Makalah :
International Conference On Educational Research And Innovation (ICERI 2014) Yogyakarta State University, 7 – 8 May 2014
The Local Government Policies In Reducing The Cost of The Nine Year
Compulsory Education Program In Salatiga - Indonesia
Bambang Ismanto [email protected]
Satya Wacana Christian University - Salatiga - Indonesia
Abstract
This study aims to identify policy on Salatiga city in improving budget allocation in solving the problem of shortage of school operating costs. The study was conducted according to the procedures of qualitative approach on policy research. The Subjects of research were Walikota, The head of Parliament, office of education, regional planning agencies, regional Inspectorate, principals, school supervisors, parents, and school committees. Research data collection is done by the study of the documentation of the budget for education and schools, depth interviews, and FGD. Research shows, the education budget (2012) has allocated approximately 35.31% and in 2013 increased by 38.44 % of the total budget. In 2013, based on research on education office, the average operating cost at the elementary school /SD as much as 774 065 (IDR) and junior high schools / SMP as 1354.615 (IDR). While the operating cost assistance to students from the central government for SD as much as 580,000 and SMP as 710,000. While the operating cost assistance / BOS to students from the Central Java Province for student of SD as 710,000 and SMP as 50,000. To reduce the costs to be paid students, government assistance allocate operating costs / BOS to students for up to 48,000 and SMP 175,000. This study concluded that the nine year compulsory education in cities Salatiga not free. The operational costs of the entire aid school, every student of SD still have to pay as much as 116 065 (IDR) and SMP 419 615 (IDR)/year.
Keywords: The nine year compulsory education, reduction, school operating cost
Introduction
Education contributes to the development of the nation. according to Schultz (1963), the outcomes of education may be classified into two categories : consumption and investment. The consumption aspect is relatedto the joy, pleasure, and similar benefits derived by students, their families, and societyas a whole. The investment component includes a variety of outputs are related to the enhancement of an individual’s or society’s producive skills and future well -being (Cohn : 179: 168).
The Law Number 20 Year 2003 states that education means conscious and well-planned effort in creating a learning environment and learning process so that learners will be able to develop their full potential for acquiring spiritual and
religious strengths, develop self-control, personality, intelligence, morals and noble character and skills that one needs for him/herself, for the community, for the nation, and for the State. Law Number 20 Year 2003 on the National Education System is perceived as the legal basis of democratization of education in Indonesia (Firman : 2008: 82). The education reforms in Indonesia were determined by the enactment of Law Number 20 Year 2003 on the National Education System as the legal framework for the development of education. The Law guarantees that students in the basic education program are free from any fees in order to facilitate easier access to education.
article 34 of law 20 of 2003 on the National Education System, it is stated that ‘The central government and local governments shall guarantee the implementation of compulsory basic education at least to the level of basic education without charging any fees’. To fulfil this mandate, the Indonesian government emphasises the implementation of the compulsory basic education program for all children. This is also in line with the international agreement on the Millennium Development Goals (MDG), which has as a goal that all children by 2015, wherever, men and women, can complete their basic education.
Compulsory nine-year basic education is a constitutional mandate that needs to be guarded together. Government, family, and community need to synergise. Thus, compulsory basic education involves various parties: government agencies and non-government institutions, and community groups. The national goals can be achieved, but there are still small areas that will present difficulties in achieving completion, either because of geographic, social, economic, or cultural barriers. (Handayani : 2009:201)
Decentralization of education is an opportunity Salatiga government in formulating policies that can enhance the quality and competitiveness of human resources. More than 35 years on the New Order government, education is centralized planned and budgeted. This resulted education programs can not solve the problems of education in the local government.
The two legal pillars of regional autonomy are: (i) Law 32/2004 on Regional Governance, which focuses on administrative and political decentralization and includes the guiding references to the devolution of expenditure responsibilities; and (ii) Law 33/2004 on Fiscal Balance governing the distribution of resources across regions. (Usaid:2007:2). In addition, there are four
organic laws which govern planning and budgeting, accounting and financial reporting, treasury and audit for local governments in the decentralization era: Law 17/2003 on State Finances provides the legal framework for a unified budget; Law 1/2004 on State Treasury prescribes a variety of financial management functions; Law 15/2004 provides for the audit of all governmental units; and Law 25/2004 on developmental planning sets out the authorities and responsibilities for various local government officials related to planning. In all, there are at least 5 laws, 9 government regulations, 5 presidential decrees, and 22 ministerial decrees that impact more or less directly on issues of planning, budgeting, accounting, financial reporting and accountability for local governments in Indonesia.
Decentralization of education is the implication of regional autonomy in Indonesia that began in 2001. Decentralization of education at the unit level of education / school based management is implemented in the school . Principal with the School Committee and stakeholders have the opportunity to optimize resources in achieving the vision , mission and goals. Resource management is done based on the principles of good governance include participation, transparency, and accountability (Ismanto:2014:462).
The limited resources of the central government, provincial and local, carries implications participation ( public ) in the planning, implementation, monitoring budgets and school education in the city of Salatiga. At the planning stage, the community participated in the preparation of the school budget, the education department budget, the budget discussion in Parliament (Ismanto:2014:464).
Method
The study was conducted by qualitative descriptive approach. The Subjects of research were Walikota, The head of Parliament, office of education, regional planning agencies, regional Inspectorate, principals, school supervisors, parents, and school committees. Research data collection is done by the study of the documentation of the budget for education and schools, depth interviews, and FGD. This research is also supported by the analysis of quantitative data on participation in education, the unit cost of education, education budget and school operational assistance.
Finding and Discussion
Salatiga has a natural strength in the formation of regional competitiveness, namely: are at the crossing of goods transportation in Central Java Province corresponding to Salatiga function as a city of trade and services, supported by agricultural production and industrial precincts. While the services sector education industry is growing rapidly as a result of the large number of schools and colleges.
Vision Development of Salatiga (2011-2016) is: " Salatiga yang Sejahtera, Mandiri dan Bermartabat ", abbreviated as SMART. Vision Salatiga on putting people at the same time as the subject and object of development. In this case the local Government acts as a facilitator and
dynamist development. The vision set out a public desire Salatiga, which focused on the main issues and problems in the area, so the government and regional development can be done effectively, efficiently and sustainably, and to guarantee the existence of regions in the future.
Education is a priority in the mission of the Basic Needs Fulfillment in the medium term development of Salatiga. Preferred education program is improving the quality of education at all levels, development of educational facilities, the availability of quality educational services and equitable access to education, and the availability of scholarships for disadvantaged students, while other development priorities are the health and development of small and medium enterprises.
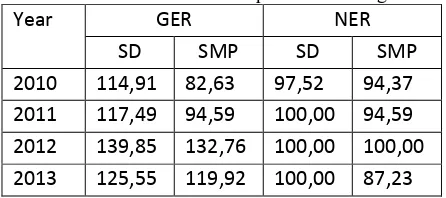
The success of primary education development in Salatiga indicated by an increase in enrollment rates and HDI. Average gross enrollment ratio (2010-2013) SD = 124.45% and SMP =107.45%.
Table 1. Education Participation in Salatiga
Year GER NER
Source : Department of Education, Youth and Sports
budget exists and the amount of the education budget allocation of Salatiga
Table 2. Local Government Education Budget in Salatiga Year Local Budget –
APBD ( IDR )
Education Budget %
2009 485.111.548.463 127.850.990.000 26,35 2010 403.923.537.000 121.848.850.000 30,16 2011 477.422.922.676 177.438.788.000 37,17 2012 571.682.186.000 196.001.367.000 34,28 2013 639.359.500.000 245.796.581.000 38,44 Source : Department of Education, Youth and Sports
According to the National Education Standard Agency, unit operating costs of education, the elementary school is 774.065, and the junior is 1354615. Central Government support operational costs through BOS was 580,000 at the elementary and junior high was 710,000. While the Central Java province adds BOS for elementary students is 30,000 and the junior was 50,000. In this scheme, primary school students still have to pay 173 791. While the junior high school students have to pay 199 409. Local government and BOS central government, provincial and central java salatiga boss received the total elementary school students is 658,000. while the junior high school students is 935 000. thus, the implementation of compulsory education, students pay up to 116 065 and junior high school have to pay.419 615 per students.
Disadvantages cost of basic education is the responsibility of society. This is in accordance with Government Regulation No. 48 of 2008 which states that education funding from the Government, local governments and communities. This is the implication of the conception that education investment will benefit the state and the individual and society. Although it is the duty of primary education. however, education was not free. decentralization of education as an opportunity for local
governments and communities in a participatory manner to improve the quality and competitiveness of human resources through education.
Conclusions
education is a shared responsibility of the central government, local governments and communities. In realizing the priority of access to basic education, the local government of salatiga provide additional BOS to elementary and junior high school students. Limitations of the sources of revenue in the budget as a problem to free of charge on the nine-year compulsory Budgeting, Volume 2009/2, ISSN 1608-7143
Cohn, Elchanan., (1979). The economics of education. Revised Edn., Massachusetts: A Subsidiary of Harper & Row Publisher, Inc.
Firman, Harry and Burhanuddin Tola, 2008, The Future of Schooling in Indonesia, CICE Hiroshima University, Journal of International Cooperation in Education, Vol.11 No.1 (2008) pp.71- 84
Handayani, Titik, Soewartoyo and Makmuri Sukarno, 2009,
Ismanto, Bambang, (2012), Financing education in community empowerment implementation the 12 year compulsory education in the District / City of Central Java Province, International Seminar Be Leading Entity In Education (Proceeding),
Faculty of Teacher Training and
Education, Satya Wacana Christian
University, Salatiga, Indonesia, June 27 th
– 28 th 2012
---, 2014, Public Participation in Budget Management School in Salatiga of Central Java Province, Indonesia, Proceedings Book of ICETSR, 2014, Malaysia Handbook on the Emerging Trends in Scientific Research ISBN: 978-969-9347-16-0
Good Governance Brief, Local
Government Financial Management Reform in Indonesia Challenges and Opportunities, No. 3 , September 2007
Psacharopoulos, George, 1987, Economics of Education, Research and Studies, Fergamon Book, Ltd, United of Kingdom