iii Maranatha Christian University
ABSTRACT
Dalam penggunaan bahasa, permainan kata merupakan salah satu bentuk pengembangan bahasa yang diciptakan secara kreatif oleh penulisnya atau pengujarnya. Permainan kata melibatkan kelenturan berbahasa karena perbendaharaan kata yang sudah ada dimodifikasi secara sengaja meskipun terkadang menyimpang dari aturan dasar berbahasa. Permainan kata juga menimbulkan efek bagi pembaca atau pendengarnya.
Dalam Tugas Akhir saya yang berjudul “Analysis of the Translation of Language Play in Lewis Carroll’s Through The Looking-Glass”, saya membahas permainan kata pada novel tersebut berikut terjemahannya dalam bahasa Indonesia, yaitu Dunia di Balik Cermin.
Saya menganalisis proses linguistik pada permainan kata yang terdapat dalam novel versi asli serta terjemahannya. Kemudian, saya menganalisis bentuk dan makna permainan kata tersebut, apakah penerjemah menggunakan bentuk dan makna yang sama, berbeda pada salah satunya, atau sama sekali tidak mempertahankan bentuk dan makna permainan kata. Saya juga menjelaskan efek dari permainan kata serta terjemahannya bagi pembaca.
ii Maranatha Christian University
Statement of the Problem ... 4
Purpose of the Study ... 4
Methods of Research ... 5
Organization of the Thesis ... 5
CHAPTER TWO: THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK ... 6
Language Play ... 6
Translation ... 11
CHAPTER THREE: ANALYSIS OF THE TRANSLATION OF LANGUAGE PLAY IN LEWIS CARROLL’S THROUGH THE LOOKING-GLASS ... 15
46
Table of the Summary Data Analysis
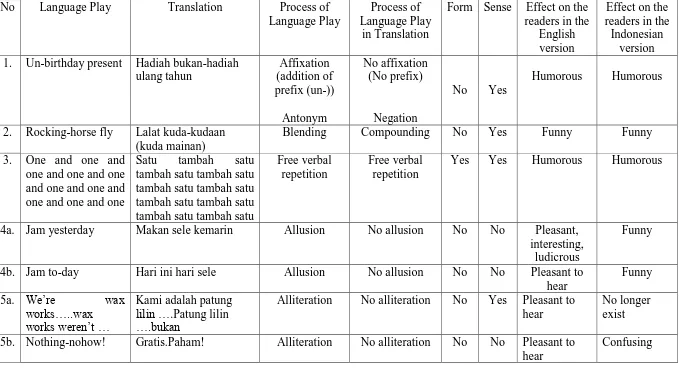
No Language Play Translation Process of
Language Play 1. Un-birthday present Hadiah bukan-hadiah
ulang tahun
2. Rocking-horse fly Lalat kuda-kudaan (kuda mainan)
4a. Jam yesterday Makan sele kemarin Allusion No allusion No No Pleasant,
interesting,
Alliteration No alliteration No Yes Pleasant to hear
No longer exist 5b. Nothing-nohow! Gratis.Paham! Alliteration No alliteration No No Pleasant to
hear
47 6a. Fire-irons falling
into the fender
Pengorek api jatuh di atas rangka besi pembatas perapian
Alliteration Alliteration No No Pleasant to hear
Pleasant to hear
6b. Fire-irons Pengorek api Compounding No
Compounding
No No Confusing, pleasant to read,
Maranatha Christian University 1
CHAPTER ONE
INTRODUCTION
1.1 Background of the study
Children’s world is not far from imagination and fiction. There are many imaginative ideas which are used in children’s fictions. In many processes of
creating children’s fictions, imagination becomes a challenge for the authors to
attract the readers’ interest towards this kind of fiction (Selviya).
Lewis Carroll is one of the authors of children’s fiction, who is “best known as the author of Alice’s Adventures in Wonderland and Through the Looking Glass” (Heureka). He also writes some other literary works, such as The Hunting of the Snark (1876), Sylvie and Bruno (1889) and others (“Lewiss Carroll Quotes”).
Helmut Werner Klug supposes in The Function of Linguistic Issues in “Alice in Wonderland” and “Through the Looking Glass” that the central theme in
Maranatha Christian University 2
while in Alice’s Adventures in Wonderland, Carroll uses the same devices to create humor (Klug 11). Crystal mentions that one of the contemporary authors at Victorian times who reflected the general interest in language play is Lewis Carroll (Crystal 60).
Language play is an action of manipulating language for the purpose of fun and enjoyment. The language that is manipulated in language play are linguistic features such as a word, a phrase, a sentence, a part of word, a group of sounds, and a series of letters. These linguistic features are literally manipulated by bending and breaking its rule in order to be language play (Crystal 1). Language is not always has function as means of communication so that people attempts to make up the language intentionally and creatively for fun. To come to this purpose, the certain rules such as in morphology and other linguistic areas are often omitted.
In my thesis I would like to analyze language play found in Lewis Carroll’s Through the Looking-Glass. I choose language play as the topic of my
Maranatha Christian University 3
Balik Cermin, as the source of data for my thesis because I would like to find the Indonesian translation of language play, compared to its source text in English.
My analysis is limited into three areas of language play which are used in Through the Looking-Glass. They are Morphology, Phonology, and Semantics. Morphology is “the study of the internal structure of words, and of the rules by which words are formed” (Fromkin and Rodman 69). Phonology is “the study of
the sound systems of language” (Crane and Whitman 1). Semantics is “the study of meaning” (Crane and Whitman 129). I choose these three areas because I found
that the language play used in Through the Looking-Glass and its translation have relevance with word formations, sounds, and meaning.
Concerning translation, in order to translate language play from English into Indonesian, translators need not only accuracy, but also enough skill or ability to translate the meaning of language play into the equivalent terms in the Indonesian language. If they still cannot find the exact translation, they have to find another similar term without changing its meaning.
In a process of translation, translators have to notice the form and the sense. The form concerns with the style or the structure of the words in the target language; while the sense concerns with the content or meaning of the source language (Hatim and Munday 10).
By analyzing language play in Lewis Carroll’s Through the Looking Glass
Maranatha Christian University 4
understand language play, they can enjoy reading novels and other literary works that contain language play better.
For other researchers, this thesis can be used as a comparison to make a better research with a similar topic. For translators, this thesis gives information about the functions of language play in children’s novels. This information helps them to produce better form and sense in translating language play. If translators translate language play in children’s novels accurately, they can convey amusing and pleasant ideas for the readers based on the source text.
798 words 1.2 Statement of the Problem
1. What forms of language play are found in Lewis Carroll’s Through the
Looking Glass?
2. What is the translation of the language play?
3. Which does the translator keep: the form, the sense, the form and the sense
or neither the form nor the sense?
4. What is the effect (s) of the language play and its translation on the
readers?
1.3 Purpose of the Study
1. To describe what forms of language play are found Lewis Carroll’s Through the Looking Glass.
Maranatha Christian University 5
3. To find out which element the translator keeps: the form, the sense, the form and the sense or neither the form nor the sense.
4. To describe the effect (s) of language play and its translation on the readers.
1.4 Method of Research
First, I read Through the Looking-Glass and its translation in the Indonesian version, Dunia di Balik Cermin. Then I noted down the words which belong to language play in the English version. After that, I compared them with the translation. Then, I analyzed how the translator translates the language play based on the theories I used. After that, I described the effect of the language play and its translation on the readers. The last step is I wrote this research report.
1.5 Organization of the Thesis
This thesis consists of four chapters. The first chapter, the Introduction, contains Background of the Study, Statement of the Problem, Purpose of the Study, Methods of Research, and Organization of the Thesis. Next, the Theoretical Framework is presented in Chapter Two. Chapter Three is the analysis of language play in Lewis Carroll’s Through the Looking Glass and its translation
30 Maranatha Christian University
CHAPTER FOUR
CONCLUSION
Having analyzed the data found in Lewis Carroll’s Through the
Looking-Glass, I categorize the form of language play into three areas of linguistic which are morphology, phonology, and semantics. From the analysis, I find six forms of language play; they are affixation, blending, compounding, alliteration, free verbal repetition and antonym.
I discover that some language play in the data involve several morphological processes. There are affixation, compounding, and blending. Data 1 contains affixation. Language play which belongs to compounding is found in data 2 and 6b; meanwhile, language play that contains blending is found in the
31 Maranatha Christian University For the readers, in data 1, the effect of language play in the source text is humorous; while, the effect of language play in the target text is also humorous. From the use of compounding in data 2, the effects of compounding in the target text are humorous. For the use of compounding in data 6b, the effect on the readers of the source text is confusing and pleasant to read; while the effect on the readers of target text is interesting. Meanwhile, the effects of language play in the source text in 4a and 4b are the readers will find it pleasant to read, interesting, and ludicrous. In the target text the effect will be confusing and ludicrous so that the readers need to know other additional information to understand the new meanings. For the use of compounding in data 6b, the effect on the readers of the source text is confusing and pleasant to read; while the effect on the readers of target text is interesting.
For the finding above, I conclude that it is very difficult to translate language play into the same form and sense in translation. Data 1 that contains affixation and data 2 that contains compounding are successfully translated into the same sense in the target text. Unfortunately, the rest of data that involve compounding are translated into different form and sense. In my opinion, the difficulty to translate into the same form and sense are due to different morphological process in the target language, especially in affixation and compounding.
32 Maranatha Christian University show negative meaning un- in English but there is no prefix in Indonesian that show negative meaning. The word tidak and bukan are not prefix and cannot be attached to a noun.
In phonology, I notice that the author uses free verbal repetition in data 3, alliteration in data 5a, 5b, and 6a.
In data 3, which contains free verbal repetition, the translator keeps both of form and sense. In data 5a, 5b, and 6a that contain alliteration, the translator does not keep the form in both of them. The translator also can not keep the sense in data 5b and 6b. However, the translator keeps the sense in data 5a.
From data 3, in the source text, the effects of language play on the readers is that the readers will find it pleasant to hear; while in the target text the readers will find it entertaining. From data 5a, the effect of language play on the readers in the source text is pleasant to hear; while in the target text the effect no longer exists. From data 5b, the effect of language play on the readers in the source text is pleasant to hear, while the effect of language play on the readers in the target text is confusing. From data 6a, the effect of language play and its translation is pleasant to hear on the readers’ ear.
33 Maranatha Christian University to the readers; however, the readers in the Indonesian version do not always get the same effect with in English version.
In semantics, I recognize that the author uses negation in data 1. I cannot find any language play that contains synonym, homophone, and homonym. In data 1, the translator keeps the sense; meanwhile only one of the forms is kept. The author and the translator use the same form. The form is antonyms.
The effect of language play which deals with semantics in data 1 is that the readers will find it humorous but ludicrous. The author plays with the negation of birthday present. What makes it humorous but ludicrous is that the readers will know that there is not antonym of birthday present, except if it is used in negative sentence. From the translation, the readers can not find the same effect, but I think the translation is entertaining for the readers because the translator tries to maintain the sense although the phrase hadiah bukan-hadiah ulang tahun is ungrammatical.
From the analysis of data 1, I conclude that language play in the novel that contains a device in semantic is easier to be translated into the same sense because the meaning usually remains the same.
In order to translate language play that contain devices in morphology, phonology, and semantic, the translator needs to translate language play carefully because they have to deliver the aims of the author in making the language play.
34 Maranatha Christian University for the translators to translate them into the same form and sense. Sometimes, the translator should keep only the form or the sense to deliver the message of the language play. When the translator fails to keep either the form or the sense, the readers of the Indonesian version will also fail in identifying the words or phrases that actually contain language play in the English version.
Personally, I am interested in the ways of the author creating language play in the novel. From the analysis of data 5, I know that the author uses logical and mathematical elements and he expresses it through language to show that he is talking about mathematics operation of addition. The author also invites the readers to imagine the term or the name of a thing such as found in data 2 and data 6b. He asks the readers to imagine rocking-horse-fly, a thing which only exists in a wonderland. It makes the readers imagine what it is like by relating it with the knowledge or information which they know about rocking-horse and horse-fly.
For further research, I suggest that any researchers, who want to take a similar topic, should find other children novels because the data that contains language play in this novel are quite limited. However, there are other topic that can be used to analyze in this novel, for example rhymes, homophone, and homonym.
35 Maranatha Christian University
BIBLIOGRAPHY
References:
Baker, M. In Other Words: A Coursebook on Translation. London: Routledge, 1992.
Catford, J.C. A Linguistic Theory of Translation. London: Oxford University Press, 1980.
Crane, L. Ben, Edward Yeager, and Randal L. Whitman. Introduction to Linguistics. Boston: Little, Brown and Company, 1981.
Crystal, D. Language Play. London: Penguin, 1998.
Fromkin, Victoria, and Robert Rodman. An Introduction to Language. New York: Holt, Rinehart, and Winston, 1983.
Hatim, Basil, and Jeremy Munday. Translation: An Advanced Resource Book. London: Routledge, 2004.
Hurford, James R., and Brendan Heasley. Semantics: A Course Book. London: Cambridge University Press, 1983.
36 Maranatha Christian University Leech, N. Geoffrey. A Linguistic Guide to English Poetry. London: Longman,
1991.
Main, C. F, and Peter J. Seng. Poems. Belmort: Wadsworth Publishing Company, 1973.
McManis, Carolyn., Deborah Stollenwerk, and Zhang Zheng-Sheng. Language Files 4th edition. Reynoldsburg: Advocate Publishing Group, 1987. Nash, W. The Language of Humour. New York: Longman Group, Inc. 1994. Newmark, P. Approaches to Translation. New York: Pergamon, 1981.
O’Grady, William., Michael Dobrovolsky, and Francis Katamba. Contemporary
Linguistics: An Introduction. Harlow: Longman, 1987.
Primary texts:
Carroll, L. Through the Looking-Glass and What Alice Found There. Tokyo: Charles E. Tuttle Company, 1995.
Hariyanto, S. Petualangan di Negeri Ajaib dan Dunia di Balik Cermin. Jogjakarta: Penerbit Narasi, 2007.
Dictionaries:
Badudu, J.S, and Sutan Mohamad Zain. Kamus Umum Bahasa Indonesia. Jakarta: Pustaka Sinar Harapan, 1994.
37 Maranatha Christian University
Klug, Helmut Werner. “The Function of Linguistic Issues in Alice in Wonderland and Through the Looking Glass.” 2000. 15 November 2009
<http://www.klugi.com/wissen/papers/anglistik/Alice_in_Wonderland.p df>
Leninimports. ”Lewis Carroll Quotes”. 2010. 21 August 2010. <http://www.leninimports.com/lewis_carroll.html>
Parkins, Keith. Heureka. “Lewis Carroll.” Clara Net, September 2005. 21 August 2010.
<http://home.clara.net/heureka/art/carroll.htm>
Selviya. ”Fiksi Anak Inspirasi sebuah Kesederhanaan”. Cornerstonestudio Wordpress, 2010. 27 September 2010
<http://cornerstonestudio.wordpress.com/2010/01/06/fiksi-anak-inspirasi-sebuah-kesederhanaan/>
Vern, S. Poythress and Wayne A. Grudem. “The Gender-Neutral Bible
Controversy”. Nashville: Broadman and Holman, 2000. 21 November 2010.
<http://www.bible-researcher.com/gnbc-ch4.html>
Absolute Astronomy. “Allusion”. Absolute Astronomy.com, 2011. 10 August 2011
<http://www.absoluteastronomy.com/topics/allusion>
Encyclopedia. “Negation”. International Dictionary of Psychoanalysis, Danon-Boileau, Laurent, 2005. 10 August 2011
<http://www.encyclopedia.com/topic/Negation.aspx>