ADVANCED TOPICS IN INFORMATION SYSTEM
CUSTOMER KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT (CKM)
By :
Dian Islamiati A.L – 1601259823
Class :
LB11
Binus University
2014/2015
Abstract
Customer Knowledge is increasingly recognized in the marketing and business world as a significant resource that can increase innovation and creativity to facilitate the emerging market opportunities and developed very rapidly, and to support the management of long-term relationship with the customer. Its collecting data about the good market products and prices as well as competitors from various sources and has long been recognized resources into a strategic key to the success of the company or business. CKM as the process of generating, disseminating, and using customer knowledge within a company or organization and between the organization and its customers.
Purpose of this paper is to explain the role of Customer Knowledge Management (CKM) to support and assist in the exchange of information within an organization and between the organization and the customer company and where the knowledge of the customer is used to manage the relationship with the customer, to improve the relationship with the customer or commonly referred to as CRM as customer service, customer retention and relationship profitability.
The method used is book study method is the method of data collection and all materials or sources obtained from books, journals, and lecturer. From results of this study produced an overview of Customer Knowledge Management (CKM). The conclusion is that the Customer Knowledge Management will provide benefits for Customer Success, Innovation and Learning organization. So that can be said that the Customer Knowledge Management is not to know what was known customers but also can be a learning experience and input for the company in distributing knowledge held by the consumer and use it to create a greater value in the eyes of consumers.
Keywords: Customer, Knowledge, Management, CKM, Knowledge Management
Jakarta, April 2015
Contents
Title Page
Abstract……….i
Contents………...ii
List Of Picture and Table………iv
CHAPTER I (INTRODUCTION) 1.1 Background………..1
1.2 Scope………2
1.3 Objective and Benefits……….2
1.4 Method of Writing………...3
CHAPTER II (THEORITICAL FRAMEWORK) 2.1 Customers………4
2.1.1 Definiton of Customer………4
2.1.2 Customer Value………..5
2.1.3 Value Received Customer (Customer Perceived Value)………6
2.2 Knowledge………..8
2.2.1 Definition of Knowledge………8
2.2.2 Type’s of Knowledge……….9
2.2.3 Methods For Creating Knowledge………...10
2.2.4 Wisdom………10
2.3.3 Components of Knowledge Management………12
2.3.4 The Four Pillars of Knowledge Management Process……….13
2.4 Customer Knowledge Management………13
2.4.1 Definition of Customer Knowledge Management………13
CHAPTER III (RESULT and DISCUSSION) 3.1 Customer Knowledge Management……….14
3.2 Customer Knowledge Management Process Model………15
3.3 Model Concept of Customer Knowledge Management………...16
3.4 Business Functions Customer Knowledge Management……….19
3.5 Implementation success factor of Customer Knowledge Management……...20
3.6 Five Types of Customer Knowledge Management……….21
3.7 General Constraints faced in implementing Customer Knowledge Management……….22
3.8 Competence of Customer Knowledge Management………...23
CHAPTER IV (CONCLUSION and RECOMMENDATIONS) 4.1 Conclusion………..25
4.2 Suggestion………...25
JOURNAL………26
BIBLIOGRAPHY………....28
APPENDICES………..29
List Of Picture
Picture 2.1 Determinants of Customer Delivered Value………..7
Picture 2.2 CustomerKnowledge Management Process Model………..15
Picture 2.3 Model Concept of Customer Knowledge Management……….17
Picture 2.4 Competence of Customer Knowledge Management……….24
PART I
INTRODUCTION
1.1 Background
With the times and technology, companies are also experiencing growth and change, from of small-scale company to large-scale company. The Development was particularly noticeable during the era of globalization, where information technology is growing rapidly and fast. So that customers can get any information and anywhere. Previously done business processes and manual or traditional way, are now beginning to use the process and computerized. Automation Process purchase, sale and the transaction can be done quickly.
With the rapid development of business, especially in the implementation and use of technology can drive business competition between companies. Everyone who runs a business to be able to compete with the market share and inter-company, and also can make new customers interested in using the products or services from our company. An important step in business is what strategies will be used by the company to be able to compete with other companies and seize the market to serve the customers and also maintain the trust and customer satisfaction in the long term. One strategy that can be done is to change the business paradigm into a customer-oriented company.
Most companies assume that they are driven by the market and customers. But there are few companies that actually manage well, and according to them is the most valuable resources, knowledge.
CKM is the process where by the company strategy liberate their customers from passive recipients of products or services, to empowerment as knowledge. CKM is how to obtain, variety, and expand knowledge of the customers.
1.2 Scope
Here is the scope of the author made are as follows:
1. Define Definition of Customer Knowledge Management.
2. Process Model of Customer Knowledge Management.
3. The model of Customer Knowledge Management concept.
4. Business Functions customer knowledge management.
5. Implementation Success Factors Customer Knowledge Management.
6. Five Styles (style) Customer Knowledge Management.
7. General Constraints faced in implementing Knowledge Management Customer.
8. Competence of Customer Knowledge Management
1.3 Objectives and Benefits
Here is the purpose of writing are as follows:
1. Customers can find out about the Customer Knowledge Management.
2. Knowing the benefits of Customer Knowledge Management.
3. Can know what are the factors of success and problems encountered in the management of customer knowledge.
The benefits of this writing include the following:
1. Be able to apply knowledge management success factors in the field of business for our company.
2. Can take advantage of customer knowledge management.
1.4 Method of Writing
CHAPTER 2
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
2.1 Customers
2.1.1 Definition of Customer
By Philip Kotler (2000) in his book Prinsiples Of Marketing are all individuals and households who buy or acquire goods or services for personal consumption.
According to Robbins, various organizations exist to meet the needs of customers. Customers who absorbs or receives the output of the organization. Customers are those who are paying attention and response output issued by the company. The customers clearly demonstrates the potential uncertainty for the organization. Tastes of customers can change, they may be dissatisfied with the products or services of that organization.
According to the expert opinions of customers can be divided into two, is :
a. Internal Customers
Customers who still have the next stage after getting the goods from the seller .customer will work to offer the item to another person.
b. External Customers
2.1.2 Customer Value
According to Ravald and Gronroos (2006 : 312) states that the value is the ratio between episodes of relationship benefits and benefits plus relationship episodes Sacrifice.
According to Kotler and Keller (2009 : 33) who, stating that customer value is the difference between total customer benefit and the amount of customer cost (the amount cost of the customer). "
The definition of customer value according to Zeithaml and Bitner in Hurriyati Ruth (2008 : 205) is "customer value is low price, what I want in a product or service, quality obtained from the price paid and what I can from what I give . "from this definition of value in addition to a comparison between what was issued with what is obtained, the value is also associated with lower monetary sacrifice as well as the expected quality”.
Competition on a global scale requires fundamental shifts in the business world. Basic mission of a business is no longer in the form of profit, but rather the creation and addition of value (value creation and value added) for customers. Profit is a logical consequence of the creation of value for the company. Based on that, it can be said that profit is the result or consequence as compared Vendor destination.
Value for the customer is a unit of the aspect ratio of the product obtained the promised product. Customer value received is the difference or ratio between the number of customer value and the amount of customer cost.
But when customers obtain high value offered by competitors, organizations require some action to maintain its market share. Value services can be expressed as the ratio of the perceived outcome and quality of services relative to the price and sacrifice issued the customer. Although actually the quantity value of services is sometimes very difficult, many customers derive value from the comparison of the past services. Some experts formulate the definition of customer value as the result of a comparison or difference between perceived benefits, this opinion in expressed.
perception of what is gained and what is given customer. There are two basic equations according to the definition of the value of the subscribe according to experts, the benefits received and expenses incurred. Understanding the value can be summarized into a customer's perception of all benefits received compared with the rest of the costs incurred as money and effort by the customer.
2.1.3 Value Received Customer (Customer Perceived Value)
According to Kotler and Keller (2009:135) : "The Value Proposition Consist of the whole cluster of benefits the company promises to deliver. Its more than the care of positioning of the offering "(The value proposition consists of a set of usability in the company offer to its customers, its more than just positioning in the offer)”.
An offer will be successful if it can deliver value Integration (value) and satisfaction (satisfaction) to consumers. Company offers to the customers present in a unit or package of benefits for customers who called the Value Proposition.
According to Morris, Value also known as "value for money" "best value" and "you get what you pay for". Understanding of the perceived value is a thorough evaluation of the usefulness of a product of an underlying consumer perceptions of a number of benefits to be received in comparison with the sacrifices done in general or consumer thinks.
Picture 2.1 Determinants of Customer Delivered Value
From the chart above as it appears that the customer delivered value is formed by two main elements, is the total customer value and the amount of customer cost.
The amount customer value is the overall monetary value received by the consumer from a set of usability that they expect from a bid. Usefulness here including in its the usefulness of the economical, functional, and psychology.
The amount of customer cost is the amount cost of their consumers expect to incur in evaluating, acquiring and using market quotes. If firms want to develop
its offer to the market, the company can do with three (3) ways to Kotler and Keller (2009: 135) :
1. Increase the amount of customer value by improving the usability of products, services, personnel and or impression of the company.
2. Reduce the cost of non-monetary consumer should be done by reducing the cost of energy, time and physical.
3. Reduce the monetary cost (price) of products that must be paid.
According to Kotler and Keller (2009:133) : "Customer perceived value is the difference between the prospective customer's evaluation of all benefits and all the costs of an offering and the perceive alternatives"
(Customer perceived value is the difference between the various uses and costs evaluated the prospect of a supply and develop alternative accepted).
Customer delivered Value will eventually be accepted by consumers and become what is the called with customer perceived value, (Customer perceived value is the difference between the various uses and costs evaluated the prospect of a supply and develop alternative accepted).
2.2 Knowledge
2.2.1 Definition of knowledge
According to Robert M.Z. Lawang, Knowledge is everything that happened or is happening in one's daily life.
According to Probst et al, Knowledge is a composite whole of understanding and expertise that individuals use to solve the problem, theory, and practice, everyday rules, and instructions for action. Knowledge is created by individuals, and display their believe about causal relationships.
According to Paul L. Tobing. Knowledge is information that is changing something or someone. Or when such information enable other person or institution to take different actions or measures are effective.
2.2.2 Type’s of Knowledge
The type’s of knowledge by Lendy Widayana, is :
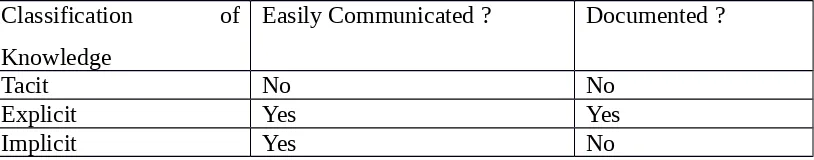
a. Tacit Knowledge is knowledge that is largely within the organization. Something that we know and experience it is difficult to be expressed clearly and completely. Tacit Knowledge is very difficult to be transferred to others, because Knowledge is stored on each. Thoughts of individuals in the organization according to their competence. Tacit Knowledge has two dimensions:
- Technical dimension, which is more informal in doing something. Technical dimensions the contain of principles and technical knowledge and experience gained as relatively more difficult to explain.
- Cognitive dimension, consisting of trust perception, idealism, values, emotions and mental difficult to explain. This dimension will shape the way a person receives everything that exists in the environment.
b. Explicit Knowledge is knowledge and experience about 'how to' described in a straightforward and systematic.
c. Implicit Knowledge is knowledge that is not visible, located between tacit and explicit.
2.2.3 Methods For Creating Knowledge
According to Davenport, the method can be used to create knowledge in the company (five models of knowledge generation) is as follows :
1. Acquisition : rent, buy, or hire the person or company that has intangible assets in accordance with company requirements. The intangible assets are expected to provide the skills and experience to be developed within the company, hire consultants, including one of them.
2. Decdicated resources, creating a specific unit responsible for the development of ideas or new ideas. Formation or development of R & D division is one example.
3. Fusion, of developing cooperation team consisting of a variety of people from backgrounds or perspectives of different expertise to create synergies.
4. Adaptation, is make adjustments to market development. This is particularly needed human resources able to absorb and utilize new knowledge and skills quickly.
5. Network, namely knowledge resulting from the formation of a team of non-structural and informal team formed by the employees based on specific interests. If these teams are increasingly widespread in the enterprise network will be formed. Networks can also be formed through direct talks, via phone, via email, and groupware to share expertise and solve problems together.
2.2.4 Wisdom
Characteristics of wisdom by Ackof is :
1. An understanding Tertiary and high awareness of human.
2. Is the answer to human problems in a certain period of time has not been answered.
3. Containing moral ethics.
4. Being in the soul and mind, which is only possessed by humans.
2.3 Knowledge Management
2.3.1 Definition of Knowledge Management
According to Townley, Knowledge Management is a set of the process of creating and sharing knowledge throughout the organization to optimize the achievement of the mission and goals of the organization. So, knowledge management is about improving the use of organizational knowledge through information management practices and organizational learning to achieve excellence competitive in decision making.
2.3.2 Type of Knowledge Management
1. Collecting and reusing structured knowledge. There are many 'knowledge in everyday life where the knowledge impact both directly and indirectly to the life of an organization or company, where everything can be used repeatedly - again without having any reexamination because it can directly be used and can saving time.
3. Create and map the structure of the knowledge required to improve performance. This project provides such an influence on the development of new products or redesign of business processes to make more explicit or open of knowledge required at certain stages.
4. Measure and manage the economic value of knowledge. Many companies have structured intellectual assets, such as patents, copyrights, software licenses and customer database. By knowing all these assets allows the company to create revenue and costs for the company.
5. Develop and disseminate knowledge from external sources. In this type of knowledge management organizations prepare and distribute to the members, with the expectation of an organization's mission is to be realized by either.
2.3.3 Components of Knowledge Management
Implementation of knowledge management in organizations involves three components:
1. Human, Successful application of knowledge management should be supported by the availability of competent human. Where humans as the main component of knowledge management in charge of implementing the management process is to learn, improve, or drain knowledge.
2. Process. The process of knowledge management process will simplify innovation or creation of knowledge and facilitate the transfer of knowledge. Where humans as the party of running this process, can be transfer his knowledge in the form of social networks and blogs and technology based.
2.3.4 The Four Pillars of Knowledge Management Process:
1. Creation of knowledge : when new knowledge is created through the process of innovation thinking to achieve the goal of a new mission.
2. Transfer of knowledge : when equalize and share knowledge through knowledge transfer.
3. The use of knowledge : when knowledge is used in the organization and apply them in achieving the mission or goals of the organization or company.
4. Storage of knowledge : when saving the current experience and past to the use or creation of new knowledge in the future. This stage is the stage that is most easily implemented.
2.4 Customer Knowledge Management
2.4.1 Definition of Customer Knowledge Management
According to Paquette, Customer Knowledge Management is a process to manage, identification of acquisition and use of knowledge consumers collectively as the process that the company employs to manage the identification, acquisition, and internal use of customer knowledge.
CHAPTER 3
RESULT and DISCUSSION
3.1 Customer Knowledge Management
CKM relating to the management and exploitation of knowledge of the customer. There are two types of customer knowledge :
1. Knowledge about customers, which may include knowledge of potential customers and customer segments as well as knowledge about individual customers.
2. Knowledge of the customers, about the range of products, such as compatibility between hardware components of a computer, and on the wider context and the market in which products and services are delivered.
The process can be classified into 3 categories:
a. Knowledge about customers is accumulated to understand the motivations of customers and address them in a personal way.
b. Knowledge to customers, includes knowledge about products, markets and suppliers.
c. Knowledge of customers, ideas, thoughts, creativity or experience consumption of certain products.
3.2 Customer Knowledge Management Process Model
Here is the process of Customer Knowledge Management Model proposed by Gebbert et al (2002)
Picture 2.2 Customer Knowledge Management Process Model (Gebbert et al,2002)
In the picture above models Customer Knowledge Management, Knowledge Management Gibbert explains that has particularly the role as a service provider that manages four aspects, is knowledge of content, competence, collaboration, and composition. The process illustrates perspective to illustrate the process of knowledge management can be applied to the sub-CRM in the process explained that the information held by companies from marketing, sales and service will be collaborated into a product or service that is then entered into the consumer process.
This is supported by technologies such as directory system expertise, management skills, and the system of E-Learning. Aspects of collaboration refers to the creation and dissemination of knowledge management among some individuals, while aspects of the composition refers to the dissemination and use of knowledge management among a number of individuals within an organization. Bueren et al (2004) further describes a technology for collaboration to include e-mail, group information and technology tools for composition, which focuses on search and navigation for explicit knowledge, can include accretion of knowledge, personalization, taxonomy and knowledge management system map. The four aspects of management CKM for EKM to include suppliers of knowledge management and knowledge management where content partners, competency, collaboration, and composition provide services that support the process in CRM, SRM, and PRM.
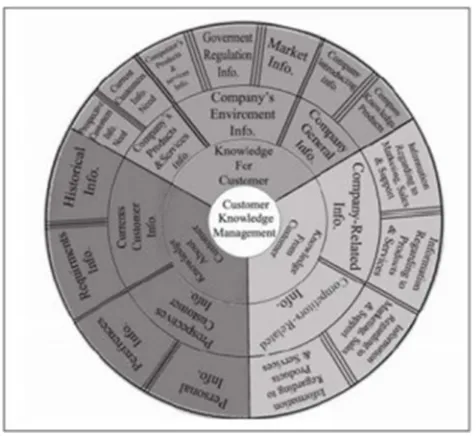
3.3 Model Concept of Customer Knowledge Management
In the picture above models Customer Knowledge Management, Knowledge Management Gibbert explains that have a role as a service provider that manages four aspects of knowledge, is : content, competence, collaboration and composition. It represents the perspective to illustrate the process of knowledge management can be applied to the sub-CRM Customer Knowledge Management in achieving effective.
Picture 2.3 Model Concept of Customer Knowledge Management
The model described above explains that the first layer categorize three types of consumer knowledge, is knowledge to customers, knowledge of the customer and the knowledge of the customer. The next layer of knowledge categories given by the organization to consumers. Then on the last layer is a detailed section of each category are given to consumer knowledge of the organization. Division contained in the above models can help any organization that wants to implement a Customer Knowledge Management. Customer Knowledge Management will provide advantages Customer Success, Innovation, and organization learning. So it can been said that the Customer Knowledge Management not pinpoint what is known by consumers, but may be more learning for the company to distribute the knowledge possessed by consumers and use it to create a greater value in the eyes of consumers.
company or organization, there are at least three benefits that can be obtained from the company, is Standarized Activity Process, System-Based Organizational Structure etc.
The first benefit of the application of Knowledge Management is a Standardized Process Activity. From the example above incident, it appears that the lack of explict Knowledge on-line activities of the company led to the company running sober without a clear operational standards and impressed. In the era of increasingly competitive business rivalry as it is today, is in fact not a wise thing when a company has entered into a climate of intense competition, still rely on Tacit Knowledge Person by Person in the absence of a clear written standards.
The next benefit of the application of Knowledge Management is a System-Based Organizational Structure, with the presence of Explicit Knowledge on each line of activity in the company, especially in activities that are considered as Core Activity, will make the company into an organization based system or System-Based Structure Oragnizational.
Another benefit of the application of Knowledge Management is Easier and Faster Business Development. With the existence of an Explicit Knowledge in the form of operating system written and organized and of course run by the perpetrators activity with discipline and commitment, of course, it will be easier in the stage of evaluating a company's operating system. Regardless of the outcome when an operational activity has been written and systemized well, will facilitate the evaluation of performance and achievement of the company, both the evaluation system and the personnel of the system actors.
There are many ways the application of Knowledge Management is a company that is a focus of concern future is changing into Explicit Knowledge to Tacit Knowledge. One of the easiest ways to change Tacit Knowledge becomes Explicit knoweledge is "systemize the routine and Humanize the Exception". This method is considered easy because it takes the actual business owners just careful observation of the activities of its operational routine and then recorded the process flow as well as revamped in hardcopy.
Customer Knowledge Management will provide advantages Customer Success, Innovation, and Organizarion Learning. So it can be said that the Customer Knowledge Management is not to know what was known by consumers, but may be more learning for the company to distribute the knowledge possessed by consumers and use it to create a greater value in the eyes of consumers. overall level of customer profiles business, then processed and converted into customer knowledge for organizational learning materials and change organizational behavior. CKM effectiveness requires active customer involvement in decision-making companies.
Business-to-customer communication to distinguish and separate the business products and services from competitors:
• Direct communication at the level of customer service.
• Public relations.
• Marketing Strategy.
• Data mining.
• Survey.
• Data warehousing.
- Customer-to customer communications to monitor gain insight and knowledge to distinguish customers:
• Weblogs.
• Discussion forums.
• Observation.
- Challenges for CKM include:
• Translating and transferring knowledge into knowledge Tacit Explicit.
• Changes in organizational culture.
• Develop strategies KM.
Results CKM is a synergy of collaboration and increased value to customers by:
• Superior products and services.
• Facilitate the commitment and customer loyalty.
• Increase the innovation, development and growth of products and services.
3.5 Implementation success factor of Customer Knowledge Management :
2. Culture
Standard culture within an enterprise is an effective productivity time, respect each other, the same angle, and maintain a good two-way communication.
3. The structure, roles and responsibilities
CKM company that takes care of the organization should be composed of people who are clearly in the structure of its staff, so that they can be responsible for their jobdesk.
4. IT Infrastructure
IT standards used must have the content, appearance and standard technology used by the public, so that will be effective for all parties can terlinat well even from non-IT though.
5. Measurement
Companies must take measurements or valuation value if appropriate application of existing standards or not. Companies must find the best way in every procedure that takes place in order to grow optimally.
3.6 Five Types of Customer Knowledge Management
a. Communities Of Creation
Another approach is generally used by every company in managing customer knowledge management is to create a community of consumers of a product or brand.
b. Prosumerism
obtained is derived from the desire of every consumer and the results do not have to worry anymore, because the product is derived from consumers.
c. Mutual Innovation
Innovation on a product is created from the end user or consumer does not come from internal sources for consumers who feel the product so that they have a quality ideas according to their views. Companies can use this to make a new innovation in the market by working with consumers in expressing their thoughts on a product and accommodate all their desires.
d, Team-based co-Learning
In addition to a double play as noted above, consumers also can be part of a team for the company in order to improve the quality and consumer satisfaction. Companies can establish relationships with customers and opening up to all the information and knowledge that they have, and together with them to share knowledge to improve the performance of the company.
e. Joint Intellectual Property
The company created an idea among consumers that they are a part of the company. This can be done by working closely with customers and regard themselves as belonging to the company is the consumer.
3.7 General Constraints faced in implementing Knowledge Management Customer
1. Inability organizational infrastructure and processes to deal with the use of knowledge of consumers. In managing customer knowledge, companies should look into the company's internal, what they have to support.
2. The issue of trust and protection are not sufficiently emphasized
consistently. Companies must look more closely at the background of every consumer that when applying the Customer Knowledge Management each party awake feelings.
3. Application of Customer Knowledge Management with the wrong mindset
Wrong thinking occurs when companies have thought that the Customer Knowledge Management is a tool to increase customer knowledge. This will be a barrier for the purpose of Customer Knowledge Management is to create value for consumers in the long run that will be beneficial to the development of the company's business. In managing the knowledge of consumers, companies also need to maintain the values and knowledge of their customers as partners rather than as a source of knowledge.
4. Dependence of the knowledge of the consumer
Companies should not depend on consumer knowledge alone but must perform data processing and further research on the knowledge possessed by consumers.
5. Diversity ignored customers
Often companies generalize perceptions and thoughts of the customers so that they only apply one or two Customer Knowledge Management approach for its customers and the result is what has been applied is not effective because people basically have thoughts and desires are different. Therefore, companies should not only look at the customer a general outline but should be grouped into categories that represent each of their thinking.
3.8 Competence of Customer Knowledge Management
Competence customer knowledge management can be divided into four sections:
1. Customer Information Process
of the customer to gain knowledge about customers who may include the need for a product or service.
2. Marketing-IT Interface
Marketing-IT interfaces lead to the marketing process and communicate information technology functions.
3. Senior Management Involvement
Senior management refers to the top management that supports the integration of customer knowledge within the company.
4. Employee & Evaluation System
Employee and evaluation system refers to the behavior of employees in line with the objectives of the company to produce and integrate customer knowledge in the company's marketing strategy.
CHAPTER 4
CONCLUSION and RECOMMENDATIONS
4.1 Conclusions
After analyzing this paper, the authors conclude some conclusions are as follows:
• CKM as a strong competitive potential, which contribute to the increased success of the company and their customers.
• CKM create new knowledge sharing platform and processes between companies and their customers.
• Sustainable strategy by which companies allow their customers to move from passive information sources and recipients of products and services to knowledge.
4.2 Suggestions
After analyzing this paper, the authors give some suggestion as follows:
• The company has more knowledge about the CKM so as to reduce misunderstandings.
Journals About Customer Knowledge Management
Definition of CKM according to Zhang (2011) in the journal entitled "Customer Knowledge Management and The Strategies of Social Software" is a process to capture, share, apply the data, information, and knowledge associated with the customer to benefit the company.
According Paquette (2006) quoted by God, Shahin, Tabanifar (2012) in the journal entitled "Analysis of Relationship between Knowledge Management and Customer Relationship Management with Customer Knowledge Management" Customer Knowledge is knowledge that is in the middle of the customer, not the knowledge of the customer itself, but rather a process to manage, identification, acquisition, and use of customer knowledge collectively referred to as Customer Knowledge Management.
According Sofianti, Suryadi, Govindaraju and Prihartono (2009) in the journal titled "Transformation of Customer Knowledge Management Through Social CRM "explains that the CKM described as an ongoing process for generating, disseminating and using customer knowledge within the company. CKM is understood as a holistic business model that is the result of the integration of some of the concepts, techniques, and methodologies related to each other and rooted in the people, processes, and technology, aimed at creating loyal and profitable customer (Al-Shammari, 2009: 19).
According to Gilbert (2003) and Bosch (2000) quoted by Nejatian, Sentosa and Piaralal (2011) in the journal entitled "The Influence of Customer Knowledge on CRM Performance of Malaysian ICT Companies: A Structural Equation Modeling Approach" says CK is a dynamic combination of customer, value and insight needed information, created, and absorbed during the process of the transaction and the exchange between the customer and the company.
According Ogunde et al. (2010) in the journal entitled "Towards an Agent-Based Customer Knowledge Management System (ABCKMS) in E-Commerce Organizations", CKM used to support knowledge between companies and customers to make the right decision.
Bibliography
Davenport, T. a. (1998). Working Knowledge : How Organization Manage What They Know. USA: Harvard Business School.
Gibbert M, L. M. (2002). Five Style of Customer Knowledge Management and How Smart Companies Use Them To Create Value. European Management Journal, 459-469.
Malhotra, Y. (1998). Knowledge Management Organization & Knowledge Workers : A View From the Front Line.
Rowley, J. (2002). Eight question for CKM in e-business. Journal of Knowledge Management, 500-511.
Tunggal, A. W. (2000). Konsep Dasar Customer Relationship Management. Jakarta: Heravindo.
Wilde, S. (2011). Customer Knowledge Management Improvement Customer Relationship Through Knowledge Aplication. Spinger.
Picture 2.1 Determinants of Customer Delivered Value
Picture 2.3 Model Concept of Customer Knowledge Management
Picture 2.4 Competence of Customer Knowledge Management
Classification of Knowledge
Easily Communicated ? Documented ?
Tacit No No
Explicit Yes Yes
Implicit Yes No