I. Introduction: Background and Rationale
This research investigates the effectiveness of Contextual Teaching and Learning (CTL) in teaching the simple present tense to eighth-grade students. The study is motivated by the observation that traditional teaching methods often fail to connect grammatical concepts to students' real-world experiences, leading to difficulties in comprehension and application. The researcher argues that CTL, with its emphasis on real-world application and meaningful connections, can overcome this limitation. This study specifically focuses on the simple present tense due to its frequent use in everyday communication and its importance in constructing various text types, such as procedural and descriptive texts, covered in the eighth-grade curriculum.
II. Theoretical Framework: CTL and the Simple Present Tense
This section lays the theoretical foundation for the study by exploring the concepts of the simple present tense and CTL. The simple present tense is defined, its grammatical forms (affirmative, negative, interrogative) are detailed, and its various functions in expressing habitual actions, general truths, and future events are explained. The theory of CTL is examined, outlining its core principles (meaningful connections, significant work, self-regulated learning, collaboration, critical and creative thinking, nurturing the individual, high standards, and authentic assessment). The eight components of CTL, along with the REACT strategy (Relating, Experiencing, Applying, Cooperating, Transferring), are discussed in relation to their pedagogical implications for language learning. The compatibility between CTL's emphasis on real-world relevance and the simple present tense's frequent use in daily life is highlighted.
III. Profile of MTs
This section provides contextual information about the research setting, MTs. Al-Husna. It offers a brief history of the school, its vision and mission statements, organizational structure, and available facilities. This information is crucial for understanding the context within which the research was conducted and for assessing the generalizability of the findings. The description of the school's resources and environment helps to evaluate the feasibility and appropriateness of implementing CTL within that specific setting.
IV. Research Methodology and Findings
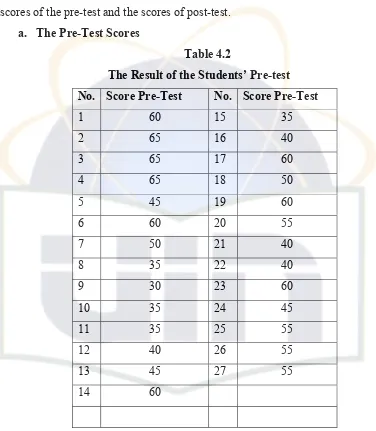
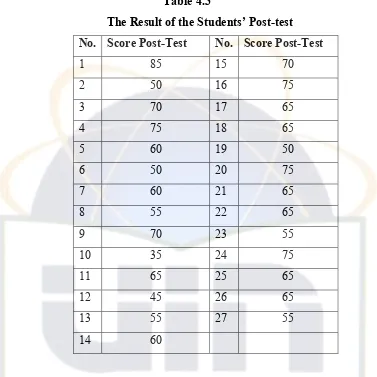
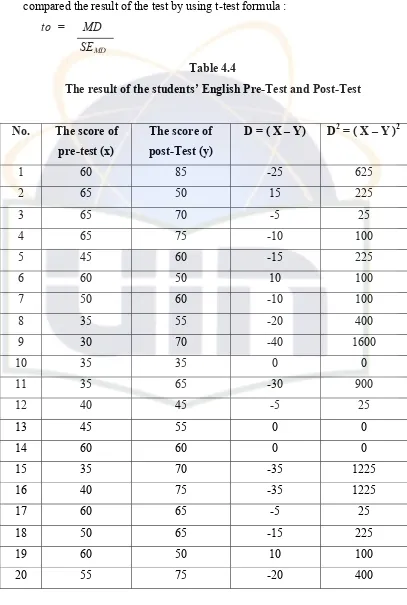
This section details the research design and methodology employed. The study utilizes a pre-experimental design, involving a pre-test and post-test to measure students' understanding of the simple present tense before and after instruction using CTL techniques. The research method, including participant selection, teaching procedures, data collection methods (tests and interviews), and data analysis techniques are described. The research findings are presented, including descriptive statistics (e.g., mean scores, standard deviations) and an interpretation of the data to determine the impact of CTL on students’ performance. Tables are mentioned that presented the results (Table 4.3: Post-Test Results and Table 4.4: Data Collection Techniques).
V. Conclusion and Suggestions
This final section summarizes the key findings of the study, addressing the research question regarding the effectiveness of CTL in improving students' understanding of the simple present tense. Based on the analysis, the researcher draws conclusions about the efficacy of the CTL approach in this specific context. The section also provides suggestions for future research and practical recommendations for teachers on how to effectively implement CTL strategies in teaching grammar, particularly the simple present tense. The limitations of the study are acknowledged, highlighting areas for future investigation.