Multicriteria Decision
Making
■ Goal Programming
■ Graphical Interpretation of Goal Programming
■ Computer Solution of Goal Programming Problems with QM for Windows and Excel
■ The Analytical Hierarchy Process
■ Scoring Models
■ Study of problems with several criteria, multiple criteria, instead of a single objective when making a decision.
■ Three techniques discussed: goal programming, the analytical hierarchy process and scoring models.
■ Goal programming is a variation of linear programming considering more than one objective (goals) in the objective function.
■ The analytical hierarchy process develops a score for each decision alternative based on comparisons of each under different criteria reflecting the decision makers preferences.
■ Scoring models are based on a relatively simple weighted scoring technique.
■ Adding objectives (goals) in order of importance, the company: 1. Does not want to use fewer than 40 hours of labor per day.
2. Would like to achieve a satisfactory profit level of $1,600 per day.
3. Prefers not to keep more than 120 pounds of clay on hand each day.
4. Would like to minimize the amount of overtime.
■ All goal constraints are equalities that include deviational
■ At least one or both deviational variables in a goal constraint must
equal zero.
■ The objective function seeks to minimize the deviation from the respective goals in the order of the goal priorities.
Goal Programming
Labor goal:
x
1+ 2x
2+ d
1-- d
1+= 40 (hours/day)
Profit goal:
40x
1+ 50 x
2+ d
2 -- d
2 += 1,600 ($/day)
Material goal:
4x
1+ 3x
2+ d
3 -- d
3 +
= 120 (lbs of clay/day)
1. Labor goals constraint
(priority 1 - less than 40 hours labor; priority 4 - minimum overtime):
Minimize P1d1-, P
4d1+
2. Add profit goal constraint
(priority 2 - achieve profit of $1,600):
Minimize P1d1-, P2d2-, P4d1+ 3. Add material goal constraint
(priority 3 - avoid keeping more than 120 pounds of clay on hand):
Minimize P1d1-, P
2d2-, P3d3+, P4d1+
■ Changing fourth-priority goal “limits overtime to 10 hours” instead of minimizing overtime:
d1+ + d4 - - d4+ = 10
minimize P1d1 -, P2d2 -, P3d3 +, P4d4 +
■ Addition of a fifth-priority goal- “important to achieve the goal for
mugs”:
Goal Programming
Alternative Forms of Goal Constraints (2 of 2)
Complete Model with Added New Goals:
Figure 9.1 Goal Constraints
Goal Programming
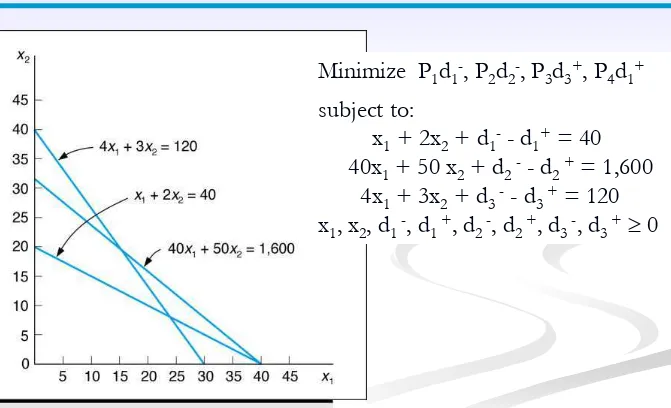
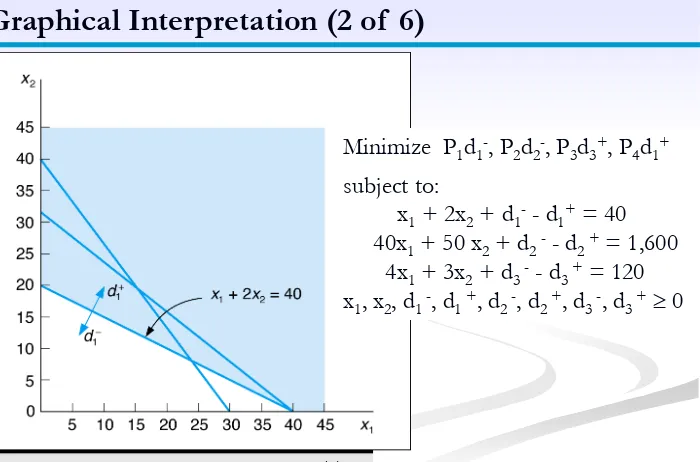
Graphical Interpretation (1 of 6)
Minimize P1d1-, P
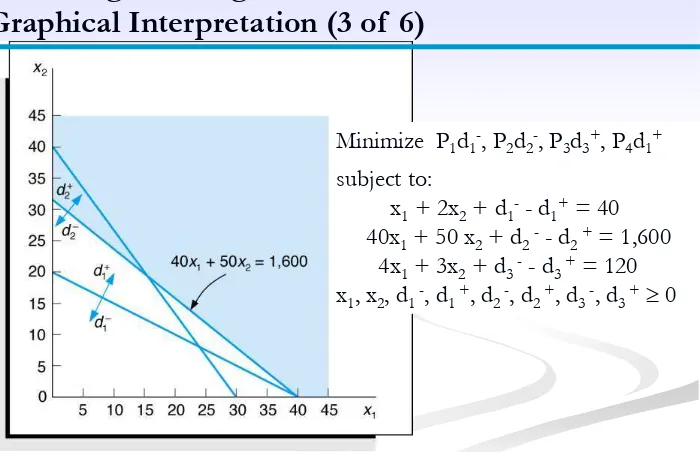
Figure 9.3 The Second-Priority Goal: Minimize d2-
Goal Programming
Graphical Interpretation (3 of 6)
Goal Programming
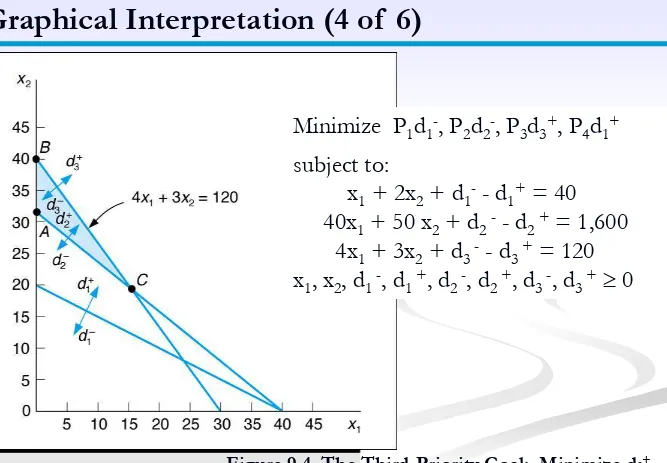
Graphical Interpretation (4 of 6)
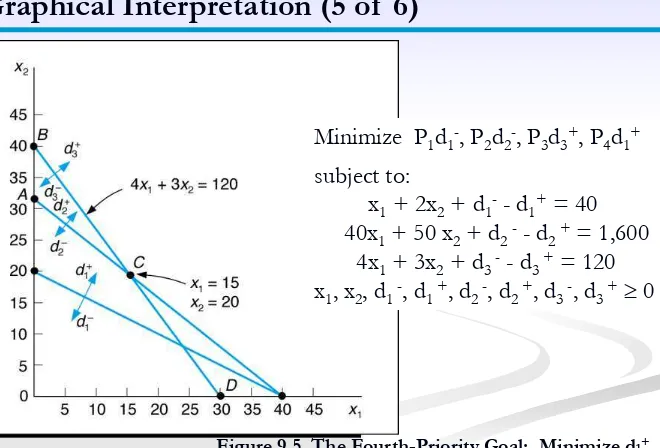
Figure 9.5 The Fourth-Priority Goal: Minimize d1+
Goal Programming
Graphical Interpretation (5 of 6)
Goal programming solutions do not always achieve all goals and they are not “optimal”, they achieve the best or most satisfactory solution possible.
Exhibit 9.3
Exhibit 9.5
Goal Programming
Goal Programming
Minimize P1d1-, P
Goal Programming
Exhibit 9.8
Goal Programming
Goal Programming
Solution for Altered Problem Using Excel (4 of 6)
Exhibit 9.10