THE USE OF VIDEO AND METACOGNITIVE STRATEGIES
TO IMPROVE STUDENTS
’
LISTENING COMPREHENSION
IN FACTUAL REPORT
( A CAR of the Eleventh Grade Students of SMA Islam Sudirman Ambarawa in the Academic Year of 2016 / 2017 )
A GRADUATING PAPER
Submitted to the Board of Examiners as a Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for Degree of Sarjana Pendidikan ( S.Pd ) in
English Education Department of Teacher Training and Education Faculty State Institute for Islamic Studies ( IAIN) Salatiga
BY :
RYNO SETTRISMAN
113 13 045
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
TEACHER TRAINING AND EDUCATION FACULTY
STATE INSTITUTE FOR ISLAMIC STUDIES ( IAIN )
DECLARATION
In the name of Allah the Most Gracious and the Most Merciful, hereby,
the researcher declares that this graduating paper is written by the researcher
himself. This paper does not contain any materials which have been published by
other people, and it does not cite any other people’s ideas except the information from the references.
The researcher is capable to account his graduating paper if in the future it
can be proved of containing others’ idea or in fact that the researcher imitates the others’ graduating paper. Likewise, this declaration is written by the researcher,
and he hopes that this declaration can be understood. The researcher will also
MOTTO
“Indeed, with hardship [will be] ease.”
( Al-Insyirah 94:6 )
“So which of the favors of your Lord would you deny?”
( Ar-Rahman 55:13 )
“And the Horn will be blown, and whoever is in the heavens and whoever is on the earth will fall dead except whom Allah wills. Then it
will be blown again, and at once they will be standing, looking on”.
DEDICATION
Deep inside this hearth, I dedicate this graduating paper to :
1. My beloved mother ( Elmianis ) and my father ( Tasman ), thank you for the
support. Your love is lasting forever in my hearth. You two are my everything
and I love the way you are.
2. My older brother ( Joni Oktami Saputra ), you are my great brother that
always indirectly teaches me about the patience and the struggle. No matter
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Firstly, in the name of Allah, The Most Gracious and The Most Merciful.
Because of him, the researcher could well finish this graduating paper as one of
the requirement for Sarjana Pendidikan in English Education Department of
Teacher Training and Education Faculty of State Institute for Islamic Studies
(IAIN) Salatiga.
Secondly, peace and salutation always be given to our prophet Muhammad
SAW who has guided us from the darkness to the brightness. The researcher
realizes that this success can not be achieved without guidance, help, advices, and
support from the other people. The researcher extends the deepest gratitude to :
1. Mr. Rahmat Hariyadi, M. Pd. as the Rector of State Institute for Islamic
Studies (IAIN) Salatiga
2. Mr. Suwardi, M. Pd. as the Dean of Teacher Training and Education Faculty
3. Mrs. Noor Malihah, Ph. D. as the Head of English Education Department
4. Mrs. Rr. Dewi Wahyu M., S.S., M.Pd as a councelor who well guided this
research. Thank you so much for the advice, suggestions, and support
5. All the lecturers in English Education Department, thank you for the
knowledge and experience that you all gave
6. All of the academic-staffs who helped the administration of this graduating
paper
7. Mr. Drs. Joko Pujianto and Mrs. Dra. Rahmi Siti Saadah as the boards of
SMA Islam Sudirman Ambarawa who allowed the researcher to conduct this
8. Mrs. Hanifikha Frindianita, S.Pd as the collaborator of this research, thank
you so much for the cooperation and collaboration
9. The students of XI MIPA 3. You all are the most amazing students that I have
ever met
10. My great friend, Rahmad Septiawan, who provided the most important book
for the development of this research. Although we come from different major,
even different campus, we could still share each other. Thank you so much for
your remarkable help
11. My reviewer, Aning Sulistyaningsih, who reviewed this research, thank you
so much. You were really nice reviewer
12. My friends of Youth Association of Bidik Misi Limardhotillah ( YA
BISMILLAH ), especially YA BISMILLAH 2013. Thank you for the
friendship, we passed so many activities together patiently, and it was really
wonderful
Salatiga, August 7th 2017
The researcher,
Ryno Settrisman
ABSTRACT
Settrisman, Ryno. 2017. THE USE OF VIDEO AND METACOGNITIVE STRATEGIES TO IMPROVE STUDENTS’ LISTENING COMPREHENSION IN FACTUAL REPORT ( A Classroom Action Research of the Eleventh Grade Students of SMA Islam Sudirman Ambarawa in the Academic Year of 2016/2017). A Graduating Paper, Teacher Training and Education Faculty, English Education Department, State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga. Counselor: Rr. Dewi Wahyu Mustikasari., S.S., M.Pd.
Keywords : Video, metacognitive strategies, listening comprehension, factual report, classroom action research.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE... i
DECLARATION ... ii
ATTENTIVE COUNSELOR’S NOTE ... iii
STATEMENT OF CERTIFICATION ...iv
MOTTO ... v
DEDICATION ...vi
ACKNOWLEDGMENT... vii
ABSTRACT ... ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... x
LIST OF FIGURES ... xiii
LIST OF TABLES ...xiv
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION A. Background of the Research ... 1
B. Problems of the Research ... 6
C. Objectives of the Research ... 6
D. Significances of the Research ... 7
E. Limitation of the Research ... 8
F. Definitions of the Key Terms ... 8
G. Graduating Paper Outline ... 10
CHAPTER II LITERATURE REVIEW A. Previous Researches ... 12
B. Concept of Language Learning Strategies 1. Definitions of Learning Strategies ... 14
2. Features of Language Learning Strategies ... 16
3. Classification of Language Learning Strategies ... 16
C. Concept of Metacognitive Strategies 1. Definitions of Metacognitive Strategies ... 17
2. Benefits of Metacognitive Strategies ... 18
4. Three Strategy Sets of Metacognitive Strategies ... 20
D. Concept of Listening Comprehension 1. Definitions of Listening Comprehension ... 23
2. Factors Affecting Listening Comprehension ... 24
3. Teacher’s role in listening activity ... 24
E. Media 1. Definitions of Media ... 26
2. Five aspects of Media ... 26
F. Concept of Video 1. Definition of Video ... 28
2. Benefits in using video in the classroom ... 28
3. Practical Techniques for Video Implication ... 29
G. Genre ... 31
H. Concept of Factual Report 1. Definition of Factual Report ... 33
2. The characteristics of Factual Report ... 33
3. Structure of Factual Report ... 33
4. Sentence Structure of Factual Report ... 34
5. Example of Factual Report ... 35
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHODOLOGY A. Location of the Research ... 37
B. Research Design ... 37
C. Subject of the Research ... 38
D. Research Schedule... 39
E. Techniques of Collecting the data 1. Test ... 39
2. Observation ... 40
3. Interview ... 40
F. Cycles of Classroom Action Research
1. Cycle I ... 41
2. Cycle II ... 47
G. Rubric of Listening Comprehension... 49
H. Techniques of Analyzing the Data
1. Qualitative Data ... 51
2. Quantitative Data ... 51
CHAPTER IV DATA ANALYSIS
A. Findings ... 54
B. Discussions ... 88
CHAPTER V CLOSURE
A. Conclusions ... 90
B. Suggestions ... 92
REFERENCES
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 2.1 Three Strategy Sets of Metacognitive Strategies ... 22
LIST OF TABLES
Table 3.1 Research Schedule ... 39
Table 3.2 Rubric of Listening Comprehension ... 50
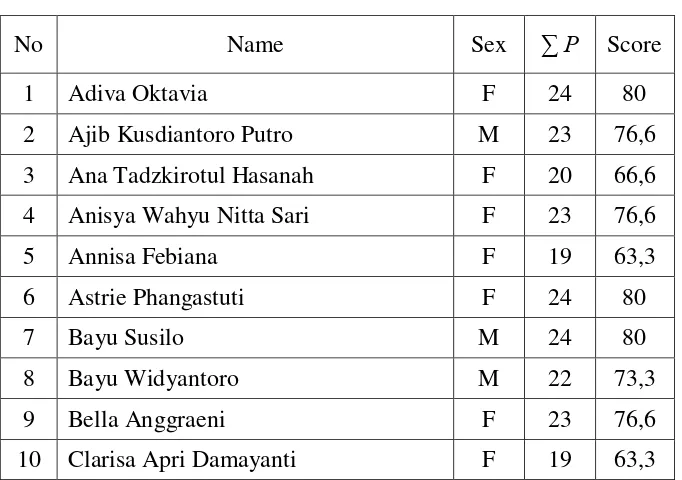
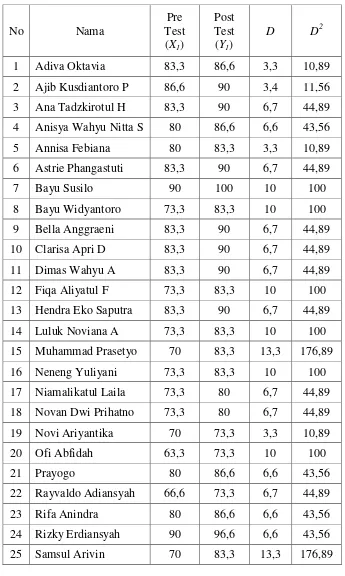
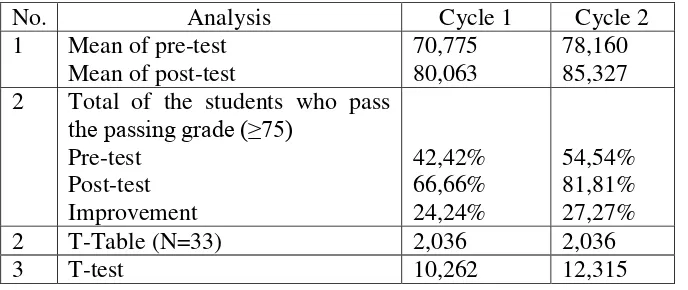
Table 4.1 Students’ Score in the Pre Test of the Cycle 1 ... 71
Table 4.2 Count of Passing Grade of the Pre Test in the Cycle 1 ... 73
Table 4.3 Students’ Score in the Post Test of the Cycle 1 ... 73
Table 4.4 Count of Passing Grade of the Post Test in the Cycle 1 ... 75
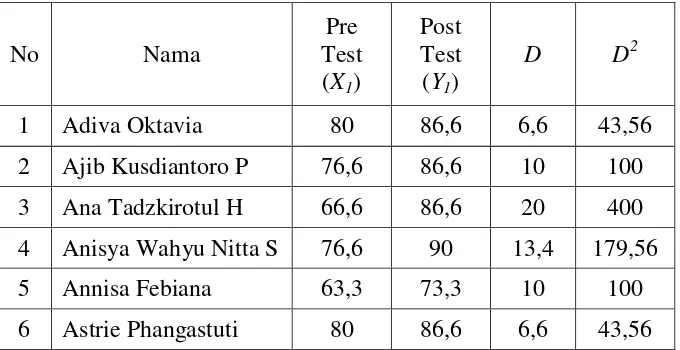
Table 4.5 Difference square of Pre and Post test Score in Cycle 1 ... 75
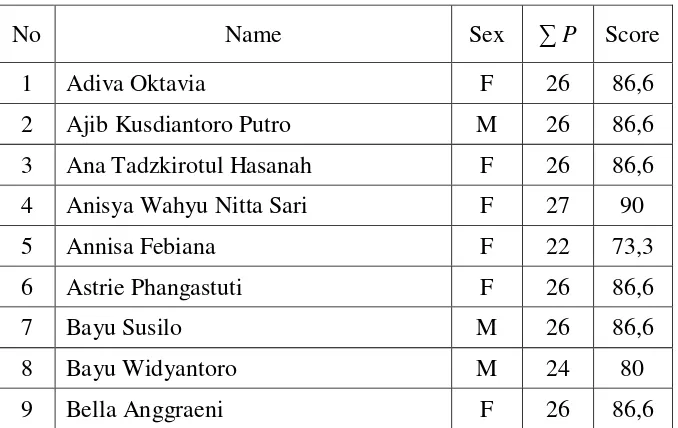
Table 4.6 Students’ Score in the Pre Test of the Cycle 2 ... 80
Table 4.7 Count of Passing Grade of the Pre Test in the Cycle 2.... ... ...81
Table 4.8 Students’ Score in the Post Test of the Cycle 2... ... ...82
Table 4.9 Count of Passing Grade of the Post Test in the Cycle 2 ... 83
Table 4.10 Difference square of Pre and Post test Score in Cycle 2 ... 84
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A. Background of the Research
As an international language, English is very important to be learnt by
people. There are so many people in the world who learn English for
communication. According to Mahu (2012, p.374), “It is now impossible to find a country where learning English has not become a norm.” People who
learn English in a country are not wondering. Mostly, they have four purposes
to be achieved, and it will be impossible to be achieved if they do not start to
learn English seriously.
Firstly, people need English in order to communicate with other people
that come from different countries and of course different languages. English
as a universal language can connect people, and it builds relationship with
each other for several important activities. For instance, building a colleague
in business to sell a product internationally, working abroad well, as well as
guiding foreigners for certain purposes communicatively.
Secondly, people need English in order to enrich their knowledge. It
will not be effective if people just try to gain knowledge in only one language.
There are so many kinds of great knowledge in term of literature that can be
acquired through English. It can be in form of books, magazines, website,
Thirdly, people need English for their academic education. In
Indonesia, there are so many universities that make it compulsory for new
students to have Test of English as Foreign Language (TOEFL) score more
than 500. It can be in doctoral degree, magister degree, or even in
undergraduate degree. To reach that score is not easy. The students have to be
accustomed to English and learn that language entirely. Moreover, people in
Indonesia also have to master English well if they mean to carry on their
education abroad, there are so many universities abroad that are really famous
and often known as world class universities which can be a better place for
education.
Fourthly, people need English in order to master technology
development. In this globalization era, the development of technology is
really rapid. People need to master and understand it to avoid for being left
behind. There are so many kinds of technology that use English as a default
language, like computers, smartphone, internet, television, etc.
That is why our government encourages all students in our country to
learn English. Nowadays, English is taught in all levels of education, e.g.
kindergarten school, elementary school, junior high school, and senior high
school. English is a subject that gets serious attention from the government.
At the last grade of junior high school, English becomes a subject that
includes in national final examination (ujian nasional). Before performing
national final examination, the students are usually given additional English
school, government also treats English as an important subject. English
becomes compulsory subject that has to be learnt by the students seriously.
The scope in learning English is really complex. When the students learn
English, they have to master four important skills. Those skills are listening,
speaking, reading, and writing. Then, among those four skills, there is a
priority.
Listening should be a priority because it is very important on
communication. The students spend so much time in listening rather than in
speaking. It is not surprising if the students can believe that a good speaker is
from good listener. This means, for being a good speaker, the one and only
way is to be a good listener first. According to Holden (2004) as cited by
Serri, Boroujeni, & Hesabi (2012, p.844), “Listening has an important effect
on communication, and as it was estimated by researchers that adults spend
40-50% of their communication time on listening, 25-30% on speaking,
10-15% on reading, and about 10% on writing”.
It is not wondering if listening can take the first position. Logically, the
students usually start to listen at first before they speak up, then, they will
read it and write it. Tabeei, Tabrizi, & Ahmadi (2012, p.13) also add that
"Listening is an important skill through which language learners internalize
linguistic information without which they cannot produce language". The
linguistic information cannot be processed without any aid of listening.
On the other hands, there are so many students who are often afraid of
of the pre-survey which was conducted by having interview in SMA Islam
Sudirman Ambarawa, the researcher found that the students were really afraid
of listening, the students often got difficulty in comprehending and focusing
to information from listening, the students were unable to catch specific detail
when they were listening, even some students could not catch general
understanding about the topic. Moreover, when the students were listening,
they also found difficulty in answering the questions accurately.
The role of English teachers are really important to overcome those
problems. Mustikasari (2011, p.155) explains that “Teacher is the center of attraction in the classroom, since he plays an important role in the classroom”.
The English teachers have to know deeply about the teaching and learning
issue when they are teaching. English teachers also have something fresh
when they are teaching. It is also in line with idea of Mustikasari (2011, p.36)
that “It is a good idea if teacher can provide something fresh that can make
the students enjoy the learning process”. Something fresh in teaching, especially in teaching listening is really various, it can be in term of media,
strategy, method, or certain technique that teachers can use, so that it can
improve students’ listening comprehension.
One of many media that can be used is video. Video is a kind of
technology that can be used by teachers in teaching and learning (Shyamlee &
Phil, 2012, p.150). The use of video in language teaching and learning is very
good. The students will automatically activate their sight sensory and their
language teaching and learning is sight sensory. This is in line with idea of
Cakir (2006, p.67) that “In language teaching and learning process, learners use his eyes as well as his ears, but his eyes are basic in learning”. As a
technology, the use of video will also train and challenge the teachers to
prepare good teaching and good learning process. It is also in line with
statement of Mustikasari (2014, p.125) that “Integrating technology for teaching and learning process is challenging to be prepared as well as
implemented”
In term of the strategy, teachers can use metacognitive strategies in
teaching and learning process. According to Anderson (1991) as cited by
Tabeei et al. (2013, p.14), “Metacognitive strategies are the most important strategy to develop learners skill and it was proposed by O'Malley & Chamot
(1990) that learners without them have no ability to monitor and regulate their
development, performance, and future learning”. The students should use
metacognitive strategies in order to develop and manage their learning. It will
automatically lead the students to be more proficient in learning. Students
who use metacognitive strategies are better in learning rather than students
who don’t use. This is in line with statement of Hauck (2005) as cited by
Tabeei et al. (2013, p.14) that “Learners who use metacognitive strategies are more proficient learners”.
Based on the explanation above, the researcher tends to propose video
and metacognitive strategies that may fix those learning problems. It is
METACOGNITIVE STRATEGIES TO IMPROVE STUDENTS’
LISTENING COMPREHENSION IN FACTUAL REPORT ( A CAR of
the Eleventh Grade Students of SMA Islam Sudirman Ambarawa in the
Academic Year of 2016 / 2017)”.
B. Problems of the Research
This research is aimed to answer these following questions:
1. How is the implementation of using video and metacognitive strategies to
improve the students’ listening comprehension in factual report at the eleventh grade students of SMA Islam Sudirman Ambarawa in the
academic year of 2016 / 2017 ?
2. How far is the improvement of the students’ listening comprehension in factual report at the eleventh grade students of SMA Islam Sudirman
Ambarawa in the academic year of 2016 / 2017 after being taught by
using video and metacognitive strategies ?
C. Objectives of the Research
Based on the statement of the problems above, the objectives of this
research are as follows:
1. To describe the implementation of using video and metacognitive
strategies to improve students’ listening comprehension in factual report
at the eleventh grade students of SMA Islam Sudirman Ambarawa in the
academic year of 2016 / 2017.
Islam Sudirman Ambarawa in the academic year of 2016 / 2017 after
being taught by using video and metacognitive strategies.
D. Significances of the Research
This research is expected to be used theoretically and practically:
1. Theoretically
This research is expected to give explanation about the use of
video and metacognitive strategies to improve students’ listening
comprehension in factual report so that it can be used by other researchers
as a reference.
2. Practically
The result of this research is expected to be useful for students,
English teachers, and institution:
a. Students
The students are expected to be able to improve their listening
comprehension by using video and metacognitive strategies.
b. English teachers
The English teachers are expected to use video and
metacognitive strategies to improve their students’ listening comprehension.
c. Institution
The quality of teaching and learning in the institution can be
E. Limitation of the Research
In this research, the researcher only focuses on the use of video and
metacognitive strategies to improve students’ listening comprehension in factual report at the eleventh grade students of SMA Islam Sudirman
Ambarawa in the academic year of 2016 / 2017.
F. Definitions of the Key Terms
To avoid misunderstanding about the title of this research, the
researcher explains the key terms used in this research. They are as follows:
1. Video
Cakir (2006, p.67) explains that video is an audio-visual material
that has grown rapidly used by teachers to stimulate and facilitate the
target language. Using video is really helpful in teaching and learning
process. It will improve the students’ listening comprehension about a material because video contains audio that students can hear and moving
pictures that the students can look at. Nowadays, integrating video in
language teaching is not hard at all. The teacher can find video for their
teaching easily. The teacher can get video either by copying it from other
teachers or by downloading it from websites which provide access to
video. There are so many websites that provide access to video that can
be used by teachers such as www.youtube.com, www.vidio.com, and
many more.
Based on the survey result of Wilson (2000) as cited by Cakir
often used to comprehend different things in language teaching. It is not
wondering if video can be enjoyable for students. It happens because
actually the students cannot stop dealing with word “Video”. Mostly, students deal with video every day. Video can be accessed in all devices
easily, such as smartphone, television, as well as computer. The more the
students can easily access it, the more they will love it. In language
teaching, teacher can use video to teach all English skills. It can be used
to teach listening, speaking, reading, as well as writing.
2. Metacognitive Strategies
Oxford (1990, p.136) states that “Metacognitive means beyond, beside, or with the cognitive. Therefore, Metacognitive strategies are
actions which go beyond purely cognitive devices, and which provide a
way for learners to coordinate their own learning process”. Coordinating the learning process is really essential for students. It will train them to
know how they learn, how far they understand and think about the
material, how far the progress that they make. It will also encourage the
students to evaluate their learning process.
3. Listening Comprehension
Tabeei et al. (2013, p.13) inform that “Listening comprehension is
an active and conscious process, in which listeners focus their own
attentions on taking the important information from the aural input,
comprehend the meaning of the input, and combine them with the
To achieve good listening comprehension, the students have to
consciously activate their sensory when listening to the material. They
also have to be well focused in obtaining, comprehending, as well as
combining the information contextually so that it can be an output.
4. Factual Report
Factual report is also known as information report or report text.
According to Kementrian Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan [Kemendikbud]
(2014, p.33), It is a factual text that provides information about different
phenomena in our life. It is used as a way to gain better understanding of
different phenomena”. Factual report is a good material for students because it will train them to know and understand various phenomena that
happen in their life. It will also train the students to be more sensitive in
their own environment. Based on syllabus of 2013 curriculum, factual
report is a material that has to be taught by English teachers in the second
semester of eleventh grade students. It has to be taught in form of
listening as well as reading.
G. Graduating Paper Outline
In order to make a systematic research, the researcher organizes this
research into five chapters, they are as follows :
Chapter I is introduction. It contains the background of the research,
problems of the research, objectives of the research, significances of the
research, limitation of the research, definitions of the key terms, and
Chapter II is literature review. It contains previous researches, concept
of language learning strategies, metacognitive strategies, listening
comprehension, media, video, genre, and factual report.
Chapter III is research methodology. It contains location of the
research, research design, subject of the research, research schedule,
techniques of collecting the data, cycles of CAR, rubric of listening
comprehension, and techniques of analyzing the data.
Chapter IV is data analysis. The data analysis contains findings and
discussions of the use of video and metacognitive strategies to improve
students’ listening comprehension in factual report at the eleventh grade
students of SMA Islam Sudirman Ambarawa in the academic year of
2016/2017.
Chapter V is closure. It contains conclusions and suggestions. After
CHAPTER II
LITERATURE REVIEW
A. Previous Researches
In order to improve the understanding about this research, the
researcher presents three relevant studies. The first research has been done by
Birjandi and Rahimi (2012). The objectives of this research was to explore the
effect of metacognitive strategy instruction on the listening performance of
EFL university students. This research applied true experimental design. The
participants of this research were 62 students studying English translation and
literature at Shahid Beheshti University which were divided into experimental
and control group based on their pre test scores. The experimental group was
given treatment by using metacognitive strategy instruction whereas the
control group received no treatment. After conducting the post test, the result
of the statistical analysis showed that the experimental group outperformed
the control group. The result of this research showed that metacognitive
strategy instruction has positive effect on the listening performance of the
students. It encouraged the students to be more responsible for the learning
process.
The second research has been done by Tavakoli and Koosha (2016)
The objective of this research was to investigate the influence of explicit
metacognitive strategy instruction on reading comprehension and self-efficacy
in English as a Foreign Language (EFL) among university students in Iran.
research were randomly assigned to either experimental group as many as 50
students, and control group, as many as 50 students. The experimental group
was given treatment by using metacognitive strategy instruction whereas the
control group received no treatment. After conducting the post test, the result
showed that experimental group outperformed the control group. The research
finding showed that if metacognitive strategy instruction is used everyday in
foreign language classroom activities and tasks, it can positively and
significantly enhance reading achievement and self-efficacy. From this
research, it can be concluded that metacognitive strategy instruction can be
also used to improve reading achievement and self-efficacy.
The third research has been done by Kim (2015). The objectives of this
research was to investigate the effect of the use of video in improving
listening comprehension of 86 students that registered in a summer session in
a Korean University. This research applied true experimental design. The
students were taught the same lessons by using authentic videos material for
ten sessions in three weeks. Pre test and post test were conducted to determine
wether autentic video materials were effective to improve students’ listening
comprehension or not. The participants of this study were organized into three
groups based on the result of their TOEIC scores. They were low group (29
students), intermediate group (29 students), and advanced group (28
students). The result of this research showed that after learning with videos,
the students’ listening comprehension in the intermediate and the advanced
improvement in those two groups was much greater than the low group. This
research also found that the students perceptions toward using the videos in
improving their listening comprehension were very good and positive.
However, the three researches above investigated the effect of using
metacognitive strategies and using video separately. The first research
explored the effect of metacognitive strategies on the listening performance.
The second research investigated the effect of using metacognitive strategies
on reading comprehension and self-efficacy, and the third research
investigated the effect of using video in improving the students’ listening
comprehension. In this research, the researcher combined metacognitive
strategies with video to improve the students’ listening comprehension in a
research.
B. Concept of Language Learning Strategies
1. Definitions of Learning Strategies
Strategy is a plan, step, conscious action to reach a purpose. This
word is very influential in teaching learning process. In education, the
term of strategy is often transformed into learning strategies (Oxford,
1990, p.8). Nowadays, the word “strategy” gets serious attention from
teachers. It is because a strategy can fix problems that happen in a class
and it can also be used to improve the quality of the teaching and learning
process such as proficiency or achievement in certain skill areas. It is in
leads to improved proficiency or achievement overall or in specific skill
areas”.
There are several researchers in the area of foreign and second
language teaching explaining the key definitions of learning strategies.
According to O’Malley and Chamot (1990) as cited by Tabeei et
al. (2013, p.16) :
Learning strategies are complex procedures that individuals apply to tasks; consequently, they may be represented as procedural knowledge which may be acquired through cognitive, associative, and autonomous stages of learning. As with other procedural skills at the different stages of learning, the strategies may be conscious in early stages of learning and later be performed without the person's awareness.
Furthermore, Yang (2009) as cited by Bidabadi & Yamat (2013,
p.31) informs that :
Learning strategies enable learners to reply to the learning situation and manage their learning in an appropriate and suitable way and allow learners to take more responsibility for their own learning and become autonomous second/foreign language learners.
One of the most comprehensive definitions comes from Oxford
(Tavakoli, 2014, p.316). Oxford (1990, p.8) explains that “Learning
strategies are the specific action taken by learner to make learning
easier, faster, more enjoyable, more self-directed, more effective, and
more transferable to new situations”
From the explanation of the experts above, it can be concluded
students are accustomed to use learning strategies in early stages, in the
future, It will be automatically active without their awareness.
2. Features of Language Learning Strategies
Language learning strategies are very good in language teaching
and learning process. When it is applied, it can give some features and
benefits to the students as well as the teacher. Oxford (1990, p.9)
explains that the students will be more self-directed in learning, the
teaching and learning process will contribute to the main goal,
communicative competence. The teacher will be able to expand their
role in their teaching, It can also be flexibly used by teacher to create
problem-oriented learning and action basis.
3. Classification of Language Learning Strategies
To improve the understanding about the learning strategies,
especially the metacognitive ones, it is necessary to know the
explanation and categorization of the language learning strategies first.
Based on O'Malley et al. (1985) as cited by Coskun (2010, p.36),
language learning strategies consist of cognitive strategies,
metacognitive strategies, and socioaffective strategies. However, in the
language learning area, one of the most widely accepted classifications
is from Oxford (Tavakoli, 2014, p.326). According to Oxford (1990) as
cited by Tavakoli (2014, p.326), “model of language learning strategies
compensation strategies, metacognitive strategies, affective strategies,
and social strategies”.
Although some researchers have different classification about
language learning strategies, but they are actually still same in the
nature. It is in line with idea of Serri et al. (2012, p.843) that “It should
be mentioned that although there are other strategies with other names
(Griffith, 2004), but it doesn't mean that they differ in nature”.
C. Concept of Metacognitive Strategies.
1. Definitions of Metacognitive Strategies
There are several definitions of metacognitive strategies explained
by the experts in the area of foreign and second language teaching. They
are as follows
According to Coskun (2010, p.36),” In simple terms,
metacognition is thinking about thinking. Its scholarly description comes
from cognitive psychology that approaches metacognition as one's
knowledge concerning one's own cognitive processes and products or
anything related to them”. Meanwhile, Tabeei et al. (2013, p.15) state that “In cognitive psychology, metacognition is defined as an executive
control which includes monitoring and self-regulation”. Furthermore,
Harris (2003) as cited by Birjandi & Rahimi (2012, p.496) informs that
"metacognition is concerned with guiding the learning process Itself”.
Based on the definitions from the three researchers above, it can be
is because metacognitive strategies can produce a way for students to
coordinate and guide their learning process. It helps students to think
about how they think. It will also help the students to monitor and
regulate the learning process independently.
2. Benefits of Metacognitive Strategies
There are so many great benefits of metacognitive strategies if
teacher can apply it in the teaching and learning process. According to
Hauck (2005) as cited by Coskun (2010, p.36), “learners who have
developed their metacognitive awareness are likely to become more
autonomous language learners”. Meanwhile, Anderson (2002) as cited by
Coskun (2010, p.36) informs that “the use of metacognitive strategies
activates one's thinking and leads to improved performance in learning in
general”. Furthermore, Bidabadi & Yamat (2013, p.32) state that “Meta
-cognitive strategies are important because they regulate and direct the
language learning process”. Moreover, Wenden (1998) as cited by
Coskun (2010, p.37) explains the eight benefits for learners who have
metacognitive abilities :
a. They are more strategic learners.
b. Their rate of progress in learning as well as the quality and speed of their cognitive engagement is faster.
c. They are confident in their abilities to learn.
d. They do not hesitate to obtain help from peers, teachers, or family when needed.
e. They provide accurate assessments of why they are successful learners.
f. They think clearly about inaccuracies when failure occurs during an activity.
h. They perceive themselves as continual learners and can successfully cope with new situations.
Based on the explanations above, metacognitive strategies are
really good for the students in the learning process. The students will
become independent, strategic, confident, fast, and diligent learners.
The students will be able to enhance their learning in general.
Metacognitive strategies will help the students to regulate and direct
their learning process, and it also helps the students to find out certain
tactic in their learning so that the students can learn effectively.
3. Metacognitive Strategies and Listening Comprehension.
Metacognitive strategies have many benefits in listening
comprehension. Coskun (2010, p.37) explains that :
Metacognitive strategies do not only help learning in general but also have a lot to offer to listening comprehension specifically. Vandergrift (1997) indicates that metacognitive strategies such as analyzing the requirements of a listening task, activating the appropriate listening processes required, making appropriate predictions, monitoring their comprehension and evaluating the success of their approach cause the difference between a skilled and a lessskilled listener. Similarly, Goh (2008) lists some of the positive effects of metacognitive strategy training on listening comprehension. She states that it improves students’ confidence and makes them less anxious in the listening process.
Furthermore, Yang (2009) as cited by Coskun (2010, p.36)
informs that :
The students should apply metacognitive strategies to improve
their listening comprehension. By applying metacognitive strategies,
the students will be more confident and less anxious in the listening
process. Moreover, the students will be able to recognize the
requirement for the listening task, make appropriate prediction before
listening, monitor and evaluate their own comprehension
independently.
4. Three Strategy Sets of Metacognitive Strategies
There are three strategy sets of metacognitive strategies.
According to Oxford (1990, p.136), “ Metacognitive Strategies include
three strategy sets; Centering your learning, Arranging and Planning your
learning, and evaluating your learning”. Oxford (1990, p.138) explains
those three strategy sets as follows :
a. Centering Your Learning
1) Overviewing And Linking With Already Known Material: Overviewing comprehensively a key concept, principle, or set of materials in an upcoming language activity and associating it with what is already known.
2) Paying Attention:
Deciding in advance to pay attention in general to a language learning task and to ignore distractors.
3) Delaying Speech Production To Focus On Listening
Deciding in advance to delay speech production in the new language either totally or partially, until listening comprehension skills are better developed. Some language theorists encourage a silent period of delayed speech as part of the curriculum, but there is debate as to whether all students require this.
b. Arranging And Planning Your Learning 1) Finding Out About The Language Learning:
2) Organizing:
Understanding and using conditions related to optimal learning of the new language; organizing one’s Schedule, physical environment and language learning notebook.
3) Setting Goals And Objectives:
Setting aims for language learning, including long-term goals.
4) Identifying The Purpose Of A Language Task:
Deciding the purpose of a particular language task involving listening, reading, speaking, or writing. For example, listening to the radio to get the latest news on the stock exchange, reading a play for enjoyment, speaking to the cashier to buy a train ticket, and so on.
5) Planning For A Language Task:
Planning for the language elements and functions necessary for an anticipated language task or situation.
6) Seeking Practice Opportunities:
Seeking out or creating opportunities to practice the new language in naturalistic situations, such as going to a second/foreign language cinema, attending to a party where the language will be spoken, or joining an international social club. Consciously thinking in the new language also provides practice opportunities.
c. Evaluating Your Learning 1) Self-Monitoring:
Identifying errors in understanding or producing the new language, determining which ones are important, tracking the source of important errors, and trying to eliminate such errors. 2) Self-Evaluating:
Evaluating one’s own progress in the new language, for instance, by checking to see whether one is reading faster and understanding more than one month or six months ago, or whether one is understanding a greater percentage of each conversation.
These three strategy sets are very good for the students to be
applied in the learning process. It is because these three strategy sets will
help the students to focus in all kinds of learning activities. This is in line
with idea of Oxford (1990, p.138) that “this set of three strategies help
learners to converge their attention and energies on certain language
Figure 2.1 Three Strategy Sets of Metacognitive Strategies
D. Concept of Listening Comprehension.
1. Definitions of Listening Comprehension.
According to Rost (2002) and Hamouda (2013) as cited by
Gilakjani & Sabouri (2016, p.124), “listening comprehension as an
interactive process in which listeners are involved in constructing
meaning. Listeners comprehend the oral input through sound
discrimination, previous knowledge, grammatical structures, stress and
intonation, and the other linguistic or non-linguistic clues”. Meanwhile,
Nadig (2013) as cited by Gilakjani & Sabouri (2016, p.124) also informs
that “listening comprehension is the various processes of understanding
and making sense of spoken language. These involve knowing speech
sounds, comprehending the meaning of individual words, and
understanding the syntax of sentences”. Furthermore, Tabeei et al. ( 2013,
p.15) add that “listening comprehension is not a passive activity in which
listener receive information and then comprehend it but it is a
process-oriented activity which process the represented aural input step by step
and combine background knowledge to information in the listening text”.
From the explanation above, it can be concluded that listening
comprehension is an active, concious, complex, and process-oriented
activity. To produce output, the students must pay attention to the
important information from what they hear step by step, comprehend and
combine it with contextual information as well as their background
2. Factors Affecting Listening Comprehension.
According to Rubin (1994) as cited by Serri (2012, p.845), there
are five factors that affect listening comprehension :
a. The characteristics of the text such as speech rate, hesitation, level of perception, stress and rhythm of text, L1 and L2 differences, redundancy, the complexity of morpheme, the order of words, discourse markers, visual support, and modification of syntax;
b. The characteristics of speakers such as language proficiency and gender;
c. The characteristics of task such as task type;
d. The characteristics of listeners such as their memory, age, gender, attention, level of language proficiency, background knowledge, and learning disability in L1;
e. The characteristics of process such as "top-down, bottom-up, and parallel processing, listening strategies, and negotiation of comprehensible input.
To reach good listening comprehension, the students have to be
able to beat those factors. They must habituate themselves to various
speech rates of listening, rhythm of text, morpheme, words order, task
type, etc. The students must also be confident while listening. They must
have perception that listening is not hard.
3. Teacher’s roles in listening activity.
To improve the students’ listening comprehension, the teacher’s
roles are really important. In the listening activity, Ahmadi (2016, p.8-9)
explains that there are several roles of the teacher. They are presented as
a. A Teacher as an Organizer.
Teachers have to organize everything which will happen in the
class such as explaining what students have to do, giving instruction
and feedback, as well as preparing good listening lessons.
b. A Teacher as an Controller.
Teachers have to accomplish the whole lessons. They have
responsibility to set what the students have to do such as when
students should speak and when they should not to. Teachers must
also explain in detail what the students should do in the listening
stages.
c. A teacher as an Evaluator
Teachers have to be able to evaluate all kinds of learning
activities and they also have to be able to measure the students’
listening performance. After evaluating, the teachers also have to be
able to give feedbacks for their students.
d. A teacher as a resource
Teachers have to help the learners to understand the meaning
of unfamiliar vocabularies, grammatical pattern, etc. Teachers also
have to give advice to the students when it is necessary.
e. A teacher as a tutor
Teachers have to be able to develop the students’ ideas and
f. A teacher as a prompter
Teachers have to be able to motivate and give
recommendation about activities that are done by the students. The
teachers also have to support the students during every stage of
listening.
In this research, the teacher’s roles were as an organizer,
controller, evaluator, resource, tutor, and prompter. The teacher organized
everything happening in the class, controlled what the students had to do,
evaluated the students’ activities, gave source of knowledge to the
students, developed the students’ ideas, motivated and gave
recommendation to the students.
E. Media
1. Definitions of Media
According to Chan, Chin, Nagami, & Sutiwan (2011, p.2), “
Medium as a means of effecting or conveying something”. In language
teaching and learning, nowadays, media are used to convey and help
learning process so that the students can learn better.
2. Five aspects of Media
According to Weidenmann (2006) as cited by Chan et al.(2011,
p.5-6), five aspects of media are as follows :
a. Hardware
Material dimension of a medium is called hardware. It can be a
b. Software
Software refers to program transmitted through hardware such
as video film, animation, etc.
c. Symbol system
Symbol system is related to how transmitted information is
coded. For instance, the information in a text is coded by symbol
system “language” but the information in a sound film is coded by
symbol system “language” added by pictorial language.
d. Sensory channels
The sensory channels capture the information which is carried
by medium, such as the eyes, ears, and hands which always
correspond to the symbol system.
e. Message
The information which is transmitted through the symbol
system is called message. For an example, a message might be
transmitted through a video film.
From the explanation above, it can be concluded that video is a
program transmitted through the hardware. The hardware transmitting the
video can be a computer, projetor, DVD player, etc. Using video in
language teaching and learning is very helpful because it is is coded by
symbol system “language” added by pictorial language. When the
students are watching the video, they will automatically active their
F. Concept of Video
1. Definition of Video
Kim (2015, p.16) explains that “video is commonly used tool
because it provides background knowledge and specific examples that
provide a focus for leaning activities while textbook-based classes might
be boring for learners”. Learning by using video is very enjoyable for the
students. Nowadays, it is not hard to get video for teaching and learning
process. There are so many websites offering video for various purposes.
Video is really positive for teaching and learning process as long as it is
used properly. This is in line with idea of Cakir (2006, p.67) that “all
audio-visual materials have positive contributions to language learning as
long as they are used at the right time, in the right place”. Furthermore,
video is also useful for teaching listening comprehension. There are so
many researchers who have demonstrated the advantages of using
captions and subtitle to enhance listening comprehension (Kim, 2015,
p.15).
2. Benefits in using video in the classroom
There are so many great benefits in using video in the classroom.
Video is interesting, challenging, and stimulating to watch. It helps to
promote comprehension and make the meaning clearer. It also motivates
the students because a video can bring real world into the classroom. It
provides authentic language input for the students. If the students want to
animal directly. They can watch that animal through video which has
been well designed. Besides, the use of video is really easy and flexible.
Teachers can stop, start, slow down, and repeat the video as much as they
can when it is necessary. To improve understanding in certain
knowledge, the teacher and the students can also focus on the certain
scene of the video.( Cakir, 2006, p.68).
3. Practical Techniques for Video Implication in the Classroom
There are some practical techniques for video implication that
teachers can use in the classroom. Cakir (2006, p.69-70) explains that
they are as follows :
a. Active Viewing
This technique can make the students enjoy the learning
process and increase satisfaction. This technique will be very useful
for the students if the teachers want to teach their students about the
main idea of the video.
b. Freeze framing and prediction
Teachers can stop the video by pressing still or pause button. It
is called freeze framing. Freeze framing helps the students to predict
and deduce futher information about the content of the video.
c. Silent viewing
In this technique, video is played with the sound off. It will
arouse the students attention to develop skill of anticipation. This
is replaced by sound on so that the students can compare their
impression.
d. Sound on and vision off
In this this technique, video is played with sound on but the
vision is obscured. The students will only hear the dialogue but
unable to see the action. This technique will help the students to
compare what they hear with what really happened in the video
visually.
e. Repetition and Role-play
Repetition is used when there are several difficult language
points that students do not understand. When students have already
understood about the content of the video, they can act out the scene
as much as they can recall.
f. Reproduction Activity
After the students watch and understand about the video, they
can reproduce about the conclusion of the video, describe what
happened, write or retell to their friends.
g. Dubbing activity
In this activity, students are asked to complete the missing
dialogue after they watch sound-off video scene. This activity can be
done by the students who have necessary language competence.
h. Follow-up activity
To create extended oral practice, the students can discuss and
share about the video to their friends. This activity can enhance
students co-operative skills.
In this research, the teacher and the researcher used freeze framing
technique. The teacher stopped the video by pressing pause button to give
time for the students to write down the answer of a question. After that,
the teacher continued to display the video. Then, the teacher stopped the
video again to give time for the students to write down the answer of next
question. This technique could also help the students to deduce and
predict further information about the content of the video.
G. Genre
According to Djuharie (2007, p.24-43) as cited by Ratminah (2014,
p.16-18), genre refers to particular text-types and it is kind or type of text.
There are some kinds of genres in English. They are as follows :
1. Factual Report.
Factual report is also known as information report or report text.
Factual report provides information about various phenomena that happen
in our life. It is used to understand about those phenomena.
2. Recount Genre
Recount genre is a kind of genres used to retell past event and has
purpose to inform that event to other people. It is also used as an
3. Procedure
Procedure is a kind of genres used to explain how to accomplish
something through sequence of steps.
4. Descriptive Genre
Descriptive genre is a kind of genres used to describe a particular
person, place, or thing.
5. Explanation
Explanation is a kind of genres that is used to explain the process
involved in the phenomena.
6. Narrative Genre
Narrative genre is a kind of genres used to entertain the reader
about a story and has purpose to make the reader or listener enjoy and
imagine about the story.
7. Spoof
Spoof is a kind of genres used to retell past event with funny and
unpredictable ending. This genre is also used as entertaintment.
In this research, the teacher taught the students about the genre of
factual report. Factual report is very good for the students because it trains
the students to be more sensitive in their environment. The teacher taught
the students about the factual report of an animal. It was about cheetahs.
The teacher also taught the students about the factual report of a
H. Concept of Factual Report
1. Definition of Factual Report
Factual report is also known as information report or report text. it
is used to provide information about various phenomena that happen in
our life. It is used to make us understand about those phenomena. Factual
report can explain many topics such as natural disasters, animals,
computer, etc. (Kemendikbud, 2014, p.33).
2. The characteristics of Factual Report
Kemendikbud (2014, p.33) points out several characteristics of
factual report. They are as follows:
a. The topic is explained in detail.
b. There is no personal views.
c. It is usually written, but it can also be used orally.
d. Facts are used to explain the topic.
e. It is explained systematically.
3. Structure of Factual Report
Kemendikbud (2014, p.34) explains that factual report is usually
written in specific structure. In factual report, there are introductory
paragraph, body paragraphs, optional glossary and bibliography.
a. Introductory Paragraph
Introductory paragraph is also called as general classification,
b. Body paragraph
Body paragraph provides detailed information in a series of
paragraphs. In factual report, There are some body paragraphs that
provide description and facts about the topic and it does not have an
ending or a conclusion. Factual report is usually ended with statement
that summarize the whole content of the topic.
c. Glossary
Glossary is only optional. It is used to explain all technical
terms that are used in factual report. Glossary is placed at the end of
factual report.
d. Bibliography
It is a list of references that are used in factual report such as
books, megazines, websites, etc. It is also optional.
4. Sentence Structure of Factual Report
Kemendikbud (2014, p.34) explains that factual report has
sentence structure as follows:
a. It uses present tense, such as live, is, are, etc.
b. It uses passive sentence, such as is eaten, are written, etc.
c. It uses words that generalize, such as many, all, most, etc.
d. It uses relational verb such as have, consists of, made up of, etc.
e. It uses technical words that are relevant to the topic.
f. It uses descriptive but factual language, such as shape, color,
5. Example of Factual Report word cheetah comes from Sanskrit
word “Citrakayah” which means unlike leopards. Even though cheetahs are often mistaken as leopards but their features are totally different. One of the distinguishing marks of cheetahs is their teardrop shaped line on each side of their nose that extends from corner of its eyes to its mouth.
Passive voice
Paragraph 2 Description
antelopes, hares etc. They use their long and heavy tails as a stabilizer and single-mindedly pursue
their intended prey. Once the cheetah has pounced, It knocks its victim off balance and grips it by the throat as it falls. However, due to their weak jaws and small teeth, cheetahs are not as effective in killing their preys as quickly as lions and leopards. Female cheetahs give birth to an average of three young ones that they rear by
conservationists are trying to help protect the habitats of these edge, National Geographic, November 2012 www. Cheetah.org
Locomotion dynamics of hunting in wild cheetahs 2013, www.nature.com
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A. Location of the Research
This research was conducted in SMA Islam Sudirman Ambarawa. It is
a private school. This school is located at Jl. Jendral Sudirman No. 2A
Ambarawa. The access to the school is not difficult because it is very near
from the main street of Ambarawa. This school was built in 1978 under
foundation of Yayasan Pusat Pendidikan Islam Sudirman. It stands in the area
of 6860 m2. The physical condition of this school is very nice to carry out the
teaching and learning process. This school has about 970 students coming
from three majors ; IPA, IPS, and Bahasa. Now, The headmaster of this
school is Drs. Joko Pujianto.
B. Research Design
This research is Classroom Action Research (CAR). According to
Hopkins (2008, p.47), “Action research combines a substantive act with a
research procedure; it is action disciplined by enquiry, a personal attempt at
understanding while engaged in a process of improvement and reform”. It can
be concluded that CAR is an action research that is conducted in the
classroom by performing real action based on research procedures. It is an
effort to make an improvement. Wallace (1998, p.57) also explains that CAR
is one of research metodologies carried out by teacher to solve problems or to
When performing the CAR, there are some key points that have to be
understood by the teacher. CAR is used to improve education. It is conducted
collaboratively, reflectively, systematically, and rationally (Kemmis and
McTaggart, 1988, p.22-25).
Based on the explanations above, it can be concluded that CAR is
very useful in teaching and learning process. It can improve education and
solve problems that happen in the class. Before implementing CAR, the
teacher and other participants need to identify problems that happen in the
class. In implementing CAR, CAR has to be implemented collaboratively,
reflectively, systematically, and rationally to improve education.It means that
the teacher needs other participants to do it together.
In this research, the researcher and the teacher (Hanifikha Frindianita,
S.Pd) worked and collaborated to solve problems that happened in the
class.The researcher took role as an observer who observed everything that
happened in the class while the teacher performed CAR for the students. The
researcher and the teacher worked together in many activities such as
planning lesson plan, discussing the proper material, discussing proper task,
etc.
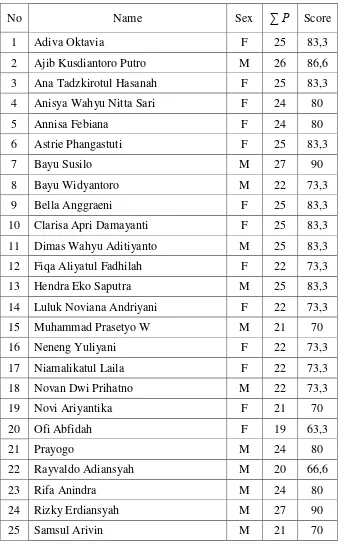
C. Subject of the Research
Subject of this research was the students of XI MIPA 3 in SMA Islam
Sudirman Ambarawa in the academic year of 2016/2017. There were as many
as 12 male students and 21 female students who participated in this research.
D. Research Schedule
Research schedule is very important before conducting a systematic
research. In this research, the researcher and the teacher presented the
research schedule as follows :
Table 3.1 Research Schedule
No Activity Date Facilitator
1. Interviewing the students and the
3. Giving treatment and conducting
post test for cycle 1
5. Giving treatment and conducting
post test for cycle 2
April 26th,
2017
The teacher
E. Techniques of Collecting the data
To collect the data for this research, the researcher used test,
observation, interview and documentation.
1. Test
a. Pre Test
Before conducting the cycles, the students were given pre test
in each cycle. It made the researcher know about the students’
contained ten questions that the students had to answer correctly,
completely, and accurately.
b. Post Test
The post test was conducted after the students carried out the
pre test and got treatments. The purpose of conducting the post test
was to know the improvement of students’ listening comprehension
after they were given treatments. In this post test, the researcher also
provided ten questions that had to be answered by the students
correctly, completely, and accurately.
2. Observation
Kothari (2004, p.96) explains that observation is a method that is
often used to know a behavioral science. In this research, when the
teacher gave the students the treatments, the researcher recorded the
process and the activities of the students as well as the teacher in form of
field notes (enclosed). After treatments were given and the post test was
carried out, the field notes would be used as a tool for making reflection.
3. Interview
The researcher used interview method to know the problems and
the issues happening in the class. Before conducting CAR, the researcher
interviewed the students as well as the teacher to look for the problems.
4. Documentation
To make documentation for this research, the researcher collected
F. Cycles of Classroom Action Research
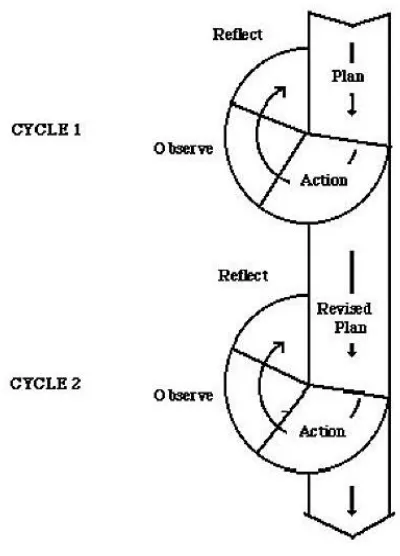
Kemmis & McTaggart (1988, p.14) explain that action research
planner is sequential programs that tachers do to engage in action. Those
sequential programs are conducted in form of the cycles. They are planning,
acting, observing, and reflecting.
Figure 3.1 Model of Classroom Action Research
Source : Kemmis & McTaggart (1988, p.14)
1. Cycle I
a. Planning
In this stage, the researcher planned what action that would be