A.
Struktur Atom, Sistem Periodik Unsur, dan Ikatan Kimia
1. Sejumlah 19,5 gram logam M yang bervalensi 1 direaksikan dengan asam sulfat berlebih dan dihasilkan 5,6 liter gas H2 pada keadaan standar. Jika dalam 1 atom
M terdapat 20 neutron maka konfigurasi elektron yang tepat adalah...
2. 5,2 gram suatu logam trivalen direaksikan dengan larutan HCl, dan menghasilkan 3,36 liter gas hidrogen (STP). Jika atom logam tersebut mengandung 28 neutron, maka bilangan kuantum elektron terakhir atom logam itu adalah...
3. Elektron terakhir dalam atom suatu unsur mempunyai bilangan kuantum n = 4 ; l = 2 ; m = -1 ; s = . Unsur tersebut dalam sistem periodik terletak pada...
4. Suatu atom netral mempunyai konfigurasi elektron 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6. Dapat dikatan bahwa atom ini...
1. Berada dalam keadaan tereksitasi.
2. Akan memancarkan energi radiasi jika susunan elektronnya berubah menjadi 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5 4s1.
3. Merupakan atom unsur gas mulia.
4. Termasuk unsur periode 4 sistem periodik. Pernyataan yang benar adalah...
5. Unsur x dengan konfigurasi elektron 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 dapat bereaksi dengan unsur Y, yang terletak pada golongan oksigen, membentuk senyawa...
6. Senyawa yang tidak dapat mengadakan ikatan hidrogen antarsesama molekulnya adalah...
1. Metanol 2. Dietil eter 3. Asam asetat 4. Asetaldehida
7. Nomor atom P adalah 15, sedangkan Br adalah 35. Bentuk molekul PBr5 adalah...
8. Senyawa berikut ini yang mempunyai dipol permanen adalah... 1. CCl4 2. BCl3 3. BeCl2 4. PCl3 5. CH4 B.
Termokimia
1. Pembakaran sempurna gas metana ditunjukkan oleh persamaan reaksi berikut ; CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + H2O = -840 kJ
Jika seluruh kalor yang dihasilkan digunakan untuk mendidihkan air yang mula-mula bersuhu 25 C maka volum air yang bisa didihkan menggunakan 24 gram metana adalah...
2. Pembakaran suatu contoh zat dalam sebuah kalorimeter bom menghasilkan kalor sebesar 25,2 kJ. Air yang berada dalam kalorimeter adalah 1000 gr dan suhunya
naik 4 . Jika kalor jenis air adalah 4,2 J.g-1.C-1, maka kapasitas kalor kalorimeter bom tersebut adalah...
3. Dalam suatu reaksi kimia dibebaskan 8,4 kJ energi. Kalor ini digunakan untuk memanaskan 100 cm3 air , maka kenaikan suhunya ialah...(kalor jenis air = 4,2 J. g-1. -1
4. Diketahui data energi ikatan rata-rata berikut: H-H = 104,2 kkal.mol-1
C-Cl = 57,8 kkal.mol-1 H-Cl = 103,1 kkal.mol-1
Kalor yang diperlukan untuk menguraikan 146 gram HCl (Ar H = 1, Cl =35,5) menjadi unsur-unsurnya adalah...
5. Dari data :
2H2(g) + O2(g) 2H2O(l) = -571 kJ
2Ca(s) + O2(g) 2CaO(s) = -1269 kJ
CaO(s) + H2O(l) Ca(OH2)(s) = -64 kJ
Dapat dihitung entalpi pembentukan Ca(OH)2 (s) sebesar...
6. Persamaan termokimia pembakaran gas etilena (C2H4) adalah :
C2H4 (g) + 3O2 (g) 2CO2 (g) + 2H2O (l) = -310 kkal
Dengan mengandaikan efisiensi 60%, maka massa air pada 20 yang dapat diubah menjadi uap pada 100 dengan membakar 1,12 m3 (STP) gas C2H4
adalah...(kalor jenis air = 1 kkal/kg. ; kalor uap air = 540 kkal/kg) 7. Diketahui kalor pembentukan siklopropana (CH2)3 (g) = -a kJ/mol
Kalor pembentukan CO2 (g) = -b kJ/mol
Kalor pembentukan H2O (l) = -c kJ/mol
Maka kalor pembentukan siklopropana (dalam kJ/mol) ialah... 8. Perhatikan diagram siklus berikut :
= -790 kJ
= -593 kJ X
Data diagram tersebut di atas, harga x adalah...
C.
Laju Reaksi
1. Amonia dapat dibakar dengan persamaan reaksi : 4NH3(g) + 5O2(g) 4NO(g) + 6H2O(g)
Jika pada waktu tertentu diketahui laju reaksi amonia sebesar 0,24 mol L-1 det-1, maka laju reaksi oksigen (O2) dan laju reaksi pembentukan H2O berturut-turut
adalah...
2S(s) + 3O2(g)
2SO2(g) + O2(g)
2. Data eksperimen untuk reaksi 2A(g) + B(g) 2AB(g) terdapat dalam tabel berikut : Percobaan [A] (mol/L) [B] (mol/L) Laju Reaksi (mol.L-1 s-1) 1 0,1 0,1 6 2 0,1 0,2 12 3 0,1 0,3 18 4 0,2 0,1 24 5 0,3 0,1 54
Dari data tersebut dapat disimpulkan bahwa persamaan laju reaksinya adalah... 3. Diperoleh data percobaan untuk reaksi H2(g) + I2(g) 2HI (g)
Sebagai berikut : [H2], M [I], M V (M.s-1) 0,1 0,1 0,16 0,1 0,2 0,32 0,2 0,2 0,64 0,3 0,3 X Harga x adalah...
4. Bila suhu suatu reaksi dinaikkan 10 , maka laju reaksinya akan menjadi dua kali lipat. Kalau pada suhu t reaksi berlangsung selama 12 menit, maka pada suhu (t + 30) reaksi akan berlangsung selama...
5. Jika pada suhu tertentu waktu paro reaksi orde pertama 2A 2B + C adalah 3 jam, maka jumlah A yang terurai dalam waktu 9 jam adalah...
6. Setiap kenaikan 10 laju reaksi menjadi 2 kali lebih cepat. Suatu reaksi pada suhu 30 laju = a, bila suhu dinaikkan menjadi 100 , maka laju reaksinya adalah...
7. Reaksi akan berlangsung 3 kali lebih cepat dari semula setiap kenaikan 20 . Jika pada suhu 30 suatu reaksi berlangsung 3 menit maka pada suhu 70 reaksi akan berlangsung selama...
8. Untuk reaksi N2O4(g) 2NO2(g) diketahui data:
= +54 kJ Ea = + 57,2 kJ
Energi aktivasi (Ea) untuk reaksi 2NO2(g) N2O4(g) adalah...
D.
Kesetimbangan Kimia
1. Pada pemanasan 1 mol gas SO3 dalam ruang yang volumnya 5 liter diperoleh gas
O2 sebanyak 0,25 mol. Pada keadaan tersebut tetapan kesetimbangan Kc adalah...
2. Tetapan kesetimbangan untuk reaksi kesetimbangan :
2A(g) + B(g) C(g) + D(g) pada suhu tertentu adalah 4. Bila pada suhu tetap, volum diubah menjadi setengah volum asal, maka tetapan kesetimbangannya adalah...
3. Dalam suatu wadah gas N2O4 terdisosiasi 50% menjadi gas NO2, sehingga
campuran gas menimbulkan tekanan total 6 atm. Harga Kp adalah... 4. Perhatikan reaksi :
2N2O(g) + N2H4(g) 3N2(g) + 2H2O(g). Jika 0,10 mol N2O dan 0,10 mol N2H4
dicampurkan dalam volum 10 liter dan dibiarkan mencapai kesetimbangan, ternyata bahwa x mol N2O telah bereaksi. Jadi, konsentrasi N2 dalam
kesetimbangan adalah...
5. Tetapan kesetimbangan untuk reaksi PCl5(g) PCl3(g) + Cl2(g)
Pada suhu 760 K adalah 0,05. Jika konsentrasi awal PCl5 0,1 mol.L-1, maka pada
keadaan setimbang PCl5 yang terurai adalah...
6. Suatu reaksi mempunyai tetapan laju reaksi ke kanan (reaksi maju) sebesar 2,3 x 106 s-1 dan tetapan kesetimbangan 4,0 x 108. Tetapan laju reaksi ke kiri (reaksi balik) dari reaksi tersebut adalah...
7. Jika COCl2 0,5 M dipanaskan pada suhu 450 , zat itu akan terurai menurut reaksi
COCl2(g) CO(g) + Cl2(g) dan pada kesetimbangan tinggal 0,1 M. Berapakah
konsentrasinya CO yang terjadi apabila COCl2 0,225 M dipanaskan pada suhu
yang sama?
8. Jika dipanaskan pada suhu tertentu, 50% N2O4 mengalami disosiasi sesuai dengan
reaksi N2O4(g) 2NO2(g). Dalam kesetimbangan perbandingan mol N2O4
A.
Struktur Atom, Sistem Periodik Unsur, dan Ikatan Kimia
1. Reaksi : 2M + H2SO4 M2SO2 + H2 H2 = = 0,25 mol M = 0,25 = 0,5 Ar = = = 39 Z = Ar – n = 39 – 20 = 19 19M : [Ar] 4s1 2. Reaksi : 2M + 6HCl 2MCl3 + 3H2 H2 = mol = 0,15 mol M = 0,15 mol = 0,10 mol Ar = = 52 Z = Ar – n = 52 – 28 = 24 24M : [Ar] 4s1 3d5 -2 -1 0 +1 +2Bilangan kuantum elektron terakhirnya : n = 3 ; l = 2 ; m = +2 ; s = +
3. 4d {
{ -2 -1 0 1 2
Jadi konfigurasi elektron selengkapnya adalah
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 5s2 4d2 atau jika disingkat [Kr] 5s2 4d2 sehingga termasuk golongan IV B, periode 5.
4. Pernyataan yang benar adalah nomor 2, 3, dan 4.
Pada keadaan dasar, atom netral yang disebutkan pada soal mempunyai konfigurasi 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 .
Jika atom tersebut menyerap energi maka satu elektron atau lebih dapat berpindah ke tingkat energi yang lebih tinggi misalnya menjadi 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5 4s1. Keadaan ini disebut keadaan tereksitasi.
Jika energi yang diserap pada proses eksitasi maka elektron-elektron kembali ke keadaan dasar.
Golongan dan periode ditentukan dari konfigurasi elektron keadaan dasar 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 , yaitu golongan VIII A (gas mulia) danperiode 3.
5. a. X dengan elektron valensi 3s2 cenderung melepas 2e. b. Y (golongan VI A) cenderung menangkap 2e.
c. Senyawa yang terbentuk adalah XY 6. (1) CH3 – OH
(2) CH3CH2-O-CH2CH3 (3) CH3-COOH
(4) CH3-C-H O
Yang tidak dapat mengadakan ikatan hidrogen adalah (2) dan (4).
7. a. Pada molekul PBr5, atom pusat P dikelilingi oleh elektron yang berasal dari :
- elektron valensi P = 5 - elektron valensi Br = 5
jumlah elektron total = 10 jumlah pasangan e = 5
b. Kelima pasangan elektron ini mengambil orientasi trigonal bipiramida. 8. Yang mempunyai dipol permanen adalah 4.
Dipol permanen terdapat pada molekul polar. Kepolaran ikatan terjadi bila atom-atom yang berikatan mempunyai perbedaan keelektronegatifan dan membentuk molekul yang tidak simetris. Dan PCl3 mempunyai bentuk yang tidak simetris
sehingga bersifat polar.
B.
Termokimia
1. Penyelesaiannya : a. CH4 =
mol
b. Kalor yang dihasilkan pada pembakaran 1,5 mol CH4
= 1260 kJ = 1260 . 103 J
c. Kalor sebanyak ini dapat mendidihkan air q = m . c .
m = ( ) = 4000 gram
d. Karena air = 1 g/mL, maka volum air = 4000 mL atau 4 liter
2. Kalor yang dihasilkan oleh reaksi dalam kalorimeter bom sebagian diserap oleh air yang ada pada kalorimeter dan sebagian oleh kalorimeter.
qreaksi = qair + qkalorimeter
= mair cair + Ckalorimeter
25200 = Ckal = 2100 J . -1 = 2,1 kJ . -1 3. Penyelesaiannya : q = m . c . 8,4 . 103 = 100 . 4,2 . = 20 4. Penyelesaiannya : HCl = = 4 mol 4H – Cl(g) 2H-H(g) + 2Cl-Cl(g) = ∑ reaktan - ∑ produk = [ ] [ ] = ( ) ( ) = 412,4 – 324 = 88,4 kJ 5. Penyelesaiannya :
Reaksi pembentukan Ca(OH)2 adalah Ca + O2 + H2 Ca(OH)2
Dengan menggunakan data di atas
(2H2 + O2 2H2O) (2Ca + O2 2CaO) CaO + H2O Ca(OH)2 + Ca + O2 + H2 Ca(OH)2 6. Penyelesaiannya :
Pengubahan air (20 ) menjadi uap air (100 ) berlangsung dalam 2 tahap
(1) Air (20 ) air (100 )
(2) Air (100 ) uap air (100 )
Jika massa air pada proses tersebut = x Kg, maka : qtotal = q1 + q2
=
= ( ) = 620x kkal
Kalor sebesar ini disuplai oleh pembakaran 1,12 m3 (STP) gas C2H4
Mol C2H4 =
= = 50 mol
( )
= -15.500 kkal
Dengan memperhatikan bahwa efisiensi perpindahan kalor adalah 60% maka :
0,6 ( ) X = 15 Kg 7. Penyelesaiannya :
Reaksi pembakaran siklopropana :
(CH2)3 + O2 3CO2 + 3H2O ∑ ∑ [ ( ) ( )] ( ) (CH2)3 = a – 3b – 3c kJ/mol 8. Penyelesaiannya : Menurut hukum Hess :
2S(s) + 3O2(g) 2SO2(g) + O2 kJ 2SO2(g) + O2 2SO3(g) + 2SO2(g) + 3O2(g) 2SO3(g) Dengan demikian : -593 + x = -790 X = -197
C.
Laju Reaksi
1. Penyelesaiannya : 4NH3 + 5O2 4NO + 6H2O VNH3 = 0,24 mol/L/s VO2 = VH2O = 2. Penyelesaiannya : [B] naik 2x V = (B) V naik 2x 2 = (2)m m = 1 [A] naik 2x V = (B)n V naik 4x 4 = (2)n n = 2 1 1 2 4Persamaan laju : V = k[A]2[B]
3. Penyelesaiannya :
Persamaan laju reaksi secara umum : V = k[H2]m[I2]n
Dari percobaan (1) dan (2) diperoleh :
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) (0,5)n = 0,5 n = 1
Dari percobaan (2) dan (3) diperoleh :
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) (0,5)m = 0,5 m = 1
Dari percobaan (1) dan (4) diperoleh :
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) = X = 1,44 4. Penyelesaiannya :
Setiap kenaikan suhu 10 maka laju reaksi = 2 kali lipat (waktu menjadi kali semula) : t 2 = t1 ( ) t (t + 30) = 12 menit t = 1,5 menit 5. Penyelesaiannya : Sisa = = 12,5 %
Jadi, yang terurai adalah 87,5 %.
6. Penyelesaiannya :
Jika setiap kenaikan suhu 10 mengakibatkan laju reaksi menjadi 2 x semula maka :
V2 = V1 ( )
V100 = a ( ) = 128a
7. Penyelesaiannya :
Jika pada setiap kenaikan 20 laju meningkat 3 kali lebih cepat, maka waktu reaksi menjadi kali waktu awal.
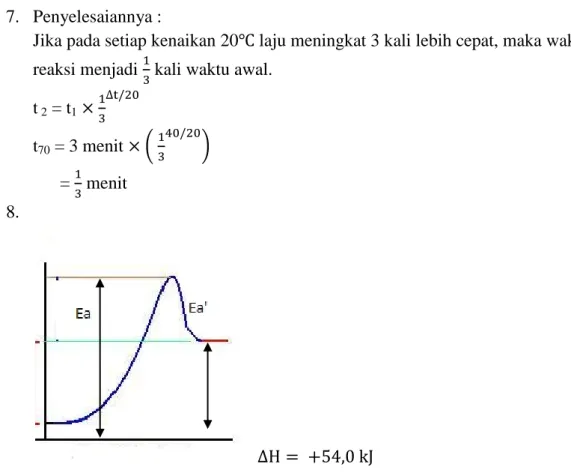
t 2 = t1 t70 = 3 menit ( ) = menit 8.
Diagram energi untuk reaksi : N2O4 2NO2 dapat dilihat pada gambar di atas.
Dari diagram terlihat bahwa : Ea = Ea’ +
Dengan
Ea = energi aktivsi untuk N2O4 2NO2
Ea’= energi aktivasi untuk 2NO2 N2O4
Dengan demikian diperoleh.. 57,2 = Ea’ + 54, 0 Ea’ = +3,2 kJ
D.
Kesetimbangan Kimia
1. Penyelesaiannya : 2O3 2SO2 + O2 Awal : 1 - - Reaksi: 0,50 0,50 0,25 + Stb : 0,50 0,50 0,25 Pada kesetimbangan : [SO3] = 0,50 mol/5L L = 0,10 M [SO2] = 0,50 mol/5L L= 0,10 M [O2] = 0,25 mol/5L L= 0,05 M[ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] = 0,5 2. Penyelesaiannya :
Tetapan keseimbangan hanya dipengaruhi oleh suhu. Oleh karena suhu tetap maka tetapan kesetimbangan juga tetap, yaitu 4.
3. Penyelesaiannya :
Jika mol N2O4 awal = a; maka N2O4 yang bereaksi = 0,5 a
N2O4 2NO2 Awal : a - Reaksi : 0,5a a + Setimbang : 0,5a a PN2O4 = PNO2 = = 4 atm Kp = 4. Penyelesaiannya : 2NO2(g) + N2H4(g) 3N2(g) + 2H2O(g) Awal : 0,10 0,10 - - Reaksi: x 0,5x 1,5x x + Stb: 0,10-x 0,10-0,5x 1,5x x Pada kesetimbangan: [N2] = 5. Penyelesaiannya : PCl5(g) PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) Awal : 0,1 - - Reaksi : x x x + Stb : 0,1 – x x x Kc = [ ] [ ] 0,05 = X2 + 0,05x – 0,005 = 0
(x + 0,1) (x – 0,05) = 0 X = 0,05 mol.L-1 PCl5 yang terurai = 6. Penyelesaiannya : 2X + 2Y 4Z ; Kc = 0,04 X + Y 2Z ; Kc = ( ) = 0,2 2Z X + Y ; Kc = = 5 7. Penyelesaiannya : COCl2 CO + Cl2 Awal : 0,5 - - Reaksi : 0,4 0,4 0,4 + Stb : 0,1 0,4 0,4 Kc = ( )( ) ( ) = 1,6 COCl2 CO + Cl2 0,225 - - X x x + 0,255-x x x Kc = ( )( ) ( ) X2 + 1,6x – 0,36 = 0 (x + 1,8)(x – 0,2) = 0 X1 = -1,8 (tidak memenuhi) X2 = 0,2 8. Penyelesaiannya : N2O4 2NO2 Awal : a - Reaksi : 0,5 a a + Stb : 0,5a a (N2O4) : (NO2) = 0,5a : a = 1 : 2
A.
Atomic structure, Periodic System of Elements, and
Chemical Association
1. A number of 19.5 grams of a metal M that has valence 1 is reacted with sulfuric acid and the resulting excess of 5.6 liters of H2 gas at standard
conditions. If in an atom M there are 20 neutrons then the appropriate electron configuration is ...
2. 5.2 grams of a trivalent metal is reacted with a solution of HCl, and produces 3.36 liters of hydrogen gas (STP). If the atom of the metal contain 28
neutrons, the final electron quantum numbers of metal atoms is ...
3. The last electron in an atom of an element has the quantum number n = 4; l = 2, m = -1; s = 1 / 2. Elements in the periodic system lies in the ...
4. An atom has a neutral electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6. These atoms can be ...
Being in an excited state.
Will emit radiation energy if the arrangement of electrons 1s2 2s2 turned into 3s2 2p6 4s1 3p5.
Is an element of the noble gas atom.
Including elements of the periodic system of period 4. The correct statement is ...
5. Element x with the electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 can be react with elements of Y, which is in group oxygen, What compound does the elements can form...
6. Compounds that can not bond with hydrogen bond is ... Methanol
Diethyl ether Acetic acid Acetaldehyde
7. P atomic number is 15, while Br is 35. PBr5 molecular shape is ...
8. The following compounds that have a permanent dipole is ... CCl4 BCl3 BeCl2 PCl3 CH4
B.
Thermochemical
1. Complete combustion of methane is shown by the following equation; CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + H2O ΔH = -840 kJ
If all the heat generated is used to boil water which temperature is 25 ° C then the volume of water that can boiled using 24 grams of methane is ... 2. Combustion of a sample substance in a bomb calorimeter produce 25.2 kJ
calor. The Water that is in the calorimeter is 1000 g and the temperature rose 4 . If the heat of water is 4.2 J.g-1. C-1, then the calor capacity of the bomb calorimeter is ...
3. In a chemical reaction, 8.4 kJ of energy released.The heat is used to heat the 100 cm3 of water, then the temperature is rising ... (heat of water = 4.2 J g-1.
4. Known bond energy data the following average: H-H = 104.2 kkal.mol-1
C-Cl = 57.8 kkal.mol-1 H-Cl = 103.1 kkal.mol-1
Heat required to decompose 146 grams of HCl (Ar H = 1, Cl = 35.5) into its elements is ...
From the data:
2H2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2H2O (l) ΔH = -571 kJ 2Ca (s) + O2 (g) → 2CaO (s) ΔH = -1269 kJ CaO (s) + H2O (l) → Ca (OH2) (s) ΔH = -64 kJ The formation enthalpy of Ca (OH) 2 (s) is ...
5. Thermochemical equation of combustion gases ethylene (C2H4) is: C2H4 (g) + 3O2 (g) → 2CO2 (g) + 2H2O (l) ΔH = -310 kcal
Assuming 60% efficiency, then the mass of water at 20 which can be converted into steam at 100 by burning 1.12 m3 (STP) of gas C2H4 is ...
(heat of water = 1 kcal / kg. ; heat of water vapor = 540 kcal / kg) 6. Known to heat the formation of cyclopropane (CH 2) 3 (g) =-a kJ / mol
Heat of formation of CO2 (g) = -b kJ / mol
Heat of formation of H2O (l) = -c kJ / mol
Then heat the formation of cyclopropane (in kJ / mol) is ... 7. Consider the following diagram of the cycle:
ΔH = -790 kJ
ΔH = -593 kJ X
Data above diagram, the price of x is ...
C.
The Rate of Reaction
1. Ammonia can be burned by the equation: 4NH3 (g) + 5O2 (g) → 4NO (g) + 6H2O (g)
If at a certain time is known rate of reaction of ammonia for 0.24 mol L-1 s-1, then the reaction rate of oxygen (O2) and the rate of reaction of formation of H2O in a row is ...
2. Experimental data for the reaction 2A (g) + B (g) → 2AB (g) contained in the following table:
Percobaan [A] (mol/L) [B] (mol/L) Laju Reaksi (mol.L-1 s-1) 1 0,1 0,1 6 2 0,1 0,2 12 3 0,1 0,3 18 4 0,2 0,1 24 5 0,3 0,1 54
From these data it can be concluded that the reaction rate equation is ...
2S(s) + 3O2(g) 2SO3(g)
3. Experimental data obtained for the reaction H2 (g) + I2 (g) → 2HI (g) As follows: [H2], M [I], M V (M.s-1) 0,1 0,1 0,16 0,1 0,2 0,32 0,2 0,2 0,64 0,3 0,3 X Price of x is ...
4. When a reaction temperature is raised 10 , the reaction rate will be doubled. If the temperature of the reaction t for 12 minutes, then at a temperature (t + 30) reaction will happen during ...
5. If at a certain temperature when half of the first order reaction 2A + 2B → C is 3 hours, then the amount of A that biodegrade within 9 hours is ...
6. Each increase of 10 the reaction rate to 2 times faster. A reaction at a temperature of 30 rate = a, when the temperature is raised to 100 , the rate of reaction is ...
7. The reaction will three times faster than the original any increase in 20 . If at a reaction temperature of 30 lasted 3 minutes then at 70 the reaction will happen during ...
8. For the reaction N2O4 (g) → 2NO2 (g) known data:
ΔH = +54 kJ + Ea = 57.2 kJ
The activation energy (Ea) for the reaction 2NO2 (g) → N2O4 (g) is ...
D.
Chemical Equilibrium
1. On heating 1 mole of SO3 in the gas space volumnya 5 liters of O2 gas
obtained as much as 0.25 mol. In such circumstances the equilibrium constant Kc is ...
2. Equilibrium constant for the reaction equilibrium:
2A (g) + B (g) C (g) + D (g) at a given temperature is 4. When the temperature is fixed, the volume is converted into a half volume of origin, then the equilibrium constant is ...
3. In a gas container 50% N2O4 dissociates into gas NO2, there by causing the
gas mixture total pressure 6 atm. The value of Kp is ... 4. Consider the reaction:
2N2O (g) + N2H4 (g) 3N2 (g) + 2H2O (g). If 0.10 mol of N2O and 0.10 mol
of N2H4 mixed in a volume of 10 liters and allowed to reach equilibrium, it
turns out that x moles of N2O has reacted. Thus, the concentration of N2 in
equilibrium is ...
5. Equilibrium constant for the reaction PCl5 (g) PCl3 (g) + Cl2 (g)
At a temperature of 760 K is 0.05. If the initial concentration of PCl5 is 0.1
mol.L -1, then the equilibrium state which decomposes PCl5 is ...
6. A reaction has a reaction rate constant to the right (forward reaction) of 2.3 x 106 s-1 and the equilibrium constant of 4.0 x 108.Reaction rate constant to the left (reverse reaction) of the reaction is ...
7. If COCl2 0.5 M heated at a temperature of 450 , this compound would
equilibrium left 0,1 M. What happens if the CO concentration is 0.225 M COCl2 heated at the same temperature?
8. When heated at a certain temperature, 50% of dissociating N2O4 in
accordance with the reaction of N2O4 (g) 2NO2 (g). In the equilibrium
A.
Atomic structure, Periodic System of Elements, and
Chemical Association
1. Reaction: H2SO4 + 2M + H2 → M2SO2 H2 = 5.6 / 22.4 = 0.25 mol M = 2 / 1 × 0.25 = 0.5 Ar = g / mol = 19.5 / 0.5 = 39 Z = Ar - n = 39-20 = 19 19m: [Ar] 4s1 2. Reaction : 2M + 6HCl 2MCl3 + 3H2 H2 = mol = 0,15 mol M = 0,15 mol = 0,10 mol Ar = = 52 Z = Ar – n = 52 – 28 = 24 24M : [Ar] 4s1 3d5 -2 -1 0 +1 +2 The last quantum number is: n = 3 ; l = 2 ; m = +2 ; s = + 3. 4d {
{ -2 -1 0 1 2
So the complete electron configuration
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 5s2 4d2 and the abreviation is [Kr] 5s2 4d2 so it lies on group IV B and 5 period.
4. Correct statement is number 2, 3, and 4.
(1) In the ground state, neutral atoms have mentioned the matter of configuration 1s2 2s2 2p63s2 3p6.
(2)If the atom absorbs energy then one or more electrons can move to higher energy levels such as 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 4s1 3p5. A condition called excited states.
(3)If the energy is absorbed in the process of excitation of the electrons return to ground state.
(4)Groups and periods determined from the electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 ground state 3s2 3p6, lie in group VIII A (noble gases) and 3 period.
5. a. X with 3s2 valence electrons tend to remove 2e. b. Y (type VI A) tend to capture 2e.
c. The compound formed is XY 6. (1) CH3 - OH
(2)-O-CH2CH3 CH3CH2 (3) CH3-COOH
(4) CH3-C-H O
Who can not hold a hydrogen bond is (2) and (4).
7. a. At the molecular PBr5, the central P atom is surrounded by electrons
originating from: valence electrons P = 5 Br = 5 valence electrons total number of electrons = 10 number of pairs electrons = 5
b. The five pairs of electrons are taken bipiramida trigonal orientation. Which have permanent dipole is 4.
Permanent dipoles contained in polar molecules. Polar bond occurs when atoms have different electronegativity and bond to form molecules that are not symmetrical. And PCl3 has an asymmetrical shape that are polar.
B.
Thermochemical
1. The Solution:
a. CH4 = 24/36 = 1.5 mol
b. Heat generated in the combustion of 1.5 moles of CH4
q = 1.5 × 840 kJ = 1260 kJ = 1260. 103 A
c. This much heat can boil water q = m. c. Δt
m =
( )
= 4000 grams
d. Because water = 1 g / mL, the volume of water = 4000 mL or 4 liters 2. Heat generated by the reaction in a bomb calorimeter partially absorbed by
the water present in the calorimeter and in part by the calorimeter. qreaction = qwater + qcalorimeter
= mwater cwater + Ccalorimeter
Ckal = 2100 J . -1 = 2,1 kJ . -1 3. The Solution: q = m. c. Δt 8.4. 103 = 100. 4.2. Δt Δt = 20 4. The Solution: HCl = = 4 mol 4H – Cl(g) 2H-H(g) + 2Cl-Cl(g) = ∑ reactan - ∑ product = [ ] [ ] = ( ) ( ) = 412,4 – 324 = 88,4 kJ 5. The Solution:
Formation reaction of Ca(OH)2 is a Ca + O2 + H2 → Ca(OH)2
By using the above data
(2H2 + O2 2H2O) (2Ca + O2 2CaO) CaO + H2O Ca(OH)2 + Ca + O2 + H2 Ca(OH)2 6. The Solution:
The conversion of water (20 ) into water vapor (100 ) takes place in two stages
Water (20 ) Water(100 )
Water (100 ) Water vapor (100 )
If the water mass is = x Kg, maka : qtotal = q1 + q2
= = ( ) = 620x kkal
Heat is supplied by the combustion of 1.12 m3 (STP) of gas C2H4
Mol C2H4 =
=
= 50 mol
( ) = -15.500 kkal
The eficiency of the heat movement is 60%, so : 0,6 ( )
X = 15 Kg 7. The Solution:
Combustion reaction of cyclopropane:
(CH2)3 + O2 3CO2 + 3H2O ∑ ∑ [ ( ) ( )] ( ) (CH2)3 = a – 3b – 3c kJ/mol 8. The Solution:
According to Hess's law:
2S(s) + 3O2(g) 2SO2(g) + O2 kJ 2SO2(g) + O2 2SO3(g) + 2SO2(g) + 3O2(g) 2SO3(g) So that: -593 + x = -790 X = -197
C.
The Rate of Reaction
1. The Solution: 4NH3 + 5O2 4NO + 6H2O V NH3 = 0,24 mol/L/s V O2 = V H2O = 2. The Solution : [B] naik 2x V = (B) V naik 2x 2 = (2)m m = 1 [A] naik 2x V = (B)n V naik 4x 4 = (2)n n = 2 1 1 2 4
The rate equation : V = k[A]2[B]
3. The solution :
The general rate equation : V = k[H2]m[I2]n
From experiment (1) and (2) :
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) (0,5)n = 0,5 n = 1
From experiment (2) and (3) :
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) (0,5)m = 0,5 m = 1
From experiment (1) and (4) :
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) = X = 1,44 4. The Solution:
Any increase in temperature of 10 the reaction rate = 2 times (time to 1 / 2 the original): t 2 = t1 ( ) t (t + 30) = 12 minutes t = 1,5 minutes 5. The solution : Excess = = 12,5 % So , which is 87,5 % degradable. 6. The Solution:
If any increase in temperature of 10 resulted in the reaction rate becomes 2 x original then:
V2 = V1 ( )
V100 = a ( ) = 128a
7. The Solution:
If at any increase in the rate of 20 increased 3 times faster, then the reaction time becomes 1 / 3 times the initial time.
t 2 = t1 t70 = 3 minutes ( ) = minutes 8. ΔH = +54. 0 kJ
Energy diagram for the reaction: 2NO2 N2O4 can be seen in the picture
above.
From the diagram shows that: Ea = Ea '+ ΔH
With
Ea = energy aktivsi N2O4 → 2NO2
Ea '= activation energy for 2NO2 → N2O4
Thus obtained .. Ea = 57.2 '+ 54, 0 Ea '= +3.2 kJ
D.
Chemical Equilibrium
1. The Solution: 2O3 2SO2 + O2 First : 1 - - Reaction: 0,50 0,50 0,25 + Eql : 0,50 0,50 0,25 In equilibrium : [SO3] = 0,50 mol/5L L = 0,10 M [SO2] = 0,50 mol/5L L= 0,10 M [O2] = 0,25 mol/5L L= 0,05 M[ [ ] [ ] ] [ ][ ][ ] = 0,5
2. The Solution:
Equilibrium constant is only affected by temperature. Therefore, the temperature remains the equilibrium constant is also fixed, which is 4. 3. The Solution:
If the first mol N2O4 = a; so N2O4 that react = 0,5 a
N2O4 2NO2 Awal : a - Reaksi : 0,5a a + Setimbang : 0,5a a PN2O4 = PNO2 = = 4 atm Kp = 4. The Solution: 2NO2(g) + N2H4(g) 3N2(g) + 2H2O(g) First : 0,10 0,10 - - Reaction: x 0,5x 1,5x x + Eql : 0,10-x 0,10-0,5x 1,5x x [N2] = 5. The Solution: PCL5 (g) PCL3 (g) + Cl2 (g) Awal : 0,1 - - Reaksi : x x x + Stb : 0,1 – x x x Kc = [ ] [ ] 0,05 = X2 + 0,05x – 0,005 = 0 (x + 0,1) (x – 0,05) = 0 X = 0,05 mol.L-1
PCl5 that decompose = 6. The Solution: 2X + 2Y 4Z ; Kc = 0,04 X + Y 2Z ; Kc = ( ) = 0,2 2Z X + Y ; Kc = = 5 7. The Solution: COCl2 CO + Cl2 Firstl : 0,5 - - Reaction : 0,4 0,4 0,4 + Eql : 0,1 0,4 0,4 Kc = ( )( )( ) = 1,6 COCl2 CO + Cl2 0,225 - - X x x + 0,255-x x x Kc = ( )( )( ) X2 + 1,6x – 0,36 = 0 (x + 1,8)(x – 0,2) = 0
X1 = -1,8 (it’s not qualified) X2 = 0,2 8. The Solution: N2O4 2NO2 First : a - Reaction : 0,5 a a + Eql : 0,5a a (N2O4) : (NO2) = 0,5a : a = 1 : 2