CLASSROOM DURING SCHOOL PRACTICE PROGRAM
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By Adi Triasmara
Student Number: 091214138
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM
DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
YOGYAKARTA
i
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM
PRACTICE TEACHERS’ PROBLEMS IN MANAGING
CLASSROOM DURING SCHOOL PRACTICE PROGRAM
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By Adi Triasmara
Student Number: 091214138
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM
DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
YOGYAKARTA
iv
“When everything seems to be going against you, remember that the
airplane takes off against the wind, not with it.”
(Henry Ford)
I DEDICATE THIS THESIS TO
MY BELOVED FAMILY
vii
ABSTRACT
Triasmara, Adi. (2013). English Language Education Study Program Practice Teachers’ Problems in Managing Classroom during School Practice Program. Yogyakarta: Sanata Dharma University.
School Practice Program is one of the compulsory subjects that must be taken by all English Language Education Study Program (ELESP) Sanata Dharma University students. The School Practice Program requires its students, who are called practice teachers, to do teachers‟ job at school. Managing classroom, which aims to create conducive learning atmosphere, is one of the jobs that a practice teacher does during the program. As stated in Keengwe and Boateng (2002), problems about classroom management may emerge during the program since teaching in a real classroom is a new experience for the practice teachers.
In this research, the researcher focused on the classroom management problems. This research attempted to answer two research problems, namely, 1) What are the ELESP practice teachers‟ problems in managing classroom during the School Practice Program? and 2) What are the possible solutions to the ELESP practice teachers‟ problems in managing classroom during the School Practice Program?
To answer the research problems, the researcher employed descriptive research and used a survey as the research design. A questionnaire and an interview were the instruments used in the research. There were 88 respondents, for the questionnaire, and 6 respondents, for the interview. The respondents were the English Language Education Study Program students in the academic year 2009, who had taken or had been taking the School Practice Program. The questionnaire consisted of 25 close-ended questions and one open-ended question. Meanwhile, the interview consisted of four questions used to verify the questionnaire results and to answer the second research problem.
The results of the research showed that the ELESP practice teachers had problems in handling classroom activities and problems in improving working conditions during the School Practice Program. Moreover, there were also other problems that could be classified into three categories, namely, problems arising from the students, problems arising from the practice teachers, and problems arising from the school facilities. Furthermore, setting rules, giving rewards and using games were three major possible solutions to the ELESP practice teachers‟ problems in managing classroom. Finally, the researcher also gave recommendations for the ELESP lecturers, for the ELESP students, and for the further researchers.
viii
ABSTRAK
Triasmara, Adi. (2013). English Language Education Study Program Practice Teachers’ Problems in Managing Classroom during School Practice Program. Yogyakarta: Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Program Pengalaman Lapangan (PPL) merupakan salah satu mata kuliah wajib bagi mahasiswa Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris (PBI), Universitas Sanata Dharma. Program tersebut mewajibkan mahasiswanya, yang disebut praktikan, untuk melakukan pekerjaan guru di sekolah tingkat menegah dan atas. Melakukan manajemen kelas merupakan salah satu pekerjaan guru yang harus dilaksanakan oleh praktikan. Keengwe dan Boateng (2002) menyatakan jika masalah mengenai manajemen kelas mungkin muncul selama program karena mengajar di sekolah merupakan pengalaman baru bagi praktikan.
Dalam penelitian ini, fokus peneliti ada pada masalah-masalah manajemen kelas. Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk menjawab dua rumusan masalah, yaitu, 1) Masalah manajemen kelas apa yang dialami oleh praktikan PBI selama menjalani Program Pengalaman Lapangan? dan 2) Apa solusi yang memungkinkan untuk menyelesaikan masalah manajemen kelas yang dialami oleh praktikan PBI selama menjalani Program Pengalaman Lapangan?
Peneliti menerapkan penelitian deskriptif dan menggunakan survey sebagai desain penelitian. Kuisioner dan wawancara merupakan instrumen penelitian yang digunakan. Ada sebanyak 88 responden, untuk mengisi kuisioner, dan 6 responden, untuk menjawab pertanyaan wawancara. Responden dalam penelitian ini merupakan para mahasiswa PBI angkatan 2009 yang sudah atau sedang menjalani PPL. Kuisioner penelitian terdiri dari 25 pertanyaan tertutup dan satu pertanyaan terbuka. Sedangkan, ada empat pertanyaan yang digunakan dalam wawancara untuk memastikan hasil kuisioner dan mendapatkan data lebih jauh.
Hasil penelitian menunjukkan bahwa praktikan PBI mengalami masalah menangani aktifitas kelas dan memperbaiki kondisi kerja. Selain itu, ada juga masalah lain yang dapat diklasifikasikan ke dalam tiga kategori, yaitu masalah yang muncul dari siwa, masalah yang muncul dari praktikan, dan masalah yang muncul dari fasilitas sekolah. Selanjutnya, penentuan aturan, pemberian apresiasi, dan penggunaan permainan merupakan tiga solusi utama guna menyelesaikan masalah manajemen kelas. Peneliti juga memberikan saran bagi dosen PBI, mahasiswa PBI, dan calon peneliti.
ix
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
First of all, I would like to say Alhamdulillah. I would like to thank the one and only Allah SWT, the most gracious and the most merciful God. I thank Allah SWT for the blessing, help, and guidance so that I can pass all the processes in the Sanata Dharma University Yogyakarta, including finishing my thesis.
Second, I would like to say that I am truly indebted to my major sponsor, Caecilia Tutyandari, S.Pd., M.Pd. I thank her for all her time, guidance, support, and patience to help me complete my thesis in the best way. Moreover, I also thank the proof readers of my thesis for the time and the advice given to me. My deepest gratitude also goes to all the ELESP lecturers who have helped me getting precious knowledge, values and experiences during my study time at the ELESP Sanata Dharma University Yogyakarta. In addition, I would like to thank the ELESP secretariat staff and the Sanata Dharma University Yogyakarta library staff.
Third, my sincere thanks go to the eighth semester students, academic year 2009 of the ELESP Sanata Dharma University Yogyakarta, who have allocated their time to participate in the process of finishing my thesis. Without their great participation, it would have been impossible to finish my thesis.
x
completing my thesis. In addition, I thank my family for all their affection, care, advice, support, and prayers.
Fifth, I would also like to thank my true best friend, Catharina Dyah Pusparini, and all my other best friends, Akbar, Benni, Aby, Adin, Jajank, Vivin, Egin, Wella, Leo, Wanda, and Br. Markus; my School Teaching Program group in SMA 11 Yogyakarta; my KKN group in Sruni; my “The Travelers” Play Performance group; my seniors; my juniors; and all of my colleagues in the Sanata Dharma University Yogyakarta. I thank them for all the support, the advice, and the unforgettable experiences that we have shared and experienced together.
At last, I would like to express my gratitude to anybody whom I cannot mention one by one that supports me in the completion of my thesis.
xiii
LIST OF TABLES
Table
C1. Questionnaire Blueprint ………... 26
D1. Percentage Results of Questionnaire Part A Number 1-5 ……….. 39
D2. Percentage Results of Questionnaire Part A Number 6-10 ……… 40
D3. Percentage Results of Questionnaire Part A Number 11-15 ……….. 42
D4. Percentage Results of Questionnaire Part A Number 16-20 ……….. 43
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter is an introductory chapter that includes six sections, which are
research background, research problems, problem limitation, research objectives, research benefits, and definition of terms, to be described and analyzed. In the research background, the researcher provides the reason why he conducts the research and why he chooses the English Language Education Study Program (ELESP) practice teachers‟ problems in managing classroom during a School Practice Program as his topic in this research. In research problems, the researcher mentions the research questions used in this research. In problem limitation, the researcher describes the limitation of the research so that the researcher can focus on the things that are surely needed to be described and analyzed. In research objectives, the researcher explains the objectives of the research. In research benefits, the researcher mentions the benefits that can be gained through the research. Furthermore, the researcher explains the definition of the terms used in the research in definition of terms section.
A. Research Background
apply them in a real classroom teaching in a high school. The students who take the School Practice Program, who are named as the practice teachers in this research, need to do the teacher‟s jobs at a high school such as planning, developing, and organizing lessons, record keeping students‟ tasks, managing
classroom, presenting subject materials, assessing student learning, and meeting professional obligations (Kelly, n.d.). Teaching in a real classroom is a new experience for the practice teachers; therefore, the practice teachers can be categorized as the beginning teachers. As it is mentioned in the United States Code 2000, the beginning teachers are those who teach in a public school for less than three complete school years. Keengwe and Boateng (2002) mention that although the beginning teachers generally feel the excitement of joining a teaching profession, it is very likely that they experience multiple challenges related to the profession that they take as teachers. In addition, Keengwe and Boateng (2002) also state that the beginning teachers‟ problems are about the delayed payment of salaries, problems about the classroom management and assessment, and inadequate learning materials. Furthermore, Rohani (2004) notes that there are two major problems in a classroom, which are teaching problems and classroom management problems. However, in this research, the researcher focuses on the practice teachers‟ problems in managing classroom during the School Practice
Program.
in SMA Negeri 11 Yogyakarta from July up to October, 2012. The researcher experienced three classroom management problems during the School Practice Program. Those problems are about a noisy class, the less-motivated students, and a lack of classroom rules. In addition, based on the observation on the guiding teacher (guru pamong) and on another practice teacher during the School Practice Program, the researcher succeeded in finding out the other classroom management problems like problems about students‟ disruptive behavior, problems about
students‟ lateness, and problems about the incomplete school facilities.
There are two main reasons that make the researcher only focus on the practice teachers‟ problems in managing classroom during the School Practice Program. The first reason is that classroom management plays a big role in the successful teaching and learning process in a classroom. Brophy and Everston (1976) mention that teachers‟ skill in managing a classroom is very important to
determine a teaching success. They say that a teacher who has inadequate skill in classroom management is quite unlikely to accomplish a teaching success, whether it is measured from student learning or by student rating. Therefore, having good classroom management skill is very crucial for every teacher, including every beginning teacher, to accomplish a teaching success. Moreover, Usman (2006) notes that students‟ achievement will be optimum when a teacher
management and classroom discipline in order to have effective classroom management. By having behavior management and classroom discipline, teachers can also avoid the stress and symptoms of burnout that come from an ineffective classroom. In conclusion, based on the two statements mentioned above, it is undeniable that classroom management has a big effect on a successful teaching and learning process in a classroom. The teachers and also the practice teachers, who are known as the teacher candidates, need to be able to manage a classroom well so that they can address students‟ need effectively.
The second reason why the researcher focuses on the practice teachers‟ problems in managing classroom during the School Practice Program is that there is a possibility that the practice teachers have problems to manage a classroom since they are still lack of experience in teaching in a real classroom. New teachers who may have a lack of experience in teaching tend to be reactive to students‟ inappropriate behavior in classroom and then remove students from
B. Research Problems
In order to find out the practice teachers‟ problems in managing classroom during the School Practice Program, two research questions are raised in this research. Those two research questions are:
1. What are the English Language Education Study Program (ELESP) practice teachers‟ problems in managing classroom during the School Practice
Program?
2. What are the possible solutions to the English Language Education Study Program (ELESP) practice teachers‟ problems in managing classroom during
the School Practice Program?
C. Problem Limitation
In accordance with the problem formulations above, this research focuses on the English Language Education Study Program practice teachers‟ experience in
D. Research Objectives
The researcher conducts this research in order to find out and to identify the English Language Education Study Program practice teachers‟ problems in managing classroom during the School Practice Program. In addition, related to the questions mentioned in the problem formulations, this research also aims to find possible solutions to the practice teachers‟ problems in managing classroom during the School Practice Program.
E. Research Benefits
The research brings many benefits for the lecturers of ELESP Sanata Dharma University, the practice teachers, the future practice teachers, and the future researchers.
1. ELESP Lecturers
2. ELESP Practice Teachers
This research is also beneficial to the ELESP practice teachers. As a subject of this research, they need to find the classroom management problems that they experience and to identify the possible solutions to those problems during the School Practice Program by filling the questionnaire designed by the researcher. Therefore, they can indirectly make careful reflection about the classroom management problems that they have experienced during the School Practice Program. Moreover, the ELESP practice teachers, who are the teacher candidates, are expected to be able to learn about how to solve problems in managing classroom when the ELESP practice teachers become real teachers in the future. 3. Future ELESP Practice Teachers
The researcher expects that this research also gives benefits to the future ELESP practice teachers, who are the ELESP students that have not taken the School Practice Program. By presenting the ELESP practice teachers‟ problems in managing classroom and the possible solutions to those problems, it is expected that the future ELESP practice teachers can anticipate the classroom management problems that may emerge during the School Practice Program. Therefore, the future ELESP practice teachers are expected not to have the same problems as the ELESP practice teachers who have previously done the School Practice Program. 4. Future Researchers
recommendations for the future researchers so that the future researchers can have more detailed research. It is expected that this research, which can be used as a reference, can be useful for the future researchers to finish their research.
F. Definition of Terms
The researcher gives the definition of terms used in this research to help the readers understand the meaning of the terms used. Therefore, the readers can understand the ideas of the research well.
1. School Practice Program
The School Practice Program is one of the obligatory subjects to be taken by the students of the Teachers Training and Education Faculty, Sanata Dharma University, which includes the students of the English Language Education Study Program. This subject aims to help the students, who are the teacher candidates, to prepare their readiness to work at school as the real teachers in the future. In this research, the term School Practice Program refers to the school program that needs to be taken by the English Language Education Study Program students. 2. ELESP Practice Teachers
term practice teachers in this research refers to all ELESP students who have taken or have been taking the School Practice Program, either in the seventh or in the eighth semester.
3. Classroom Management
Oliver and Reschly (2007) state that the word classroom management refers to the teachers‟ ability to organize classrooms and to manage their students‟
behavior. Moreover, classroom management is also defined as the process of organizing and conducting a class so that it runs smoothly (Clark and Starr, 1991). Furthermore, Rohani (2004) mentions that the term classroom management refers to all the teaching and learning activities in the classroom that create conducive learning atmosphere. In addition, Orlich at al. (2007) define classroom management as the teachers‟ methods of establishing organization, disciplinary
10
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
This chapter provides the theories related to this research. This chapter consists of two sections, which are theoretical description and theoretical framework. The first section, which is the theoretical description, provides a review of some relevant theories and similar research. Meanwhile, the second section, which is the theoretical framework, provides a summary of all related theories and similar research put in the theoretical description.
A. Theoretical Description
There are three different major points explained in this section. Those three points are the theories on the effective teacher, the theories on classroom management, and a brief summary of the research on classroom management.
1. Effective Teacher
a. Definitions of Effective Teacher
able to assess the progress of his students. In addition to the two definitions that are previously mentioned, an effective teacher is a teacher who is able to motivate his students to learn because the students are aware of the importance of learning, not because they are afraid of the teacher (Darhim, n.d.).
b. Characteristics of Effective Teacher
There are some characteristics that need to be possessed by a teacher in order to successfully make himself an effective teacher. One of those characteristics is related to the teachers‟ ability to manage a classroom. As cited in Wong and
Wong (2010), Good and Brophy (1973) mention that there are three characteristics of the effective teachers. Those characteristics are that teachers are extremely good classroom managers, teachers know how to teach a lesson for student learning and mastery, and teachers have positive expectations for a student success. Therefore, the first characteristic that needs to be possessed by effective teachers is about the classroom management. Teachers need to be extremely good classroom managers. The second characteristic is related to the teachers‟ ability to
teach so that the students can learn and master the teaching materials. Meanwhile, the third characteristic is that the teacher should believe in the students‟ success.
Torff (2005), as cited in Wong and Wong (2010), also has similar characteristics of effective teachers. He mentions that effective teachers should possess classroom management skills, possess lesson implementation skills, and have ability to establish rapport with students. Furthermore, Wong and Wong (2010) state that classroom management, lesson mastery, and positive expectations are three characteristics of an effective teacher. Based on the theories above, therefore, it is undeniable that the ability to manage a classroom is immensely important for teachers, including the practice teachers.
Further, based on the Indonesian Law of National Education No. 14/2005 Chapter 4, four competences must be possessed by a teacher. Those competences are a pedagogical competency, a personal competency, a social competency, and a professional competency. The pedagogical competency refers to the teacher‟s ability to design, to conduct, and to evaluate a teaching. Moreover, it also refers to the teacher‟s ability to make the students able to make use of their biggest
potential in learning. The personal competency refers to the teacher‟s characteristics as someone who is mature, stable, wise, and commanding. The social competency refers to the teacher‟s ability to communicate and to build a good relation with students, colleagues, and society. Meanwhile, the professional competency refers to the teacher‟s mastery of the subject matter and on the school
curriculum.
2.Classroom Management
five important aspects are: 1) the definitions of classroom management, 2) the importance of classroom management, 3) the goals of classroom management, 4) the factors influencing a classroom management success, and 5) the specific problems of classroom management.
a. Definitions of Classroom Management
The term classroom management has been defined in many different ways by teachers and researchers. As cited in Risk (1958), the term classroom management is closely related to the actions and strategies applied by the teachers to maintain order (Doyle, 1986). In addition, as cited in Yasar (2008), classroom management is defined as a term that describes all teacher efforts to oversee the classroom activities classroom including learning, social interaction, and student behavior (Martin, Yin, & Baldwin, 1998). They believe that the term classroom management has three dimensions, which are instructional management, people management, and behavior management.
The instructional management dimension is based on the daily routines of the classroom and allocation of materials. The people management dimension is centered on how the teacher perceives the students and how they view their relationship with the students. The final dimension, behavior management, is somewhat similar to the concept of classroom discipline but differs in that it focuses on a teacher‟s pre-planned methods of preventing misbehavior, rather than simply on their reaction to it once it occurs (p. 2).
Furthermore, as it is mentioned in the definition of terms in the Chapter I, Oliver and Reschly (2007) state that the term classroom management refers to the teachers‟ ability to organize classrooms and to manage the behavior of their
b. Importance of Classroom Management
It is mentioned by Kauchak and Eggen (2011) that classroom management is important to teachers and to general public.
For teachers, effective classroom management creates an environment in which they can teach and students can learn. For the public at large, effective classroom management is a clear, visible sign that schools and teachers are in charge and know what they‟re doing. (p.2)
Therefore, classroom management does not only have an impact for teachers, but also for public at large. In addition, as cited in Oliver and Reschly (2007), the inability of teachers to effectively manage classroom behavior often contributes to the low achievement of at-risk students (Donovan & Cross, 2002; Harrell, Leavell, van Tassel, & McKee, 2004). Therefore, having been able to manage a classroom is important to teachers. Teachers can create a positive learning environment, which means that they can teach and their students can learn well, when they are able to manage their classroom effectively. Moreover, students‟
achievement also becomes one of things affected by the teachers‟ ability to manage classroom.
c. Goals of Classroom Management
The description of each goal stated by Kauchak and Eggen (2011) can be seen as follows:
1) Creating a Positive Classroom Climate
It is explained in the book that the term positive classroom climate refers to the students‟ feeling in the classroom. When the classroom climate in the
classroom is positive, students feel physically and emotionally safe, feel connected to their teachers and peers, and are worthy of love and respect.
2) Creating a Community of Learners
3) Developing Learner Responsibility
Students need to be responsible for every action that they do. Teachers need to help students understand that they are responsible for creating a positive learning environment. Teachers need to make students obey the classroom rules because the rules make sense, not because they are afraid of punishments. Students must feel that the rules are made to protect their rights and others‟.
4) Maximizing Opportunities for Learning
Extending the school year and the school day becomes one of the ways to maximize time for learning. However, as cited in Kauchak and Eggen (2011), it is not as simple as it appears on the surface, because simply allocating more time to a topic may not result in significant increases learning (Weinstein & Mignano, 2007). In addition, there are four dimensions of time in the classroom. They are: 1) allocated time, 2) instructional time, 3) engaged time, and 4) academic learning time.
d. Factors Influencing a Classroom Management Success
Suryana (2006) mentions that there are two major factors that can support
teachers to have a classroom management success. Those two major factors are physical and socio-emotional factors. The description about each factor can be seen as follows:
1) Physical Factor
in the classroom that are categorized as a physical factor influencing a classroom management success. Those four physical conditions are the classroom itself, the seating arrangement, the ventilating and lighting adjustment, and the stuffs storage arrangement.
2) Socio-emotional Factor
In contrary to the physical factor, the socio-emotional factor refers to the non-physical conditions that affect the teaching and learning process, the students‟
motivation, and the effectiveness in reaching the learning goals. In this factor, there are four aspects that are important. Those aspects are the teacher‟s leadership, the teacher‟s behavior, the teacher‟s voice, and the teacher-student
relationship in the classroom.
e. Specific Problems in Classroom Management
There are five specific problems in classroom management (Risk, 1958). Those specific problems are: 1) handling attendance, 2) handling instructional materials, 3) handling classroom activities, 4) regulations of physical conditions, and 5) improving working conditions. Therefore, here is a brief description of each problem above:
1) Handling Attendance
the class early, that student should show the admit slip quickly at the beginning of the class so that there is no interruption in the middle of a teaching process.
2) Handling Instructional Materials
Ineffective handling instructional materials can cause a waste of valuable time in the classroom. Teacher needs to decide what routine or procedure related to the activity of handling instructional materials considered to be effectively and efficiently applied in the classroom. For instance, a teacher may assign his students to have a duty to distribute heavy materials like reference books or workbooks.
3) Handling Classroom Activities
One general principle of handling classroom activities is that teacher should realize the fact that all classroom activities should be able to facilitate the teacher and the students to reach the learning objectives. The application of certain routines is highlighted in this point. Certain routines are applied to prevent confusion and waste of time and effort in the classroom activities. The school bell that signals the teacher to ask his students to be ready to work in their own seats is one of the examples of how teacher handles classroom activities.
4) Regulations of Physical Conditions
get enough light so that teachers need to turn on the lights to help those students learn without lighting problem.
5) Improving Working Conditions
In this point, it is emphasized that teachers need to give their attention to student practices or activities that may disrupt the effectiveness of classroom work. For example, a teacher needs to tell students that they are not allowed to have unnecessary books, papers, or other materials that are not related to the subject matter on hand. If it is known that students truly need to bring those things, teachers must ensure that those things are placed out of the way so that they do not disrupt classroom activities.
3.Research on Classroom Management
The third point of the theoretical description part is about the research on classroom management. The research, which is briefly explained in this point, is on classroom management issues for teaching assistants in the United States, on a case study of classroom management in Singapore, and on classroom management problems, reasons, and solutions in the Information Technology class.
a. Classroom Management Issues for Teaching Assistants
researchers got 304 usable responses. For those responses, the researchers succeeded to find the top fifteen classroom management problems experienced by Teaching Assistants in the United States. Some of the problems were: 1) student comes to class unprepared, 2) student arrives late for class, 3) student is eating and/or drinking during class, 4) student packs up books before the class session is to end, 5) etc.
b. Classroom Management: A Case Study
This research was conducted by Professor Fan Yi in Singapore. In this research, he aimed to prove that effective classroom management in an English language class is meant to create a positive classroom climate for learning. To have that aim reached, the researcher conducted a case study by recording some classroom management problems in the English language class and evaluating the strategies related to the problems.
The findings of the research showed that there were three major classroom management problems in the English language class. Those problems were: 1) tense class atmosphere, 2) poor motivation, and 3) poor participation. Furthermore, the researcher believed that remedial strategies are appropriate to solve those problems.
c. A Qualitative Study on Classroom Management and Classroom Discipline
Problems, Reasons, and Solutions: A Case of Information Technology
Class
aimed to find the classroom management problems faced by Information Technology teachers and to reveal the underlying reasons and the possible solutions to the problems. The subjects of this study were 14 school administrators, 14 teachers, and 17 parents. The data were collected through an interview.
After the data were analyzed, it could be concluded that the classroom management problems faced by Information Technology teachers in Turkey were about lack of motivation, breaking the rules and routines, and lack of hardware in classrooms (Erdogan et al., 2010). Meanwhile, classroom environment, classroom size, insufficient time management, a lack of rules, and a lack of teachers‟ management skills became the underlying reasons of those problems. Furthermore, the possible solutions tothe problems were related to the improvement in teacher qualification, giving punishment, ignoring misbehavior, understanding reasons behind the problems, and meeting with parents.
B. Theoretical Framework
The aims of this research are to find the ELESP practice teachers‟ problems in managing classroom during the School Practice Program and to find the possible solutions to those problems. The researcher gives the explanation of the theoretical framework used in the research as follows in order to show the contribution of each theory in the theoretical description part.
manage a classroom well is one of the characteristics that must be possessed by effective teachers. Moreover, since this research is closely related to the term classroom management, the researcher provides general information about classroom management in the theoretical description as a basic theory of this research. The theory about the definition of classroom management, the importance of classroom management, the goals of classroom management, and the factors influencing a classroom management success are used to give the readers a view that the issue about classroom management is important since the effect of classroom management is significant to the teaching and learning activity. Furthermore, the researcher also includes a theory about specific problems in classroom management. The researcher includes this theory to guide him to make the research instruments used in this research.
Afterwards, the researcher summarizes similar research on problems in classroom management. The summary of the research in the theoretical description helps the researchers to develop the research instruments of this research.
23
CHAPTER III
METHODOLOGY
This chapter describes the methodology of this research. Furthermore, this chapter is divided into six parts, which are research method, research setting, research participants, instruments and data gathering technique, data analysis technique, and research procedure.
A.Research Method
Due to the fact that this research aims to find what the English Language Education Study Program practice teachers‟ problems in managing classroom during the School Practice Program are and to find what the possible solutions to the problems are, the researcher used descriptive research. As it is mentioned by Gall, Gall, and Borg (2007), descriptive research is a type of quantitative research that involves making careful descriptions of educational phenomena. In addition, they also mention that descriptive studies are concerned with determining the “what is” research questions, such as what have been the reactions of school
administrators to innovations in teaching physical science? or what kind of activities typically occur in sixth-grade art classes.
collecting information from a sample. Moreover, the survey used in this research is a cross-sectional survey that included questionnaire and interview as the research instruments to collect the data. Gall, Gall, and Borg (2007) mention that questionnaires and interviews can be used to collect data about phenomena that are both observable and not directly observable such as inner experience, opinions, values, and the like.
Therefore, in this research, the researcher collected the data used in the research by asking questions, in form of questionnaire and interview, to a group of people that was called as a sample. While the questionnaire was used to answer the first research problem, the interview was mainly used to answer the second research problem. In addition, the data gathered in this research were the numeric data, which were gathered from the close-ended questionnaire, and the textual data, which were gathered from the open-ended questionnaire and the interview.
B.Research Setting
C.Research Participants
Ary, Jacobs, and Sorensen (2010) mention that studying a very large population in a survey is often difficult or even impossible. Thus, researchers need to select a sample, which is a smaller portion of the population for the study.
In this research, the researcher also selected a sample of the population, which consisted of the eighth semester students of the English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University in the academic year of 2009, who have taken or have been taking the School Practice Program. The participants of the research were 88 students, who were randomly chosen from the population. In choosing the sample of the study, the researcher employed probabilistic simple random sampling.
D. Instruments and Data Gathering Technique
1. Instruments
There were two instruments used in this research. Those instruments were a questionnaire and an interview.
a. Questionnaire
A set of questionnaire consisting of close-ended and open-ended questions was set to answer the first research problem. The questionnaire was divided into two parts, which were part A and part B. In Part A, the researcher put some possible problems about the classroom management. The possible problems listed in Part A were categorized into five categories as follows:
Table C1. Questionnaire Blueprint
Question No. Category Description
1 – 5 Handling Attendance These five statements gathered information about whether or not the practice teachers have problems in handling attendance during the School Practice Program.
6 – 10 Handling Instructional Materials
Question No. Category Description
11 – 15 Handling Classroom Activities
These five statements gathered information about whether or not the practice teachers have problems in handling classroom activities during the School Practice Program.
16 – 20 Regulations of Physical Conditions
These five statements gathered information about whether or not the practice teachers have problems about the regulations of physical conditions during the School Practice Program.
21 – 25 Improving Working Conditions
These five statements gathered information about whether or not the practice teachers have problems in improving working conditions during the School Practice Program.
this option did not give significant contribution to the research. In addition, as cited in Tsang (2012), Kulas, et al. (2008) claim that the option neither agree nor disagree may not really represent the opinion of “neither agree nor disagree.” Therefore, there were only four options in Part A questionnaire used in this research. Those options were strongly agree (SA), agree (A), disagree (D), and strongly disagree (SD).
In Part B, it was a type of open questionnaire with an open-ended question in which the participants were free to write their idea about the other classroom management problems that they experienced during the School Practice Program.
b. Interview
The use of interview in this research was to verify the questionnaire result and to answer the second research problem, which is related to the possible solutions to the classroom management problems found in the first research problem. There were four questions used in the interview in order to help the researcher find the answer of the second problem. The interview questions and results then could be seen on the appendices.
2. Data Gathering Technique
Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University in the academic year of 2009, who have taken or have been taking the School Practice Program. Furthermore, the researcher also conducted an interview with six students who were randomly chosen.
The questionnaire was aimed to answer the first research problem, which is related to the English Language Education Study Program practice teachers‟ problems in managing classroom during the School Practice Program. Meanwhile, the interview was used to answer the second problem in this research which is related to the possible solution to the classroom management problems.
E. Data Analysis Technique
The data gathered from the questionnaire were the data to answer the first research problem, which is about the English Language Education Study Program practice teachers‟ problems in managing classroom during the School Practice
Program. Meanwhile, the data gathered from the interview were used to answer the second problem, which is about the possible solution to the classroom management problems emerged. The data gathered from the questionnaire were counted, displayed in table, interpreted, and described in a detailed description. Then, the data from interview were interpreted and represented in form of a description in order to help the readers understand the findings.
have taken or have been taking the School Practice Program. The questionnaire distributed consisted of two parts, which were Part A and Part B. In Part A, there were four degrees of participants‟ responses to the statements used in the
questionnaire. Those four degrees were: 1 that represented strongly disagree (SD), 2 that represented disagree (D), 3 that represented agree (A), and 4 that represented strongly agree (SA). Meanwhile, in Part B, the participants were free to write the other classroom management problems that they experienced during the School Practice Program. After getting the data from the questionnaire, the researcher counted the percentage of each answer, presented the data in tables, interpreted the data, and gave a description about the findings to make it more understandable. Moreover, the researcher used formula χ = 100% to count
the percentage of the data in the close-ended questionnaire. „Mean‟ was represented by the symbol χ. Meanwhile, ∑x represented total answers and N
represented total respondents.
results of the interview in a form of a description in order to make the readers easier to understand the research findings.
F. Research Procedure
In conducting this research, the researcher followed the six basic steps in the survey research proposed by Ary et al. (2010). Those six basic steps are: (1) planning; (2) defining the population; (3) sampling; (4) constructing the instrument; (5) conducting the survey; and (6) processing the data. Based on those six based steps, the detailed procedure of this research could be seen as follows: 1. Planning
At the beginning of the research, the researcher selected a problem related to the problems in education, especially the educational problems in the English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University. Then, the researcher decided to select classroom management problems emerged during the School Practice Program as the topic of this research. After having consultation with the sponsor, the researcher formulated two research problems used in the research. Furthermore, the researcher also read related literatures in form of books, journals and paper to get the theories on classroom management.
2. Defining the Population
year of 2009 that have taken or have been taking the School Practice Program. It was because there was a possibility that they experience classroom management problems during the School Practice Program.
3. Sampling
The sample was the eighth semester students of the English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University the academic year of 2009 that have taken or have been taking the School Practice Program. The sample was representative because the researcher wanted to conduct a survey about the English Language Education Study Program practice teachers‟ problems in managing classroom during the School Practice Program. However, because of the time limitation, the researcher decided to pick 88 students out of 160 students in total as the sample of this research.
4. Constructing the Instrument
The researcher decided to use the questionnaire and the interview to gain the data needed in this research. There were two parts in the questionnaire used in this research. The first part, which was Part A, was a close-ended questionnaire that required the participants to choose whether they were strongly agree, agree, disagree, or strongly disagree on the statements in the questionnaire. Meanwhile, the second part, which was Part B, was an open-ended questionnaire that required the participants to write down the other classroom management problems that they experienced during the School Practice Program.
decided the theory that could be used as the underlying literature to make the questionnaire. Then, the researcher generated the statements for the questionnaire based on the theory used. Adjusting the questionnaire format was the next step. The researcher decided the cover, the font, and the layout of the questionnaire. After that, the researcher consulted his questionnaire to his sponsor to gain feedback. Then, the researcher conducted a pilot test to ten participants of the sample to check whether or not the statements were clear and whether or not the questionnaire could answer the problems of the research. After doing a pilot test, the researcher revised his instruments based on the ten selected participants‟ comments. Then, the researcher conducted another pilot test. After getting a positive result from the second pilot test, the researcher considered the questionnaire fixed.
from the respondents about the general thing that the practice teacher needed to do to cope with the classroom management problems emerging in the classroom. 5. Conducting the Survey
The survey was conducted by distributing the questionnaire and conducting the interview. The questionnaires were distributed on March 18, 2013. The researcher gave an explanation about the purpose and the significance of the survey. Then, the researcher gave the participants about 15-20 minutes to fill the questionnaire. After the data from the questionnaire were successfully collected, the researcher conducted the interview with six participants, who were randomly chosen, on May 30, 2013.
6. Processing the Data
35
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
This chapter presents and discusses the research results obtained from the research. This chapter also answers the problems in this research, which are what the English Language Education Study Program (ELESP) practice teachers‟ problems in managing classroom during the School Practice Program are and what the possible solutions to the problems are. The researcher distributed the questionnaires and interviewed six respondents in order to obtain the research findings.
A. English Language Education Study Program (ELESP) Practice Teachers’ Problems in Managing Classroom during the School Practice Program
In order to answer the first problem of the research, which is about the English Language Education Study Program practice teachers‟ problems in managing classroom during the School Practice Program, the researcher used a questionnaire as the research instrument.
1. Data Presentation
a. Data Presentation of the Close-Ended Questionnaire
The close-ended questionnaire consisted of 25 items that were classified into five parts. The statements and the classifications of the close-ended questionnaire were based on the theory from Risk (1958). He classifies classroom management problems into five parts, which are about handling attendance, handling instructional materials, handling classroom activities, regulations of physical conditions, and improving working conditions. The researcher put five items on each classification so that the total items in the close-ended questionnaire were 25. The reason why the researcher adapted the Likert scale instead of using the yes-no type of questionnaire was because the researcher wanted to know the agreement level of the respondents with the statements provided in the close-ended questionnaire. There were four responses provided in the close-close-ended questionnaire, which were: 1. strongly disagree (SD), 2. disagree (D), 3. agree (A), and 4. strongly agree (SA). Furthermore, the statements provided in the close-ended questionnaire were all positive. They consisted of the things that the practice teachers might do in order to avoid the classroom management problems. Therefore, from the results of the questionnaires, the researcher categorized the results as follows:
Disagree : The practice teachers found that they did not always do or did not always have the item on the questionnaire so that it was likely for the practice teachers to experience classroom management problems.
Agree : The practice teachers found that they commonly did or had the item on the questionnaire so that it was unlikely for the practice teachers to experience classroom management problems.
Strongly Agree : The practice teachers found that they always did or had the item on the questionnaire so that it was very unlikely for the practice teachers to experience classroom management problems.
However, to come up with the categorization above, the researcher had checked 20 % of the respondents, which meant 18 respondents, whether or not the respondents had the same point of view as the researcher. After the researcher checked the respondents‟ point of view about the items and the results of the questionnaire, the researcher concluded that the researcher and the respondents had the same point of view to analyze the questionnaire data. The respondents agreed that if the items on the questionnaire were not experienced by the practice teachers, classroom management problems were likely to happen.
1. Handling Attendance
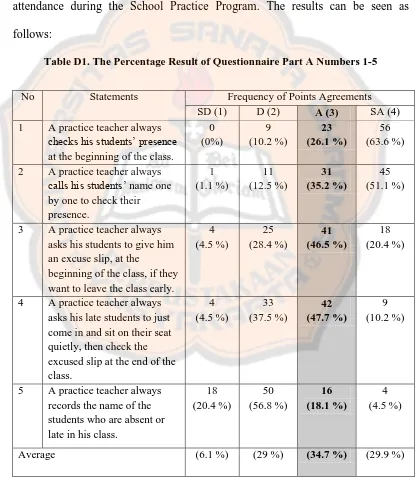
The first classification of classroom management problems was about handling attendance. This classification was related to the administrative procedures and attendance regulations. Therefore, the researcher set five items for this part to know whether or not the practice teachers had problems in handling attendance during the School Practice Program. The results can be seen as follows:
Table D1. The Percentage Result of Questionnaire Part A Numbers 1-5
No Statements Frequency of Points Agreements
SD (1) D (2) A (3) SA (4)
1 A practice teacher always
checks his students‟ presence
at the beginning of the class.
0
2 A practice teacher always
calls his students‟ name one by one to check their
3 A practice teacher always
asks his students to give him an excuse slip, at the
beginning of the class, if they want to leave the class early.
4
4 A practice teacher always
asks his late students to just come in and sit on their seat quietly, then check the excused slip at the end of the class.
5 A practice teacher always
Based on the data of the questionnaire, 34.7 % of the 88 practice teachers answered „agree‟ to the items in the questionnaire numbers 1 up to 5, which meant
it was unlikely for the practice teachers to have classroom management problems related to the handling attendance. While 29.9 % of the 88 practice teachers answered „strongly agree‟ to the items in the questionnaire numbers 1 up to 5,
which meant that it was very unlikely for the practice teachers to have handling attendance problems.
2. Handling Instructional Materials
The second classification of the classroom management problems was about the handling instructional materials. This classification was closely related to the teachers‟ routines to handle the instructional materials. Risk (1958) mentions that
much valuable time might be wasted because of an ineffective handling of instructional materials. In order to know whether or not the practice teachers experienced problems in handling instructional materials during the School Practice Program, the researcher put five items related to the activities of handling instructional materials in this classification. The results of the questionnaire for the second classification of the classroom management problems can be seen as follows:
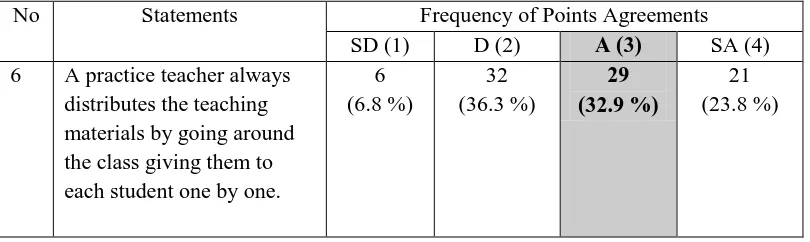
Table D2. The Percentage Result of Questionnaire Part A Numbers 6-10
No Statements Frequency of Points Agreements
SD (1) D (2) A (3) SA (4)
6 A practice teacher always
No Statements Frequency of Points Agreements
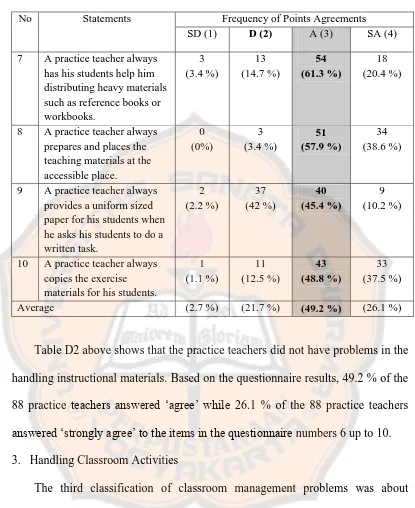
SD (1) D (2) A (3) SA (4)
7 A practice teacher always
has his students help him
8 A practice teacher always
prepares and places the
9 A practice teacher always
provides a uniform sized
10 A practice teacher always
copies the exercise
Table D2 above shows that the practice teachers did not have problems in the handling instructional materials. Based on the questionnaire results, 49.2 % of the 88 practice teachers answered „agree‟ while 26.1 % of the 88 practice teachers answered „strongly agree‟ to the items in the questionnaire numbers 6 up to 10.
3. Handling Classroom Activities
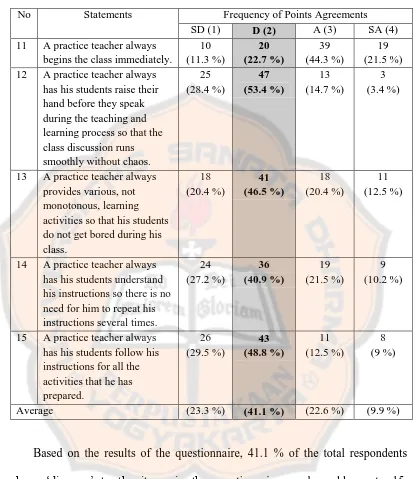
Table D3. The Percentage Result of Questionnaire Part A Numbers 11-15
No Statements Frequency of Points Agreements
SD (1) D (2) A (3) SA (4)
11 A practice teacher always
begins the class immediately.
12 A practice teacher always
has his students raise their
13 A practice teacher always
provides various, not monotonous, learning activities so that his students do not get bored during his class.
14 A practice teacher always
has his students understand his instructions so there is no need for him to repeat his instructions several times.
15 A practice teacher always
has his students follow his
4. Regulations of Physical Conditions
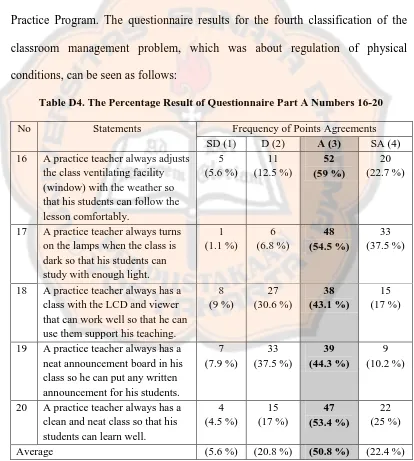
Regulations of physical conditions were the fourth classification of the classroom management problems. This was related to how teachers could handle physical conditions in the class so that the students felt comfortable to learn in the class. The researcher set five items in this part to know whether or not the practice teachers had problems about regulations of physical conditions during the School Practice Program. The questionnaire results for the fourth classification of the classroom management problem, which was about regulation of physical conditions, can be seen as follows:
Table D4. The Percentage Result of Questionnaire Part A Numbers 16-20
No Statements Frequency of Points Agreements
SD (1) D (2) A (3) SA (4)
16 A practice teacher always adjusts
the class ventilating facility (window) with the weather so that his students can follow the lesson comfortably.
17 A practice teacher always turns
on the lamps when the class is dark so that his students can study with enough light.
18 A practice teacher always has a
class with the LCD and viewer that can work well so that he can
19 A practice teacher always has a
neat announcement board in his class so he can put any written announcement for his students.
20 A practice teacher always has a
Table D4 shows that 50.8 % of the respondents answered „agree‟ to the questionnaire items numbers 16 up to 20. It meant that it was unlikely for the practice teachers to have classroom management problems in the regulations of physical conditions. Meanwhile, 22.4 % of the respondents chose „strongly agree‟. 5. Improving Working Conditions
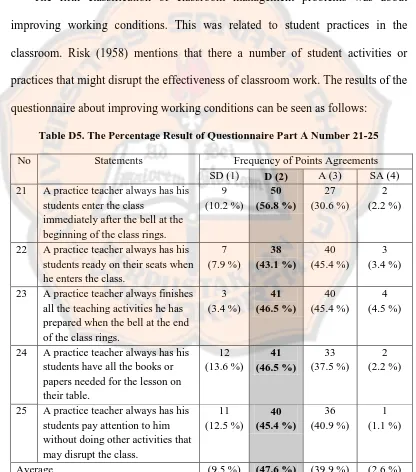
The fifth classification of classroom management problems was about improving working conditions. This was related to student practices in the classroom. Risk (1958) mentions that there a number of student activities or practices that might disrupt the effectiveness of classroom work. The results of the questionnaire about improving working conditions can be seen as follows:
Table D5. The Percentage Result of Questionnaire Part A Number 21-25
No Statements Frequency of Points Agreements
SD (1) D (2) A (3) SA (4)
21 A practice teacher always has his
students enter the class
immediately after the bell at the beginning of the class rings.
22 A practice teacher always has his
students ready on their seats when he enters the class.
23 A practice teacher always finishes
all the teaching activities he has prepared when the bell at the end of the class rings.
24 A practice teacher always has his
students have all the books or papers needed for the lesson on their table.
25 A practice teacher always has his
Based on the data gathered from the questionnaire, 47.6 % of the total respondents chose „disagree‟ to the items numbers 21 up to 25 in the
questionnaire. It meant that it was likely that the practice teachers experienced classroom management problems related to the improving working conditions. Meanwhile, there were 9.5 % of the 88 practice teachers chose „strongly disagree‟.
b. Data Presentation of the Open-Ended Questionnaire
The open-ended questionnaire consisted of only one question. The researcher asked the respondents to mention the other classroom management problems that they experienced during the School Practice Program. After getting the result of the open-ended questionnaire, the researcher categorized the answer of the respondents into three categories. Those categories were: 1) the classroom management problems arising from the students, 2) the classroom management problems arising from the practice teachers, and 3) the classroom management problems arising from the school facility. Furthermore, these three parts are discussed on the discussion part.
2. Discussion
classifications were about: 1) handling attendance, 2) handling instructional materials, 3) handling classroom activities, 4) regulations of physical conditions, and 5) improving working conditions. Therefore, the researcher analyzed the questionnaire results as follows:
In the first classification of the classroom management problems by Risk (1958), which was about handling attendance, there were five items on the close-ended questionnaire to be discussed. The first item was about whether or not the practice teachers always checked their students‟ presence at the beginning of the class. Based on the questionnaire results, 63.6 % of the 88 respondents answered „strongly agree,‟ which meant that the majority of the practice teachers always
checked their students‟ presence at the beginning of the class. The second item was whether or not the practice teachers called their students‟ name one by one to check their students‟ presence. The majority of the respondents, 51.1 % out of the
88 respondents, answered „strongly agree.‟ It meant that most of the practice teachers tended to use the technique of calling their students‟ name one by one to check their students‟ presence regularly. The third questionnaire item in the
handling attendance part was about whether or not the practice teachers always asked their students to give an excuse slip at the beginning of the class if their students wanted to leave the class early. The results of the questionnaire showed that 46.5 % of the total respondents answered „agree‟ to that third item. It meant
In the fourth item of handling attendance questionnaire, the results showed that the majority of the respondents, who were 47.7 % of the total respondents answered „agree‟ to the item stated that the practice teachers always asked their
students who came late to just come in and to sit on their seat quietly then checked the students‟ excuse slip at the end of the class. It meant that the majority of the respondents did not let the interruption caused by students who came late happen. In addition, the last item in the questionnaire of handling attendance was about whether or not the practice teachers always recorded the name of the students who were absent or late in their class. The majority of the respondents, 56.8 % out of the 88 respondents, answered „disagree‟ to that item. It meant that the practice
teachers might think that students‟ lateness or absence was not that big a deal. Furthermore, the average of the handling attendance questionnaire, close-ended questionnaire numbers one up to number five, showed that the majority of the respondents, who were 34.7 % in percentage, answered „agree.‟ It meant that it was unlikely that the practice teachers experienced classroom management problems related to the handling attendance.
techniques to distribute the teaching materials since the practice teachers might think that distributing them by going around the class was not effective. The next item was about whether or not the practice teachers always had their students help them to distribute heavy materials such as reference books or workbooks. The majority of the respondents, who were 61.3 % in a percentage, answered „agree‟ to that item. It meant that the majority of the practice teachers could save their time and energy by not distributing heavy materials alone but by asking for students help. As for the fourth item, in the handling instructional materials part, the results showed that the majority of the respondents, who were 57.9 % in a percentage, answered „agree‟ to the item stated that the practice teachers always
prepared and placed the teaching materials at the accessible place. It meant that the majority of the practice teachers were aware that they needed to prepare and place the teaching materials at the accessible place in order to save their time in getting the teaching materials that had been prepared.
The fourth item of the handling instructional materials was about whether or not the practice teachers always provided a uniform sized paper for their students when the practice teachers asked their students to do a written task. The majority of the respondents, 45.4 % out of the 88 respondents, answered „agree‟ to that item. It meant that the practice teachers understood that by giving a uniform sized paper to their students for doing a written task, the practice teachers could quicken their time to distribute, to collect, and to check their students‟ written task. The
Based on the questionnaire results, the majority of the respondents, who were 48.8 % in a percentage, answered „agree‟ to that item. It meant that the practice teachers were aware that by copying the exercise materials for their students, they could save their time better compared to the practice teachers that wrote exercise materials on the board. In conclusion, the average of the handling attendance questionnaire showed that the majority of the respondents, who were 49.2 % of 88 respondents, answered „agree.‟ It meant that it was unlikely that the practice teachers experienced classroom management problems related to the handling instructional materials.
teachers to have a chaotic discussion during the teaching and learning process. The third item in the handling classroom activities questionnaire discussed whether or not the practice teachers always provided various, not monotonous, learning activities so that the students did not get bored during the class. The results showed that 46.5 % out of 88 respondents answered „disagree‟ to the item number thirteen in the questionnaire. The results showed that sometimes the practice teachers did not provide various activities so that their students might get bored during the class.
practice teachers. The average results showed that 41.1 % of the respondents answered „disagree‟ to the statement numbers eleven up to fifteen. It meant that it
was likely that the practice teachers experienced classroom management problems in handling classroom activities.