Tangerang Selatan in the 2015-2016 Academic Year.
)
“A Skripsi”
By:
Derin Periyana
1112014000032
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
FACULTY OF EDUCATIONAL SCIENCES
ii
Selatan in the 2015-2016 Academic Year). Skripsi of Departement of English Education at Faculty of Educational Sciences of State Islamic University Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta, 2016.
Advisor I : Dr. Atiq Susilo, M.A.
Advisor II : Sunardi Kartowisastro, Dipl.Ed.
The aim of this study was to find emperical evidance whether teaching using blended learning model was effective or not on students’ reading comprehension of exposition text. This study used quantitaive method and quasi-experiment design. The sample of this study was two classes which was devided into experimental class and controlled class. XI IPS 2 as experimental class consisted 30 students and XI IPS 3 as controlled class consisted. The sample was taken by using purposive sampling. Students in experimental class were taught by using blended learning model while the controlled class without using blended learning model. The isntrument was test and it was devided into pre-test and post-test. The data among pre-test, post-test and gained score were analyzed by using t-test. The pre-test result showed that there was no significant deferences between both classes. Then post-test showed that p=0,101 and it was grater than α=0,05, it meant no significance deffernces in both classes. Furthermore, gained score result showed that p= 0,466 and it also grater than α=0,05. Moreover based on manual calculation the t0 (tvalue)= 0,762 and tt (ttable)= 1,672, it meant that t0 (tvalue) < tt (ttable) (0,762 < 1,672). Based on the calculation of t-test, it was proved that null hypothesis (H0) was accepted. It meant there was no significant difference of students’ reading comprehension achievement of exposition text between students who were taught through blended learning model and students who were taught without blended learning model.
iii
ABSTRAK
Derin Periyana (1112014000032). The Effect of Using Blended Learning Model on Students’ Reading Comprehension of Exposition Text. (A Quasi-experimental Study at the Eleventh Grade of SMA Negeri 4 Kota Tangerang Selatan in the 2015-2016 Academic Year). Skripsi Jurusan Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Fakultas Ilmu Keguruan Universitas Islam Negeri Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta, 2016.
Pembimbing I : Dr. Atiq Susilo, M.A.
Pembimbing II : Sunardi Kartowisastro, Dipl.Ed.
Tujuan dari penelitian ini adalah untuk menemukan bukti empiris apakah pengajaran dengan menggunakan model blended learning adalah efektif atau tidak dalam meningkatkan pemahaman membaca siswa/i dalam teks eksposisi. Penilitian ini menggunakan metode quantitative dan disain quasi-experimen. Sampel dalam penelitian ini adalah 2 kelas yang dibagi menjadi kelas eksperimen dan kelas kontrol. Kelas XI IPS 2 sebagai kelas eksperimen berjumal 30 siswa/i dan XI IPS 3 sebagai kelas kontrol berjumlah 30 siswa/i. Sampel di ambil dengan menggunakan purposive sampling. Siswa/i di kelas eksperimen di ajarkan mengunakan model blended learning sedangkan kelas kntrol tanpa mengunakan model blended learning. Instrumen yang digunakan adalah tes dan tes tersebut di bagi menjadi pre-test dan post-test. Data dari pre-test, post-test dan sekor perolehan di analisa mengunakan t-test. Hasil dari pre-test menunjukan tidak ada perbedaan yang signifikan antara kedua kelas. Kemudian hasil post-test menunjukan bahwa p= 0,101dan itu lebih besar dari α= 0,05, ini berarti tidak ada perbedaan yang signifikan di kedua buah kelas. Selanjutnya, pada skor perolehan menunjukan p=0,466 dan ini juga lebih dari α=0,05. Lebih lanjut, berdasarkan perhitungan manual t0 (tvalue)= 0,762 dan tt (ttable)= 1,672, ini berarti bahwa t0 (tvalue) < tt (ttable) (0,762 < 1,672). Berdasarkan perhitungan t-test di buktokan bahwa null hipotesis (H0) diterima. Berarti tidak ada perbedaan yang signifikan dari pnecapaian pemahaman membaca siswa/i dalam teks eksposisi antara siswa/i yang diajarkan mengunakan model blended learning dan tanpa blended learning.
v
Praise be to Allah, Lord of the worlds, for blessing the writer and giving knowladge, strength, guidance, marcy, and chance to finish his study. Peace and salutation be upon the prophet Muhammad peace be upon him who has brought mankind from the dark into the light.
This research has taken long process to finish it. It would not be finished without the support of the writer family, lecturers, teachers, friends and institution. Moreover, the writer is pleased to acknowladge those people who have helped and supported the writer to finish this research under the title “The Effectiveness of Using Blended Learning Model on Students’ Reading Comprehension of Exposition Text. (A Quasi-experimental Study at the Eleventh Grade of SMA Negeri 4 Kota Tangerang Selatan in the 2015-2016 Academic Year)”. Therefore, hopefully this “Skripsi” will be usefull for the writer to have the degree of “S.Pd”.
First of all, the writer would like to express his greatest gratitude to his dearest parents, Mr. Mujiyono and Mrs. Darinah, and also his little brother Mu’arrafih. Furthermore, his deepest gratitude is to his advisors, Dr. Atiq Susilo, M.A., and Sunardi Kartowisastro, Dipl.Ed., for their valuable guidance, suggestion, advice and support for his research. Moreover, his deepest gratitude is also to his academic advisor Siti Nurul Azkiyah, M.Sc., Ph.D, for her guidance and suggestion during the writer study at the university.
Furthermore, the writer would like to express his sincere gratitude to:
1. All the lecturer especially those of English Education Departent for shering their knowladge and their patience in teaching the writer.
2. Dr. Alek, M.Pd., as the head of Department of English Education.
vi
4. Dr. Prof. Ahmad Tahib Raya, M.A., as the Dean of Faculty of Tarbiya and Teachers’ Training.
5. Mr. Suhermin, M.Si., as the head master at SMA Negeri 4 Kota Tangerang Selatan for giving the writer permission in conducting the research.
6. Mrs. Nina Herlina, S.Pd as the English subject teacher at SMA Negeri 4 Kota Tangerang Selatan for her guidance during conducting the research at school. 7. All Students XI IPS 2 and XI IPS 3 at SMA Negeri 4 Kota Tangerang Selatan
academic year 2015-2016 as the writer sample of the research.
8. Khairun Nisa, S.Pd., as the writer closed friend, for her suport and advice to the writer.
9. All friends of the class B in academic year 2012 and also all friends at “Kosan Griya Semanngi” Arief Prayoga, Agung Harisman Yuliyanto, and Andre Anang Pratama, for their freindship and togetherness.
Finally the writer relizes that this “skripsi” could not finish without any critiqs and suggestion. Moreover, the writer will be glad to have some suggestion in order to make this “skripsi” better.
Jakarta, 29 December 2016
v
ABSTRAK ... iii
ACKNOWLEDGMENT ... iv
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... v
LIST OF TABLES ... viii
LIST OF FIGURES ... ix
LIST OF APPENDICES ... x
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION ... 1
A. Background of the Study ... 1
B. Identification of the Problem ... 5
C. Limitation of the Problem ... 5
D. The formulation of the Problem ... 5
E. The objective of the Study ... 5
F. Significance of the Study ... 5
CHAPTER II: THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK ... 7
A. Reading ... 7
1. General Concept of Reading ... 7
2. Reading Comprehension ... 8
3. Purpose of Reading ... 9
4. Types of Reading ... 9
5. Elements Affecting Reading Comprehension ... 10
B. Exposition Text ... 11
1. Understanding Exposition Text ... 11
2. Generic Structure of Exposition Text ... 12
3. Grammatical Features of Exposition Text ... 13
C. Blended Learning ... 13
1. General Concept of Blended Learning ... 13
2. The Strength of Blended Learning ... 16
vi
4. Designing Blended Learning Program ... 18
5. Quipper School as a Online Learning Platform for Blended Learning ... 20
D. Previous Study ... 21
E. Framework of Thinking ... 22
F. Theoretical Hypotheses ... 23
CHAPTER III: RESEARCH METHODOLOGY ... 24
A. Place and Time of the Research ... 24
B. Research Method and Design ... 24
C. Population and Sample ... 26
D. Instrument of the Research... 26
E. Data Collection Techniques ... 27
F. Procedure of Intervention ... 27
G. Techniques of Data Analysis ... 28
1. Normality Test ... 28
2. Homogeneity Test ... 28
3. Hypothesis Test ... 28
H. Statistical Hypothesis ... 30
CHAPTER IV: FINDING AND DISCUSSION ... 32
A. Description of the Data ... 32
1. Students’ Score in Pre-test ... 32
2. Students’ Score in Post-test ... 33
3. Students’ Gained Score ... 34
B.Preliminary Analyses ... 35
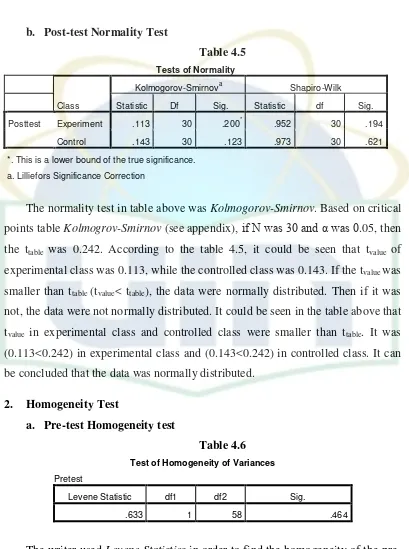
1. Normality Test ... 35
a. Pre-test Normality Test ... 35
b. Post-test Normality Test ... 36
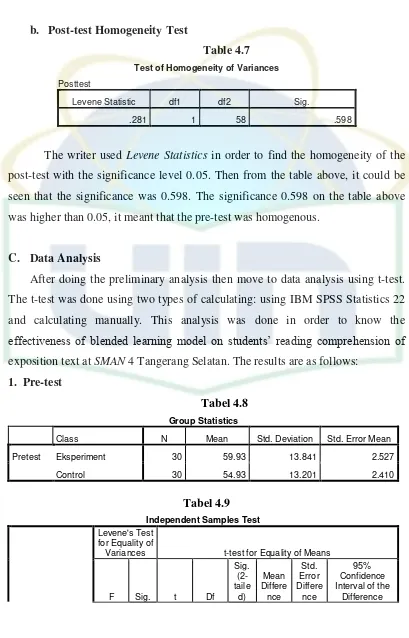
2. Homogeneity Test ... 36
a. Pre-test Homogeneity test ... 36
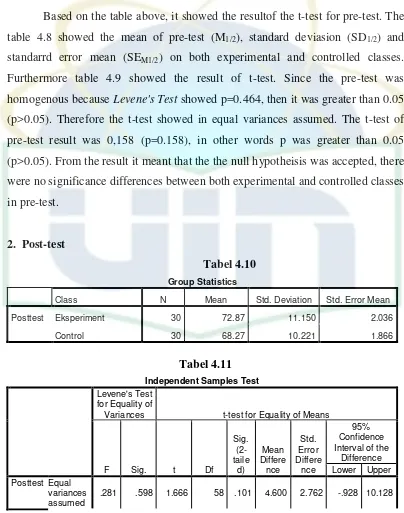
b. Post-test Homogeneity test ... 37
vii
D. Hypothesis Testing ... 42
E. Discussion ... 43
CHAPTER V: CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION ... 45
A. Conclusion ... 45
B. Suggestion ... 45
REFERENCES ... 47
viii
LIST OF TABLE
Table 3.1 Time of Research ... 24
Table 4.1 The Score of Pre-test ... 32
Table 4.2 The Score of Post-test ... 33
Table 4.3 The Gained Score ... 34
Table 4.4 Pre-test Normality Test ... 35
Table 4.5 Post-test Normality Test ... 36
Table 4.6 Pre-test Homogeneity Test ... 36
Table 4.7 Post-test Homogeneity Test ... 37
Table 4.8 Group Statistics of Pretest Score ... 37
Table 4.9 Independent Samples Test of Pre-test Score ... 37
Table 4.10 Group Statistics of Pre-test Score ... 38
Table 4.11 Independent Samples Test of Pre-test Score ... 38
Table 4.12 Group Statistics of Gained Score ... 39
ix
x
LIST OF APPENDICES
Appendix 1 English Subject………50
Appendix 2 ANATES Result of Pre-test……….54
Appendix 3 ANATES Result of Post-test………...55
Appendix 4 Kisi-Kisi Soal………..57 Appendix 5Instrument of Pre-test………...59
Appendix 6 Instrument of Post-test……….65 Appendix 7 Lesson Plan………..71 Appendix 8 Students’ Daily Exercise………...104 Appendix 9 Steps to Analyze Normality, Homogeneity and T-test Using SPSS………...…105 Appendix 10 Pre-test Score of Experimental Class………..107
Appendix 11 Pre-test Score of Controlled Class………..108
Appendix 12 Post-test Score of Experimental Class………109
Appendix 13 Post-test Score of Controlled Class………110 Appendix 14 Gained Score of Experimental Class………..111 Appendix 15 Gained Score of Controlled Class………..112
Appendix 16 Comparison of Students Gained Score………..113 Appendix 17 Students Score at Quipper-School………..114
Appendix 18 Tabel Nilai Uji Kritis Kolmogrov-Smitnov……….. 122 Appendix 19 Tabel Fungsi Distribusi pada Distribusi Probabilitas t-Students………123 Appendix 20 Surat Pengesahan Proposal Skripsi………126 Appendix 21 Surat Keterangan Penelitian dari Sekolah……….127
Appendix 22 Surat Bimbingan Skripsi………...128
Appendix 23 Reference Endorsement Sheet………...…130
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter contains general preview of this study. Those are background of the study, identification of problem, limitation of the problem, the formulation of the problem, the objective of the study, and significance of the study.
A. Background of the Study
Nowadays, in new era, gadgets and internet become a need for everyday activity. Gadgets and internet as ones of the products of developing technology are possible to help people fulfill their need. For general people, the technology is usually employed for communicating with friends or colleagues in everyday life, until sending credential information.
Students these days can also employ technology for importance of their education. For instance, internet provides almost any information to help them learning more about the materials they have learned in school. Likewise, several website on internet offer online courses which is free. Those are possible to be accessed on learning courses platform, such as widely known platform coursera. This is beneficial to help them develop their knowledge.
Not only free courses, but also free e-books are frequently found on internet. In Indonesia, the government is concerned with the use of technology in education. It is proven by Ministry of National Education and Culture and its website bse.kemdikbud.go.id/ providing free e-books for students. Here students can freely download Buku Sekolah Elektronik or Electronic School Book. Therefore, every student has the same chance to read and learn from the same school textbook. In addition, access to internet services are often employed to share new information regarding school activities or homework, either by teacher or students.
2
with internet and gadgets, which in this case are laptop and smart phone. Almost all of them have smart phones and laptop, and they frequently use them to access internet services, usch as sharing new information regarding homework.
This is in line with the explanation of Ismail Cawidu as the Communication and Information Minister. According to him, there are 73 million internet users in Indonesia, and half of that number or around 58,4 percent includes the age between 12 and 34. They can spend five hours for online using laptop or personal computer, and about two hours by using mobile device.1 Observing the age of most of the internet users, it is likely that students include in that number. Furthermore, SMA N 4 Kota Tangerang Selatan itself understands the importance of having internet access in school area. An interview, which was conducted by the writer, with one of the teachers there revealed that SMA N 4 Kota Tangerang Selatan has Wi-Fi signal which can be used freely by the students and teachers.
However, despite the advantages and familiarity of the developing technology, there are several problems regarding its utilization. Here the writer finds several problems in relation with the utilization of the developing technology, particularly in its utilization for facilitating teaching and learning of reading comprehension. However, before explaining the problems, the writer tries to explain the reasons of why reading comprehension becomes important to be mastered and therefore becomes the focus skill in this study. The first reason is because reading is one of English skills and it falls into the category of receptive skills. It is therefore important to master it in everyday life since, for instance, it relates with one of the productive skills which is writing skill. Reading comprehension is beneficial for people to help them master writing skill as by having reading comprehension ability, they can receive input of vocabularies they can use in their writing. Not only will people receive vocabulary inputs, but also the knowledge of how to use those vocabularies in appropriate way.
The second reason is in according with Indonesian last curriculum. It is stated there that reading must be mastered by students of Junior and Senior High School.
1
Jakarta Post, “Internet Users in Indonesia Reach 73 Million”,
To be specific, it is stated in “Peraturan Menteri Pendidikan Nasional Republik Indonesia No.23 Tahun 2006 Tentang Standar Kompetensi Lulusan untuk Satuan Pendidikan Dasar dan Menengah dalam Mata Pelajaran Bahasa Inggris” that reading is one of skills which must be mastered by students.For senior high school students, a greater demand is put in that skill. The demand includes mastery of recount, narrative, procedure, descriptive and report, news items, spoof, hortatory exposition, discussion and review. Those genres are recount, narrative, procedure,descriptive and report, news items, spoof, hortatory exposition, discussion and review.2
In regards with utilization of developing technology for facilitating teaching and learning of reading comprehension, the writer tries to discuss three problems underlying the importance of employing technology for the teaching. The first problem is most of teachers in SMA N 4 Kota Tangerang Selatan only implement traditional model in teaching reading comprehension. They only employ face to face teaching and learning activities in the class. To be specific, most of teachers there only use paper-based or visual-based teaching and learning activities using projector in delivering the materials without using internet as one of technology widely used to develop their teaching media.
The second problem is that most of students often do not use internet for academic purpose. According to writer interview with several students in SMA N 4 Kota Tangerang Selatan, it is revealed that they only use internet for chatting with their friends, playing video game, or streaming videos which are only for entertainment. It is hardly found that student employs internet access for academic purposes or for online learning. Therefore, it would be more useful if they use internet for online learning, or read beneficial materials which can increase their knowledge and improve their reading comprehension.
The third one is time limit in teaching reading. Most of teachers in school commonly have to teach four English skills in limited time. In SMA N 4 Kota Tangerang Selatan itself, reading is only taught two meetings per week, with 90
2
Peraturan Mentri Pendidikan Nasional Republik Indonesia Nomor 23 Tahun 2006, http://staff.unila.ac.id/radengunawan/files/2011/09/Permendiknas-No.-23-tahun-2006.pdf,
4
minutes per meeting. Such amount of learning time is insufficient for students to practice reading. In addition, to acquire successful reading comprehension, students need the presence of many component capabilities since comprehension relies on decoding skill, knowledge in several skill, and cognitive processing capability.3
There are a lot of ways to solve such problem. Yet, the writer believes that an effective way to solve the problem is by using blended learning. Blended learning is the combination of face-to-face traditional instructions and e-learning which part of e-learning opportunities is created online. Blended learning itself is the result of rapid growing of technology and the emergence of internet in educational area. It is a proof that growing realization of technology can also play important role in the daily classroom routine and as the key component to be quality reading instruction.4 Moreover, in the area of receptive skill especially reading, the role play of web based environment is in providing exposure. Reading on screen, learners can access meaning on demand by clicking on hyperlink to find out the maning of a word.5
Likewise, by using e-learning, students can access learning materials easily from anywhere and everywhere. It allows teaching and learning activities to be conducted not only inside the classroom, but also outside classroom as Charismiadji argues that blended learning is a powerful solution for an enhanced second-language learning experience.6 Realizing the effectiveness of blended learning, the writer is going to investigate the extent of blended learning on
students’ reading comprehension of exposition text of 11th grade at SMA N 4 Kota
Tangerang Selatan.
3
Diane August, et al, Assessing Reading Comprehension in Bilingual, The Elementary School Journal, Vol. 107, No. 2, 2006, p. 222
4
Pamela J. Farris et al, Teaching Reading a Balanced Approach For Today’s Classrooms, (New York: McGraw-Hill Companies, 2004), p.29
5
Pate Sharma and Barney Barrett, Blended Learnin Using Technologyin and beyond The Language Classroom, (Oxford: Macmillan, 2007), p.11
6
B. Identification of Problem
Based on the background of study, there are several problems which can be identified as follow.
1. Teachers only implementing traditional teaching learning activity without any part of using internet to develop their media.
2. Students miss use in using internet not for academic purpose. 3. Time limit for teaching reading in school.
C. Limitation of the Problem
As previously stated, there are several problems causing students’ low reading comprehension of narrative text. From the problems, the writer will focus on the
effectiveness of blended learning model on students’ reading comprehension of
exposition text of eleventh grade in SMA N 4 Kota Tangerang Selatan.
D. The formulation of Problem
The formulation of this problem is “Is blended learning model effective for developing students’ reading comprehension of exposition text?”
E. The Objective of Study
This study is aimed to prove and to find empirical evidence whether the implementation of blended learning model is effective or not on students reading comprehension of expositon. The writer also wants to analyze the cause and effect between independent variable which is blended learning model, and dependent variable which is reading comprehension of exposition text.
F. Significance of Study
The writer expects that the significance of this study can provide useful information for:
6
2. English Teachers of 11th grade of Senior High School, the result of this study can help them as an alternative model in teaching learning activity that they can choose.
3. Students in 11th grades of Senior High School who learn English in reading exposition text, this study attempts to help them increase their achievement in reading comprehension of exposition text.
7
CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
This chapter the writer would like to describe some kinds of theories related to the study. Those theories focus on general conception of reading, reading comprehension, perpose of reading, kinds of reading, elements affecting reading comprehension, understanding exposition text, generic structure of exposition text, grammatical features of exposistion text, general conception of blended learning, the strengths of blended learning, the weaknesses of blended learning, designing blended learning program, previous study, framework of thinking and theoretical hypothesis.
A.Reading
1. General Concept of Reading
Many experts have definitions about reading. According to Allington and Strange, Reading is an active cognitive process that does indeed require using graphics (letter) and phonic (sounds) information; but for fluent readers particularly, the language based cues—semantic (meaning) and syntactic (grammar) seem to be far more important than graphic and phonic cues.1 Similar with Allington and Strange, Nuttall state the view of reading offered is essentially concerned with meaning from mind to mind: the transfer of massage from writer to reader.2 It can be seen that reading is an activity.
Meanwhie, Harmer states that reading is an exercise dominated by the eyes and the brain. The eyes receive masseges and the brain then has to work out the significance of these masseges.3 Similar with harmer, Gough and Tunmer in Oalkhil et al book’s, states in simple view of reading in two main components: word decoding and language comprehension. Word reading (or decoding) refers to the ability to read singgle word in context, Language comprehesion refers to
1
Richard Allington and Michael Strange, Learning Through Reading in The Content Area, (Toronto: D.C. Heath and Company, 1980), p.16
2
Christine Nutall, Teaching Reading Skills in a Foreign Language, New Edition, (Oxford: Heinemann, 1996), p. 3
3
8
our ability to understand words, sentences and text.4 It can be seen that reading is exercise which is involve two main components, those are word reading (the ability to read) through eyes as a tool and language comprehesion (the abiity to understand) through brain as a tool.
From those expert above, It can be concluded that reading is an activity in getting meaning (or message) from the writer to the reader. In doing reading activity our eyes and brain are work systematically to receive the massages then understanding it. Furthermore, reading consists of two main components those are word decoding and language comprehension.
2. Reading Comprehension
Talking about reading it cannot be separeted from reading comprehension. When reading something people need the ability to comprehending the message which the writer states in text. However, comprehending what people read is more than just recognizing and understanding the word. True comprehension means making sense of what you read and connecting ideas in the text to what you already know. It also means remembering what you have read. In other word, comprehending means thinking while you read.5
Furthermore, Farris states that reading comprehension is the process of understanding the message that the author is trying to convey. Very simply, it is making meaning from the written text at hand.6 Understanding a written text means extracting the required information from it as efficiently as possible.7 It can be seen that reading comprehesion is a ability in understanding the message of the text that the writer want to convey. It is not only understanding the meaning but also synthesize it with reader perior knowladge.
4
Jane Oakhil et al, Understanding Teaching Reading Comprehension (A Handbook), (New York: Routladge,2015) p.2
5
Beatrice S. Mikulecky and Linda Jeffries, Advanced Reading Power: Extensive Reading, Vocabulary Building, Comprehension Skills, Reading Faster, (New York: Longman, 2007), p.74
6
Pamella J. Farris, Teaching Reading a Balanced Approach For Today’s Classrooms, (New York: McGraw-Hill Companies, 2004) p. 321
7
3. Purpose of Reading
People have a reason why they read something. If someone find a pearson who read a novel then they ask their reason why they read novel then finding another one who read a novel and asking the same thing, the answer of each of them probably different. It will find the variety of reasons for reading. Whatever the reasons of people for reading, they read because they need to have something from the text. It is called message: it might have been facts, but could just as well have been enjoyment, ideas, feelings. Whatever the reasons, readers probably needed to have the message that the writer intended.8
Furthermore, according to Grellet there are only two mains reason for reading. First is reading for pleasure and the second one is reading for getting information.9 Similar with Grallet, Harmer states that very often that people read something because it interests them or at least it will interest them. Sometimes, however, it is not the fact that a text might be interesting which couses some one to read it, it is rather the usefulness of the text which promps this action.10 It can be concluded that someone reads because of two main reasons which are for pleasure and getting information.
4. Types of Reading
Nutall describes reading into two approaches, those are intensive reading and extensive reading:11
a. Intensive Reading
Intensive reading is reading shorter text, to extract specific information. This is more accurate activity involving reading for detail.12Intensive reading involves approaching the text under the guidance of a teacher or a task which forces student to focus on text. The aim is to arrive at an understanding, not only of what the text means, but of how the meaning are produced. The „how’ is as
8
Martha Rapp Rudell, Teaching Content Reading and Writing, Fifth Edition, (Haboken: John Willey and Sons, inc, 2008) p. 95
9
Francoise Grellet,op. cit., p. 4
10
Jeremy Harmer, op. cit., p.182
11
Christine Nutall, op. cit, p. 38—39
12
10
important as the „what’, for the intensive lesson is intended primarily to train strategies which the student can go on to use with other text.13
b. Extensive Reading
Extensive reading involves somewhat longer texts, those texts can be journal articles, technical reports, longer essay, and books and reading of this type almost always involves a focus on meaning.14 It is often assumed that in order to understand whole message of a particular reading material (e.g., a book), understanding the parts (sentence, paragraphs, chapters) of which it is made up is necessary. However, obtaining understanding of a text adequately often could be done without grasping every part of it To understand the whole needs reading strategies which can be trained only by practice a longer text.15
5. Elements Affecting Reading Comprehension
According to National Reading, Panel in Tompkins article states that there are some elements affecting students reading comprehension. Those elements are divided into two main categories reader and text.
a. Reader
1) Background Knowladge
Students activate their world and literary knowladge to link what they know to what they are reading.
2) Vocabulary
Students recognize the meaning of familiar words and apply word-learning strategies to understand what they’re reading.
3) Fluency
Students have adequate cognitive resources available to understand what they’re reading when they read fluently.
4) Comprehension Strategies
13
Christine Nutall. loc. cit.
14
Douglas Brown, Language Assessment Principles and Classroom Practices, (California: Longman, 2004) p. 212
15
Students actively direct their reading, monitor their understanding, and troubleshoot problems when they occur.
5) Comprehension Skill
Students automatically note details that support main ideas, sequence ideas, and use other skills.
6) Motivation
Motivated students are more engaged in reading, more confident, and more likely to comprehend successfully.
b. Text 1) Genres
Genres have unique characteristics, and students’ knowledge of them
provides a scaffold for comprehension. 2) Text Structure
Students recognize the important ideas more easily when they understand the patterns that authors use to organize text.
3) Text Features
Students apply their knowledge of the conventions and literary devices used in texts to deepen their understanding.16
B.Exposition Text
1. Understanding Exposition Text
According to Anderson and Anderson an exposition is a piece of text that presents one side of an issue. The perpose of an exposition is to persuade the reader or listener by presenting one side of an argument. The exposition includes advertaisment, spoken arguments, editorilas, and legal defences.17 Furthermore, Decker states that exposition means explanation, simply an exposing of
16 G.E Tompkins, “Reading Comprehension Factors”, http://www.education.com/reference/article/reading-comprehension-factors/, October 24,2016.
17
12
information or ideas. Its primarly function of exposition itself is merely to explain.18
Based on those expert exposition text means a text that have one sides of issue, the issue is supported by series of arguments that relevant to the issue. The arguments have to consist of fact and relevants information with the issue. Moreover, The function of exposition text is to persuade the reder or listener to do something that the writer is stated on the text.
2. Generic Structure of Exposition Text
The generic structure of exposition text according to Anderson and Anderson mainly consists of three sections. Those are an introductury statement, a series of argumnet, and a conclusion. Those sections are described below:
First, an introduction statement, this section introduce the author’s point of view whicih is called the thesis of argument and the introduction can include preview arguments that may folow in the text.
Second, a series of arguments that aim to convice the reader. A new paragraph is used for each new arguments. Each new paragraph begins with a topic sentence that introduce the arguments which is folowed by supporting details. Those suporting can be facts, chart or diagram that can support the topic sentence.
Third, a conclusion. This part is the clossing of exposition text. in giving conclusion the authors can sum up their point of view in their arguments. In analitical exposition the conclusion can be restatement of the writer thesis and arguments. However, in hortatory exposition the writer give recommendation for the reader. The recommendation consists of should or should not do by the reader based on their arguments.19
Since, this study is focusing on hortatory exposition, here is the example of hortatory exposition text:
18
Randall E. Decker, Patterns of Exposition 9, (Canada: Little,brown & Company, 1984)
19
Drinking Cofee has Health Benefits
Drinking coffee may not harm people, Tea, coffee and soda are few bevarages which contain drug called caffeine. In its natural state ,caffeine, a silky crystalline substance, is a white or yellow powder, which is bitter tasting and adorless.why should I say that? I propose some arguments as fellows:
First, we drink cofee to make us stay awake, because coffee consist of cafeine. Second, drinking coffee is good for your helath, because it can expidate our urination. Third, some therapeitic uses caffeine to help anagesics work more effeciently, to relieve depression to drug addcits and to kill skin figures
Thus if we want to say that first, we may drink coffee, without feeling scare of bad impact of the caffeine; second, do not drink too much; third, drink cofee for therapeutic purposes, at leat we need not to addict to coffee.20
3. Grammatical Features of Exposition Text
Exposition usually includes the following grammatical features as follows. a. Words that express the author’s attitude (modality), for example, will, may,
must, always, rarely. b. Emotive noun and verbs
c. Adverbs that show a time sequence and link the arguments.21
C.Blended Learning
1. General Concept of Blended Learning
A lot of scholars share similar definitions of blended learning. Here the writer discusses three similar definitions defined by three scholars. The first one is
20
Herman Benyamin, Advanced Learning English 2, (Bandung: Grafindo Media Pratama, 2012) p.212-213
21
Mark Anderson Kate Anderson, op cit., p. 22
Thesis
Arguments
14
defined by Sherma. According to Sherma, blended learning is a process of integrated combination of traditional learning (face-to-face) with web based online approach (online teaching).22 Alya also defines blended learning as the purposeful integration of traditional model (face-to-face) and online learning.23 Then the last, Li Zhingan, et al.define blended learning as the combination of traditional classroom-based approach and e-learning for delivering instruction.24 Based on the definitions stated previously, the writer sees blended learning as a model of teaching and learning activity which combines face-to-face and online learning.
The term of blended learning is used to describe any course that incorporates the web into the curriculum, Ko and Rossen defined blended as falling into three subcategories:
a. Web enhanced, these are courses with associated web sites that contain material relevant to the course (the syllabus, a list of web based resources, a course calendar, a reading list, lecture notes, or an electronic bulletin board where student can post question of a general nature). Instructor often uses web-enhanced resources to reduce the flow of paperwork and to offer their students an optional method of obtaining course related information.
b. Media enhanced, courses where relevant course material such as videotape lectures or associated graphics are posted to a website for use by students as a form of review. Often such sites recreate the activities in a classroom, such as the lecture and ensuing discussion. Media-enhanced courses are often to use to support web-augmented classes.
c. Web augmented, any course in which a portion of class work is done exclusively on the web, augmenting, and often replacing, work that normally be done in traditional classroom. Generally, such work is both posted and completed using course management system. It can consist of a number of
22Pete Sharma, Key Concept in ELT „Blended Learning’,
ELT Journal, 2011, Vol. 64/4, p. 456
23
Jesica S. Alya, Blended Learning as New Approach to Social Work Education, Journal of Social Work Education, 2009, Vol. 45, No. 2, p. 277
24
Zhingang Li et al, Switching to Blended Learning: The Impact on Students’ Academic
disparate mix-and-match elements. For example, students may be asked to view a digital video , then asked to post a short response about the video on electronic bulletin board. Or students may be asked to assemble a web page of their own on a certain topic, which they then must themselves post on the course website.25
For some resons, some people may confuse in dfifferentiating the terminology of blended learning with some others likes e-learning, distance learning and face to face which always comes out when we talk about blended learning. For detail, Mason and Rennie define it clearlly on the figure bellow:
Figure 2.1 The relationship among blended learning, elearning, distance learning,and face to face learning.
25
16
From the picture above it could be seen that distributed education is a broader term which includes aspects of ditance and online education, as well as blending with face-to-face learning.26
From paragraphs above can be seen that blended learning is a learning model which is combination of face-to-face learning and online learning. Blended learning itself defines into three specific categories which are web enhanced, media enhanced, and web augmented. The term of blended learning itself is a part of distance learning which consist of online learning, but also consist of face-to-face (traditional) learning in the scope of distributed education the largest term.
2. The Strengths of Blended Learning
Teaching language in 50 EFL students in meaningful, creative, and collaborative way without turning the blended class into a circus is a huge challenge, particularly in a learning environment where students are encouraged to take an active role. Blended instructional model using traditional resource and online technology for learning purposes are not new.27 In informal education such as courses, blended learning model is their usual learning model. A lot of courses have employed this learning model because it gives opportunities for development of teachers, learners and learning itself. Those opportunities can increase students’ motivation and responsibility, a student-centered approach based on individualization, and also accepting the new and dynamic learner’s and teacher’s roles.28
Furthermore, Krasnova and Sidorenko state that blended learning can be used to achieve the following pedagogical goals.
a. To prepare students for independent and productive activity which can develop several skills. Those skills are constructive and algorithmic thinking,
26
Robbin Mason and Frank Rennie, Elearning The key Concept, (New York: Routladge Tylor & Francis Group, 2006) p.xvii
27
Joy Egbert and Elizabeth Hanson Smith ed, CALL Environment Research, Practice and Critical Issue, Second Edition, (Washington: Teachers of English to Speaker of Other Languages, Inc, 2007) p. 404
28
creative thinking due to decreasing amount of reproductive activity, communicative skills on the basis of performing team projects, ability to find solutions in computer-simulated situations, research skills, and skills of information culture and information processing.
b. To implement the social order which includes preparing specialists to working with information technologies, and preparing specialists to independent lifelong learning by means of information technologies.
c. To intensify all levels of the educational process which includes increasing effectiveness and teaching quality due to the use of information technologies, exposing and using stimuli of cognitive activity promotion, and deepening interdisciplinary connections.29
3. The Weaknesses of Blended Learning
Although, there are many benefits of blending online technology and multimedia tool with traditional classroom setting and how the integration may affect on students learning. However, there are some pitfalls that occur in a blended learning environment. The pitfalls vary and can be overwhelming. These problems, no matter how small can affect on overall course plan. Here are the most common pitfalls:
a. The success of delivering online chats or video also depends on the type of technology which are available. A slow internet connection may cause voice chat program failure. It would be wise to update and test the software and hardware.
b. Because students may work on online assignments independently outside the class, some may encounter difficulty in using the tools. It will be better to provide learner support and web links to help pages.
c. Students sometimes forget their user names and/or passwords despite constant reminders from the teachers to write them down. Remind students frequently to jot down important information and keep it in safe place.
29
18
d. Teachers may find themselves with uncooperative technical support staff. Teachers should be persistent in asking for help. Several things need to be done by ourselves, but look for others who share the same commitment to teaching and learning and can offer online support.
e. Some educators argue that the internet and technology in general tend to put less financially privileged students at a disadvantage. However, whether in an EFL or ESL context, there will always be issues regarding equal access to technology.30
4. Designing Blended Learning Program
Blended instruction is a mix of synchronous settings (face-to-face) and asynchronous settings, in which the teacher and students are not together in same time. When not meeting in class, students use online courseware to work on assignments at times convenient for them.31 For detail, the position of blended learning between online learning and offline learning (face-to-face), Meason and Rennie describe a schematic description of blended learning on the figure 2.2 below.32
Figure 2.2 A Schematic description of blended learning
In Planning for a blended course of this sort, it is important to examine the traditional and online components available and the tools that will be needed. To create checklist is by considering the following question.
a. Does school, institution and classroom have the online tools and the internet access which are needed for teaching online class?
b. What Multimedia equipment/online tools will be used to present an activity? c. What sort of online activities are the teachers going to be conducted?
d. How the time and places of the online meeting will be arranged?
30
Joy Egbert and Elisabeth Hanson-Smith, op. cit., p. 418
31
Sharon E. Smaldino, et al, Instructional Technology and Media for Learning, Tenth Edition, (Edinburg: Person Education Limited, 2014), p. 101
32
e. How the instructional events will be planned to fulfill the need for variety and and cmplexity in learning?33
Then here are following guidelines should help language teachers in choosing the right blend:
a. To provide opportunities for collaboration
b. To provide the learning content (for example: syllabus, lessons plan) in all the different media types to be used (online and offline)
c. To provide learner support (for example technical question, how to use, guidelines)
d. To understand all the type of technologies that can deliver learning (e.g., be able to operate multimedia equipment, manage online tools, have technical support in hands).
e. To provide feedback and opportunities for learner self-assessment.34
Many things that teachers can do for teaching in online learning, here Ko and Furthermore, Rossen provides some practical suggestion that teachers can do for teaching in online learning to support traditional course:
33
Joy Egbert and Elisabeth Hanson-Smith, op. cit, p. 411—412
34
20
a. Posting lectures online b. Using a discussion board c. Using online testing tools
d. Providing online counseling, advice, mentoring, and support e. Assessing group project
f. Using web as the presentation medium g. Web-based exercise
h. Online team teaching35
5. Quipper School as a Online Learning Platform for Blended Learning
Quipper School is a FREE online platform for teachers and students. Quipper School consists of two parts: LINK for teachers, and LEARN for students.
a. Quipper School Link is where teachers menage their classes online and check
student’s progress. Here are something teachers can do using quipper school
link.
To send assignments and practice examination.
To create educational content, view student progress and download analytic.
To facilitating collaboration with some teacher in the school.
b. Quipper School Learn is where students study, it consits of some fetures such as follows.
Students is facilitated with assigment and general study.
Students can message the teacher if there is some topics that need teacher assitance.
Students can learn fun and enjoy because it is facilitated by gamification feature.36
35
Susan Ko and Steve Rossen, op. Cit., pp. 241—257
36Quipper, “What is Quipper School”,
D. Previous Study
Regarding the effect of blended learning on students reading comprehension of exposition text, there are two researchers that have conducted the study:
The first study was conducted by Asih Wahyuni, et al. The focus of their study was to find whether blended learning may gave alternative way instruction in teaching reading and it could improve student’s score, attitude and motivation in reading. The participants of their study were second years EFL learners who studied at Faculty of Teachers Training and Educational Sciences in Bogor. To collect the data, they used three instruments which were classroom observation, documentation of student’s gained score and student result in online learning activity, the last was interview. Through their study, they proved that blended learning could improve student’s score and it could be interactive way in teaching reading in Indonesian University Context.37
The second study was by Fatemeh Behjat, et al. This study was an attempt to discover whether conventional or blended learning could better enhance the reading comprehension for EFL learners. 107 Iranian students majoring in English at Abaden Islamic Azad University and Zand institute of Higher Education in Shiraz were selected as sample. They used test as their instruments and divided sample into two groups of experiment and control. For the treatment the experimental group received the instruction in classroom and assignment in virtual mode. The control group got instruction and assignment in conventional mode. The result proved that blended learning could help learners outperform in their reading comprehension. Moreover, they suggest that this model of learning could be used in developing other skills.38
37
Asih Wahyuni et al, Blended Learning is Teaching Reading: a Pedagogical Practice to Teaching English as a Foreign Language in an Indonesian University Context, The 61 TEFLIN International Conference, 2014
38
22
The third study was conducted by Sri Wantoro under title ”Blended
Learning; Incorporating Moodle into Clasroom Reading Comprehension Activities (A Case Study at a Senior High School in Pangkalpinang)”. Her study investigated in using Moodle to support face to face calssroom reading-comprehension activities since managing reading in classroom is not sufficient. Moodle would be used as a tool of blended learning activities. The participants were students in Senior High School at Pangkalpinang. She used four data collecting techniques, those were observation, interview, questionnaires, and document analysis. The result found that usning moodle as a tool of blended learning toward students reading comprehension was positive. It means that moodle facilitated them in learning process, supported their outside learning activitie, supported students reading comprehension activities, and it builded students-students and students teacher social interaction.39
The Fourth study was conducted by Zahra Zahedi at Islamic Azad University. The aim of his study was to find the effect of blended instruction and face-to-face reading intruction on the use of reading strtegies by Irabian EFL learners. The sample of this sutudy was Iranian EFL learners which consited of 30 students of experimental class and 30 students of controlled class. The experimental class had treatment blended learning instruction on seven reading strategies along seven meetings while the controlled class had face-to face instruction. He used test and reading strategies questionnaire as the instruments of his study. The result proved that blended learning instruction was more effective then face-to-face instruction on their students’ reading strategies.40
E.Framework of Thinking
Reading is one of skill which is important. Since, reading is related to other language skill especially writing skill. Reading is useful for people
39
Sri Wantoro, Blended Learning; Incorporating Moodle into Clasroom Reading Comprehension Activities (A Case Study at a Senior High School in Pangkalpinang, (Bandung: Indonesia University of Educarion, 2014).
40
especially student. Through reading student will got more information. To get more information in reading student need the ability to understand the message in text, it is why comprehension is needed in reading.
Despite of the usefulness in reading, student sometimes meet some problems that affect on students in learning reading, especially in reading comprehension. Those problems such as teachers who always implementing traditional model in teaching reading, and time limit in teaching reading in several school.
Blended learning is one of solution for helping students in learning reading comprehension. Blended learning is combination between face to face and online learning that can be one of solution in teaching and learning activity. Since, it integrate to online learning students can have more time in learning reading and teacher will have more time in teaching it. Through the online learning teacher can give students extra reading material as a support of face-to-face activity in classroom. This extra reading material is useful in learning and practicing reading in order to developed students reading comprehension.
F. Theoretical Hypothesis
There are two kinds of hypothesis in this research.
H1: By using blended learning model. It will effect students reading comprehension achievement of exposition text al 11th grade of SMA N 4 Kota Tangerang Selatan.
24
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This chapter contains reserach methodology. Those are place and time of research, research method and design, population and sample, instrument of the research, data collection techniques, procedure of intervention, technique data analysis and statistical hypothesis.
A. Place and Time of the Research
[image:38.595.109.519.227.664.2]This Research was taken a place at SMA N 4 Kota Tangerang Selatan which is located at Jl. WR. Supratman Komp. Pertamina Pondok Ranji, Ciputat Timur, Kota Tangerang Selatan, Provinsi Banten, on the second semester. Since, the school curriculum only provided 4 meetings in teaching hortatory exposition text. Then this research was conducted in 4 days treatment, it was started on May 2nd 2016 and ended on May 23rd 2016. Below was the table of research agenda:
Table 3.1 Time of Research
NO. Agenda Date
1. PRETEST Monday, May 2
nd 2016
2. TREATMENT DAY 1 Monday, May 9
th 2016
3. TREATMENT DAY 2 Thursday, May 12
th 2016
4. TREATMENT DAY 3 Monday, May 16
th 2016
5. TREATMENT DAY 4 Thursday, May 19
th 2016
6. POSTTEST Monday, May 23
rd 2016
B. Research Method and Design
findings that are systematic, generalizable, and open to replication by other investigators.1 Furthermore, Creswell states quantitaive method have some characteristics which are describing a reserch problem through the description of trends or a need of explenation of the relationship among variabeles; providing a major role for the literature through suggesting the research questions to be asked and justifying the research problem; creating purpose statement, research question and hypotheses that are specific; collecting numerical data; analyzing trends, comparing group, or relating variable using statistical data; writing the research report using standard, fixed structure and evaluation criteria.2 Then, this research was conducted to find out the empirical evidence of the effectiveness of using blended learning model on students reading comprehension.
Since this study used quantitaive method, the design was used quasi-experimental. Quasi-experimental designs are “almost” true experimental designs, except that the participants are not randomly assigned into group. In quasi-experimental research, the researcher studies the effect of treatment on experimental and controlled groups.3
This study was conducted to prove whether there was cause and effect between two variables. Those two variables were Independent variable (mostly presented by X) which is blended learning and dependent variable (mostly Presented by Y) which is reading comprehension of exposition text. In this quasi-experimental design used two groups which were divided into quasi-experimental group and controlled group. The experimental group was given treatment which was blended learning model and the controlled group was not given blended learning model but convensional/traditional model.
1
Donald Ary et al, Introduction to Research in Education, Eigth Edition, (Belmont: Wadsworth Cenage Learning, 2010) p. 23
2
John W Creswell, Educational Research, Planning, Conducting, and Evaluating Quantitative and Qualitative Research, Fourth Edition, (Boston: Pearson Education. Inc, 2012) p. 13
3
26
C. Population and Sample
The population of this study is 11th grade of students at SMA N 4 Kota Tangerang Selatan which consisted of around 350 students. This grade had 10 classes, each class consisted around 35 students. This grade also divided into two programs, those were science class and social class. This population was chosen because exposition text was taught in that grade.
The process of gaining the sample of study, the writer used purposive sampling to find sample. Purposive sampling was one of form in nonprobability sampling which was also referred to judgment sampling, it is means that sample elements judged to be typical, or representative for the research, the sample was chosen from the population.4 Then, based on the writer’s interview with the
writer’s supervisor who teached eleventh grade in social class at SMA N Kota 4 Tangerang Selatan was chosen from two classes which had similar characteristic in learning English. Those classes were XI Social 2 as experimentall class and XI Social 3 as controlled class, each class consisted 35 students.
D. Instrument of the Research
The research instruments used here was reading test which focused on reading comprehension of exposition text test. The test instrument was divided into two sections: pre-test and post-test. The pre-test and post-test instrument were used multiple-choice questions which were taken from some books of English 11th grade related to reading in exposition text and other resources. The writer created 25 multiple-choice questions for pre-test and 25 for post-test, then before the test administer to students, the writers checked the validity and the reliability of the test instruments. To measure validity of the instrument the writer will use content validity and reliability of the instrument, the writer used ANATEST. The result of ANATEST was atteched at the appendix.
4
E. Data Collection Techniques
Data collection technique used pre-test and post-test. A pretest provides a measure on some attribute or character that assess for participants in an experiment before they receive treatment, while posttest is conducted after treatment.5 The pre-test was given to both groups of experimental and controlled in order to findout student abilities in reading comprehension of exposition text before giving treatment using blended learning. After the treatment, post-test was distributed into both classes, the function of this post-test was to find out whether any improvement in reading ability between experimental class which had been given treatment with controlled class which was not deserve any treatment.
F. Procedure of Intervention
Before doing the research, the writer asked the subject teacher which class was appropriate for the writer to cunduct the research. Since she only teached social class then she proposed XI social 2 adn X1 social 3 as the sample for reserach. From her suggestion the writer chosed those class and chosed XI social 2 as the experiment class and XI social 3 as a control class.
Each group attended two meetings per week except day off. The duration of the research was six meetings including pre-test and post-test. The first meeting was for pre-test, the second to fifth meetings were for giving intervention, and the last meeting was for post-test. In addition, the writer’s roles in this study was the one who given intervention or treatment for experimental group and controlled group.
Here as the sport the online meeting the writer used quipper school. Through this learning platform, students got additional online materials telling about exposition text, online assignment about exposition text and facilitated with online messaging if they wanted to ask, then those were integrated with face-to-face learning activity. Students got print feedback after doing online learning and discussed it in face to face meeting in order to develop students reading comprehension skill.
5
28
.
G. Techniques of Data Analysis
. The writer used t-test for analyzing the score of pre- and post-test of both control group and experimental group. The t-test was useful in finding the statistical differences between experimental and control group. To analyze those data, the writer used IBM SPSS Statistics 22 program. Before doing t-test, the writer analyzed the normality and homogeneity first. Bellow was the step of data analysis.
1. Normality Test
Normality test was used to know whether the data distributed normal or not. Here the steps in doing normality test using IBM SPSS Statistics 22: This normality test used Kolmogorov-Smirnov table. Furthermore in checking whether the data was normally distrubuted or not, the criteria could be seen as the follow: If the tvalue was smaller than ttable (tvalue< ttable), the data was normally distributed. While if the tvalue was greater than ttable (tvalue> ttable), the data was not normally ditributed. For steps in finding the normality in IBM SPSS Statistics 22, it could be seen on appendix
2. Homogeneity Test
Homogeneity test is used to measure whether the data comes from homogenous variance or not. Same as normality for homogeneity used IMB SPSS Statistics 22. This homogenity test used Levene Statistics table. In order to know whether the data comes from homogenous variance or not we take a look on sig column, if the sig more than 0,05 it means data comes from homogenous variance. For steps in finding the homogenity in IBM SPSS Statistics 22, it could be seen on appendix.
3. Hypothesis Test
first take a look in sig (2-tailed), at first line was the result if the data were homogeny and second line if the data were not homogeny. If the sig result > 0,05 (there is no effect), if the sig result < 0,05 ( there is an effect).
Furtehermore, the writer also calculating t-test manually, in order to find whether there was differences between calculating using SPSS and manually.
Here the t-test statistical analysis pettern.
t
o=
Explanation:
t
o=
the value of „t’ countM1 = Mean variable of experimental class M2 = Mean variable of controlled class SEM1 = Standard error of experimental class SEM2 = Standard error of controlled class
The procedures used are as follow: a. Determining Mean Variable X:
M1 = ∑
b. Determining Mean Variable Y:
M2 = ∑
c. Determining Deviation Standard of Score of Variable X:
SD1=
√
∑
d. Determining Deviation Standard of Score of Variable Y:
30
e. Determining Standard Error of Mean Variable X:
SEM1 =
√
f. Determining Standard Error of Mean Variable Y:
SEM2 =
√
g. Determining Standard Error of difference of Mean Variable X and Mean Variable Y:
SEM1 - M2 = √
h. Determining to with formula:
t
o=
i. Determaining ttable on significance degree 5%, on degrees of freedom: df = (N1 + N2) - 2
H.Statistical Hypothesis
The statistical hypothesis states as below.
1. Null Hypothesis (Ho)= It means there is no significant difference of students’ reading comprehension achievement of exposition text between students who are taught through blended learning and students who are taught without blended learning.
2. Alternative Hypothesis (Ha) = It means there is a significant difference of
The criteria to prove the hypothesis as the follow:
1. If t0 (tvalue) > tt (ttable) H0 is rejected and Ha is accepted in significance degree 5%, or in SPSS if p < α or sig 2-tailed is smaller than alpha 0.05.
2. If t0 (tvalue) < tt (ttable) Null hyphotesis, H0 is accepted in significance degree 5% or in SPSS if p > α or sig 2-tailed is greater than alpha 0.05.
Moreover, the degree of freedom in this study: df = (N1 + N2) – 2
= (30+30) -2
= 60-2
= 58
32
CHAPTER IV
FINDING AND DISCUSSION
This chapter shows the result of this study. It consists of description of the data, preliminary analysis, data analysis, hypothesis testing, and discussion.
A. Description of the Data
The main instrument of this research is test. The test was administered in beginning and the end of the research. It was conducted to both classes which were experimental class (XI IPS 2) and controlled class (XI IPS 3) each class consists of 30 students. Furthermore, the result of the test would be described below.
1. Students’ Score in Pre-test
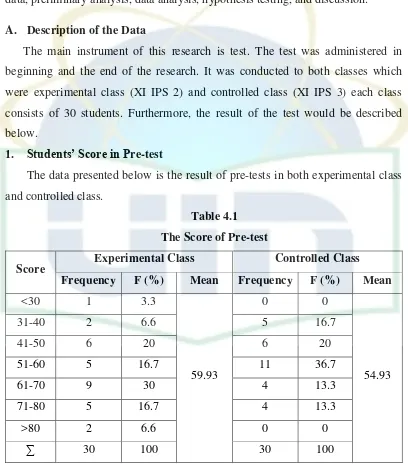
[image:46.595.108.516.203.670.2]The data presented below is the result of pre-tests in both experimental class and controlled class.
Table 4.1
The Score of Pre-test
Score Experimental Class Controlled Class
Frequency F (%) Mean Frequency F (%) Mean
<30 1 3.3
59.93
0 0
54.93
31-40 2 6.6 5 16.7
41-50 6 20 6 20
51-60 5 16.7 11 36.7
61-70 9 30 4 13.3
71-80 5 16.7 4 13.3
>80 2 6.6 0 0
∑ 30 100 30 100
scores which the students got in experimental class appeared to be in range of 61-70 which consist of 9 students (30%). While in controlled class the most frequent score appeared to be in range of 51-60 which consist of 11 students (36,7%). Then students who had score above 80 consist of 2 students in experimental class and 0 in controlled class, students who had score >80 had above average of reading comprehension. Students mean score in experimental class was 59.93 and students mean score in controlled class was 54.93, so the difference between them was 5. The lowest score in experimental class was 28 and the highest was 84, while the lowest score in controlled class was 32 and the highest 80. More detail of students scores and calculation were attached in the appendix.
2. Students’ score in Post-test
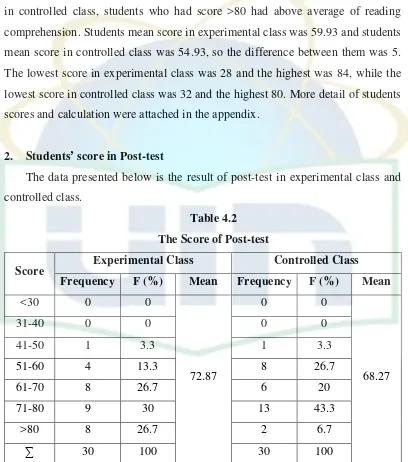
[image:47.595.109.517.192.654.2]The data presented below is the result of post-test in experimental class and controlled class.
Table 4.2
The Score of Post-test
Score Experimental Class Controlled Class
Frequency F (%) Mean Frequency F (%) Mean
<30 0 0
72.87
0 0
68.27
31-40 0 0 0 0
41-50 1 3.3 1 3.3
51-60 4 13.3 8 26.7
61-70 8 26.7 6 20
71-80 9 30 13 43.3
>80 8 26.7 2 6.7
∑ 30 100 30 100
34
classes. The experimental class consists of 9 (30%) students and more in controlled class consists of 13 (43.3%) students. Then students who got score >80 consist of 8 (26.7%) in experimental class and 2 (6,7%) in controlled class. There was also improvement of mean score in both classes. In experimental class the mean score was 72.87 and 68.27 in controlled class, then difference of mean score between them was 4.6, it was 0.4 smaller than in pre-test which was 5. Then the highest post-test score in experimental class was 90 and the lowest score was 48. While in controlled class the highest score also 90 and the lowest score 44. More detail of post-test scores and calculation were attached in the appendix.
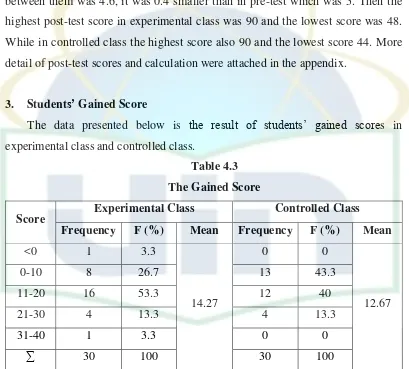
3. Students’ Gained Score
[image:48.595.108.517.223.592.2]The data presented below is the result of students’ gained scores in experimental class and controlled class.
Table 4.3
The Gained Score
Score Experimental Class Controlled Class