i A Skripsi
Submitted to the Faculty of Language Education In a Partial Fulfillment of the requirements
For the Degree of
Sarjana Pendidikan
Irma Agustin
20120540047
English Education Department
Faculty of Language Education
Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta
iv
Table of Contents ... iv
List of Table ... vi
List of Figures ... viii
Acknowledgment ... ix
Abstract ... x
Chapter One ... 1
Introduction ... 1
Background of the research ... 1
Statement of the problem ... 3
Research question ... 4
Purpose of the research ... 4
Significant of the research ... 4
Outline of the research ... 5
Chapter Two ... 6
Literature Review ... 6
The Definition of Motivation ... 6
Kinds of Motivation ... 7
The Function of Motivation ... 9
The Definition of Vocabulary ... 9
Types of Vocabulary ... 10
The Definition of Vocabulary Mastery ... 11
The Relationship between Students' Learning English Motivation and Their Vocabulary Mastery ... 12
Conceptual Framework ... 16
Hypothesis ... 18
Chapter Three ... 19
v
Validity and Reliability ... 23
Data Analysis ... 27
Chapter Four ... 30
Finding and Discussion ... 30
Findings ... 30
Students' Learning English Motivation ... 30
Vocabulary Mastery ... 42
The Relationship between Students' Learning English Motivation and Their Vocabulary Mastery ... 43
Discussion ... 46
Chapter Five ... 49
Conclusion and Recommendation ... 49
Conclusion ... 49
Recommendation ... 50
References ... 51
vi
Table 3.3 Categories of vocabulary mastery ... 23
Table 3.4 Criteria of validity ... 24
Table 3.5 Validity of Pearson product moment ... 24
Table 3.6 Reliability statistic ... 26
Table 3.7 Reliable items ... 26
Table 3.8 Category of the motivation score ... 28
Table 3.9 Category of vocabulary mastery score ... 28
Table 3.10 Coefficient correlation interpretation ... 29
Table 4.1 Question 7 ... 31
Table 4.2 Question 10 ... 31
Table 4.3 Question 11 ... 32
Table 4.4 Question 12 ... 32
Table 4.5 Question 13 ... 33
Table 4.6 Question 14 ... 34
vii
Table 4.10 Question 20 ... 36
Table 4.11 Question 21 ... 37
Table 4.12 Question 23 ... 37
Table 4.13 Question 25 ... 38
Table 4.14 Question 26 ... 39
Table 4.15 Question 27 ... 39
Table 4.16 Question 28 ... 40
Table 4.17 Question 29 ... 41
Table 4.18 Question 30 ... 41
Table 4.19 The mean value of motivation ... 42
Table 4.20 Finding of vocabulary test ... 43
Table 4.21 Normality Data ... 45
Table 4.22 Linearity Data ... 45
ix
capability to finish this undergraduate thesis. I would like to present my sincere appreciation to Mr. Suryanto as my supervisor who has given advice, suggestion, correction and motivation in completing this skripsi. By his support, this
undergraduate thesis works so well.
Most importantly, I would like to say huge thanks to my family who
always support and fire me up to finish this research. Especially for my father Mr. Robani and my beautiful mother Mrs. Sutinah for the support, prayers, love,
giving material I need, and support me all the time in my life.
Beside my parents, I would like to say thank to my sister Ratna Sari who have given her correction and motivation in completing this skripsi and my little
brother Irvan Manggala. Once again, thank for your support bro and sis. And also I would like to say thank to my true friends, Selly Herdiati, Faradina Indah
Kartika, Mentari Purnamasari and Merisa Kurniawati for their help and support during my study.
x
know vocabulary mastery at English Education Department of Universitas
Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta (EED UMY) and to find out the relationship between
students’ English learning motivation and their vocabulary mastery. This research
was conducted in English Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta. The population of English Education Department of Universitas
Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta batch 2013 was 166 students. The participant in this research was 97 students of English Education Department of Universitas
Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta batch 2013. This research used quantitative approach and correlation methodology.
This research used two instruments namely questionnaire to find out
students learning motivation and vocabulary test to find out students vocabulary mastery. The research found that students’ at English Education Department of
Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta batch 2013 had high motivation. It was supported by the motivation with mean value was 96,38. The research also found out that vocabulary mastery was low category with mean value 23,42. The last
result showed that the relationship between students’ English learning motivation
and vocabulary mastery was low criteria of correlation.
The correlation was a positive correlation with the correlation value was 0,209 and probability value 0,040 meaning there was a significant correlation
xi
vocabulary mastery and the hypothesis of H0 was rejected.
Chapter One
Introduction
Background of the Research
Vocabulary is very important for students in speaking, writing, listening and reading comprehension. Students who master vocabulary well may be able to understand the meaning which is contained in reading text. Students are also able
to speak English fluently, improve listening skill, and writing skill if they master a lot of vocabularies.
According to Zhou (2015), vocabulary can be a criterion to see the students' problem in their learn process (p.2). Students with learning problem in learning process will have less vocabulary mastery. They will have difficulty to
express their thought because they do not understand the meaning of vocabulary and they will difficulty to communicate with others. On the other hand, students
who have high vocabulary mastery will be easy to express their thought because they understand the meaning of vocabulary and they can use it to communicate
with others.
Students who have intrinsic motivation in learning English activity will engourage themselve to learn without external reward. Students will learn to study
Students who have high motivation in learning English will undergo a lesson without complaint and they learn diligently and they can improve their
vocabulary mastery in learning English. Students who have low motivation will be different from those who have high motivation.
The previous research with the title “A Correlation Study between English
Learning Motivation, Vocabulary Mastery and Reading Comprehension of the First Grade Students of SMA Negri 3 Surakarta in the Academic year of
2012/2013” conducted by Lestari (2013) found that there is a correlation between
English learning motivation, vocabulary mastery, and reading comprehension.
The result of the research shows a significant level.
Students who have a high motivation tend to be excited, serious and intent in following every subject at the university or anywhere. Indeed, students who do
not have high motivation to learn will be lazy and do not care about the subject. The environment surround students, such as friends in the classroom and campus
are greatly affecting the students' learning motivation. Thus, this study will be conducted to know the relationship between students learning English motivation and their vocabulary mastery. This research has not been done in Universitas
Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta (UMY), so the researcher wants to do this research with the title The Relationship between Students’ English Learning
Motivation and their Vocabulary Mastery at English Education Department
Statement of the Problem
Motivation in learning process must be owned by students, especially when they learn English. Students’ motivation of English Education of
Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyaakarta batch 2011 is fair motivation (Maulana,
2015). Based on the background, statement of the problem of motivation and vocabulary mastery are interconnected because motivation affects students
learning activities.
The researcher exposed some problems related with either learning motivation or vocabulary mastery. Based on depth informal interview with some students of sixthsemester of English Education Department of English Education
of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyaakarta batch 2013, the researcher found that many students are lazy to attend the class because the lecturers are very discipline
and it makes them feel tense and uncomfortable with the lesson so that they are lazy to learn. The students also rarely studied unless they got task or examination
from the lecturer thus affect their vocabulary mastery. So this research will find out whether motivation affects vocabulary mastery.
The researcher will conduct this study to know the current students
learning motivation at English Education of Universitas Muhammadiyah
Yogyakarta batch 2013, vocabulary mastery and the correlation between learning
Research Question
There are three research questions in this research:
1. How is students’ motivation in learning English ability at EED UMY? 2. How is vocabulary mastery at EED UMY?
3. What is the relationship between students’ English learning motivation
and their vocabulary mastery at EED UMY?
Purpose of the Research
The purpose of the research is to know the motivation in learning English ability at EED UMY, to know vocabulary mastery at EED UMY, and to know the relationship between students’ English learning motivation and their vocabulary
mastery at EED UMY batch 2013.
Significance of the Research
The result of this research is expected to give some benefits.
1. Students. This research is expected to give very useful information
about the relationship between students’ English learning motivation
and vocabulary mastery to university students especially of EED UMY.
2. Lecturer. The result of this research is expected to provide a greater
understanding of the relationship between students’ English learning
3. Researcher. This research can be a reference for other researchers that would carry out the same research.
Outline of the Research
This paper is developed into five chapters:
Chapter I covers the introduction: the general background of motivation and vocabulary, statement of the problem, research question, the purpose of the research, significance of the research and the outline of the study. Chapter II
contains a review with regard to motivation in learning English, vocabulary mastery, the relationship between English learning motivation and vocabulary
mastery, and conceptual framework. Chapter III talk about the method of study that consisted of research design, population, and sample. Chapter IV presents the data collection method and data analysis. Chapter V contains the conclusions of
Chapter Two
Literature Review
This chapter discusses the literature related to the subject of this research.
The subject consists of motivation and vocabulary mastery. Sub-subject of learning motivation consists of the definition of motivation, factors that affect motivation, types of learning motivation, definition of vocabulary, type of
vocabulary, vocabulary mastery and the last is the relationship between English learning motivation and vocabulary mastery. These topics will be discussing
bellow.
Definition of motivation
Motivation isa complex statement in individual's self that directs to
certain behavior or stimulus to a certain goal (Purwanto, 2004, p.61). Motivation is a process which gives someone a spirit, direction, and persevering behavior. It
means that motivated behavior is full energy, statistical data and long lasting (Santrock 2011, p.510).
According to Yusuf as cited by Saefullah (2012), motivation derives from
word motive which means individual condition which forces students to do some activities to get an achievement (p.290). Motives are the center of our lives; they
functions such as it energizes, or causes students to act some activities, it directs behavior toward the achievement of specific goals, and it maintains the effort used
in reaching those goals (p.183). Gerrig and Zimbardo (2005) said that motivation is the common term for "all the processes involved in starting, directing, and
maintaining physical and psychological activities" (p.362). DuBrin (1994) stated that motivation is a reason for doing everything (p.93).
According to Lahey (2012), the term motivation refers to an internal state that
activates and gives direction to our thoughts (p.351). King (2013) stated that motivation is the forces that move students to behave, think, and feel the way they
do (p.325). In addition, a motivated behavior is energized, directed, and sustained (King, 2013. p.325). From that theory, it can be concluded that motivation is a force that gives students directs them in life to do some activities to achieve
certain result or goal.
Kind of motivation
Motivation is very important to encourage that give students energy and spirit in learning activities. Motivation is divided into two; there are intrinsic
motivation and extrinsic motivation.
Intrinsic motivation. According to Santrock (2011), intrinsic motivation
is motivation from within individual self to do something for certain goal (p.514).
force of learning that comes from inside of individual self and does not need stimulation from the outside (p.74). According to Santrock (2003), intrinsic
motivation is a desire in individual self to be competent and do something professionally (p.476). According to Lahey (2012), intrinsic motivation is an
individual motive stimulated by the inherent nature of the activity their pleasure of mastering something new or its nature or its nature consequences (p.362).
Reynolds and Miller (2003) stated that students who are intrinsically motivated
should be interested in the task, enjoy it, be more likely to be cognitively engaged,
and also perform at high levels (p.113).
Extrinsic motivation. Extrinsic motivation is to do something to get something
else; it is a way to achieve certain goal (Santrock, 2011. p.514). Santrock (2011) also said that extrinsic motivation is often influenced by external incentives such
as reward and punishment. According to Saefullah (2012), extrinsic motivation is stimulus from outside. Hapsari (2005) said that extrinsic motivation is a force to
learn that given by others such as passion and advice from teachers, parents, siblings and those who beloved (p.74). A student who gets motivation from other people such as friends, teacher and parents will have the motivation to achieve a
goal. Extrinsic motivation is the willingness to gain something with the aim to obtain external rewards (Santrock, 2003. P.476). According to Lahey (2012),
extrinsic motivation is a motivation that is external to the activity and not an inherent part of it. It means that external motivation is human motives active by
The function of motivation
Motivation has a very important function in the learning process especially English learning activities. According to Sadiman as cited by Saefullah,
(2012.p.296) motivation has three functions;
1. Force students to act. It means that motivation as an engine of each
activity to be carried.
2. Motivation has a function to determine a direction to be taking. It
means that every student has a goal to be achieved.
3. The last function is selecting actions. It means that students should
select their activities before they do something to achieve a goal.
The definition of vocabulary
Vocabulary is very important in a language, especially English. Vocabulary is an aspect of English to be learned. Bintz (2011) says that
vocabulary is critically important because a word is an instrument for thinking about the meanings which it expresses (p.44). In addition, McCarten (2007) said that vocabulary is the most important component in the success of learning a
language (p.26). Hornby (2010) stated that vocabulary is all the words that an individual knows or uses (p.1722). Also, Agtin & Hilmiyati (2014) said that
of the basis for how good learners can perform speaking, listening, reading, and
writing (Richards & Renandya, 2002,p.255).
Besides, Manser as cited by Halimatussa’diyah (2012) says,” Vocabulary
is total number of word in a language or list of words with their meanings ... used for teaching a foreign language (p.2)”. As a result, vocabulary is important to
communicate with others. Thus, vocabulary must be mastered by students, because it will make them understand the meaning of some words or sentences
more easily.
Students must master the vocabulary to understand the meaning of written and
spoken messages. Moreover, students should mastery vocabularies in order to be good communication with others. In conclusion, students need to master several vocabularies to be a success in learning English.
Type of vocabulary
Vocabulary is divided into two kinds; receptive vocabulary and
productive vocabulary.
Receptive vocabulary. Haycraft as cited by Hatch and Brown (1995) said that
receptive vocabulary is words that students recognizes and understands when they
occur in a context, but which the students cannot produce correctly (p.370). According to Alqahtani (2015), receptive vocabulary is words that learners
vocabulary is a passive process to memorize vocabularies which are rarely used in daily communication or conversation in English.
Productive vocabulary. Haycraft as cited by Hatch and Brown (1995)
stated that productive vocabulary is words which "the students understand, can
pronounce correctly and use constructively in speaking and writing" (p.370). According to Alqahtani (2015), productive vocabulary is the words that the learners understanding and correctly and use constructively in speaking and
writing (p.25). Moreover, Merikivi & Pietila (2014) said that productive
vocabulary is "the words in productive vocabulary are not merely recognized, but
they can also be produced" (p.488). In summary, productive vocabulary is
vocabulary which is understood and used by the students to communicate in their
daily life.
Definition of vocabulary mastery
According to Hornby (2010), mastery is great knowledge about an
understanding of a particular thing (p.946). Similar definition mentions that "vocabulary is a set of words that are the basic building blocks used in the
generation and understanding of sentences" (Mukoroli, 2011.p.6). It means that in
learning vocabulary, learners should know and understand the meaning and use the meaning in a sentence.
Vocabulary mastery is a great individual skill in using words of a language, which is acquired based on their own interests' needs and motivation (Alqahtani, 2015, p.26). Vocabulary will affect students in the use of a language. According to
words stated that vocabulary mastery is skill toward a group of words which includes the knowledge of the meaning, the knowledge about the classes of words,
and the knowledge about how to use it (p.79). In conclusion vocabulary mastery is knowledge about words, its meaning, how to pronounce it and how to use it in
context correctly.
The relationship between students learning English motivation and
their vocabulary mastery. Chossri and Intharaksa (2011) stated thatmotivation
has a positive impact in English learning to achieve successful in future students education. It means that motivation has a positive correlation with English
learning. In addition, the relationship between languange learning motivation and foreign language achievement as mediated by perfectionsm: the case of high school EFL learn (Dashtizade & Farvardin, 2016). Those researcheres founded
significant correlation between learning motivation and foreign language achievement.
Based on the previous theory in chapter two motivations consist of two aspects, they are intrinsic and extrinsic motivation. The research conducted by Fitriana et al., (2012) with the title "A correlation between learning motivation
and vocabulary mastery and reading competence." The study was carried out at SMP Negeri 4 Surakarta, the academic year 2011-2012. The research has three
variables there are learning motivation, vocabulary mastery and reading
competence. The objectives of this investigation are to reveal whether there is any relationship between students' learning motivation and their reading competence,
ability, and to reveal the relationship between students' learning motivation and their vocabulary mastery simultaneously and reading competence. The research is
quantitative research using questionnaire and test to collect the data. The data are analyzed using statistical calculation method by using simple correlation and
multiple linear regressions. The study found there is a significant positive correlation between learning motivation and reading competence, there is a positive significant correlation between vocabulary mastery and reading
competence, and there is a positive significant correlation between learning motivation and vocabulary mastery simultaneously as well as reading
competence. The similarity between the researchers is variable in one of the variables which are motivation variable. The differences between two researchers are the purpose and analyze. The purpose of this research are to know the
motivation in English learning ability at EED UMY, to know vocabulary mastery at EED UMY, and to know the relationship between student, English learning
motivation and their vocabulary mastery. This research analysis use product moment.
Other research is a research by Lestari (2013), with the title " A correlation
study between English learning motivation, vocabulary mastery and reading comprehension of the first grade students of SMA Negeri 3 Surakarta in the
Academic year of 2012/2013". The research conducted at SMA Negeri 3
Surakarta in the academic year 2012/2013 which consists of ten classes with the population 318 students. The research has 3 variables there are learning
research are to find out the correlation between (1) students English learning motivation and reading comprehension, (2) students vocabulary mastery and
reading comprehension, and (3) students English learning motivation and
vocabulary mastery toward reading comprehension. The research found there is a
significant positive correlation between English learning motivation and reading comprehension. The finding shows that there is a positive correlation between reading comprehension and vocabulary mastery. The finding also shows that there
is a positive correlation between English learning motivation and vocabulary mastery separately or simultaneously and reading comprehension. This research is
quantitative research using questionnaire and test to collect the data. The research uses cluster random sampling technique. The data analyzed using simple
correlation and multiple regression correlations. The similarity between the two
researches is motivation. The differences between two researches are the purpose and the analysis method. The purposes of this research are to know the motivation
in English learning ability at EED UMY, to know vocabulary mastery at EED UMY, and to know the relationship between students’ English learning
motivation and their vocabulary mastery. This research analysis uses pearson
product moment correlation.
In addition, Putri (2016) with the title "Correlation study of students'
motivation and students' vocabulary mastery toward reading comprehension at SMPN 31 Bandar Lampung". The sample of the research is 28 students of SMPN 31 Bandar Lampung. The research has three variables there are motivation,
find out whether there is a significant correlation between students' vocabulary mastery and motivation toward their reading comprehension or not. The analysis
uses product moment correlation. The result of the research shows a significant positive correlation between students' motivation and vocabulary mastery toward
their reading comprehension. The similarities between the two types of research are motivation and analysis method. The difference between two types of research is the objectives. The objectives of this investigation are to know the motivation in
English learning ability at EED UMY, to know vocabulary mastery at EED UMY, and to know the relationship between students' English learning motivation and
their vocabulary mastery.
Moreover , relationship between Iranian EFL learners, motivation and the use of vocabulary learning stategies (Delzendehrouy, Zamanian & Tayyebi,
2014). Those research found significant correlation between motivation and the use of vocabulary learning stategies.
Thus, the difference of result depends on the site where the research is conducted and becomes the motive of the researcher to conduct this research at EED UMY, so that the researcher interested in this study to know the correlation between students’ English learning motivation and their vocabulary mastery at
Conceptual Framework
Students who have high motivation either extrinsic motivation or intrinsic
motivation will learn English not only grammar, pronunciation but also
vocabulary seriously. Vocabulary is an important part of language, if the students
improve their vocabulary mastery, it will be easy to express their thought because they understand the meaning of vocabulary and they can use it to communicate
with others.
On the other hand, students who have low motivation will not study English seriously so their vocabulary will not improve and they will face
difficulty to express their thought without mastering vocabulary. Thus, motivation
will increase the students' vocabulary mastery. The scheme of the correlation between students learning English motivation and their vocabulary mastery is
Figure 2.1
Conceptual Framework
Motivation
Vocabulary Reading
Improve
Listening Studying English
Hypothesis
H0: There is no significant correlation between students’ English learning
motivation and their vocabulary mastery at EED UMY.
Ha: There is a significant correlation between students’ English learning
Chapter Three
Research Method
This chapter describes the methodology in the research and how it will be done from the beginning to the end. It consists of four parts: research design,
population and sample, data collecting method and data analysis. The research design discusses the design and the reason for choosing this design. The population and sample explain about the subject of the research. The data
collecting method explain the way the researcher collecting the data and in the data analysis will give an explanation about how to analyze the data.
Research Design
The research focussed on the relationship between students' learning English motivation and their vocabulary mastery. This research is correlational
research. It determines the correlation of a variable with other variables
(Sukmadinata, 2010, p.56). Creswell (2012) also said that "a correlation research
design is a statistical test to determine the tendency or pattern for two (or more) variables or two sets of the data to vary consistently" (p.338).
Population and Sample
Population. In this research, the population is students at English
Education Department of UMY batch 2013. According to Creswell (2012), a
object or subject that has certain qualities and characteristics which are
determined by the researcher (p.117). The total population of students in batch
2013 is 166 students.
Sample. The research sampling that be used is convenience sampling.
Based on Cohen, Manion, and Morrison (2011), convenience sampling is accidental or opportunity sampling (p.155). Cohen et al. (2011) also said that convenience sampling chooses the nearest individuals to serve as respondents
(p.155). This research took 97 students from 166 students in EED UMY batch 2013 as respondents.
Data Collection Method
Firstly, the research asked permission to the students to become the respondents of this research. Second, before the researcher asked the students to
fill out the questionnaire and vocabulary test, the researcher explained the objectives of the test. The questionnaire consists of 30 items with likert scale.
The data collection methods that are used in this research are questionnaire and vocabulary test. The researcher gave the questionnaire and vocabulary test to students of English Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah
Yogyakarta (EED UMY). The questionnaire was used to gather the data of English learning motivation while vocabulary test was used to determine the
students of sixthsemester of EED UMY batch 2013 and only 97 questionnaire for
[image:31.595.113.272.233.319.2]retruned.
Table 3.1
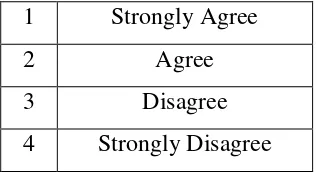
The categories of the questionnaire are:
1 Strongly Agree
2 Agree
3 Disagree
4 Strongly Disagree
Vocabulary test consists of 60 English words which have translated by students in Indonesian. It is divided into four categories. The first category is from number 1-15 consisted of 15 familiar English words to indicate very low
vocabulary mastery. The second category is from 16 -30 consisted of 15 familiar English words to indicate low vocabulary mastery. The third category is from
number 31-45 consisted of 15 English words to indicate high vocabulary mastery. The last category is from number 46-60 comprising unfamiliar English words to
indicate very high vocabulary mastery.
Instruments of the Study
The instruments of the data collection helped the researcher to find out the
correlation between students learning English motivation and their vocabulary mastery. The instruments of the research are questionnaire and test of vocabulary. The instrument of the questionnaire is to measure motivation and test of
The questionnaire consists of 30 statements used to find out students' motivation. The vocabulary test is used to measure the students' vocabulary
mastery. The vocabulary test was adapted from Meara (1992) that consists of 60 vocabularies (p.98). The researcher taken some vocabulary test level 4 and then
the researcher classified some easy vocabulary, moderate vocabulary and difficult vocabulary as the indicator to measure the students' vocabulary because Meara (1992) said that level 1 and level 2 is the basic level that represented the core of
English vocabulary (p.4) while level 3 up to 6 represented advanced. The students' of sixth semester at English Education department of Universitas Muhammadiyah
Yogyakarta batch 2013 should master advanced vocabulary that was why the researcher taken level 4 to find out their vocabulary mastery.
Questionnaire
The questionnaire used 4 point scales to observe EED UMY students’
motivation namely strongly agree, agree, disagree and strongly disagree. The
[image:32.595.115.505.614.744.2]scale used in this study will be presented in the following table.
Table 3.2
Scale of questionnaire
No. Rating scale Descriptive Statement
Favorable Unfavorable
1. 1 Strongly Disagree 4 1
2. 2 Disagree 3 2
3. 3 Agree 2 3
Vocabulary
The vocabulary test adapted from Meara with kind of receptive vocabulary
because the students can translate the meaning of a word or sentence. The vocabulary test consisted of 30 numbers of words. The test is divided into four
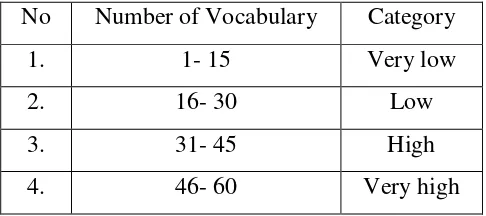
categories, the first category is very low, the second is low, the third is high, and the last is very high The first category from number 1-15 is very low, the second category from 16 -30 is low, the third category from number 31-45 is high, and
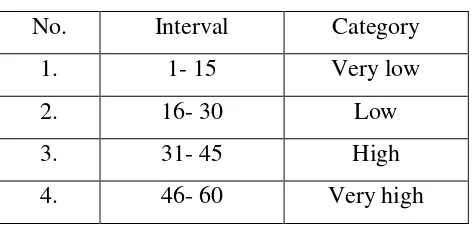
[image:33.595.113.356.440.548.2]the last category from number 46-60 is very high. The categories of vocabulary mastery drawn in the table.
Table 3.3
Categories of vocabulary mastery
No Number of Vocabulary Category
1. 1- 15 Very low
2. 16- 30 Low
3. 31- 45 High
4. 46- 60 Very high
Validity and Reliability of the questionnaire
Validity. Validity is an essential aspect of effective research (Cohen et al.,
2011,p.179). Instrument validity shows that result of measurement illustrates the aspect of variables which are measured (Sukmadinata, 2010, p.228). Validity test
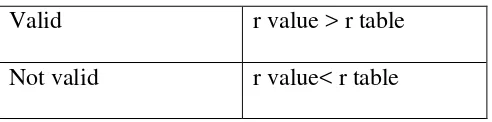
to find r value of each question. The question was valid if r value is higher than r table and the question was not valid if r value is lower than r table. The r value
[image:34.595.109.355.296.357.2]was obtained from the number of question (n=30). Therefore r table of this number is 0.361. The criteria items validity is presented in the table below.
Table 3.4
The criteria of validity
Valid r value > r table
Not valid r value< r table
The data analysis result of the validity test of the questionnaire is
[image:34.595.109.431.488.747.2]presented in the following table.
Table 3.5
Validity of Pearson product moment
No. Items r value r table Description
1. Items 1 0.344 0.361 Not valid
2. Items 2 0.283 0.361 Not valid
3. Items 3 0.148 0.361 Not valid
4. Items 4 0.295 0.361 Not valid
5. Items 5 0.309 0.361 Not valid
6. Items 6 0.352 0.361 Not valid
7. Items 7 0.437 0.361 Valid
8. Items 8 0.305 0.361 Not valid
9. Items 9 0.189 0.361 Not valid
10. Items 10 0.375 0.361 Valid
12. Items 12 0.433 0.361 Valid
13. Items 13 0.379 0.361 Valid
.14. Items 14 0.614 0.361 Valid
15. Items 15 0.424 0.361 Valid
16. Items 16 0.296 0.361 Not valid
17. Items 17 0.499 0.361 Valid
18. Items 18 0.349 0.361 Not valid
19. Items 19 0.533 0.361 Valid
20. Items 20 0.524 0.361 Valid
21. Items 21 0.526 0.361 Valid
22. Items 22 0.092 0.361 Not valid
23. Items 23 0.437 0.361 Valid
24. Items 24 0.347 0.361 Not valid
25. Items 25 0.586 0.361 Valid
26. Items 26 0.534 0.361 Valid
27. Items 27 0.577 0.361 Valid
28. Items 28 0.455 0.361 Valid
29. Items 29 0.456 0.361 Valid
30. Items 30 0.494 0.361 Valid
The questionnaire of this research consisted of 30 items. Moreover based on the criteria of validity test the item that valid are 18 items. There are items
number 7, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 17, 19, 20, 21, 23, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29 and 30. The items that not valid are 12 items; there are items number 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 16, 18, 22 and 24
Reliability. Creswell (2012) stated that reliability means that score from
coefficient formula. The calculation of reliability coefficient uses Cronbach's Alpha formula which uses data obtained from the result of the scale of a group of
respondents. The reliability coefficient (rxx’) are in the range of number from 0 to 1,00 (Azwar, 2013, p.112). The measurement instrument is reliable if the
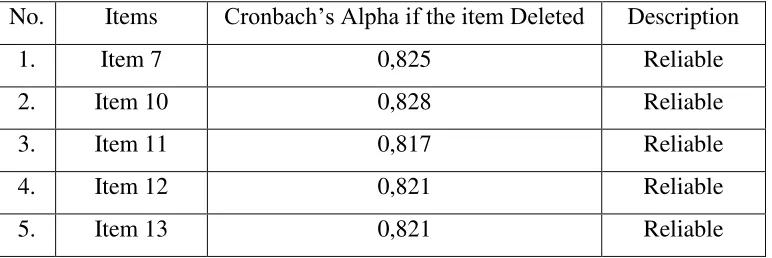
reliability coefficient approaches 1,00. Based on the result of a reliability test using Cronbach’s Alpha, after the reliability test of 18 items that are valid, all of
the items were defined reliable. The reliability of 18 items was reported in the
[image:36.595.109.328.400.471.2]table below.
Table 3.6
Reliability statistics Cronbach’s Alpha
N of items
0,828 18
[image:36.595.109.495.626.755.2]The reliability of the questionnaire was 0,828. The items that were reliable displayed in Table 3.8.
Table 3.7 Reliable items
No. Items Cronbach’s Alpha if the item Deleted Description
1. Item 7 0,825 Reliable
2. Item 10 0,828 Reliable
3. Item 11 0,817 Reliable
4. Item 12 0,821 Reliable
Analysis of Data
In this research, the data were collected from questionnaire and vocabulary test to find out the relationship between students learning English motivation and vocabulary mastery. The researcher used descriptive and inferential statistic to
analyze the data. According to Sugiyono (2010), descriptive statistics is a
statistical analysis which is used to analyze the data by making a real description
about the data that has been collected by the researcher (p.207). Also, Sugiyono (2010) said that inferential statistic is a statistical technique that is used to analyze the data of sample and the result is applied to the population (p209).
To analyze the data, the researcher used the mean value and standard deviation. The category of motivation and vocabulary are drawn in the following
table.
6. Item 14 0,814 Reliable
7. Item 15 0,823 Reliable
8. Item 17 0,816 Reliable
9. Item 19 0,817 Reliable
10. Item 20 0,821 Reliable
11. Item 21 0,821 Reliable
12. Item 23 0,824 Reliable
13. Item 25 0,817 Reliable
14. Item 26 0,817 Reliable
15. Item 27 0,812 Reliable
16. Item 28 0,822 Reliable
17. Item 29 0,820 Reliable
Table 3.8
Category of the motivation score
No. Interval Category
1. 1- 30 Very low
2. 31- 60 Low
3. 61- 90 High
4. 91- 120 Very high
The table above shows the categories of students' motivation level. The
score between 1 to 30 indicated a very low category. The score 31 to 60 indicated a low category. The score 61 to 90 indicated a high category, and the score
between 91 to 120 indicates a very high category.
Table 3.9
Category of vocabulary mastery score
No. Interval Category
1. 1- 15 Very low
2. 16- 30 Low
3. 31- 45 High
4. 46- 60 Very high
The table shows the categories of students’ vocabulary mastery. The score
between 1 to 15 indicated very low category, the score 16 to 30 indicated low
category, the score 31- 45 indicated high category, and the score between 46- 60 indicated very high category,
[image:38.595.113.349.457.572.2]motivation and vocabulary mastery. According to Tuhuleley (2015), the data of product moment analysis should be interval or ratio and it should be normal
distributed data (p.67). The data will be analyzed using SPSS version 22.0. The correlation criteria value is divided into five categories namely very low, low,
moderate, strong and very strong (Sugiyono , 2013. p.231) in the following the table.
Table 3.10
Coefficient correlation interpretation
Coefficient (r) Relationship
0,00- 0,199 Very low
0,20- 0,399 Low
0,40- 0,599 Moderate
0,60- 0,799 Strong
Chapter four
Finding and Discussion
In this section, the researcher shows the finding and discussion of the research. The findings section describes the result of the data statistical analysis.
The discussion section presents the findings with further explanation.
Findings
In this part, the researcher presents the findings of those three research question. The first is finding of students’ motivation in learning English ability at
EED UMY. In order to answer the first research question this research used
questionnaire. The second is the finding of vocabulary mastery at EED UMY. This research used vocabulary test to identify vocabulary mastery of students’ at
EED UMY. The last is the finding of the relationship between students’ English
learning motivation and their vocabulary mastery at EED UMY.
Students’ motivation. The first research question is "how is students'
motivation in learning English ability at EED UMY." The motivation is reflected on 18 statements that involved items. The result of sample responses is presented
Table 4.1
Q7. The discipline lecturer did not make me enthusiastic in learning English.
Frequency Percent
Valid Strongly Disagree 34 23,3
Disagree 50 34,2
Agree 8 5,5
Strongly Agree 5 3,4
Total 97 100,0
Based on the table above, related to the statement of the item that said "the
discipline lecturer makes me excited in learning English." The responses are 5 students (5,2%) choose strongly disagree, 8 students (8,2%) said disagree, 50
students (51,5%) mentioned agree, 34 students (35,1%) stated strongly agree. It means that most of the students are enthusiastic to learn English with the discipline lecturer.
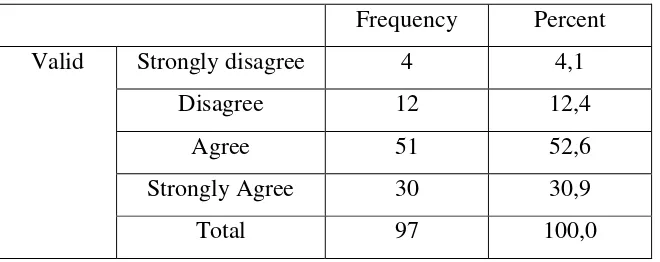
Table 4.2
Q10. I learn English so that I can be a professional teacher.
Frequency Percent
Valid Strongly disagree 4 4,1
Disagree 12 12,4
Agree 51 52,6
Strongly Agree 30 30,9
Total 97 100,0
From table 4.2, it shows that 4 students (4,1%) stated very disagree, 12
[image:41.595.149.479.571.702.2](30,9%) said strongly agree. It means that many students learn English to be a professional teacher.
Table 4.3
Q11. I learned English to write good English articles.
Frequency Percent
Valid Strongly disagree 0 0
Disagree 7 7,2
Agree 61 62,9
Strongly Agree 29 29,9
Total 97 100,0
In the statement "I learned English in order to write good English articles" can be seen that seven students (7,2%) voted disagree, 61 students (62,9%) chose
agree and 29 students (29,9%) stated strongly agree. It means that many students learn English because they want to write good articles.
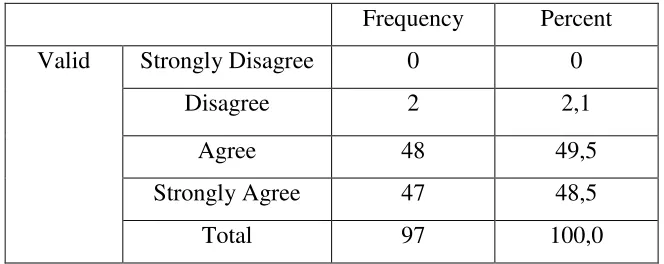
Table 4.4
Q.12. I watch a movie to improve my vocabularies.
Frequency Percent
Valid Strongly Disagree 0 0
Disagree 2 2,1
Agree 48 49,5
Strongly Agree 47 48,5
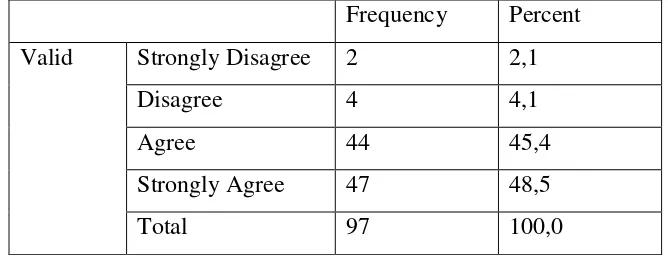
[image:42.595.146.478.579.711.2]From table 4.4, it shows that 2 students (1,1%) stated disagree, 48 students (49,5%) chose agree, and 47 students (48,5%) said strongly agree. It means that
[image:43.595.143.481.302.432.2]many students watch a movie to improve their vocabularies.
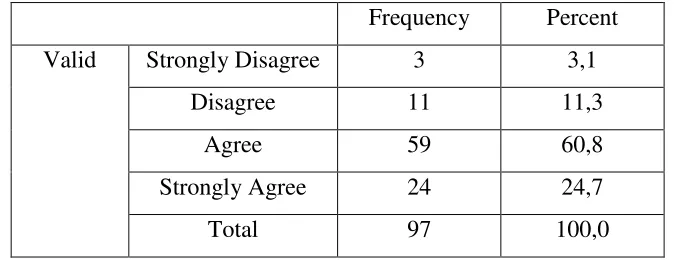
Table 4.5
Q13. I go to campus and study English in order to get a high Grade Point Average (GPA).
Frequency Percent
Valid Strongly Disagree 3 3,1
Disagree 11 11,3
Agree 59 60,8
Strongly Agree 24 24,7
Total 97 100,0
The result on table 4.5 shows that there are three students (3,1%) of the samples strongly disagree with statement of "I go to campus and study English in
order to get a high GPA." There are 11 students (11,3%)of sample voted disagree, 59 students (60,8%) answered agree and 24 students (24,7%) of the sample chose
Table 4.6
Q14. I always pay attention to the lecture given by the lecturers.
Frequency Percent
Valid Strongly Disagree 0 0
Disagree 10 10,3
Agree 63 64,9
Strongly Agree 24 24,7
Total 97 100,0
In the statement "I always pay attention to the lecture given by the lecturers" can be seen that there were ten students (10,3) chose disagree, 63 students (64,9) voted agree, and 24 students (24,7%) voted strongly agree. It
means that most of the students always pay attention to the lecture given by the lecturer.
Table 4.7
Q15. Parents are always giving spirit to the students to attend the lectures.
Frequency Percent
Valid Strongly Disagree 2 2,1
Disagree 4 4,1
Agree 44 45,4
Strongly Agree 47 48,5
Total 97 100,0
From Table 4.7, the researcher found out the result of a statement "Parents are always giving spirit to the students to attend the lectures". There were 2
[image:44.595.144.478.531.660.2]students stated agree, and 47 students (48,5%) confirmed strongly agree. It means that most of the students always have spirit given by their parents and family to
[image:45.595.149.478.290.421.2]attend the lectures.
Table 4.8
Q17. I learned English so that later I can explain the material to my students clearly.
Frequency Percent
Valid Strongly Disagree 0 0
Disagree 4 4,1
Agree 40 41,2
Strongly Agree 53 54,6
Total 97 100,0
The result on Table 4.8 shows that there are four students (4,1%) of the sample disagreed with the statement of "I learned English so that later I can
explain the material to my students clearly". There are 40 students (41,2%) of the sample agreed with the statement, 53 students (54,6%) of the sample answered strongly agree. It means that many students learned English so that later they can
Table 4.9
Q19. I am not serious in learning English because many friends are lazy to learn
it.
Frequency Percent
Valid Strongly Disagree 33 34,0
Disagree 60 61,9
Agree 4 4,1
Strongly Agree 0 0
Total 97 100,0
In the statement "I am not serious in learning English because many friends are lazy to learn it." Most of students chose agree (61,4%), 33 students
(34,0%) chose strongly agree, and 4 students (4,1%) chose disagree. It means that most of students are serious in learning English and they not affected by peer friends who are lazy to learn.
Table 4.10
Q20. I memorize English vocabulary so I can understand English conversation.
Frequency Percent
Valid Strongly Disagree 0 0
Disagree 4 4,1
Agree 59 60,8
Strongly Agree 34 35,1
Total 97 100,0
From Table 4.10 shows that 4 students (4,1%) stated disagree, 59 students
[image:46.595.146.479.565.699.2]many students memorize new English vocabulary so they can understand English conversation.
Table 4.11
Q21. I learn new vocabularies to improve my vocabulary mastery.
Frequency Percent
Valid Strongly Disagree 0 0
Disagree 0 0
Agree 55 56,7
Strongly Agree 42 43,3
Total 97 100,0
The result on Table 4.11 shows that there are 55 students (56,7%) of the sample agreed with statement of "I learn new vocabularies to improve my
vocabulary mastery". There are 42 students (43,3%) chose strongly agree. It means that many students learn new vocabularies to improve their vocabulary
mastery.
Table 4.12
Q23. I am lazy to read English book because it will not make me mastering
English.
Frequency Percent
Valid Strongly Disagree 29 29,9
Disagree 60 61,9
Agree 6 6,2
Strongly Agree 2 2,1
[image:47.595.146.476.620.750.2]In the table above, 2 students (2,1%) chose strongly disagree, 6 students (6,2%) voted disagree, 60 students (61,9%) stated agree, and 29 students (29,9%)
[image:48.595.146.479.302.435.2]argued strongly agree. It means that most of students read English book because they think it will make them mastering English.
Table 4.13
Q25. The advice given by parents influences my learning spirit.
Frequency Percent
Valid Strongly Disagree 0 0
Disagree 1 1,0
Agree 52 53,6
Strongly Agree 44 45,4
Total 97 100,0
The result on the table 4.13 shows that there is one student (1,0%) of the sample disagreed with the statement of "The advice given by parents influences
Table 4.14
Q26. I am learning English seriously in order to get a TOEFL score over 550.
Frequency Percent
Valid Strongly Disagree 2 2,1
Disagree 3 3,1
Agree 49 50,5
Strongly Agree 43 44,3
Total 97 100,0
From the table 4.14 the researcher found out the result of the statement "I
am learning English seriously in order to get a TOEFL score over 550". There were 2 students (2,1) said strongly disagree, 3 students (3,1%) confirmed
disagree, 49 students (50,5%) stated agree, and 43 students (44,3%) chose strongly agree. It means that most of the students are learning English seriously because they want to get a TOEFL score over 550.
Table 4.15
Q27. I do and collect the task given by lecturer so that I can graduate with cum
laude predicate.
Frequency Percent
Valid Strongly Disagree 1 1,0
Disagree 10 10,3
Agree 51 52,6
Strongly Agree 35 36,1
[image:49.595.146.479.581.708.2]From table 4.15, the researcher found out the result of the statement “I do
and collect the task given by lecturer so that I can graduate with cum laude
predicate." There were 1 student (1,0%) chose strongly disagree, 10 students (10,3%) said disagree, 51 students (52,6%) stated agree, and 35 students (36,1%)
[image:50.595.145.480.355.487.2]confirmed strongly agree. It means that most of the students do and collect the task given by lecturer because they want to graduate with cum laude predicate.
Table 4.16
Q28. I seldom learn about English material to improve my TOEFL score.
Frequency Percent
Valid Strongly Disagree 8 8,2
Disagree 61 62,9
Agree 25 25,8
Strongly Agree 3 3,1
Total 97 100,0
In the statement "I seldom learn about English material to improve my TOEFL score" most students voted agree (62,9%), other students chose disagree
Table 4.17
Q29. I do not want to speak English fluently.
Frequency Percent
Valid Strongly Disagree 50 51,5
Disagree 40 41,2
Agree 3 3,1
Strongly Agree 4 4,1
Total 97 100,0
From the table 4.17 above, there are 4 students (4,1%) stated strongly
disagree, 3 students (3,1%) voted disagree, 40 students (41,2%) argued agree, and 50 students (51,5%) chose strongly agree. It means that most of students are
interested to speaking English fluently.
Table 4.18
Q30. I learn English in order to understand the English reading materials.
Frequency Percent
Valid Strongly Disagree 0 0
Disagree 1 1,0
Agree 54 55,7
Strongly Agree 42 43,3
Total 97 100,0
From Table 4.18, it showed that 1 student (1,0%) stated disagree, 54
students (55,7%) voted agree, and 42 students (43,3%) chose strongly agree. It means that most of students learn English in order to understand the English
[image:51.595.144.480.509.643.2]The result showed that students' motivation at EED UMY is high. It is supported by the means value 96,38. Based on the criteria of the mean value,
[image:52.595.114.421.288.408.2]96,38 is belong to high category of motivation. The mean value motivation criteria are presented in the table.
Table 4.19
The mean value of motivation.
Number of Students
Precent
(%) Category
0 0 very low
0 0 Low
58 59,8% High
39 40,2% very high
Total 97 100%
The result on the table 4.19 shows that no student (0%) who has very low criteria of motivation and there are no student (0%) who has low motivation.
Moreover, students with high percentage are 59,8% who has high criteria, of motivation and there are 40,2% students with very high criteria of motivation.
Vocabulary mastery at EED UMY. The second research question of this
research is “How is vocabulary mastery at EED UMY”. Based on the vocabulary
Table 4.20
Finding of vocabulary test
Number of Students
Percent
(%) Category 8 8,2% Very Low 77 79,4% Low 12 12,4% High
0 0% Very High
Total 97 100%
The result on the table 4.20 shows that students with a very low score of
vocabulary test are eight students (8,2%). Students with Low score of vocabulary test are 77 students (79,4%). Moreover, students with a high score of vocabulary
mastery test are 12 students (12,4%) and there are no student (0,0%) who has very high vocabulary mastery. Based on the result, it can be seen that the students of EED UMY batch 2013 have low vocabulary mastery. It is supported by the mean
value of vocabulary mastery is 23,42.
The relationship between students’ English learning motivation and
their vocabulary mastery at EED UMY. The third research question is what is
the relationship between students’ English learning motivation and their
vocabulary mastery at EED UMY”. Before analysis the correlation the reseacher
Table 4.21
Normality data
Based on the table 4.21 above, the significant value of 0,000 is smaller than 0,05, it can be concluded that the data is not normality.
Table 4.22
Linearity data
ANOVA Tablea
Sum of Squares Df
Mean
Square F Sig. Vocabulary Mastery * Motivation Between Groups (Combined)
,138 1 ,138 ,698 ,405 Within Groups 18,769 95 ,198
Total 18,907 96
a. With fewer than three groups, linearity measures for Vocabulary Mastery * Motivation cannot be computed.
One-Sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test
Unstandardized
Residual
N 97
Normal Parametersa,b Mean ,0000000
Std. Deviation ,44216832
Most Extreme Differences Absolute ,387
Positive ,387
Negative -,348
Test Statistic ,387
Asymp. Sig. (2-tailed) ,000c
a. Test distribution is Normal.
b. Calculated from data.
Based on the table 4.23, significant value is 0,405 greater than 0.05. It means that there is a significant linear correlation between learning motivation
and vocabulary mastery.
The result of the correlation between those two variables will be explained in the
following table.
The relationship between students’ English learning motivation and their
vocabulary mastery at EED UMY.
Motivation Vocabulary Mastery
Motivation Pearson Correlation 1 ,209*
Sig. (2-tailed) ,040
N 97 97
Vocabulary Mastery
Pearson Correlation ,209* 1
Sig. (2-tailed) ,040
N 97 97
*Correlation is significant at the 0,05 level (2-trailed)
Based on the table, the result of the Pearson correlation analysis shows that the number of correlation between students’ English learning motivation and
vocabulary mastery is 0,209. The correlation is significant because the probability value is 0,040. The criteria of significant correlation based on Tuhuleley (2015,
Table 4.22
The criteria of significant correlation
Significant The value is <0,05 Not Significant The value is >0,05
Therefore, it could be said that the correlation between students’ English learning
motivation and vocabulary mastery is low criteria of correlation
(Sugiono,2013,p.231).
Discussion
The researcher conducted the research to investigate the fact of English
learning motivation and vocabulary mastery. After explained the calculation and the data analysis of the data result, this part presents the discussion which refers to
previous calculation and analysis.
The researcher collects the data of English learning motivation from questionnaire score. The data that were analyzed would be used to identify the frequency of the students’ English learning motivation. To clarify the students’
English learning motivation, the researcher used the value of mean to know the category of English learning motivation. Based on the finding of students’ English
learning motivation above, it could be seen that the mean value is 96,38. Most of the students (59,8%) indicated that they are in high motivation. The rest of 40,2% students are in the very high motivation. It means that students’ English learning
motivation at EED UMY is high. Reynolds and Miller (2003) stated that students
high level (p.113). Thus the result showed that most students of sixth semester at English Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta batch
2013 that have high learning motivation so they are interested in learning English activity.
Mukoroli (2010) stated that vocabulary is a set of words that is the basic building blocks used in understanding of sentence. In order to identify the students’ vocabulary mastery at EED UMY batch 2013, the researcher used
vocabulary test. Students should know and understand the meaning in a sentence with vocabulary test. The researcher also uses mean value, to know the category of students’ vocabulary mastery. Based on the finding the mean value of students’
vocabulary mastery is 23,42. It means that the students of EED UMY batch 2013 have low vocabulary mastery. It is supported by the result of vocabulary mastery
of EED UMY batch 2013 that 77 students (79,4%) are in the low category of vocabulary mastery.
According to Chossri and Intharaksa (2011) motivation has a positive impact in English learning. It means that learning motivation at English Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarata have a
positive impact for students in English learning. The result shows that the relationshipbetweenstudents' English learning motivation and their vocabulary
Based on the correlation criteria value by Sugiyono (2013), the result presents that the correlation number is in a low criteria with the number correlation is 0,209
Chapter Five
Conclusion and Recommendation
This chapter is divided into two sections. The first section presents the summary of the research finding. The second section of the research gives several
recommendations for this research to lecturer, students, and further researcher.
Conclusion
This research investigated 97 students of English Education Department students’ batch 2013 of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta. This research
found that the students have high motivation. It means that students have full
energy, spirit and direction to learn English; In fact, most of the students at English Education Department batch 2013 are in the low category of vocabulary mastery by the mean 23,42. It is supported by the result of vocabulary test of 77
(79,4%) students are in a low category.
The final result explained that there is a relationship between students’
English learning motivation and vocabulary mastery at EED UMY batch 2013 in a positive correlation but in low criteria. The findings show that the probability value is 0,040 and the number of the correlation is 0,209. To sum up, the
correlation between those two variables are in low correlation category. The low correlation indicates that high motivation is not the main factor to increase
Recommendation
Based on the research findings about the relationship between students’
English learning motivation and vocabulary mastery, the researcher gives some
recommendation to the lecturers, students, and researchers.
1. For the lecturers. The lecturer should apply the learning method that can
increase students’ vocabulary or interesting learning media such as using
game or video.
2. For students. The students could improve their vocabulary mastery with
many ways, for example translating unfamiliar words, listening and translating the Englsih song. It was useful for students to improve their vocabulary mastery.
3. For researchers. The other researchers who were interested to investigate
the same topic, the research suggested using another technique in
Reference
Agtin, R., and Hilmiyati, F. (2014). Meningkatkan penguasaan kosakata Bahasa
Inggris dengan menggunakan media gambar. Jurnal primary. 6(2), 197– 214.
Alqahtani, M. (2015). The importance of vocabulary in language learning and
how to be taught. International journal of teaching and education. 3(3). doi 10.20472/TE.2015.3.3.002.
Azwar, S. (2013). Penyusunan skala psikologi. Yogyakarta: Pustaka Pelajar.
Bandu, D. J., and Marzuki, A.G. (2014). A corroletion study between vocabulary mastery and reading comprehension of PAI students of Tarbiyah STAIN
Datokarama Palu, Istiqara. 2(1), 75-94.
Bintz, W. P. (2011). Teaching vocabulary across the curriculum. Middle school journal :www.nmsa.org.
Choosri, C., and Intharaksa, U. (2011). Relationship between motivation and students English learning achievement: A students of the second year
vocational certificate level hatyai technical college students. International conference on humanities and social sciences. Prince of Songkla University:
Faculty of Liberal Arts.
Creswell, J.W. (2012). Education research: Planning, Conduction, and Evaluating
quantitative and qualitative research. Boston: Pearson Education.
Dashtizade, P., and Farvardin, M. T. (2016). The relationship between language learning motivation and foriegn language achievement as mediated by
perfectionsm the case of high school EFL learners. Jurnal of language cultural education. 4(3).
Delzendehrouy, N., Zamanian., and Tayyabi, G. (2014). The relationship between Iranian EFL learners’ motivation and the use of vocabulary learning strategies.
Journal of studies in learning and teaching English. 2(5), 19-39.
DuBrin, A.J. (1994). Applying psychology: individual and organizational effectiveness. Mexico: Prentice-Hall International.
Fitriana, F. N., Nurkamto, J., and Pudjobroto, A. H. (2012). A correlation between
learning motivation and vocabulary mastery and reading comprehension. Solo: Universitas Sebelas Maret.
Gerrig, R. J., and Zimbardo, P.G. (2005). Psychology and life. Boston: Pearson Education.
Halimatussa’diyah, P. (2012). Teaching English vocabulary using story telling
technique at English Grade students of MTsN Cilamaya Karawang. Bandung: STKIP Siliwangi Bandung.
Hatch, E., and Brown, C. (1995). Vocabulary, semantics, and language education.
New York: Cambridge University Press.
Hornby, A.S. (2010). Oxford advance learner’s dictionary. London: Oxford
University Press.
King, L. A. (2013). Experience psychology. New York: The McGraw-Hill Companies.
Kyriacou, C. (2011). Effective teaching: Theory and practice. Bandung: Nusa
Media.
Lahey, B. B. (2012). Psychology an introduction. New York: The McGraw-Hill
Companies.
Lestari, F. I. (2013). A correlation study between English learning motivation, vocabulary mastery and reading comprehension of the first grade students of
SMA Negeri 3 Surakarta in the academic year of 2012/2013. Surakarta: Universitas Sebelas Maret.
https://eprints.uns.ac.id/11244/1/319322709201309511.pdf
Maulana, M. K. (2015). The correlation between students’ motivation and students’ English speaking skill at English Education Department Universitas
Muhammadiyah Yogyakartya.Yogyakarta: Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta.
Merikivi, R. & Pietila, P. (2014). Vocabulary in CLIL and in mainstream education. Journal of language teaching and research, 5 (3), 487- 497. doi:
10.4304/jltr.5.3.
McCarten, J. (2007). Teaching vocabulary lesson from the corpus lesson for the
classroom. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Mukoroli, J. 2011. Effective vocabulary teaching strategy for the English for
academic purpose ESL classroom. MA TESOL collection. 501.
Purwanto, N. (2004).Psikologi pendidikan. Bandung: PT Remaja Rosdakarya.
Putri, R.Y. (2016). Correlation study of students’ motivation and students’
vocabulary mastery toward reading comprehension at SMPN 31 Bandar Lampung. Lampung: Universitas Lampung.
http://digilib.unila.ac.id/22644/18/SCRIPT%20WITHOUT%20DISCUSSION
%20CHAPTER.pdf
Reynolds, W. M., and Miller, G. E. (2003). Hand of psychology. New Jersey:
John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Richards, J. C. & Renandya, W. A. (2002). Methodology in language teaching an
anthology of current practice. Edinburgh, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Santrock, J. W. (2011). Psikologi pendidikan. Jakarta: Kencana Prenada Media
Group.
Santrock, J. W. (2003). Adolescence: Perkembangan remaja. Jakarta : Erlangga.
Saefullah. (2012). Psikologi perkembangan dan pendidikan. Bandung CV Pustaka
Setia.
Sugiyono. (2010). Metode penelitian pendidikan: Pendekatan kuantitatif, kualitatif
dan R&D. Bandung: Alfabeta.
Sugiyono. (2013). Statistik untuk penelitian. Bandung: Alfabeta.
Sukmadinata, N. S. (2010). Methode penelitian pendidikan: Pendekatan
kuantitatif, kualitatif dan R&D. Bandung: Alfabeta.
Tuhuleley, S. (2015). Statistik pendidikan. Yogyakarta: Fakultas Agama Islam
UMY.
Zhou, Z. D. Y. (2015). Empirical studies on English vocabulary learning strateg in Mainland China over the past two deade. Journal of arts & humanities, 04(2),
Appendies Appendix 1. the Questionnaire
QUESTIONNAIRE
Baca dan pahamilah setiap pernyataan berikut. Kemudian isilah respon jawaban sesuai dengan keadaan anda sendiri, dengan cara memberi tanda silang (x) pada pilihan jawaban berikut:
1 = Sangat Setuju (SS) 2 = Setuju (S)
3 = Tidak Setuju (TS)
4 = Sangat Tidak Setuju (STS)
No Pernyataan 1 2 3 4
1. Saya belajar bahasa Inggris karena ingin berkomunikasi dengan orang asing secara lancar.
SS S TS STS
2. Saya mempelajari bahasa Inggris dengan baik untuk mendapatkan beasiswa melanjutkan sekolah di luar negeri.
SS S TS STS
3. Saya malas menghafalkan grammar (tata bahasa Inggris) karena sulit.
SS S TS STS
4. Saya mengikuti kuliah dengan rajin supaya mendapat pujian dari dosen.
SS S TS STS
5. Saya mempelajari bahasa inggris karena ingin berbicara dengan lancar seperti teman saya.
SS S TS STS
6. Dukungan dari keluarga tidak berpengaruh terhadap prestasi belajar saya.
SS S TS STS
7. Dosen yang disiplin membuat saya tidak bersemangat dalam mempelajari bahasa Inggris.
SS S TS STS
8. Saya tidak bersemangat belajar bahasa inggris karena pengaruh teman.
SS S TS STS
9. Saya mempelajari bahasa Inggris dengan tekun supaya mendapatkan hadiah dari orang tua.
SS S TS STS
10. Saya belajar bahasa inggris dengan tekun supaya jadi guru profesional.
SS S TS STS
berbahasa Inggris dengan baik.
12. Saya menonton film berbahasa Inggris untuk menambah kosakata baru.
SS S TS STS
13. Saya rajin masuk kuliah dan belajar bahasa inggris supaya mendapat IPK yang tinggi.
SS S TS STS
14. Saya selalu memperhatikan mata kuliah yang diberikan dosen.
SS S TS STS
15. Orang tua selalu memberikan semangat saat mengikuti perkuliahan.
SS S TS STS
16. Saya malas menghafal kosakata bahasa Inggris yang baru setiap hari.
SS S TS STS
17. Saya mempelajari bahasa Inggris agar kelak dapat menjelaskan materi kepada anak didik saya hingga paham.
SS S TS STS
18. Saya mendengarkan lagu berbahasa inggris untuk menambah kosakata.
SS S TS STS
19. Saya tidak serius mempelajari bahasa inggris karena banyak teman saya yang malas belajar bahasa inggris.
SS S TS STS
20. Saya menghafalkan kosakata bahasa Inggris agar dapat mengerti percakapan dalam bahasa Inggris.
SS S TS STS
21. Saya belajar kosakata baru supaya penguasaan kosakata saya meningkat.
SS S TS STS
22. Saya belajar bahasa inggris agar orang-orang kagum kepada saya.
SS S TS STS
23. Saya malas membaca buku berbahasa inggris karena tidak akan m