A BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF CONJUNCTIONS IN ARTICLES OF THE JAKARTA POST NEWSPAPER
A PAPER
BY
LIJA SEFRIANA M REG. NO 062202076
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH SUMATERA FACULTY OF LETTERS
DIPLOMA III ENGLISH DEPARTMENT MEDAN
▸ Baca selengkapnya: jakarta post researchers have found a technique
(2)Approved by Supervisor,
Dra. Masdiana Lubis, M.Hum NIP : 131284311
Submitted to Faculty of Letters University of North Sumatera
In partial fulfillment of the requirements for DIPLOMA (D-III) IN ENGLISH.
Approved by
Head English Study Program,
Dra. Syahyar Hanum, D.P.F.E NIP.130702287
Approved by the Diploma III of English Study Program Faculty of Letters, North Sumatera University
Accepted by the board of examiners in partial to fulfillment requirements for D-III Examination of the Diploma III English Study Program, of the Faculty of Letters, North Sumatera University
The examination is held on the ………
Faculty of Letters, University of North Sumatera. Dean,
Drs. Syaifuddin, M.A.Ph.d NIP.132098531
Board of Examiner and Reader:
AUTHOR’S DECLARATION
I, Lija Sefriana M, declare that I am the sole author of this paper. Except were reference is made in the text of this paper, this paper contains no material published elsewhere or extracted in whole or in part from a paper by which I have qualified for or awarded another degree.
No other person’s has been used without due acknowledgement in the main text of the paper. This paper has not been submitted for the award of another degree in any tertiary education.
COPYRIGHT DECLARATION
Name : Lija Sefriana M
Title of paper : A Brief Description of Conjunctions In Articles of The Jakarta Post Newspaper
Qualification : D-III / Ahli Madya Study Program : English
I am willing that my paper should be available for reproduction at discreation of the librarian of the Diploma III English Study Program Faculty of Letters USU on the understanding that users are made aware of their obligation under law of the Republic of Indonesia.
ABSTRACT
Kertas karya yang berjudul “A Brief Description of Conjunctions In Articles of The Jakarta Post Newspaper” ini mendeskripsikan tentang penggunaan konjungsi dalam kalimat yang terdapat pada harian The Jakarta Post. Penyusunan kertas karya ini menggunakan sepuluh artikel sebagai sample atau data. Adapun alasan penulis memilih topik ini karena ingin mengetahui sejauh mana para jurnalis dari harian tersebut menggunakan konjungsi dalam tulisan-tulisan yang mereka hasilkan. Pembahasan dalam kertas karya ini berpedoman pada beberapa buku tentang tata Bahasa Inggris sebagai referensi atau rujukan yang dapat mendukung ide atau pendapat penulis tentang topik ini. Kemudian penulis membaca, menghitung, dan mengklasifikasikan jenis konjungsi yang terdapat pada artikel-artikel di harian The Jakarta Post, untuk mendapatkan jenis konjungsi yang paling dominan digunakan para jurnalis harian The Jakarta Post. Kertas karya ini diharapkan dapat bermanfaat bagi pembaca.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
First of all, I would like to thank to Almighty God for blessing and giving me an opportunity to accomplish this paper. Furthermore, I would like to express my deepest gratitude to all the people who have been around me to give support accomplish this paper:
1. Drs. Syaifuddin M.A.Pa.D., the Dean of Faculty of Letters, University of North Sumatera.
2. Dra. Syahyar Hanum, D.P.F.E., the Head of English Diploma Study Program.
3. My supervisor, Dra. Masdiana Lubis, M.Hum., thank you very much for your advices, suggestion, guidance, and help since I began to write this paper.
4. My reader, Drs. Muhizar Muchtar, M.S.
5. All lecturers, especially at English Diploma III Study program, who have taught and given me knowledge during the years of my study in this faculty.
6. My beloved family, my dad D. Manurung, my mom K. Saragi, and my sister, Flora. Thank you for everything, for your love, care, and encourage.
7. My special thanks to Indra Ambarita, who has given me support and encourage me to carry on writing this paper.
8. My best friends Mediana, Netty, Melati, Dwi, Naomi, Rut Sri Novita thanks for always accompanied me when we go home everyday.
Finally, I do realize that this paper is still far from being perfect. Therefore, I welcome any constructive critics and suggestions toward this paper.
Medan, May , 2009 The Writer
TABLE OF CONTENTS
AUTHOR’S DECLARATION COPYRIGHT DECLARATION
ABSTRACT ... i
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ... ii
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... iv
1. INTRODUCTION The Background of Study ... 1
The Scope of Study ... 3
The Objective of Study ... 3
The Significance of Study ... 3
The Method of Study ... 3
2. PRINCIPLES IN USING CONJUNCTIONS Definition of Conjunctions ... 5
Functions of Conjunctions ... 6
Types and Classification of Conjunctions ... 6
Coordinate Conjunctions ... 6
Subordinate Conjunctions ... 10
3. THE DESCRIPTION OF CONJUNCTIONS IN ARTICLES OF THE JAKARTA POST 3.1 Data ... 14
3.2.1 The Conjunction ‘And’ ... 17
3.2.2 The Conjunction ‘Or’ ... 18
3.2.3 The Conjunction ‘But’ ... 19
3.2.4 The Conjunction ‘Because’ ... 20
3.2.5 The Conjunction ‘Before’ ... 21
3.2.6 The Conjunction ‘After’ ... 22
3.3 The Most Dominant Conjunctions Used In ten Articles Of The Jakarta Post 23 4. CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS 4.1 Conclusions ... 26
4.2 Suggestions ... 27
REFERENCES ... vi
REFERENCES
Ehrlich, Eugene. English Grammar. 3rd ed. USA The Mc Graw-Hill Companies, Inc, 2000. Hasibuan, Sofia Rangkuti. English Language Structure. Jakarta Djambatan, 2000.
Kardimin, Akhmad. Essential English Grammar. Yogyakarta Pustaka Pelajar, 2005. Junaidi, Suryadi. Complete English Grammar. Yogyakarta Pustaka Pelajar, 2007.
Kardimin, Akhmad. Fundamental English Grammar. 1st ed. Yogyakarta Pustaka Pelajar, 2004.
Olivia, W. CH. M. Developing English Sentence. Jakarta Great Media, 2003.
Murphy, Raymond. English Grammar In Use. 2nd ed. England Cambridge University Press, 1985.
Purwanto, Hadi. BBC English Grammar. Pekalongan CV Bahagia, 1994.
Kaplon, Jeffrey P. English Grammar Principles And Facts. USA Prentice-Hall, Inc, 1995. Kardimin, Akhmad. Perfect Structure For Better TOEFL. 1st ed. Yogyakarta Pustaka
Pelajar, 2007.
Junaidi, S. and Suwono, Eko. 2004. Matematika SMP Kelas 3. Surabaya: Esis/Erlangga Harris.2009. About Conjunction. http//www.virtualsalt.com/conjunct.htm.
ABSTRACT
Kertas karya yang berjudul “A Brief Description of Conjunctions In Articles of The Jakarta Post Newspaper” ini mendeskripsikan tentang penggunaan konjungsi dalam kalimat yang terdapat pada harian The Jakarta Post. Penyusunan kertas karya ini menggunakan sepuluh artikel sebagai sample atau data. Adapun alasan penulis memilih topik ini karena ingin mengetahui sejauh mana para jurnalis dari harian tersebut menggunakan konjungsi dalam tulisan-tulisan yang mereka hasilkan. Pembahasan dalam kertas karya ini berpedoman pada beberapa buku tentang tata Bahasa Inggris sebagai referensi atau rujukan yang dapat mendukung ide atau pendapat penulis tentang topik ini. Kemudian penulis membaca, menghitung, dan mengklasifikasikan jenis konjungsi yang terdapat pada artikel-artikel di harian The Jakarta Post, untuk mendapatkan jenis konjungsi yang paling dominan digunakan para jurnalis harian The Jakarta Post. Kertas karya ini diharapkan dapat bermanfaat bagi pembaca.
1. INTRODUCTION
1.1 The Background of Study
Conjunction is one of the items in grammar, a body rules specifying how meaning are created in English. Conjunction is a word that links words, phrases, and clauses. It can be said that conjunctions were “linking “ or “ joining “ words which joined together various things. If a conjunctions “joined” words, then any word that occur between others would be a conjunctions
(Ehrlich, 2000 142).
There are many definitions of conjunctions which are proposed by people or scientist like Robert Harris and Richard Nordquist. Harris (2009) states that as their name implies, conjunctions join together element of thought words, phrases, sentences, and paragraph. Or
Nordquist (2009) also states that conjunctions is part of speech (or word class) that serves to connect words, phrases, clauses, or sentences.
Talking about English especially English sentence we can not avoid talking about conjunctions, since conjunction is one of the elements that construct a sentence. Using conjunctions in English whether it is written or spoken is not an easy to do because the usage of conjunctions are different that make many problems we have to face. As what they said one of conjuctions that can not be used to join two ideas into a single sentence.
When we use conjunctions incorrectly in this way, the result is called to “run-on” sentence, run-on sentences are grammatical incorrect (Edu, 2009). When we used conjunctions, we should consider their function and meaning.
Here, conjunctions and used to add some information. So by mastering conjunctions, our language will be developed.
There are some functions of conjunctions in writing article, such as, relate the ideas in the following text logically to each other, express the logical flow explicity, express a polite directive in speech. Unlike adverbs, conjunctions do not modify. They are used for the purpose of connecting.
Writing articles should present good English Grammar based on Lee (2009) who states that language used in the articles of The Jakarta Post Newspaper also has to present Good English Grammar and clean messages so the readers can understand the language in the articles.
Many people have done research about conjunctions. For example, Elen (2006) says that conjunctions are words that link ideas they bring one idea or piece of information into some kinds of relationships with another idea or piece of information. In this way, they help to create continouity or ‘flow’ in a text. If ideas and information are not clearly linked by appropriate conjunctions, your readers have to try to work out the relationships by themselves. Your writing may also appear very descriptive since it is continually making statement without showing the relationship between them.
1.2 The Scope of Study
In writing this paper, the writer just want to focus on the usage of and, or, but, because, before, after conjunctions in ten business articles of The Jakarta Post Newspaper issued on June
9, 2008; January 29, 2009; January 30, 2009; February 11, 2009 and February 21, 2009.
1.3 The Objective of Study
The objectives of the study are
1. To describe the usage of conjunctions especially and, or, but, because, before, and after found in ten business articles of The Jakarta Post.
2. To find out the most dominant conjunctions used in ten business articles of The Jakarta Post Newspaper.
1.4 The Significance of Study
Obviously the significances of study this paper are
2. To make readers know in details about conjunctions used in the articles of The Jakarta Post newspaper
3. To be used as a literature for further study.
1.5 The Method of Study
sentences of conjuctions. There are ten business articles which are chosen randomly. Miffin (2009) states that writing randomly means that having no specific pattern, purpose, or adjective.
2. PRINCIPLES IN USING CONJUNCTIONS
2.1 Definition of Conjunctions
Conjunction is a word which is used to link or join words, phrases, or clauses. In a sentence, most of conjunctions are from another parts of speech, especially from preposition (Kardimin, 2004:167).
Examples:
Fida and Rama wrote a letter. He warned me but I did not heed.
In the above sentences, we can see that the word and in the first sentence joins two nouns Fida and Rama. It is a joining word. But, in the second sentence joins two groups of words: He warned me but I did not heed. It is also joining word. They are conjunctions.
Conjunctions must be distinguished from relative pronouns, relative adverb and preposition that are also connecting words.
Examples:
This is a motorcycle that Jack bought. ( relative pronoun) This is the place where he was murdered. (relative adverb)
He stood behind me. (preposition)
the two parts of the sentences. The preposition governs the noun or the pronoun while also joining the two words.
2.2 Functions of Conjunctions
Generally, the functions of conjunction are to link or join words, phrases, and clauses. Kardimin (2004:167) said that the functions of conjunction are parts of speech that connect words, phrases, clauses, and sentences. The most common one: “and”, “but”, and “or”. while, “because”, “so”, and “however” are also conjunctions.
2.3 Types and Classifications of Conjunctions
There are two types of conjunctions, Coordinate Conjunctions and Subordinate Conjunctions.
2.3.1 Coordinate Conjunctions
Coordinate conjunctions are used to link some words, phrases, and clauses. Besides that, coordinate conjunctions are used to link the elements of sentences that have equal level. The function of coordinate conjunction is to join to sentences that do not rely on each other for meaning together.
faintly reminiscent of the “joining” notion a rule that they can occur only between two words or phrases of the same type – two nouns, two sentences, and so forth.
Examples:
Tony and Cathy went. (two nouns)
Tony eat and drink. (two verbs)
Tony eat and Cathy drink. (two sentences)
According to the explanation above, coordinate conjunctions can be classified into four kinds. They consists of:
1. Cumulative Conjunctions
Cumulative conjunction is a group of conjunctions that joins two statement of fact. The usage is to add one thought to another. Cumulative conjunctions are as, and, both… and, also, as well as, no less… than, not only… but also, not only… but, again, furthermore, likewise, besides,
moreover, and in addition.
The position of and, both… and, also, as well as, no less… than, again, furthermore, likewise, moreover, and in addition is in the middle of sentence. But, the position of not only…
Examples:
Yogi is a smart and handsome boy. He is both the lazy boys and a drunkard.
Not only Rudy but all students involves to this problem.
2. Alternative Conjunctions
Alternative conjunction is a group of conjunctions that expresses a choice between two things. The usage is to indicate alternative or choice between two things. Alternative conjunctions are or, either… or, neither… nor, or, else, and otherwise.
The position of or, else and otherwise is in the middle of sentence. But, the position of either… or, and neither… nor is in the beginning of the sentence
Examples:
You must participate or He will be fined.
Neither is He hard working nor is He resourceful.
You must take a rest otherwise You will lose your health
3. Adversative Conjunctions
The position of adversative conjunctions is in the middle of sentence.
Examples:
She is a smart girl nevertheless be often make mistakes.
Siska like to go a picnic, however, she have no money.
I was reading a magazine while my mother slept in the living room.
4. Illative Conjunctions
Illative conjunction is a group of conjunctions which show meaning of an event or another actions, or show the conclusions. The usage is to express an interence. Illative conjunctions are therefore, thus, consequently, because of, as a result, accordingly, hence, so, for this reason,
regardless of, so then, and for.
The position of illative conjunctions is in the middle of sentence.
Examples:
Budi was punished because of he was guilty.
He will be rewarded, so he is trustworthy.
2.3.2 Subordinate Conjunctions
Subordinate conjunctions are words which are used to link subordinate clauses with the main clauses in the complex sentence. Main clauses can stand alone, do not depend on subordinate clauses while subordinate clauses can not stand alone, should depend on the main clauses. Most of subordinate conjunctions are from preposition.
Subordinate conjunctions combined elements of sentences-clauses-which is less of equal. The most general of subordinate conjunctions are after, although, as, as if, as long as, because, before, how, if, in order that, so, so that, though, till, unless, until, when, where, wherever, while,
why, and yet. Relative pronouns that, what, which, and who are also used as subordinate
conjunctions.
Subordinate conjunctions can be classified into six kinds. They consists of:
1. Conjunctions of Reason
Conjunctions of reason are because, because of, since, as, and for. Their positions is in the middle of sentence, but sometimes is in the beginning of sentence before noun. The usage is to express or illustrate a reason of an event.
Examples:
It is hard for us to speak English because we never practice it.
2. Conjunctions of Result
Conjunctions of result are so that, and in order to. Their positions is in the middle of sentence. The usage is to express or to illustrate a result or consequence of an event.
Examples:
I eat so much in order to make I have stomachache. It rained so heavily that all tanks breached.
He ran so fast so that made himself tired.
3. Conjunctions of Conditional
Conjunction of conditional are if, unless, as, and as if. Their position is in the middle of the sentence but “if” may be put in the beginning of sentence before noun. The usage is to express or illustrate a concession of an event.
Examples:
You will get lose unless you study hard.
If you agree I shall accompany you. He talked alone as if He were drunk.
4. Conjunctions of Concession
Examples:
Although I am so busy, I still phone you.
She buys some clothes eventhough she do not have much money.
My father is an honest man though he is poor.
5. Conjunctions of Comparison
Conjunctions of comparison are as… as, than, and more… than. Their positions is in the middle of the sentence. The usage is to express or illustrate a comparison of an event.
Examples:
My father as tall as my uncle
A car more expensive than a motorcycle.
The sea is deeper than the mountains are high.
6. Conjunctions of Situation
Conjunctions of situation are until, after, before, since, as, as soon as, and as long as. Their position is in the middle of sentence, but “after” may be put in the beginning of sentence. The usage is to express or illustrate the situation of an event.
Examples:
Wait here until I come back.
REFERENCES
Ehrlich, Eugene. English Grammar. 3rd ed. USA The Mc Graw-Hill Companies, Inc, 2000. Hasibuan, Sofia Rangkuti. English Language Structure. Jakarta Djambatan, 2000.
Kardimin, Akhmad. Essential English Grammar. Yogyakarta Pustaka Pelajar, 2005. Junaidi, Suryadi. Complete English Grammar. Yogyakarta Pustaka Pelajar, 2007.
Kardimin, Akhmad. Fundamental English Grammar. 1st ed. Yogyakarta Pustaka Pelajar, 2004.
Olivia, W. CH. M. Developing English Sentence. Jakarta Great Media, 2003.
Murphy, Raymond. English Grammar In Use. 2nd ed. England Cambridge University Press, 1985.
Purwanto, Hadi. BBC English Grammar. Pekalongan CV Bahagia, 1994.
Kaplon, Jeffrey P. English Grammar Principles And Facts. USA Prentice-Hall, Inc, 1995. Kardimin, Akhmad. Perfect Structure For Better TOEFL. 1st ed. Yogyakarta Pustaka
Pelajar, 2007.
Junaidi, S. and Suwono, Eko. 2004. Matematika SMP Kelas 3. Surabaya: Esis/Erlangga Harris.2009. About Conjunction. http//www.virtualsalt.com/conjunct.htm.
3. THE DESCRIPTION OF CONJUNCTIONS IN ARTICLES OF THE JAKARTA POST
3.1 Data
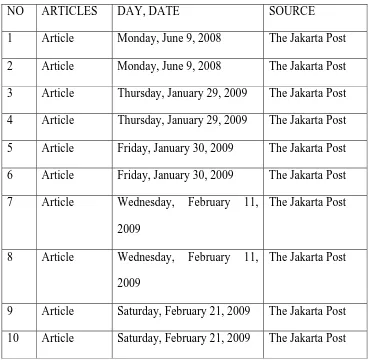
[image:26.595.75.446.370.730.2]It has already been mentioned in the previous chapter that the data are selected from “Jakarta Post” daily newspaper. The data were collected from June 9, 2008 up to February 21, 2009. The data of the articles were recorded randomly. The list of data can be seen in the table 1 below.
Table 1
NO ARTICLES DAY, DATE SOURCE
1 Article Monday, June 9, 2008 The Jakarta Post 2 Article Monday, June 9, 2008 The Jakarta Post 3 Article Thursday, January 29, 2009 The Jakarta Post 4 Article Thursday, January 29, 2009 The Jakarta Post 5 Article Friday, January 30, 2009 The Jakarta Post 6 Article Friday, January 30, 2009 The Jakarta Post 7 Article Wednesday, February 11,
2009
The Jakarta Post
8 Article Wednesday, February 11, 2009
The Jakarta Post
3.2 Data Analysis
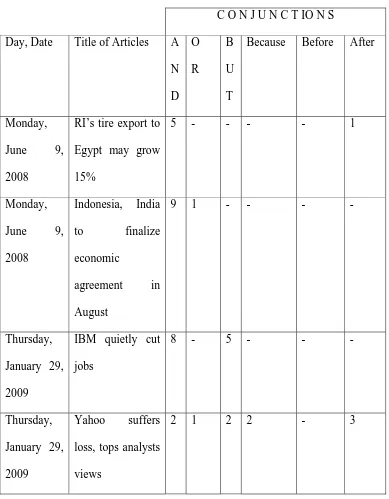
[image:27.595.70.459.232.731.2]After collecting the data, the writer classified the data based on such conjunction and, or, but, because, before and after. They can be seen in the table 2 below.
Table 2
C O N J U N C T IO N S Day, Date Title of Articles A
N D O R B U T
Because Before After
Monday,
June 9, 2008
RI’s tire export to Egypt may grow 15%
5 - - - - 1
Monday, June 9, 2008 Indonesia, India to finalize economic agreement in August
9 1 - - - -
Thursday, January 29, 2009
IBM quietly cut jobs
8 - 5 - - -
Thursday, January 29, 2009
Yahoo suffers loss, tops analysts views
Friday, January 30, 2009
Tokyo electric to extend Alaska LNG
1 0
1 - 2 1 -
Friday, January 30, 2009
Antam rushes for gold mines
7 - 1 - - -
Wednesday, February 11, 2009
Lower economic growth
necessitates domestic focus
5 1 1 - 1 -
Wednesday, February 11, 2009
Antam to acquire full ownership of PT CSD
6 1 - 1 - 1
Saturday, February 21, 2009
ASEAN citizens will get hotel discounts in Indonesia
4 - 1 - - -
Saturday, February 21, 2009
Import duties varied to help real sector
6 1 1 - - -
Total 6 2
6 1 1
5 2 5
3.2.1 The Conjunction ‘And’
The conjunction and belongs to cumulative conjunctions used to add one thought to another. The other words of cumulative conjunctions are as both… and, also, as well as, no less… than, not only… but also, not only… but, again, furthermore, likewise, besides, moreover,
and in addition.
There are sixty two conjunctions found in ten articles of The Jakarta Post. Some of them are mentioned below.
Examples:
According to the Association, Indonesia’s total tires exports reached $820 million in
2007, mostly the Southest Asia, The Middle east, and Azerbaijan.
We already have the blueprint on the partnership and hope to finalize all negotiation
in August.
IBM says the cut are simply part of its ongoing efforts to watch costs, and the
company won’t release specific numbers, even as report of firings stream in from of IBM facilities across the country.
It’s my job to make sure e look at anything that makes sense for the company and
creates long-term value for shareholders.
There are bigger renewals due this year from Australia and Indonesia.
We want to make a majority in the project should the price be attractive and suitable
The government must go all out to prevent illegal imports in order to support the
Rupiah and at the same time, Indonesia’s economic growth.
The processing plant is now on limited care and maintenance.
We also plan to develop tourism in Lombok and Sumbawa.
But the most important thing is for there to be an intensified dialogue among related
stakeholders problems and achievable solutions.
3.2.2 The Conjunction ‘Or’
Or is one of alternative conjunctions which is used to indicate alternative or choice
between two things. The other words of alternative conjunctions are, either… or, neither… nor, else, and otherwise.
There are six alternative conjunctions found in six articles of The Jakarta Post. The other four articles do not use this conjunctions.
Examples:
The economic partnership, Andi said, would include the lowering or removal the
trade restrictions, in particular on taxes, most goods and service and investment.
Alaska is the cheapest supplier of LNG to Japan with utilities paying an average
41.320 Yen (US$460) per metric ton, or about $8.8 per million British thermal units.
ARC was unable to secure a financing partner or find funding for the Cibaliung gold
mines.
If a country lowers a trade barrier or opens up a market, it has to do so for the same
Rather it is on and off, depending whether the ports are being “inspected” or not.
3.2.3 The Conjunction ‘But’
But is adversative conjunctions which is used to express opposition or contrast between
two sentences. The other words of adversative conjunctions are however, though, although, eventhough, inspite of, despite, regardless, yet, nevertheless, while, still, and whereas.
There are eleven conjunctions but found in the six articles of The Jakarta Post . Some of them will be mentioned below.
Examples:
With the recession forcing tech companies to announce thousands layoffs, IBM corp.
is joining the fray but not advertising it.
Since thousands of jobs are cut every year but are usually added back in other places.
Employees weren’t identified by name, but the position and the workers’ ages were
listed.
In Vermont, IBM remained tight-lipped about essex junction facility, but State Labor
Commisioner Patricia Moulton Powder said the total number would be less than 500.
He said he has until February 26 to find another job in IBM, but he put his chance at
”slim to none”.
Yahoo inc. stumbled to a fourth quarter loss of US$ 303 million, but the slumping
3.2.4 The Conjunction ‘Because’
Because is one of conjunctions of reasons, which is used to express or illustrate a reason
of an event. The other words of conjunctions of reason are because of, since, as, and for.
There are five conjunctions of reason because in three articles of The Jakarta Post, and some of them will be mentioned below.
Examples:
Yahoo refrained from looking beyond March because the economic is so fragile.
The setback wasn’t as bad as it appeared because the loss stemmed from charger
taken to cover the diminishing value of Yahoo’s European operations and cutbacks that included layinoff 1,500 employees last month.
We will need to take this matter to the shareholders, because taking over PT CSD
would also mean taking over it debts.
3.2.5 The Conjunction ‘Before’
Before is one of conjunctions of situation which is used to express or illustrate the
situation of an event. There are two conjunctions of situation before found in two articles of The Jakarta Post.
Examples:
Regarding Indonesia’s Arun LNG project we still have not decided what to do with it
We now expect a more prolonged down turn with any growth trend for global
economics unlikely to emerge before 2010.
3.2.6 The Conjunction ‘ After’
After is one of the conjunctions of situation which is used to express or illustrate the
situation of an event. The other words of conjunctions of situation are until, before, since, as, as long as, and as soon as.
There are five conjunctions of situation after found in three articles of The Jakarta post.
Examples:
After an 18-months investigation, Egypt dropped in March a plan to impose a 40
percent antidumping tax on Indonesia tires.
In an expressions of investors’ relief, Yahoo’s dropping shares picked up more than 5
percent after the results were released Thursday.
After substracting the company’s advertising commissions, Yahoo’s revenue totaled
$1.37 billion, matching analysts estimates.
Yahoo shares gained 60 cents, 5.3 percents, in extended trading, after finishing the
regular session at $11.34.
After the transactions is completed, Antam will fund and manage Cibaliung with
3.3 The Most Dominant Conjunctions Used In Ten Articles of The Jakarta Post
To get the percentage of the conjunctions used in all articles, I apply Junaidi and Suwono’s formula (2004:40) as follows:
The formula:
X = The percentage of each conjunctions
Y = The total number each conjunctions
N = The total number of conjunctions
= 91
The percentage of conjunctions used in all articles are as the following:
1. The percentage of conjunctions issued on Monday, June 9, 2008 with the title of RI’s tire export to Egypt may grow 15 % are conjunction and 5,49%, conjunction after 1,09%, while conjunction or, but, because and after are 0%
2. The percentage of conjunctions issued on Monday, June 9, 2008 with the title of Indonesia, India to finalize economic growth in august are conjunction and 9,89%, conjunction or 1,09%, while conjunction but, because, before, and after are 0%.
X = x100% N
3. The percentage of conjunction issued on Thursday, January 29, 2009 with the title of IBM quietly cut jobs are conjunction and 8,79%, conjunction but 5,49%, while conjunction or, because, before, and after are 0%.
4. The percentage of conjunction issued on Thursday, January 29, 2009 with the title of Yahoo suffer loss, tops analysist views are conjunction and 2,19%, conjunction or 1,09%, conjunction but 2,19%, conjunction because 2,19%, conjunction after 3,29%, while conjunction before is 0%.
5. The percentage of conjunction issued on Friday, January 30, 2009 with the title Tokyo electric to extend Alaska LNG are conjunction and 10,9%, conjunction or 1,09%, conjunction because 2,19%, conjunction before 1,09%, while conjunction but and after are 0%.
6. The percentage of conjunction issued on Friday, January 30, 2009 with the title of Antam rushes for gold mines are conjunction and 7,69%, conjunction but 1,09%, while conjunction or, because, before, and after are 0%.
7. The percentage of conjunction issued on Wednesday, February 11, 2009 with the title of Lower economic growth necessitates domestic focus are conjunction and 5,49%, conjunction or 1,09%, conjunction but 1,09%, conjunction before 1,09%, while conjunction because and after are 0%.
9. The percentage of conjunction issued on Saturday, February 21, 2009 with the title ASEAN citizens will get hotel discounts in indonesia are conjunction and 4,39%, conjunction but 1,09%, while conjunction or, because, before, and after are 0%.
[image:36.595.83.401.338.560.2]10. The percentage of conjunction issued on Saturday, February 21, 2009 with the title Import duties varied to help real sector are conjunction and 6,59%, conjunction or 1,09%, conjunction but 1,09%, while conjunction because, before, and after are 0%.
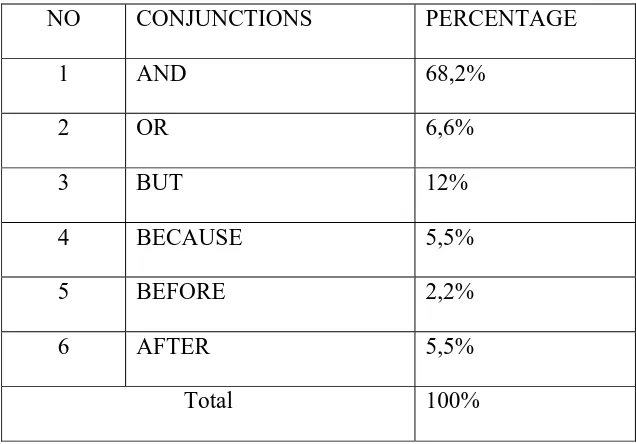
Table 3. the percentage of conjunctions in ten articles
NO CONJUNCTIONS PERCENTAGE
1 AND 68,2%
2 OR 6,6%
3 BUT 12%
4 BECAUSE 5,5%
5 BEFORE 2,2%
6 AFTER 5,5%
Total 100%
4. CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS
4.1 Conclusions
Based on the finding the most dominant use and frequent appearance of classification of conjunctions in those The Jakarta Post article can be seen as follows:
Conjunction and stand at the figures 68,2%.
Conjunction or stand at the figures 6,6%.
Conjunction but stand at the figures 12%.
Conjunction because stand at the figures 5,5%.
Conjunction before stand at the figures 2,2%.
Conjunction after stand at the figures 5,5%.
4.2 Suggestions
Based on the conclusions, there are some suggestions for all people who are interested in reading, writing, especially the readers, writers, and students:
The readers, writers, and students have to master in using conjunctions because it always
appear in the reading or articles.
For the writers and journalist they should used conjunction in the writings properly and
clearly.
Furthermore, this study can be used as a source of information in explaining about
conjunction.
I really appreciate if there are some constructive critism and suggestion as this paper is
APPENDICES
The Jakarta Post. RI’s tire export to egypt may grow 15%. Monday, June 9, 2008
The Jakarta Post. Indonesia, India to finalize economic agreement in August. Monday, June 9, 2008
The Jakarta Post. IBM quietly cut jobs. Thursday, January 29, 2009
The Jakarta Post. Yahoo suffers loss, tops analysts views. Thursday, January 29, 2009
The Jakarta Post. Tokyo electric to extend Alaska LNG. Friday, January 30, 2009
The Jakarta Post. Antam rushes for gold mines. Friday, January 30, 2009 The Jakarta Post. Lower economic growth necessitates domestic focus.
Wednesday, February 11, 2009
The Jakarta Post. Antam acquire full ownership of PT CSD. Wednesday, February 11, 2009
The Jakarta Post. ASEAN citizens will get hotel discounts in Indonesia. Saturday, February 21, 2009