L. Benčič1 and M. Mele1
1
Institute and Academy for Multimedia, Ljubljana, Slovenia
Abstract. The project Urban-planning game represents a way of democratic involvement of the public in the shaping of the future of historic towns by way of an interactive game. It is based on cooperative behavior between the inhabitants, the experts and the government. The object of the game is acquiring ideas and guidelines for a lasting development on the basis of people's needs and problems. As a possible way of communication I propose a publicly accessible cooperative nonzero-sum game on the playground of Geographic information system technology. The player has a free use of symbolic infrastructural elements. He can arrange them in the urban space according to his experience, needs and wishes and in agreement with his co-players. The end of the game is supposed to represent work and life in a modern town, organized according to the player's plans.
1.
The Circumstances for the Formation of the Project
The idea for the Urban-planning game appeared in Split in Croatia in 2004. The town of Split is an obvious example of the gap between 2000 years of history of the urbanistically unsurpassable Diocletian's palace and between the present which shows a disorganized picture and its everyday problems.
2. Comparable Projects and Theoretic Findings
I got very few useful practical cases that could serve me as a model or comparison and that I could test (CLUG [02], SimCity [07], DuBes [08]…).
Three parts of the theoretical basis of the game were formed: democracy, future of towns and game theory.
These chapters confirm my original idea and its benefits for protection of cultural heritage and help understand the backgrounds of urban systems [03], [04].
Crowding, swarming and socializing are a basic right and frequent phenomena in the modern society. Crowds create goods and exploit them. But they also have to strike and keep the balance. This balance could be called - the Social game. One segment of the social game works in the sphere of urban systems. This segment could be called – the Urban-planning game.
The more there would be active communication, that is, understanding, negotiating, learning between the players, the greater and more precious would the stock of knowledge be.
Knowledge of social behaviour, on which the proposals for the realization of the lasting development are based, is always insufficient and all information is welcome [05], [06].
This kind of game and the information from its contents can be used by experts to predict the future and lasting development of towns as one of the methods for gaining and supplementing their bases of knowledge [01]. (It does not replace the existing methods of sociological research.)
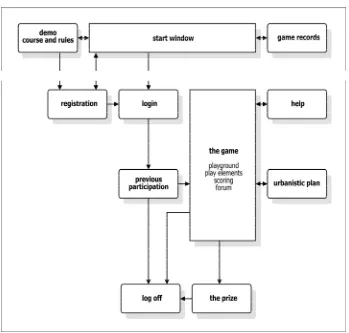
3. Concept of my Urban-planning Game (Fig. 1.)
3.1 Rules of the Game
3.1.1 Object of the Game
The object of the game is defined according to the basic guidelines of the urbanistic plan:
Promotion of city government and its orientation towards an open dialogue with
citizens
Tools for data collection and communication with citizens (following their thoughts
and doubts, their distress and enthusiasm…)
Social cooperation which encourages involvement of citizens and their interaction on the level of the game (find out the opinions of others, negotiate with other citizens, allow for, understand and accept the freedom of thinking which is different from theirs…)
Collecting ideas - guidelines for predicting future development and cultural heritage protection
Education Awareness
3.1.2 Elements of the Game
basic components: actual projects anticipated in urbanistic plan place-area: game surface is a GIS map of town or part of town roles: players are all citizens in their actual roles
events: arranging elements on the playground, forum, marking, prize coupons
3.1.3 Mode of Playing
Number of players is not limited. The game is over for the player when he arranges the symbols on the game surface, scores the sufficient amount of points and gets the coupon. The starting points for players are given in the description of the symbols which represent the projects, in UP (urbanistic plan) and in Help window.
3.2 Game Levels – Model:
3.2.1 First Third:
Registration of a new or login of a registered player. The registration comprises user name, password, local appurtenance, status of the player, profession of the player. Demo window shows the course and the rules of the game.
3.2.2 Second Third:
compulsory ones and some of the optional ones without exceeding the proposed joint value. The player has at his disposal the rules of the game in text form and a short presentation of the urbanistic plan.
Players, registered with the same role and local appurtenance can see each other's decisions and can discuss, negotiate and evaluate the projects in the forum window. After discussion the player independently decides on final arrangement and selection of projects, saves it and submits it for marking.
According to location's suitability for realization and cost and logistics justification the player is awarded points. More points represent a more suitable solution from the viewpoint of above stated criteria.
3.2.3 Third Third:
On Mosaic – a lottery game the player's prize appears (if justified). The prize is a randomly chosen mosaic square representing one of the game sponsors and as such the sponsor's prize. The coupon is printed; the player collects it and logs off.
Best scores of previous games are available to players regardless of their participation. They represent temporary arrangement of projects and are the indicators of the will and needs of citizens. They are presented by a GIS map and statistic data.
4. Scenario of my Urban-planning Game
4.1 Course of Game
The player arranges symbols of urbanistic elements on the game surface according to real life needs and tries to score as many points as possible. While playing the game he can consult other players on the forum and compare his solutions with theirs. By scoring points he can win the prize.
4.2 Players (Activities, Actions)
main game window and decides about his symbol arrangement. He saves the arrangement and submits it to marking according to three criteria. If he wants a better score which can be awarded, he can repeat the arranging, saving and marking. The player can temporarily exit the game, take time to think or check something in real world. He can continue the game by resuming registration anywhere and anytime. More players create a cooperative atmosphere; maximum number of players can only be limited technically. All players, regardless of their role in the game have equal possibilities for point scoring and prizes.
4.3 Elements of Game (Use, Aims, Communication, Interdependence)
Elements of the game are the playground (GIS map), existing and planned buildings and locations which are the subject under discussion of the urbanistic plan for the area on GIS map.
Playground: An indispensable layer in GIS application is a map of the area, a register of environmental units or database of all buildings in the area. Descriptions in the base offer data about contents, purpose, use and quality of environmental units, proprietors, managers, price and conditions of environmental unit acquisition and all other data necessary for making selections and decisions, for example for public transport planning, finding the most suitable locations for shops, hospitals, schools etc. When we roll the mouse over a marker on a map a flag with the address and data appears. So we can check at the beginning of the game all environmental elements which are available as game elements, and after arranging all elements which have been placed on the map and complement missing locations or substitute former buildings.
4.3.1 Existing Buildings:
Static: changes not possible (for example cultural heritage)
Dynamic: it is possible to change the purpose, renovate, demolish, change into static (indicate, select, delete, edit data, go back to previous or starting positions). Changes affect the value of the building.
Value in points changes.
4.3.2 Locations:
Static: changes not possible (for example archaeological site)
Dynamic: it is possible to build, change into static location (indicate, select, delete, edit data, go back to previous or starting positions). Changes affect the value of the building.
Value in points changes.
4.3.3 Planned Buildings:
Dynamic: it is possible to determine a suitable location for realization (to indicate, select, delete, edit data, go back to previous or starting positions).
Planned buildings are shown as symbols outside the GIS map and have data necessary for making decisions and justifying the choice of future location and the information about the actual score (number of points). The player selects, drags and places the symbols of environment elements on the game surface.
Dynamic elements can be marked, selected, dragged and deleted, the data can be edited and it is possible to go back to previous or starting positions. While arranging selected elements on the map the existing database is supplemented with new, just selected elements and their characteristics and new relations in the environment are made.
4.4 Artificial Intelligence and Marking (Desired Behaviour)
The tools of artificial intelligence deal with the evaluation of the value and quality of proposals. During the game, after every move of the player calculating realization costs, acquiring and collecting logistic information and predicting possible development of town is in course. The player gets the new value of points scored. Location suitability, cost justification and logistics of new proposals are evaluated. Above average score enables the player to participate in prize-winning competition. Evaluation takes place according to rules and criteria established in urbanistic, economic and logistic field. Methods, already tested in such analyses are used. The total sum of all three analyses represents the player's final score.
4.5 Multi-player Possibilities of the Game
The relations between players are cooperative. On the forum the players discuss possible solutions of their problems. Players, registered with the same role and local appurtenance can see each other's decisions in the forum window and can discuss, negotiate and evaluate the projects. After discussion the player independently decides on final arrangement and selection of projects, saves it and submits it for marking. Proposals and decisions of the other players do not affect marking and awarding prizes.
5. Conditions for Realization
The next phase anticipates the realization.
I designed a Urban-planning game. I prepared the concept. I planned the scenario (playing technique, navigation, list of elements and functional claims of the user interface).
I devised the realization plan.
The game is realizable under following conditions: - finding an investor who will secure finances, - expert and legal support of the government agencies,
6. Conclusion
The urban-planning game represents an example of a concept of democratic involvement of the public in the shaping of the future of a town by way of an interactive game. It is based on cooperation and anticipates thinking and creative players.
References
1. Cecchini, A., Indovina, F. (1992). Strategie per un futuro possibile, Franco Angeli, Milano. 2. Feldt, A. G. (1972). CLUG Community Land Use Game, New York.
3. Gantar, P. (1985). Urbanizem, družbeni konflikti, planiranje, Založba Krt, Ljubljana. 4. Hočevar, M. (2000). Novi urbani trendi, FDV, Ljubljana.
5. Pogačnik, A. (1988). Kvantitavne metode v prost. in urb. planiranju, FAGG, Ljubljana. 6. Toš, N. (1988). Metode družboslovnega raziskovanja, DZS, Ljubljana.
7. simcity.ea.com (31. 7. 2006)