“THE EFFECTIVENESS OF
MIND MAPPING STRATEGY IN
WRITING DESCSRIPTIVE TEXTS FOR 8 GRADERS
”
THESIS
Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree
Sarjana Pendidikan
Iis Hidayah Romadhloni 112011051
ENGLISH DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF LANGUAGE AND LITEATURE
SATYA WACANA CHRISTIAN UNIVERSITY
SALATIGA
ii
“THE EFFECTIVENESS OF
MIND MAPPING STRATEGY IN
WRITING DESCSRIPTIVE TEXTS FOR 8 GRADERS
”
THESIS
Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree
Sarjana Pendidikan
Iis Hidayah Romadhloni 112011051
ENGLISH DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF LANGUAGE AND LITEATURE
SATYA WACANA CHRISTIAN UNIVERSITY
SALATIGA
vi
COPYRIGHT STATEMENT
This thesis contains no such material as has been submitted for examination in any course or accepted for the fulfillment of any degree or diploma in any university. To the best of my knowledge and belief, this contains no material previously published or written by any other person, except where due references is made in the text
Copyright @ 2015 Iis Hidayah Romadhloni and Athriyana Santye Pattiwael, M.Hum
All rights reserved. No part of this thesis may be reproduced by any means without the prior written permission of at least one of the copyrights owners of the English Department of Satya Wacana Christian University, Salatiga.
1
“THE EFFECTIVENESS OF MIND MAPPING STRATEGY IN
WRITING DESCSRIPT
IVE TEXTS FOR 8 GRADERS”
Iis Hidayah Romadhloni
ABSTRACT
The study aims at finding the effectiveness of using mind mapping as a prewriting strategy in order to help the students in writing descriptive texts, and to uncover the aspects of effectiveness addressed by the students after the treatment of mind mapping strategy. The participants were 64 Eighth-graders of State 1 Junior High School (SMPN 1) Banyubiru, Indonesia. This research used a mixed method of quantitative and qualitative study particularly quasi experimental with questionnaire and interview techniques. This study used Independent samples t-test in order to analyze and compare the statistical data. The statistical result showed significant difference of progress shown by the experimental class as compared to the control class. It indicated that mind mapping was effective to help the students write the descriptive text. Furthermore, the result of questionnaires and interviews showed that most of the students give positive responses toward the use of mind mapping strategy in writing descriptive text. In particular, mind mapping facilitated the students to organize their idea, plan students’ writing, deal with the writing elements, write enjoyably, understand the writing content and improve their writing achievement.
Keywords: mind mapping strategy, writing, descriptive text
INTRODUCTION
2
students in my teaching practicum site, most of the students said that writing is difficult to learn as it demands them to express their ideas, organize the ideas and discover some new vocabulary related to the topic written. As Nurlaila (2013) claims, one part that makes the students feel that writing is difficult is when they have to convey their ideas to be written on the paper.
In order to help solve the students’ difficulties in writing, an appropriate learning strategy is very important. O’Malley & Chamot (1990) define learning strategy as a part of second language acquisition which includes the particular belief and behavior to figure out, learn and maintain the original information that is done by someone. Moreover, a study by O’Malley & Chamot (1990) suggested that the success of L2/FL learners is determined by their awareness of their own learning strategies. Related to the definition about learning strategy above, one of the strategies that can be used to solve the students’ problems in writing is pre-writing strategy. Pre-writing strategy is defined as experimental writing that helps the students to start writing and find new ideas before writing. (Mahnam & Nejadansari, 2012).
3
is especially useful in determining the relationship between ideas. It will distinguish what ideas are appropriate to be included in your writing, let alone when there are lots of ideas coming and you do not know how to organize them appropriately. Clearly, Murley (2007) adds, mind mapping can maximize the brain’s ability in associating numbers with visual
qualities and as a result, the memory will be able to store more facts.
In line with that, several studies regarding mind mapping strategy have previously been conducted. The first is the study by Nurlaila (2013) about the effectiveness of mind mapping technique to teach descriptive texts. The participants were seventh graders in a junior high school in Bandung. This study used a mixed method of pre experimental design, particularly one group pretest-posttest design, questionnaire and interview techniques to analyze the data. The result of this study was mind mapping technique was effective to improve students’ score in writing descriptive texts. Moreover, based on the questionnaire and interview data, the results showed that most students responded positively to this technique in terms of mind mapping technique motivated them to write descriptive text in an enjoyable way, increased vocabulary and creativity and help the students to plan their writing.
The second is the study by Supriyanto (2013) about the effect of mind mapping strategy on the students writing ability. The participant was 22 second-semester students in English Department of Islamic University of Malang. The study used quasi-experimental pretest and posttest design. The score was analyzed by using ANCOVA. The finding showed that the students taught by mind mapping strategy got better scores than those taught by conventional teaching because it could help the students to deal with the writing elements such as grammar and the use of vocabulary.
4
University and Nagoya City University. The finding showed that mind mapping strategy helped the students to organize the idea, and through images and key words made in mind mapping, the students could understand more about their writing content.
Although those three studies bring the same topic about the use of mind mapping strategy to teach writing, the focuses of the studies were different. Nurlaila (2013) focused on applying mind mapping in the descriptive text, Supriyanto (2013) focused more on the effect of mind mapping strategy in writing ability, and Backwell (2009) focused on applying mind mapping to write an essay. The present study is conducted to investigate the effectiveness of using mind mapping as a pre-writing strategy to write a descriptive text.
The study is conducted to answer these two research questions:
1. Is mind mapping strategy effective to help the students in writing a descriptive text?
2. In what ways is the mind mapping strategy effective to help the students in writing a descriptive text?
This study aims to find out whether mind mapping strategy is effective to help the students write a descriptive text and to describe the aspect(s) of the effectiveness addressed by the students after they are given the treatment of mind mapping strategy.
5
6
LITERATURE REVIEW
DIFFICULTIES IN EFL WRITING
It is a well known fact that writing is one of the difficult skills to learn. It is because writing requires cognitive and linguistic strategies. Rao (2007) states that the difficulties in writing that many students often face are how to find an interesting topic and the lack of ideas. In other words, the students find it difficult to decide the topic to write, and to express their ideas. While Rao (2007) supports that lacking of ideas becomes the factor that affects the students’ ability in writing, Farooq, Uzair, & Wahid (2012) point out that there are three factors contributing to the students’ difficulties in writing such as poor understanding of structure, interference of L1 use and lack of vocabulary. Meanwhile, Siahaan (2013) emphasizes that the difficulties faced by EFL students in writing descriptive texts are more on the grammatical errors and generic structure. Moreover, White (2007) adds that basically the students lack the skill of organizing the content of writing such as not focus on the composition’s central image, the subject being described, and wordiness.
To sum up, the EFL students’ difficulties in writing, especially when they have to write
a descriptive text, are related to the understanding of the generic structure, the limited grammatical knowledge, the skill in organizing the content and the conciseness of the paragraphs.
PREWRITING STRATEGIES
7
individual to activate prior background knowledge, discover new ideas and specify areas of the research. In conclusion, the definition of prewriting strategy based on both theories above is a process done before the real writing activity that helps the individuals to find new and supporting ideas for their writing piece.
Lanon (2011) suggests five different kinds of prewriting strategies. They are free writing, listing, reporter’s question, journaling and clustering or mind mapping. Free writing or fast writing is a technique to write freely without any concern about accurate grammar, punctuation and spelling. The second technique is listing which enables the students to list some specific and disorder ideas or questions without worrying about the relationship of the paragraphs. The third is reporter’s questions which include 5w & 1h (who? what? why? where? when? and how?) questions to guide the students to find specific ideas and details about a particular topic. Next technique is journaling which involves the students to check and recheck certain events, topics or ideas. And the last is clustering or mind mapping, whose process includes writing a key word and write down other ideas that sprout from it by
c o n n e c t i n g l i n e s .
8
the students are required to consider the organization of the content by using graphic organizer.
Basically, what Mogahed (2013) and Lanon (2011) suggest in categorizing the parts of prewriting strategy are almost the same. Both theories imply some parts like free writing, brainstorming, mind mapping, listing and questioning. However, Lanon (2011) makes the category simpler and easier to understand. This study relies on Lanon (2011)’s theory as it is
easy to follow and understand.
MIND MAPPING STRATEGY
As mind mapping is one of the strategies that can facilitate writing, some experts tried to define the meaning of mind mapping strategy differently. One of the well-known experts of this field is Tony Buzan (1993, 2006) who defines mind map as a figure which functions as a tool to sort out thoughts and organize words, tasks or other relations that set central key words and branches that usually contain words, colors, short phrases and pictures. As mind mapping is one of the sub-part of pre writing strategy, Mc Crimmon (2009) analyzes that mind map is the prior process that the writer usually does before starting to write a paragraph which needs a certain time to do. Thus, based on those definitions, the researcher tries to conclude that mind mapping is a technique used before starting writing which functions to sort out ideas that usually contain words, colors, phrases or pictures. Moreover, it organizes the relationship between central ideas and branches.
9
something better. In line with Tee et al. (2014), Polson (2004) proposes that mind map can facilitate to develop memory. Secondly, Manham and Najedansari (2012) state that mind mapping can help the students to sort out the information being written. It is supported by Davies (2010) who says that the relationship of the diagram in mind mapping will help the writer understand the relationship of the ideas and analyze each component better.
So, based on the theory of mind mapping above, this study will follow Buzan’s (2006) theory in implementing the mind mapping process. The process includes setting central key words and branches that usually contain words, colors, short phrases or pictures to sort out information, ideas, words or other relations.
THE ASPECTS OF EFFECTIVENESS OF MINDMAPPING STRATEGY IN
STUDENTS’ EFL WRITING
One of the main focuses on this study is to find the effectiveness of the use of mind mapping strategy. The definition of effectiveness based on Oxford Advance Learner’s dictionary is the degree to which something is successful in producing the desired result. Related to the definition mentioned, the term of effectiveness in this study can be described as the degree of how successful the mind mapping strategy is to facilitate the students’ writing so that they can improve their writing achievement.
Based on the previous studies done by some experts, the researcher classifies the aspects of effectiveness of mind mapping strategy in students’ EFL writing. Firstly, mind mapping is effective to help the writer organize the ideas as suggested by Supriyanto (2013) and Backwell (2009). Secondly, it is effective to plan the students’ writing as stated by
10
11
REASERCH METHODOLOGY
TYPE OF RESEARCH
To answer the two research questions, the researcher used a mixed method of quantitative and qualitative research, particularly quasi experimental group pretest and posttest, with questionnaire distribution and interviews. The quantitative method, the quasi- experimental group pre-test-posttest, was employed to answer the first research question: is mind mapping strategy effective to help the students in writing descriptive text. The qualitative method using a questionnaire and interviews was employed to answer the second research question: in what ways is mind mapping strategy effective to help the students in writing descriptive text.
CONTEXT OF THE STUDY
The context of this study was in SMP Negeri 1 Banyubiru. This School was chosen because the researcher had conducted teaching practicum in this school so that it made the researcher get the permission from the school more easily. Besides that, the researcher also had been familiar with the situation of the school and the 8 graders that became the participants of this study.
PARTICIPANTS
12
classes. Besides that, the ability of both classes was comparable when the researcher measured the mean of their mid-term English test which means of control group is 57,56 and experimental group is 56,87. Further, the 8 graders were chosen as participants because descriptive writing became the subject of their second semester and their writing ability considered low as they were still beginners in learning English. Hence, it was hoped that both classes were able to cooperate well in giving their contribution during the data collection.
Moreover for the interview session, the participants were chosen by using the grade intervals to get more thorough data. For each interval, the researcher randomly chose the same number of representatives to be interviewed. The intervals used were as follows:
Interval Sampling
0-25 4 students
26-50 4 students
51-74 4 students
75-100 4 students
INSTRUMENTS OF DATA COLLECTION
In this study, three kinds of instruments were used to collect the data: writing test, a 4-likert-scale questionnaire and semi structured interview questions.
13
scoring criteria also represent some aspects in scoring the descriptive text. There were four aspects graded to measure students’ writing ability in descriptive text such as content, vocabulary, generic structure and language feature. The point of each criterion ranges from one up to five, the maximum total score is 20.
A questionnaire was given to the experimental class. This instrument was used to find the aspect(s) of effectiveness after the students were given the treatment of mind mapping strategy. The questionnaire consists of 10 items of closed ended questions by using likert-scale. The students were asked to respond to each statement on four scales. 1 representing strongly disagree, 2 disagree, 3 agree and 4 strongly disagree. The questionnaire items were developed from the aspects of the effectiveness of mind mapping strategy theories discussed in the previous chapter. The questionnaire was written in the Indonesian language to make it easier for the participants to understand the statements.
The Interview was also given to the experimental class in order to get the richer data of the aspect(s) of effectiveness. It was developed based on the questionnaire items in order to get the richer data of the qualitative research. The type of the interview was semi structured interview which enables the interviewer to develop the interview questions during the interview session and it consists of seven main questions.
RESEARCH PROCEDURE
14
study showed that those 3 instruments of data collection worked well: thus, the researcher didn’t make any changes to continue the next steps.
Secondly, administering pre tests to both, control and experimental classes. Thirdly, conducting treatments for both classes, here the experimental class was treated by using mind mapping strategy and control class was treated by using conventional method. Fourthly, administering post test for both classes. Fifthly, administering questionnaire to all students in experimental class. The last step was conducting interviews with 16 students from experimental class.
DATA ANALYSIS PROSEDURE
Two main analyses were done to analyze the collected data in order to answer the two research questions. The first is running an Independent Samples T-test to investigate the effectiveness of the mind mapping strategy. The second was conducting a qualitative analysis of the questionnaire and interview data in order to uncover the aspects of effectiveness of the mind mapping strategy. To investigate the effectiveness of mind mapping strategy, first of all an Independent Samples T-test of both groups’ means of the pre-test scores was run to determine whether the two groups’ performances were comparable. If they were, another
Independent Samples t-test was run comparing the means of the two groups’ progress scores (pre test scores -post test scores) to find out whether mind mapping strategy was effective. The software used in analyzing the test was SPSS 16. To answer the first research question the researcher determined the null and alternative hypotheses. The Ho of this study was “mind mapping is not effective to help the students improve their writing ability and
overcome the difficulties in writing descriptive texts”. While the Ha was “mind mapping is
15
writing descriptive texts”. Finally, the data analysis results were presented in the form of
tables and numbers followed by brief explanations.
16
FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
The discussion of this section is divided into two sessions based on the research questions on this study. Firstly, it discusses the statistical analysis of the effectiveness of mind mapping strategy to write descriptive texts which aim at answering the first research question. Meanwhile, the second is the analyses of the questionnaire and interview data which aim at describing the aspects of effectiveness to answer the second research question.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS ON THE EFFECTIVENESS OF MIND MAPPING
STRATEGY TO HELP THE STUDENTS IN WRITING DESCRIPTIVE TEXT
17
INDEPENDENT SAMPLES T-TEST OF PRE TEST RESULTS
This Independent samples t-test was run to determine whether the performances of the two groups (control and experimental groups) were comparable in the beginning of the study.
Normal Distribution Test
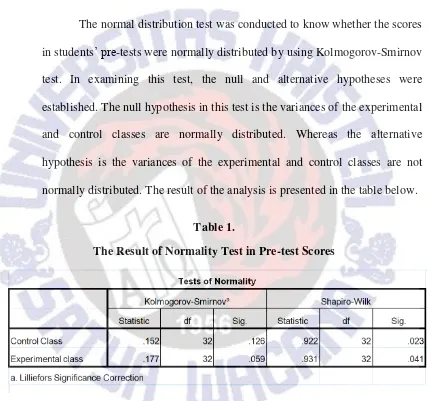
The normal distribution test was conducted to know whether the scores in students’ pre-tests were normally distributed by using Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. In examining this test, the null and alternative hypotheses were established. The null hypothesis in this test is the variances of the experimental and control classes are normally distributed. Whereas the alternative hypothesis is the variances of the experimental and control classes are not normally distributed. The result of the analysis is presented in the table below.
Table 1.
The Result of Normality Test in Pre-test Scores
18
accepted and the alternative hypothesis was rejected. Hence, it can be concluded that both of the group were normally distributed.
Homogeneity of Variance
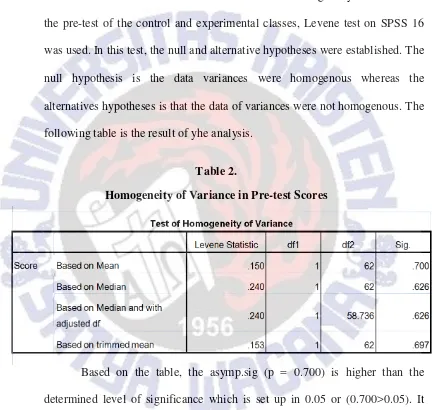
The Homogeneity of variance test was conducted after the normal distribution test was administered. To find out the homogeneity of variance in the pre-test of the control and experimental classes, Levene test on SPSS 16 was used. In this test, the null and alternative hypotheses were established. The null hypothesis is the data variances were homogenous whereas the alternatives hypotheses is that the data of variances were not homogenous. The following table is the result of yhe analysis.
Table 2.
Homogeneity of Variance in Pre-test Scores
19 Independent Samples t-test
The last step after knowing the normal distribution and homogeneity is running the independent samples t-test to find out the equity of students’ pre-test score means in both classes. In this pre-test the writer also set up the null and alternative hypotheses. The null hypothesis is the students’ pre-test score means are not significantly different and the alternative hypothesis is the students’ pre-test score means are significantly different in both classes. The results of independent sample t-test on the pre-test scores are shown in the table below.
Table 3.
The Mean of Pre-test scores in Control and Experimental Classes
Table 4.
Independent T-test of Pre-test scores in Control and Experimental
20
In this test, the significance level established was 0.05 with the df = 62. Based on the statistical Table 4 above, the significance value (p = 0.890) is higher than 0.05 or (p > α). It means the null hypothesis is accepted and the
alternative hypothesis is rejected. Hence, there is no difference between control and experimental classes’ means.
Based on the normality test, homogeneity test, and the independent samples t-test that have been administered, both classes had comparable abilities in writing descriptive texts. Therefore, both classes were comparable and could be used as the samples of this research.
INDEPENDENT SAMPLES T-TEST OF BOTH CLASSES’ PROGRESS
This Independent samples t-test on students’ progress scores (posttest scores – pretest scores) was run to investigate whether the mind mapping strategy was effective to help the students write descriptive texts.
Normal Distribution Test
21
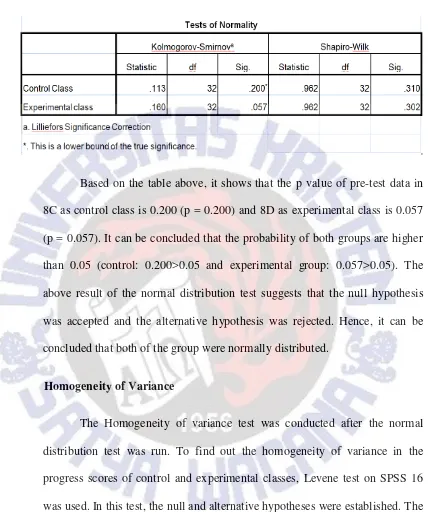
Table 5.
The Result of Normality Test in Progress Scores
Based on the table above, it shows that the p value of pre-test data in 8C as control class is 0.200 (p = 0.200) and 8D as experimental class is 0.057 (p = 0.057). It can be concluded that the probability of both groups are higher than 0.05 (control: 0.200>0.05 and experimental group: 0.057>0.05). The above result of the normal distribution test suggests that the null hypothesis was accepted and the alternative hypothesis was rejected. Hence, it can be concluded that both of the group were normally distributed.
Homogeneity of Variance
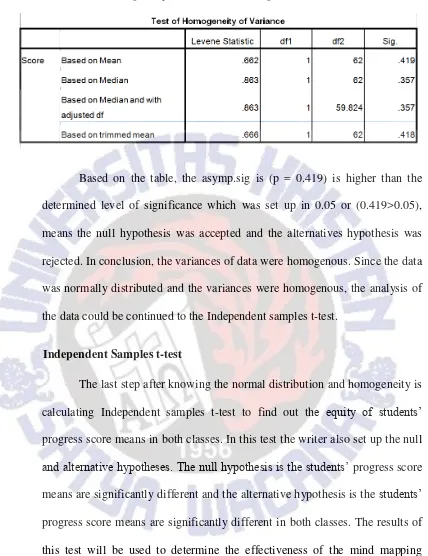
The Homogeneity of variance test was conducted after the normal distribution test was run. To find out the homogeneity of variance in the progress scores of control and experimental classes, Levene test on SPSS 16 was used. In this test, the null and alternative hypotheses were established. The null hypothesis is the data variances were homogenous whereas the alternative hypothesis is that the data of variances were not homogenous. The following table is the result the analysis.
22
Homogeneity of Variance in Progress Scores
Based on the table, the asymp.sig is (p = 0.419) is higher than the determined level of significance which was set up in 0.05 or (0.419>0.05), means the null hypothesis was accepted and the alternatives hypothesis was rejected. In conclusion, the variances of data were homogenous. Since the data was normally distributed and the variances were homogenous, the analysis of the data could be continued to the Independent samples t-test.
Independent Samples t-test
The last step after knowing the normal distribution and homogeneity is calculating Independent samples t-test to find out the equity of students’ progress score means in both classes. In this test the writer also set up the null and alternative hypotheses. The null hypothesis is the students’ progress score means are significantly different and the alternative hypothesis is the students’ progress score means are significantly different in both classes. The results of this test will be used to determine the effectiveness of the mind mapping strategy in helping students write descriptive texts. The results of independent t-test on progress score means are shown in the table below.
23
The Mean of Progress scores in Control and Experimental Classes
[image:30.595.100.536.77.626.2]Table 8.
Independent T-test of Progress scores in Control and Experimental Classes
In this test, the significance level established was 0.05 with the df = 62. Based on the statistical table above, the significance value is lower than 0.05 or 0.007 < 0.05. It means the null hypothesis is rejected and the alternative hypothesis is accepted. Hence, the progress score mean of the experimental group (M = 27,81) was significantly different from that of the control group (M = 19.53).
Based on the normality, homogeneity, and Independent samples t-test that have been administered, it can be concluded that mind mapping technique was effective to improve students’ ability in writing descriptive texts.
24
mind mapping strategy. It can be seen from the means and independent samples t-test of both classes after analyzing the scores. In the pre test, it showed that control class gets the higher means than experimental class, however the t-test explained that both classes had comparable ability in writing descriptive texts. After analyzing the progress scores of pre and post test of both classes, it is found that the progress’ means of experimental class is higher than the
control class and from the t-test result; the difference is significant. It meant mind mapping treatment in experimental class was successfully done as the progress mean of score in this class was higher than that of the control class. Thus, it can be concluded that mind mapping strategy is effective to help the students to write descriptive texts. This result is in line with Nurlaila’s (2013) and Suyanto’s (2009) studies which stated that mind mapping is effective to improve students’ writing ability.
THE ASPECTS OF EFFECTIVENESS OF MIND MAPPING STRATEGY TO HELP
THE STUDENTS IN WRITING DESCRIPTIVE TEXT
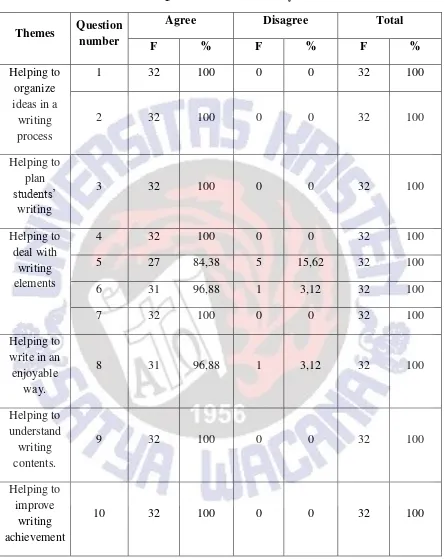
The second sub-session presents the analysis from questionnaire and interview data to answer the aspects of effectiveness of mind mapping strategy. The responses to the questionnaire were classified into six themes on the basis of the summary of the aspects of effectiveness found in the previous studies. The six themes of the aspect of the effectiveness of mind mappind strategy are: helping to organize the ideas, plan students’ writing, deal with writing elements, write in an enjoyable way, understand the writing contents, and improve writing achievement. The data is reported in a form of a frequency table. Some excerpts from interview results are included to support the findings.
25 Table 9.
Result of Questionnaire Data Analyses
Themes Question number
Agree Disagree Total
F % F % F %
Helping to organize ideas in a
writing process
1 32 100 0 0 32 100
2 32 100 0 0 32 100
Helping to plan students’
writing
3 32 100 0 0 32 100
Helping to deal with
writing elements
4 32 100 0 0 32 100
5 27 84,38 5 15,62 32 100
6 31 96,88 1 3,12 32 100
7 32 100 0 0 32 100
Helping to write in an enjoyable
way.
8 31 96,88 1 3,12 32 100
Helping to understand
writing contents.
9 32 100 0 0 32 100
Helping to improve
writing achievement
10 32 100 0 0 32 100
26
students (100%) agreed that mind mapping strategy help them to organize their ideas, plan their writing, understand their writing contents, and improve writing achievement. 31 students (96.88%) agreed that mind mapping strategy helped to write in an enjoyable way, showed. Meanwhile, the third theme that mind mapping strategy helped to deal with the writing elements, received various responses. All 32 students (100%) agreed that mind mapping strategy helped to find new vocabulary (question no.4) and improve creativity (question no.7), 31 students (96.88%) agreed that mind mapping strategy helped them to understand grammar, and only 27 students (84.38%) agreed that mind mapping strategy could help them improve their vocabulary.
Further, in order to get the richer explanation of the aspect of effectiveness from the students, based on the percentage data in table 7, the following part attempted to describe those aspects briefly based on the 6 big themes.
1) Mind mapping helps to organize the ideas in writing process.
The result of the first theme based on Table 7 above indicated that all of the students (100%) approved that mind mapping helped them to organize the ideas in the writing process. Here are some comments from the students related to the first theme.
“mind mapping sangat membantu karena saat membuat mind mapping ide dapat terklasifikasi dengan baik.” (S22-B)
(Mind mapping helps to write descriptive text because when making mind mapping I can classify the idea well.)
“Mind mapping membantu mengklasifikasikan isi dan topic per paragraf. selain itu juga bantu megklasifikasi kata atau vocabulary yang mau saya gunakan menulis.” (S14-B)
27
“Menurut saya melalui klasifikasi vocab-vocab atau kata di mind mapping ide jadi lebih mengalir saat menulis paragraf.” (S4-B)
(In my opinion, through the classification of vocabularies or words in mind mapping, I can be more productive when writing a paragraph.)
“….mind mapping bantu saya untuk mengelompokkan kata yang setema, jadi paragrafnya gak campur aduk. Jadi lebih urut dan bagus.” (S5-B)
(…Mind mapping helps to grouped the words which is under the same
theme, so it doesn’t make the paragraph muddle and it becomes more well-organized)
“Misalnya bisa bantu menyusun mana yang harus di tulis dulu jadi paragrafnya bisa jadi lebih urut.” (S19-B)
(For example it can help me to arrange the paragraph so that the paragraph becomes well-organized)
“Melalui mind mapping ide bisa dikelompokkan dengan baik.”(S22-B)
(Through mind mapping, the idea can be classified well.)
From the excerpts, the data revealed five ways of how mind mapping help the students organize the idea. Mind mapping strategy helps the students to organize the idea in several ways: grouping or classifying ideas, classification of the content and topic, classification of vocabulary, grouping the words under several themes, and arranging the ideas in a paragraph. By doing so, the students expressed that their writing process is much more productive and well organized. This finding is in line with Backwell’s (2009) and Supriyanto’s (2013) studies that found that mind mapping is effective to help the writer to organize the ideas.
2) Mind mapping helps the students to plan students’ writing
Related to the second theme, here are the comments of the students: “balon-balon di mind mapping yang berisi ide awal, memudahkan saya untuk merencanakan hal apa saja yang mau saya tulis di paragraf.”
(S17-B)
28
“Menutut saya, itu memudahkan untuk menglasifikasi isi per paragaf karena saya sudah membuat rencana untuk ditulis dalam paragaraf.” (S15-B)
(In my opinion, mind mapping helps to classify the content in each paragraph because I have made a plan to be written in the paragraph later.)
Based on the excerpts above, the result of the second theme revealed that mind mapping helped them to plan their writing as supported by Nurlaila (2013), Ling (2004) & Fictorius (2013). The students reported that the rough ideas in bubbles helped them to plan their writing more easily. Furthermore, the content of the paragraph could be classified well when the students made mind mapping.
3) Mind mapping helps the students to deal with writing elements.
The students’ opinions about the third theme are mostly positive that mind mapping help them to deal with the writing elements such as vocabulary, grammar and creativity in the process of writing descriptive texts. Here are some statements given by the students related to the third theme.
“…..bisa tanya langsung ke guru atau teman kalau gak bisa.” (S21-B)
(….I can directly ask the information to the teacher or friends if I do not understand it yet.)
“ Bisa cari vocab di kamus saat membuat mind mapping. Waktunya banyak.”(S25-B)
(I can look it up in the dictionary when I make mind mapping because I have more time to do it.)
“Bisa tanya langsung ke guru atau teman. Terus mind mapping juga memudahkan buat nyari kata yang tepat atau sesuai yang mau digunakan.” (S13-B)
(I can directly ask the information to my friends or teacher. Besides that it makes me easier to find the appropriate vocabulary that I am going to use.)
29
mind mapping helped the students to find new vocabulary. The excerpt also discovered that it helped the students in a way of time availability to look up in the dictionary, the chance to ask some information to the teacher or friends and the chance to find related or appropriate vocabulary to use in their writing.
The next one is about how mind mapping facilitates the students to improve their vocabulary. The following comments are the students’ opinions of how mind mapping could facilitate them to improve their vocabulary.
“Saat membuat mind mapping saya tidak hanya sekedar mencari vocabulary baru tapi secara tidak langsung kita juga lebih mudah mengingat vocabulary yang kita cari tersebut saat memvisualisasikannya ke dalam gambar.” (S27-B)
(When making mind mapping I do not only look for the new vocabularies but also it facilitates me to remember those vocabularies easier when visualize it into the pictures.)
“Saat membuat mind mapping saya bisa mengklasifikasikan
vocabulary sesuai kelasnya jadi hal itu bisa lebih membantu saya dalam mengingat vocabulary baru.” (S12-B)
(When making mind mapping I can classify the vocabulary based on their classes so it is easier for me to remember the new vocabulary.)
“karena pas buat mind mapping kita gak langsung nulis jadi kalimat tapi per kata, jadi lebih mudah mengingat vocab baru yang kita temukan tadi.” (S17-B)
(Because when I am working with mind mapping, I do not directly write those new vocabularies into sentences but words, thus it is easier to remember new vocabularies that just found.)
30
vocabulary. In conclusion, this finding is in line with the previous study done by Nurlaila (2013) that mind mapping helps the students to enrich their vocabulary.
Then, most of the students explicitly reported that mind mapping helps them to understand the grammar.
“…saya bisa lebih paham sama tenses yang mau dipakai dengan lihat catatan atau kalau belum jelas ya tanya guru.” (S27-B)
(… I become understand more about tenses that I am going to use by
reread my notes or I can ask it to my teacher if I haven’t understood yet.)
“Soalnya saya jadi lebih bisa mbedain dan memilih tenses mana yang harus dipakai dengan tanya ke guru, teman atau melihat catatan. Intinya punya waktu lebih untuk itu.” (S15-B)
(I can be more careful to differentiate and choose which tenses I should used in a paragraph by asking to the teacher, friends or reread the notes. Basically, I can have more time to do all those things.)
It has been reported that mind mapping helps the students to deal with the writing elements such as grammar (Supriyanto, 2013). The previous statements above also reflect that mind mapping helps the students to deal with grammar especially in terms of the availability of time to seek the information from the teacher or friends related to the grammar used, the availability of time to choose appropriate tenses they are going to use and the availability of time to read their notes. By doing so, they can understand the grammar used.
Lastly, related to the third theme, the students also experienced that mind mapping helped them to improve creativity in writing. Here are some reports related to writing creativity improvement.
31
(Working with mind mapping is like joining an art class. I can draw and use color pencil. It is so fun, so I can do my writing enthusiastically. )
“Dengan membuat mind mapping tingkat kestressan dalam menulis menurun sehingga kreativitas meningkat karena kita menikmati proses menulis.” (S6-B)
(By making mind mapping the degree of stress is decreased, as a result my creativity is increase because I enjoy the process of my writing.)
“mind mapping bantu saya merefresh otak sebelum bikin paragraf deskripsi, Miss. Nah… dari situ saya jadi lebih menikmati saat menulis paragraf.” (S14-B)
(Mind mapping helps to refresh my mind before making paragraph. From that thing, I become more enjoy when writing a paragraph.)
The excerpts above revealed that there were at least three ways of how mind mapping helped the students to deal with the writing elements especially how it improved their writing creativity. First, mind mapping facilitated fun writing by visualization of the ideas second, it reduced the stress level of the students. Third, it could refresh students’ mind. Thus, the students became more productive, and they enjoyed the writing process. This finding is in line with Nurlaila’s (2013) finding that mind mapping helps the students to improve creativity of writing.
4) Mind mapping helps the students to write in enjoyable way.
Most of the students reported that mind mapping helped them to write in an enjoyable way. It is stated in the reports bellow.
“Saya menikmati membuat mind mapping soalnya boleh gambar-gambar kaya di kelas seni rupa.” (S2-B)
(I enjoy the process of making mind mapping because I can draw like I join the art class.)
“…karena saya jadi gak tegang dan stres saat bikin paragraf soalnya saya boleh gambar sesuatu di mind mapnya.” (S16-B)
(When I make mind mapping, I can draw something there. As a result
it doesn’t make me feel so stressful and wrought-up when making the
[image:38.595.91.527.212.694.2]32
“Karena boleh pake pulpen warna-warni dan menggambar, jadi membuat mind mapping jadi menyenangkan.” (S25-B)
(It is fun because I can use color pencil and drawing.)
Firstly, based on the excerpt above, mind mapping helped the students to write in an enjoyable way, especially through visualization such as drawing pictures and using color pencils. In other words, it facilitated the fun writing to the students. As a consequence, the degree of stress could be reduced and the students felt more fun to do their writing.
“Saya senang dan menikmati buat mind mapping karena kita gak melulu langsung disuruh bikin paragraf tapi membuat perencanaanya dulu.” (S19-B)
(I enjoy making mind mapping because by doing it I don’t directly write something in a form of paragraph yet I can make the planning first.)
Secondly, the student expressed that they got new knowledge about how to plan their writing before writing a paragraph.
Based on the finding above, it can be assumed that the finding is in line with the statement that mind mapping helps students to write in an enjoyable way as stated by (Nurlaila, 2013), and creates the learning environment as stated by Tee et.al.,(2014).
5) Mind mapping helps the students to understand the writing contents
All of the students reported that mind mapping helped them to understand their writing contents. It is particularly in terms of the guidance of how the information should be delivered as mentioned in the excerpt bellow.
33
(When writing a paragraph after making mind mapping, I feel that I am more guided so that the written information can be delivered easier and better).
Besides that, mind mapping also helped the students to understand the writing contents in a way of how they could arrange the contents of the text in each paragraph as stated in the excerpt bellow.
“…. saya jadi lebih paham kalau di paragraf pertama, kedua dan seterusnya mau nulis apa. Misal paragraf pertama di paragraf deskripsi, saya harus nulis nama, tanggal lahir, nama orang tua dll sedangkan di paragraf dua misalnya saya harus nulis hobi, karakteristik, ciri-ciri fisik dll.” (S12-B)
(…. I become understand more about what should I write in first,
second and so on paragraph, For example in the first paragraph I have
to write name, date of birth, parents’ name and etc whereas in the
second paragraph I have to write hobby, characteristic and physical appearance. )
In summary, the students expressed that the written information could be delivered more easily and in a better way after making mind mapping. Shortly, it can be stated that this finding is in line with Farrand, Hussain, & Henessy (2002) and Backwell (2009) who stated that mind mapping helps the students to understand the writing contents. It is also supported by Manham and Najedansari (2012) who stated that mind mapping can help the students to sort out the information being written. Moreover Davies (2010) adds that the relationship of the diagrams in mind mapping will help the writer understand about the relationship of the paragraphs and analyzes each component better.
6) Mind mapping helps the students to improve writing achievement.
34
“sesudah tau mind mapping nilai test akhir descriptive saya kemarin jadi bagus dibandingkan yang pertama.” (S22-B)
(After learning mind mapping, my post test is better than my pre test.)
“sekarang saya jadi gak bingung lagi kalau disuruh nulis paragraf karena bisa mulai dulu pakek mind mapping.” (S5-B)
(Now I am not confused when I have to write a paragraph as actually I can begin it by planning my writing using mind mapping.)
“Saya jadi lebih mudah menulis teks deskripsi dengan baik karena kita sudah buat rencana dulu sebelum menulis.” (S21-B)
(I can write a good descriptive text more easily because I have made the plan before writing.)
“saya jadi lebih paham gimana cara nulis teks descriptive yang bener, gak asal tulis saja.” (S4-B)
(I can understand better how to write a descriptive text correctly and not just shuffle up my writing.)
The above statements pointed out that mind mapping helped them to improve their writing achievement especially to improve their writing scores. Besides that, they also reported that mind mapping helped them to improve their ability to understand how they should write descriptive texts appropriately and correctly. Moreover, the students didn’t end up in confusion as mind mapping facilitated them to plan their writing. This finding is in line with the study done by Riswanto & Prandika (2012) and Ling (2004) that mind mapping is effective to improve writing achievement.
35
CONCLUSION
The aims of the study are to investigate the effectiveness of using mind mapping as a pre-writing strategy in order to help the students to write descriptive text, and uncover the aspects of effectiveness addressed by the students after given the treatment of mind mapping strategy.
In this study, the result is divided into two parts, the first is the result from statistical analysis to answer research question no. 1 and the second is the result from questionnaire and interview data to answer research question no. 2. From the study, the writer found that mind mapping was effective to help the students to write descriptive text. It can be seen from the result of pre and post test of both classes. Based on the analyses, there were changes between pre and post test scores of both classes especially in experimental class which was treated with mind mapping strategy. It can be seen from the means and independent samples t-test of both classes after analyzing the scores. In the pre test, it showed that control class got the higher means than experimental class, however the t-test explained that both classes had comparable ability in writing descriptive texts. After analyzing the progress score means of both classes, it is found that the progress score means of experimental class is higher than the control class and the Independent Samples T-test result showed that the difference was significant. Hence, it can be summed up that mind mapping was effective to help the students to write descriptive texts.
36
the idea in a paragraph. Secondly, mind mapping helped to plan students’ writing in terms of making a rough idea in the bubbles and classifying the content in each paragraph. Thirdly, mind mapping helped to deal with writing elements. In finding new vocabulary and improve vocabulary, mind mapping helped the students in several ways such as provided time availability to look up in the dictionary, chance to ask some information to the teacher and friends, visualization and classification of the ideas and facilitate to memorize vocabulary in the form of words. Then, in helping to deal with the grammar, mind mapping help them in terms of the availability of time to seek the information from the teacher, choose appropriate tenses used and read the notes. Further, in improving their writing creativity, mind mapping facilitate fun writing by visualization of the ideas, reduced the stress level of the students and refresh students mind. Fourthly, Mind mapping helped the students to write enjoyably by facilitating fun learning to the students. Fifthly, mind mapping helped the students to understand their writing content in terms of providing guidance of how information should be delivered clearly and how the content should be arranged in each paragraph. Sixthly, mind mapping helped the students improve their writing achievement in terms of their grades, their ability and understanding to write the text. From both results, it can be concluded that mind mapping was effective to help the students to write descriptive texts.
37
help to write in an enjoyable way, help the students to understand the writing contents, and improve their writing achievement.
The limitations of this study are the time limit when treating the experimental group with mind mapping strategy and when administering the post test to the experimental group. The limited time made the treatment unable to be done well as the teacher should explain so many things related to mind mapping strategy. Further, in the post test the students took a longer time to finish their test than the time that the writer expected. Due to the limitation of time, both of those things couldn’t be done well.
38
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
My greatest thanks to Allah SWT, who always guides, blesses, loves and sends the incredible people listed below as His arms to hugs, His eyes to watch, His ears to hear, and His hands to catch me when I fall down during my hard time finishing this thesis so that I always have strengths and courage to finish it.
Ma’am Athriyana Santye Pattiwael, as my supervisor and advisor. Thank you very much for all your supports, helps, guidance, kindness, and advices. I really appreciate all you have done to me.
Mbak Gita Hastuti, as my examiner. Thank you very much for your willingness to examine my thesis.
Bu Neny Isharyanti, thank you very much for your willingness to help me explaining a very confusing statistical analysis so that I can finish my thesis.
For my mother and father thank you for always supporting and praying for me. Thank you for always remind me not to forget to pray and have breakfast every morning. I love you.
Thanks a million to Bu Ambar, the English teacher of 8 graders of SMP N 1 Banyubiru who has allowed me to use the classes to do my research.
The Headmaster of SMP N 1 Banyubiru, Pak Indarto. Thanks for giving me permission to do my research in the school.
39
All the students in 8C, 8D and 8F, thank you for being the nice participants and give me the precious experience in collecting the data for my thesis. You all have stolen my heart guys. I love you all. Keep dreaming!
Mbak Desi Rochmanawati (2010ers), Thank you for helping me explaining about how to work with Wilcoxon signed-rank test. It so mean to me, mbak.
Ardiansyah Amanda Saputra, Thank you for your support and patience in hearing my jeremiad about my thesis.
Thanks a bunch to “Akamaru”, my charming laptop which has worked very hard
during my thesis execution.
And for all those people that I could not mention one by one, Thanks for being there. You are blessings for me. Love you and God Bless.
Salatiga, August 20th , 2015
40
REFERENCES
Backwell, B (2009). Mind Mapping and Writing Fluency. Sugiyama. 11, 65-78 Buzan, T. (1993). The mind map book. London : BBC Books.
Buzan, T. (2006). Learning skills : Mind mapping : Mind mapping, whole brain note taking. Uses both sides of your brain to study subjects usually only study left brain. (Online). Available at : http://digilib.unnes.ac.id (accessed on November 20th 2014)
Buzan. T. (2007). Buku pintar mind map untuk anak . Jakarta : PT Gramedia Pustaka Utama. Coakes, S. J., & Steed, L. G. (2001). SPSS: Analysis Without Anguish. New Jersey: John
Willey and Sons.
Collidge, Frederick L. (2000). Statistic ( A Gentle Introduction). London : Sage Publication Ltd.
Crimmon, M. (2009). Writing with a Purpose. Boston : Hoaghton Miffin Company.
Davies, M. (2010). Concept Mapping, Mind Mapping and Argument Mapping : What are the differences and do they matter? Milan: Springer.
Departemen Pendidikan Nasional. (2006). Kurikulum tingkat satuan pendidikan. Jakarta : Depdiknas.
Farrad, P., Hussain, F., Hennessy, E. (2002). The Efficacy of the ‘Mind Map’ Study Technique. Medical Education, 36 (5), 426-431.
Farooq,M.S., Uzair, M., & Wahid, S.(2012). Opinion of Second Language Learners about Writing Difficulties in English Language. South Asia Studies, 27, 183-194.
Fictorius, T. (2013). The Use of Mind Mapping Technique in EFL Classroom. Retrieved November 3, 2014, from https://www.academia.edu/3823093/The_use_of_mind-mapping_technique_in_the_EFL_classroom.
Hidayat, A. (2012, July 2). Uji Statistik. Retrieved November 6, 2014, from Statistikian Blogspot: http://statiskian.blogspot.com/2012/07/uji-t-paired-dengan-SPSS.html.
Hoskin, T. (2012). Parametric and nonparametric: Demystifying the terms. Mayo Clinic CTSA BERD Resource. Retrieved April 21, 2015, from http://www. mayo. edu/mayo-edudocs/center-for-translational-science-activities-documents/berd-5-6.pdf.
41
Ling, C.W. (2004). The Effectiveness of Using Mind Mapping Skills in Enhancing Secondary
One and Secondary Four Students’ Writing in a CMI School. University of Hong Kong, Masters dissertation.
Mahnam, L., & Nejadansari, D. (2012). The differences of Pre-writing strategies on Iranian EFL Writing Achievement. International Education Study, 5, 154-160.
Murley , Diane. (2007). Instructional system program. Pensylvania : Pensylvania State University.
Mogahed, M.(2013). Planning out Pre-writing Activities. International Journal of English Literature, 4 (3), 60-68.
Nurlaila, A.P.(2013) . The Use of Mind Mapping Technique in Writing Descriptive Text.
Joural of English Education, 1 (2), 9-15.
O’Malley, J.M., Chamot, A.U. (1990). Learning strategies in Second Language Acquisition. New York : Cambridge University Press
Oxford advanced learners’ dictionary (8th edition). (2010). Oxford : Oxford University Press. Polson, K. (2004). MindMapping in Learning and Teaching: Pupil and Teacher Perspective.
Glashies, Scotland : Scottish Borders.
Riswanto & Putra, P. (2012). The Use of Mind Mapping Strategy in Teaching of Writing at SMAN 3 Bengkulu, Indonesia. International Journal of Humanities and Social Science, 2 (21), 60-68.
Siahaan, J. (2013). An Analysis of Students’ Ability and Difficulties in Writing Descriptive
Texts.(Doctoral thesis, UPI University, Bandung) Retrieved from http://repository.upi.edu/656/1/S_ING_0808966_TITLE.pdf
Supriyanto, J. (2013). The Effect of Mind Mapping Strategy on The Students’ Writing Ability. 3 (1), 184-190.
Tee, T.K., Azman, M.N.A., Mohamed, S., Muhamad, M., Yunos, J., Yee, M.H., Othman, W., (2014). Mind Mapping : An Efficient Technique for Mote-Taking. International Scholary and Scientific Research and Innovation, 8, 28-31.
Uunsen, A. 2009. Changing teachers’ attitude toward writing, teaching of writing and
assessment of writing. Retrieved from Acrobat Reader-(2009-10.pdf). September 23 2014.
Westwood,P. (2008). What teachers need to know about reading and writing difficulties. Austria : ACER Press.
42
APPENDIXES
QUESTIONNAIRE
Adik-adikku yang saya sayangi,
Saya adalah mahasiswa Fakultas Bahasa dan Sastra Inggris (FBS), Progdi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, UKSW meminta kesediaan Anda untuk mengisi kuesioner tentang aspek-aspek apa saja yang mind mapping strategi berikan untuk membantu menulis teks diskripsi.
Untuk itu saya mohon kesediaan Anda untuk meluangkan waktunya untuk mengisi kuesioner ini. Jawaban yang anda berikan tidak bernilai benar atau salah, karena itu jawablah pertanyaan dengan jujur sesuai dengan keadaan diri Anda dan pastikan tidak ada pernyataan yang terlewati. Atas kesediaannya saya ucapkan terima kasih.
Instruksi Pengisian:
Berikan tanda centang (V) pada pilihan jawaban yang sesuai dengan pendapat Anda. Adapun jawaban yang tersedia adalah sebagai berikut:
SS = Sangat Setuju
S = Setuju
TS = Tidak Setuju
STS = Sangat Tidak Setuju
NO Pernyataan SS S TS STS
1
Mind mapping strategy berguna untuk membantu proses menulis teks diskripsi.
2.
Mind mapping membantu saya mengorganisir tulisan yang saya tulis.
3.
Mind mapping berguna untuk merencanakan apa yang akan saya tulis dalam teks diskripsi.
4
43 5.
Mind mapping membantu saya mengembangkan jumlah vocabulary yang saya miliki.
6.
Mind mapping membatu saya memahami grammar yang akan saya pakai dalam menulis teks diskripsi.
7.
Mind mapping meningkatkan kreativitas saya dalam menulis teks deskripsi.
8.
Menulis paragraph deskripsi menggunakan mind mapping adalah hal menyenangkan.
9.
Mind mapping strategy membantu saya agar lebih memahami topik yang saya tulis.
10.
Mind mapping membantu saya dalam meningkatkan kualitas menulis teks diskripsi.
Jika Anda bersedia diwawancarai, dimohon untuk mengisi identitas diri Anda dibawah ini : NIS :
44 INTERVIEW QUESTIONS
1. Apakah Anda senang membuat mind mapping sebelum menulis teks diskriptif? mengapa?
2. Sebelum menggunakan mind mapping, apakah Anda pernah menemui kesulitan saat guru Anda menyuruh Anda untuk menulis ?
3. Kesulitan apa yang biasanya Anda hadapi saat menulis?
4. Biasanya hal apa yang Anda lakukan untuk mengatasi masalah tersebut?
5. Setelah mendapat strategi yang disebut dengan mind mapping strategi, apakah menurut Anda strategi ini membantu Anda dalam mengatasi masalah dalam menulis? contohnya pada hal-hal sebagai berikut :
- mengorganisir ide
- membantu merencanakan apa yang akan Anda tulis. - memahami grammar yang dipakai dalam menulis paragraf
- mencari atau menambah vocab yang akan Anda gunakan untuk menulis. - membantu mengembangkan kreatifitas menulis
- membantu menciptakan suasana yang menyenangkan dalam menulis. - membantu memahami topik yang akan ditulis.
- membantu meningkatkan kualitas menulis
45 TEACHING PROCEDURE
Class type Meeting
Date of collecting
the data Type of activity
Experimental class (8D 1st meeting Thu, 26-2-2015
Giving a pre-test to the students.
2nd
meeting Tue, 3-3-2015
Explain about descriptive text and mind mapping strategy. (treatment)
3rd
meeting Tue, 5-3-2015
Giving a post test to the students and conducting questionnaire
4th meeting
The timeline is attached bellow.
Conduct semi structured interviews to 16 students.
Control class (8C) 1st meeting Fri, 27-2-2015
Giving a pre-test to the students.
2nd
meeting Wed, 6-3-2015
Explain about descriptive text without treating them with mind mapping strategy. (conventional teaching) 3rd meeting
46 (timeline for interview)
Class type Meeting
Date of collecting
the data Type of activity
Experimental
class
(8D
1st meeting
Fri, 10-4-2015
Giving piloting interview (1 student)
2nd meeting
Wed, 15-5-2015
Interview (4 students) 3rd
meeting
Fri,17-5-2015
Interview (4 students) 4th
meeting
Fri,24-5-2015
Interview (4 students) 5th
meeting
Fri,25-5-2015
47 RUBRIC FOR WRITING TEST
Aspect
Score
Criteria
Content
1 The content is not indeed relevant with the topic at all. 2
There are many confusing things; many contents are not relevant with the topics so that the meaning cannot be easily
comprehended.
3 The content that is not relevant still exist but it is understandable and it is not too bad.
4 There are several words that are used irrelevantly but do not influence the intended meaning much.
5 The topic and the content are very relevant.
Vocabulary
1 Poor and irrelevant word; they do not fit the sentences meaning related to the topic and situation given.
2 There are still lots of words used inappropriately.
3 The words have already been related with the topic and situation; however, they do not have any variation yet.
4
The words are generally relevant with the situation and have enough variation, but there are sometimes inappropriate words, which do not change the meaning of the sentence.
5 The words used are selected and have variation; they are relevant with the situation and condition so the meaning make sense.
Generic Structure
1 The generic structure of the content is very bad and it often does not consist of orientation and resolution.
2 So many disorderliness are found in the content of the writing but don’t make the readers confused yet.
3 The generic structure of the writing is not neither too god nor too bad.
4 The generic structure of the writing is not in good, but this is actually not appropriate.
5 Every part of the writing is in good order, either in orientation, complications and resolution.
Language Feature
1 There are many irrelevant uses of descriptive language, many errors in using verbs, tense and linking words.
2 There are some irrelevant uses of descriptive language, many errors in using verbs, tense and linking words.
3 There are a little bit irrelevant but do not change the whole meaning, generally it still accepted.
4 Generally accurate, the use of descriptive languages, verb, tense and linking words.
48 RESEARCH PROCEDURE’S DIAGRAM
In collecting the data, there will be some steps that should be conducted as mentioned on the diagram bellow.
Data Collection Procedure
Conducting the pilot test
(5 Students)
Conducting pre-test for
both classes
Conducting the treatment
Conducting post test for
both classes
Conducting interview
Administering questionnaire
Pre test
Treatment
Questionnaire
Post test
Control
class
Without
mind map
Experimental class.
(All Students : 32)
Experimental class.
(16 Students)
Experimental
class
49
PRE AND POST TEST RESULT
CONTROL CLASS (8C)
No. Name Pre test Post test Progress
Score
1. Student 1 (S1-A) 40 45 5
2. Student 2 (S2-A) 55 60 5
3. Student 3 (S3-A) 45 70 25
4. Student 4 (S4-A) 35 50 15
5. Student 5 (S5-A) 40 70 30
6. Student 6 (S6-A) 35 60 25
7. Student 7 (S7-A) 55 55 0
8. Student 8 (S8-A) 45 60 15
9. Student 9 (S9-A) 30 45 15
10. Student 10 (S10-A) 30 55 25
11. Student 11 (S11-A) 30 65 35
12. Student 12 (S12-A) 55 70 15
13. Student 13 (S13-A) 35 70 35
14. Student 14 (S14-A) 45 45 0
15. Student 15 (S15-A) 50 60 10
16. Student 16 (S16-A) 55 80 25
17. Student 17 (S17-A) 35 65 30
18. Student 18 (S18-A) 55 60 5
19. Student 19 (S19-A) 40 40 0
20. Student 20 (S20-A) 35 55 20
21. Student 21 (S21-A) 50 95 45
22. Student 22 (S22-A) 40 60 20
23. Student 23 (S23-A) 45 85 40
24. Student 24 (S24-A) 25 55 30
25. Student 25 (S25-A) 30 65 35
26. Student 26 (S26-A) 45 60 15
27. Student 27 (S27-A) 45 60 15
28. Student 28 (S28-A) 55 60 5
29. Student 29 (S29-A) 50 70 20
30. Student 30 (S30-A) 50 60 10
31. Student 31 (S31-A) 35 60 25
32. Student 32 (S32-A) 30 65 30
50 EXPERIMENTAL CLASS (8D)
No. Name Pre test Post test Progress
Score
1. Student 1 (S1-B) 40 75 35
2. Student 2 (S2-B) 50 50 0
3. Student 3 (S3-B) 50 75 25
4. Student 4 (S4-B) 55 80 25
5. Student 5 (S5-B) 45 80 35
6. Student 6 (S6-B) 45 65 20
7. Student 7 (S7-B) 30 75 45
8. Student 8 (S8-B) 35 65 30
9. Student 9 (S9-B) 50 70 20
10. Student 10 (S10-B) 30 65 35
11. Student 11 (S11-B) 35 75 40
12. Student 12 (S12-B) 45 70 30
13. Student 13 (S13-B) 35 80 45
14. Student 14 (S14-B) 45 95 50
15. Student 15 (S15-B) 45 95 50
16. Student 16 (S16-B) 40 50 10
17. Student 17 (S17-B) 55 65 10
18. Student 18 (S18-B) 35 65 30
19. Student 19 (S19-B) 25 50 25
20. Student 20 (S20-B) 35 70 35
21. Student 21 (S21-B) 55 70 15
22. Student 22 (S22-B) 30 45 15
23. Student 23 (S23-B) 30 65 35
24. Student 24 (S24-B) 30 55 25
25. Student 25 (S25-B) 45 70 25
26. Student 26 (S26-B) 50 70 20
27. Student 27 (S27-B) 50 85 35
28. Student 28 (S28-B) 45 70 25
29. Student 29 (S29-B) 45 70 25
30. Student 30 (S20-B) 35 60 25
31. Student 31 (S31-B) 40 65 25
32. Student 32 (S32-B) 55 80 25
∑ (Mean) 41,71 69,37 27,81