THE USE OF REFLECTION TO ENHANCE ELESP
STUDENTS’ SELF
-AWARENESS IN LEARNING
STRUCTURE II
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Rosa Faras Trisnasih Irianto
Student Number: 121214074
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
i
THE USE OF REFLECTION TO ENHANCE ELESP
STUDENTS’ SELF
-AWARENESS IN LEARNING
STRUCTURE II
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Rosa Faras Trisnasih Irianto
Student Number: 121214074
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
iv
“Keep your
thoughts
positive because your thoughts become your words.
Keep your words positive because your words become your behaviors.
Keep your behaviors
positive because your behaviors become your habits.
Keep your habits
positive because your habits become your values.
Keep your values positive because your values become your
destiny
.”
-Mahatma Gandhi-
I dedicate this thesis to
My Parents,
My Family,
vii
ABSTRACT
Irianto, Rosa F. T. 2016. The Use of Reflection to Enhance ELESP Students’ Self
Awareness in Learning Structure II. English Language Education Study Program,
Departement of Language and Arts Education, Faculty of Teachers Training and Education, Yogyakarta: Sanata Dharma University.
This study analyzed the use of reflection to enhance students’ self-awareness in learning Structure II. Reflection is aimed at helping the students to consider events that have occurred in the past and then use that evidence to enhance the learning situation in the future (Gibson, 2012). Reflection allows the students to learn more
about students’ own selves, so the students can take responsibilities to their learning and engage in the learning process. In this study, the researcher was interested in employing reflection in Structure II course because the students are not accustomed to writing a reflection in courses which have rules like grammar. This can help the students to understand their level in learning Structure II and raise their awareness of improving their learning. As such, in this study, there is one research question to be answered: How did the students’ reflections enhance their self-awareness in learning Structure II?
This study employs qualitative research methodology. The researcher used reflection and interview as data gathering techniques to answer the research question. In addition, the data gathered were analyzed by using the analytic five-phase cycle data analysis by Yin (2011) to answer the research question. The participants of this study were three students of the English Language Education Study Program (ELESP), Sanata Dharma University who received a ‘D’ score in the previous course in academic year 2015/2016.
The findings showed that the reflections could enhance students’ self -awareness in learning Structure II. All of the students proved that reflections helped them to raise their awareness of the problems they faced in learning Structure and the importance of problem solving strategies. Moreover, reflections increase students’ awareness of their intrinsic motivation to learn structure and reflect their feelings in learning.
viii ABSTRAK
Irianto, Rosa F. T. 2016. The Use of Reflection to Enhance ELESP Students’ Self
Awareness in Learning Structure II. English Language Education Study Program,
Departement of Language and Arts Education, Faculty of Teachers Training and Education, Yogyakarta: Sanata Dharma University.
Penelitian ini meneliti tentang penggunaan refleksi untuk meningkatkan kesadaran diri siswa dalam belajar Structure II. Refleksi bertujuan untuk membantu siswa untuk menilik kembali kejadian di masa lalu dan menjadikannya bukti untuk meingkatkan pembelajaran di masa mendatang (Gibson, 2012). Refleksi membuat siswa belajar tentang dirinya sendiri, maka siswa dapat bertanggungjawab pada pembelajaran mereka dan terlibat di dalam proses belajar. Penelitian ini, peneliti tertarik untuk menggunakan refleksi pada matakuliah Structure II karena siswa tidak terbiasa menggunakan refleksi dalam matakuliah yang menerapan peraturan seperti tata bahasa. Ini dapat membantu siswa untuk mengerti level mereka dalam memahami Structure II dan meningkatkan kesadaraan mereka dalam memperbaiki cara belajar mereka. Seperti dalam penelitian ini, terdapat sebuah rumusan masalah yang akan dijawab yaitu: Bagaimana penggunaan refleksi siswa dapat meningkatkan kesadaran diri mereka dalam mempelajari Structure II.
Penelitian ini menggunakan penelitian kualitatif sebagai metode. Peneliti menggunakan refleksi dan wawancara sebagai teknik pengumpulan data. Lalu, data yang sudah terkumpul dianalisa menggunakan analiytic five-phase oleh Yin (2011) untuk menjawab rumusan masalah. Peserta dalam penelitian ini adalah tiga siswa dari Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma yang mendapat nilai D pada matakuliah prasyarat dari matakuliah Structure II tahun pelajaran 2015/2016.
Hasil penelitian menunjukan bahwa refleksi dapat meningkatkan kesadaran diri siswa dalam belajar Structure II. Semua siswa menunjukkan bahwa refleksi membantu mereka dlm meningkatkan kesadaran siswa terhadap masalah yang mereka alami dalam mempelajari Structure dan pentingnya strategi penyelesaian masalah. Selain itu, refleksi dapat meningkatkan kesadaran siswa terhadap motivasi intrinsik yang mereka miliki dan merefleksikan perasaan mereka dalam belajar
Structure.
ix
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
I would like to thank Jesus Christ for always giving me endless blessing,
everlasting love and strengths. I know that I am nothing without His help and
blessings. I believe that He has provided great plans for my future.
My deepest gratitude goes to my beloved advisor, Veronica Triprihatmini,
M.Hum., M.A.for her willingness to spend her time reading and correcting my thesis.
Her guidance in the process of finishing this thesis and her recommendations on what
I had to do in order to accomplish this thesis made me confident that I could
accomplish this thesis when I started doubting my ability.
I would also like to express my sincere thankfulness to all the lecturers and
staff who have given me great time during my study and great experience for me to
remember. My gratitude also goes to the participants, for their cooperation and
willingness in helping me obtain the data.
My special regards and gratitude are presented to my beloved parents, R.B
Isnan Irianto and T. Enggar Sriasih, for their prayers, support, love and
encouragement. I would also like to express my gratitude to my brother and sister.
My special gratitude is also sent to Vita, Dita, Ejin, Ajeng and Indras for
their patience in accompanying and supporting me, and helping me to proofread my
thesis in their precious time. I would also like to give my special gratitude to Pak
x
I would like to thank my partner in my life, Rizky, as the one who always
supports and cheers me up. Then, I thank my friends in class small C for being a
great family during my study in Yogyakarta.
Last but not least, I thank the people whose names I cannot write down on this
paper. I wish them all the best.
xi
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE PAGE……….………..… i
APPROVAL PAGES……….……. ii
DEDICATION PAGE……….…... iv
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY……….…. v
PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI……….….. vi
ABSTRACT……….... vii
ABSTRAK……….…... viii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS……….... ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS……… xi
LIST OF TABLE………. xiii
LIST OF FIGURES..………... xiv
LIST OF APPENDICES………. xv
CHAPTER I. INTRODUCTION….……….…... 1
A. Research Background………... 1
B. Research Problems………... 3
C. Problem Limitation………... 4
D. Research Objectives………....……... 4
E. Research Benefits………..………... 4
F. Definition of Terms………..……... 5
CHAPTER II. REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE... 7
A. Theoretical Description………..…….……... 7
1. Review of Related Research……….…….. 7
2. Reflection……….…... 9
xii
b. The Process of Reflection….……….……. 10
2. Self-awareness………. 13
B. Theoretical Framework……….……... 16
CHAPTER III. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY…..………... 18
A. Research Method………..…... 18
B. Research Setting……….……….…. 20
C. Research Participants……….………..………. 21
D. Research Instruments & Data Gathering technique ………... 21
E. Data Analysis Technique……….. 24
F. Research Procedure……...………... 26
CHAPTER IV. RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION... 28
A. The Reflections Raise Students’ Awareness of the Problems They Faced in Learning Structure……….………... 28
B. The reflections raise students’ awareness of the importance of problem solving strategies in learning Structure……… 34
C. The reflections Increased Students’ Awareness of Their Intrinsic Motivation to Learn Structure………. 41
D. The reflection increased students’ awareness of reflecting their Feelings……… 44
CHAPTER V. CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS... 49
A. Conclusion.……….………...…... 49
B. Recommendations……….……….………...….... 50
REFERENCES……….…... 52
xiii
LIST OF TABLE
Table Page
xiv
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure Page
2.1 A Model of Reflection in the Learning Process……….….… 11
xv
LIST OF APPENDICES
Appendix A. Consent Form ...………...…… 56
Appendix B. Self-reflection Blueprint………..……….……… 57
Appendix C. Sample of Self-reflection ……….… 59
Appendix D. Sample of Disassembled Data..……… 61
Appendix E. Themes and Significant Statements (Reassembled Data)……….… 62
Appendix F. Interview Blueprint………...… 71
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter provides background information related to the research. It
describes six main parts in this research, namely research background, problem
formulation, problem limitation, research objective, research benefits, and
definition of terms.
A.Research Background
The students need reflection to help them in noticing and correcting their
own mistakes to be successful in their studies. In other words, reflection helps
them to find the strengths and weaknesses in their own learning processes.
According to Ghaye (1998), reflection is the process of learning to affect future
action. Therefore, the students are responsible to improve themselves based on the
previous learning processes and get involved more in the future processes.
Besides, the students are able to be aware of their learning processes by writing a
reflection. In addition, the researcher has an experience in making a reflection.
The researcher found difficulties in learning Structure such as memorizing the
patterns and the functions of English sentences in each chapter. Then the
researcher wrote a reflection to understand the problem and find the solution to
solve it.
Previous research done by Walker as cited in Boud (1985, p.59-60) proves
to raise their level of awareness. Therefore, they become more aware in
recognizing situation which might lead them to deeper insights. The awareness of
feeling in the learning situation can be the basis of reflection that lead to a deeper
appreciation of the learning process and of the learner's ways of experiencing.
Furthermore, after doing reflection, Gibson (2012) finds that the highest learning
gain is awareness includes strengths, weaknesses, and priorities for the future
development.
English Language Education Study Program (ELESP) students will be
disappointed when they receive a D for Structure, because this subject is one of
the basic elements in speaking and writing skills in English. They are expected to
speak and write the sentences with correct grammar (Panduan Akademik
Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, 2012). Moreover, many ELESP students describe
Structure II as one of the most difficult course in Semester II. The students do not
understand the actual reasons which make them fail. As a result, they come to hate
the course or the ways the lecturer teaches them. The students have to work hardly
in doing a lot of practices to master it.
Based on the ELESP student’s opinion, structure is the most difficult
course because they need to memorize the patterns in doing a lot of practices. It is
difficult for some students to understand and follow the material. The fact can be
seen from their failure in the quizzes and the tests. They could not work on the
tests successfully and got low scores in the final assessment. It might be caused by
some problems in the Structure learning process. Therefore, they need to reflect
students are familiar with reflection in some courses such as Book Report or Basic
Reading, but they rarely do reflection in Structure class which contains basic
components and the rules of English sentence. Nonetheless, whether or not the
students can do the experience successfully, this research is intended to help
students to understand their capability and improve their scores in Structure II.
Based on the explanation above, this study aims to know the use of
reflection applied by the students of Structure II class in ELESP of Sanata
Dharma University to enhance their self-awareness. In the reflection, the students
are invited to make sense of their practice, state whatever they feel and share their
strengths and weaknesses which have to be improved. When the students make
reflection, they recall and examine their learning to know what they are doing and
how far they have learned. Hendricks (1981) states that the reflection is known as
a willingness to examine values, beliefs, and past actions. It can help the students
to understand their capability in learning Structure and make them aware of their
strengths and weaknesses.
B.Problem Formulation
The problem in the research background resented is formulated into one
question which is how did students’ reflections enhance their self-awareness in
C.Problem Limitation
This research is limited to the analysis of reflection applied by the students
of Structure II who had a D in the prerequisite course, particularly in Structure
class. Therefore, the participants of this research are limited. The participants are
three students of Structure II class in ELESP of Sanata Dharma University in
academic year 2015/2016. The researcher wants to investigate students who got D
in the Structure I. In semester two, students need to struggle with new concept of
Structure which is different from what they had learned in senior high school.
D.Research Objective
There is one objective related to the research problem. The objective of
this research is to present the use of reflection to enhance ELESP students’ self
-awareness in learning Structure II.
E.Research Benefits
This research is aimed to give benefits to students, lecturers, and readers as
mentioned below.
1. The ELESP Students
This research is to give students the understanding about the use of
reflection to enhance students’ self-awareness in learning Structure II. Hopefully,
students can find their weaknesses and strengths so they can evaluate themselves
2. The ELESP Lecturers
This research is to give information to the lecturers whether students’
reflection helps them in their teaching and learning process. Hopefully, lecturers
can use the reflection to help their students to reduce weaknesses and develop
students’ strengths.
3. Readers
This research is to give an overview on the use of reflection to enhance
students’ self-awareness in learning Structure. Hopefully, it gives the readers new
knowledge and information about the use of reflection for their life.
F. Definition of Terms
This section provides the definition of terms used in this research. There
are three terms conducted on this research. The following is the definition of each
term.
1. Reflection
Students need reflection to understand their capability and use it to make
an improvement in their learning process. According to Ghaye (1998), reflection
is an activity of looking back on previous learning and making sense to the
learning practice, which involves the ability of making choices and taking
responsibility for the future action. The good and meaningful reflection practice is
continuous, connected, challenging, and contextualized (Eyler, Giles, and
Schmiede, 1996). Therefore, it is good that reflection is implemented in their
ELESP students of Sanata Dharma University. This term is used in the next
chapter, so it can help the readers to understand the next part easily. In this
research, reflection refers to an activity which helps the students to improve their
learning process based on the previous learning experience.
2. Self-awareness
Self-awareness is capability of people to notice themselves and take
themselves in past, present, and future condition (May as cited in Kuswara, 1987).
Self-awareness allows students to have a clear perception of students’ personality,
including strengths and weaknesses, thoughts, beliefs, motivation, and emotion.
Self-awareness helps students to understand their capacity in the process of
learning. Self-awareness makes students actively identifies, processes, and stores
information in their learning environment. Students need self-awareness to control
their learning behavior. Having a clear understanding of thought and behavior
patterns helps students to enhance students’ willingness in learning activity. In
this research, self-awareness refers to recognition which makes the students to be
interested in improving their learning. This term is used in the next part of this
research because the students’ self-awareness is related to reflection. Therefore,
the researcher wants the reader to be familiar and understand the main idea easily.
3. Structure II
In ELESP, Structure II is a course which is designed to train students with
a deeper understanding on English tenses, particularly on past perfect tense, past
perfect progressive tense, future simple tense, future progressive tense and future
prepared to produce grammatically correct sentences with various pattern to have
good writing and speaking. There are four level of Structure course in ELESP that
are Structure I, Structure II, Structure III, and Structure IV. In this case the
researcher wants to investigate Structure II class because in this situation students
7
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
This chapter presents the theoretical description and theoretical framework
of the research. The theoretical description provides some theories and concepts
used as the foundation of this research. Meanwhile, the theoretical framework
presents the relationship between the basic theories used in this research and how
those theories support the research.
A.Theoretical Description
In this section, the researcher discusses the theories that support this
research. There are two main points explained in this section. Firstly, the
researcher describes the theories of reflection that cover the nature of reflection
and reflection process. Secondly, the researcher presents the theory of
self-awareness. However, in the beginning of this part, the researcher also discusses
some related studies which are related to this research.
1. Review of related research
The research which is conducted by Ong (2004), shows that reflection
helps students in their learning. She conducted a qualitative research in which
students of Republic Polytechnic became the participants. She chose 10 students’
journal randomly from different modules and discipline background and
their self-awareness. Thus, she describes that reflection has an important role in
students learning since it relates the new learning material and prior knowledge
and enhances self-awareness.
Furthermore, Jensen (2009) conducted similar research in using reflective
journal to improve students’ self-awareness. The research was conducted in
Aalborg University Denmark. The participants of this research were foreign
students. In connecting students’ experiences toward the subject, the students
were demanded to make a personal portfolio in a form of reflective journal where
they could reflect their experiences on the subject. In the research, Jensen
examined students’ reflective journal and found that most of the students are
aware of what they have learned and 60% of the students showed improvement in
their learning capability.
Next, previous research done by Walker as cited in Boud et al. (1985)
approves that reflection in written form helped people who would be exercising
leadership to raise their level of awareness. Therefore, they became more aware in
recognizing situation which might lead them to deeper insights. In addition,
Gibson (2012) in his journal entitled Reflect-select-defend: A model for student
teacher reflection, he finds that the highest learning gain is in awareness include
strengths, weaknesses, and priorities for future development. The awareness of
understanding feeling in a learning situation can be the basis of reflection. It might
lead to a deeper appreciation of the learning process and of the learner's way of
Those studies show that reflection helps students in their learning
especially in improving students’ self-awareness. Thus, a study on reflection is
beneficial to be conducted in order to use it in Indonesia context, more
specifically at ELESP of Sanata Dharma University.
2. Reflection
In this section, the researcher presents the description of reflection. There
are two points to be discussed, they are the nature of reflection, and reflection
process.
a. The Nature of Reflection
According to Ghaye (1998), future action is affected by doing reflection
continuously through looking back and making sense of learning. Taylor presents
reflection as a stage in the learning process which occurs after an activity has been
done towards the latter part of a one-semester course, for instance (Taylor, 1981
as cited in Boud et al., 1985).The capacity to reflect is developed to different
stages in different people and it may be this ability which characterizes those who
learn effectively from experience.
Continuous, connected, challenging, and contextualized are the principles of
good and meaningful reflection practices (Eyler, Giles, and Schmiede,
1996).Continuous means reflection must be ongoing. Then connected means
reflection links academic goals and intellectual development. Next, it is
challenging because reflection provides an opportunity to explore uncomfortable
and unfamiliar feelings and ideas. Moreover, contextualized means reflection can
Reflection supports students to recognize their experiences so that they can
integrate their experience and learning process. Gibson (2012) describes that
reflection is aimed at helping the students to consider events that have occurred in
the past and then use that evidence to enhance the learning situation in the future.
This allows students to respond to experiences using a more critical thinking,
challenge themselves to experience personal growth and development, and share
their opinions and feelings with their friends. Watson (1996) describes that
reflection takes students to think and action a step beyond what they usually do.
This is important to draw upon learners' prior experience and to provide
opportunities for them to be engaged actively in what they are learning.
b. The Process of Reflection
Reflection is a form of response of the learner to their experience (Boud et
al., 1985). There are two main components: the experience and the reflective
activity based upon the experience. Boud et al. (1985) says that one of the most
important ways to enhance learning is to strengthen the link between the learning
experience and the reflective activity which follows the learning. Kolb (1984)
describes that it is important to combine action and engagement with reflective
thinking to develop greater understanding. The process of reflection has a
reflective, theoretical and practical side; without reflection, it is hollow and
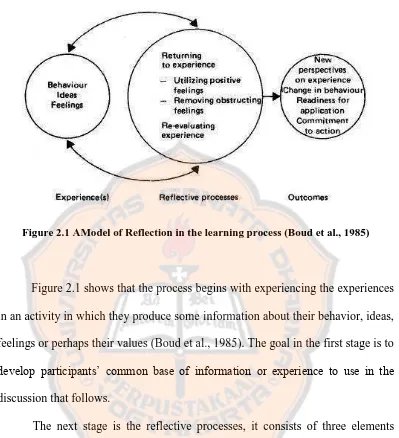
Figure 2.1 AModel of Reflection in the learning process (Boud et al., 1985)
Figure 2.1 shows that the process begins with experiencing the experiences
in an activity in which they produce some information about their behavior, ideas,
feelings or perhaps their values (Boud et al., 1985). The goal in the first stage is to
develop participants’ common base of information or experience to use in the
discussion that follows.
The next stage is the reflective processes, it consists of three elements
which are important in the reflective process. According to Boud et al. (1985), the
first element, returning to experience is the replaying of the past experience in the
mind of the learner. This activity can help students to get better understanding of
their past events and help to ensure that our reflection is onthe basis of the actual
events as we experienced them at the time, rather than in terms of what we wished
had happened. Each individual may have had a different experience, even though
events can bring us to an awareness of the feelings presented during the initial
experience.
The second element, attending to feelingshas two aspects: using positive
feelings and removing obstructing feelings (Boud et al., 1985). The use of positive
feelings involves focusing on positive feelings about learning and the experience
which is subject to reflection. This may involve the conscious recollection of good
experiences, attention to pleasant aspects of the immediate environment, or the
anticipation of the possible benefits to be derived from the processing of events.
The use of our positive feelings is particularly important as they can provide to
help us seeing events more sharply and they can provide the basis for new
affective learning. According to Boud et al. (1985), removing obstructing feelings
is a necessary precursor to a rational consideration of events. It involves whatever
needs to be done in order to remove impediments to a thorough examination of
the experience.
Then, the third element is re-evaluating experience which, although it is
the most important, is often not completed if the preceding two are omitted. Some
form of evaluation might have taken place at the time of the experience and may
in the learner's mind be part of the experience itself. In this critical stage, students
begin to examine what are the obstacles they experienced and why it can be
happened. The question can be focused on the meaning or importance of the
activity, for example what kinds of things happened and why?. The discussion
personal destructive habits. In this stage, the students are trying to thinking
reflectively about what the reasons are and why they choose to act like that.
The outcomes of reflection may include a new way of doing something,
the clarification of an issue, the development of a skill or the resolution of a
problem.A new cognitive map may emerge, or a new set of ideas may be
identified (Boud et al., 1985). The changes may be quite small or they may be
large. The students could involve the development of new perspectives on
experience or changes in behaviour.What is important is that the learner makes a
commitment of some kind on the basis of his or her learning. Action ends the
reflective process for the time being and some benefits of reflection may be lost if
they are not linked to action.
3. Self-awareness
Lier (1996) states that to learn something new, people must first notice
their habits and the process of the noticing is an awareness of its existence,
obtained, and enhanced by paying attention to it. Students have to notice and
focus on their attention to learn something new. This noticing and focusing
process can be described as awareness. According to Goleman (1996),
awareness is a continuous attention the inner state of a person. In this state of
self-reflection, thought is observing and digging experience, include emotion.
Self-awareness is capacity which makes people to observe themselves and take
themselves in past, present, and future time (May as cited in Kuswara, 1987). In
addition, Hendricks (1981) defines awareness as willingness to examine all our
they find the truth about their learning. They examine their learning whether it
meets their learning needs which lead them to take on the responsibility of the
truth they have found.
Self-awareness is one of the important components of Emotional
Intelligence. Lier (1996) describes self-awareness as knowing what you are doing
and why. In this research, self-awareness deals with knowing and examining what
we have done in the learning activity. Self-awareness in intelligence is ability to
recognize emotions and sort out feeling, aware of the existence of emotion, know
the strengths and the limit of self. Students need self-awareness to develop their
quality of learning process. Personal development starts at a point of
self-awareness; in fact, it may as well be the ultimate end (Johns, 2005).
Self-awareness makes students understand that they need to change their destructive
habits. In addition, students who have good self-awareness will develop
themselves effectively. It is impossible to develop and grow themselves with a
lack of self-awareness (Johns, 2005).
Besides, Deci (1975) states that the awareness can satisfy the intrinsic need
for feelings of competence and self-determination or any of the specific motives
that develop out of the basic motivational propensity and increase the positive
affect. Conceptually, the awareness cause the person to establish goals which he
expects will lead to the rewards, intrinsic or extrinsic which lead to satisfaction.
According to Brown (2007), when students perform certain activities for internal
Moreover, Gebhard and Oprandy (1999) explain four avenues to
self-awareness namely problem solving, seeing what happens, seeing what it is, and
clarifying feelings. The first avenue is problem solving. Being aware of their
learning, students need to solve problems they face. As an instance, there is a
student who gets a bad mark for a particular subject. The student tries to
understand what causes the bad mark. The student finds that he rarely studies the
subject. Then he tries to solve the problem by studying more to understand better.
Here, the student changes his behavior and gains awareness of his own learning
and practice to solve his problem.
The second avenue is seeing what happens in the learning can be done by
trying the opposite to the usual things. For example, a student usually reads the
materials before the class that helps him a lot in his earning. To see what happens
in the learning, he needs to do the opposite by coming to class without reading the
materials in advance. Through this, self-awareness can be obtained.
The third avenue is seeing what it is. In this avenue, there are two-lane
avenues to obtain the self-awareness. The first is contrasting what we do with
what we think we do. To accomplish this, keeping record of what we have done is
needed. Here, students can obtain their self-awareness by writing a reflection. The
second lane is considering what we believe in light of what we do. It deals with
finding out whether student’s beliefs match the actual processes or not. For
example, a student believes that he has done the best he could in the exam. He
believes that he will get good mark. In fact, he doesn’t get good mark for his exam
students can see what the learning is by contrasting what we do with what we
think and considering what we believe in what we do.
The last avenue to self-awareness is clarifying the feelings. By exploring
their feelings of the learning, students are able to gain learning awareness. The
feelings about thing are able to affect the behavior. Hence, clarifying the
emotional side is needed and reflections are suited to this avenue.
B.Theoretical Framework
The theories above are the basis that is used by the researcher to answer
the research problem of this study. There is one research problem in this study;
how did students’ reflection enhance their self-awareness in learning structure II.
The researcher uses Boud’s reflection model theory in order to guide the
participants in doing good reflection. Boud et al. (1985) designs a reflection
model in the learning process because it is important to combine experience and
reflection to gain good outcomes and develop greater personal development.
To find out the use of reflections in enhancing the students’ awareness, the
researcher divided the discussion into some parts. The first, to figure out the
students’ awareness of many problems they faced in learning structure, the
researcher uses Walker’s statement about reflection helps students to be more
aware in recognizing situation. The second, in order to discover the students’
awareness of problem solving strategies, the researcher uses Gebhard and
Oprandy’s (1999) theory about problem solving skill. The third, to find out the
(2007) statement of internal interest and satisfaction which is refers to intrinsic
motivation. The last, to know the importance of reflecting student’s feelings in
learning, the researcher uses Gebhard and Oprandy’s (1999) theory about the
18
CHAPTER III
METHODOLOGY
This part discusses the methodology of the research. It comprises the
research method, research setting, research participants, research instrument and
data gathering technique, data analysis technique, and research procedure.
A.Research Method
This research aims to investigate the use of reflection to enhance students‟
self-awareness in learning structure II. Therefore, the method of this study is
descriptive qualitative research. According to Merriam (2002), the key of
qualitative research comes with the idea that meaning is constructed by
individuals in interaction with their world. Ary et al. (2010) says qualitative
research has words and images of the data form. Fraenkel and Wallen (2009)
support that one of qualitative research characteristics is that the data form
consists of words and images. A qualitative approach was chosen in this study
because it could provide a deeper understanding of social phenomena that would
be obtained from purely quantitative data (Silverman, 2005).
In addition, the idea of the study is to identify the use of reflection to
enhance students‟ self-awareness. There were some types of qualitative research
and the researcher employed descriptive research as the method in this research.
a picture of a situation as it naturally happens. Then, Burns and Grove (2003)
describe a qualitative approach as a systematic subjective approach used to
describe life experiences and situations to give them meaning. Moreover,
Holloway and Wheeler (2002) refer to qualitative research as a form of social
enquiry that focuses on the way people interpret and make sense of their
experience and the world in which they live. Researcher used the qualitative
approach to explore the behavior, experiences and feelings of people. For the
purpose of this research, descriptive research was used to obtain a picture of the
use of reflection to enhance students‟ self-awareness in learning Structure II.
Because of that reason, the researcher chose descriptive qualitative research as the
method and qualitative approach in this research.
According to Merriam (2002), there are four strategies for promoting
validity and reliability in a qualitative research namely triangulation, member
checks, peer reviews, self-reflexivity or researcher‟s position. Those strategies
ensure for adequate treatment in a qualitative research inquiry and it can support
the findings of a research. However, the researcher only used one strategy namely
member checks. According to Merriam (2002), member checks is “taking data
and tentative interpretations back to the people from whom they were derived and
asking if they were plausible.” (p.31). In the reflection process and interview
section, the participants were asked confirmation about interpretation of the data.
B.Research Setting
The research was conducted in the second semester of the 2015/2016
academic year. The setting was in Sanata Dharma University. It was chosen
because the researcher is a student in Sanata Dharma University and this helped
the the research to process the research. The researcher chose to do a research in
Structure II because that was a transition experience from the first prerequisite
subject. The reflection as a process in the learning process which occurs after
important activity has taken place, towards a one-semester course, for instance
(Taylor, 1981 as cited in Boud et al., 1985).
The data gathering was done five times for each participant since there
were three respondents in this research. Therefore, there were fifteen meetings in
this research. Besides, the time for meeting was flexible in purpose of making
participants feel comfortable and free to share their experiences. The research
began from the middle of February until thebeginning of April. The meeting was
C.Research Participants
The researcher used non-probability and purposive sampling. According to
Parahoo (1997), in non-probability sampling researcher uses their judgment to
select the subjects to be included in the study based on their knowledge of the
phenomenon. In addition, the sample of purposive sampling has been chosen for a
specific purpose (Cohen, Manion, and Morrison, 2007). The researcher chose the
samples which fulfilled the researcher‟s specific needs. In order to answer the
research problems, the participants of this research were three students of ELESP,
Sanata Dharma University who received a D in the prerequisite subject. The
researcher chose the students who received a D because the researcher thought
that it was easier to identify the progress of the research.
There were three students accepted and confirmed that they were willing to
be participants in this research. Holloway and Wheeler (2002) say that sample
size does not influence the importance or quality of the study and there are no
guidelines in determining sample size in qualitative research.
D.Research Instrument and Data Gathering Technique
In this section, the researcher discusses the instruments used in this
research. The researcher used the students‟ reflection and interview technique to
collect the data, so the data were in the form of reflections and interview
transcript. In descriptive research, the researcher was the primary data collection
instrument because the data from participants were words in the context of the
instruments‟ are the researcher can have adaptability, responsiveness, knowledge,
ability to handle sensitive matters, ability to see the whole picture, ability to
clarify and summarize (Lincoln and Guba, 1985). It aims to collect the detailed
description of participants‟ experience. According to Fraenkel & Wallen (2012),
the participants‟ written and oral self-report can also be evaluated. The researcher
used two instruments for the data gathering techniques. The researcher used
reflection and interview from the participants.
1. Reflection
In order to get information about the use of reflection to enhance students‟
self-awareness, the researcher asked the students to write some reflections. In this
research, the researcher used the students‟ reflections as the document to collect
data. Documents are good data collection because they can provide good
descriptive information (Ary et al., 2010). In addition, Bernard (1988) has similar
description about document study that it has always been an important component
of qualitative research. The document study has advantages such as it is flexible
and it allows the access to subjects that may be difficult to research through direct
personal contact. There were some questions of the reflection to know the
participants‟ experience in details during Structure II. The question of the
reflection should cover participants‟ understanding of the experience so they
would get benefits. The first benefit is reflection allows us to put and to use what
students learn from experience (Gardiner as cited in Tarvin, 1991). The second
benefit is reflection helps raise students‟ awareness as learners and to see that we
students‟ learning involvement in their own learning because they begin to
perceive the purpose for their assignment (Campbell, 2000).
2. Interview
In order to get better understanding of the participants‟ refection, the
researcher conducted interview. The researcher used interview as secondary data
to support the main information about the use of reflection to enhance students‟
self-awareness in learning Structure II. Interview is a suitable instrument to know
deeper about people‟s experience (Ary et al., 2010). In order to gather the data,
this interview used open-ended items. Open-ended questions have a number of
advantages: they are flexible; they allow the participant to review so that she may
go into more depth; they enable the interviewer to test the limits of the
participant‟s knowledge; they encourage cooperation and help establish rapport;
and they allow the interviewer to make a truer assessment of what the participant
really believes.
The researcher used Bahasa Indonesia or the participants‟ first language
to conduct both the reflection and the interview. The reasons why the reflection
and the interview were conducted in Bahasa Indonesia as the first language were
the researcher wanted to know the truth about participants‟ experience without
misconception. Then, Bahasa Indonesia made participants comfortable to write
E.Data Analysis Technique
The data analysis technique that the researcher used to analyze the data in
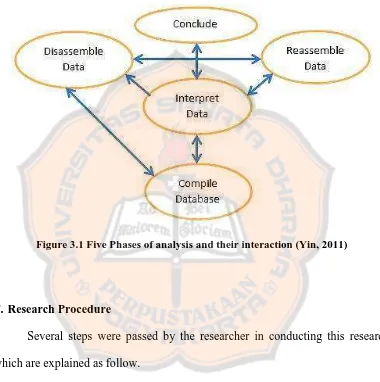
this study was Analytic Phases in qualitative research by Yin (2011). There were
five steps, namely compiling, disassembling, reassembling (and arraying),
interpreting and concluding.
1. Compiling
The first phase of qualitative data analysis process is compiling. The
researcher should start by sorting the field notes amassed from your fieldwork and
other data collection (Yin, 2011). The function of this step is to make the
researcher understand the condition of the participants‟ experiences. In this step,
the researcher needed to read and listen to the data for many times to get better
understanding about the data. Then, for oral data from interview, the researcher
made transcripts to be read many times. Compiling, means putting them in some
order and then the finished compilation might be considered a database (Yin,
2011).
2. Disassembling
The second phase of analytic phase is disassembling. This step calls for
breaking down the compiled data into smaller fragments or pieces, which may be
considered a disassembling procedure (Yin, 2011). The procedure is, the
researcher should choose new labels or codes to the fragments or pieces.
However, the researcher could choose to use coding or no coding because there is
researcher did not use coding in disassembling data. The researcher directly
analyzed the original data and made notes.
3. Reassembling
This third phase may be considered a reassembling procedure. The
researcher used the substantive themes to recognize the disassembled fragments
(Yin, 2011). The rearrangements and recombination may be facilitated by
depicting the data graphically or by arraying them in list of the theme.
4. Interpreting
The fourth phase is interpreting the reassembled data. This step involves
using the reassembled material to create a new narrative, with accompanying
tables and graphics and it will become the key analytic portion of your draft
manuscript (Yin, 2011). Initial interpretations may lead to the desire to recompile
the database in some fresh ways, or to disassemble or reassemble the data
differently. All of these sequences are represented by the respective one-way and
two-way arrows.
5. Concluding
The fifth and final phase is concluding. It calls for drawing the
conclusions from the entire data. Such conclusions should be related to the
interpretation in the fourth phase and through it to all of the other phases of the
cycle (Yin, 2011).
The diagram of five phases of analysis and their interaction can be seen
types of arrows, which are one-way and two-way (Yin, 2011). The two arrows
means the researcher could go back in particular phases.
Figure 3.1 Five Phases of analysis and their interaction (Yin, 2011)
F. Research Procedure
Several steps were passed by the researcher in conducting this research
which are explained as follow.
1. Asking Permission
The researcher gave consent form which the content was about asking
permission to the participant who got D in Structure I. Afterwards, the researcher
asked permission to the Structure II lecturer to get some information about the
2. Preparing the research instrument
There were two research instruments used by the researcher, namely
reflection and interview. The reflection was designed to get the data needed. Then,
the interview was conducted as the evidence of the reflection.
3. Using the instrument
The researcher asked the participants to make reflection. The reflection
was to share the participants‟ experiences in Structure II, understand their
weaknesses and strengths, and explore the information in depth. It was held on
19th February until 3rd April, five times for each participant. Furthermore, the interview was to support the reflection. It was held on the last meeting of this
research. The reflection and interview were done in Bahasa Indonesiain order to
prevent the misunderstanding of the participants about the questions and answer.
It made the participants feel more comfortable to answer and share their
experiences honestly.
4. Analyzing the data
The data obtained from two phases, namely analyzing document results of
students‟ reflectionsand interviewing three students, were analyzed by comparing
them to the theories. Then, the researcher reported the results of data analysis in
research results and discussion after completing all procedures.
5. Making Conclusions
The researcher made conclusions from the results after analyzing the data.
28
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
This chapter presents and discusses the results of the research which are
obtained from the reflection and the interview guided by the researcher. The
researcher elaborated the use of reflection to enhance the students‟ self-awareness
into four main parts. First, the researcher discussed the students‟ awareness of
many problems they faced in learning structure. Second, the researcher discussed
the students‟ awareness of the importance of problem solving strategies in
learning. Third, the researcher elaborated the intrinsic motivation that appeared in
the reflection. The last, the researcher deliberated the importance of reflecting
student‟s feelings in learning.
There were five phases conducted in this study, namely compiling,
disassembling, reassembling, interpreting and concluding. After conducting the
first and the second phase, the researcher moved to the third phase, namely
reassembling. In this phase, the researcher clustered the data into four substantive
themes. The themes are all about the use of reflection to enhance students‟ self
-awareness in learning structure II.
A.Reflections Raise Students’ Awareness of the Problems They Faced in
Learning Structure
This part discusses the problems faced by the students in learning
no willingness, grumble, lack of memorization, and difficulty in understanding of
the material.
The first student, AL, said that she had poor time management. In the
statement, she had a lot of tasks. However, she also joined some organizations in
her campus. AL also said that she got tired easily after attending organization, so
she was not interested in studying. She could not handle her time well in order to
balance her study time and organization time.
“Di minggu kedua ini aku ngerasa pengaturan waktuku kacau. Aku
mulai ikut organisasi di kampus dan itu bener-bener buat capek. Aku jadi males buat belajar karena udah capek duluan. Nah, waktu kumpul organisasi itu sehari sebelum kelas Structure, jadi kadang
aku ngerjain tugasnya di kelas.” (AL, day 2)
In the second week, I felt that I had poor time management. I started to join organization in the university and it made me very tired. I was lazy to study because I had already tired. In addition, the time for organization was a day before structure class, so sometimes I did the tasks in the class. (AL, day 2)
Then, the second student, DE, also experienced poor time management.
However, DE‟s experience was different from AL. In the statement, DE explained
that she had poor time management in learning structure, because she spent most
of her time to hang out with her friends and did not pay much attention about her
tasks and her study time. It was difficult for her to understand the material
because she did not have enough time to study the material. Her bad time
management caused her not focus on studying.
ngerjainnya. Gimana mau ngerti karena belajar aja enggak pernah.” (DE, day 1)
My big problem was time management. Because of I like to hang out with my friends so I did not care about my tasks. It made me could not overcome many tasks and did not know how to solve it. How could I understand if did not study. (DE, day 1)
Besides, DE said that she was procrastinating her time to study. DE was
not having eagerness to study or practice by her own. She stated that she never
studied or practice without lecturer‟s instruction, which means she always studied
or practiced if her lecturer gave them some instructions. Unfortunately, DE knew
that she had a task from the lecturer but she still procrastinated her time to do it.
Here is the example of the DE‟s reflection in day 3.
“Aku pernah dimarahi oleh dosen karena enggak bikin
tugas.Sebenernya itu karena aku nunda buat ngerjainnya sampe aku lupa buat ngerjain.(DE)
She has ever been scolded by the lecturer because I did not work on my tasks. Actually it was because I procrastinated to do it until I forgot to do it. (DE)
After that, the third student, SA, had same problem with DE in managing
his time. SA said that he was lazy and he tended to be a procrastinator. He chose
to use his time to do useless thing like playing game or watching soccer in late
night. SA said that he liked to study a day before the test. He argued that the
treatment above helped him to memorize the material. However, the material just
lasted only for a moment and then he forgot it after the test. Here is the example
“Aku enggak pernah belajar kalau enggak ada tugas dan aku biasanya belajar malemnya kalau ada tes atau kuis.Ya memang sih nyantol tapi banyak lupanya.Hal itu membuat nilaiku enggak
maksimal.”(SA)
Then, the second and the third problems faced by the students were lack of
memorizing ability and difficult in understanding the course. Here are the
examples of AL‟s reflection in day 1.
“Ada banyak banget masalah saat aku belajar Structure. Saking banyaknya aku tidak bisa mengatur dan menyelesaikan semua permasalahanku. Aku sering kabur dari masalahku di kelas Structure. Alasan utama yang aku punya adalah aku tidak mengerti pelajaran itu dan itu membuatku sulit untuk mengingat mengenai pelajaran itu. Misalnya aku belajar tentang perfect tense, aku tau rumusnya kayak gimana tapi kalo pas ngerjain soal tanpa liat catatan pasti aku kebalik-balik sama rumus tenses lain. Aku juga tidak ngerti perfect tense itu kapan digunakan. Lalu, menurutku penjelasan dosen itu gak jelas.”(AL)
There were many problems when I learned Structure. Therefore, I could not handle and solve my problems. I usually escaped from my problems in structure class. The main reason was because it was difficult to be understood and it made me difficult to memorize that subject. For example, I studied perfect tense, I knew the patterns but when I did a task without saw my note I was confused with other tenses. I also did not understand when perfect tense is used. Then, I
thought the lecturer‟s explanation was not clear. (AL)
perfect tense, karena V3 jarang dipake sebelumnya jadi aku merasa
tidak familiar.” (AL)
I also had another problem in memorizing new material quickly. For example I could not remember the V3 from perfect tense, because V3 was seldom to be used before so I felt unfamiliar. (AL)
AL explained that she had problem in learning structure. She said that she
had difficulty in understanding new material when doing tasks without seeing her
notes. It was confusing for her to choose the right tenses used in sentences. It was
difficult for her to memorize all of the material because they were unfamiliar for
her.
The second student, DE, also had problem in understanding the material.
She said that Structure has many patterns and its functions which made her
confused. She explained that she usually confused to detect the right pattern used
in the error analysis.
“Aku suka bingung kalotugas error analysis. Kan gak ada instruksinya kalo harus pake pattern yang mana sama pas nyocokin
ke soalnnya yg susah dimengerti.” (DE, day 2)
I was confused in the tasks of error analysis. There was no instruction to use what pattern and when match the pattern and the task which was difficult to be understood.” (DE, day 2)
Next, the fourth problem faced by the third student, SA, was no
willingness to study Structure. SA explained that he had problem in willingness to
study Structure. It was difficult for him to gain willingness to study because he
thought that structure was really difficult to be understood. However, he said that
was only a secondhand book from his brother. The appearance of the structure
book was not in a good quality.
“Sebelumnya aku enggak niat belajar, aku pikir kok susah amat Structure buat di pelajari.Boro-boro belajar buat Structure niat buat
buka bukunya aja enggak.Buku yang aku punya itu lungsuran dari kakak tingkat jadi bukunya kucel dan udah gak jelas.(SA, day 1)
I had no intention to study before, because I thought it was difficult. Not only had no intention to study Structure, but I also had no intention to open the Structure guideline book. (SA, day 1)
Then, the last problem was grumble. The student who had problem in
grumbling is AL. She explained that she usually grumbled about difficult tasks
before trying to answer it. She also grumbled about her structure class schedule
because it was started in the early morning. She said that she was ever absent from
the class because she came late.
“Biasanya aku suka mengeluh tentang tugas-tugas sulit yang dikasih dosen. Terus mbak kelas structure ku itu pagi jadi sering mepet datengnya, pernah aku dateng telat dan aku tidak boleh ikut sama
dosenku.” (AL, day 3)
I usually grumbled about some difficult tasks from the lecturer. Then, my structure class was early morning so I often came close to the time. I ever came late and the lecturer told me not to join the class. (AL, day 3)
Based on the result of students‟ reflections, all of them said that they found
some problems. The problems were poor time management, no willingness,
grumble, lack of memorization, and understanding the material. Walker said that
reflection helps students to be more aware in recognizing situation which might
lead them to deeper insights (Walker as cited in Boud et al., 1985). In this case,
own problem in learning Structure. It proves that reflections raise students‟
awareness of the problems they faced in learning structure.
B.The reflections raise students’ awareness of the importance of problem
solving strategies in learning Structure
This part discusses students‟ awareness of the importance of problem
solving strategies in learning Structure. Problem solving strategies is needed by
the students to overcome their problems. Each student has different strategies to
solve their own problems. Based on the problems faced by the students, they had
to solve their problems in order to develop their learning. The first problem was
poor time management. Here were the problem-solving strategies used by the
students to overcome their learning obstacles.
AL said that she had poor time management to study because of her
campus organization schedule. After doing reflection, AL tried to overcome her
problem by making agenda to help her in recognizing her study time. She
explained that agenda could help her in managing her study time. She listed her
leisure time and tried to study on it. After that, she could take rest after attending
organization in her campus because she had already study Structure.
“Aku mulai nulis kegiatan dan waktu luang ku dalam seminggu. Nah dari situ aku tau kalo hari jumat sama sabtu aku punya waktu buat belajar. Sekarang kalo pulang organisasi aku bisa langsung tidur
karena udah belajar kemarennya.” (AL, day 2)
I started to list my activities and my leisure time in a week. Then, I knew that on Friday and Saturday I had time to study. Now, I can
take rest after attending organization because I had already studied.”
Then, DE had poor time management because she spent most of her time
to hang out with her friends and did not pay much attention about her tasks and
her study time. In the process of the reflection, she found that she was careless
about her study and she decided to solve her problem by managing her time. She
tried some strategies to solve it. DE strategy was almost same as AL, she made
agenda. First, she listed all of her activity except basic activity and the detail time.
Next, she tried to decrease some useless activity and increase beneficial activity.
She began to decrease her hangout activity and increase her study time. This
activity helped her to realize that she had some destructive attitudes and to think
the solution to decrease it. Here is the DE‟s reflection in day 1.
“Solusi yang bisa aku lakuin yaitu mencoba mengatur waktu buat
belajar.Aku harus mencoba untuk berlatih untuk dapat pemahaman yang mumpuni mulai dari sekarang. Aku enggak mau tertinggal sama teman-teman kelasku. Pertama-tama aku niru temen kelasku yang selalu menulis jadwal kegiatannya di buku agendanya. Aku membuat buku agendaku sendiri dan mulai menulis kegiatan yang aku lakukan dalam satu hari, lalu aku melihat kalo perbandingan jalan-jalan sama belajar gedean jalan-jalannya. Jadi, aku mulai deh untuk mengurangi jalan-jalan dan menambah waktu untuk
belajar.”(DE)
The solution which I could do was managing my time to study. I should try to practice from now to get better understanding. I did not want to be left behind by my classmates. First, I imitated my classmate who always wrote her activity on her book. I made my report book and started to write my activity all day on it. Then I saw the percentage of hang out and study, and I found that I spent many time for hang out. Therefore, I began to decrease time for hang out and increase time for study. (DE)
Then after doing reflection, DE found her weaknesses namely poor time
management. However, she found some ways to solve her problems such as made
decreased hang out time which she considered as her obstructing activity and she
increased her study time as beneficial activity. It means that her self-awareness of
her problem solving skill was enhanced. It could be seen from her changes in
behavior with her action to be better than her past.
Moreover, DE said that she had ever been scolded by the lecturer because
she procrastinated her time until she forgot to do the tasks. Then, she decided to
change it. She did the exercise first even before the lecturer made it as the
assignment as her. Therefore, when the exercise became the assignment DE had
already finished it. Here is the DE‟s reflection in day 3.
“Nah, jadi aku sekarang selalu ngerjain latihan sebelum jadi
tugas.Biar kalo itu jadi tugas aku udah selese duluan.Urusan bener salahnya belakangan.”(DE)
Therefore, I always did the exercise first even before it became the assignment. Then, if it became the assignment I had already finished it. The answer was wrong or true it would be thought later. (DE)
In addition, SA said that he was a lazy person and a procrastinator. He
could not manage his time to study. He liked to play games and watch soccer in
night. After doing reflection, he decided to make a change to be a diligent person
by studying the material from the lecturer. He recognized that his bad score were
made because of his attitude. Here is SA‟s reflection in day 2.
“Aku adalah tipe orang yang males belajar tapi menginginkan nilai yang tinggi. Tapi setelah aku melakukan refleksi ini pikiranku jadi terbuka untuk melihat dunia dari segi yang realistis.Setiap ada pengumuman kuis untuk minggu depan, aku mencoba untuk berlatih setiap hari dengan tujuan agar aku familiar sama tipe-tipe
pertanyaan sesuai topik.” (SA)