THE EFFECT OF TEACHING STRATEGIES AND COGNITIVE
STYLE ON READING COMPREHENSION
A THESIS
BY:
MERLIN HELENTINA NAPITUPULU Registration Number: 809115014
Submitted to the English Applied Linguistics Study Program in
Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of
Magister Humaniora
ENGLISH APPLIED LINGUISTICS STUDY PROGRAM
POSTGRADUATE SCHOOL
THE EFFECT OF TEACHING STRATEGIES AND COGNITIVE
STYLE ON READING COMPREHENSION
A THESIS
BY:
MERLIN HELENTINA NAPITUPULU Registration Number: 809115014
Submitted to the English Applied Linguistics Study Program in
Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of
Magister Humaniora
ENGLISH APPLIED LINGUISTICS STUDY PROGRAM
POSTGRADUATE SCHOOL
ABSTRACT
Napitupulu, Merlin Helentina. 890115014. The Effect of Teaching Strategies and Cognitive Style on Reading Comprehension. A Thesis. English Applied Linguistics Study Program. State University of Medan. 2013.
ABSTRAK
Napitupulu, Merlin Helentina. 890115014. The Effect of Teaching Strategies and Cognitive Style on Reading Comprehension. Thesis. Program Linguistik Terapan Bahasa Inggris. Universitas Negeri Medan. 2013.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
First of all, the writer would like to express her deepest gratitude to the Almighty God for his great blessing, mercy and guidance during the study at the English Applied Linguistics Study Program, Postgraduate School State University of Medan and the completion of this thesis.
In the process of writing this thesis, the writer has to confess that many people have given her support, care, attention and bright ideas. In this relation, she would like to express her special appreciation to Prof. Dr. Lince Sihombing, M.Pd., as her first adviser, for her strong support, comments, criticism and bright ideas in shaping up this thesis and Prof. Dr. Berlin Sibarani, M.Pd., her second adviser, for his understanding efforts and the valuable suggestions and correction.
She would like to give massive gratitude to the reviewers and examiners for the valuable inputs to be included in this thesis. She also writes to express thanks to all lecturers who have given her the valuable knowledge during her study at the English Applied Linguistics Study Program, Postgraduate School State University of Medan. The writer would like to thanks the Head of SMA Yayasan Perguruan Husni Thamrin Medan who has permitted her to conduct the research in SMA Yayasan Perguruan Mariana Napitupulu, S.Pd. who have given support and motivation during the process of writing this thesis.
Last but not least, her very special gratitude also goes to her close friends: Afdhalina, Asni Juliana, Linda Fitri Ibrahim, Linda Astuti Rangkuti and all friends who can not be further mentioned here for their kind friendship. May God bless them all.
Medan, June 5th, 2013 The writer
Table of Contents 1.1 Background of the Study ……….…………..1
1.2 Research Problems ………...……….…...6
1.3 The Objectives of the Study …………...……….………..6
1.4 The Scope of the Study ………...6
1.5 The Significances of the Study ………..……….….………..7
Chapter II: Review of Literature 2.1 Students’ Achievement on Reading Comprehension ……….………...8
2.2. Reading Comprehension ………...9
2.3 Types of Reading Process ………...12
2.4 The Factor Affecting Reading Comprehension ………..14
2.5 Levels of Reading Comprehension ………...18
2.6 Assessment of Reading Comprehension ………...20
2.7 Teaching Strategies ……….22
2.9 Relevant Studies ………..43
2.10 Conceptual Framework ………...45
2.10.1 The Effect of CSR and REAP Strategy on Reading Comprehension ………....………..45
2.10.2 The Effect of Reflective and Impulsive Cognitive Style on Reading Comprehension ………..………...46
2.10.3 The Interaction between Teaching Strategies and Cognitive Style on Reading Comprehension ……….………...47
3.4 The Instruments for Collecting Data ………...52
3.4.1 Reading Comprehension Test ………..52
3.4.2 Questionnaire of Cognitive Style ……….…53
3.5 Control of Treatment ………...55
3.5.1 Internal Validity ………...55
3.5.2 External validity ………...…56
3.6 Instrument Validation ……….….56
3.6.1 Validity of Reading Comprehension Test ………56
3.6.2 Validity of Questionnaire ………...58
3.7 Reliability ………....59
3.7.1 Reliability of Reading Comprehension Test ………60
3.7.2 Reliability of Questionnaire ………...60
3.8 The Procedure of Treatment ……….………...60
3.9 The Technique of Analyzing Data ………..63
Chapter IV: Data Analysis and Discussion
4.1 The Description of Research Data ……….………..65
4.2 Data Analysis ………..66
4.2.1 Students’ Reading Comprehension Achievement Taught by Using CSR Strategy ………...66
4.2.2 Students’ Reading Comprehension Achievement Taught by Using REAP Strategy ………..67
4.2.3 Students’ Reading Comprehension Achievement of Group of Students with Reflective Cognitive Style ………69
4.2.4 Students’ Reading Comprehension Achievement of Group of Students with Impulsive Cognitive Style ……….70
4.2.5 Students’ Reading Comprehension Achievement of Group of Students Taught by Using CSR Strategy with Reflective Cognitive Style ……….72
4.2.6 Students’ Reading Comprehension Achievement of Group of Students Taught by Using CSR Strategy with Impulsive Cognitive Style ……….73
4.2.7 Students’ Reading Comprehension Achievement of Group of Students Taught by Using REAP Strategy with Reflective Cognitive Style ……….75
4.2.8 Students’ Reading Comprehension Achievement of Group of Students Taught by Using REAP Strategy with Impulsive Cognitive Style ………...76
4.3 Analysis Requirement Testing ………78
4.3.1 Normality of the Test ………...78
4.3.2 Homogeneity Testing ………...79
4.3.2.1 Group of Teaching Strategies ………..………79
4.3.2.2 Group of Cognitive Styles …………...………79
4.3.2.3 Group of Interaction………..….………..80
4.4 Hypothesis Testing ………..80
4.5 Discussion ………...87
4.5.2 The Differences between Cognitive Styles on the Students’
Achievement in Reading Comprehension ………89
4.5.3 The Interaction between Teaching Strategies and Cognitive Styles on the Students’ Achievement in Reading Comprehension ……….91
4.6 Research Limitation ………91
Chapter V: Conclusions and Suggestions 5.1 Conclusions ………...92
5.2 Suggestions ……….……….92
References ...94
LIST OF TABLES
Page Table 1. Reading Comprehension Score of X Grade Level Students
of Y.P Husni Thamrin Senior High School Medan………..…..……….3
Table 2. The Graphic Chart of REAP Strategy ………...30
Table 3. The Strengths between Collaborative Strategic Reading and REAP Strategy ………...33
Table 4. The Weaknesses of Collaborative Strategic Reading and REAP Strategy …….………..…....34
Table 5. Comparison of Reflective Cognitive Style and Impulsive Cognitive Style ……….……….……42
Table 6. Factorial Research Design 2X2 ……….….…...50
Table 7. Table of Specification Reading Comprehension Test ………...53
Table 8. The Validity Reading Comprehension Test Result ………..…………57
Table 9. The Validity Cognitive Style Result ……….58
Table 10. Reliability of Reading Comprehension Test Result ………..…..60
Table 11. Reliability of Cognitive Style Result ……….……….60
Table 12. The Procedure of Treatment in the Two Groups …….………..…..61
Table 13. The Procedure of Treatment in the Two Groups ……….……….…...62
Table 14. Summary of Research Data Description ……….………….…...65
Table 15. Data Distribution of Students’ Reading Comprehension Taught by Using CSR Strategy ……….………….…...66
Table 16. Frequency Distribution of the Scores of Students Taught by Using CSR Strategy ……….………..………..66
Table 17. Data Distribution of Students’ Reading Comprehension Taught by Using REAP Strategy ……….………..………...67
Table 19. Data Distribution of Students’ Reading Comprehension Achievement
of Group of Students with Reflective Cognitive Style …..………...69
Table 20. Frequency Distribution of the Scores of Students with Reflective Cognitive Style ……….…...69
Table 21. Data Distribution of Students’ Reading Comprehension Achievement of Group of Students with Impulsive Cognitive Style ………70
Table 22. Frequency Distribution of the Scores of Students with Impulsive Cognitive Style ………71
Table 23. Descriptive Statistics of Students’ Reading Comprehension Taught by Using CSR Strategy with Reflective Cognitive Style ………72
Table 24. Frequency Distribution of the Scores of Students Taught by Using CSR Strategy with Reflective Cognitive Style ………....72
Table 25. Descriptive Statistics of Students’ Reading Comprehension Taught by Using CSR Strategy with Impulsive Cognitive Style ………....73
Table 26. Frequency Distribution of the Scores of Students Taught by Using CSR Strategy with Impulsive Cognitive Style ………....74
Table 27. Descriptive Statistics of Students’ Reading Comprehension Taught by Using REAP Strategy with Reflective Cognitive Style ………...……..75
Table 28. Frequency Distribution of the Scores of Students Taught by Using REAP Strategy with Reflective Cognitive Style ………...…………..75
Table 29. Descriptive Statistics of Students’ Reading Comprehension Taught by Using REAP Strategy with Impulsive Cognitive Style ………..76
Table 30. Frequency Distribution of the Scores of Students Taught by Using REAP Strategy with Impulsive Cognitive Style ……….77
Table 31. Summary of the Result of Normality Testing ...78
Table 32. Result of Homogeneity Testing of Teaching Strategies ………..………...79
Table 33. Result of Homogeneity Testing of Cognitive Styles ………...…79
Table 34. The Result of Homogeneity Testing of Group Interaction ……….80
Table 35. Result Summary of Research Data ………81
Table 36. ANOVA Testing Result ……….81
LIST OF FIGURES
Page
Figure 1. Histogram on Students’ Reading Comprehension Achievement
Taught by Using CSR Strategy ……….……67 Figure 2. Histogram on Students’ Reading Comprehension Achievement
Taught by Using REAP Strategy ……….……...68 Figure 3. Histogram on Students’ Reading Comprehension Achievement
of Group of Students with Reflective Cognitive Style ………….…………70 Figure 4. Histogram on Students’ Reading Comprehension Achievement
With Impulsive Cognitive Style ………...……….…...71 Figure 5. Histogram on Students’ Reading Comprehension Achievement
Taught by Using CSR Strategy with Reflective Cognitive Style …………73 Figure 6. Histogram on Students’ Reading Comprehension Achievement
Taught by Using CSR Strategy with Impulsive Cognitive Style…..…...74 Figure 7. Histogram on Students’ Reading Comprehension Achievement
Taught by Using REAP Strategy with Reflective Cognitive Style .……….76 Figure 8. Histogram on Students’ Reading Comprehension Achievement
LIST OF APPENDICES
Page
Appendix A. Reading Comprehension Test ……….97
Appendix B. Questionnaire ……….………104
Appendix C. The Validity of Reading Comprehension Test ………..105
Appendix D. The Output of Test Validity Result ………...107
Appendix E. The Validity Test Result and Reliability of Reading Comprehension Test ………..116
Appendix F. The Validity of Cognitive Style Questionnaire ……….118
Appendix G. The Output of Questionnaire Validity Result ………...119
Appendix H. The Validity and Reliability Result of Cognitive Style Questionnaire ………...120
Appendix I. Tabulation of Research Data ……….121
Appendix J. Summary of Research Data ………...123
Appendix K. Description of Students’ Score ………..124
Appendix L. Normality Test ………...126
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
1.1 Background of the Study
Reading is one great habit that can truly change the life forever. Reading can entertain and enrich people with knowledge – the only thing that does not decay with time. Reading used as a means of communication, sharing information and ideas. Like all languages, it is a complex interaction between the text and reader which is shaped by the reader’s prior knowledge, experiences, attitude, and language community which is culturally and socially situated.
Reading is used as the foundation of all knowledge and the foundation for a proper education. Good reading can be helpful to obtain the current information as it is necessary. Then, reading as one of four language skills has big roles in learning and teaching at school. It is supported by Brown (2000:185) who states that reading is arguable and the most essential skill for success in all educational contexts and remains a skill paramount importance as one creates assessment of language ability. Students need to be able to learn from their reading. The successful reading performance is a strong predictor of students’ academic performance. By giving the students reading instruction, it means that giving the students a prospective future to explore the knowledge.
2
reading actually is. Although strong reading skills can help the students well in language arts and reading class, that is only the beginning.
The students have to use reading skills in every single subject they ever study and in almost every aspect of life. For example, the students need to comprehend challenging science textbooks as well as directions and word problems on texts. The students who struggle with reading comprehension may fall so far behind in school that they have limited opportunities as an adult, as reading is not as simple as what most people think. Many times when people asked, what they have already comprehended from their readings, they cannot explain it precisely.
Reading comprehension is characterized as an active process of comprehending. Since information, knowledge, science and technology can be obtained from the internet, books, articles, and other reading materials in order to improving the students’ reading skill. Reading comprehension are influenced by reading material, child’s own personality, attitudes, interest, motivation, cognitive style, self-efficacy, habit, environment and another factors.
In the 2006 Educational Unit Level Curriculum (Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan Pendidikan : KTSP) of Senior High School, reading is regarded as the backbone of other language skills. It is clearly stated that through reading students can develop other language skills such as writing and speaking. The students of Senior High School are expected to be able to comprehend the short functional text and simple essay such as in report, narrative, and analytical exposition in their daily lives context and the students can also grasp information and improve their knowledge.
3
information appropriately. Consequently, students will need to read the text two or three times to comprehend the text well.
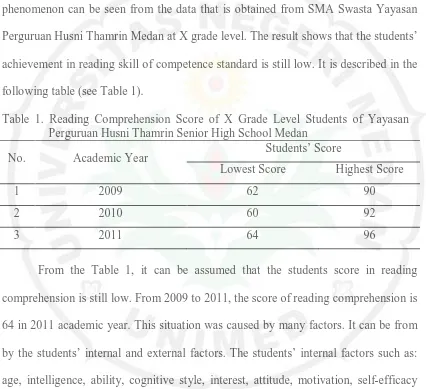
In such case, students still fail in comprehending the reading text. The phenomenon can be seen from the data that is obtained from SMA Swasta Yayasan Perguruan Husni Thamrin Medan at X grade level. The result shows that the students’ achievement in reading skill of competence standard is still low. It is described in the following table (see Table 1).
Table 1. Reading Comprehension Score of X Grade Level Students of Yayasan Perguruan Husni Thamrin Senior High School Medan
No. Academic Year Students’ Score
Lowest Score Highest Score
1 2009 62 90
2 2010 60 92
3 2011 64 96
From the Table 1, it can be assumed that the students score in reading comprehension is still low. From 2009 to 2011, the score of reading comprehension is 64 in 2011 academic year. This situation was caused by many factors. It can be from by the students’ internal and external factors. The students’ internal factors such as: age, intelligence, ability, cognitive style, interest, attitude, motivation, self-efficacy and other factors. The external factors include teachers, environment, materials, strategy and other factors.
4
McNamara (2007:6) defines reading comprehension strategy as a cognitive or behavioral action that is enacted under particular contextual conditions, with the goal of improving some aspect of comprehension. It means that the successful readers know when and how to use deliberate strategy to repair comprehension.
There is a great evidence of the importance of reading strategy. The implication is that teaching reading strategy to struggling readers may be a key toward helping them to improve comprehension. As a teacher, we may need to improve the quality of teaching process in the classroom. The teaching-learning process will be interesting if the students are active in responding the teacher’s stimuli. It can be done by offering some strategies that force them to participate in the classroom. In this study, the researcher applies two strategies that have been done successfully by some linguist experts to be applied to improve students’ reading comprehension, they are: REAP Strategy and Collaborative Strategic Reading.
The first strategy is Collaborative Strategic Reading (CSR) strategy. CSR as one strategy to that have function to make the students understand how to comprehend the text. CSR strategy consists of a set of strategy designed to enhance students’ understanding of text. Collaborative Strategic Reading applies four basic strategies to assist their comprehension: making predictions prior to reading (preview strategy), monitoring reading and learning to enhance vocabulary development (click and clunk strategy), identifying main ideas (get-the-gist strategy), and summarizing key ideas. The purpose of this strategy is to teach students to focus on the main ideas that emerged from the text and to assist with comprehension.
5
allows students to visually organize the information as they follow the stages of reading. The students can see the strategy in action. They will internalize the stages of reading. The teachers should use this strategy because REAP supports increased comprehension. Because the students revisit the text for each of the stages of REAP, students will internalize the content of reading. They have to think about putting the main idea in their own words.
In the process of teaching and learning, it is not enough by applying some strategies, to improve the quality of teaching process in the classroom it is very important to include the students’ internal factors, such as cognitive style. Every student has different cognitive style to comprehend the text. It suggests that the teachers might help the students' cognitive style as the manner by which individuals perceive information in the environment and the patterns of thought that they use to develop a knowledge base about the world around them.
6
1.2 Research Problems
This research is aimed at answering the following research problems.
1. Is the students’ achievement on reading comprehension taught by using CSR Strategy higher than that of taught by using REAP Strategy?
2. Is students’ achievement on reading comprehension for reflective cognitive style higher than that of impulsive cognitive style?
3. Is there any interaction between teaching strategy and cognitive styles in students’ achievement on reading comprehension?
1.3 The Objectives of the Study
In carrying out the research, it is necessary to state the objectives of the study clearly. So, the objectives of this study are:
1) if the students’ achievement on reading comprehension taught by using CSR Strategy is higher than that of taught by using REAP Strategy,
2) if students’ reading comprehension achievement of reflective cognitive style is higher than students’ reading comprehension achievement of impulsive cognitive style, and
3) if there is interaction between teaching strategy and cognitive styles on students’ achievement on reading comprehension.
1.4 The Scope of the Study
7
expected to give clearer description on the effect of teaching strategies and cognitive styles in students’ achievement on reading comprehension.
1.5 The Significances of the Study
The findings of the study are expected to be useful theoretically and practically. Theoretically the findings are expected:
1) to be the input for the teachers and educational institutions,
2) to enrich the researcher’s knowledge who are interested in research especially related to English teaching strategy in Senior High School,
3) to give a lot of contribution to improve the teachers’ capability in teaching, the educational institutions and other researchers who want to apply the teaching strategies.
Practically, the findings are expected:
1) to inform the teachers to decide which strategy is more effective to develop and improve the students’ reading comprehension,
2) to provide a solution to the problems that faced by the students in comprehending a text during the reading process,
3) to improve the students’ ability on reading comprehension to the higher level of reading comprehension skill.
92
CHAPTER V
CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS
5.1 Conclusions
Based on the research finding and discussion, the conclusion can be drawn as follows:
1. The students’ reading comprehension achievement taught by using CSR strategy is higher than that of students taught by using REAP strategy.
2. The students’ reading comprehension achievement with reflective cognitive style is higher than that of the students with impulsive cognitive style.
3. There is significant interaction between the teaching strategies and cognitive styles on students’ achievement in reading comprehension.
5.2 Suggestions
In connection with the conclusions, there are some suggestions stated as the following:
1. English teachers are recommended to use CSR and REAP strategies in teaching reading comprehension because these two strategies can improve the students’ achievement on reading comprehension. In addition, teachers should recognize the students’ cognitive styles of each student when they are applying the strategies in teaching.
93
3. Other researchers may take a further research in the area of CSR and REAP strategies that can be used to improve students’ achievement on reading comprehension.
94
REFERENCES
Alderson, J. C. 2000. Assessing Reading. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Alexander.1988. Teaching Reading 3rd Ed., Boston: Foresman Inc.
Allen, Janet. 2004. Tools for Teaching Content Literacy. Portland, Maine: Stenhouse Publishers.
Anderson & Krathwohl. 2001. A Taxonomy for Learning, Teaching, and Assessing.
New York: Longman.
Ary, D. 2011. Introduction to Research in Education 8th Ed., USA: Wardsworth.
Brassel, et all. 2008. Comprehension that Works. Oceanus Drive Huntington Beach: Shell Education.
Bromley, K. D. 1985. Precise Writing and Outlining Enhance Content Learning. Reading Teacher Journal, 38, 406-411.
Brooks, et all. 2004. Adult Reading Test. London: Pearson Education
Brown, H. D. 2000. Principles of Language Learning and Teaching. New York: Longman.
Brown, H. D. 2004. Language Assessment: Principles and Classroom Practices. New York: Longman.
Carroll, J. B. 2000. The Analysis of Reading Instruction: Perspectives from Psychology
and Linguistics. Scientific Studies of Reading, 4, 3-17.
Danielle, S. 2007. Reading Comprehension Strategies: Theories, Interventions, and Technologies. New Jersey: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers.
Dornyei, Zoltan. 2005. The Psychology of the Language Learner, New Jersey: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers.
Felder, Richard M. 2005. Applications, Reliability, and Validity of the Index of
Learning Styles. International Journal of Engineering Education, 21, 103-112.
Fitri, A. 2010. The Effectiveness of Collaborative Strategic Reading (CSR) on the Reading Comprehension Achievement of the Fourth Semester Students of PGSD Suryalaya. West Java: Malang Digital Library.
Grabe, W and F. Stoler. 2002. Teaching and Researching Reading. Harlow: Pearson Education.
Grabe, William. 2009. Reading in a Second Language: Moving from Theory to Practice. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Imtiaz, S. 2004. Metacognitive Strategies of Reading Among ESL Learners. South Asian Language Review Journal, 14, 34-43.
95
Klinger, Vaughn, et all. 2000. Collaborative Strategic Reading during Social Studies in
Heterogeneous Fourth Grade Classroom. Longmont, Co: Sopris West.
Klingner, Vaughn, et all. 2001. From Clunk to Click: Collaborative Strategic Reading.
Longmont, Co: Sopris West.
Klingner, Vaughn, et all. 2004. Collaborative Strategic Reading: “Real World” Lessons from Classroom Teachers. Special Education, 25, 291-302.
Hannu, K., & Pallab, P. 2002. A Comparison of Concurrent and Retrospective Verbal Protocol Analysis. American Journal of Psychology, 113,387-404.
Ibrahim, Linda Fitri. 2011. The Effect of Instructional Strategies and Self Efficacy on Students’ Achievement in Reading Comprehension. (Unpublished Thesis). Postgraduate School UNIMED , Medan.
Louise, Spear-Swerling. 2006. Assessment of Reading Comprehension. Retrieved: http://www.Idonline.org./spearswerling/Assessment of Reading Comprehension July 2nd 2011.
Manzo, R. 1978. Expansion Models for the ReQuest, CAT, GRP, and REAP: Reading/Study Procedures. Journal of Reading, 28, 498-503.
Marzano, R. J. (2000). Designing a New Taxonomy of Educational Objectives. Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press.
McNeil. 1992. Reading Comprehension New Directions for Classroom Practice. Los Angeles: University of California.
McNamara, Danielle,S. 2007. Reading Comprehension Strategies. New Jersey: Lawrence Associaties, Inc., Publisher
Messick, S. 1984. The Nature of Cognitive Styles: Problems and Promise in Educational
Practice. Educational Psychologist Journal, 2, 59- 74.
Nohenriady 2011. Using Collaborative Strategic Reading (CSR) to Improve the Eighth
Graders' Reading Comprehension at MTsN Sungai Pandan South
Kalimantan.Thesis (Online). Downloaded on 16th June 2012.
Novita, Dian. 2011. The Effectiveness of Collaborative Strategic Reading (CSR) for Teaching Reading Comprehension at Muhammadiyah University of Sidoarjo. (Unpublished Thesis). Universitas Muhammadiyah Sidoarjo.
Nuttal. 1996. Teaching Reading Skills in a Foreign Language. Bath: Heinemann.
Palmquist, R. A. 2001. Cognitive Style and Users’ Metaphors for the Web. New York: International University Press.
Paran, A. 1996. Reading in EFL: Facts and Fiction. London: Prentice Hall.
Pranita, Novia. 2009. The Effect of REAP Strategy to Comprehend Reading Text of the
96
Piaget, M. 1982. Constructive Aspects of Learners’ Comprehension and Memory. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates
Rahmah, Nur. 2011. The Effect of Teaching Strategies and students’ Achievement in Reading
Comprehension. (Unpublished Thesis). Postgraduate School Unimed, Medan.
Ramayani. 2011. The Effect of Teaching Techniques and Curiosity on Students Achievement in Reading Comprehension. (Unpublished Thesis). Postgraduate School Unimed, Medan.
Samuel, S. 2004. Theoretical Models and Processes of Reading. Newark:
International Reading Association.
Smith, C. C. and Bean, T. W. (1980). The Guided Writing Procedure: Integrating Content Reading and Writing Improvement. Reading Teacher Journal, 29, 220-294.
Smith, Frank. 2004. Understanding Reading. London: Lawrence Elburn Associates Publisher.
Spielberger, Charles. 2002. Encyclopedia of Applied Psychology. Florida: Elsevier Academic Press.
Strode, S.L. 1993. An Adaptation of REAP for the Developmental Reader. Journal of Reading, 36, 568-569.
Suhermannsyah. 2012. The Effect of Teaching Strategies and Intrinsic Motivation on Students’ Achievement in Reading Comprehension. (Unpublished Thesis). Postgraduate School Unimed, Medan
Wang, T.H. 2008. The Effect of Modified Collaborative Strategic Reading on EFL Learners’ Reading Comprehension. Changhua: National Changhua University of Education.
Weir. 1990. Communicative Language Testing. London: Prentice Hall.
Witkin, H.A., et all. 1977. Cognitive Styles and Their Education Implications. Review of