentifikasikan makna gagasan dalam teks berbentuk: recount dan
descriptive”. In addition the text used is descriptive and recount text. Thus, it also
conforms to the suggested text.
No item The question
20
“They are date from the colonial days.”(line 10)