RINGKASAN
OPTIMASI FORMULA SEDIAAN SIRUP MUKOLITIK IN
VITRO FRAKSI TERSTANDAR BUNGA KEMBANG SEPATU
(Hibiscus rosa-sinensis L.)
DISERTASI
Untuk memenuhi sebagian persyaratan
mencapai derajad Doktor (Dr.) pada program Doktor
Diajukan Oleh:
MIMIEK MURRUKMIHADI 08/276481/SFA/00032
Kepada
PROGRAM PASCASARJANA PROGRAM STUDI ILMU FARMASI
FAKULTAS FARMASI UNIVERSITAS GADJAH MADA
YOGYAKARTA 2012
ABSTRACT
Hibiscus Flower (Hibiscus rosa-sinensis L.) has been used traditionally against cough. It was potential as secretolytic agent, but a standardized syrup is still needed in order to obtain optimum pharmalogycal effect. The objective of this research was to obtain an optimum – standardized fraction syrup formula of Hibiscus flower by Simplex Lattice Design Method, as well as to determine its in vitro mucolytic activity and stability both physically and chemically.
Standardized fraction of Hibiscus flower was obtained by macerating the flower with petroleum ether, followed by 70% ethanol solution, and fracinationated with ethyl acetate. The fraction containing alkaloid was defined as standardized fraction. Optimalitation of the syrup containing standardized fraction obtained by Simplex Lattice Design software Design Expert® method version 7.1.
Marker compound (alkaloid) isolation of Hibiscus flower was done by Thin Layer Chromatrography (TLC), Vaccum Liquid Chromatography (VLC), Preparative Thin Layer Chromatrography (PTLC). The marker was then identified according to UV-Vis, IR, GCMS, and NMR data. The marker concentration was determined by KLT densitometer. The syrup obtained from optimation process was tested by in vitro for its mucolytic activity, and also tested for its physical and chemical properties, its resistence to microbial contamination as well as respondent tolerability.
The result of the study shows that the marker obtained contains 4 compounds, identified as Glycine,N,N-dimethyl, methyl ester ; 2-propanamine,N,N-dimethyl ; 1,2-Ethane diamine ; N,N,-dimethyl Glycine while Glycine,N,N-dimethyl, methyl ester and 1,2-Ethane diamine are the major components (53.83 %, 30.96 %). The optimum formula was defined as glycerin (37.13%), sorbitol solution 70% (49.32%), CMC-Na 0.5% (13.54%). Physical response of the optimum formula from this study was comparable to the prediction especially on viscosity and pouring comfortability but not in taste and acidity. Syrup formula was less stabil in 4 weeks of storage viewed in the acidity and viscosity level. Standardized syrup showes in vitro mucolytic activity, and at 2.0% equal to acetylcystein syrup 0.1%. The presence of marker syrup was undetectable after storing at 27oC, 40 oC, 55 oC, and 70 oC for 4 weeks.
Key word: hibiscus flower, optimation of syrup, standardized fraction, mucolytic, in vitro
Pendahuluan
Beberapa penyakit seperti bronkitis dan infeksi saluran nafas menghasilkan mukus (Ikawati, 2006). Peningkatan produksi mukus terjadi pada kondisi tersebut, dan mukus yang diproduksi sifatnya kental, sehingga hal ini berpengaruh pada
pernafasan. Secara fisiologis silia tidak mampu mengeluarkan mukus karena terlalu kental (Hitner and Nagle, 1999). Mukus kental dapat dikeluarkan melalui proses pengenceran. Bunga kembang sepatu (Hibiscus rosa-sinensis L.) termasuk salah satu obat tradisional yang dipakai masyarakat sebagai peluruh dahak atau pengencer mukus (Departemen Kesehatan, 1985).
Banyak penelitian terhadap kembang sepatu, akan tetapi penelitian mengenai formulasi fraksi dari bunga kembang sepatu sebagai mukolitik secara in vitro belum ada. Penelitian yang telah dilakukan antara lain Ekstrak etanolik bunga kembang sepatu mampu menghambat pertumbuhan Mycobacterium tuberculosis yang sensitif dan resisten (Ruban and Gajalakshmi, 2012). Ekstrak etanolik akar kembang sepatu mempunyai aktivitas sebagai antiimplantasi (Vasudeva and Sharma, 2008). Ekstrak petroleum eter, hidroalkohol, dan kloroform bunga kembang sepatu mampu menurunkan tekanan darah (Siddiqui et al., 2006). Gauthaman et al. (2006) melaporkan khasiat bunga kembang sepatu dalam meningkatkan senyawa antioksidan endogen miokardial, sehingga berefek kardioprotektif.
Penggunaan bunga kembang sepatu secara langsung dinilai tidak praktis, efektif, dan acceptable. Penggunaan dalam bentuk fraksi terstandar bunga kembang sepatu dinilai lebih efektif, sehingga perlu diformulasikan dalam sediaan sirup. Senyawa penanda (marker) merupakan suatu senyawa yang dapat dijadikan untuk menilai jaminan kualitas fraksi sebagai zat aktif. Dengan demikian fraksi akan mempunyai kualitas yang konstan.
Sirup merupakan bentuk sediaan cair yang mempunyai nilai lebih antara lain dapat digunakan oleh hampir semua usia, cepat diabsorpsi, sehingga cepat menimbulkan efek. Fraksi mempunyai karakteristik rasa yang tidak enak dan mengandung bagian-bagian yang tidak larut. Bahan-bahan tambahan sangat diperlukan untuk membuat sediaan sirup yang acceptable dari fraksi bunga kembang sepatu. Gliserin ditambahkan sebagai kosolven untuk zat aktif yang sukar larut. Bagian fraksi yang sukar larut didispersikan dengan penambahan CMC Na. Rasa yang tidak enak dikurangi dengan penambahan sorbitol. Komposisi yang proporsional antara ketiga bahan tersebut perlu dicari untuk menghasilkan sirup yang acceptable. Simplex Lattice Designe (SLD) merupakan salah satu metoda yang sesuai untuk optimasi formula sirup fraksi dengan ketiga komponen tersebut (Bolton, 1996). Oleh karena itu, perlu dilakukan penelitian mengenai optimasi formula sediaan sirup mukolitik fraksi terstandar bunga kembang sepatu (Hibiscus rosa-sinensis L.).
Adanya penelitian secara ilmiah tentang obat tradisional diharapkan mempercepat penerimaan oleh masyarakat luas dan kalangan medis sehingga dapat dipertanggungjawabkan secara ilmiah sekaligus membantu kelestariannya. Metodologi Penelian
Bahan
MSD), IR (Perkin Elmer Spectrum 100), NMR (Bruker Avance 400 NMR spectrometer Rheinstetten, Germany) dan KLT-densitometer (CAMAG TLC
Jalan Penelitian
1. Determinasi tanaman
2. Pembuatan fraksi terstandar dengan cara maserasi dengan etanol 70% dan fraksinasi dengan etilasetat.
3. Isolasi senyawa penanda (alkaloid) dengan VLC dan KLTP dan penetapan kadar alkaloid dengan KLT-densitometri.
4. Identifikasi senyawa dengan spektrofotometer UV-Vis, IR, GC-MS dan NMR. Selanjutnya fraksi etanolik disebut sebagai fraksi terstandar.
5. Uji aktivitas mukolitik secara in vitro dengan menghitung penurunan viskositas mukus dengan larutan uji (larutan mukus dapar fosfat pH7 dan ekstrak etanolik, fraksi etanolik dan fraksi etilasetat) terhadap larutan mukus, dengan menggunakan viskometer Ostwald.
6. Optimasi sirup fraksi terstandar dengan mengkombinasikan gliserin, sorbitol dan CMC Na dengan menggunakan metode Simplex Lattice
Design (SLD).
7. Uji sifat fisik sirup hasil optimasi.
8. Uji stabilitas kimiawi sirup hasil optimasi dengan menggunakan suhu 27, 40, 55, dan 700C.
Analisa Data
Data yang diperoleh (aktivitas mukolitik secara in vitro, sifat fisik sirup fraksi terstandar, aktivitas mukolitik secara in vitro) diuji dengan Anova dan t-tes dengan taraf kepercayaan 95%. Stabilitas kimia sirup dianalisa secara deskriptif. Hasil dan Pembahasan
Setelah dicocokkan dengan acuan baku (Backer and Van den Brink, 1965), maka tanaman tersebut adalah Hibiscus rosa-sinensis L.
Rendemen ekstrak yang didapat adalah sebanyak 32,09 %, kemudian rendemen fraksi etanolik sebesar 84,50% dan fraksi etilasetat sebesar 13,91 %.
Ekstrak etanolik kadar 1,00, 1,25, dan 1,50% menunjukkan adanya aktivitas mukolitik secara in vitro, dan pada kadar 1,00% menunjukkan aktivitas mukolitik yang setara dengan aktivitas mukolitik asetilsistein 0,10%.
Viskositas mukus dengan adanya fraksi etanolik dari ekstrak etanol bunga kembang sepatu menunjukkan adanya penurunan dibandingkan dengan kontrol negatif (lebih kecil), sehingga dapat diartikan bahwa fraksi etanolik dengan kadar 0,60, 0,80 dan 1,00% mempunyai aktivitas mukolitik secara in vitro.
Setelah dianalisis dengan anova dan uji t LSD, maka didapatkan hasil bahwa viskositas dengan variasi kadar fraksi etanolik berbeda bermakna dengan kontrol negatif. Hal ini mempunyai arti bahwa fraksi etanolik dengan kadar 0,60, 0,80, dan 1,00% mempunyai aktivitas mukolitik dengan menurunkan mukus secara in vitro dan setara dengan kontrol positif (asetilsistein 0,10%). Hal ini menunjukkan bahwa fraksi etanolik lebih efektif dari pada ekstrak etanolik. Fraksi etilasetat 0,60, 0,80, dan 1,00% mempunyai viskositas yang lebih kecil daripada
kontrol negatif, artinya fraksi etilasetat pada kadar tersebut berefek sebagai mukolitik. Setelah diuji dengan anova dan diteruskan dengan uji t LSD hasilnya berbeda signifikan, sehingga dapat dikatakan bahwa secara in vitro fraksi etilasetat pada kadar tersebut dapat menurunkan viskositas mukus, walaupun tidak ada kadar fraksi etilasetat yang mempunyai viskositas yang tidak berbeda bermakna dengan kontrol positif (asetilsistein 0,10%) yang artinya secara in vitro fraksi etilasetat belum ada yang mempunyai aktivitas mukolitik yang setara dengan aktivitas mukolitik asetilsistein 0,10%.
Gambar 1 (d) terlihat hasil pemisahan yang baik. Alkaloid terpisah dari senyawa lain serta terbentuk noda bulat panjang berwarna merah setelah disemprot dengan pereaksi Dragendorff. Noda terletak pada hRf 13. Penggunaan fase gerak etilasetat : metanol 1:5 menghasilkan noda yang lebih baik dibanding dengan fase gerak yang lain (Gambar 1a, 1b, 1c, 1e).
(a) (b) (c) (d) (e)
Gambar 1. Hasil pemisahan dengan berbagai variasi fase gerak: (a) toluen : etilasetat : dietilamin (7 : 2: 1); (b) etilasetat : metanol (9 : 1); (c) etilasetat : metanol (1:1); (d) etil asetat : metanol (1:5); (e) etilasetat : metanol (1:9)
0 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 10 hRf
Fraksinasi dengan menggunakan metode Vacuum Liquid Chromatography
(VLC) menghasilkan 7 fraksi dan fraksi 6 dan 7 yang mengandung alkaloid
sebagai senyawa penanda dengan kadar sebanyak 0,35 ± 0,03% yang ditentukan dengan KLT-densitometer.
Isolat alkaloid teridentifikasi sebagai senyawa Glycine,N,N-dimethyl,
methyl ester ; 2-propanamine,N,N-dimethyl ; 1,2-Ethane diamine ; dan N,N,-dimethyl Glycine. Berdasarkan atas data GC-MS komponen terbesar adalah Glycine,N,N-dimethyl, methyl ester dan 1,2-Ethane diamine. Dalam penelitian ini
belum dapat dilakukan uji aktivitas mukolitik pada senyawa alkaloid karena dalam isolat terdapat 4 senyawa. Dilihat dari strukturnya maka tidak ada yang mirip dengan asetilsistein, sehingga senyawa penanda dalam bunga kembang sepatu bukan merupakan senyawa yang berkhasiat.
Formula optimum sirup ditentukan dengan data sifat fisik tujuh formula sirup pada minggu ke-0. Penentuan formula optimum dilakukan dengan metode
Simplex Lattice Design dengan software Design Expert® versi 7.1. Karakteristik
sifat fisik sirup yang digunakan dalam penetapan formula optimum adalah viskositas, waktu tuang, tanggaanp responden, dan pH.
Berdasarkan analisis dengan menggunakan software Design Expert® versi
7.1 untuk memprediksi formula optimum sirup fraksi terstandar bunga kembang sepatu diperoleh dihasilkan superimposed dari contour plot respon viskositas, waktu tuang, derajat keasaman, dan tanggapan responden sirup fraksi terstandar bunga kembang sepatu seperti yang terlihat pada gambar 2. Superimposed yang diperoleh menunjukkan daerah yang berwarna kuning yang menunjukkan daerah
yang memberikan respon optimum. Pada daerah tersebut didapatkan satu prediksi formula optimum dengan nilai desirability sebesar 0,994 (gambar 2).
Gambar 2. Superimposed dari contour plot respon viskositas, waktu tuang, derajat keasaman, dan tanggapan responden sirup fraksi terstandar bunga kembang sepatu
Komposisi formula optimum yang diperoleh dari analisis menggunakan
software Design Expert® versi 7.1 adalah gliserin sebesar 37,13%; larutan sorbitol
70% sebesar 49,32%; dan mucilago CMC-Na 0,5% sebesar 13,54%, Prediksi respon yang diperoleh dari prediksi formula optimum yaitu viskositas sebesar 7,28 mPaS, waktu tuang sebesar 2,98 detik, pH sebesar 3,55, dan tanggapan responden sebesar 3,29.
Prediksi respon yang diperoleh dari analisis menggunakan software Design
Expert® versi 7.1 selanjutnya dibandingkan dengan respon yang diperoleh pada
percobaan. Formula optimal yang didapat dari software Design Expert dibuat dan dilakukan evaluasi sifat fisik untuk dibandingkan dengan sifat fisik formula
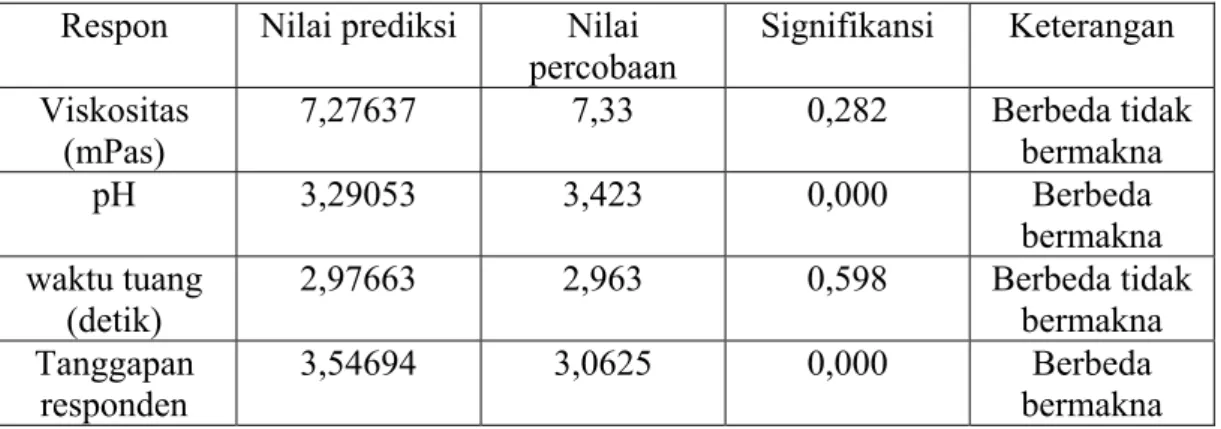
prediksi. Analisis yang digunakan adalah one sample t-test dengan taraf kepercayaan 95%. Berikut ini adalah hasil one sample t-test untuk viskositas, pH, dan waktu tuang, dan tanggapan responden formula optimal (tabel 1).
Respon viskositas dan waktu tuang berbeda tidak bermakna antara prediksi software Design Expert® versi 7.1 dengan hasil percobaan, sedangkan respon pH dan tanggapan responden berbeda bermakna antara prediksi software
Design Expert® versi 7.1 dengan hasil percobaan.
Tabel 1. Hasil Uji One Sample T-test Formula Optimal Sirup Hasil Prediksi Software Dibandingkan dengan Hasil Percobaan
Respon Nilai prediksi Nilai percobaan
Signifikansi Keterangan Viskositas
(mPas) 7,27637 7,33 0,282 Berbeda bermakna tidak pH 3,29053 3,423 0,000 Berbeda
bermakna waktu tuang
(detik) 2,97663 2,963 0,598 Berbeda bermakna tidak Tanggapan
responden
3,54694 3,0625 0,000 Berbeda bermakna
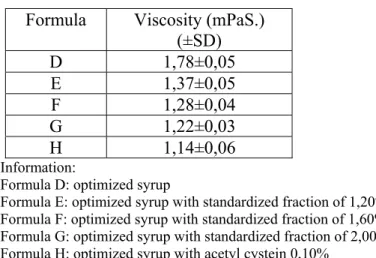
Formula optimum sirup fraksi terstandar bunga kembang sepatu, kemudian diuji aktivitas mukolitiknya secara in vitro dilihat dari penurunan viskositas sirup dalam larutan mukus dapar 20%. Hasilnya dapat dilihat dalam tabel 2 berikut.
Tabel 2. Aktivitas Mukolitik secara In Vitro (Viskositas) Sirup Fraksi Terstandar Bunga Kembang Sepatu Dengan Berbagai Konsentrasi
Formula Viskositas (mPaS.) (±SD) D 1,78±0,05 E 1,37±0,05 F 1,28±0,04 G 1,22±0,03 H 1,14±0,06 Keterangan :
Formula E: sirup hasil optimasi dengan fraksi terstandar 1,20% Formula F: sirup hasil optimasi dengan fraksi terstandar 1,60% Formula G: sirup hasil optimasi dengan fraksi terstandar 2,00% Formula H: sirup hasil optimasi dengan asetilsistein 0,10%
Tabel 2 menunjukkan aktivitas mukolitik secara in vitro, dalam hal ini adalah viskositas sirup fraksi terstandar bunga Kembang Sepatu dengan konsentrasi 1,20%, 1,60%, dan 2,00% dibandingkan dengan aktivitas mukolitik sirup asetilsistein 0,10%. Semakin tinggi konsentrasi fraksi terstandar bunga Kembang Sepatu yang digunakan, semakin kecil viskositas sirup. Hal ini berarti bahwa semakin banyak fraksi terstandar yang digunakan maka aktivitas mukolitik secara
in vitro semakin meningkat.
Setelah diuji dengan t-tes dengan taraf kepercayaan 95 % maka hasilnya adalah sirup formula hasil optimasi yang mengandung fraksi terstandar kadar 1,20; 1,60; dan 2,00% mempunyai aktivitas mukolitik secara in vitro dengan kadar fraksi terstandar 2,00% mempunyai aktivitas mukolitik setara dengan aktivitas mukolitik sirup dengan asetilsistein 0,10% secara in vitro.
Stabilitas sirup fraksi terstandar bunga kembang sepatu diketahui juga dengan menyimpan sirup pada suhu 270C, 400C, 550C, dan 700C selama 4 minggu. Keberadaan alkaloid setelah sirup fraksi terstandar bunga kembang sepatu disimpan dalam suhu 270C, 400C, 550C, dan 70 0C ditentukan dengan KLT-densitometer.
Análisis penentuan kadar digunakan metode KLT-densitometri, yaitu dengan melakukan scanning bercak pada λ 200 nm sehingga didapatkan suatu nilai hubungan antara AUC dengan kadar seri larutan baku sehingga diperoleh suatu persamaan regresi sebagai persamaan kurva baku Y = A+BX, untuk perhitungan
kuantitatif terhadap kadar senyawa dengan memasukkan nilai AUC yang didapat sebagai nilai Y, pada persamaan. Namun pada senyawa alkaloid dalam sediaan sirup fraksi ini tidak dapat ditentukan secara KLT-densitometri karena harga hRf senyawa penanda pada fraksi yang telah diformulasikan dalam sediaan sirup mengalami perubahan. Dilihat dari nilai hRf yang nampak, maka senyawa penanda mengalami peningkatan polaritas. Hasilnya dapat dilihat dalam gambar 3, sehingga dapat dikatakan bahwa suhu berpengaruh pada keberadaan alkaloid, dengan naiknya suhu, alkaloid mengalami kerusakan. Suhu berpengaruh pada kecepatan reaksi. Semakin tinggi temperatur, maka semakin besar tetapan kecepatan suatu reaksi atau reaksi semakin cepat. Kenaikan suhu 100C dapat menyebabkan kenaikan kecepatan reaksi sebesar 5,5 kali (Yoshika and Stella, 2002), sehingga penyimpanan pada suhu yang tinggi menyebabkan kerusakan alkaloid.
Kemungkinan lain bahwa adanya komponen sirup juga berpengaruh pada keberadaan alkaloid sebagai senyawa penanda yaitu karena kemungkinan terjadi interaksi sehingga tidak mempunyai hRf yang sama.
Di dalam sirup terdapat asam tartrat yang merupakan asam lemah yang akan bereaksi dengan N dari alkaloid yang bersifat basa lemah sehingga menghasilkan garam lemah yang kelarutannya kecil, jadi tidak dapat terelusi dengan baik.
hRf
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 Kiri Kanan
Gambar 3. Hasil Penotolan Seluruh Sampel /sirup yang mengandung fraksi terstandar (kanan 6-25), larutan baku (kiri 1-5) dengan fase diam silika gel 60 F254 dan fase gerak etilasetat : metanol (1:5)
Kesimpulan
1. Fraksi terstandar bunga kembang sepatu (Hibiscus rosa-sinensis L.) dengan kadar 0,60, 0,80, dan 1,00% mempunyai aktivitas mukolitik dengan adanya penurunan nilai viskositas larutan mukus usus sapi secara in vitro dan mempunyai aktivitas mukolitik setara dengan aktivitas mukolitik asetilsistein 0,10%.
2. Fraksi fraksi terstandar bunga kembang sepatu mengandung senyawa alkaloid sebagai senyawa penanda yang merupakan alkaloid golongan alifatis yang mengandung gugus hidroksil, gugus amina, ikatan karbon rangkap dua dan ikatan karbon rangkap tiga. Senyawa alkaloid dengan kadar 0,35 ± 0,03% dalam fraksi terstandar terdiri dari 4 senyawa, teridentifikasi sebagai
0 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 10
Glycine,N,N-dimethyl, methyl ester ; 2-propanamine,N,N-dimethyl ; 1,2-Ethane diamine ; N,N,-dimethyl Glycine. Berdasarkan atas data GC-MS
komponen terbesar adalah Glycine,N,N-dimethyl, methyl ester dan 1,2-Ethane
diamine.
3. Komposisi formula optimum sirup fraksi terstandar bunga kembang sepatu adalah gliserin sebesar 37,13%; larutan sorbitol 70% sebesar 49,32%; dan mucilago CMC-Na 0,5% sebesar 13,54%. Formula optimum yang diperoleh mempunyai respon viskositas dan derajat keasaman yang berbeda dengan prediksi respon yang diberikan oleh software Design Expert® versi 7.1,
sedangkan untuk respon waktu tuang dan respon tanggapan responden menunjukkan hasil yang sama. Sirup fraksi terstandar bunga kembang sepatu kurang stabil selama 4 minggu penyimpanan ditinjau dari respon derajat keasaman dan waktu tuang. Setelah sirup fraksi terstandar disimpan selama 4 minggu pada suhu 270C, 400C, 550C, dan 700C, maka keberadaan alkaloid tidak bisa dideteksi dengan KLT-densitrometer.
4. Sirup fraksi terstandar dengan kadar 1,20; 1,60; dan 2,00% mempunyai aktivitas mukolitik secara in vitro dan sirup dengan kadar 2,00% mempunyai aktivitas mukolitik yang sama dengan aktivitas mukolitik sirup asetilsistein 0,10%.
Daftar Acuan
Backer, C. A., dan Van den Brink, B. R. C., 1965, Flora of Java
(Spermatophytales Only), Vol. I, 3-6, 32-34, 41, 239-240,
Bolton, S., 1997, Pharmaceutical Statistics Practical and Clinical Application, 3rd Edition, 610-619, Marcel Dekker Inc., New York.
Departemen Kesehatan, 1985, Tanaman Obat Indonesia, Jilid Pertama, 44, Jakarta, Departemen Kesehatan Republik Indonesia.
Gauthaman, K.K., Saleem, M.T.S., Thanislas, P.T., Prabhu, V.V., Krishnamoorthy, K.K., Devaraj, N.S., and Somasundaram, J.S., 2006, Cardioprotective Effect of the Hibiscus rosa sinensis Flowers in An Oxidative Stress Model of Myocardial Ischemic Reperfusion Injury in Rat,
BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 6, 32-39.
Hitner, H. and Nagle, B., 1999, Basic Pharmacology, Fourth Edition, 409, Glencoe McGraw-Hill, New York.
Ikawati, Z., 2006, Farmakoterapi Penyakit Sistem Pernafasan, Cetakan Pertama, 27, 29-30, 32, Laboratorium Farmakoterapi dan Farmasi Klinik Bagian Farmakologi dan Farmakoterapi Fakultas Farmasi Universitas Gadjah Mada, Yogyakarta.
Ruban, P. And Gajalakshmi, K., 2012, In Vitro Antibacterial Activity of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis Flower Extract Against Human Pathogens, Asian Pasific
Journal of Tropical Biomedicine, 2, 5, p. 399-403.
Siddiqui, A.A., Wani, S.M., Rajesh, R., and Alagarsamy, V., 2006, Phytochemical and Pharmacological Investigation of Flowers of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis Linn, Indian J. Pharm. Sci., 68 (1), 127-130.
Vasudeva, N. and Sharma, S.K., 2008, Post-Coital Antifertility Activity of
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis Linn. Roots, eCAM, 5 (1), 91-9.
Yoshioka, S. and Stella, V.J., 2002, Stability of Drugs and Dosage Forms, 30-39, Kluwer Academic Publishers, New York.
SUMMARY
FORMULA OPTIMATION OF HIBISCUS FLOWER (Hibiscus
rosa-sinensis L.) STANDARDIZED FRACTION MUCOLYTIC
SYRUP PREPARATION IN VITRO
DISERTATION
As one of the requirement to obtain PhD degree
Proposed by:
MIMIEK MURRUKMIHADI 08/276481/SFA/00032
For
POST GRADUATE PROGRAM PHARMACY STUDY PROGRAM
FACULTY OF PHARMACY UNIVERSIONTY OF GADJAH MADA
YOGYAKARTA 2012
ABSTRACT
Hibiscus Flower (Hibiscus rosa-sinensis L.) has been used traditionally against cough. It was potential as secretolytic agent, but a standardized syrup is still needed in order to obtain optimum pharmalogycal effect. The objective of this research was to obtain an optimum – standardized fraction syrup formula of Hibiscus flower by Simplex Lattice Design Method, as well as to determine its in vitro mucolytic activity and stability both physically and chemically.
Standardized fraction of Hibiscus flower was obtained by macerating the flower with petroleum ether, followed by 70% ethanol solution, and fracinationated with ethyl acetate. The fraction containing alcaloidwas defined as standardized fraction. Optimalitation of the syrup containing standardized fraction obtained by Simplex Lattice Design software Design Expert® method versionon
7.1. Marker compound (alkaloid) isolation of Hibiscus flower was done by Thin Layer Chromatrography (TLC), Vaccum Liquid Chromatography (VLC), Preparative Thin Layer Chromatrography (PTLC). The marker was then identified according to UV-Vis, IR, GCMS, and NMR data. The marker concentration was determined by TLC densitometer. The syrup obtained from optimation process was tested by in vitro for its mucolytic activity, and also tested for its physical and chemical properties, its resistence to microbial contamination as well as respondent tolerability.
The result of the study shows that the marker obtained contains 4 compounds, identified as Glycine,N,N-dimethyl, methyl ester ; 2-propanamine,N,N-dimethyl ; 1,2-Ethane diamine ; N,N,-dimethyl Glycine while Glycine,N,N-dimethyl, methyl ester and 1,2-Ethane diamine are the major components (53.83 %, 30.96 %). The optimum formula was defined as glycerin (37.13%), sorbitol solution 70% (49.32%), CMC-Na 0.5% (13.54%). Physical response of the optimum formula from this study was comparable to the prediction especially on viscosity and pouring comfortability but not in taste and acidity. Syrup formula was less stabil in 4 weeks of storage viewed in the acidity and viscosity level. Standardized syrup showes in vitro mucolytic activity, and at 2.0% equal to acetylcystein syrup 0.1%. The presence of marker syrup was undetectable after storing at 27oC, 40 oC, 55 oC, and 70 oC for 4 weeks.
Key word: hibiscus flower, optimation of syrup, standardized fraction, mucolytic, in vitro
INTRODUCTION
Some diseases such as bronchitis and respiratory tract infection produced mucus secretion (Ikawati, 2006). The increase of mucus production occurred in such condition and the mucus has thick consistency, which affect the breathing function. Physiologically the cilia cannot eliminate the mucus as it was too thick (Hitner and Nagle, 1999). The thick mucus can be eliminated through dissolution process. Hibiscus flower (Hibiscus rosa-sinensis L.) is one of the traditional medication utilized in the community as mucolytic agent (Ministry of Health, 1985).
Many researches had been conducted on hibiscus flower. Nevertheless, research on fractioned formula of hibiscus flower as in vitro mucolytic agent has not existed yet. The previous researches are, for example, ethanol extract of hibiscus flower to inhibit the growth of antibiotic sensitive and resistant
Mycobacterium tuberculosis yang sensitif (Ruban and Gajalakshmi, 2012). Anti –
implantasi activity of hibiscus flower’s root ethanol extract (Vasudeva and Sharma, 2008). The anti – hipertensive properties of petroleum ether, hydro alcohol, and chloroform of hibiscus flower extract (Siddiqui et al., 2006). Gauthaman et al. (2006) reported the effect of hibiscus flower in increasing endogenous anti oxiandt component in myocardium to bring cardio protective effect.
The direct use of hibiscus flower was considered unpractical, ineffective and unacceptable. The use of hibiscus flower in standardized fraction was considered
more effective, thus need to be formulated in syrup preparation. Marker compound is a compound which can be utilized to assess the quality of fraction as active ingredients. That way, fraction will have a constant quality.
Syrup is a liquid preparation which has many advantages, such as acceptable for almost all age group, easily absorbed and having a faster effect. Fraction had some disadvantaged characteristic such as unfavorable flavor and having parts which cannot be dissolved. Additions of ingredients are necessary to make an acceptable syrup preparation of hibiscus flower fraction. Glycerin was added as co solvent for in dissolved active ingredients. The in dissolved fraction part was dispersed with the addition of CMC Na. The flavor was improved by adding sorbitol. Proportional composition between the three ingredients needs to be formulated to gain an acceptable syrup preparation. Simplex Lattice Design (SLD) was one of the appropriate methods to optimize the fraction syrup formula containing the three components (Bolton, 1996). Therefore, a research on optimizing the mucolytic syrup formula of standardized fraction hibiscus flower (Hibiscus rosa-sinensis L.) needs to be conducted.
Scientific research on traditional medicines was expected to encourage community and medical society acceptance towards traditional medicines as it has a strong scientific basis as well as to preserve the heritage of Indonesian traditional medicine.
Research Methodology Means
(MSD), IR (Perkin Elmer Spectrum 100), NMR (Bruker Avance 400 NMR spectrometer Rheinstetten, Germany) and TLC-densito meter (CAMAG TLC
Scanner 3).
Process of Reserach
1. Determination of plant species
2. Production of standardized fraction by maceration with ethanol 70% and fractination with ethyl acetate.
3. Isolation of marker compound (alcaloid) using VLC and PTLC and determination of alcaloid concentrationwith TLC-densitometry.
4. Identification of compound using spectrophotometer UV-Vis, IR, GC-MS and NMR. Next, ethanolic fraction was refer as standardized fraction.
5. Testing in vitro mucolytic activity by counting the decrease of mucus viscosity using test liquid (buffer phosphate mucus liquid fosfat pH7 and ethanolic extract, ethanolic fraction and ethyl acetate fraction) against mucus by using Ostwald viscometer.
6. Syrup optimation of standardized fraction by combining glyserin, sorbitol and CMC Na by using Simplex Lattice Design (SLD) method. 7. Testing the physical stability of optimation syrup result.
8. Testing chemical stability of of optimation syrup result by exposing it to temperature of 27, 40, 55, and 700C.
9. Testing the in vitro mucolytic activity of optimation syrup result.
Data Analysis
The obtained data (in vitro mucolytic activity , physical stability of standardized fraction syrup, in vitro mucolytic activity ) was tested with Anova and t-test with reliability of 95%. Chemical stability of of optimation syrup was analyzed descriptively.
Result and Review
After matched with main reference (Backer and Van den Brink, 1965), the plant was being identified as Hibiscus rosa-sinensis L.
Obtained extract was as much as 32, 09 %, followed by ethanolic fraction as much as 84, 50% and ethyl acetate fraction as much as 13,91 %.
Ethanol extract with the concentration of 1,00, 1,25, and 1,50% shows in vitro mucolytic activity, and at concentration of 1,00% shows mucolytic activity equal to mucolytic activity of acetyl cystein 0,10%.
Mucus viscosity are decreasing with the presence of ethanolic fraction of ethanol extract of hibiscus flower, if being compared to negative control (lower), which conclude that ethanolic fraction with the concentration of 0,60, 0,80 and 1,00% had in vitro mucolytic activity .
After being analyzed with anova and t test LSD, the result was that viscosity with varied concentration of ethanolic fraction were significantly differs,
compared to negative control. This means that ethanolic fraction with concentration of 0, 60, 0, 80, and 1, 00% has mucolytic activity by decreasing mucus viscosity in vitro equals to positive control (acetyl cystein 0, 10%). This shows that ethanolic fraction is more effective than ethanol extract.
Ethyl acetate fraction of 0, 60, 0,80, and 1,00% has lower viscosity than negative control, which means ethyl acetate fraction at that concentration level functioned as mucolytic. After tested with anova and followed with t test LSD, the result was significantly different, so as concluded that ethyl acetate fraction at that level of concentration can decrease in vitro mucus viscosity, even if there are no concentration of ethyl acetate fraction which has significantly different viscosity with (acetyl cystein 0,10%), which means in vitro mucolytic activity of ethyl acetate fraction is not equal with mucolytic activity of acetyl cystein 0,10%.
Picture 1 (d) shows result of good separation. Alcaloid was being separated from other compounds, forming red – long –round stain after being sprayed with Dragendorff reagent. The stain was located at hRf 13. The use of moving phase of ethyl acetate : methanol 1:5 result in better staining compared to other moving phase (picture 1a, 1b, 1c, 1e).
(a) (b) (c) (d) (e)
Picture 1. Separation result using varied moving phases: (a) toluene : ethyl acetate : diethil amine (7 : 2: 1); (b) ethyl acetate : methanol (9 : 1); (c) ethyl acetate : methanol (1:1); (d) ethyl acetate : methanol (1:5); (e) ethyl acetate : methanol (1:9)
Fractination using Vacuum Liquid Chromatography (VLC) method result in 7 fraction and fraction 6 and 7, containing alcaloid as marker compound with concentration level of 0,35 ± 0,03%, determined using TLC-densito meter.
Alcaloid isolate was identified as Glycine,N,N-dimethyl, methyl ester ; 2-propanamine,N,N-dimethyl ; 1,2-Ethane diamine ; and N,N,-dimethyl Glycine compounds. Based on GC-MS data, the largest component is Glycine,N,N-dimethyl, methyl ester and 1,2-Ethane diamine. In this research, mucolytic activity test on alcaloid compound cannot be conducted yet, for in the isolate there are 4 compounds. Seen from the structure, none resembles acetyl cystein, thus, marker compound in hibiscus flower was not the therapeutic agent.
Syrup optimal formula was determined by data of physical features of seven syrup formula on week - 0. The deteremination of optimal formula was
0 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 10 hRf
conducted by using Simplex Lattice Design with Software Design Expert® versionon 7.1. characteristic of physical features of the syrup used in optimal formula determination is viscosity, pouring time, respondent opinion, and pH.
Based on analysis using Software Design Expert® versionon 7.1 to predict
optimal formula of standardized fraction syrup of hibiscus flower, we obtained superimposed result of contour plot on viscosity response, pouring time, acidity level, and respondent opinion on standardized fraction syrup of hibiscus flower as seen on picture 2. The obtained superimposed showed yellow parts which refers to parts of optimal response. In that part we obtained a prediction of optimum formula with desirability value of 0,994 (picture 2).
Picture 2. Superimposed result of contour plot on viscosity response, pouring time, acidity level, and respondent opinion on standardized fraction syrup of hibiscus flower
Composition of optimal formula, obtained from analysis using Software Design Expert® version 7.1 are glycerine as much as 37,13%; sorbitol solution
70% as much as 49,32%; and mucilago CMC-Na 0,5% as much as 13,54%. Response prediction obtained from optimal formula prediction was viscosity as
much as 7,28 mPaS, pouring time as much as 2,98 second, pH as much as 3,55, and respondent opinion as much as 3,29.
Response prediction obtained from analysis using Software Design Expert® version 7.1 was then compared to response obtained from the research.
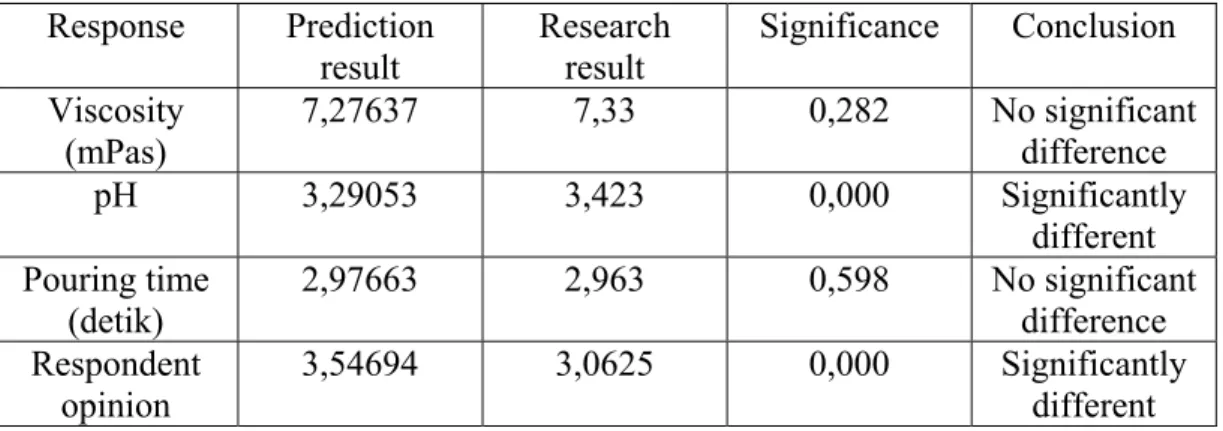
Optimal formula obtained from Software Design Expert was produced and evaluated for its physical features to be compared with physical features of prediction formula. Analysis that was being used is one sample t-test with reliability level of 95%. The following are the result of one sample t-test for viscosity, pH, pouring time, and Respondent opinion on formula optimal (table 1).
Viscosity response and pouring time shows no significant difference between software Design Expert® version 7.1 prediction with research result, whereas pH response and Respondent opinion differ significantly between
software Design Expert® version 7.1 prediction and the research result.
Table 1. Test result of One Sample T-test Sirup Optimal Formula, Software prediction result compared to research result
Response Prediction
result Research result Significance Conclusion Viscosity (mPas) 7,27637 7,33 0,282 No significant difference pH 3,29053 3,423 0,000 Significantly different Pouring time (detik) 2,97663 2,963 0,598 No significant difference Respondent opinion 3,54694 3,0625 0,000 Significantly different Optimal formula of hibiscus flower standardized fraction syrup was then tested for its in vitro mucolytic activity, assessed from the decrease of syrup
viscosity in buffer mucus solution 20%. The result can be seen in the following table 2.
Table 2. In vitro mucolytic activity (Viscosity) of hibiscus flower standardized fraction syrup formula with various concentration levels
Formula Viscosity (mPaS.) (±SD) D 1,78±0,05 E 1,37±0,05 F 1,28±0,04 G 1,22±0,03 H 1,14±0,06 Information:
Formula D: optimized syrup
Formula E: optimized syrup with standardized fraction of 1,20% Formula F: optimized syrup with standardized fraction of 1,60% Formula G: optimized syrup with standardized fraction of 2,00% Formula H: optimized syrup with acetyl cystein 0,10%
Table 2 shows in vitro mucolytic activity, in this case was the viscosity of standardized fraction hibiscus flower syrup with the concentration of 1,20%, 1,60%, and 2,00% compared with the mucolytic activity of acetyl cystein syrup 0,10%. The higher concentration level of standardized fraction hibiscus flower syrup being used will cause the lower viscosity of the syrup. This shows that the more standardized fraction being used will increase the in vitro mucolytic activity.
After being tested using t-test with reliability level of 95 %, the result is optimized formula syrup containing standardized fraction with concentration level of 1, 20; 1, 60; and 2 ,00% has in vitro mucolytic activity. Standardized fraction with concentration level of 2,00% has in vitro mucolytic activity equal to in vitro mucolytic activity of acetyl cystein 0,10%.
Stability of standardized fraction hibiscus flower sirup was discovered after storage of syrup at the temperature of 270C, 400C, 550C, and 700C for 4 weeks.
Alcaloid presence after standardized fraction hibiscus flower syrup was stored in temperature of 27 0C, 40 0C, 55 0C, and 70 0C was determined with TLC-densitometer.
Analysis of concentration level determination using TLC-densitometri method, which was by conducting scanning on stains on λ 200 nm so as obtained a related value between AUC with main solution serial concentration level to obtain a regression function as main curve function Y = A+BX, for quantitative measurement on compound’s concentration level by inserting AUC value which was obtained as Y value, on the function. However, the alcaloid compound in this fraction syrup preparation can not be determined with TLC-densitometri for the value of hRf in the marker compound on the formulated fraction in the syrup preparation had altered. Seen from the emerging hRf value, the marker compound had a polarity increase. Which can be seen in picture 3, so as to say that temperature can affect the presence of the alkaloid, with the temperature increase, alcaloid will be destroyed. Temperature also affects reaction velocity. The higher the temperature, the higher the constant for reaction velocity or the reaction will go faster. The increase of 100C will cause the increase of reaction velocity as much as 5, 5 times (Yoshika and Stella, 2002). Hence, storage at high temperature will cause alcaloid damage.
Other possibility is that the presence of syrup components will also affect the presence of alcaloid as marker compound due to the possibility of chemical interaction so the hRf value will not be the same.
hRf
The syrup contains tartrate acid, a weak acid which will react with N of the alcaloid which is a weak base and resulting in weak salts of low solubility, so it cannot be finely elucidate.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 Left Right
Picture 3. Result of pointing of all syrup simple containing standardized fraction (right: 6-25), main solution (left: 1-5) with static phase of silica gel 60 F254 and moving phase of ethyl acetate: methanol (1:5)
Conclusion
1. Standardized fraction syrup of hibiscus flower (Hibiscus rosa-sinensis L.) with concentration level of 0,60, 0,80, and 1,00% has in vitro mucolytic activity with the decrease of viscosity value of mucus liquid in cow’s intestine and has the mucolytic activity equal to acetyl cystein 0,10%.
2. Standardized fraction syrup of hibiscus flower has alcaloid compound as marker compound which was an alyphatic alcaloid containing hidroxyl and
0 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 10
amine bond, double and triple strand carbon bond. Alcaloid compound with the concentration level of 0,35 ± 0,03% in the standardized fraction consist of 4 compound, identified as Glycine,N,N-dimethyl, methyl ester ; 2-propanamine,N,N-dimethyl ; 1,2-Ethane diamine ; and N,N,-dimethyl Glycine. Based on GC-MS data, the largest components are Glycine,N,N-dimethyl, methyl ester and 1,2-Ethane diamine.
3. Composition of optimal formula standardized fraction hibiscus flower syrup are glycerine as much as 37,13%; sorbitol solution 70% as much as 49,32%; and mucilago CMC-Na 0,5% as much as 13,54%. Optimal formula obtained has viscosity response and acidity level which was different to response prediction given by Software Design Expert® version 7.1, whereas for the
pouring time and respondent opinion shows the similar result. Standardized fraction syrup of hibiscus flower is less stable in 4 weeks of storage assessed from the acidity level and pouring time. After the standardized fraction syrup was being stored for 4 weeks in temperature of 270C, 400C, 550C, and 700C, the alcaloid presence cannot be detected with TLC-densitrometer.
4. Standardized fraction syrup with concentration level of 1,20; 1,60; and 2,00% has in vitro mucolytic activity and syrup with concentration level of 2,00% has equal mucolytic activity to acetyl cystein syrup 0,10%.
Reference
Backer, C. A., and Van den Brink, B. R. C., 1965, Flora of Java
(Spermatophytales Only), Vol. I, 3-6, 32-34, 41, 239-240,
Wolt’rs-Noordhoff, Groningen, The Netherlands.
Bolton, S., 1997, Pharmaceutical Statistics Practical and Clinical Application, 3rd Edition, 610-619, Marcel Dekker Inc., New York.
Ministry of Health, 1985, Indonesian Medicine Herbs, First edition, 44, Jakarta, Ministry of Health Republic of Indonesia.
Gauthaman, K.K., Saleem, M.T.S., Thanislas, P.T., Prabhu, V.V., Krishnamoorthy, K.K., Devaraj, N.S., and Somasundaram, J.S., 2006, Cardioprotective Effect of the Hibiscus rosa sinensis Flowers in An Oxidative Stress Model of Myocardial Ischemic Reperfusion Injury in Rat,
BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 6, 32-39.
Hitner, H. and Nagle, B., 1999, Basic Pharmacology, Fourth Edition, 409, Glencoe McGraw-Hill, New York.
Ikawati, Z., 2006, Pharmacotherapy of Respiratory System Disease, First Edition, 27, 29-30, 32, Pharmacotherapy Laboratorium and Clinical Pharmacy of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapy Faculty of Pharmacy University of Gadjah Mada, Yogyakarta.
Ruban, P. And Gajalakshmi, K., 2012, In Vitro Antibacterial Activity of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis Flower Extract Against Human Pathogens, Asian Pasific
Journal of Tropical Biomedicine, 2, 5, p. 399-403.
Siddiqui, A.A., Wani, S.M., Rajesh, R., and Alagarsamy, V., 2006, Phytochemical and Pharmacological Investigation of Flowers of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis Linn, Indian J. Pharm. Sci., 68 (1), 127-130.
Vasudeva, N. and Sharma, S.K., 2008, Post-Coital Antifertility Activity of
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis Linn. Roots, eCAM, 5 (1), 91-9.
Yoshioka, S. and Stella, V.J., 2002, Stability of Drugs and Dosage Forms, 30-39, Kluwer Academic Publishers, New York.