DESIGNING ENGLISH SPEAKING INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIALS FOR THE FIRST GRADE STUDENTS
OF SMK PARAMITHA 2CENTRALJAKARTA
A Thesis
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Julianus Risang Adi Nugroho Student Number: 051214126
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
i
DESIGNING ENGLISH SPEAKING INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIALS FOR THE FIRST GRADE STUDENTS
OF SMK PARAMITHA 2CENTRALJAKARTA
A Thesis
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Julianus Risang Adi Nugroho Student Number: 051214126
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
iii
iv
I dedicate this thesis to Jesus Christ,
v
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY
I honestly declare that this thesis, which I have written, does not contain the work or parts of the works of other people, except those cited in the quotations and references, as a scientific paper should.
Yogyakarta, 21 September 2011 The Writer
vi
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN
PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIAH UNTUK KEPENTINGAN AKADEMIS
Saya yang bertanda tangan di bawah ini, saya mahasiswa Universitas Sanata Dharma:
Nama : Julianus Risang Adi Nugroho
NIM : 051214126
Demi pengembangan ilmu pengetahuan, saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma karya ilmiah saya yang berjudul:
DESIGNING ENGLISH SPEAKING INSTRUCTIONAL
MATERIALS FOR THE FIRST GRADE STUDENTS OF
SMK
PARAMITHA 2
CENTRAL JAKARTA
Dengan demikian, saya memberikan kepada Perpusatakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma hak untuk menyimpan, mengalihkan dalam bentuk media lain, mengelolanya dalam bentuk data, mendistribusikan secara terbatas, dan mempublikasikannya di internet atau media lain untuk kepentingan akademis tanpa perlu meminta izin dari sayamaupun memberikan royalti kepada saya selama tetap mencantumkan nama saya sebagai penulis.
Demikian pernyataan ini saya buat dengan sebenarnya. Dibuat di Yogyakarta pada tanggal 20 September 2011 Yang menyatakan,
vii
ABSTRACT
Nugroho, J. R. A. 2011. Designing Speaking Instructional Materials for the First Grade Students of SMK Paramitha 2 Central Jakarta. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
Nowadays, the application of Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan Pendidikan
(KTSP) in SMK Paramitha 2 makes the school have responsibility to improve the learning process based on the school situation. Several majors in SMK education program and different needs of English as a compulsory subject become the reason for different demands of English subject materials. In other words, the demands of English subject in every SMK have to be adapted to the certain program which is taken by the students, one of the examples is SMKParamitha 2
that runs education programs in tourism sector.
This study aims to promote the model materials in teaching English speaking for the first grade students of SMKParamitha 2. To achieve that goal, educational research and development was used as a method in this study. Five steps were adapted from educational research and development are: (1) research and information collecting, (2) planning, (3) develop preliminary form of product, (4) evaluation, and (5) revision of designed materials.
In designing the model of speaking instructional materials for the first grade students of SMKParamitha 2, six steps were adapted from Kemp’s model in this study. There are (1) learner characteristic, (2) considering goals, and listing the topics, stating general purposes, (3) learning objectives, (4) select teaching or learning activities and instructional resource, (5) evaluation, and (6) revision.
The purposes of evaluation in this study were to obtain necessary data and revise the designed materials. Instruments adapted in this evaluation are questionnaires. The questionnaires were distributed to two English teachers from
SMK Paramitha 2, two lecturers from English Education Program in Sanata Dharma University, and one English conversation instructor for hotel staff.
The designed materials consist of three main parts, those are (1) Pre-activity, (2) Whilst, and (3) Post-activity.
viii
ABSTRAK
Nugroho, J. R. A. 2011. Designing Speaking Instructional Materials for the First Grade Studentsof SMK Paramitha 2 Central Jakarta. Yogyakarta: Program Studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Dewasa ini, penerapan Kurikulum Satuan Pendidikan (KTSP) di SMK Paramitha 2 membuat sekolah mempunyai tanggung jawab untuk mengembangkan pembelajaran sesuai dengan situasi sekolah. Berbagai macam jurusan di dalam SMK dan kebutuhan akan Bahasa Inggris yang berbeda-bedalah maka diperlukanlah materi Bahasa Inggris yang berbeda-beda pula. Dapat dikatakan bahwa kebutuhan Bahasa Inggris di setiap SMK harus sesuai dengan bidang yang dijalaninya, salah satunya SMK Paramitha 2 yang bergerak dalam bidang pariwisata.
Studi ini bertujuan untuk mengusulkan contoh materi pengajaran speaking
untuk siswa SMK Paramitha 2 tingkat pertama. Untuk mencapai tujuan tersebut, penelitian dan pengembangan kependidikan, digunakan sebagai metode dalam studi ini. Lima langkah yang diadaptasi dari penelitian dan pengembangan kependidikan adalah sebagai berikut: (1) penelitian dan pengumpulan informasi, (2) perencanaan, (3) penyusunan contoh materi pengajaran, (4) pengujian, dan (5) perbaikan materi.
Dalam penyusunan contoh materi pengajaran speaking untuk SMK Paramitha 2, enam langkah dari model pengajaran Kemp diadaptasi dalam studi ini. Enam langkah tersebut adalah (1) karakter Siswa, (2) perumusan tujuan dan pemilihan topik, (3) penyusunan tujuan pembelajaran, (4) penyusunan materi dan aktivitas dalam mengajar, (5) evaluasi, dan (6) perbaikan materi yang telah tersusun.
Dalam studi ini, tujuan dari evaluasi adalah untuk memperoleh data untuk memperbaiki materi yang telah disusun. Instrumen yang digunakan dalam evaluasi adalah kuesioner. Kuesioner tersebut dibagikan kepada dua guru Bahasa Inggris SMK Paramitha 2, dua Dosen Program Studi Bahasa Inggris Universitas Sanata Dharma, dan satu pengajar percakapan untuk hotel staff.
Materi yang disusun terdiri dari tiga bagian utama, yaitu (1) Pre-activity, (2) Whilst, dan (3) Post-activity.
ix
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
I realize that I would not have been able to complete this thesis without the help from many people. First, I would like to send my greatest gratitude to Jesus Christ who has given me this opportunity in my life to complete this thesis.
I would like to express my gratitude to all people who have given their time, energy, ideas, and support during the completion of this thesis.
My appreciation goes to my sponsor, Ag. Hardi Prasetyo S.Pd., M.A.. I really appreciate his guidance, support, patience, and precious time during the completion of this thesis. I would also like to thank to all members of Harjo Kamto family for giving me an endless support in this completion of this thesis.
I thank my best friends from ex-De Britto: Papin, Somad, Moyo, and Yudo, ex-Mertoyudan: Kang Gendruk, for their care and support as well as the great adventures we have done together. My thanks are also directed to all my friends, especially puri, mas yoyo, retno bere, mas andi, lusi, nana, stepi, epri, and others who can not be mentioned one by one for their support and help. I would also like to give my sincere grateful to the teachers of SMK Paramitha 2, especially to Lambertus Doni Ledjap, S.S and Ormas Rajaguguk, S.Pd for the guidance and cooperation, and also the PBI lecturers, especially to G. Punto Aji, S.Pd., M.Hum. and Caecilia Tutyandari, S.Pd., M.Pd. who have helped me evaluate the materials I have designed and for their suggestions and comments.
With Love,
x
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE PAGE ... i
APPROVAL PAGES ... ii
PAGE OF DEDICATION... iv
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY ... v
PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI ... vi
ABSTRACT ... vii
ABSTRAK ... viii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ... ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... x
LIST OF TABLES ... xiv
LIST OF FIGURES ... xv
LIST OF APPENDICES ... xvi
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION ... 1
1.1Background of the Study ... 1
1.2Problem Formulation ... 4
1.3Problem Limitation ... 4
1.4Objectives of the Study ... 4
1.5Benefits of the Study ... 5
xi
CHAPTER II: REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE ... 7
2.1Theoretical Description ... 7
2.1.1Speaking ... 8
2.1.1.1The Nature of Speaking ... 8
2.1.2Teaching Speaking ... 9
2.1.3The Characteristics of Good Speaking Activities ... 11
2.1.4Communicative Language Teaching (CLT) ... 12
2.1.5Vocational School ... 14
2.1.5.1Comparison Between General and Vocational Education ... 14
2.1.6Instructional Design Model ... 16
2.1.6.1Kemp’s Instructional Design Model ... 16
2.2Theoretical Framework ... 18
CHAPTER III: METHODOLOGY ... 21
3.1Method ... 21
3.1.1Research and Information Collecting... 21
3.1.2Planning ... 21
3.1.3Develop Preliminary Form of Product ... 24
3.1.4Preliminary Field Testing ... 24
3.1.5Main Product Revision ... 25
3.2The Research Participants ... 25
3.3The Research Instruments ... 25
xii
3.5Data Analysis Technique ... 26
3.6Research Procedure ... 28
Chapter IV: RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSIONS ... 30
4.1The Steps of Development of Designed Materials ... 30
4.1.1Learner Characteristic ... 30
4.1.1.1The Result of Distributing the Questionnaires ... 31
4.1.1.2The Result of Interviewing the Teacher ... 34
4.1.2Considering Goals, and Listing the Topics, Stating the General Purposes ... 36
4.1.3Learning Objectives ... 37
4.1.4Selecting Teaching or Learning Activities and Instructional Resource ... 38
4.1.5Evaluation ... 43
4.1.6Revision ... 43
4.2The Findings and Discussions on the Designed Materials Evaluation 44
4.2.1Preliminary Field Testing ... 44
4.2.1.1The Result of Respondent’s Opinions on the Designed Materials ... 45
4.2.1.2The Respondents’ Comments and Suggestions on the Designed Materials ... 48
4.2.2Main Product Revision ... 49
xiii
CHAPTER V: CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS ... 54
5.1Conclusions ... 54
5.2Suggestions ... 55
xiv
LIST OF TABLES
Table 1: The Competency Standard, Basic Competence, and Indicators
of the Proposed Model of Speaking Instructional Materials ... 22
Table 2: Points of Agreements ... 27
Table 3: The Result of Need Analysis Questionnaire ... 31
Table 4: List of Topics from What They Like Most ... 32
Table 5: List of Activities from What They Like Most ... 32
Table 6: The Description of Competence Standard, Basic Competence, and Topic of Each Unit ... 36
Table 7: The List of Indicators of the Design ... 37
Table 8: The Description of Design Materials ... 40
Table 9: The Description of the Respondents of the Evaluation Material Design ... 44
Table 10: Points of Agreements of Preliminary Field Testing Questionnaire ... 45
Table 11: The Result of Respondents’ Opinion ... 45
xv
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 1: Kemp’s Model: the Relationship of Each Step in the Plan
to Other Steps ... 17 Figure 2: Theoretical Framework in This Study ... 20 Figure 3: The Stages of R&D Cycle Which Match with the Instructional
xvi
LIST OF APPENDICES
APPENDICES ... 59
Appendix 1: Letters of Permission ... 60
Appendix 2: Questionnaire for Need Analysis ... 63
Appendix 3: List of Interview Questions ... 68
Appendix 4: Questionnaire for Expert Validation ... 70
Appendix 5: Syllabus and Lesson Plan of the Designed Materials ... 78
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This study deals with developing speaking instructional materials for first grade students of SMK Paramitha 2. This chapter consists of six points. There are background of the study, problem formulation, problem limitation, objectives of the study, benefits of the study, and definition of terms.
1.1Background of the Study
Indonesia is trying to make a better image of vocational school. This is done due to the stereotype that vocational schools are not as favorites as the senior high school ones. In Indonesia, the vocational schools are referred to as Sekolah Menegah Kejuruan (SMK), while the senior high schools are referred as Sekolah Menengah Atas (SMA). There are so many students in this country who consider
2
careers that require practical expertise. Practical expertise here refers to the expertise used in the certain working environment such as engineering, accounting, and tourism. The examples of the working environment mentioned above are commonly found in many countries, including Indonesia. From all the three, tourism is one of the Indonesian fundamental sectors. As the consequences, the tourists will need people that could become the bridge between them and the world before their eyes. SMK graduates are not only those who are more ready to fill the position or apply to the job vacancies offered by tourism and other working environments than the SMA graduates, but also can be the ones who gain more advantages in the real working environment because they focus more on the learning-by-doing than common curriculum offered in SMA education.
3
SMK Paramitha 2 is one of examples of tourism vocational schools in Jakarta, which has good potential for improving the tourism sector in Indonesia. The school applies Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan Pendidikan (KTSP) as the curriculum. The school has two programs, the regular one and the international one. The regular program deals with the hotel sector, while the international deals with the travel sector. Both programs require English communication skills, because the graduates will directly interact with the foreigners.
4
happens because they have no specific speaking text book for tourism students. Therefore, the writer chooses SMK Paramitha 2 as the subject of the research.
1.2Problem Formulation
After doing observation in SMK Paramitha 2 the writer finds some problems and concludes the main problems for the thesis are:
1. How is the speaking instructional material for SMK Paramitha 2 students designed?
2. What does the instructional material for SMK Paramitha 2 students look like?
1.3Problem Limitation
This thesis only focused on how to design speaking instructional material and what the instructional material for SMK Paramitha 2 looks like.
The participants of this research are the first grade students of SMK Paramitha 2, because the first grade students are in the basic level. They have not decided whether they want to become a guide, front office staff, or others.
1.4Objectives of the Study
The objectives of this research are:
1. To design the speaking material for the first grade students in SMK Paramitha 2.
2. To provide the appropriate speaking materials for the first grade students in
5
1.5Benefits of the Study
This thesis has many advantages, especially in education sector. First, the advantages for SMK Paramitha 2 are this design can be used as the material in the learning process and also can be used to improve the students’ English skills and to increase students’ interest in learning process.
Second, the advantages for PBI are this design can be used as an example for the PBI students who want to make new research about design and it can be used as a new way to teach in vocational school.
Third, the advantages for the other research are this design can be used as an example to make new thesis about design and as reference.
1.6Definition of Terms
There are several terms the writer uses in this study. The definitions of terms are as follows:
1. Instructional Design
Instructional design in this study is the process of systematic planning that establishes a way to examine instructional problems and needs, sets a procedure for solving them, and then evaluate the results (Kemp, 1977).
2. Speaking
Speaking is an active and productive interactions that make us use aural mediums, such as; mouth, lips, tongue, and other activities (Widdowson, 1979). 3. Instructional Materials
6
teacher and the students as a useful means of discussion in teaching and learning activity (Dick and Reiser, 1989).
4. Vocational school
7
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
There are two important points that will be discussed in this chapter. There are theoretical description and theoretical framework.
The theoretical description discusses basic theories of speaking, communicative language teaching, vocational school in general and instructional design.
The theoretical framework discusses the relation among the concepts stated previously as the basis of designing speaking instructional materials for the first grade students of SMKParamitha 2.
2.1Theoretical Description
8
2.1.1Speaking
The researcher attempts to design a set of speaking materials for the first grade students of SMKParamitha 2. Therefore, this section will discuss the basic theory of speaking skill.
2.1.1.1The Nature of Speaking
According to Louma (2004), there is a section who discusses three significant areas in spoken discourse for assessing speaking: purpose of talk, the speaking situation and speaker roles.
Louma (2004) stated the variation within spoken language use. The first is purpose of talk, which is represented by talking to chat and talking to inform that is quoted from Brown. Louma (2004, p. 22) stated that Brown, Anderson, Shillcock, and Yule (1984) define chatting as the exchange of amicable conversational turn with another speaker. The primary purpose is to make and maintain social contact, to oil the social wheels, and thus chatting forms a large part of anyone’s social life.
9 (channel or mode and form of speech), Norms (norms of interpretation and norms of interaction), and Genre (categories).
The third is speaker roles. It is represented in roles, role relationship and politeness that are quoted from Grice (1975). The speakers are influenced by speaker roles and role relationship in choosing of words in interaction. It also influenced the quality of politeness in the talk. Louma (2004) stated Grice (1975) gives four conversational maxims: quantity (give sufficient information but not too much), quality (say only what you know to be true), relation (be relevant) and manner (be brief, clear and orderly).
2.1.2Teaching Speaking
Based on Rivers (1968), the teaching of speaking skill is more demanding on the teacher than the teaching of any other language skills; the teacher will need to give the students many opportunities to practice the speaking skill. Consequently, it is essential for the teacher to give the learners many opportunities to practice speaking skill. When the teacher provides more complicated matter of the foreign speech to be answered, the learners ability will be greater developed also. Rivers (1968) stated teacher will need to use his imagination in devising situations which provoke the students to the use of the language in the expression of his own meaning.
There are some cases that makes speaking difficult based on Brown et al
(2000): 1. Clustering
10 2. Redundancy
The speaker has an opportunity to make meaning clearer through the redundancy of language.
3. Reduced forms
Contractions, elisions, reduced vowels, etc., all form special problems in teaching spoken English.
4. Performance variables
One of the advantages of spoken language is that the process of thinking as you speak allows you to manifest a certain number of performance, hesitations, pauses, backtracking, and corrections.
5. Colloquial language
Make sure the students are acquainted with the words, idiom, and phrases of colloquial language.
6. Rate of delivery
The tasks in teaching spoken English is to help learners achieve an acceptable speed along with other attributes of fluency.
7. Stress, rhythm, and intonation
This is the most important characteristic of English pronunciation. The stress-timed rhythm of spoken English and its intonation patterns convey important messages.
8. Interaction
11 Speaking comes naturally to humans, but it is not as simple as it seems. Sometimes people feel afraid or nervous to speak in front of people or a large group.
According to Davies (2000), there are some implications for teaching: a. Try to create relaxed atmosphere in your classes so that most learners are not
frightened of speaking in front of the rest of the class. And do as many speaking activities as possible in pairs and groups, so that the learners can speak English without the rest of the class listening.
b. Expose the learners as much as possible to naturally pronounce speech, and also integrate some pronunciation work into your lessons. They will not learn to pronounce intelligibly, or to develop speaking skill in general, if they do not hear enough natural speech.
c. Accustom the learners to combine listening and speaking in real time, in natural interaction. Perhaps the most important opportunity for this is in the general use of English in the classroom.
2.1.3The Characteristics of Good Speaking Activities
12 foster better speaking, rather than having students speak only to focus on specific language construction.
According Davies (2000), based role play or simulations, script-based conversations, and form-script-based interviews or surveys are examples of activities designed to encourage learners to communicate as naturally as possible. In natural communication, attention is not usually focused on the language used, but the message it conveys.
2.1.4Communicative Language Teaching (CLT)
One of approaches in language teaching which is going to use to develop the speaking instructional materials for first grade students of SMKParamitha 2 is Communicative Language Teaching (CLT). According to Richards (2001, p. 36) “CLT is a broad approach to teaching that resulted from communication as the organizing principle for teaching rather than a focus on grammatical system of the language.”
According to Richard and Rodgers (2001) CLT is the best considered an approach than method. CLT refers to a varied set of principles which reflect a communicative view of language and language learning and which can be used to support a wide variety of classroom procedures. These principles include:
1. Through using the language, the learners learn to communicate.
2. The goal of classroom activities is at authentic and meaningful communication.
3. Fluency is an important aspect of communication.
13 5. Learning is a process of creative construction and involves trial and error.
Brown (2000) offers six interconnected characteristic as a description of CLT, namely:
1. Classroom goals are focused on the entire component of communication competence and not restricted to grammatical or linguistic competence.
2. Language techniques are designed to engage learners in the pragmatic, authentic and functional use of the language for meaningful purposes. Organizational language terms are not the central focus but rather aspects of language that enable the learner to accomplish those purposes.
3. Fluency and accuracy are seen complementary principles underlying communicative techniques. At times fluency may have to take on more importance than accuracy in order to keep learners meaningfully engaged in linguistic use.
4. Students in communicative classroom, students ultimately have to use the language productively and receptively, in unrehearsed context outside the classroom.
5. Students are given opportunities to focus on their own learning process through an understanding of their own styles of learning and through the development of appropriate strategies for autonomous learning.
6. The role of the teacher is a facilitator and guide.
14 There are three kinds of materials considered in CLT:
a. Text-based materials
Text-based materials are materials that based on the texts that help the teacher to initiate conversation. The examples of these materials are visual cues, pictures, and sentence fragments.
b. Task-based materials
In order to support CLT classes, a variety of games, role play, and task-based communication activities have been prepared. These are usually in the form of one-of-a-kind items: exercise handbooks, cues cards, pair communication practice, and learners-interaction practice.
c. Realia
Realia might be included as proponents of CLT. This might include language based realia such as sign, magazines, newspaper, or visual sources around which communicative activities can be built (maps, pictures, etc).
2.1.5Vocational School
According to Lauglo and Lilis (1988) vocationalization is intended to ease school leavers into jobs or self employment, under conditions of widespread youth unemployment. In line with Wenrich, (1974), vocational and technical educational is for people-youth and adult interested in preparing for and progressing in a career in some types of satisfying and productive work.
2.1.5.1Comparison between General and Vocational Education
15
Menengah Tingkat Atas) or SMA (Sekolah Menengah Atas) to SMU (Sekolah Menengah Umum) and according to Keputusan Menteri Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan Republik Indonesia No. 0490/U/1992, there is a change from SMKTA
(Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Tingkat Atas) to SMK (Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan).
Based on Keputusan Menteri Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan Republik Indonesia No. 0490/U/1992, Pasal 1, vocational school is a senior educational form which is held to continue and to enlarge the basic education to prepare the students for job requirements and to develop professionalism. Based on
Keputusan Menteri Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan Republik Indonesia no
035/0/1997, pasal 1, general school is a senior educational form which is held to continue and to enlarge the basic education and also to prepare the students for the next step of education and to develop professionalism.
Based on Keputusan Menteri Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan Republik Indonesia No. 0490/U/1992, Pasal 2, there are some purposes of SMK:
a. Preparing the student to continue to the next step of the education or to enlarge the basic education.
b. Increasing the student’s skill as the society in establishing interrelationship with socio-cultural environment and the nature.
c. Increasing the student’s skill to develop themselves in line with the development of science, technology, and art.
d. Preparing the student to enter the fieldwork and to develop the professionalism. The purposes of SMU are:
16 b. Increasing the student’s skill as the society in establishing interrelationship
with socio-cultural environment and the nature.
c. Increasing the student’s skill to develop themselves in line with the development of science, technology, and art.
2.1.6Instructional Design Model
In designing instructional materials, Hutchinson and Waters (1987), proposed a theory of need analysis, which consists of three important points. The first is necessities. It is what the learners need learn to achieve the target situation. The second is lacks. It is something that has not been mastered by the learners so they need to learn about it. The last is wants. It is the learners’ perception about their needs and lacks that have not been mastered yet.
In designing the materials, the researcher tries to discuss Kemp’s model. The researcher prefers those model because the flexibility and clearly procedures.
2.1.6.1Kemp’s Instructional Design Model
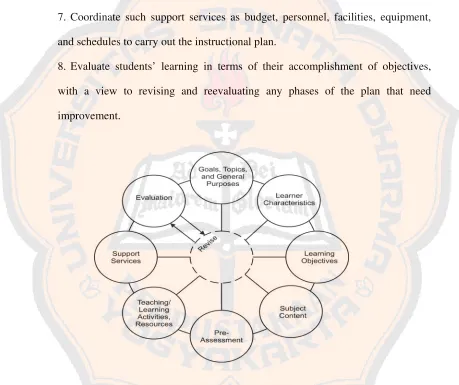
Kemp (1977) proposes a program development. It consists of eight interdependence elements which are related to others and affected each other. The Kemp’s programs were as follow:
1. Consider goals, and then list topics, stating the general purposes for teaching each topic.
2. Enumerate the important characteristics of the learners for whom the instruction is to be designed.
17 4. List the subject content that supports each objective.
5. Develop pre-assessments to determine the student’s background and present level of knowledge about the topic.
6. Select teaching/learning activities and instructional resource that will treat the subject content so students will accomplish the objectives.
7. Coordinate such support services as budget, personnel, facilities, equipment, and schedules to carry out the instructional plan.
8. Evaluate students’ learning in terms of their accomplishment of objectives, with a view to revising and reevaluating any phases of the plan that need improvement.
Figure 1: Kemp’s model: the Relationship of Each Step in the Plan to Other
Steps (Kemp, 1977).
18 cases, it can be simplified or reordered phases of this plan and improved (Kemp, 1977).
2.2. Theoretical Framework
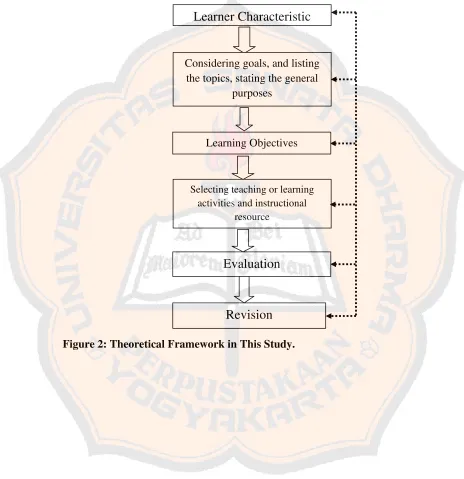
Kemp’s theory would be used to answer the two problems in this thesis. To provide guidance in designing speaking instructional material for first grade students of SMK Paramitha 2, there are steps adapted from Kemp’s instructional design.
The steps in Developing the Model of Instructional Speaking Materials: 1. Learner Characteristics
This step was conducted to recognize and respect the individual learner. It has been done by obtaining the information about the learners’ capabilities, need, and interests.
2. Considering Gals, and Listing the Topics, Stating the General Purposes
This step included defining skills, stating objectives based on the curriculum and the syllabus that is used in the school. The researcher prepared the materials and developed the product in this step.
3. Learning Objectives
The step was conducted to make the clear objectives. The steps include making and stating clear objectives.
4. Select Teaching or Learning Activities and Instructional Resource
19 5. Evaluation
The purpose of this step was to evaluate the materials that had been implemented. It requires experts’ verification. This step was conducted to gain feedback from the experts and used to categorize the materials, what want well from the material, what were the lacks of the materials, or what needs to be improved from the material. To evaluate it, the researcher distributed the questionnaires.
6. Revision
20 To obtain a clearer idea on the theoretical framework which is applied in this study, the researcher’s theoretical framework is presented below in figure 3.
Figure 2: Theoretical Framework in This Study.
Selecting teaching or learning activities and instructional
resource
Evaluation
Learner Characteristic
Revision
Learning Objectives Considering goals, and listing21
CHAPTER III
METHODOLOGY
This chapter explains the methodology which is used to solve the problems stated in the first chapter. It covers the method, the research participants, the research instruments, data gathering technique, data analysis technique, and research procedure.
3.1Method
Educational Research and Development is a process to develop and validate educational products (Borg & Gall, 1983). Educational Research and Development was adapted within this study as the guidelines to propose the model of speaking instructional materials. The goal of educational research is not only developing the product but also increasing educational products. Some steps adapted from educational Research and Development in order to propose the model of speaking instructional materials were follows:
3.1.1Research and Information Collecting
22
by interviewing the English teacher and distributing the questionnaire to the students.
3.1.2Planning
The most important aspect of planning an instructional product is the specific objectives to be achieved by the product (Borg & Gall, 1983). This step was to state objectives of the proposed model of speaking instructional material. The statement of objectives is presented in table 1.
Table 1: The Competency Standard, Basic Competence, and Indicators of the
Proposed Model of Speaking Instructional Materials
No. Competency Standard
Basic Competence
Indicators
1. Communicating in English in
- The students are able to indentify greeting expressions.
- The students are able to mention greetings expressions.
- The students are able to respond greeting expressions.
-The students are able to use greetings expressions in simple present tense sentences even in written or orally.
-The students are able to identify leave taking expressions.
- The students are able to mention leave taking expressions.
- The students are able to respond leave taking expressions.
23
- The students are able to identify the expressions of introducing. -The students are able to mention introducing expressions
- The students are able to respond introducing expressions.
-The students are able to introduce themselves or others in simple present tense sentences even in written or orally.
3. Communicating in English in
- The students are able to identify regret expressions.
- The students are able to mention regret expressions.
- The students are able to respond regret expressions.
-The students are able to use regret expressions in simple present tense sentences even in written or orally. - The students are able to identify apology expressions.
- The students are able to mention apology expression.
- The students are able to respond apology expressions.
-The students are able to use apology expressions in simple present tense sentences even in written or orally.
4. Communicating
- The students are able to identify thanking expressions.
- The students are able to mention thanking expressions.
- The students are able to respond thanking expressions.
24
present tense sentences even in written or orally.
3.1.3Develop Preliminary Form of Product
This step consists of several steps which were taken in designing the proposed model of speaking instructional materials. It included three steps which had been done to produce the intended materials. Those steps were as follows: 1. Materials Gathering
The materials covered spoken texts, written texts, tasks, and pictures. The material will be taken from the internet and textbooks.
2. Material Editing
The Materials had been gathered were edited to achieve the appropriate materials for first grade students of SMKParamitha 2.
3. Designing Speaking Instructional Material
After the material had been edited, the next step was to develop the instructional materials based on the outline made in the mapping step.
3.1.4Preliminary Field Testing
25
3.1.5Main Product Revision
The next step adapted from educational research and development was revising the instructional materials. The result of the evaluation was to find out whether the designed materials were appropriate or not.
3.2The Research Participants
The participants of this research are twenty five first grade students and one of English teacher of SMK Paramitha 2. The designed materials which are enclosed in the questionnaires were distributed to the students and the teacher will have an interview
.
3.3The Research Instruments
26
3.4Data Gathering Technique
To make the design material for the first grade students of SMKParamitha 2 were addressed in Central Jakarta, the data were gathered on May 2011 by distributing questionnaires to one class of first grade students of SMK Paramitha 2 and interviewing one of the English teachers of SMKParamitha 2. The students are asked to answered the questions on the questionnaires and the teacher is asked to answered the questions were given. The results of questionnaires and interview will be combined as a based to design the speaking materials. After the material designed, it will be evaluated by one of English conversation instructor for hotel staff, two teachers from SMK Paramitha 2, and the two of lecturers from Sanata Dharma University.
3.5 Data Analysis Technique
The data analysis from the library study and survey study would be analyzed in different way. The data obtained from the library study were analyzed in the form of description. The data were gained from several resource books.
The data from research survey would be analyzed in the form of percentage. The researcher analyzed the data as the data needed have been gathered. The participants’ opinions in the form of closed questions were shown statistically. The participants’ opinions in the form of open questions were shown in sentences.
27
Note:
m = the total number of the students who choose certain answer n = the total number of the students
In post-design survey questionnaires, there will be a mean. The formula to measure the mean of the data collected would be calculated as follow:
Note: ∑: Sum
i: point of agreements, 1 until 4 Xi: score for the i data
Fi: the number of respondents who choose certain answer n: the totals of data X
N: the total number of the respondents
The data obtained trough questionnaires is in the form of scores. There are four agreements are applied as follows:
Table 2. Points of Agreements
Points of Agreements Scores
Strongly disagree 1
Disagree 2 Agree 3
28
3.6Research Procedure
There were several steps to conduct this research: 1. Conducting a library research
A number of textbooks and literatures concerning speaking and role play, theory of need analysis, instructional design model were consulted to find guidance in designing appropriate materials.
2. Observation
The observations were done by interviewing the teacher and distributing the questionnaires to the students. The purpose is to get the information about the learners' characteristics and learning objectives.
3. Designing the proposed model of speaking instructional materials
This step involved the development of preliminary form of the product. The proposed model of speaking instructional materials will be designed based on the learners’ necessities, lacks, and wants.
4. Conducting evaluation
The purpose of the evaluation was to find whether the designed materials were appropriate for first grade students of SMK Paramitha 2. It was done by distributing the questionnaires to the lecturers from Sanata Dharma University, two English teachers from SMK Paramitha 2, and one English conversation instructor for hotel staff.
29
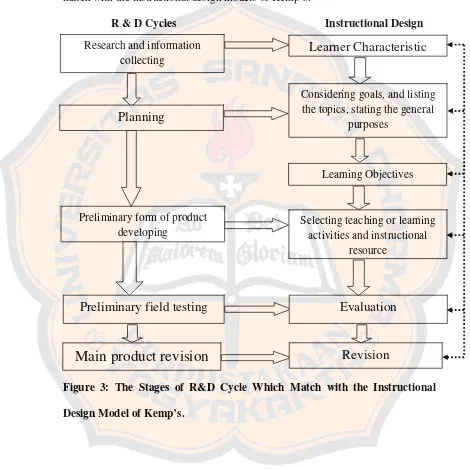
The researcher made a figure 3 to show the stages of R&D cycle which match with the instructional design models of Kemp’s.
R & D Cycles Instructional Design
Figure 3: The Stages of R&D Cycle Which Match with the Instructional
Design Model of Kemp’s.
Research and information collecting
Preliminary form of product developing
Preliminary field testing
Main product revision
Planning
Selecting teaching or learning activities and instructional
resource
Evaluation
Learner Characteristic
Revision
Learning Objectives Considering goals, and listing30
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSIONS
In this chapter, the researcher would like to describe the result and discussion of the findings of the study, and the presentation of the designed materials. This chapter is divided into three parts. The first part is the stages of the materials design development. This part provides the answer to the first formulated problem. The second part is the findings of the study. The third part is the presentation of speaking instructional material for the first grade students of SMK Paramitha 2. This part provides the answer to the second formulated problem. The complete design of speaking instructional material is presented on appendix 6.
4.1The Steps of the Development of the Designed Materials
With the intention of answering the first problem formulation of this research, the researcher used the steps of Kemp’s models. The Instructional Design Models are in line with Borg and Gall’s Educational Research and Development (R&D) cycle to design the materials. Those steps are (1) Learner Characteristic, (2) Considering goals, and listing the topics, stating the general purposes, (3) Learning Objectives, (4) Selecting teaching or learning activities and instructional resource, (5) Evaluation, (6) Revision.
4.1.1Learner Characteristic
31
sheets for twenty five first grade students of SMK Paramitha 2. Here is the discussion of the result of interview and the questionnaire.
4.1.1.1The Result of Distributing the Questionnaires
The researcher distributed questionnaires to the first grade students of
SMK Paramitha 2. The number of the participants was twenty five students. The questionnaires are divided into two parts; there are closed and open-ended questions. The explanation of the questionnaire result is presented below:
A.Closed Questions
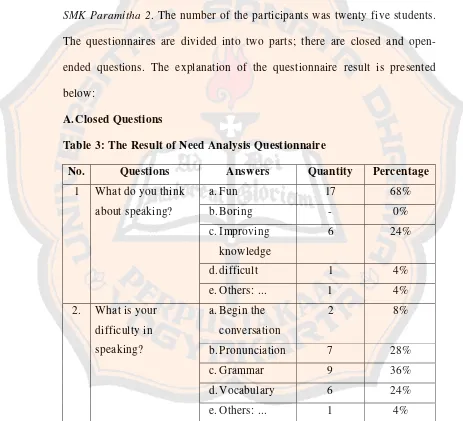
Table 3: The Result of Need Analysis Questionnaire
No. Questions Answers Quantity Percentage
1 What do you think about speaking?
a.Fun 17 68%
b.Boring - 0%
c.Improving knowledge
6 24%
d.difficult 1 4%
e.Others: ... 1 4%
2. What is your difficulty in speaking?
a.Begin the conversation
2 8%
b.Pronunciation 7 28%
c.Grammar 9 36%
d.Vocabulary 6 24%
32
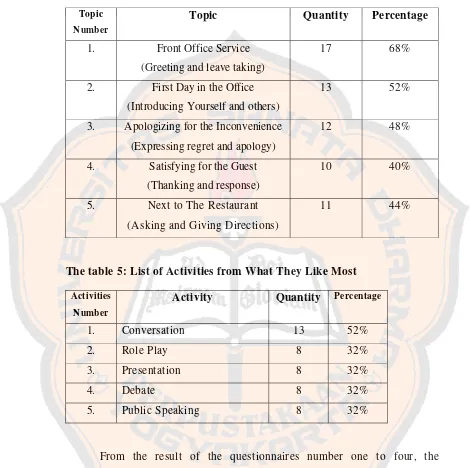
Table 4: List of Topics from What They Like Most
Topic Number
Topic Quantity Percentage
1. Front Office Service (Greeting and leave taking)
17 68%
2. First Day in the Office (Introducing Yourself and others)
13 52%
3. Apologizing for the Inconvenience (Expressing regret and apology)
12 48%
4. Satisfying for the Guest (Thanking and response)
10 40%
5. Next to The Restaurant (Asking and Giving Directions)
11 44%
The table 5: List of Activities from What They Like Most
Activities Number
Activity Quantity Percentage
1. Conversation 13 52%
2. Role Play 8 32%
3. Presentation 8 32%
4. Debate 8 32%
5. Public Speaking 8 32%
33
Related to the difficulties in speaking, most of them (36%) agree that they have difficulties in grammar and others in vocabularies (28%), in pronunciation (24%), and in starting the conversation (8%).
From the topic lists’ result, most of the students like Greeting and Leaves Taking as the first unit (68%), Introducing Yourself and Others as the second unit (52%), Expressing Regrets and Apologies as the third unit (40%), Thanking and Responses as the fourth unit (48%), and like Asking and Giving Directions as the fifth unit (44%). Here the researcher decides only four topics that will be designed, the first until the fourth.
From the activities’ result, most of the students like conversation as their favourites activity (52%), the second is role play (32%), the third is presentation (32%), the fourth is also presentation (32%), and the last is public speaking (32%). Here the researcher designed the material using this kind of activities. The activities will be chosen according to the material.
B.Open-Ended Questions
Almost all of the students in the class describe that they like conversation as the thing they like most in English. There are many reasons such as; conversation builds the imagination of the students. They can imagine the situational and expressions freely.
34
sometimes it can be a boring activity. They also need more review about the lesson that they have learned before.
They expect that they need to experience a new style of teaching especially in speaking. They need more practices than theories in the class and more activities that provide more students’ participation. Some of them even need an English teacher that speaks English in their class.
From the gathered data of the distributed questionnaire, the researcher draws a conclusion of students’ need, lack and wants in learning speaking, as follows:
1. The students need more practice in speaking, and the materials should be interesting materials.
2. The students have difficulties in grammar and vocabulary so they have less motivation to speak.
3. The students want more conversation in English subject.
4.1.1.2The Result of Interviewing the Teacher
35
modelling as a kind of technique by giving some examples first and then the teacher asked the students to repeat or reply it. She described that one from three meetings in a week were allocated for English speaking subject. In area of teaching principle, she lacked knowledge about approaches, methods, and techniques, so she only taught English subject based on the situation on the class and automatically she did not know the most appropriate approaches, methods, and techniques for her class. In her opinion, there were three difficulties in teaching speaking: making them speak, adding and finding the vocabulary, and improving the pronunciation. She also described that students’ need was more vocabulary. In her opinion, vocabulary was the first step to speak. The other lack of the students was less motivation to speak. In her experiences in teaching English, she included some activities in her speaking class, such as; watching video and listening to the conversation. She also said that in teaching English, there was no fixed handbook for the tourism school, so she gathered the materials from many sources, such as; internet and LKS.
36
4.1.2Considering Goals, and Listing the Topics, Stating the General
Purposes
The researcher adapted School Based Curriculum or Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan Pendidikan (KTSP) in this study. The standard competence of the materials design was the goal in this study. After that the basic competences were the general purposes of the designed material. After determining the goal, the researcher listed topics that were used in the designed materials.
The goal, the list of the topic, and the general purposes of the design material for the first grade students of SMK Paramitha 2 are presented below:
Table 6: The Description of Competence Standard, Basic Competence,
and Topic of Each Unit.
Unit 1
Front Office Service
Competence standard: Communicating in English in Novice Level
Basic competence: Comprehending basic expressions for social interaction
Topic: Front Office Service
Unit 2
First Day in the Office
Competence standard: Communicating in English in Novice Level
Basic competence: Comprehending basic expressions for social interaction
Topic: First Day in the Office
Unit 3
Apologizing for the
37
Inconvenience Basic competence: Comprehending basic expressions for social interaction.
Topic: Apologizing for the Inconvenience
Unit 4
Satisfying for the Guest
Competence standard: Communicating in English in Novice Level
Basic competence: Comprehending basic expressions for social interaction
Topic: Satisfying Service for the Guest
4.1.3Learning Objectives
The researcher used these steps in making the indicators. The indicators must be stated clearly and carefully, so the teachers will not have different perception related to the objectives. The characteristic of the indicators are specific, observable, and measurable. The objectives can be measured by the outcomes of the design.
Table 7: The List of Indicators of the Design
Unit 1
Front Office
Service
- The students are able to indentify greeting expressions. - The students are able to mention greetings expressions. - The students are able to respond greeting expressions. - The students are able to use greetings expressions in
simple present tense sentences even in written or orally. - The students are able to identify leave taking expressions. - The students are able to mention leave taking expressions. - The students are able to respond leave taking expressions. - The students are able to use leave taking expressions in
38
Unit 2
First Day in
the Office
- The students are able to identify the expressions of introducing.
- The students are able to mention introducing expressions - The students are able to respond introducing expressions. - The students are able to introduce themselves or others in
simple present tense sentences even in written or orally.
Unit 3
Apologizing
for the
Inconvenience
- The students are able to identify regret expressions. - The students are able to mention regret expressions. - The students are able to respond regret expressions.
- The students are able to use regret expressions in simple present tense sentences even in written or orally.
- The students are able to identify apology expressions. - The students are able to mention apology expression. - The students are able to respond apology expressions. - The students are able to use apology expressions in simple
present tense sentences even in written or orally.
Unit 4
Satisfying for
the Guest
- The students are able to identify thanking expressions. - The students are able to mention thanking expressions. - The students are able to respond thanking expressions. - The students are able to use thanking expressions in
simple present tense sentences even in written or orally.
4.1.4Selecting Teaching or Learning Activities and Instructional
Resource
39
The detailed information is explained in the following description.
1. Pre-activity
In this part, the role of the teacher is very important. The teacher should be able to make a relaxed atmosphere for the students to learn the materials and was still close to the topic. Pre-activity makes a bridge to the students between their experiences and the topic of each unit. There are some examples of activities in this part, for example: games, answering the questions, and talking about the pictures.
2. Whilst Activity
This section is divided into four parts. The first is previewing the examples of dialogue related to the discussed topic. This part the teacher gives some examples to the students in several forms and asks the students to list difficult vocabulary and expressions related to the discussed topic. The second part is teacher gives guidance about the proper pronunciation of the expressions related to the discussed topic and then asks the students to repeat after him/her, then the next parts are matching the expressions and completing sentences. These are used as a bridge before the students go to the main activities. The main activities are Shocking Times and Speak Up.
Shocking Times is a students’ activity which is still guided by the teachers in practicing speaking activity using the first and second parts. The last part is
40
3. Post-activity
This section reviews all the activities. The teacher gives some feedbacks to the students. The teacher gives overall comment and the things that must be improved as an input for a better performance. At the end of the lesson unit, there will be a Time to Reflect activity as a reflection about the progress of the performance, comments, and suggestions from the students for their groups and submitted to the teacher then the teacher summarizes it before give it back to the students.
Table 8: The Description of Design Materials
No. Topic Main
•Answering the questions •Talking about the pictures b.
Whilst-activity
•Reading the dialogue •Listing the vocabulary •Listing simple present tense
sentence
•Matching the expressions •Completing the sentences •Shocking Times:
Responding orally (individually) •Speak Up:
41
•Giving feedback and comments •Giving suggestions
b. Students:
•Making reflection 2. First Day in
the Office
a. Pre-activity
•Games
•Answering the questions •Talking about the pictures b.
Whilst-activity
•Reading the dialogue •Listing the vocabulary •Listing simple present tense
sentence
•Matching the expressions •Completing the sentences •Shocking Times:
Responding orally (individually) •Speak Up:
Making dialogue and performing the conversation (in group at least 3 persons)
c. Post-activity
a. Teacher:
•Giving feedback and comments •Giving suggestions
b.Students:
•Making reflection 3. Apologizing
for the
Inconvenience
a. Pre-activity
•Games
42
•Reading the dialogue •Listing the vocabulary •Listing simple present tense
sentence
•Matching the expressions •Completing the sentences •Shocking Times:
Responding orally (individually) •Speak Up:
Making dialogue and performing the conversation (in groups of 3-4 persons)
c. Post-activity
a. Teacher:
•Giving feedback and comments •Giving suggestions
b.Students:
•Making reflection 4. Satisfying for
the Guest
a. Pre-activity
•Games
•Answering the questions •Talking about the pictures b.
Whilst-activity
•Reading the dialogue •Listing the vocabulary •listing simple present tense
sentence
•Matching the expressions •Completing the sentences •Shocking Times:
43
No. Topic Main Activity
Teaching Technique
•Speak Up:
Making dialogue, preparing role-play, and performing the
conversation (in groups of 3-4 persons)
c. Post-activity
a. Teacher:
• Giving feedback and comments • Giving suggestions
b. Students:
• Making reflection
4.1.5Evaluation
After finishing the designed materials, the researcher distributed evaluation questionnaire to the respondents. The respondents were an English teacher of SMK Paramitha 2, and two lecturers of English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University. Based on the result of the materials evaluation questionnaires, the researcher found that the designed materials were acceptable and good for the first grade students of
SMK Paramitha 2 based on the result of respondents’ opinions in page 48-49.
4.1.6Revision
44
4.2The Findings and Discussions on the Designed Materials Evaluation
After designing the materials, the researcher gathered the evaluators’ opinions, feedbacks, and suggestions as the foundation in revising and arranging the final product of the material. There are four parts of the finding and discussion, those are preliminary field testing, main product revision, main field testing, and operational product revision.
4.2.1Preliminary Field Testing
In this step, the researcher presents the data gathered from the evaluation. The evaluators have a compulsory to give their opinions and suggestion by completing the provided questionnaires. The evaluators are one of English conversation instructor for hotel staff, two teachers from SMK Paramitha 2, and the two of lectures from Sanata Dharma University.
The discussion of the description of the respondents and the data presentation are as follows:
Table 9: The Description of the Respondents of the Evaluation Material
Design
Respondents
Sex Educational Background
Teaching Experience (in year)
F M S1 S2 S3 <5 5-10 11-15 16-20 20>
English teacher 1 1 2 - - - 1 - - 1
English
lecturers
1 1 - 2 - - - 2 - -
45
4.2.1.1The Result of Respondents’ Opinions on the Designed Materials
This part presents the respondents’ opinion on the designed materials by stating their agreement and disagreement and by choosing one of four points of agreement. The questionnaire is expected to achieve feedback dealing with the appropriateness of designed materials for the first grade students of SMK Paramitha 2.
The Table of Point of Agreement of Preliminary Field Testing Questionnaire is presented below:
Table 10. Points of Agreements of Preliminary Field Testing
Questionnaire
Point of Agreement Meaning
1 Strongly disagree
2 Disagree 3 Agree
4 Strongly Agree
Afterwards, the next is the table of the result of respondents’ opinions.
Table 11. The Resultof Respondents’ Opinions
No. Questions
Frequency of points of agreement
(Quantity of the Person) Mean
1 2 3 4
46
No. Questions
Frequency of points of agreement
(Quantity of the Person) Mean 1 2 3 4
3
.
Pre-activity:
a. The activities can stimulate the students’ interest to get involved actively in the learning process.
20%
(1)
80%
(4)
2.8
b. The questions in brainstorming session can bring the students get into the topic.
80%
(4)
20%
(1)
3.2
c. The pictures can help the students to imagine based on the topic.
80%
(4)
20%
(1)
3.2
4. Whilst-activity:
a. The dialogues describes the daily situation in tourism
80%
(4)
20%
(1)
3.2
b.The expressions in the material are appropriate to the topic.
80%
(4)
20%
(1)
3.2
c. The expressions in the material are easily to be understood.
80%
(4)
20%
(1)
3.2
d.The vocabulary is appropriate to the topic.
e. The vocabulary is easily to be understood.
f. The instructions in the activities are clear and easily to be understood.
20%
g.The activities are appropriate to the topic.
h.The activities have improved the students’ experience in learning.
20 %
i. The activities can improve the students’ ability in speaking.
47
No. Questions
Frequency of points of agreement
(Quantity of the Person) Mean 1 2 3 4
5. Post-activity:
a. The material design provides the reflection about learned material.
20%
b.The material design stimulates students to apply in the daily life.
60%
(3)
40%
(2)
3.4
6. The material design can increase the students' motivation in learning.
20%
(1)
80%
(4)
2.8
7. The material design is appropriate to English learning process in SMK Paramitha 2.
8. Overall the material design is well formulated.
From the result of the expert validation, it can be concluded that the designed materials were good and acceptable for the first grade students of
48
4.2.1.2The Respondents’ Comments and Suggestions on the Designed
Materials
This part elaborates the respondents’ comments and suggestions on the designed materials by providing them four open-ended questions. The purpose of those questions is to give the respondents much freedom in stating their opinions about the designed materials. From the open-ended questions, all respondents stated that the researcher had a good idea and interesting layout in developing the design. There was a need to conduct more exploration on the existing design based on the respondents’ comments and suggestions.
The respondents’ comments’ and suggestions’ are as follow: 1. Lesson Plan
One respondent stated that the lesson plan was still needed many improvements such as indicator and the description of the material.
2. Grammar and vocabularies
One respondent stated that the designed materials needed to be checked in the grammar and the word choices.
3. Instruction
Some instructions on the design materials were still not well formulated. Some parts needed clearer instruction for example in Speak Up
49
4. Teaching and learning activities
Two respondents stated that the layout design was too crowded and need to improve. The activities in the material design were too monotonous and need some activities to make it rich.
One respondent stated that the design is suitable for the condition of the class and the goals.
4.2.2Main Product Revision
After evaluating the designed material, the researcher revised the designed materials based on the respondent’s comments, feedback, and suggestions. There was a need to conduct a deeper exploration on the some parts of the designed materials. In order to create better designed materials, the researcher revised the materials based on respondents’ opinions and suggestions, as follows:
1. Related to some grammatical mistakes, the researcher revised those grammatical mistakes of the designed materials.
2. Related to the same misspelling mistake, the researcher revised those misspelling mistakes of the designed materials.
50
4. The respondent suggested that the lesson plans were not well formulated. The researcher reorganized and added some parts in order to make them clearer and meet the purpose of the lesson plan.
4.3The Presentation of the Designed Materials
In order to answer the second question in the problem formulation, the researcher presents the final version of the designed materials in this part. The designed materials consist of three units and topics.
Those are presented in the table below:
Table 12. List of Units and Topics of the Designed Materials
UNIT 1 Front Office Service
UNIT 2 First Day in the Office UNIT 3 Apologizing for the Inconvenience
UNIT 4 Satisfying for the Guest
Unit 1: Front Office Service, this purpose is to provide some cases and situations for the students that commonly happen in the first time they meet someone or guests in tourism context. The examples of the dialogue like Welcoming Guest and Handling Check-in and Handling Room Booking by Phone. This unit is accomplished based on the English lesson syllabus for Vocational School with the basic competence of comprehending basic expressions for social interaction.
51
Introducing Yourself as Hotel Staff, Introducing Yourself and Your Co-Workers, Explaining Your Job. This unit is accomplished based on the English lesson syllabus for Vocational School with the basic competence of comprehending basic expressions for social interaction.
Unit 3: Apologizing for the Inconvenience, this purpose is to provide some cases and problem situations to the students that commonly happen in tourism context. The examples of the dialogue like Handling Problems in the Restaurant, Rescheduling, and Handling Complaint in Hotel. This unit is accomplished based on the English lesson syllabus for Vocational School with the basic competence of comprehending basic expressions for social interaction.
Unit 4: Satisfying for the Guest, This purpose is to provide some cases and situations after finishing service for the guest to the students that commonly happen in tourism context. The examples of the dialogue like Please Bring My Luggage and Here is the Room’s Key. This unit is accomplished based on the English lesson syllabus for Vocational School with the basic competence of comprehending basic expressions for social interaction.
The learning process in each unit is divided into three sections, namely Pre-activity, Whilst-activity, and Post-activity, the explanation of each section is as follow:
1. Pre-activity
This section presents the introduction of the unit, the questions in the
Pre-52
activity lets the students to imagine the topic and brainstorm their ideas of the pictures which are related to the topic of each unit. Pre-activity takes 15-17 minutes in each meeting in the beginning of the class.
2. Whilst-activity
This section presents the content of the unit; the examples of the dialogue, the expressions and some tasks related to the dialogues and the expression are the minor section in Whilst. The major sections are Shocking Times and Speak Up. In Shocking Time, the teachers provide situations, some clues, or to do list that are used to perform the students’ ability to speak spontaneous. After mastering the minor section and completing the Shocking Times, the next part is Speak Up. In unit one until three the researcher lets the students to make the conversation and perform it in front of the class as the
Speak Up activity (the conversation is done in group 2-4 students). In unit four there will be role play and the students perform the role play in front of the class (the role play is done in group of 3-4 students).
3. Post-activity
53
overall comments and the things that must be improved as an input for a better performance.