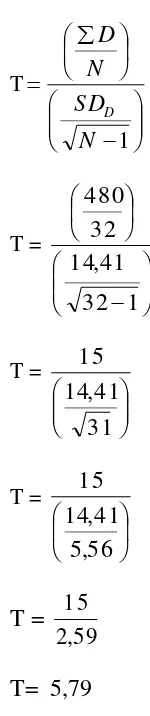i
THE USE OF RECIPROCAL TEACHING TECHNIQUE TO
IMPROVE STUDENTS’
READING SKILL
(A Classroom Research of the Tenth Years Students of SMK N 1 Ngablak in the Academic Year of 2014/2015)
A GRADUATING PAPER
Submitted to the Board Examiners as a Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Sarjana Pendidikan Islam (S.Pd.I)
English Education Departement of Teacher Training and Education Faculty State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga
BY:
INDI NIKMATUL INAYAH 113 10 083
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTEMENT
TEACHER TRAINING AND EDUCATION FACULTY
ii
DECLARATION
In the name of Allah,
Hereby, the writer declares that this graduating paper is written by the writer
herself. This graduating paper is original work and it contains no material previously published or written by other people and other people’s idea except the information from
reference.
This declaration is made by the writer, and she hopes that this declaration can be
understood.
Salatiga, March 14th 2015 The writer
Indi Nikmatul Inayah
iii
MINISTRY OF RELIGIOUS AFFAIRS
STATE INSTITUTE FOR ISLAMIC STUDIES(IAIN) SALATIGA
Jl. Tentara Pelajar02 Tlp (0298) 323433Fax 323433 Salatiga 50731 Website :www.iainsalatiga.ac.id E-mail : administrasi@iainsalatiga.ac.id
Salatiga, March 14th 2015
Setia Rini, M. Pd
The Lecturer of English Education Department State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga
ATTENTIVE COUNSELOR’S NOTE
Case: Indi Nikmatul Inayah’s Graduating Paper
Dear:
Dean of Teacher Training and
Education Faculty
Assalamu’alaikum Wr. Wb.
After reading and correcting Indi Nikmatul Inayah’s graduating paper entitled“THE USE OF RECIPROCAL TEACHING TECHNIQUE TO IMPROVE STUDENTS’ READING SKILL”. I have decided and would like to propose that this paper can be accepted by the Teacher Training and Education
Faculty, I hope this paper would be examined as soon as possible.
Wassalamu’alaikum Wr. Wb.
Counselor
Setia Rini, M. Pd
iv
THE USE OF RECIPROCAL TEACHING TECHNIQUE TO IMPROVE STUDENTS’ READING SKILL (A Classroom Action Research of Tenth Years Students of SMK N 1 Ngablak in the
Academic Year of 2014/2015)
WRITTEN BY:
INDI NIKMATUL INAYAH NIM: 113 10083
Has been brought to the Board of Examiners of English and Education Department of Teacher Training and Education Faculty at State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga on April 11th 2015 and hereby considered to completely the requirements of the degree of Sarjana Pendidikan Islam (S.Pd.I) in English and Education.
Board of Examiners,
Head : Dr. Sa’adi, M. Ag. Secretary : Setia Rini, M. Pd.
1st Examiner : Sari Famularsih,S.Pd.I, M. A.
2nd Examiner : Rr. Dewi Wahyu Mustikasari, M. Pd.
Salatiga, April 11th 2015
Dean of Teacher Training and Education Faculty
Suwardi, S. Pd., M. Pd.
v
Motto
“Life cannot become boring when we establish contact with the one
who gives happiness.”
vi
DEDICATION
This graduating paper is dedicated to:
1. My beloved parents, my mother (Eko Wahyuningsih) and my father
(Subandi) who always pray, guide, motivate me to become better
person.
2. My beloved brothers and sisters (Alwi, Najib, And Mita) and my big
family who fill my life with love and affection.
vii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Bismillahirrahmanirrahim,
In the name of Allah, the most gracious and merciful, the king of universe and space.
Thank you to Allah because the writer can complete this graduating paper as one of
requirement to finish the study in English Department of States for Institute Islamic Studies
Salatiga.
This graduating paper would not have been completed without support,
guidance and help from individual and institution. Therefore, I would like to express
special thanks to:
1.
Dr. Rahmat Hariyadi, M. Pd. as the Rector of State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga.2.
Suwardi, S. Pd., M. Pd. as the Dean of Teacher Training and Education faculty of State Institute Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga.3.
Noor Malihah, Ph. D. as the Head of English Language Teaching Department of State Institute Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga4. Setia Rini, M. Pd. as consultant who has brings up, espoused, and given the
writer advices, suggestions and recomendations for this graduating paper
from beginning until the end. Thank you for your patience and care.
5. All lecturers in the English Language Teaching Departmentwho have given
much knowledge, the writer deeply thanks to you all.
6. My beloved family, thanks for your spirit and patient.
7. All of staffs who have helped the writer in processing of graduating paper
viii
8. All friends of C class and all friends in English Department. Thank for your
friendship and kindness.
9. Special thanks someone who help and accompany directly in working with
this thesis; Dwi who always help me and standing beside me.
10.Tenth year students of SMK N 1 Ngablak in the academic year of
2014/2015 especially X - ATU and Mr. Istingal, M. Pd.
11.Those cannot be mentioned one by one.
Eventually, this graduating paper is expected to be able to provide useful
knowledge and information to the readers. The writer is pleased to accept more
suggestion and contribution for the improvement of this graduating paper.
Salatiga, March 14th 2015
The writer
Indi Nikmatul Inayah
ix
ABSTRACT
Inayah, Indi Nikmatul. 2015. “The Use of Reciprocal Teaching Technique to Improve
Students’ Reading Skill in Tenth Years Students of SMK N 1 Ngablak in the Academic Year of 2014/2015)”. A Graduating Paper. Educational Faculty. English Department. State Institute of Islamic Studies (STAIN). Consultant: Setia Rini, M.Pd
Keywords: reading skill; Reciprocal Teaching;
This research is mainly aimed to develop the students’ reading skill through Reciprocal Teaching Technique. This research will answer these main questions (1) How is the implementation of students’ reading skill using Reciprocal Teaching Technique? (2) How is the result of the study after using Reciprocal Teaching
Technique in the students’ reading skill at the tenth year students of SMK N 1
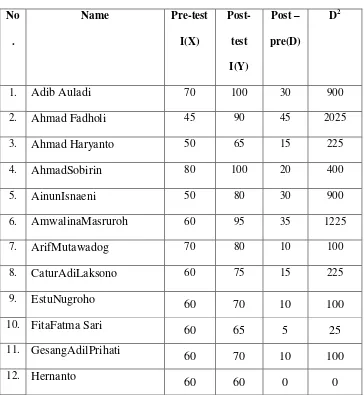
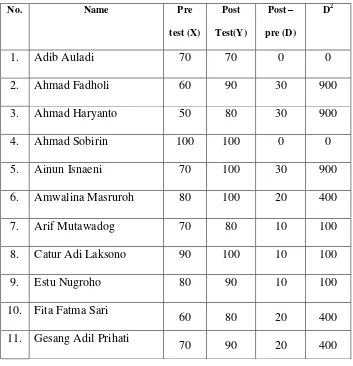
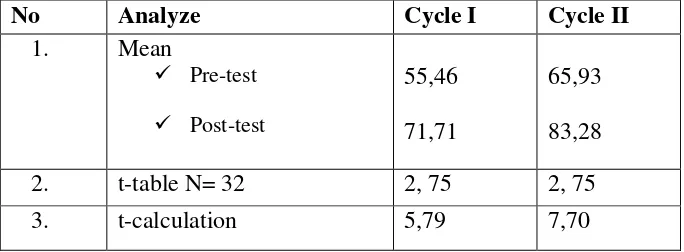
Ngablak in the Academic Year of 2014/2015? Thirty three students of tenth years students of SMK N 1 Ngablak 2015 were instructed through Reciprocal Teaching Technique to improve their reading skill. The methodology of this research used Classroom Action Research (CAR). It is conducted in two cycles. Each cycle consists of planning, action, observation, and reflection. From the result, the researcher found several finding on it. The calculation result shows that T-calculation if cycle 1 is 5.79 and cycle 2 is 7.70. it could be seen from the result of mean score of each cycle that post-test is 71,71 higher than pre-test 55,46 in the cycle I, and post-test is 83,28 higher than pre test 65,93 in the cycle II. Furthermore, the result of t-test calculation in cycle I is 5,79 and cycle II is 7,70 t table with N = 32 is 2,75. It means that the use of Reciprocal Teaching is able to
x
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE i
DECLARATION ii
ATTENTIVE COUNSELOR NOTES iii
PAGE OF CERTIFICATION... iv
MOTTO v
H. Research Organization 8
CHAPTER II: THEORITICAL FRAMEWORK
A.Reading 9
1. Definition of Reading 9
2. Kind of Reading 12
3. Factors that Influence Reading ……… 13
4. Principles of Learning Reading 14
B.Reading Skill 12
1. Definition of Reading skill 16
C.Reciprocal Teaching
1. Definition of Reciprocal Teaching ……… 18
xi
3. Advantage reciprocal teaching ………... 21
4. How to use reciprocal teaching ……….. 22
5. The Significance of Reciprocal Teaching ……….. 24
D.Type of Paragraph 24
1. Narrative Paragraph 24
2. Purpose of narrative text 25
3. Type of Narrative 25
4. Generic structure of Narrative 27
5. Language Feature of Narrative ……….. 28
6. The Example of Narrative Text 29
CHAPTER III: METHODOLOGY OF RESEARCH
A. Setting of the Research 32
B. Subject of the Research 33
C. Method of the Research 34
D. Research Procedure 35
E. Research Procedure 35
F. Technique of Collecting Data ………. 37
G. Technique of Analyzing Data ………. 40
CHAPTER IV: DATA ANALYSIS
A. Research Findings …………..………. 43
B. Analysis and Discussion 63
CHAPTER V: CLOSURE
A. Conclusion ... 67 B. Suggestion ... 68
REFERENCES
xii LIST OF TABLES
Table 3. 1 The List of X- ATU 2 Class Group of SMK N 1 Ngablak 38 Table 3. 2 Students’ Observation Sheet 40
1 CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION
A. BACKGROUND OF THE STUDY
In order to communicate with others, people use language. They must
use language because language is the main factor to share their ideasto
theothers in this life. English is regarded as an international language. It is
very important because it is used broadly in the world that function as a
communication means by which people from different nations or country
interact. In Indonesia, it has been tought in schools from elementary school up
to university.
In many second or foreign language teaching situations, reading
seemed a special focus. There are a numberof reasonfor this and one of them
is manyforeign languagestudents often have as oneof their most important
goal. They wantto be able to read for information and pleasure, for the career,
andfor study in purposes. In fact most EFL situasions, the ability to read in a
foreign language is all that students ever want to acquire (Richards, 2003:
213).
To improve students’ skill in English, there are four main skills which
must be attained by students. They are reading, writing, speaking and listening
skill. Reading is one of skills which has many contribution in enhancing and
enriching students’ knowledge. Through reading, they can get new
information in any aspect. Besides that, they will have to read lengthy
2
don’t know what the meaning is, so they will fail in completing the
assignments.
Reading is seen as a stucture hierarchy of sequenced and separate skills
which is built up to create meaning. Since it is active cognitive process,
reading is closely related to other activites suc as thinking, interesting, making
preception, making generalization, and of course comprehending the
content(Konza, 2007: 84). Reading is complex process which involves not
only the text but their experience to comprehend it.
Learning reading is more than just recognizing words in a written text.
Students should be able to comprehend or understand the meaning of the text.
(Duffy, 1997: 60) stated that comprehension appears to happen in two stages.
The first stage occurs during the actual reading activity. The student examines
the message and simultaneously recognize words and meaning through skill
with the graphemic, syntactic, and semantic systems. The second stage occurs
anytime during or following Stage 1. In this stage, the written message has
been translated or received and can be subjected to a more thoughtful analysis.
There are some factors that influence students’ reading comprehension,
one of them is teacher. The teacher uses a conventional method in teaching
reading and it can make teaching learning boring. During the teaching learning
process, the teacher transfers information in monotonous approach. The
teacher also spends more time in structure than in reading skill, so the students
do not have time to learn reading. The strategy is low for helping the student
in learning English. The strategy should be able to motivate and interest the
3
Palincar and Brown (1984: ) defined that Reciprocal Teaching is a
cooperative reading technique for low-achieving readers in native language
contexts. This technique asks students working in groups to several learning
strategies designed to improve reading ability.In this strategy, students are
expected to be active reader and they should understand what the content of
the text by asking questions, make prediction and then check their prediction.
From the statement above, we know that comprehension skill is needed
in reading activity. However, the condition of students in Indonesia especially
students in SMK N 1 Ngablak have poor comprehension skill. In teaching and
learning process, the tenth years students of SMK N 1 Ngablak face some
difficulties when their teacher deliver the materials. It can be seen from their
reactions in learning English. Some of them are bored, sleepy and do not pay
attention to their teacher explanation. Eventhough their teacher has given some
strategies and methods to make the students excited in learning English. But in
the reality, the students still face the difficulties in reading comprehension.
From the explanation above, it gives an inspiration to the writer to
conduct a researchentitled “The Use of Reciprocal Teaching Technique to
Improve Students’ Reading Skill(A Classroom Action Research of the Tenth
Years of SMK N 1 Ngablak in the Academic Year of 2014/2015)”
B. PROBLEM STATEMENTS
Based on the phenomenon above, this research is aimed at giving
4
1. How is the implementation of students’ readingskill using reciprocal
teaching technique for the tenth years students of SMK N 1 Ngablak in the
Academic Year of 2014/2015?
2. How is the result of the study after using reciprocal teaching technique in
the students’ reading skill of the tenth years students of SMK N 1 Ngablak
in the Academic Year of 2014/2015?
C. OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY
Based on the problem statement, the objectives of this classroom
action research are described as follows :
1. To identify the implementation of students’ reading skill usingreciprocal
teaching technique for the tenthyears students of SMK N 1 Ngablak in the
Academic Year of 2014/2015.
2. To find out the result of the study after usingreciprocal teaching technique
in the students’ reading skill of the tenth years students of SMK N 1
Ngablak in the Academic Year of 2014/2015.
D. BENEFITS OF THE STUDY 1. The English Teacher
It is expected that the result of the study could be useful by the
teachers to develop suitable tecniques in teaching reading based on the
the objective that has already determined. .
5
For the students it is useful to help them to improve their learning
performance by using the tecnique to assistthe students in understanding
the reading materials and developing their reading skill.
E. LIMITATION OF THE STUDY
Based on the problem statement , the writer realizes that it is impossibe
to carry out a classroom action research based on all the problem above. The
writer limits the problem to the teacher’s monotous techniquein teaching
reading skill, the writer used reciprocal teaching technique to teach reading of
the tenth grade ofSMK N 1 Ngablak in the academic year of 2014/2015.
F. DEFINITION OF THE KEY TERMS
To make easier in understanding this research, the researcher defines
the key terms as follows:
1. Reciprocal Teaching
Reciprocal Teaching(Palincar & Brown 1984: ) is guided reading
comprehension strategy that encourages students to develop the skills that
effective readers and learners do automatically (summarize, question,
clarify, predict and respond to what they are reading). Students use these
four comprehension strategies on a common text, in pairs or small groups.
Reciprocal Teaching can be used with fiction, non fiction.
2. Technique
Technique is a way of doing something, especially one that needs
6 3. Improve
Improve is become or make better, make a good use of something.
(Oxford Dictionary, 2003: 216)
4. Reading
Reading is a learning process in which the skills of word recognition
and comprehension are mutually supportive. In reading activity, students
are expected to recognize and understand about what they read especially in
a text. Without understanding the text students can’t grasp the implied
message in a text. (Duffy, 1977: 5)
5. Student
Student is person who studiying at the collage or university (Oxford
Dictionary, 2003: 429)
6. Skill
According Dunnette (1976: 33) skills is capacity needed to
implementing some tasks, which is the development of training result sand
experience gained.
G. REVIEW OF PREVIOUS RESEARCHES
In this graduating paper, the writer takes some reviews from other
thesis. The first research is done by Nur Ifka Elfiani (2013) entitle “The Use of numbered head together method to Improve Students’ speaking Skill” (A
Classroom Action Research at the Second Grade Year Students of SMK
7
analyzed implementation of numbered toghether method to improvement of
students’ speaking skill trough numbered toghether method is significant.
The second research report by Astri Rahmawati with her research
paper entitled ”The Use of group investigation strategy to improve students’
reading skill” (A Classroom Action Research of X.2 Class of MAN
Tengaran,Semarang in the Academic Year of 2013/2014).There was a
significant improvements. The student has lack motivation so it could
influence of students reading skill. After the using group investigation
strategy the students reading skill incrases.
Different from previous research, this research will observe the
students reading skill progress by using reciprocal teaching tecnique. This
observation aims the use reciprocal reading tecnique and it will be connected
with the syllabus.
H. RESEARCH ORGANIZATION
The researcher wants to arrange the graduating paper in order to the
reader can catch the content easily. It is divided into five chapters.
Chapter I is Introduction. It is consists of background of study,
problem statements, objectives of the study, benefit of the study, limitation of
the study, definition of key terms, and review of previous research.
Chapter II is Theoretical Framework which discuss about definition
ofreciprocal teaching technique, the steps of reciprocal teaching technique,
8
Chapter III explains about Methods of Research that consist of setting
of the research, subject of the research, method of the research, procedure of
the research, technique of collecting data and technique of data analysis.
Chapter IV is Data Analysis. Consist of cycle I, cycle II, analysis,
discussion, and result of each cycle.
Chapter V is Closure. The writer states summary of the study includes
9 CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED THEORIES
A. Reading
1. Definition of Reading
Reading is a learning process in which the skills of word
recognition and comprehension are mutually supportive. In reading
activity, students are expected to recognize and understand about what
they read especially in a text. Without understanding the text students can’t
grasp the implied message in a text. (Duffy, 1977: 5)
According to Nunan (2003: 68), “reading is a fluent process of
readers combines information from text and their own background
knowledge to build meaning”.
Harris and Sipay (1980: 179), states that reading comprehension
ability is taught to be a set of generalized knowledge acquisition skills that
permits people to acquire and exhibit information gained as a consequence
of reading printed language. Reading is an active process (not a product,
like history) in which readers shift between sources of information (what
they know and what the text says), elaborate meaning strategies, check
their interpretation revising when appropriate, and use the social context to
focus their response (Walker, 1996: 4)
Manzo (1996: 5) defined reading as the act of simultaneously
reading the lines, reading between the lines, and reading beyond the lines.
10
order to construct the author’s basic message. The next part, reading
between the lines, making to the act of making inferences and
understanding the author’s implied message. Thus, reading beyond the
lines involves the judging of the significance of the author’s message and
applying it to the other areas of the background and knowledge.
Currently, Wallace (2001), Richards (2002) argued that reading is a
reader centered activity. A reader, while reading is constantly employed
some strategies, helps himself to obtain whim he or she wants for reading.
In other words, reading presently concerned more with the process, by
which a reader attempts to understand the test he or she reads.
Reading is used to get the main point or the most important
information. It is an effort to understand the content of the text, and also to
know the massage from the writer. In addition reading is used to get an
idea, pleasure or feeling that is expressed by the writer.
From the information above, the writer thinksthat reading is an
active and interactive activity to produce the word and tries to understand
the content of reading text. By reading, the students can enlarge on enrich
their knowledge and experience because the information they need is serve
in written form.
There are many experts who present various definition of reading.
According to Dechant (1982: 3) definitions of reading are divided into two
major types:
11
With the first type of reading definition, in which reading is
equated with the interpretation of experience generally, we might
speak of reading pictures, reading faces, or reading the weather.
Spencer (1946) as quoted by Dechant (1982: 4) reading is
performed whenever one experiences sensory stimulation. On the other
hand, the meaning of reading based on this type is the reading-
readiness program in which experience with concrete object is
emphasized, visual and auditory discrimination are stressed and
students are required to interpret pictures and conversation.
Reading as interpretation of experience has implications for both
the reading teacher and also the students who learning to read. Teacher
of reading must become expert in reading students. They must
understand their students and must be able to identify the personal
differences in students which may lead to achievement differences
between students. Another implication is that students must be readers
of experience before they can become further readers.
b. Reading as Interpretation of Graphic Symbols
In Dechant (1982: 4-5) there are presented the definition of
reading by many experts. Some of them are DeBoer and Dallmann
(1960: 19) consider that reading involves the comprehension and
interpretation of ideas symbolized by the written or printed page.
While Bond and Thinker (1967: 22) point out that reading involves the
recognition of printed or written symbols which serve as stimuli for the
12
Based on the definition above, the writer concludes that reading
requires identification and comprehension. Reading involves an
interaction between the writer and reader. Without a reader,
communication via printed page is impossible; writing has no purpose
without a reader.
2. Kind of Reading
According to Kustaryo (1988: 11), there are some kind of reading.
They are:
a. Reading for meaning
Reading for meaning is reading to understand the messages which are
written in the text. We didn’t read aloud during we are reading.
b. Reading aloud
The purpose of this reading is not just to understand the text, but also to
to give information to the listeners.
c. Reading for comprehension
Reading for comprehension means reading with understanding about
what have read.
3. Factors that Influence Reading
Cameron (2001) stated that some factors in foreign language learning
context can influence the learning tasks. They are:
a. The nature of the written forms of the first language.
Each language is structured differently, so when we meet a new
13
b. The learners’ previous experience in the first language literacy.
When a young learner learns the second language, literacy, knowledge,
and skill he/she only partly develops for the first language
c. The learners’ knowledge of the language.
Oral skill to learn a new language is an important factor in order to be
literate. Children gain much literary experience before they come to
school. The teacher of foreign language can be expanded children’s
experience of literacy in the new by creating environmental print for the
classroom.
d. Age of starting learn to read clearly overlaps with the first language
reading experience.
There are many factors that may make learning to read a very different
experience for different ages. Transferability of knowledge, skills, and
strategies across language depends closely on how the two written
language work: it will be different for each pair of language and for
each direction of learning.
4. Principles of Learning Reading
There are some principles behind the teaching of reading (Harmer,
2001: 70), here are:
a. Reading is not passive skill
Reading is an incredibly active occupation. To do it
unsuccessfully, we have to understand what the word mean, see the
pictures the words are painting, understand the arguments, and work out
14
do these things – then we only just scratch the surface of the text and we
quickly forget it.
b. Students need to be engaged with what they are reading
As with everything else in lessons, students who are not
engaged with the reading text, not actively interested in what they are
doing, are less likely to benefit from it.
c. Students should be encouraged to respond to the content of reading text,
not just to the language
It is important to study reading texts for the way they use
language, the number of paragraphs they contain and how many times
they use relative clauses. But the meaning, the message of the text, is
just as important and we must give students a chance to respond to that
message in some way. It is especially important that they should be
allowed to express their feeling about the topic
d. Prediction is a major factor in reading
When we read texts in our own language, we frequently have a
good idea of the content before we actually read. Books cover give s a
hint what’s in the book, photographs and headlines hint at what articles
are about and report look like report before single word.
e. Match the task to the topic
One decision has been taken about what reading text to the
students are going to read, we need to choose good reading task, the
right kind of questions, engaging and useful puzzle etc.
15
Any reading text is full of sentence, words, ideas, description
etc. it does not make sense just to get students to read it thendrop it to
move on to something else. Good teachers integrate the reading text
into interesting class sequences, using the topic for discussion and
further tasks, using the language for study and later activation.
B. Reading Skill
Reading skill is the ability to relate the textual material to one’s own
knowledge by comprehending the text (Fauziati, 2008: 133). The purpose of
reading activity is language ideas. In reading, the process of reading activity is
language ideas. In the reading the process of thinking is very urgent and vital,
because the students read the text and do not morely move their eyes along the
sentence they read. Instead the sometime, their minds work to get the message.
Goodman (1982: 135) in Fauziati (2010: 33) states that based on
psycholinguistic perceptive reading is considered as “psycholinguistic
guessing game” the reader constructs a message which is encoded by a writer.
This act of meaning construction is a ongoing, cyclical process of sampling
from the input text, predicting, testing, and confirming or revising these
prediction and further sampling.
According to Grant (1991: 79) the aims of using a reading text at
intermediate level and advance level are:
1. To teach basic reading comprehension skill
2. To teach real life reading skill such as reading for gist and reading
16
3. To develop flexible reading skill, varied according to purpose
4. To develop critical reading skill
5. To develop the students knowledge of vocabulary or idiom
6. To reinforce certain grammatical features
7. To act as stimulus for oral or write work later on.
According to Johan (2000: 1) reading skills are grouped into:
a. Deducing the meanings of Words from Context.
Deducing the meanings of words from context is way to see the
words of phrases that precede or follow those words, so it can be
functions as a way to know of speech, and finally the right meaning in the
discourse can be known without having to look at the dictionary.
b. Understanding the forms and Meaning of Non-idiomatic Phrases
It is different from idiomatic phrases that the form and meaning
has been fixed, so it tends as the material which memorized so, the
phrases non-idiomatic are formed based on certain rules and are
unlimited.
c. Recognizing and Understanding Rhetorical Structures
Rhetorical structures is functional relationship between the
meaning that described by elements of language in a reading text. This
structure is basic of a text frame and closely related to the type of topic
that written, the purpose of the authors, and readers are addressed by the
authors.
The skills to know and understand this rhetorical structure includes
17
punctuation, and specific structure that are used by the writer to describe
or convey an idea or message purposed.
These rhetorical structures are described, explicitly with the
existence of specific discourse markers and there are those only known
through the readers’ familiarity with the form of reading text organizing
in English.
This rhetorical structure found at the level of sentences,
paragraphs, or intersentence, and at overall reading level.
C. Reciprocal Teaching
1. The Definition of Reciprocal Teaching
Palincar and Brown (1984) defined that Reciprocal Teaching is
a cooperative reading technique for low-achieving readers in native
language contexts. This technique asks students working in groups to
several learning strategies designed to improve reading ability.
Reciprocal teaching refers to an instructional activity that take
place in the form of dialog between teachers and students regarding
segment of text. The dialogue is structured by the use of four
strategies: predicting, clarifying, questioning, summarizing. The
teacher and students take turns assuming the role of teacher in leading
this dialogue.
Hartman (1994) stated that Reciprocal Teaching is a technique
used in teaching reading through five stages, they are:
18
Instructor models and explains coordinate use of four reading
strategies: predicting, clarifying, questioning, and summarizing.
Stage 2: Student learning and Practice
Instructor directly instructs students on the four strategies and
their coordinated use. Students get guided practice and feedback from
the instructor.
Stage 3: Teacher-Students Groups
Instructor leads dialogues about text in small groups, repeatedly
modeling the strategies. Students take turn leading dialogues, getting
feedback from the instructor.
Stage 4: Students Group
Students take turn leading dialogues using the four strategies in
small group with the other students. Students give each other feedback
on strategies use. The instructor moves from group to group observing
progress and providing assistance as needed. Instruction phases out.
Stage 5: Students Self Regulation
Students competently use the four reading ability strategies and
provide their own feedback.
2. The Purpose of Reciprocal Teaching Technique
The purpose of reciprocal technique is to facilitate a group of
effort between teacher and students as well as among the students in
the task of bringing meaning to the text. Each strategy was selected for
19
a. Summarizing provide the opportunity to identify and integrate the most important information in the text. Text can be summarized
across sentence, across paragraphs, and across the passage a whole.
b. Question generating reinforces the summarizing strategy and carries the learner one more step along in the comprehension
activity. When students generate questions, they first identify the
kind information that is significant enough to provide the substance
for a question. They than pose this information in question form
and self-test to ascertain that they can indeed answer their own
questions. Question Generating is a flexible strategy to the extent
that students can be taught and encouraged to generate questions at
many levels.
c. Clarifying is an activity that is particularly important when working with students who have a history of comprehension
difficulty. These students may believe that not be particularly
uncomfortable that the word, and in fact the passage, are not
making sense.
d. Predicting occurs when students hypothesize what the author will discuss next in the text. In order to the successfully, the students
must activate the relevant background knowledge that they already
process regarding the topic. The students have a purpose for
reading that is too confirm or disprove their hypotheses.
Furthermore, the opportunity has been created for the students to
link the new knowledge they will encounter in the text with the
20
facilitates use of texts structure as students learn that headings,
subheading and questions imbedded in the text are useful means of
anticipating what may occur next.
In summary, each of these strategies was selected as a means of aiding students to construct meaning from the text as well as a
means of monitoring their reading to ensure that they fact
understand what they read.
3. Advantages of Reciprocal Teaching Technique?
Here are some following advantages of Reciprocal Teaching Technique
according to Palinscar and Brown (1984):
a. It encourages students to think about their own thought process during reading.
b. It helps students learn to be actively involved and monitor their
comprehension as they read.
c. It teaches students to ask questions during reading and helps make the text more comprehensible.
4. How to use reciprocal teaching
Before Reciprocal Teaching can be used successfully by your
students, they need to have been taught and had time to practice the
four strategies that are used in reciprocal teaching (summarizing,
questioning, predicting, clarifying).
One way to get students prepared to use reciprocal teaching:
21
a. Put students in groups of four.
b. Distribute one note card to each member of the group
identifying each person's unique role:
1) Summarizer
2) Questioner
3) Clarifier
4) Predictor
c. Have students read a few paragraphs of the assigned text
selection. Encourage them to use note-taking strategies such as
selective underlining or sticky-notes to help them better prepare
for their role in the discussion.
d. At the given stopping point, the Summarizer will highlight the
key ideas up to this point in the reading.
e. The Questioner will then pose questions about the selection:
1) Unclear parts
2) Puzzling information
3) Connections to other concepts already learned
f. The Clarifier will address confusing parts and attempt to
22
g. The Predictor can offer predictions about what the author will
tell the group next or, if it's a literary selection, the predictor
might suggest what the next events in the story will be.
h. The roles in the group then switch one person to the right, and
the next selection is read. Students repeat the process using
their new roles. This continues until the entire selection is read.
(Source: ReadingQuest)
i. Throughout the process, the teacher's role is to guide and
nurture the students' ability to use the four strategies
successfully within the small group. The teacher's role is
lessened as students develop skill.
5. The Significance of Reciprocal Teaching
The students can get more ability in reading. It will improve the
students’ knowledge; improve their reading skills, and more abilities in
gaining information of texts. Students can also get their motivation in
learning English and increase their initative English.
D. Narrative Text
1. Definition of Narrative Texts
Narrative texts are a text type we use when we want to entertain or
to instruct (Pearson). According to Kistonto (2007) a narrative text is a
type of spoken or written text that tells a story of one character or more
who face certain problematic situations. Based on Rigby Heinemann
23
may be based on fact. Narratives are written in many different forms, like
fable, legend, folktales, science fictions, romance, horror, etc. and each
form has distinctive characteristics. According to Rigby Heinmann (2002:
21), there are some features of narratives. They are divided into:
2. Purpose or social function of the Narrative Text
Sudarwati and Grace (2007: 154) stated that the purpose of
narrative text is to amuse, entertain and engage the reader in an
imaginative experience. Some narratives also have other purpose, e.g. they
may seek to explain a phenomenon (myths and legend) or to teach a lesson
(fables). A narrative story deals with complications or problematic events
which lead to a crisis and in turn finds a resolution.
3. Types of Narrative Text are:
According to Kistonto (2007) there are type of narrative text:
a. Fableis a succinct fictional story, in prose or verse, that features
animals, mythical creatures, plants, inanimate objects, or forces of
nature which are anthropomorphized (given human qualities), and
that illustrates a moral lesson (a "moral"), which may at the end be
expressed explicitly in a pithy maxim.
b. Legend (Latin, legenda, "things to be read") is a narrative of
human actions that are perceived both by teller and listeners to
take place within human history and to possess certain qualities
24
participants includes no happenings that are outside the realm of
"possibility", defined by a highly flexible set of parameters, which
may include miracles that are perceived as actually having
happened, within the specific tradition of indoctrination where the
legend arises, and within which it may be transformed over time,
in order to keep it fresh and vital, and realistic.
c. Ballad is a form of verse, often a narrative set to music. Ballads
were particularly characteristic of British and Irish popular poetry
and song from the later medieval period until the 19th century and
used extensively across Europe and later the Americas, Australia
and North Africa. Many ballads were written and sold as single
sheet broadsides. The form was often used by poets and
composers from the 18th century onwards to produce lyrical
ballads. In the later 19th century it took on the meaning of a slow
form of popular love song and the term is now often used as
synonymous with any love song, particularly the pop or rock
power ballad.
d. Folktales are a general term for different varieties of traditional
narrative. The telling of stories appears to be a cultural universal,
e. Fairy Tale is a type of short narrative that typically features such
folkloric characters, such as fairies, goblins, elves, trolls, dwarves,
giants or gnomes, and usually magic or enchantments. However,
only a small number of the stories refer to fairies. The stories may
nonetheless be distinguished from other folk narratives such as
25
events described) and explicitly moral tales, including beast
fables.
f. Science fiction is largely based on writing rationally about
alternative possibilities. It is similar to, but differs from, fantasy in
that, within the context of the story, its imaginary elements are
largely possible within scientifically established or scientifically
postulated laws of nature (though some elements in a story might
still be pure imaginative speculation).
g. Modern fantasy is literature written by a known author that is set
either in make-believe or imaginary world with which places,
people and creatures could not exist in and/or have events that
could not possibly happen such as tiny people, talking animals, or
traveling through time.
4. Generic Structure of the Narrative Text
According to Sudarwati and Grace (2007: 154) there are general
structure of narrative text:
a. Orientation
Sets the scene: where and when the story happened, introduces
the participants of the story: who and what is involved in the story.
b. Complication
Tells the beginning of the problem which leads to the crisis
26 c. Resolution
The problem (the crisis) is resolved, either in a happy ending or
in sad (tragic) ending.
d. Reorientation
This is a closing remark to the story and it is optional. It
consists of a moral lesson, advice or teaching from the writer.
Note: Sometimes the writer also put his judgment or a certain event. This is called Evaluation. e.g. Once there lived a girl named Snow
White.
She was a kind-hearted girl
evaluation
5. Language features of the Narrative Text
a. A Narrative focuses on specific participants: often individual or
participants with defines identities. Major participants are human, or
sometimes animals with human characteristic.
b. Mainly use action, verbal or mental processes (verbs of perception:
think, realize, feel, etc.)
c. It usually use past tenses (Simple Past Tense and Past Continuous
Tense).
d. Direct and indirect speeches are often used (some dialogs are used in
27
e. Descriptive language is used to create listeners’ or readers’
imagination.
f. Can be written in first person (I, We) or third person (he, she, and they)
( In choose – your-own-advantages, the reader is involved in the story
a major character and addressed as” you”.
g. Temporal conjunctions are also used.
1) As the sentence introducers: Then,... ; After that, ... ;
Finally, ... etc.
2) As time introducers (adverbial clauses: ... before ... ; After
... ; While ... During ... etc.
6. Example of Narrative Texts
One day there was a monkey. He wanted to cross a river. There he saw a
crocodile so he asked the crocodile to take him across the other side of the river. The
crocodile agree and told the monkey to jump on its back. Then the crocodiles swam
down the river with the monkey on his top.
Unluckily, the crocodile was very hungry, he stopped in the middle of the
river and said to the monkey, “My father is very sick. He has to eat the heart of the
monkey.Sohewill be healthy again.”
At the time, the monkey was in dangerous situation and he had to think hard.
Then he had a good idea. He told the crocodile to swim back to the river bank.
“What’s for?” asked the crocodile. “Because I don’t bring my heart,” said the
monkey. “I left it under a tree, near some coconuts in the river bank.”
The crocodile agreed and turned around. He swam back to the bank of the river. As
28 Then he climbed up to the top of a tree.
“Where is your heart?” asked the crocodile. “You are foolish,” said the
monkey to the crocodile. “Now I am free and I have my heart.”
There are general structure of narrative text: According to Sudarwati and Grace
(2007: 154)
1. Orientation:
The participants or characters of the story are a smart monkey and dull
crocodile. The time set is just one day. The story takes place in a river.
2. Complication:
Every narrative text must consist of conflict or problem. A simple definition of
problem is when something goes and it is not what we want. In the story the
complication start when the crocodile want to eats the monkey. Of course the monkey
don not want to be the crocodile's meal and that is the problem which sets the whole
story.
3. Resolution:
A problem must be resolved. It can succeed or fail. In this story, the monkey
succeeds to solve the problem. He get free from the hungry crocodile.
To have clear understanding, take a look at the following example of narrative text
about the way of a smart monkey getting free from from a hungry dull crocodile.
Moral value:
30 CHAPTER III
METHODOLOGY OF RESEARCH
A. Setting of the Research
The research was conducted at SMK N 1 Ngablak. SMK N 1 Ngablak
is located in Magelang - Kopengstreet, Bandungrejo, Ngablak, Magelang
Km.26 phone /Fax (0293)5528121 Magelang 56194. It is a new school unit in
Magelang that has three skills subject. They are: Agriculture Technology,
Animal Husbandry, and Marketing.
SMK N 1 Ngablak is one of the SMK inMagelang, established in
2002-2003 with Magelang Regent Decree No. 24, 2003.In the face of
increasingly fierce competition with public schools, the management SMK N
1 Ngablak created educational programs with the aim to improve services to
the stakeholders.
SMK N 1 Ngablak committed to education and training as the
fulfillment of the needs of the labor market by establishing a noble, superior,
cultured, as well as independent and forward-looking human resource.
The place selection was based on the consideration where the teacher’s
SMK N 1 Ngablak and the Institution never conducted research about
31 B. Subject of The Research
In this research, the writer choosed SMKN 1 Ngablak as object of the
study especially the tenth years students. The tenth years students consist of
nine class groups, but the writer took one class group, X- ATU 2. The number
of the participants are32 students. They are 12 girls and 20 boys. Their native
language is Bahasa Indonesia. The average age of the participants are16 years
old. They have been taught English since the first year of school. They get
English lesson which is each meeting along with two hours lesson; one hour
lesson is 45minutes.
The problems that students faced were how to start to read, lack of
vocabulary, and poor comprehension skill. In teaching and learning process, the
tenth years students of SMK N 1 Ngablak face some difficulties when their
teacher deliver the materials. It seems at their reactions in learning English.
Some of them are bored, sleepy and do not pay attention to their teacher
explanation.
TABLE 3. 1
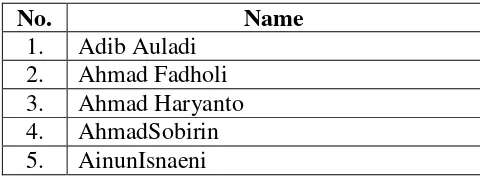
List of X- ATU Class Group of SMK N 1 Ngablak in the Academic Year Of 2014/ 2015
No. Name
1. Adib Auladi
2. Ahmad Fadholi
3. Ahmad Haryanto
32
16. Lukman Ahmad Riyanto
17. MeitaWulanKusumaWardhani
Source: SMK N 1 Ngablak 2014
C. Method of Research
The writer used classrom action research (CAR) in this research. The
researcher and the observer take a note everything occur in teaching and
learning process. Manurung in Sam’s (2010: 57) stated that classroom action
research is the new actions in decision and implementation process toward
students in a class or another who involved in school as an alternative problem
33
an observation toward activity that is purposely raised and occured in a class
to solve the problem in that class. In this case, the researcher analyzed the
problem of the student’s reading skill occurred in the learning process and
found it which was then solved by Reciprocal Teaching Strategy.
Arikunto (2010: 132) stated that clssroom action research is done to
improve the effectiveness of teaching methods, giving assignments for
students, assessment, and so forth.
This research is focused on the teaching reading in the EFL process.
The strategyof the research is regarded as the appropriate method for the
students. The aim of this research is to enhance the students’ reading skill.
D. Procedures of Research
In the classroom action research there are some models that can be
applied. The model that usually applied is the model by Kemmis&Mc Taggart.
There are four steps in this model i.e planning, action, observation and
reflection. Those four steps in the action research is called a cycle. In a
classroom action research, researcher did two cycles. (Arikunto, 2010: 140)
1. Planning
Sam’s (2010: 74) stated that in the planning, there are three
activities:
a. Decide target competence
b. Design learning in cycle 1 and cycle 2
c. Design test instrument consist of multiple choice question which
is taken representatively from the target competence that will be
34
d. Make learning schedule consist of cycle 1 and cycle 2.
While according to Arikunto (2010: 138) when we compose the
planning, we should explain about what, why, when, where, who, and
how the action is done.
In this research, firstly researcher made lesson plan, decided the
schedule, prepared material that appropriate with the strategy and made
test instrument consist of pre- test and post test
2. Action
Action is the implementation of the planning’s contain. In this
stage, researcher must remember and obey the planning that h/ she
made before. (Arikunto, 2010: 139)
In this research, researcher applied the action based on her
planning. Researcher obeyed the lesson plan and applied the strategy in
teaching and learning process.
3. Observation
Sam’s (2010: 74) stated that the observation is done during the
action and the teacher follows the teaching strategy that is designed by
researcher.
In this research, researcher used observation guidance which
consists of indicator that is designed according to the focus of research.
Besides that, researcher also used some tools such camera or video
recorder to help researcher in analyse the data. This observation
35
what can be seen, heard, and observed during teaching and learning
process.
4. Reflection
Reflection is done by analyze how far the result of students’
behavior before and after the action. (Sam’s, 2010:74)
In this research, the reflection is done by discussing with the
collaboratorto know the result of teaching and learning process by
apply the strategy. By reflection, researcher can get input about to
improve the next action in the next cycle.
E. Technique of Collecting Data
The researcher presents the act of collecting data as follows:
1. Test
Arikunto (2010: 226) stated that test is used to measure the
students’ basic ability and achievement. He mentions that there are two
kinds of achievement test which usually used by school:
a. Test made by the teacher; that arranged by certain
procedure, but it has not been examined many times so
its characteristics and strength has not been known.
b. Standardized test; a test that usually has been available
in a testing institution and has been guaranteed its
effectiveness.
In this research, researcher collected data by using test made by
teacher because by doing test, she is able to know the improvement of
36
Pre- test is used to know the students’ ability in learning English
especially in reading lesson. While post- test, is used to measure how
far do their improvement after applying the strategy in reading lesson.
Pre and post-test are to knowing the differences of the students ability
before and after the teacher used the strategy.
2. Observation
Observation is written note about what is seen, heard, and
experienced in collecting data and reflection toward qualitative data.
Observation is used to get the certain target which is observed. (Sam’s,
2010: 93)
In this research, researcher uses observation sheet to know how
far the students’ motivation before and after applying Reciprocal
Teaching Strategy. This instrument gives monitor and records the
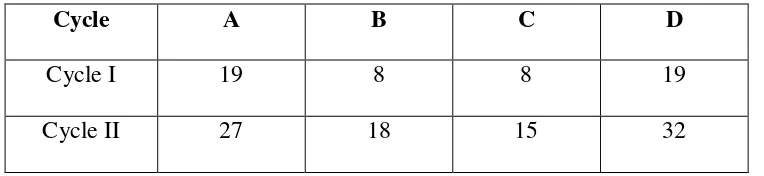
students’ involvement during the lesson. In the observation sheet, there
are four aspects that are consider focuses, those are: paying attention,
activeness in asking question, activeness in responding question and
enthusiasm in doing test. In this instrument, the teacher gives point in
each aspect based on the situation of students. The table below show
the example of observation sheet as follow
TABLE 3.2
STUDENTS’ OBSERVATION SHEET
No Name A B C D NOTE
1
37 3
4
5
Explanation:
A: Paying attention,
B: Activeness in asking question C: Activeness in responding question D: enthusiasm in doing test
3. Documentation
According to Arikunto (2010: 274), documentation is an
activity to look for variable like notes, transcribes, books, newspapers,
magazines, etc. In this method, researcher holds a check- list to look
for the variable that had been decided.Whether the wanted variable is
rises, then the researcher gave a check (√) in the check- list form.
In this research, researcher used camera or video recording to
help the observation process. After that she would transcribe the result
of observation activity.
F. Technique of Data Analysis
The researcher conducted the classroom action research of teaching
reading using Reciprocal Teaching strategy at tenthyears students of SMK
N 1 Ngablak. In analyzing data, the researcher used mixing qualitative and
quantitative approach. According to Johnson and Christensen (2007) qualitative
research relies primarily on the collection of qualitative data (i.e.,
38
While Lodico (2006: 6) stated that quantitative approaches summarize
data using numbers. Hypotheses and methods of data collection are created
before the research begins. This technique is used to know the students’
score of reading skill in each cycle. According to Hadi (1981: 246) the
formula is:
1. Mean
Where,
: Mean of students’ score
: The sum of students’ score
: The total number of students
2. SD (Standard Deviation)
√ ( )
Where,
: Deviation Standart for one sample t-test
: Different between pre-test post-test
: Number of observation in sample
3. T-test
To be able to know whether there is a significant improvement
or not between pre-test and post-test, researcher using t-test after
39
o
t
1
N
SD
N
D
D
Where,
: T-test for the differences of pre-test and post-test
: Deviation Standart for one sample t-test
: Different between pre-test and post-test
40 CHAPTER IV
DATA ANALYSIS
In this chapter, the writer would like to analyze the data gathered from the
action research activities. The data was obtained from teaching learning process and
evaluation. The data analysis is functioned to measure the students’ reading skill
improvements by applying Reciprocal teaching Technique.
This chapter focuses on analyzing the collected data. The researcher gives the
details of the findings. This chapter is likely the main discussion of the research
conducted. It displays the finding of the collected data since in the beginning until the
end of the research. In the research, the data consist of field note, the result pre-test
and post-test. The action of this research consists of two cycles, cycle I and cycle II.
The two cycles are treatment of implementation of the Reciprocal teaching Technique
in the reading comprehension. For the whole stages of every cycle will be explained
in the description below.
A. Research Findings
In this research, the writer acted as the teacher and learning process
observed by her partner Heri Narko. The writer arranged two cycles, each cycle
consist of planning, action, observing and reflection. The whole steps of this
research are explained in the description bellow:
1. Cycle 1 a. Planning
41 1) Lesson plan
In order to control the teaching learning process, the writer
used the lesson plan as teaching guidance in learning process.
a. Material
In the first cycle, the writer prepared the material about the
explanation of narrative text.
b. Teaching aid
The writer prepared some instrument, such as: blank paper and
board marker.
c. Sheet for classroom observation
Sheet for classroom observation was prepared in order to know
the condition of teaching learning process.
d. Test (pre-test and post test)
Pre-test was a test that was given to the students before the
teaching learning process. Meanwhile, post-test was a test that was
given to the students after teaching learning process was conducted.
The test was the teacher asked to the students to answer some
questions about narrative text.
b. The implementation of the action
On Tuesday 24 February 2015 Mr.Istingal as English teacher,
the researcher and her collaborator entered in the class X – ATU 2, the
condition of the class was quite and the teacher accosted the students
soon. He gave greeting and asked about their condition. Mr.Istingal
42
English temporary. The students accepted well. Furthermore, the
teacher opened the lesson by introducing herself and checked the
student’s present. In the first meeting,it was followed by 32 students in
the class.
Before the lesson, she gave the pre test for students in 10
minutes about narrative text without Reciprocal Teaching Technique.
She divided the sheets and walked around the class in order to check
the students along doing the test. Actually, she found that most of
students were confused in doing the test. Some of them asked their
friends, and others asked to the teacher.
When pre-test going on, the students still often asked
vocabulary to the teacher and they also discussed with other friends
doing the pre test. Then, she said to the students to do by themselves as
they can. After the students had finished the pre-test, she collected and
began the teaching learning process.
Afterwards, the teaching learning process was begun. The
teacher asked the students about narrative text.
Teacher : “Ok class, today we will discuss about
narrative text. What is narrative text it
self?”
Rohamim : “Teksdongeng, Miss, ( It is about legend)
Teacher : ”Yes, you are right! Then who wants to
explain it completely?”
Wuri : “tekstentangcerita, Miss. (It is about
43
Teacher : ya, boleh, ada yang lain? (Yes, right, any
other answer)”
The students kept silent, and then the teacher gave the material and
explained to them.
Teacher : ”(Teks narrativeadalah teks yang berisi cerita
untuk menghibur para pembacanya). Narrative
text is a text that contain astory to amuse the
reader.
Teacher :“What is the goal of the text? Please, raise your
hand!”
Adib : “Untukmenghiburpembaca, (To amuse the
reader)”
Teacher : “Yes, you’re right.Lalu, siapa yang tahu
generic structurenya? Then, who knows the
generic structure?”
Class become noisy again, some of students tried to answer.
Students : “Orientation, complication, and resolution!”
Teacher : “Very good! Tenses apa yang digunakan dalam
teks narrative? What tense is used in Narrative
Text?
Students : “Past tense!”
Teacher : “Good! Now, what are the language features of
narrative text?
44
Then teacher gave the detailed explanation of narrative text.
After it, the teacher gave them excercise (used Reciprocal Teaching
Technique). The researcher purposes the procedures of teaching
reading trough Reciprocal Teaching Technique as follow:
1. Predicting
In the first step, the teacher encourages the students to
predict about what the students think regarding what will be
discussed next in the text.
2. Questioning
In the second step instruction, the teacher encourages the
students to generate an appropiate questions for the passage
to monitor how deep their comprehension is.
3. Clarifying
In the step instruction, the teacher encourage the students to
identify what makes a given text difficult and seek an
understanding of difficult new vocabulary, unclear reference
words or unfamiliar words.
4. Summarizing
In the last instruction, the teacher encourage the students to
identify and intergrate the most important information (idea
and massage) in the text
Some of them very enthusiastic answer the teacher’s questions.
But, there are several students who shy when the teacher asked them to