I. Introduction: The Significance of Learning Objectives in Microteaching
This section establishes the context of the research by highlighting the importance of well-defined learning objectives in lesson plans, particularly within the context of a microteaching course for prospective English language teachers. It underscores the role of learning objectives as crucial components for effective teaching, guiding instructional design, material selection, activity implementation, and assessment development. The section also emphasizes the connection between theoretical knowledge acquired in prior courses (like Instructional Design, Approaches, Methods, and Techniques, and Curriculum and Material Development) and their practical application in microteaching. The lack of mastery in formulating learning objectives, as a potential gap between theory and practice, is presented as the research's central focus. The researcher aims to investigate the extent of student mastery and identify recurring problems, laying the groundwork for the subsequent methodological and analytical sections.
1.1 Research Background and Context
This subsection provides background information on the English Language Education Study Program (ELESP) at Sanata Dharma University, outlining the program's aim to produce well-rounded English teachers proficient in both language use and pedagogical skills. The introduction of the Microteaching course as a crucial bridge between theory and practice is highlighted. The significance of lesson plans, specifically the formulation of learning objectives within these plans, is established as a pivotal element for effective teaching. This section lays the groundwork for understanding the research's focus on the mastery of creating effective learning objectives within the microteaching environment.
1.2 Problem Formulation and Research Questions
This subsection formally articulates the research questions that drive the study. The central question revolves around the mastery level of microteaching students in formulating learning objectives. A secondary research question investigates the common problems encountered by students during this process. These questions directly address the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application, providing a clear focus for the analysis and interpretation of the data gathered from student lesson plans.
1.3 Research Objectives and Scope
This subsection defines the research objectives, clarifying the goals of the study. The primary objective is to quantitatively assess the students’ mastery of formulating learning objectives based on the analysis of their lesson plans. The secondary objective aims to qualitatively identify and categorize the common errors and challenges observed in their objective formulations. These clearly defined objectives guide the methodology and data analysis process, ensuring a consistent and focused approach throughout the study.
1.4 Significance of the Study and Definitions of Key Terms
This subsection discusses the expected contribution of the research to both students and lecturers. For students, the findings offer insights into their strengths and weaknesses, enabling focused improvement. For lecturers, the study provides valuable feedback to tailor teaching strategies and address specific learning difficulties. It also includes clear definitions of key terms used throughout the research, such as 'mastery,' 'learning objectives,' and 'microteaching class,' ensuring clarity and avoiding ambiguity. This section links the research to the broader pedagogical context and strengthens its relevance to practical teaching.
II. Literature Review: Theoretical Underpinnings of Lesson Planning and Objective Formulation
This chapter reviews relevant literature on lesson planning and objective formulation, providing a theoretical framework for the research. It analyzes different models of course design and the role of beliefs, needs assessment, and material development in creating effective learning experiences. The section critically examines various taxonomies of learning objectives (cognitive, psychomotor, and affective domains), emphasizing the importance of clear, measurable, and observable objectives. The ABCD model for objective formulation (Audience, Behavior, Condition, Degree) is also presented as a framework for evaluating the quality of student-generated learning objectives. The chapter concludes by synthesizing these theories to establish a coherent theoretical framework to guide data analysis.
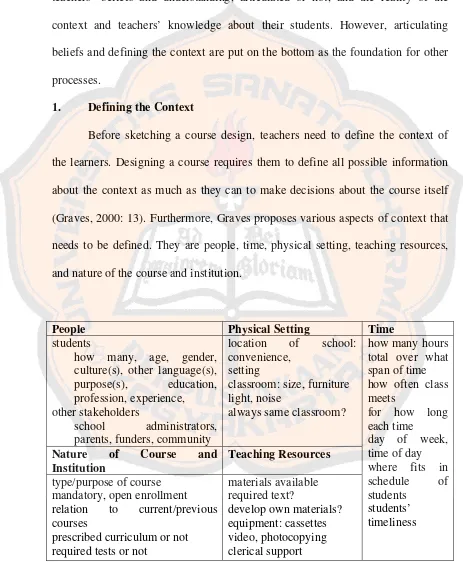
2.1 Defining the Context of Learning
This subsection explores the importance of understanding contextual factors when designing a course, encompassing learners' characteristics (age, background, language proficiency), the physical learning environment, available resources, and institutional constraints. This emphasizes the holistic approach required to create a relevant and effective learning experience. The discussion includes the challenges that might arise from diverse learning contexts and how these need to be addressed in the design process. It underlines that a thorough needs assessment considers not only target proficiency, but also learners' current abilities and aspirations.
2.2 Articulating Beliefs about Language, Learning, and Teaching
This subsection delves into the significance of teachers' beliefs about language, learning, and teaching in shaping their instructional approaches. It explores different perspectives on language (e.g., structural, functional, communicative), learning theories (behaviorism, cognitivism, constructivism), and teaching methodologies. This highlights how teachers’ beliefs significantly influence their course design, including their selection and formulation of learning objectives. By understanding these underlying beliefs, the research can better interpret the choices and approaches of the student participants.
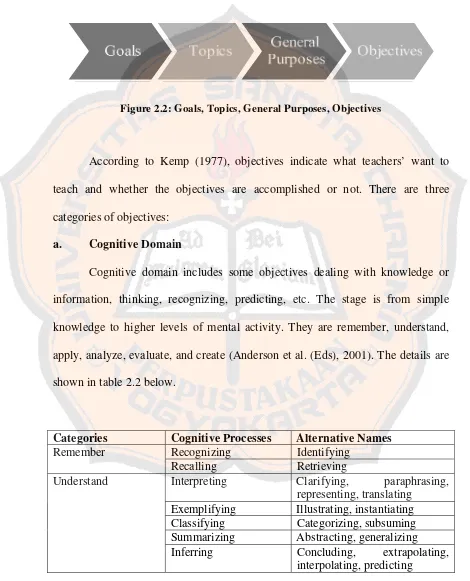
2.3 Conceptualizing Content and Formulating Goals and Objectives
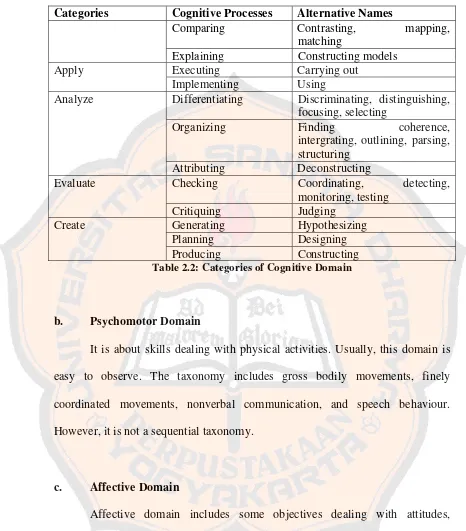
This subsection discusses the process of selecting and organizing course content, aligning it with overarching goals and specific learning objectives. It examines different types of syllabi and the relationship between goals, general purposes, and learning objectives. It clarifies the distinctions between goals and objectives and emphasizes the importance of creating measurable and observable learning objectives. The discussion includes various taxonomies of learning objectives, particularly the cognitive domain, and the criteria for well-defined objectives. This sets the stage for analyzing the quality of the learning objectives created by the student participants.
2.4 Assessing Needs and Organizing the Course
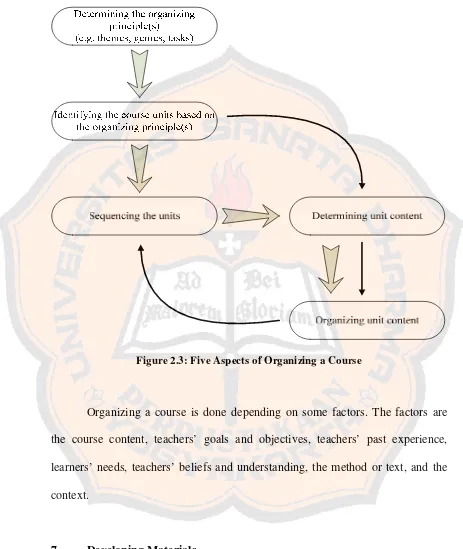
This subsection covers the process of needs assessment, both pre-course and ongoing, emphasizing the crucial role it plays in aligning instruction with learners' needs and expectations. It explores the distinction between target needs (what learners need to achieve) and learning needs (how learners will achieve those targets). It also discusses the process of organizing the course, including sequencing learning activities, selecting materials, and integrating different aspects of the syllabus. This underscores the systematic planning required to achieve the learning objectives efficiently and effectively.
2.5 Developing Materials and Adapting Textbooks
This subsection focuses on the development and adaptation of teaching materials, emphasizing the alignment with learning objectives and learner needs. It discusses considerations for creating engaging and relevant activities and the process of adapting existing textbooks to better suit the specific context and learners. The discussion incorporates the importance of authentic materials, cross-cultural understanding, and the integration of different language skills. This provides the theoretical grounding for analyzing the materials and activities in the student lesson plans, examining their alignment with the stated learning objectives.
2.6 Designing an Assessment Plan
This subsection highlights the crucial role of assessment in evaluating the effectiveness of the learning process. It discusses different types of assessment (formative, summative, informal, formal), underscoring their importance in tracking progress, providing feedback, and measuring learning outcomes. This section emphasizes the necessity of aligning assessment methods with the learning objectives, ensuring that assessments accurately measure what students have learned. This is essential in determining whether learning objectives have been successfully met.
2.7 Theoretical Framework
This subsection synthesizes the key theoretical concepts discussed previously to present a cohesive theoretical framework for guiding data analysis. It integrates the significance of context, beliefs, needs assessment, objective formulation, material development, and assessment in the overall process of effective lesson planning. This framework serves as the foundation for interpreting the findings of the study.
III. Methodology: Research Design and Data Collection
This section outlines the research methodology employed to answer the research questions. It details the research design (document analysis), the selection of participants (microteaching students), and the data collection instruments (lesson plans and interviews). The data analysis techniques used to assess the mastery level and identify common problems in learning objective formulation are clearly described. This section provides a transparent account of the research procedures, allowing for critical evaluation of the study's rigor and validity.
3.1 Research Design and Method
This subsection describes the qualitative document analysis as the primary research method. The rationale for choosing this method is explained, emphasizing its suitability for investigating the characteristics of written materials (student lesson plans) and gaining insights into the students’ understanding of learning objective formulation. The use of primary data sources (student-created lesson plans) is justified, emphasizing the direct connection to the phenomenon under study. This sets the methodological approach for the entire research.
3.2 Participants and Sampling
This subsection details the selection of participants: 18 students from six microteaching classes. The sampling strategy (purposive sampling with a random element) is explained, justifying the choice of this method to ensure representation across different classes while minimizing bias. The inclusion criteria, emphasizing students' completion of prerequisite courses related to instructional design and curriculum development, are outlined to ensure that the participants possess the necessary theoretical knowledge. This ensures the sample’s relevance to the research questions.
3.3 Data Collection Instruments
This subsection outlines the data collection instruments used. The primary instrument was the students’ lesson plans, providing direct evidence of their objective formulation skills. Supplementary data was collected through semi-structured interviews to clarify ambiguities and gain deeper insights into the students’ thinking process. The role of the researcher and a proofreader in ensuring data quality and validity are also discussed. This section ensures transparency in data collection procedures, enhancing the credibility of the study’s findings.
3.4 Data Analysis Techniques
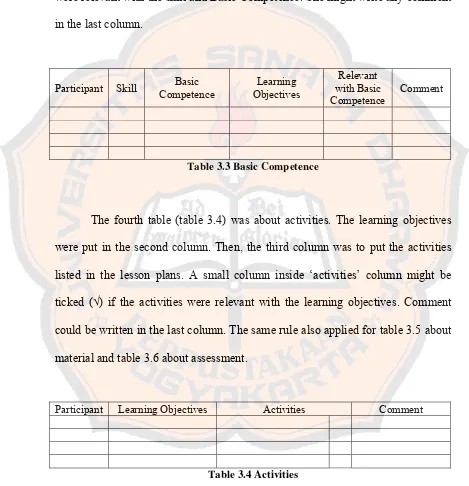
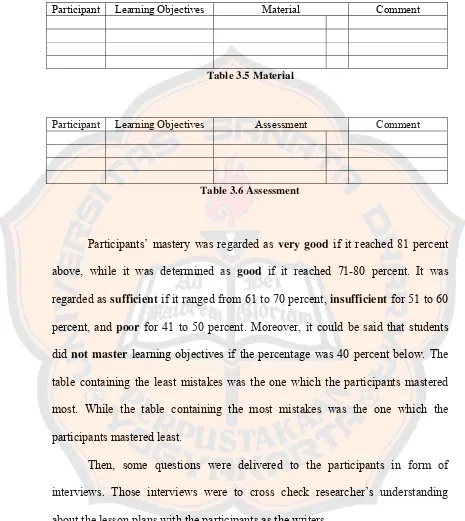
This subsection explains the data analysis procedures. It describes the use of tables to categorize learning objectives based on the ABCD model (Audience, Behavior, Condition, Degree) and other relevant frameworks. The coding scheme used to identify and categorize common problems in learning objective formulation is outlined. The process of qualitative analysis of interview data, used to provide context and insights into the quantitative findings, is also described. This section meticulously details the steps taken to transform raw data into meaningful results.
IV. Research Findings and Discussion: Analysis of Student Mastery and Identified Problems
This chapter presents the research findings, analyzing the students’ mastery levels in formulating learning objectives and categorizing the problems encountered. It integrates both quantitative (mastery percentages) and qualitative data (problems identified), providing a comprehensive account of the students' performance. The discussion section interprets the findings, linking them to the theoretical framework established in Chapter 2 and exploring potential contributing factors to the observed results. This chapter provides a critical assessment of student performance and offers valuable insights into the challenges faced in applying theoretical knowledge to practical lesson planning.
4.1 Microteaching Students’ Mastery in Formulating Learning Objectives
This subsection presents the quantitative results of the analysis of student lesson plans. It reports the percentage of students demonstrating mastery in different aspects of objective formulation, such as audience, behavior, condition, and degree elements. This quantitative data helps assess the overall level of student competency in this essential skill. The results are presented systematically, allowing for comparisons across different components of the learning objectives, highlighting strengths and weaknesses.
4.2 Problems Encountered in Students’ Learning Objective Formulation
This subsection presents the qualitative findings, focusing on the common problems identified in student lesson plans. It categorizes these problems, such as unclear or incomplete formulations, lack of alignment between objectives and other lesson components (activities, materials, assessments, Basic Competences), and other issues related to the ABCD model. The qualitative data provides rich contextual insights into the specific challenges faced by students in translating theoretical knowledge into practice. This section provides an in-depth understanding of the issues hindering the students’ effective formulation of learning objectives.
4.3 Discussion of Findings
This subsection interprets the findings in light of the theoretical framework presented in Chapter 2. It examines the relationship between the quantitative mastery scores and the qualitative problems identified, providing a comprehensive understanding of the students’ performance. The discussion explores potential reasons for the observed strengths and weaknesses, considering factors like prior learning experiences, teaching beliefs, and the complexity of objective formulation. This section offers insights into the factors contributing to the observed patterns in student performance, linking them to established learning theories and practical teaching considerations.
V. Conclusions and Suggestions: Implications for Practice and Future Research
This chapter summarizes the key findings of the research and offers conclusions based on the analysis. It discusses the implications of the findings for teaching practice, providing recommendations for lecturers to improve instruction and guidance on learning objective formulation for students. It also suggests avenues for future research, proposing areas for further investigation based on the limitations and potential extensions of the current study. This chapter reflects upon the broader implications of the study and directs future research efforts.
5.1 Conclusions
This subsection summarizes the main findings, reiterating the key conclusions drawn from the analysis of student mastery and identified problems. It succinctly states the overall level of student proficiency in learning objective formulation, highlighting significant strengths and weaknesses. This concisely reiterates the most important findings of the research.
5.2 Suggestions for Lecturers, Students, and Future Researchers
This subsection offers practical recommendations for improving instruction and student learning. It proposes strategies for lecturers to enhance their teaching of lesson planning and learning objective formulation, suggesting specific approaches to address the identified problems. It also provides guidance for students on improving their skills in this area. Finally, it outlines potential avenues for future research, suggesting areas that warrant further investigation. This section provides actionable insights for stakeholders and lays the foundation for future research in this area.