lS BN : 97 8-979 -1 97 9 5-S-9
PROSIDII\iG
Srh/rPostuM
ILMIAH
IKATAN
ARSITEK
LANSEKAP
INDONESIA
201
0
Pemberdoyoon
Peron Serto
Profesi
Arsitek Lonskop
dolcm
Mengotosi Mosoloh
Kerusokon
Lingkungon
don
Bencono Alom
Melolui
Pendekoton
Konservosi
don
Penotqon
Ruong
Bogor,
l0
November
2010
NASIONAL
dllerblrkon oleh: beke{osomo dengon:
@l[ffik-SAMBUTAN
KEruA
I.IMI.IM PN
TALI
SIMPOSIUM ITMIAH NASIONAT
IKATAN ARSITEK TANSEKAP INDONESIA TAHUN 2O1O
Bismillahirahmanirahim
Assalamu'alaikum warahmatullah wabarakatuh Salam sejahtera untuk kita semua dan selamat pagi
Yang terhormat
Direktur
DP2M,Direktorat Penelitiandan
Pengabdian kepada Masyarakat, Direktorat Jenderal Pendiciikan Tinggi - Kenrenterian Pendidikan lJasional RlRektor lnstitut Pertanian Bogor
para Dekan dan perwakilan dari
23
Universitasdi
lndonesia, baik Negeri maupun Swasta yang mempunyai program Pendidikan Arsitektur LanskapKetua Foi'um Pendidikan Arsitektur Lanskap lndonesia (FPALI)
para
pembicara,Prof Tong
lvlahnAhn dari
Seoul National Universitydan dari
Kementerian Lingkungan Hidup RlPara Undangan dan Peserta Simposium Nasionalyang berbahagia
pertama tama marilah ki[a bersama sama memanjatkan puji dan syukur kehadirat Allah SWT, Tuhan
yang Maha Esa, atas segaia karunia yanE dilimpahkan Nya kepada kita semua sehingga dapat hadir
ditempat yang sejuk ini, di IPB lnternational convention center dalam keadaan sehat walafiat'
pada kesempatan yang terhormat ini perkenankanlah saya menyampaikan apresiasiyang tinggi serta ucapan terimakasih kepada Pemerintah lndonesia,dalam hal ini Direktorat Penelitian dan Pengabdian
kepada
Masyarakat, Kementerian PendidikanNasional
Rl,
yang
telah
memberikan untukpertamakalinya Bantuan Pengembangan Himpunan Profesi kepada
lkatan Arsitek
Lansekaplndonesia (iALl)
Bantuan pengembangan Himpunan Profesi ini kami peroleh dalam bentuk Hibah dengan mengajukan
proposal untuk menyelenggarakan Simposium llmiah Nasional, lkatan Arsitek Lansekap lndonesia (lALl) tahun 2010, dengan tema
"
Pemberdayaan Peran Serta Profesi Arsitektur Lansekap dalam mengatasi Masalah Kerusakan Lingkungan dan Bencana Alam Melalui Pendekatan Konservasidan
PenataanRuang".
Dituangkan dalam SURAT PERJANJIAN PENUGASAN, Dalam Rangka program Hibah Bantuan Pengembangan Himpunan Profesi, nomor 018/SP.SlP/DP2MN\|2010, pada tanggal 28 Juni 2010 dan berakhir pada tanggal 1 Desembet 2010.Simposium
llmiah
Nasional ini,dipandang pentinguntuk
diselenggarakanguna
menampung,menggalang Naskah llmiah, Konsep, Pemikiran-pemikiran dan Hasil Rekayasa serta Perencanaan dari para professional dalam bidang Arsitektur Lanskap di seluruh lndonesia, yang bertujuan untuk
meningkatkan kepedulian dan peran serta para peneliti, akademisi dan para profesional di bidang Arsitektur Lanskap dalam upaya mengatasi permasalahan kerusakan lingkungan dan bencana alam
melalui pendekatan konservasi dan penataan ruang.
Dalam Penyelenggaraan Simposium llmiah Nasional lkatan Arsitek Lansekap lndonesia tahun 2010 ini, kami bermitra dengan Departemen Arsitektur Lanskap dan Lingkungan Fakultas Pertanian, lnstitut
Pertanian Bogor. Untuk
itu
kami Pengurus Nasional lkatan Arsitek Lansekap lndonesia, sangat menghargai dan menyampaikan penghargaaan yang tinggi atas ker.jasama yang baik ini.Bapak, lbu dan peserta Simposium Nasioitalyang saya hormati,
Tema dari Simposium llmiah Nasional
ini
sangat tepat,yatu
penekanannya kepada pemberdayaanperan serta dari profesi Arsitektur Lanskap, maka kami sebagai insan Arsitek Lanskap lndonesia,
sebagai profesi yang turut beftanggung jawab terhadap pengelolaan sistem ruang luar, merasa perlu untuk memberikan kontribusi pemikiran yang sampaisaat ini belum sepenuhnya dilkut sertakan dalam
tahap kebuakan-kebijakan dan selama ini pula lebih banyak mempunyai kesempatan pada tahap pelaksanaannya saja.
Keberaclaan Arsitek Lanskap masih dianggap sebagai pelengkap, hanya menjadi kebutuhan yang bersifat tersier dengan paradigma beautyfikasi sebagai konsep pengembangan bentang alamnya. Untuk itu melalui berbagai seminar, workshop dan simposium, karni berusaha merebut posisi profesi
ini guna lebih dapat memberikan sumbangan pemikiran secara universal, makna dari pentingnya
keberadaan suatu lansekap di lndonesia, pentingnya penataan ruang luar yang mewujudkan
ruang-ruang
di
nusantarayang
nyaman, produktifdan
berkelanjutan sesuai yang diamanatkan olehlnternational Federation of Landscape Architecture ( IFLA ) dalam World Congress di Suzhcu - China
pada bulan Juli 2010, ciimana intinya adalah Arsitek Lanskap didorong untuk terlibat langsung cialarn upaya pengurangan pernanasan global.
Melalui delegasi lALl, serta beberapa anggota lALl yang tuiut serta dalam kongres dunia ini, juga
telah
menyampaikan isu-isu strategis termasuk rnenyangkut keberadaan profesi lansekap dilndonesia.
Bapak lbu clan pesefia Simposium Nasionalyang saya hormati,
Didalam penyelenggaraan Simposium Nasional
ini, kami
membentuk gugus tugas termasukdidalamnya membentuk tim reviewer dan editor serta mengundang pembicara dari dalam dan luar
negeri. Makalah yang telah diterima adalah merupakan pemikiran alternatif untuk penyelesaian
masalah kerusakan lingkungan dan
budaya.
Para kontributor makalah terdiri dari para profesionaldan akademisi, termasukjuga yang sedang menyelesaikan program magister dan program doktor,
yang berasal dari komunitas dalam organisasi institusi pendidikan tinggi bidang Arsitektur Lanskap
yang
tergabung dalam Forum Pendidikan Arsitektur Lansekap lndonesia (FPALI), maka pada kesempatanini
kami sangat menghargai upayadan
karyadari
seluruh kontributor yang telahmenyampaikan makalahnya. Atas kerjasama yang baik ini dan sesuai dengan waktu yang telah
ditentukan, maka
tim
Simposiurn Nasionalini
telah berhasil menjaring serta selanjutnya dapatmenyeleksi
58
Naskah llmiah yang layak diterbitkan pada berkala ilmiah pada tingkat nasional, internasional, atau beraspirasi internasional..Dengan adanya kerjasama berupa Penugasan dari DP2M Direktorat Pendidikan Tinggi Kementerian Pendidikan Nasional Rl kepada lkatan Arsitek Lansekap lndonesia, maka kami dari Asosiasi Profesi
menyatakan bahwa
ini
adalah momentum awal dari kiprah profesi Arsitek Lanskap untuk lebihmemberikan kontribusi kepada bangsa dan negara guna menjaga alam Nusantara "agar tidak salah urus" yang dapat mengakibatkan kerusakan alam yang akhirnya menjadi masalah bersama yang sulit dikendalikan, karena evaluasi lanskap harus dimulai dari aspek manusianya, sehingga definisi apapun
tentang lanskap harus sudah mencakup dimensi sosial didalamnya.
Kenyamanan suatu lingkungan selain dapat terjadi karena karakteristik ruang yang sudah ada "given",
tetapijuga harus tetap mengutamakan azas manfaat sepefti berguna, ekonomis, sehat, aman, serta bersinergi dengan aspek produktif dan pembangunan berkelanjutan.
Bapak lbu dan peserta Simposium yang saya hormati,
Demikianlah sambutan Simposiufi llmiah Nasi'onal lkatan Arsitek Lansekap lndonesia tahun 2010.
Semoga Simposiurn ini menjadi pemacu semangat bagi lALl -organisasi profesi kita- untuk dapat menyelenggarakan secara rutin kegiatan semacarn inipada tahun-tahun mendatang.
Sedikit catatan dari profesi:
Para arsitek lanskap hendaknya dapat menjadi
pionir
dalam upaya konservasi, preservasi danperencanaan sistematis dari pemanfaatan sumber daya alam, sehingga manusia dan karyanya dapat
dibawa pada keharmonisan dengan sistem alami. Rasa bahagia akan timbul dari kesederhanaan,
ambilsecukupnya dari alam, maka kita akan hidup damai, nyaman dan ceria.
Semoga Allah SWT, Tuhan Yang tviaha Esa Senantiasa memberikan bimbingan dan karunia kepada kita semua.
Wasalammuallaikum Warahmatullahi Wabarakatuh
Hengki Triyogo Heksanto
DAFTAR
ISI
SUB.TOPIK
1 :PERENCANAAN
DAN
PERANCANGAN
1.
Agung Yansusan Sudarwin, Nia Kurniasih Pontoh, Bagas Dwipantara PutraPrinsip Perancangan Ekologis Pada Ruang Terbuka Hijau Publik cii Taman Kota Tegalega Banduno
2.
Akhmad Arifin Hadi, Einar Kretzler, Dr. Barty Warren-KreEschmarCommunicating And Evaluating Landscape Design Concepts Online With A
Virtual Reality Landscape Model
3.
AzrarHadiPublic Participation ln Open Space lnspection
4.
Bambang Sulistyantara, Fitriyana Budiwatilnterfunction Of Green Open Space Pian As Eartquake Evacuation Camp at Padang City, West Sumaiera
5.
Bambang Sulistyantara, Muhammad RizkiPenyusunan Apiikasi Penyimpan Basis Data Pohon Berbasis Koneksi lnternet Dengan Studi Kasus Kota Jakana Barat (Trees Database Aplication
Construction Based on lnternet Connection ltiith Case Study Of West Jakarta, lndonesia)
6.
Bambang Sulistyantara, Prita lndah PratiwiLandscape Pianning of Tourisnr Destination anO
the
Formulation of Tourism Program Alternative at Graha Tirta, Jatiluhur, Purwakarta District, West Java7.
Edy Saputra YuTata HUau Hunian MultiMassa dan Dampaknya Terhadap Perilaku Gated
Community (Green Design of Multi Mass Housing and lmpact On The Behavior Cf lts Gated Community)
8.
FirmansyahPengembangan Metode Assessment Kualitas Visual Lansekap Kampus Di
lndonesia, Kasus: Kampus Ul Depok dan tTB Bandung (A Development Of
Landscape Visual Quality Assessment Method of Campus ln lndonesia, Case Study: Campus Of lndonesia University (Ul) at Depok, and Campus Of
Bandung lnstitut Of Technology (lTB) at Bandung)
9.
Fitri RahmafitriaAnalisis Bahaya Lanskap Berbasis Konservasi Dalam Perencanaan Wana Wisata Kawah Putih
-
Jawa Barat (Conservation Based Landscape Hazard Analysis ln Kawah Putih Forest Recreation-
West Java)10.
lqbal Muhammad, Afra DN Makalew, Vera D DamayantiPerencanaan Lanskap Jalur lnterpretasiWisata Sejarah Budaya Jalan Slamet Riyadi Kota Surakarta (Landscape Planning of Historical-Cultural Tourism lnterpretation Trail at Slamet Riyadi Street, Surakarta)
11.
Lis Noer Aini / Agus Nugroho Setiawan / Arif Muda RambePerencanaan Tata Hijau SungaiBerdasarkan Konsep Ekologi, Studi Kasus Sungai Code Kota Yogyakarta (Ecologigal Planning Concept of Code River Case in Yogyakarta)
12.
Ludfie HamdriPrasyarat (Keharusan) Minimal Ruang Terbuka Terhadap Pengembang Perumahan Sebagai Bagian Manajemen Peftumbuhan Perkotaan Yang Cepat Berkembang
Halaman
1
13
20
2Ll
33r'
q3
52
88
5
.r' ,tMoch Saepulloh, Siti NurisYah
Perencanaan Lanskap Kawasan Pasar Terapung Sungai Barito Banjarmasin Kalimantan Selatan Sebaqai Kawasan Wisata'Budaya (Landscape Planning of
Floating Market Area at Barito River, Banjarmasin, South Kalimantan as CulturalTorusim ar.ea)
Moharharadlsrok Nugroho, Yong Hoon Son
Study of Usage of Cig Park As An Useable, Enjoyable And Manageable Place (Case Study:i21th Century Park - Matsudo, Japan, And City Park -Malang, lndonesia)
Nanang SuGlldiat, lndung Sitti Fatimah
Perencariaari Lanskap Jalan Tol Kanci- Pejagan Pada
Oemardi
ain Landscape Consultant, Bogor (Landscape Planning of Kanci- Pejagan Tollroad ln Oemardi_Zain Landscape Consultant, Bogor)Rahman Andra Wijaya
Menuju Kualitas Lanskap Yang Lebih Baik Rahman Andra Wijaya
Landscape of a Settlement: A Tale of Newfounci Farm and Cringleford
Resa Maharani, Tati Budiarti
Studi Potensi Lanskap Perdesaan Untuk Pengembangan Agrowisata Berbasis Ir4asyarakat Di Kecamatan Cigombong Kabupaten Bogor (Potencies Study of
Rural Landscape For Agrotourism Based on Community Development ln
Cigombong Resicient, Bogor)
Rezky Khrisrachmansyah
Penataan Kawasan Pemukiman Bantaran Sungai Perkotaan Berbasis Ecological Design Studi Kasus: Bantaran Sungai Ciliwung (Pulau Geulis) Kelurahan Babakan Pasar, Kota Bogor (Settlement Plan Of Urban River Bank Based On EcologicalDesign Case Study: Geulis lsland ln Ciliwung River, Babakan Pasar Village, Bogor)
Siti Nurisyah, Lisa Anisa
Perencanaan Lanskap Riparian Sungai Martapura Untuk Meningkatkan
Kualitas Lingkungan Alami Kota Banjarmasin (Riparian Landscape Planning of Martapura River to lncrease the Banjarmasin City's Natural Environment
Quality)
Siti Nurul Rofiqo lrwan, Mukhlison, Nahda Kanara
Kajian Permasalahan Ruang Hijau Kota Yogyakarta Untuk Pengembangan Lanskap Hutan Kota Dan Urban Greenway (Analysis On Yogyakafta Green Space For Development Of Urban Forestry Landscape And Urban Green Way)
SitiZulfa Yuzni
Lake Toba Tourism Area Management Based On EcologicalApproaches Ugit Mulgiati, Nizar Nasrullah, Bambang Sulistyantara
Pengaruh Penutupan VegetasiTerhadap Kenyamanan Kota (The lmpact of Vegetation Converage to the City Amenity)
Wasissa Titi llhami, Siti Nurisyah
Perencanaan Lanskap Kawasan Wisata Pesisir Yang Berkelanjutan
Studi Kasus : Pesisir Teluk Pacitan, Jawa Timur
(Sustainable Landscape Planning For CoastalTourism Region, Case Study ln Pacitan Bay, East Java)
101
13.
108 14.
11
{5.
12
16.
.n
17.
18.
12
135
155
i80
19.
20.
21.
13
11
22.
23.
24.
PROSIDING SIMPOSIUM ILMIAH NASIONAL IALI 2O1O
SUB-TOPIK
2:KONSERYASI
LANSKAP,
LINGKUNGAN
&
BI,IDAYA
Halaman
25.
Agnes Kristandi, Nurhayati Hadi SusiloArifin
1Perencanaan Lanskap Kawasan Wisata Sejarah Perkampungan Portugis di Kampung Tugu, Jakarta Utara (Landscape Planning'on HistoricalTourism of Portugis Residence at Kampung Tugu, North Jakarta)
26.
AiDariah
11Tindakan Konservasi Secara Vegetatif pada Lansekap Pertanian (Vegetative Conservation Measures At Agricultural Landscape)
27.
I G.A.A. Rai,Asmiwyati, .N. L.P.Darwini, lda Ayu Mayun, A.A. Sri PradnyaParamita
'18'
Pola Pekarangan Rumah Tradisional Bali Di Kota Denpasar (Study OfBalinese Traditional Homegarden ln Denpasar)
28.
Annisaa Elok Perrnatasaridan Aris Munandar 28ldentifikasi Hubungan Perilaku Vandalisnre Dengan Setting Pada Kebun Raya Cibodas, Kabupaten Cianjur (ldentification Of Relationship Between
Vandalism Behavior And Setti;rg ln The Botanical Garden At Cibodas, Cianjur)
29.
Aris Munandar, Kaswanto, HS Arifin, AndriantoKusumoarto
38 Pengembangan Metode Penilaian Elemen Keindahan Lanskap BerbasisLandform dan Landcover Untuk Pengelolaan Lanskap Berkelanjutan (Developing Assessment Method of Landform and Landcover Based Landscape Aesthetic Quality for Sustainabie Landscape Management)
30.
Bambang Sulistyantara, Aris Munandar, NorilMllankra
5,-Residential Landscape Analysis Based On Energy Conservation
31.
DhaniBlshak
50 Rencana Program lnvestasijangka Menengah dan Pelestarian WarisanAiam Kota Sabang
32.
Eka Kurniawati, Siti Nurisyah, Fredian TonnyNasdian
1Strategi Pengembangan Ruang Terbuka berbasis Komunitas di Kecamatan
Pontianak Kota, Kalimantan Barat (Development Strategy for Community-Based Park in Pontianak Kota District, West Kalimantan)
33.
GunawanBudiyanto
1Teknologi Konservasi Lanskap Gumuk Pasir Pantai Parangtritis Bantul Diy (Conservation Technology Of Sand Dunes Landscape
ln
Parangtritis Beach Bantul DIY)34.
Moh. Sanjiva Refi Hsb, Nurhayati Hadi SusiloArifin
8 Karakteristik Dan Faktor-Faktor Yang Mempengaruhi Lanskap BudayaRumah Larik Limo Luhah Di Kota Sungai Penuh, Kerinci, Jambi
(Characteristics And Factors That Affecting Cultural Landscape Cf Rumah Larik Limo Luhah ln Sungai Penuh, Kerinci, Jambi)
35.
Mohammad Zaini Dahlan, Nurhayati Susilo HArifin
BPerencanaan Lanskap Kawasan Wisata Budaya Di Kampung Budaya Sindang Barang, Bogor (Pendekatan Community Based Planning) (Landscape Planning On CulturalTourism Of Kampung Budaya Sindang Barang, Bogor - Community Based Planning Approach)
36.
Muhammad lftironi, FathmyAzizah
103
r
Revitalisasi Kawasan AIun-Alun Kota Magelang Slogan Magelang Kota "Harapan" Sebagai Konsep Perancangan (Magelang Town Square Revitalization Magelang City Slogan "Harapan" As A Design Concept)
Naniek Kohdrata, Putu Edhi Sutrisna
Konservasi Subak Anggabaya: Suatu Model Konservasi Lanskap Bali (The Conservation of Subak Anggabaya: A Conservation Model of Balinese Landscape)
Neneng L Nurida
Alley Cropping: Teknik Konservasj Vegetatif Untuk Lahan Kering Terdegradasi Mendukung Konservasi Lanskap Lahan Pertanian (Alley Cropping: Vegetative Conservation Technique For Degraded Upland To Support Landscape Ccnservation Of Agricultural Land)
Rustam Hakim Manan, Quintarina Uniaty
Pendekatan Konsep Eco-Development Pada Pengembangan Kawasan Pasca Pertambangan Timah
Sidik Haddy Tala'ohu, Deddy Erfandi, dan lshak Juarsah
Penataan Lahan Pasca Penambangan Batubara (Land Management Post
CoalMining)
Stephanus Hanny Rekyanto, Yanto Santosa, Syartinilia
Model Kesesuaian Habitat Potensial Banteng (Bos Javanicus) Di Taman Nasional Ujung Kulon dengan Menggunakan Regresi Logistik (Potential Habitat Suitability Model Fcr Banteng (Bos Javanicus) In Ujung Kulon National Park Using Logistic Regression)
Sumantris lndri, Aris Munandar
Evaluasi Perseptual Kualitas Estetika Dan Ekologi Kebun Raya Cibodas T. Vadari, A. Rachman
Aplikasi Geo-Splash Versi 1.0 Untuk Merancang Disain Teknik Konservasi
Tanah Di Lanskap DAS Kali Babon Taufan Madiasworo
Revitalisasi Kawasan Bersejarah Perkotaan dalam Perspektif Penataan Ruang, Studi Kasus ; Kampung Melayu Semarang (Revitalization Of Urban Heritage Area ln Spatial Planning Perspective, Case Study: Kampung Melayu Semarang)
Umi Haryati, TatiBudiarti dan Afra D Makalew
Rekomendasi Teknik Konservasi Tanah Dan Air Untuk Pelestarian Lanskap Pertanian Lahan Kering Di Das Bagian Hulu (Kasus Dataran Tinggi Gunung Salak, Das Cisadane) (Recomeridations Of Soilp.nd Water Conservation
Techniques For Sustainability
Of
Upland Farming Landscape ln Upper Watershed (CaseOf
Gunung Salak Highlands, Cisadane Watershed))SUB-TOPIK 3
:GREEN INFRASTRUCTTIRE
46.
Alinda F.M. Zain, Azhari Syarief, Soedodo HardjoamidjodjoDeteksi Penurunan Ruang Terbuka
Hijau
dan
Dampaknya Terhadap Peningkatan Kawasan Rawan Banjirdi
Kota Padang (Urban Green Space Detection and Flooding Prediction in Padang)47.
Bambang Sulistyantara, Esti BudiartiEvaluasi Kondisi Pohon Pada Beberapa Jalur Jalan Arteri Di Kota Jakarta
Pusat, Provinsi DKI Jakarta (Tree Condition Evaluation
Of
Some Arterial Roads At CentralJakarta City, Province of DKI Jakarta)49.
Djajeng Poedjowibowolnfrastruktur Limbah Terpadu Dalam Taman Lihgkungan permukiman (lntegrated Waste lnfrastructure in Environmental Settelement Park)
37. 110
183
Halaman
1
11 38.
12
135 39.
40.
41.
155 42.
43.
13
45.
Dini Rosmalia
Pengembangan Kawasan Berbasis Kondisi Fisik Lokal Studi Kasus Kawasap
Paninggahan, Solok, Sumatera Barat (Development Area Based
on
Local Physical Condition, Case Study Area Paninggahan, Solok, West Sumatera)lwan lsmaun
Kajian Hidrologis Kawasan Parkir Timur Senayan
-
Jakarta Ninrvono JogaKota Lestari: lnfrastruktur Hljau Kota
Pangesti Nugrahani dan Endang Triwahyu Prasetyawati
Tanaman Semak Hias Lanskap Jalan Sebagai Fitoindikator Pencemaran Udara SO2 di Perkotaan
Siti Nurisyah, Jafar Shodiq
Perencanaan Kampung Berbasis Lingkungan (Ecovillage)
di
KawasanPenyangga
Taman Nasional
Ujung Kulon
Banten,
Kasus
KampungCimenteng, Desa Taman Jaya, Kecamatan SumLrr, Kabupaten Pandeglang,
Propinsi Banten (Ecoviiiage Landscape Planning
at
Buffer Areaof
Ujung Kulon National Park, Case studyat
Kampong- Cimenteng, TamanJayi
Village, Banten Province)
SUB-TOPIK
4
:GREEN
BLIIDING
54.
Bambang Deliyanto, Aris MunandarPerformansi Eco-Spatial
Behavior
Pada Penghunian Rumah Susun KotaBaru Bandar Kemayoran, Jakarta (Eco Spatial Behavior Performance Of Occupancy Settlement ln Kemayoran New Town Flats, Jakarta)
55.
Lestari Suryandari, Yodi DanusastroPeranan
Riset
Dan
Peningkatan Keterampilan Arsitek Lanskap DalamMenghadapi Penerapan Konsep Green Building (The Role of Research and Competency
of
Professional Landscape Architect Facing Application ofGreen Building Concept)
56.
Ning PurnomohadiCreating Herbal Medicine & Kitchen Garden ln and Around Settlement, ln A
'Green Building' Development Approach
57.
SitiSujatini, Euis Puspita DPeran Serta Arsitek Dalam Rangka Mengendalikan Kerusakan Lingkungan (Arch itect's Com mitment t n O rdei To Coniot Environ mental Damagei)
25
30
51.
52.
53.
Halaman
1
12
ABSTRAK
KARYA
POSTER
1.
Dewi Rezalini Anwar, Sugiarto, Ray Agung SucikaTaman Pisang Wajah Baru Ruang Terbuka Kota yang Ekologis
2-
Dina safarinanugraha, Dwi setyanti, Hartono wijaya, Juniar Adi, MedriaShekar Rani, Moch. Rizki, Mohammad Tarmizibin Mohd.lsmail
Tropical Plant conservation parks The
Buffer
oneof
Bogor Botanical Garden3.
Fitri RahmafitriaPerencanaan Tahura lr H Juanda Melalui Pendekatan Bahaya Lanskap dan Preferensi Visual
4.
Padmana Grady prabasmaraConnectibility Green I nfrastructure As G reenways
5.
Putri Wulandart dan Aris MunandarDesain Penanaman Menuju Konsep Eco-City Di Klaster Pine Forest, Sentul,
city, Bo-gor (Planting Design towards Eco-city concepts in clutser pine
Forest Sentul City, Bogor)
6.
Rustam Hakim MananLansekap Desain Proposal Sekolah Taman Kanak-Kanak rjan Sekolah Dasar
7.
Rustam Hakim MananPerancangan Kawasan penerima pusat pemerintahan Kabupaten Tangerang-propinsi Banten
8.
Rustam Hakim MananPenghijauan Perkantoran Geostech BppT Serpong
9.
Siti Nurul Rofiqo lrwan dan KaharuddinStudi Kenyamanan Aktivitas di Hutan Kota Kampus Universitas Gadjah Mada
Studi Kasus: Klaster Agri Ugm
{0.
sugeng Triyadi S., lndra Budiman Syamwir, Andi Harapans.,
rsmair,Endang Ruhiyat 5
Pemanfaatan Potensi Lokal Dalam perancangan Kawasan Bekas Tambang Timah di Bangka Belitung
Halaman
1
LANDSCAPE PLANNING
OF TOURISM
AREA AND FORMULATION
OF
TOURISM
PROGRA,MMED
ALTERNATIVES
IN
GRAMA TIRTA JATILUHUR,
PURWAKARTA
DISTRICT, PROVINCE OF
WEST JAVA
Bambang Sulistyantara' Prita lndah Pratiwi2
t L".trr*,
at Departement of Landscape Architecture, Faculty of Agriculture, Bogor Agricultural University (lPB) , Student of Bachelor Program at Departement of Landscape Architecture, Faculty of Agriculture, Bogor Agricultural University
(rPB)
ABSTRACT
Grama Tirta Jatiluhur (GTJ) is tourism area which is located in the eastern of lr. H. Djuanda water reservoir. This tourism area is one of potential tourism destination in Purwakarta which has many objects and
attractions. The purpose of this research are to identify and analyze natural tourism resources, to analyze land
suitability of tourism area, to analyze ecological value of green open space, to analyze characteristics and
perseptions of tourists in GTJ, to decide touring plan based on objects and attractions. This research use qualitative and quantitative descriptive method. The qualitative descriptive method consists of potentials and
constrains of biophysical aspects, technical aspects, and social aspects. Whereas, the quantitative descriptive method consist of Geographlc lnformation System (GlS) processing by: (1) overlaying thematic maps of
physical-biophysical aspects, objects and attractions potentials variables using software ArcView 3.2 and (2) calculating the value of nature by using extention ClTYgreen 5.4. The results of this research are Landscape Planning of Tourism Area and Formulation of Tourism Programme Alternatives with ecologically sustainable development.
The landscape plan consists of touring plan, space, vegetation, circulation, activities, facilities, and tourism programmes. There are two kinds of tourism programme alternatives, such as daily and incidental tourism
programmes.
Kelnruord: Landscape Planning, Tourism Area, Land Suitability, GIS Processing. Touring Plan
PREFACE Background
Purwakarta District
is
one
of
regionwhich has natural potentials such as range of hills and famous tourism object, lr. H. Djuanda Reservoir which is developed as tourism area in
the
easternof
it
and calledas
Grama TirtaJatiluhur.
Grama
Tirta
Jatiluhur(GTJ)
haslandscape
nature
resources
and
goodpotentials such as diversity of object and tourist aftraction. topography, vegetation, and easy in
accessibility. Resources
in
tourism
activityaccording to Gold (1980) are destination place
for
people whotour and
do
tourism activitywhich is the unity of space and attract them to
make a tour.
According
to
Holden (2000), tourismdevelopment in destination place includes using
of
physic
dan
natural resourcesand
thencauses economy, culture, and ecology impact
in tourist destination place which is developed.
The existence
of lr.
H. Djuanda Reservoir asone
of
tourism objects
that has
a
tight relationship with the impact of tourism activitiesaround it. The increase of reservoir volume is
PROSTDTNG STMPOSTUM TLMTAH NASIONAL lALl 2010 I
caused
by
environmentaldegradation
in uppercourse, sedimentationthat
entered the reservoir, and not friendly-
tourism activity or over caryingcapacity.ln
order
that
nature continuance in tourism area is guarded and sustainable, so it is needed landscape )tanning and formulation oftourism
programme.Tourism
programmed,especially nature tourism
is
madeto
createphysic
environmentor
landscape
whichsupport
users
recreationalactivity,
needs,satisfaction and their comfort, which planning process start from personality and characteristic comprehension and also policy in using the site
for tourism area (Knudson, 1980).
Objectives
The purpose of this research are:
1.
to
identify and analyze natural tourismresources,
2.
to
analyze
land
suitabilitY
andecologicalvalue of green open space of tourism area,
3-to
analyze
characteristics
and perseptions of tourist in GTJ, andbs.
4.
to decide touring plan based on objects and attractions.Benefit
The result of this research
is
as inputfor
local governmentof
Purwakarta District intourism development
in
Purwakarta District,especially
for
GTJ manager and also anothertourism areas. Besides
that,
landscape planthat
is
made can support conservation effortwater catchment area around
lr.
H.
Djuanda Reservoir.METHODOLOGY
Time and Location of Research
This research
is
donein
Grama TirtaJatiluhur Tourism Area, Jatiluhur Subdistrict,
Purwakafta District, Province
of
West
Java(Picture
1). This
researchtook
place
from March untilJuly 2010. [image:12.597.82.295.245.499.2]Pwwakarta
Map
Grama Tirta Jatiluhw Map Figure 1. Research Location MapMaterial dan Tool of Research
The material that
is
usedin
researchare orientation map, masterplan, questionnaire,
dan literature. Meanwhile, tools which is used
are Global Positioning System, digital camera,
scetching
tools,
and
computer
in
dataprocessing
by
using softwareArc
View 3.2, Ekstension CITY green5.4,
AutoCAD 2006, Adobe Photoshop CS4, Microsoft Word 2007, dan Microsoft Excel 2007.Phase and Method of Research
This research use systematic approach
methode
who
is
describedby
Gold
(1980).Methode
consists
of
preparation,inventarization,
analysis, synthesis,
andplanning. Research
is
done until
planning phases:44
suB-roPrK rPreparation. Preparation phase includes setting
the purpose of research and searching general
information about existing condition in research location.
lnventari
ation
Data
interpretation includebiophysical,
tourism resources, social, andtechnical aspects. The way of data collection
includes
field
surveying,
questionnairedistibuting, interviewing with tourist
and
GTJ manager, studying literature.Analysis
Biophysical,tourism
resources,social, and technical aspects that are collected
then
done
by
processingand
arranging.Analysis which is done are:
a.
Biophysical aspect potentials evaluationanalysis
in
tourism
area
by
usingqualitative descriptive method.
b.
Tourism objectand
attraction aspectpotentials evaluation analysis
are
toanalyze of tourism object and attraction
potentials spatially have scored by GIS processing based on
the
standard bylnskeep (1991).
c.
Land suitability analysisis
to
analyzeland
suitabilityof
5
variables havescored by GIS processing based on the
standard
by USDA
(1968),Hardjowigeno,
et al.
(1968),
and Direktorat Jenderal Perlindungan Hutandan KonservasiAlam in Mulyati (2007).
d.
Ecological value analysisis
to identifylandcover,
to
observe the character ofgreen open space
spatially,and
toanalyze
ecological benefitof
greenopen space
(carbon storage,
airpollution removal, storm water control) by GIS processing.
e. Characteristic, perception, and tourists preferences analysis are to analyze the
result
of
questionnaire
aboutcharacteristic, perception,
and
tourist preferencesof
tourism areaby
usingqualitative descriptive method.
Synthesis
This result of this phase is zoningbased on land suitability for tourism area. The form of this zoning is block plan that is will be
planned.
Planning This phase is produced a landscape
plan
of
nature tourism area that consider theconcept. The landscape plan consists of touring
plan, space, vegetation, circulation, activities,
facilities, and tourism programmes
GENERAL CONDITIONS
Grama
Tirta
Jatiluhur Tourism
Area(GTJ)
is
located in the westernof
Purwakarta District, Jatiluhur Sub District, Province of WestJava.
Site boundaries of GTJ are:
1.
North
:Kutamanah
and
Cikao Bandung Village.2.
South
: lr. H. Djuanda Reservoir3.
East
:Jatimekar, Jatiluhur, Cilegong,and Kembang Kuning Village.
4.
West
:lr. H. Djuanda ReservoirBiophysical Aspect
a. Topography
GTJ Tourism Area is undulating area with
slope 3-70%. The highest levation
(27i
m) is inthe
southernof
site
which
is
adjacent to Cilegong Village. The lowest elevation (100 m) is in the southwestern to northern of site which is adjacent to lr. H. Djuanda Reservoir.b. Geology dan Soil
Based on Cianjur Geological Map, West Java which
is
published by Direktorat Geologi1972, geology structure
in
Jatiluhur area are:(1)
Miosin Stone
(quartzsand stone
andmembers of limestone), (2) Old Volcanic Stone
(sand stone, tuff, dan conglomerate), and (3)
another
Terobosan
Stones.
This
area composedof
soil varieties basedon type
of source stone: (1) association of yellowish grayGrumosol, grayish Regosol, and grayish yellow Mediterranean include area of the southern site;
(2)
associationof
yellowishred
Latosol andLitosol include area of the middle site; and (3) gray alluvial includes covers
a
fractionof
thenorthern site.
c.
ClimateThe monthly temperature average of GTJ
Tourism Area from 2005 until 2009 is obtained
the
highest monthly average 26.7 oC and the lowest monthly average 25.9 oC. Air humidity is obtained the highest monthly average 90.1 o/oand the lowest monthly average 88.4o/o. Rainfall
is the highest monthly average 21.17 mmlday
and the lowest monthly average 14.35 mm/day.
The
highest monthly wind speed average atnoon 5.81
km/hour
dan
the
lowest
3.O2km/hour.
The
highest monthlywind
speedaverage at night 2.06 km/hour and the lowest
0.72 km/hour.
PROSTDTNG STMPOS|UM |LMTAH NASTONAL rALr
2010
Id. Hydrology
GTJ Tourism Area is located in Citarum and Cikao River Basin Region. Water needs for
tourism area is obtained from Citarum River then pumped into Biki Baru Pump to be cleared, then pumped into Biki Lama. From BikiLama,
water is pumped into Cimumput Reservoir and Pos Gereja that is distributed to consumer and tourism area. Tourism area uses lr. H. Djuanda Reservoir as main tourism object. This reservoir has average voume 1.825.400.000 m3 and reservoir water level average 98,66 m. e. Vegetations dan Animals
Vegetations
in
tourismarea
grow
upnaturally
or
cultivated. Groupingof
vegetationtypes:
(1)
forest vegetation,such
as
mixedforest, production forest, and protected forest,
(2) shrub vegetation, (3) talun, mixed garden, and yard, (4) shifting vegetation, and (5) ekoton
vegetation. Ekoton
is
transition area betweenaquatic and terrestrial
that
has biota diversityand
it
is
very
sensitiveto
disturbances orchanges from the outside. Animals in tourism area such as insect, reptile, livestock (goat and cock), cat, and bird.
Tourism Aspect
Based
on the
resultof
Rencana IndukPengembangan Pariwisata Daerah (RIPPDA)
Kabupaten Purwakarta Tahun
2001
studies,tourism area
in
Jatiluhur, especially GTJ hastourism
object
and
attraction potentials inPurwakarta District. There are tourism objects
and aftractions: (1) main dam, (2) floating dock
(dermaga
apung)
and
kampungair
dock(dermaga kampung air), are the place for boat
to
dock and recreation area, (3) land tourismobject,
(4)
Jatiluhur WaterWorld and
openstage,
are
water recreation mode area, (5) fishing pond, (6) servis/ fish auction, (7) floatingnet fish farming area, this area
is
rented andmanaged
by
Jatimekar Village communities,and
(8)
operationalbuilding, consists
of bangunan PLTA Division, Forth Division, DamSub Division and Loka Riset Pemacuan Stok lkan.
Social Aspect
a.
History and The Objectives of Tourism Area EstablishmentThe
locationof
Jatiluhur tourism areaproject
developmenttook
a
part
of
localplantation
land,
Perhutani's land,and
Ir.
H.Djuanda Reservoir. Pembangkit Listrik Tenaga
Air (PLTA) and its irrigation tools were finished-built in 1967, it became main tourism object that motivated tourism development
in
PurwakartaDistrict. After looking nature potentials where
was exlsted around lr. H. Djuanda Reservoir, so
Perum
Jasa
Tirtall
Tourism Unit started to expand its tourism assets.b. Demography of Jatiluhur Sub District
Jatiluhur Sub District has width 6.011 Ha which is consists of farming land 725 Ha, land
fishery/ pond
12
Ha,
settlement and garden2.755 Ha, and industrial area 478 Ha. Jatiluhur
Sub District consists of dari 10 villages. Based
on inhabitants census in 2009, the number of communities in Jatiluhur Sub District are 63.847
people.
The
most of communities in JatiluhurSub
Districtare
worker 10.508 people, thenfarmer 4.515 people, seller 2.836 people, civil
employee
952
people,home
industry 376 people, and TNI POLRI 87 people.Tourist
The
most
of
GTJ
touristsare
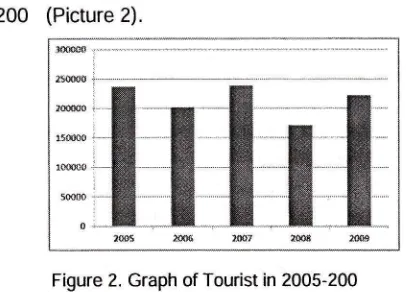
family groups and businessman. There is the number [image:14.597.324.530.168.314.2]of tourists who visit tourism area in 2005 until 2009 (Picture 2).
Figure 2. Graph of Tourist in 2005-2009
TechnicalAspect
Based on President Decision Number. 32
year
1990 about
Managementof
ProtectedArea, divides the protected area into: (1) area
that provide protection to the bottom of its area,
(2) local
protected,(3)
nature and
cultural reserves, and(
) disturbed-disaster areaLocal
protectedarea
includes border river, the area around the lake or reservoir, andthe
area around spring water. The criteria ofborder
river
based
on
President DecisionNumber 32 year
1
0
is at least 100 meters oneither side
of
major rivers and 50 meters on46
suB-roPrK reither side of creeks outside the settlement. For
the
river in the settlement, border river whichis
estimated enoughto
buildthe
inspection road 10-15 meters.Tourist
The
most
of
GTJ
touristsare
family groups and businessman There is the numberof tourists who visit tourism area in 2005 until
200
(Picture 2).Figure 2. Graph of Tourist in 2005-200
The criteria in the lake or reservoir is land
along the edge of the lake or reservoir that its
width is proportional to the shape and physical
condition of the lake
or
reservoir between50-100
meters
from
the
highest
tide
point landward.ANALYSIS
Biophysical Aspect Analysis
a.
Potentials Evaluation AnalysisPotentials evaluation
analysis
usesualitative descriptive method
is
to
analyzepotentials and constrains of biophysical aspect
in tourism area, so the
e
isting potentials can be used and the constrains will be solved well.b.
Land Suitability AnalysisLand suitability analysis
uses
uantitativedescriptive method
by
GIS
processing withscoring landscape resources variables (soil,
slope,
vegetation, landcover,and
landuse).Then
the
thematicmaps
are
combined byoverlay techni ue. The result of land suitability
analysis is zoning of suitability area for tourism
area
from
marginallysuitable,
moderately suitable, and highly suitable area.c.
Ecological Value AnalysisEconomic
benefit
and
landcover distribution ofe
isting and GTJ planning area in200
(Google Earth Plus tahun 200)
can beobserved
and
analyzed.From spatial
andffi 287
attribute data that is analyZed with GIS method
by using Arc View 3.2, ekstension CITY green
5.
obtained the following results:E
isting AreaAnnual Air Pollutant Removal Saving:
3,511 is
e
uivalent toRp.
3
1.5
.000,-Annual
Stormwater
Saving:
8,15
ise
uivalenttoRp.
33.
31.000,-Total Annual
Saving: '1,
0
ise
uivalent toRp.
825.030.000,-Planning Area
Annual Air Pollutant Removal Saving:
1 2,02
ise
uivalent.to Rp 1.58.2
1.000,-Annual Stormwater
Saving:
1
,
I
is
e
uivalentto Rp.1.5
2.883.000,-Total Annual
Saving:
3
,01
ise
uivalent toRp.
3.1
1.1
.000,-.Through the image projection the benefit of tourism area is obtained uite high economic
benefit. Green open space
5
(325.28 ha) oftotal area
is
importantto
be
maintained andpreserved
in
order that tourism area can be sustainable.Tourism Resources Aspect Analysis
Tourism Object and Attraction
Potentials Evaluation AnalysisThe
analysis whichis
usedis
tourismobject
and
attraction potentials
evaluationanalysis through scoring and
then
overlayedwith landscape resources potentials. Evaluation
is
classifieduse five
criterias according to lnskeep('l
1). This evaluationis
based on atourism object and attraction value, accessibility
that are available to reach tourism objecy and
attraction, location
of
tourism object
andattraction from main road, tourism facilities, and environment impact..
The result of evaluation shows that there
are
high
potentialsof
tourism object and attractions and'l
medium potentials of tourism object and attraction.Social Aspect Analysis
a.
Tourists Characteristic AnalysisBased
on
visit
data whichis
obtainedfrom GTJ manager, the number of tourists for
the
five last years (2005 until 200)
with theaverage number of tourists is
222.13
people.Domestic
tourists
who
visit
it
come
fromPROSIDING SIMPOSIUM ILMIAH NASIONAL IALI 2O1O
Jakarta, Bogor, Depok, Bekasi, and Bandung, meanwhile
the
mostof
foreign tourists comefrom Japan, Korea, Netherlands, America, and Australia.
b.
Tourists Perception AnalysisA great number of tourists
is
employee,(51 respondents). That tourist group is 20 until
30
years
old
(
respondents).They
visittourism area
to
refresh.The
mostfre
uentlyvisited tourism object is Jatiluhur Water World
selected by 32 respondents with visit time 1-hours.
c.
Tourists Preferences AnalysisThere
are
tourists
preferences to landscape planning, almost of respondents want outdoor tourism activities(
8 respondents) that issuppofted by supporting tourism facilities. Besides of that. the most of respondents agree with sport facilities development
(83
respondenS). They also agree with pedestrian path(
respondents) and bicycle path development(5
respondents).d.
Technical Aspect AnalysisBased
on
Regulationof
PurwakartaDistrict Number
8
year
1
1
and
President Decision Number 32 year1
O, the using of thearea around the reservoir is as
a
recreation ortourism area with the river border within 50-'100 meters to the mainland, so the type of tourism
developed
is
classified
as
semi-intensivetourism. ln addition, the using of the river border
area is as a tourism area with the border line is
100 meters
to
mainland,the
restof
area is directed to conservation function.SYNTHESIS
ln
synthesis phaseis
determined blockplan based on the analysis. This Block plan is
used as basic in landscape planning. Based on
the result
of
analysisis
obtained three zonesare yaitu highly potential, moderately potential, and marginally potentialzone (Tabel 't).
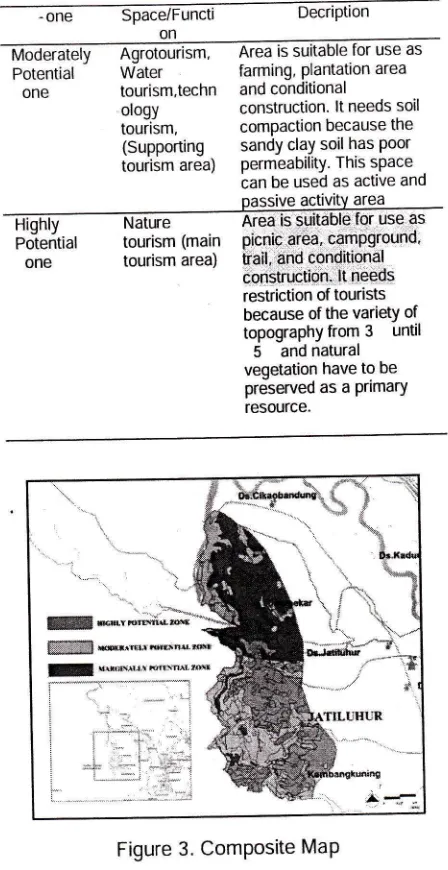
Tabel '1. oning in Synthesis Phase
one SpacdFuncti
DecriptionMarginally
Potential
one
Welcome area
Service and tourism
supporting
area
Area is used as conservation area and
conditional construction. lt
needs soil compaction because the clay soil has
poor permeability and landscape engineering with retaining wall (slope
over 15 ). This space is directed to service area
where is used as active
and passive activity area
1
on
Potential
- Water
farming, plantation areaone
tourism,techn and conditionalologY
construction' lt needs soiltouiGm,
comPaction because the (Supporting sandy clay soil has poortourism
area)
permeability This spaceban be used as active and oassive activitY area
Fo:tuitiur
tourism (main picnic qrea, campgrouno'one
tourismarea)
fail, and conditional construction. lt needs restriction of tourists because of the variety of topograPhyfrom3
until5
and natural vegetation have to be preserved as a Primary resource. [image:16.603.69.293.47.482.2]-one Space/Functi
DecriPtionFigure 3. ComPosite MaP CONCEPT
Basic Goncept
Planning concePt develoPed
in
GTJ Tourism Area is nature tourism area integratedwith
its
supportingtourism.
The
concept applicationof
landscape suchas
a
model of development plan that is adjusted to characterof
landscape resources, tourism object andattraction potentials
associated
with
thechallenge level of tourism.
Spatial ConcePt
'
The area is divided intosi
spaces, suchas
welcome, service and tourism supporting, main tourism, supporting tourism, buffer, and conservation area.Vegetation ConcePts
This vegetation concept
is
divided into four zones, such as main, development, buffer,dan conservation
zone.
Vegetation concePtsplanned
in
main zone are timber
plants,48
suB-roPlK Iagricultural
plants,
and
food
crops
zone. Development zone is directed to the plant whichhas
good
architectural
form.
Buffer andconservation zone are directed to the plant with ecological function.
Circulation ConcePt
Circulation concept
of
tourismarea
isdivided
into three
paths,
such
as
primary,secondary, and tertiary circulation
path'
Theprimary
circulationpath
is a
path
which connects to main area, whereas the secondary circulationPath
connectsto
the
groups of tourism object and attraction in tourism area'The function
of
tertiary circulation pathis
toconnect
to a
tourism facility
with
anothertourism facilities
in
each
groupsof
tourismobject and attraction.
Activity and FacilitY GoncePt
Tsurism activity concepts planned are
such as high (nature tourism), medium (water tourism and technology tourism), and low level
of
tourismchallenge
(agro tourism). Facilityconcept is divided into two kinds of facility, such
as main and complement facility' The main is
facility
for
using
of
tourism
activity, whilecomplement is public facility, sign system, and
site furniture.
LANDSCAPE PLANNING
Landscape planning is based on nature
based tourism concepts:
(1)
educative value,(21
recreationvalue,
(3)
benefit
to
localcommunities, manager,
tourists,
and
localgovernment,
(
)
increasing the participation oflocal
communities(5)
orientationon
theconservation interest of tourism area'
The
aPProachin
this
research
isresources and tourist activity approach,
so
itproduces space necessity and touring plan that connects to tourism areas with certain use and
different types of tourist groups.
Space Plan
Based on landscape planning concept
of
GTJ
Tourism
and
the
data has
beenanalyzed spatially, observed
from
potentialsand constrains.
The
area
is
divided into sispaces, such as:
Welcome area, is main entrance for tourists to
enter GTJ Tourism Area'
Service and tourism supporting area, planned in
order
to get
information aboutGTJ
and theservices provided by GTJ manager at a glance'
Main tourism area,
is
tourism area developedas semi
intensive
tourism area. Thereis
the main tourism object, such as forest with various attractions.Supporting
tourism
area,
consistsof
semiintensive
and
intensive tourism
sub
arealocated
in
border reservoir area, main dam,wetland area, and plantation area.
Buffer area, is area with its function
to
support tourism aread in GTJ Tourism Area from the outside interference.
Conservation area,
is
area with its function to protect GTJ Tourism Area from damage and conserve soil and water.Vegetation Plan
Green space division
is
divided into for zones, such as main development, buffer, andconservation zone. Main zone
is
divided intotimber plants zone, agricultural plants, and food
crops zone. Timber plants
are
directed tosuppoft
nature tourism activity.Food
crops(paddy)
and
agriculture plants(kind
of
fruitplants)
are
directed
to
strengthen physic character of agriculture area.Development zone
is
directedto
artisticand architectural function, such as plants which
have good canopy form, flowers, leaves, trunk,
fruit, and
seed. Buffer zoneis
directed intoecological function that ameliorate the climate
and
protecttourism area
from the
outsideinterference. Conservation zone
is
directed todevelop
area
whichhas
a
slopeover
25 border reservoir area for ecological function.Circulation Plan
Circulation
plan
of
GTJ
Tourism
isdivided
into three
paths
such
as
primary,secondary,
and
tertiary circulation path. Theprimary circulation path
is
plannedfor
Two-wheeled vehicle users, Four-wheeled vehicle
users,
and
pedestrianwith
its
function
is connectto
main areas, whilethe
secondarycirculation
path
connectsto
the
groups of tourism object and attractionin
tourism area.The tertiary circulation
path
is
accessed bypedestrian that connects
to a
tourism facility with another tourism facilities in each groups of tourism object and attraction.Activity and Facility Plan
Activity plan
of
tourism areais
dividedinto active and passive activity. Tourism activity
plan
planned suchas
high (nature tourism),medium (water tourism
and
technologyPROSIDING SIMPOSIUM ILMIAH NASIONAL IALI 20.IO
tourism),
and low
levelof
tourism challenge (agrotourism).Main facilities planned
in
GTJ TourismArea such
as
(1)
acomodation,(2)
publicservice facilities and office, (3) restaurant,
(
) water tourism, (5) nature tourism,( )
tourismtransportation, and
(
)
souvenir shop. Besidesof
that, there are tourism supporting facilitiessuch as interpretation board, bench and picnic
table, workship place, restroom, public phone,
post office, children playground, sport arena, swimming pool, and another facilities.
The
lmplementation
Plan
of
Tourism ProgrammedDevelopment
and
increaseof
e
istingtourism object and attraction
is
aimto
attracttourists
interestto
e
plore
kind
of
tourismactivities
in
GTJ
Tourism
Area.
Theimplementation
of
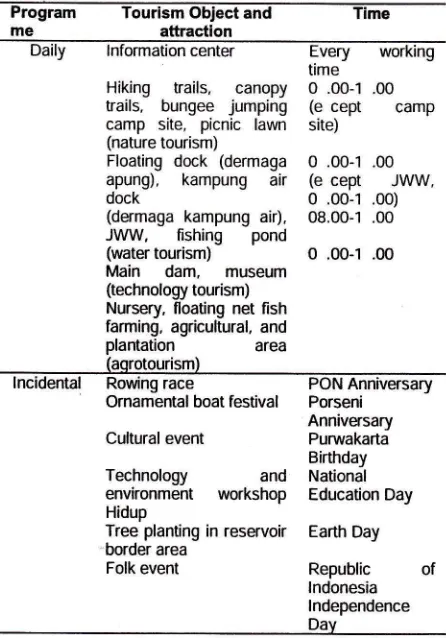
tourism object and attraction [image:17.598.310.533.351.670.2]is planned on weekdays and certain days.
Tabel 2. The lmplementation Plan of Tourism Object and
Attraction Program me
Tourism ObJect and attraction
Cultural event Technology environment Hidup
Daily
lnformation centerEvery
workingtime
Hiking
trails,
canopy 0 .00-'l .00 trails, bungee jumping (ecept
campcamp site, picnic
lawn
site) (nature tourism)Floating dock (dermaga 0 .00-1 .00 apung), kampung
air
(ecept
JWW,dock
0 .00-1 .00)(dermaga kampung
air),
08.00-1 .00JI/VW,
fishing
pond(water
tourism)
O .00-1 .00Main dam,
museum(technology tourism)
Nursery, floating net fish farming, agricultural, and
plantation
area(aqrotourism)
lncidental Rowing
race
PON AnniversaryOrnamental boat
festival
PorseniAnniversary
Purwakarta Birthday
and
National workshop Education DayTree planting in reservoir Earth Day border area
Folk event
Republic
of lndonesia lndependenceDav Touring Plan
Touring
plan
is
basedon
accessibility and typeof
attractionsin
accordanceto
tour package selection, such as touring circuit and longer stay. Touring plan is planned into touringplan map.
CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATION
Conclusion
Based
on
biophysical,tourism object
andattraction
potentials,
social,
and
technicalaspect, GTJ Tourism Area has great potentials
for tourism development which is the most of
tourism object and attraction have high potential
value.
The
highly
potentialzone has
width1 .0
ha(30.8
),
the moderately potentialzone
20
.8
ha(3
.2
),
and the marginallypotential zone
18
.
ha
(32.2
).
Economicbenefit from green open space of
e
isting areawith total
annualsaving
Rp.
825.030.000,-,while total annual saving of planning area Rp.
3.1
'1.1
.000,-. Tourism concept
that
is developedis
nature tourismwith
landscaperesources
and
also
tourism object
andattraction potentials
to
maintain landscapereources and tourism sustainability.
Recommendation
The following are suggestions that can be applied:
1. This
landscape planninguses
landscaperesource approach,
the
researchcan
bedone
by
using social
approachto
localcommunities in order that communities can
participate in achieving sustainable tourism.
2.
The main strategy of landscape planning isma imizing
the
allocationof
green openspace
aroundtourist
attraction,such
as planting of green ways, corridors, and parks.This strategy can be implemented by local
government
to
increase green open space that serves as a recreation or tourism.REFERENCE
Gold SM. '1 80. Recreation Planning and Design New York: Mc Graw-Hill Book Company.
Hardjowigeno S, Widiatmaka.
1
8. Evaluasi Kesesuaian lahan dan Perencanaan Tata Guna Lahan. Yogyakarta: Gadjah Mada University Press. HoldenA.
2000. Environment and Tourism. London:Routledge.
lnskeep E.
1
1. Tourism Planning: An lntegrated andSustainable Development Approach VNR Tourism
and Recreation Series. New York: Van Nostrad Reinhold.
Rosmalia
D.
2008. Rencana Pengembangan Koridor Sungai Ciliwungdi
Jakarta sebagai KawasanEkowisata. tesis. Bogor: Program Pascasa{ana, lnstitut Pertanian Bogor.
,ts
i#:r#':ffi
-n.i , - :: :.t'Pi:Jr :.}{,*. , s. .'i ,'.:'*.rr:; i r:l- ./*
t-l:GF"",il)
,r$^R1'1d15ff (S tntiDs{4ft 4&{:lflte11}as
rl{LalY#.ffral{.Iu*g
fjflTni?PmT$&!;* B{l$o*
510
ffi
:itl,P nn"rtAs&8
Ru*\tiA*cll mIjt
ulHai &*scrsn:B*slav ffiilt{i!ffi tlf IS.461 A@{Sf
^J"[m{r&:*Friw,l lgl{ r}rtr 41ffi ,
'r*$l{nm^ &M, li,t!!lI:
nn4ffi&flfi
L[i-N,R.TR
b. t sffi sl&':t^sina i4. As
nFlf,sl"EllnA11:
it-FtltovIll BY
ffifa?s s*$..i
',s